Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for cmm qc
In today’s competitive manufacturing landscape, sourcing quality Coordinate Measuring Machines (CMM) for effective quality control (QC) is paramount for international B2B buyers. The challenge lies not just in selecting the right equipment but in ensuring that it meets stringent specifications while remaining cost-effective. This comprehensive guide addresses critical aspects of CMM QC, including various types of machines, their applications across different industries, and strategies for supplier vetting to ensure reliability and performance.
As the global market evolves, understanding the nuances of CMM technology becomes essential for businesses, particularly those in regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, including countries like Saudi Arabia and Brazil. This guide empowers decision-makers by providing insights into the latest advancements in CMM technology, cost considerations, and best practices for implementation. By equipping buyers with the knowledge to make informed purchasing decisions, this resource aims to enhance operational efficiency and product quality, ultimately driving business success in a rapidly changing environment.
Whether you are looking to invest in your first CMM or seeking to upgrade your existing quality control processes, this guide serves as a valuable tool to navigate the complexities of sourcing and implementing CMM technology effectively.
Understanding cmm qc Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Bridge CMM | Fixed bridge structure; versatile measurement range | Aerospace, automotive, and heavy machinery industries | Pros: High accuracy, suitable for large parts. Cons: Requires significant floor space. |
| Gantry CMM | Large, overhead structure; ideal for big components | Shipbuilding, construction, and large-scale manufacturing | Pros: Excellent for oversized items. Cons: Limited portability and high cost. |
| Horizontal Arm CMM | Compact design; measures smaller parts effectively | Electronics, medical devices, and precision parts | Pros: Space-efficient, fast measurements. Cons: Limited measurement range. |
| Portable CMM | Handheld device; flexible and mobile measurement | Field inspections, assembly verification | Pros: Highly versatile, easy to use. Cons: May sacrifice some accuracy compared to stationary models. |
| Optical CMM | Uses laser or optical scanning; non-contact method | Quality assurance in delicate or sensitive materials | Pros: Non-destructive, high-speed measurement. Cons: More expensive, requires specific training. |
What Are the Key Characteristics of Bridge CMMs for B2B Buyers?
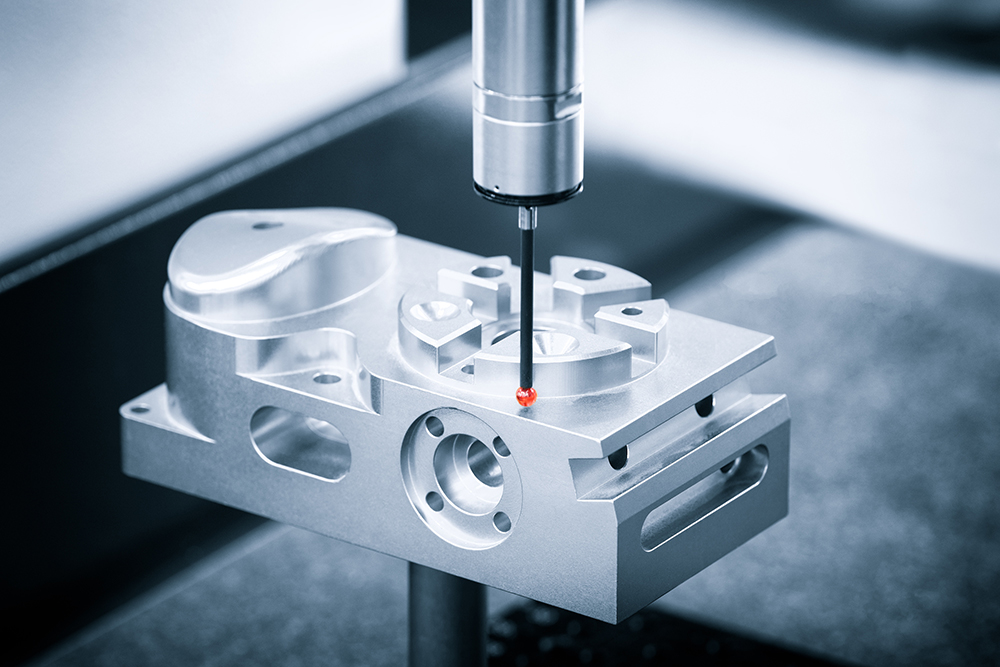
Bridge Coordinate Measuring Machines (CMMs) are characterized by their fixed bridge structure, providing a stable platform for high-precision measurements. They are particularly suitable for industries such as aerospace and automotive, where large components need precise dimensional checks. When considering a Bridge CMM, buyers should evaluate their floor space availability, as these machines require significant room. Additionally, the high accuracy and versatility make them a valuable investment for manufacturers focused on quality control.
How Do Gantry CMMs Cater to Large-Scale Manufacturing Needs?
Gantry CMMs feature a large overhead structure that allows for the measurement of oversized components, making them ideal for shipbuilding and construction industries. Their design accommodates large workpieces while maintaining accuracy. Buyers should consider the high cost and limited portability of Gantry CMMs, but their efficiency in handling large-scale measurements can justify the investment. Companies focusing on large assemblies will find these machines beneficial for ensuring quality throughout production.
What Are the Advantages of Horizontal Arm CMMs for Precision Parts?
Horizontal Arm CMMs are compact and designed for measuring smaller parts efficiently. They are commonly used in industries like electronics and medical devices, where precision is critical. Buyers looking for a space-efficient solution will appreciate the quick measurement capabilities of Horizontal Arm CMMs. However, potential limitations in measurement range should be considered, especially for businesses that handle larger components alongside smaller ones.
Why Choose Portable CMMs for On-Site Measurements?
