Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for citric passivation of stainless steel
In the quest for robust corrosion resistance, sourcing effective citric passivation solutions for stainless steel is a critical challenge faced by manufacturers worldwide. As industries increasingly demand environmentally friendly and efficient processes, citric acid passivation has emerged as a superior alternative to traditional methods. This guide delves into the comprehensive landscape of citric passivation, exploring its types, applications, and the nuances of supplier vetting. We will also address cost considerations and regulatory compliance, ensuring that buyers are equipped with the knowledge needed to make informed decisions.
For international B2B buyers from regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe—where the demand for high-quality stainless steel components is on the rise—understanding the intricacies of citric passivation can significantly impact product performance and longevity. This guide empowers procurement professionals by providing actionable insights into sourcing practices, industry standards, and the latest advancements in citric passivation technologies. By navigating this critical aspect of metal finishing, buyers can enhance their supply chain efficiency, minimize risks, and ultimately secure a competitive edge in their respective markets.
Understanding citric passivation of stainless steel Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Citric 1 | 4-10% citric acid solution, 140-160°F, 4 min immersion time | Medical devices, aerospace components | Pros: Quick process; effective. Cons: Higher temperature may require specialized equipment. |
| Citric 2 | 4-10% citric acid solution, 120-140°F, 10 min immersion time | Automotive parts, food processing equipment | Pros: Balanced time and temperature; versatile. Cons: Slightly longer processing time. |
| Citric 3 | 4-10% citric acid solution, 70-120°F, 20 min immersion time | General industrial applications | Pros: Lower temperature; energy-efficient. Cons: Longer immersion may affect production speed. |
| Citric 4 | Customizable parameters; includes additives for enhanced performance | High-performance aerospace applications | Pros: Tailored solutions; improved corrosion resistance. Cons: May require more complex setup. |
| Citric 5 | Similar to Citric 4 but allows for more extensive customization | Specialized sectors with unique needs | Pros: Highly adaptable; meets specific industry standards. Cons: Potentially higher costs for customization. |
What Are the Characteristics of Citric 1 Passivation?
Citric 1 passivation utilizes a 4-10% citric acid solution at elevated temperatures (140-160°F) for a brief immersion period of only four minutes. This rapid process is particularly suited for high-demand industries such as medical devices and aerospace components, where time efficiency is crucial. Buyers should consider the need for specialized equipment to maintain high temperatures, as this may increase initial investment costs.
How Does Citric 2 Passivation Work?
Citric 2 passivation operates with similar citric acid concentrations but at slightly lower temperatures (120-140°F) for a longer duration of ten minutes. This method strikes a balance between processing speed and effectiveness, making it ideal for automotive parts and food processing equipment. B2B buyers should weigh the versatility of this method against the marginally longer processing times compared to Citric 1.
Why Choose Citric 3 Passivation?
Citric 3 passivation is characterized by its lower temperature range (70-120°F) and longer immersion time of twenty minutes. This option is energy-efficient and suitable for general industrial applications, particularly where heat-sensitive materials are involved. While the longer immersion time may slow production, the energy savings can offset costs, making it an attractive option for budget-conscious buyers.
What Are the Benefits of Citric 4 Passivation?
Citric 4 passivation offers the flexibility of customizable parameters and the inclusion of additives that enhance performance. This method is particularly beneficial for high-performance aerospace applications where superior corrosion resistance is critical. Buyers should consider the complexity of setup and potential for increased costs associated with customization, but the improved performance can justify the investment.
How Does Citric 5 Passivation Differ?
Citric 5 passivation allows for extensive customization beyond Citric 4, catering to specialized sectors with unique requirements. This flexibility ensures compliance with specific industry standards, making it an ideal choice for manufacturers in niche markets. While the adaptability can lead to higher costs, the tailored approach provides significant value for B2B buyers seeking precision in their corrosion resistance solutions.
Key Industrial Applications of citric passivation of stainless steel
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of citric passivation of stainless steel | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Medical Devices | Passivation of surgical instruments and implants | Enhances corrosion resistance, ensuring safety and longevity of devices. | Compliance with FDA and ISO standards; sourcing from certified suppliers. |
| Aerospace | Treatment of aircraft components | Reduces risk of failure due to corrosion, enhancing safety and performance. | Adherence to AMS 2700 standards; reliable supply chain for critical components. |
| Food Processing | Passivation of equipment in food manufacturing | Prevents contamination and ensures hygiene, extending equipment life. | Certifications for food safety compliance; eco-friendly disposal options. |
| Oil & Gas | Protection of pipelines and valves | Increases operational efficiency and reduces maintenance costs. | Resistance to harsh environments; sourcing from suppliers with proven track records. |
| Construction | Passivation of stainless steel structures | Improves durability and aesthetic appeal, reducing lifecycle costs. | Consideration for local environmental regulations; long-term supply agreements. |
How is Citric Passivation Used in Medical Devices and What Problems Does It Solve?