Portable CMMs offer flexibility and mobility, allowing for measurements in various locations, such as assembly lines or field inspections. Their handheld design makes them easy to operate, which is crucial for companies that need quick quality checks without transporting items back to a stationary machine. While they may sacrifice some accuracy compared to fixed models, their versatility makes them an attractive option for B2B buyers focused on efficiency and convenience.
What Makes Optical CMMs a Unique Choice for Sensitive Materials?
Optical CMMs utilize laser or optical scanning for non-contact measurements, making them suitable for delicate or sensitive materials. They are often employed in quality assurance processes where traditional contact methods might cause damage. Buyers interested in high-speed measurements and non-destructive testing will find Optical CMMs advantageous. However, the higher costs and the need for specialized training should be factored into purchasing decisions.
Key Industrial Applications of cmm qc
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of cmm qc | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Aerospace | Precision measurement of aircraft components | Ensures compliance with stringent safety and performance standards, reducing risk of recalls and enhancing reliability. | Certifications for aerospace standards (e.g., AS9100), equipment calibration, and support for complex geometries. |
| Automotive | Quality control of engine and chassis parts | Reduces production costs through early defect detection and minimizes rework, improving time-to-market. | Supplier reputation, technology compatibility, and after-sales support. |
| Electronics | Measurement of circuit boards and electronic enclosures | Enhances product reliability and performance by ensuring precise fit and function of components. | Need for rapid prototyping, flexibility in measurement capabilities, and data integration with design software. |
| Medical Devices | Verification of implantable devices and surgical instruments | Guarantees safety and efficacy in critical applications, ensuring compliance with regulatory requirements. | Regulatory compliance (e.g., ISO 13485), adaptability to various materials, and ability to handle complex geometries. |
| Heavy Machinery | Inspection of large machined components | Improves operational efficiency by ensuring parts meet specifications, reducing downtime from equipment failures. | Ability to measure large parts, robustness of equipment, and local service availability for maintenance. |
How is CMM QC Applied in the Aerospace Industry?
In the aerospace sector, Coordinate Measuring Machines (CMM) are critical for the precision measurement of aircraft components. These machines ensure that parts meet stringent safety and performance standards, which is paramount in this heavily regulated industry. International buyers should consider suppliers that hold relevant certifications, such as AS9100, and can provide equipment that is calibrated and capable of handling complex geometries typical of aerospace components.
What Role Does CMM QC Play in Automotive Quality Control?
CMM technology is widely used in the automotive industry to conduct quality control on engine and chassis parts. By allowing manufacturers to detect defects early in the production process, CMMs significantly reduce production costs and minimize rework, thus speeding up time-to-market. Buyers in this sector should prioritize suppliers with a strong reputation for quality, technology compatibility, and robust after-sales support to ensure seamless integration into their existing production lines.
How is CMM QC Used in Electronics Manufacturing?
In electronics manufacturing, CMMs are employed to measure circuit boards and electronic enclosures, ensuring that all components fit and function precisely. This level of accuracy enhances product reliability and performance, which is crucial in a competitive market. Buyers should look for suppliers that offer rapid prototyping capabilities and flexible measurement systems, alongside data integration options with existing design software to streamline their workflows.
Why is CMM QC Essential for Medical Devices?
The medical device industry relies heavily on CMM technology for the verification of implantable devices and surgical instruments. This ensures that products are safe and effective, meeting rigorous regulatory requirements. Buyers should focus on suppliers that comply with ISO 13485 standards, possess the ability to adapt to various materials, and can handle the intricate geometries often found in medical applications.
How Does CMM QC Benefit Heavy Machinery Manufacturing?
In heavy machinery manufacturing, CMMs are crucial for inspecting large machined components. By ensuring that parts meet exact specifications, manufacturers can improve operational efficiency and reduce the likelihood of equipment failures that lead to costly downtimes. Buyers in this sector should consider the ability of suppliers to measure large parts accurately, the robustness of the equipment, and the availability of local service for ongoing maintenance.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘cmm qc’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Navigating Complex Specifications for Quality Control
The Problem: B2B buyers often face the challenge of ensuring that their products meet stringent specifications. This complexity can become overwhelming, especially when dealing with multiple suppliers across different regions like Africa and South America. Miscommunication regarding the specifications can lead to significant delays and increased costs due to rework or rejected shipments. For instance, a manufacturer in Brazil may need to ensure that parts produced in Europe adhere to specific dimensional tolerances, and any discrepancy could halt production lines.
The Solution: To overcome this challenge, buyers should invest time in developing clear and comprehensive specifications that can be easily communicated to all stakeholders. Utilizing Coordinate Measuring Machines (CMM) during the initial stages of production can help verify that the prototypes meet the required standards before full-scale manufacturing begins. Buyers can also implement standardized reporting formats for quality checks, ensuring that all suppliers understand the specifications uniformly. Additionally, engaging with a CMM provider who offers training or support can facilitate smoother operations and reduce misunderstandings.
Scenario 2: The Dilemma of Equipment Compatibility
The Problem: Buyers frequently encounter compatibility issues between their existing quality control equipment and new CMM technologies. For example, a company in the Middle East may have invested in a specific type of measuring equipment that does not integrate well with the latest CMM models, resulting in costly downtime and inefficiencies. This lack of compatibility can also lead to data discrepancies, making it difficult to maintain a cohesive quality control process.
The Solution: Before purchasing a CMM, buyers should conduct a thorough compatibility assessment of their current equipment and software systems. This can be achieved by consulting with CMM manufacturers and requesting demonstrations of how their systems can integrate with existing technologies. Additionally, consider opting for modular CMM solutions that can be scaled and adapted to fit various applications and environments. A robust vendor partnership is essential; seek suppliers who provide extensive support and integration services to ensure a seamless transition to new quality control processes.
Scenario 3: Managing High Volume Production Demands
The Problem: As production demands increase, companies often struggle to maintain quality control without compromising speed. For instance, a manufacturer in Europe might face challenges in scaling their operations while ensuring that each component is accurately measured and meets quality standards. This situation can lead to bottlenecks in production, especially if the CMM processes are slow or require extensive manual input.
The Solution: To effectively manage high volume production while maintaining quality, buyers should consider investing in automated CMM systems that can handle large batches with minimal human intervention. Automation can significantly speed up the measurement process and reduce the likelihood of human error. Additionally, implementing real-time data analysis tools that interface with the CMM can provide immediate feedback on quality metrics, allowing for rapid adjustments in the production process. Training staff to utilize these technologies efficiently can further optimize production flows and enhance overall quality control strategies.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for cmm qc
What Are the Key Materials Commonly Used in CMM QC Applications?
When selecting materials for Coordinate Measuring Machines (CMM) in quality control (QC) applications, it is essential to consider their properties, advantages, and limitations. Below, we analyze four common materials: granite, aluminum, steel, and composite materials, focusing on their relevance to international B2B buyers.
How Does Granite Perform as a Material for CMM QC?
Granite is a traditional choice for CMM bases due to its natural stability and rigidity. Its key properties include excellent dimensional stability, resistance to thermal expansion, and high compressive strength. Granite is also non-magnetic, which is crucial for precision measurements.
Pros: The durability of granite makes it suitable for long-term use, and its low thermal expansion ensures accuracy even under varying environmental conditions. Additionally, granite bases are often cost-effective.
Cons: However, granite can be heavy and may require specialized handling during installation. It is also susceptible to chipping if not properly maintained.
Impact on Application: Granite’s compatibility with various measuring probes makes it ideal for intricate measurements across different media.
Considerations for International Buyers: Compliance with international standards like ASTM and DIN is crucial, as is understanding local sourcing options to mitigate shipping costs.
What Are the Advantages of Aluminum in CMM QC?
Aluminum is frequently used for CMM components due to its lightweight and corrosion-resistant properties. It offers a good balance between strength and weight, making it suitable for mobile CMM applications.
Pros: The ease of machining aluminum allows for customization and rapid production, which is beneficial for manufacturers with specific needs. Its corrosion resistance also extends the lifespan of components.
Cons: However, aluminum is less rigid than granite or steel, which may affect measurement precision in certain applications. It can also be more expensive than other materials if high-grade alloys are used.
Impact on Application: Aluminum is particularly effective in environments where weight is a concern, such as portable CMM systems.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should ensure that aluminum components meet relevant standards like JIS and ASTM to guarantee quality and performance.
Why Choose Steel for CMM QC Applications?
Steel is another common material used in CMM QC applications, particularly for structural components. Its high tensile strength and durability make it suitable for heavy-duty applications.
Pros: Steel provides excellent stability and is less prone to deformation under load, ensuring accurate measurements. It is also widely available and relatively cost-effective.
Cons: On the downside, steel is susceptible to corrosion if not properly treated, which can lead to maintenance challenges. Additionally, its weight can be a drawback in portable applications.
Impact on Application: Steel is ideal for fixed installations where high stability is required, particularly in harsh environments.
Considerations for International Buyers: Compliance with international standards and local regulations regarding steel quality is essential, especially in regions with strict manufacturing guidelines.
What Role Do Composite Materials Play in CMM QC?
Composite materials, often a combination of resin and fiber, are increasingly used in CMM applications due to their unique properties. They offer high strength-to-weight ratios and can be engineered for specific applications.
Pros: Composites are lightweight and resistant to thermal expansion, making them suitable for precision applications. They can also be molded into complex shapes, allowing for innovative designs.
Cons: However, composites can be more expensive than traditional materials, and their long-term durability may not match that of metals or granite. They also require careful handling during production.
Impact on Application: Composites are particularly effective in specialized applications where traditional materials may not suffice, such as in aerospace or automotive industries.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should be aware of the specific certifications required for composite materials, as standards can vary significantly by region.
Summary of Material Selection for CMM QC
| Material | Typical Use Case for cmm qc | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Granite | Base for CMM | Excellent dimensional stability | Heavy and prone to chipping | Low |
| Aluminum | Structural components | Lightweight and corrosion-resistant | Less rigid than granite or steel | Medium |
| Steel | Heavy-duty structural components | High tensile strength | Susceptible to corrosion | Medium |
| Composite | Specialized applications | High strength-to-weight ratio | More expensive and less durable | High |
This guide provides valuable insights for international B2B buyers, particularly in emerging markets, to make informed decisions regarding material selection for CMM QC applications. Understanding the properties, advantages, and limitations of each material can significantly impact product performance and compliance with regional standards.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for cmm qc
What Are the Key Stages in the Manufacturing Process of CMM QC?
The manufacturing process for Coordinate Measuring Machines (CMM) involves several critical stages that ensure the final product meets stringent quality requirements. The primary stages include material preparation, forming, assembly, and finishing.
Material Preparation
The process begins with the selection and preparation of materials. High-quality metals, such as granite for the base, aluminum for the frame, and specialized alloys for components, are typically used. These materials undergo rigorous testing to ensure they meet specific standards for durability and stability. Proper material preparation is crucial as it influences the machine’s precision and longevity.
Forming
In the forming stage, the raw materials are shaped into the necessary components using techniques such as CNC machining, casting, and milling. CNC machining is particularly favored for its ability to produce complex geometries with high precision. This stage is vital as it lays the foundation for the accuracy of measurements taken by the CMM.
Assembly
Once the components are formed, they proceed to the assembly stage. Skilled technicians carefully assemble the CMM, ensuring that each part is installed correctly to maintain alignment and stability. This process may involve adjustments to ensure that the mobile table and measuring probe operate smoothly along the defined axes. Precision in assembly is paramount, as even minor misalignments can lead to significant errors in measurements.
Finishing
The final stage is finishing, which includes surface treatment and calibration of the CMM. Surface treatments like anodizing or painting enhance durability and protect against environmental factors. Calibration is a critical step where the machine is tested against known standards to ensure it provides accurate measurements. This step often involves using certified calibration blocks and fixtures to validate the machine’s performance.
What International Standards and Quality Checkpoints Are Relevant for CMM QC?
Quality assurance is an integral aspect of the manufacturing process for CMMs. Compliance with international standards such as ISO 9001 is essential, as it establishes a framework for consistent quality management systems across organizations. Additionally, industry-specific certifications like CE for Europe and API for the oil and gas sector may also be relevant, depending on the application of the CMM.
Quality Checkpoints
To ensure comprehensive quality control, manufacturers often implement various checkpoints throughout the production process:
-
Incoming Quality Control (IQC): This initial checkpoint assesses the quality of raw materials and components before they enter the production line. It ensures that only materials meeting specified criteria are used.
-
In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): During the manufacturing process, periodic inspections are conducted to verify that operations adhere to established standards and that any deviations are corrected immediately.
-
Final Quality Control (FQC): At this stage, the completed CMM undergoes thorough testing to confirm that it meets all specifications and standards. This includes functional testing, performance evaluation, and final calibration.
What Common Testing Methods Are Used in CMM Quality Assurance?
Various testing methods are employed to validate the performance and accuracy of CMMs, ensuring they meet the required specifications. Common methods include:
-
Dimensional Inspection: This method involves measuring the dimensions of components and assemblies against specified tolerances. CMMs themselves are often used to perform these inspections, providing precise measurements that can be documented for quality assurance.
-
Functional Testing: This test assesses whether the CMM operates as intended across its measurement range. It evaluates the response time, accuracy, and repeatability of measurements.
-
Environmental Testing: This involves subjecting the CMM to various environmental conditions, such as temperature fluctuations and humidity, to determine its operational stability under different circumstances.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control?
For B2B buyers, particularly those in regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, ensuring supplier quality is vital for maintaining production integrity. Here are actionable strategies to verify supplier quality control:
-
Conduct Audits: Regular audits of suppliers can provide insights into their quality management systems and adherence to international standards. These audits can be performed in-person or remotely and should assess all quality checkpoints.
-
Request Documentation: Suppliers should provide documentation of their quality control processes, including IQC, IPQC, and FQC reports. This documentation should detail the procedures followed and the results of any tests conducted.
-
Engage Third-party Inspectors: Utilizing third-party inspection services can offer an unbiased evaluation of the supplier’s quality control processes. These inspectors can conduct thorough evaluations and provide certification reports that verify compliance with industry standards.
What Are the Quality Control and Certification Nuances for International B2B Buyers?
International B2B buyers must navigate various quality control and certification nuances when sourcing CMMs. Understanding the specific requirements for different markets is crucial for compliance and successful transactions.
-
Certification Variability: Different regions may have unique certification requirements. For example, CE marking is mandatory for products sold in the European Union, while specific certifications may be required in the Middle East or Africa. Familiarizing oneself with these certifications can prevent compliance issues.
-
Cultural and Regulatory Differences: Buyers should be aware of cultural differences that may impact communication and negotiations with suppliers. Additionally, understanding local regulations regarding quality standards can help buyers make informed decisions.
-
Risk Management: Buyers should develop risk management strategies to mitigate potential quality issues. This includes having contingency plans for sourcing from alternative suppliers and ensuring that all contracts include clauses related to quality assurance.
By understanding these manufacturing processes, quality assurance standards, and verification methods, B2B buyers can make informed decisions when sourcing CMMs, ensuring they acquire high-quality products that meet their operational needs.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘cmm qc’
Introduction
This practical sourcing guide is designed for B2B buyers seeking to procure Coordinate Measuring Machines (CMM) for quality control (QC) purposes. By following this step-by-step checklist, you can ensure that you make informed decisions, select reliable suppliers, and ultimately enhance your manufacturing quality assurance processes.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Before initiating the procurement process, it’s essential to establish clear technical specifications for your CMM. Consider factors such as measurement range, accuracy, and the type of probes required. Detailed specifications will help you communicate effectively with potential suppliers and ensure that the equipment meets your operational needs.
- Measurement Range: Determine the maximum dimensions of the parts you will measure.
- Accuracy Requirements: Define the tolerances and precision needed for your quality control processes.
Step 2: Research the Market Landscape
Understanding the market landscape is crucial for identifying potential suppliers. Conduct thorough research on various manufacturers and distributors of CMMs, focusing on their reputation, customer reviews, and market presence.
- Reputation: Look for suppliers with a strong track record in quality and customer satisfaction.
- Customer Reviews: Analyze feedback from businesses similar to yours to gauge the reliability of the products.
Step 3: Evaluate Potential Suppliers
Before committing, it’s crucial to vet suppliers thoroughly. Request company profiles, case studies, and references from buyers in a similar industry or region. Don’t just rely on their website; delve deeper into their operational capabilities and past performance.
- Case Studies: Request examples of previous successful implementations to assess their expertise.
- References: Speak with existing customers to understand their experiences and satisfaction levels.
Step 4: Verify Supplier Certifications
Ensure that the suppliers you are considering possess relevant certifications and quality standards. Look for ISO certifications or industry-specific standards that demonstrate their commitment to quality management.
- ISO Certifications: Verify that they are compliant with standards such as ISO 9001 or ISO 17025.
- Industry Standards: Confirm adherence to specific standards applicable to your industry, which can be critical for regulatory compliance.
Step 5: Request Demonstrations or Samples
To assess the functionality and performance of the CMM, request live demonstrations or samples. This step allows you to evaluate the equipment’s capabilities in real-time and ensures that it aligns with your expectations.
- On-Site Demonstrations: If possible, arrange for a supplier to demonstrate the machine at your facility.
- Sample Measurements: Request samples of parts similar to what you will be measuring to test the machine’s accuracy.
Step 6: Compare Pricing and Total Cost of Ownership
Once you have shortlisted potential suppliers, compare their pricing structures and consider the total cost of ownership (TCO). TCO includes not just the initial purchase price but also maintenance, training, and any potential operational costs.
- Initial Costs vs. Long-Term Value: Look for suppliers who offer a good balance between upfront investment and long-term savings.
- Maintenance and Support: Factor in ongoing costs for maintenance contracts and technical support.
Step 7: Negotiate Terms and Finalize the Contract
Once you have selected a supplier, it’s time to negotiate terms and finalize the contract. Discuss warranties, service agreements, and delivery timelines to ensure all aspects are covered before signing.
- Warranties: Ensure that the warranty period is sufficient and covers potential defects.
- Service Agreements: Clarify the terms of post-purchase support, including maintenance and training services.
By adhering to this checklist, B2B buyers can navigate the complexities of sourcing CMMs for QC effectively, ensuring they select the right equipment and supplier for their needs.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for cmm qc Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components in CMM QC Sourcing?
When considering the sourcing of Coordinate Measuring Machines (CMM) for quality control (QC), understanding the cost structure is vital for international B2B buyers. The primary cost components include materials, labor, manufacturing overhead, tooling, quality control, logistics, and profit margins.
-
Materials: The quality of materials used in CMM manufacturing significantly influences pricing. High-grade materials ensure durability and precision, which are essential for accurate measurements. Buyers should assess the material quality against their specifications to ensure they are not overpaying for unnecessary enhancements.
-
Labor: Labor costs encompass both direct and indirect wages associated with the production of CMMs. Skilled labor is required for assembly and calibration processes, which can vary by region. In areas like Europe, labor costs tend to be higher, while regions in Africa and South America may offer lower rates, impacting overall pricing.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes costs related to facility maintenance, utilities, and equipment depreciation. Overhead can vary significantly based on the supplier’s operational efficiency and geographic location. Buyers should inquire about the overhead costs included in the pricing to ensure transparency.
-
Tooling: The initial investment in tooling can be substantial, especially for custom CMMs. The complexity of the tooling required for specific measurements will affect the overall cost. Buyers should evaluate whether the tooling costs are being amortized over a long production run or if they are charged upfront.
-
Quality Control: CMMs are integral to the QC process, and the associated costs must be considered. This includes the costs of calibration, testing, and certification to industry standards. Buyers should ensure that the supplier’s QC processes align with their quality requirements to avoid additional costs down the line.
-
Logistics: Shipping and handling costs can vary significantly based on the Incoterms used, shipment volume, and destination. International buyers should account for potential tariffs, insurance, and freight costs, which can add up quickly.
-
Margin: Suppliers will include a profit margin in their pricing, which can be influenced by market demand and competition. Understanding the standard margins in the CMM QC industry can help buyers negotiate better deals.
How Do Price Influencers Affect CMM QC Sourcing?
Several factors can influence pricing in CMM QC sourcing, making it essential for buyers to evaluate these elements:
-
Volume/MOQ: The minimum order quantity (MOQ) can significantly affect pricing. Suppliers often provide discounts for larger volumes, making it advantageous for companies with high production needs.
-
Specifications and Customization: Custom requirements can lead to increased costs. Buyers should clearly define their specifications and assess whether customization is necessary, as standard models might offer cost savings.
-
Materials and Quality Certifications: The choice of materials and necessary certifications (ISO, ASME) can influence costs. Buyers should weigh the benefits of high-quality materials against their budget constraints.
-
Supplier Factors: The reputation, experience, and geographical location of suppliers can impact pricing. Established suppliers may charge more due to their proven track record, while emerging suppliers might offer competitive rates to gain market share.
-
Incoterms: Understanding the implications of different Incoterms can affect overall cost. Buyers should clarify who is responsible for shipping, insurance, and duties to avoid unexpected expenses.
What Are the Best Tips for Negotiating CMM QC Prices?
International B2B buyers should adopt strategic approaches to negotiate better pricing for CMM QC sourcing:
-
Understand Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Evaluate not just the initial purchase price but also maintenance, operational costs, and potential downtime. A lower upfront cost may lead to higher long-term expenses.
-
Leverage Relationships: Building strong relationships with suppliers can lead to better pricing and terms. Consider establishing long-term partnerships that may yield benefits over time.
-
Be Prepared to Walk Away: If the terms don’t meet your budget or quality standards, be willing to explore other suppliers. This can provide leverage in negotiations.
-
Investigate Local Suppliers: For buyers in Africa, South America, and the Middle East, sourcing locally can reduce logistics costs and lead to more favorable pricing.
-
Request Multiple Quotes: Obtaining quotes from several suppliers can provide a clearer picture of market pricing and help identify the best deal.
By understanding the cost structure, pricing influencers, and effective negotiation strategies, international B2B buyers can make informed decisions when sourcing CMM QC solutions.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing cmm qc With Other Solutions
Exploring Alternatives to CMM QC Solutions for Quality Control
In the realm of quality control, businesses often seek the most efficient and effective solutions to ensure their products meet stringent specifications. While Coordinate Measuring Machines (CMM) are widely recognized for their precision in measuring physical and geometrical characteristics, several alternatives exist that may better suit specific operational needs. This analysis compares CMM QC with alternative methods such as Laser Scanning and Optical Measurement Systems, providing insights for B2B buyers to make informed decisions.
| Comparison Aspect | CMM QC | Laser Scanning | Optical Measurement Systems |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | High precision; suitable for complex geometries | High speed; less precise for detailed measurements | Good precision; effective for surface inspections |
| Cost | Higher upfront investment; ongoing maintenance costs | Moderate initial costs; lower maintenance | Lower initial costs; potential for higher operational costs |
| Ease of Implementation | Requires skilled operators; longer setup time | Generally user-friendly; quicker setup | User-friendly; minimal training required |
| Maintenance | Regular calibration needed; higher maintenance demands | Low maintenance; infrequent recalibration | Moderate maintenance; calibration needed periodically |
| Best Use Case | Ideal for parts with tight tolerances | Best for large-scale scanning and reverse engineering | Effective for quality assurance in assembly lines |
In-Depth Analysis of Alternatives
What Are the Benefits and Drawbacks of Laser Scanning?
Laser scanning technology offers rapid data collection and is particularly advantageous for large or complex objects. Its ability to capture detailed surface geometries makes it ideal for reverse engineering and quality inspections of intricate designs. However, while it provides speed, it may not match the precision of CMMs for parts requiring exact dimensional tolerances. Additionally, the initial investment can be moderate, but the overall cost may rise with the necessity for software and processing capabilities.
How Do Optical Measurement Systems Compare?
Optical measurement systems utilize cameras and light to assess the geometrical characteristics of parts. They are known for their ease of use and quick setup, often requiring minimal training for operators. This technology is effective in assembly line settings for ensuring that components fit together correctly. However, while they can deliver good precision for surface measurements, they may struggle with measuring internal features or complex geometries, potentially leading to less comprehensive inspections compared to CMM QC.
Making the Right Choice for Your Quality Control Needs
When selecting a quality control solution, B2B buyers should carefully evaluate their specific requirements, including the types of parts being measured, the necessary precision levels, and budget constraints. CMM QC remains a leading choice for high-precision applications, particularly in industries with stringent tolerances such as aerospace and automotive. Conversely, for businesses focused on speed and ease of use, laser scanning and optical measurement systems may provide sufficient accuracy while reducing operational complexities.
Ultimately, the decision should align with the operational goals and the specific context of the manufacturing process, ensuring that the chosen solution enhances overall productivity and quality assurance.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for cmm qc
What Are the Key Technical Properties for CMM QC?
Understanding the technical specifications of Coordinate Measuring Machines (CMM) is crucial for B2B buyers in ensuring quality control (QC) processes are effective and reliable. Here are some critical specifications to consider:
-
Material Grade
CMMs are typically constructed from high-grade materials such as granite for the base and aluminum or steel for the structure. The choice of material affects the machine’s stability and accuracy. For B2B buyers, selecting a CMM made from premium materials ensures longevity and minimizes measurement errors, which is essential for high-precision industries such as aerospace and automotive. -
Measurement Tolerance
Tolerance refers to the allowable deviation from a specified measurement. In CMMs, tighter tolerances translate to higher precision in measurements. For businesses producing parts with strict specifications, understanding the measurement tolerance of a CMM can help in assessing whether it meets their production requirements and reduces the risk of costly reworks. -
Probe Type and Range
The probe is integral to a CMM’s operation, and various types exist, including mechanical, optical, and laser probes. Each type has a different measurement range and capability, impacting the kinds of materials and geometries that can be effectively measured. B2B buyers should consider the probe type that best fits their specific application, as it influences both the accuracy of measurements and the versatility of the machine. -
Axis Configuration
CMMs come in different configurations, such as 3-axis, 5-axis, and even 7-axis systems. The axis configuration determines the complexity of shapes that can be measured and the machine’s overall efficiency. For buyers, selecting the appropriate axis configuration is vital for optimizing measurement processes and ensuring compatibility with their production needs. -
Software Integration
The software used in conjunction with a CMM plays a crucial role in data analysis and reporting. Advanced software can provide detailed visual representations and statistical analysis of measurements. B2B buyers should assess the software capabilities to ensure it aligns with their data management needs, facilitating better decision-making and quality assurance.
What Are Common Trade Terms Related to CMM QC?
Familiarity with industry terminology can enhance communication and negotiation in B2B transactions. Here are some essential terms:
-
OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
An OEM is a company that produces parts or equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer. In the context of CMMs, OEMs often provide proprietary technology and components. Understanding OEM relationships can help buyers identify quality sources and gauge the reliability of the equipment. -
MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ refers to the smallest number of units a supplier is willing to sell. Knowing the MOQ is crucial for buyers, especially those looking to manage inventory costs effectively. It can influence purchasing decisions, particularly for smaller manufacturers that may not require large quantities. -
RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a document sent to suppliers requesting pricing and terms for specific goods or services. For CMM equipment, submitting an RFQ can help buyers gather competitive quotes, enabling informed decision-making based on price and specifications. -
Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
Incoterms are a set of internationally recognized rules that define the responsibilities of sellers and buyers in international transactions. Understanding these terms helps B2B buyers clarify shipping costs, risks, and responsibilities, which is particularly important when importing CMM technology from overseas. -
Calibration
Calibration is the process of adjusting the accuracy of a measuring instrument. Regular calibration of CMMs is essential to maintain measurement precision. B2B buyers should prioritize suppliers who offer calibration services, as this ensures compliance with industry standards and enhances product quality assurance. -
First Article Inspection (FAI)
FAI is a process that verifies that the manufacturing process is capable of producing parts that meet specified requirements. This is critical for quality assurance in CMM operations. Buyers should ensure that their suppliers conduct FAI to confirm that the initial production runs meet the necessary tolerances and specifications.
By grasping these technical properties and trade terms, B2B buyers can make informed decisions that enhance their quality control processes and overall operational efficiency.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the cmm qc Sector
What Are the Key Market Trends Affecting the CMM QC Sector?
The Coordinate Measuring Machine (CMM) market is experiencing significant transformation driven by globalization, technological advancements, and evolving customer demands. International buyers, particularly in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, must stay attuned to these dynamics. A notable trend is the increasing adoption of automation and Industry 4.0 technologies, which enhance operational efficiency and accuracy in quality control processes. This shift enables manufacturers to minimize human error and streamline their production lines, making CMMs integral to modern manufacturing.
Another emerging trend is the rise of cloud-based data management solutions that facilitate real-time data sharing and analysis. Buyers can leverage these solutions for improved collaboration across international supply chains, ensuring that quality control measures are consistently applied. Additionally, as industries increasingly focus on precision engineering, the demand for high-accuracy CMMs is surging. This is particularly relevant for sectors such as aerospace, automotive, and medical device manufacturing, where the cost of non-compliance can be substantial.
Market dynamics also reflect a growing emphasis on localized sourcing strategies. As geopolitical tensions and supply chain disruptions become more common, international buyers are seeking suppliers closer to home to mitigate risks. This trend is especially pertinent for regions such as Europe and the Middle East, where manufacturers are investing in regional capabilities to bolster their competitiveness.
How Are Sustainability and Ethical Sourcing Influencing the CMM QC Sector?
Sustainability is becoming a pivotal factor in sourcing decisions for international B2B buyers in the CMM QC sector. The environmental impact of manufacturing processes is under scrutiny, prompting companies to adopt greener practices. This includes the use of energy-efficient machinery, waste reduction strategies, and sustainable materials. Buyers are increasingly favoring suppliers who prioritize environmental stewardship, which can enhance brand reputation and customer loyalty.
Ethical sourcing is equally important, as stakeholders demand transparency and accountability throughout the supply chain. Companies are expected to ensure that their suppliers adhere to ethical labor practices and environmental regulations. Certifications such as ISO 14001 (Environmental Management) and ISO 45001 (Occupational Health and Safety) are becoming essential for suppliers to demonstrate their commitment to sustainability and ethical practices.
Moreover, the use of eco-friendly materials in the production of CMMs is gaining traction. Manufacturers that incorporate recycled or sustainably sourced materials into their products can not only reduce their carbon footprint but also attract a growing segment of environmentally conscious buyers. This shift towards sustainable and ethical sourcing not only addresses regulatory pressures but also aligns with the values of modern consumers, ultimately driving long-term business success.
What Is the Historical Context of CMM Technology in B2B Sourcing?
The evolution of Coordinate Measuring Machines dates back to the 1960s when they were first developed for precision engineering. Initially, CMMs were mechanical devices requiring manual operation, which limited their efficiency and accuracy. As technological advancements emerged, particularly in computerization and automation during the 1980s and 1990s, CMMs transformed into sophisticated digital systems capable of high-precision measurements.
This technological evolution has led to widespread adoption across various industries, with significant implications for B2B sourcing strategies. Today, CMMs are vital for quality assurance, enabling manufacturers to meet stringent regulatory standards and consumer expectations. The historical context underscores the importance of continuous innovation in the CMM QC sector, highlighting the need for international buyers to seek out suppliers that are not only current with technology but also proactive in adopting emerging trends. By understanding this evolution, buyers can make informed sourcing decisions that align with their operational and strategic objectives.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of cmm qc
-
How do I ensure quality control in my manufacturing process using a CMM?
To guarantee effective quality control with a Coordinate Measuring Machine (CMM), it’s crucial to establish a clear measurement plan that aligns with your product specifications. Begin by defining the critical dimensions and tolerances necessary for your parts. Utilize the CMM to perform first article inspections and regular checks throughout the production cycle. This proactive approach helps identify deviations early, reducing costs associated with rework and delays. Additionally, ensure that your team is trained in CMM operations and data interpretation for optimal results. -
What is the best CMM for my manufacturing needs?
Selecting the right CMM depends on several factors, including the size and complexity of the parts you manufacture, the level of precision required, and your budget. For high-precision applications, a bridge-type CMM may be ideal, while a portable CMM could suit smaller, less complex components. Evaluate the machine’s software capabilities, ease of use, and support services offered by the supplier. Engaging with your engineering team can also provide insights into the specific measurement challenges you face, guiding you towards the best solution. -
What should I consider when vetting CMM suppliers for international trade?
When sourcing CMM suppliers internationally, consider their reputation, certifications, and experience in your industry. Request references and case studies to gauge their reliability and quality of service. It’s essential to assess their compliance with international standards, such as ISO 9001, which indicates a commitment to quality management. Additionally, consider their logistics capabilities, including shipping times and customs handling, to ensure a smooth procurement process. A supplier with local support or service centers can also provide valuable post-purchase assistance. -
Are there customization options available for CMMs?
Yes, many CMM manufacturers offer customization options to meet specific measurement needs. Customizations can include specialized probes, software configurations, or tailored fixtures that accommodate unique part geometries. Discuss your requirements with potential suppliers to explore available options and ensure that the CMM aligns with your operational processes. Custom solutions can enhance measurement accuracy and efficiency, ultimately leading to better quality control outcomes. -
What is the minimum order quantity (MOQ) for CMMs from suppliers?
The minimum order quantity (MOQ) for CMMs can vary significantly between suppliers and is often influenced by factors such as machine type and specifications. Some manufacturers may allow single-unit purchases, especially for portable or smaller CMMs, while others might have higher MOQs for larger, more complex machines. When negotiating with suppliers, clarify the MOQ and explore options for bulk purchases or leasing arrangements, which can offer flexibility in managing your budget and equipment needs. -
What payment terms should I expect when sourcing CMMs internationally?
Payment terms for international CMM purchases typically range from upfront payments to installment plans. Many suppliers require a deposit upon order confirmation, with the balance due prior to shipment. It’s essential to discuss payment methods that suit your financial practices, such as letters of credit or wire transfers. Ensure you understand any additional fees related to currency conversion and international transactions, as these can impact the overall cost of procurement. -
How can I ensure the accuracy of measurements taken with a CMM?
To maintain measurement accuracy with a CMM, regular calibration and maintenance are essential. Establish a routine calibration schedule based on the manufacturer’s recommendations and the frequency of machine use. Train operators in proper measurement techniques, including temperature control, part positioning, and probe selection, to minimize variability. Additionally, implementing a quality assurance program that includes periodic audits of measurement processes can help identify and rectify potential issues before they affect production. -
What logistics considerations should I keep in mind when importing CMMs?
When importing CMMs, logistics play a critical role in ensuring timely delivery and minimizing costs. Consider factors such as shipping methods, customs regulations, and import duties applicable in your country. Engage a reliable freight forwarder with experience in handling industrial equipment to navigate these complexities. Additionally, plan for potential delays by allowing adequate lead time for shipping and customs clearance. Having a clear understanding of these logistics can prevent disruptions in your production schedule.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.
Top 8 Cmm Qc Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. HLH Prototypes – Coordinate Measuring Machine (CMM)
Domain: hlhprototypes.com
Registered: 2012 (13 years)
Introduction: Coordinate Measuring Machine (CMM) is a quality control equipment used to measure physical and geometrical characteristics of parts during the manufacturing process. It consists of three main parts: a stable base (often a heavy granite slab), a mobile table that defines the X-axis, and a measuring probe that moves along the Y and Z axes. The CMM uses a defined coordinate system to identify unique …
2. QC Training Services – CMM Basics Course
Domain: qctraininginc.com
Registered: 2015 (10 years)
Introduction: {“course_name”: “Coordinate Measuring Machine (CMM) – Basics”, “provider”: “QC Training Services, Inc.”, “course_delivery”: “Training for Teams (virtual live or in-person)”, “target_audience”: [“inspection personnel”, “engineering personnel”, “production personnel”, “entry level inspectors”, “individuals entering dimensional measurement and CMM programming”], “prerequisites”: [“basic measurement-r…
3. KEYENCE – Portable CMM
Domain: keyence.com
Registered: 1996 (29 years)
Introduction: CMM (Coordinate Measuring Machine) by KEYENCE is a portable measuring system designed for easy measurement of 3D/GD&T features. Key features include:
– Handheld probe for ease of use and full range of motion.
– No required CNC programming and no moving parts, enhancing accessibility for users with no previous CMM experience.
– Automatically records measurement data and generates detailed inspectio…
4. ZipRecruiter – CMM Inspector Role
Domain: ziprecruiter.com
Registered: 2010 (15 years)
Introduction: This company, ZipRecruiter – CMM Inspector Role, is a notable entity in the market. For specific product details, it is recommended to visit their website directly.
5. CMM – Urban Development and Environmental Coordination
Domain: cmm.qc.ca
Registered: 2001 (24 years)
Introduction: La Communauté métropolitaine de Montréal (CMM) se concentre sur plusieurs champs d’intervention, notamment : 1. Aménagement : Mise en œuvre du Plan métropolitain d’aménagement et de développement (PMAD). 2. Environnement : Coordination de la Trame verte et bleue à l’échelle métropolitaine. 3. Développement économique : Élaboration du Plan métropolitain de développement économique (PMDE) et program…
6. Teletecsi – Coordinate Measuring Machines (CMMs)
Domain: teletecsi.com
Registered: 2008 (17 years)
Introduction: Coordinate Measuring Machines (CMMs) are essential tools in precision machining for quality control. Key components include a heavy base (often granite), a moveable bridge or gantry for X and Y-axis movement, and a probe for Z-axis measurement. CMMs measure work piece dimensions by recording XYZ coordinates as the probe contacts the workpiece. There are two main types of probes: touch probes, whic…
7. CMM Technology – Quadra-Chek 5000 CMM Measuring Software
Domain: cmmtechnology.com
Registered: 1999 (26 years)
Introduction: Quadra-Chek 5000 CMM Measuring Software is an easy-to-use retrofit software package designed for CMMs. It was voted #1 for “ease of use” by field service engineers. Requires only one day of training on-site. Features include pull-down menus, user-definable window positions, and tool settings for simplified measuring. It retrofits CMMs from the 1980s and 1990s with QC-5300 DCC software, enhancing p…
8. ZEISS – Multisensor Coordinate Measuring Machines
Domain: zeiss.com
Registered: 1995 (30 years)
Introduction: Multisensor coordinate measuring machines (CMMs) from ZEISS include a range of models designed for various applications. Key products include:
– ZEISS SPECTRUM family: Entry-level CMMs for various measurement tasks.
– ZEISS CONTURA: Flexible measurement tasks in the performance class.
– ZEISS MICURA: Designed for small components with tight tolerances.
– ZEISS PRISMO family: Flexible measureme…
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for cmm qc
In the rapidly evolving landscape of manufacturing and quality control, strategic sourcing for Coordinate Measuring Machines (CMM) has emerged as a critical factor for success. By prioritizing quality assurance through CMM technologies, businesses can enhance operational efficiencies and reduce costs associated with rework and delays. The ability to accurately measure physical and geometrical characteristics allows manufacturers to meet stringent specifications and maintain competitive advantage.
International B2B buyers, particularly from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, should recognize the value of investing in advanced CMM solutions. These technologies not only foster product excellence but also support the development of sustainable practices in their operations. As markets continue to globalize, aligning with suppliers who offer innovative CMM solutions can lead to enhanced collaboration and market responsiveness.
Looking ahead, the demand for precision and quality will only increase. By embracing strategic sourcing for CMM technologies, businesses can position themselves at the forefront of their industries. Engage with reputable suppliers and explore the potential of CMM to elevate your quality control processes—your commitment to excellence will set you apart in the global marketplace.