In the medical device industry, citric passivation is critical for ensuring the safety and effectiveness of surgical instruments and implants. By removing free iron from stainless steel surfaces, the process significantly enhances corrosion resistance, which is vital for preventing infections and ensuring the longevity of devices. Buyers in this sector must ensure compliance with FDA and ISO standards, sourcing from suppliers who can provide documentation and certifications to validate the passivation process.
What Role Does Citric Passivation Play in Aerospace Applications?
Aerospace applications require the utmost reliability, and citric passivation serves as a protective measure for aircraft components. The treatment minimizes the risk of corrosion-related failures, which can have catastrophic consequences. For international buyers, particularly in regions like Europe and the Middle East, adherence to AMS 2700 standards is essential. This necessitates sourcing from suppliers with a robust quality assurance process to ensure that all components meet stringent safety regulations.
How Does Citric Passivation Benefit the Food Processing Industry?
In the food processing industry, citric passivation is used to treat equipment such as mixers, conveyors, and storage tanks. This process prevents the leaching of harmful contaminants, ensuring that food products remain safe for consumption. Furthermore, the enhanced corrosion resistance extends the lifespan of equipment, reducing replacement costs. Buyers must consider suppliers who can provide certifications for food safety compliance, as well as environmentally friendly disposal options for any waste generated during the passivation process.
Why is Citric Passivation Important for Oil & Gas Operations?
In the oil and gas sector, citric passivation protects pipelines and valves from the harsh corrosive environments typical of extraction and transportation processes. This treatment not only increases operational efficiency but also significantly reduces maintenance costs associated with corrosion damage. Buyers in this industry should prioritize sourcing from suppliers with a proven track record of delivering high-quality, durable products that can withstand extreme conditions.
How Does Citric Passivation Enhance Construction Projects?
In construction, citric passivation is applied to stainless steel structures and components, such as railings and facades, to improve durability and aesthetic appeal. This treatment protects against rust and staining, thereby reducing lifecycle costs associated with maintenance and repairs. For international B2B buyers, it’s crucial to consider local environmental regulations and ensure that suppliers can meet these standards while providing long-term supply agreements to secure consistent quality.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘citric passivation of stainless steel’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Overcoming Cost Concerns with Citric Passivation
The Problem:
Many B2B buyers, particularly in regions with emerging markets such as Nigeria and Brazil, face significant budget constraints when it comes to sourcing passivation processes for stainless steel. The initial investment in high-quality citric acid solutions may seem daunting, especially when compared to traditional methods like nitric acid passivation, which can be perceived as cheaper upfront. However, the hidden costs associated with safety hazards, environmental compliance, and inefficient processes can lead to higher long-term expenses.
The Solution:
To mitigate these cost concerns, buyers should conduct a thorough cost-benefit analysis comparing citric acid passivation to traditional methods. Engage with suppliers who provide comprehensive data on the long-term savings associated with citric acid, such as reduced waste treatment costs, lower health risks, and minimal regulatory compliance burdens. When specifying citric acid passivation, emphasize the use of advanced products like CitriSurf®, which not only offer effective corrosion resistance but also align with safety and environmental standards. By investing in quality solutions upfront, companies can avoid costly incidents and ultimately achieve a better return on investment through improved product durability and reduced maintenance costs.
Scenario 2: Ensuring Compliance with Industry Standards
The Problem:
In industries such as aerospace and medical devices, compliance with stringent industry standards like ASTM A967 and AMS 2700 is non-negotiable. B2B buyers often struggle with the complexities of these standards, particularly when transitioning from traditional nitric acid methods to citric acid passivation. Failure to meet these standards can lead to product recalls, legal ramifications, and a tarnished reputation.
The Solution:
To ensure compliance, buyers should collaborate closely with their passivation suppliers to understand the specific requirements of the applicable standards. This includes requesting documentation and validation of the citric acid passivation processes used, especially if transitioning from nitric acid. Establish a clear protocol for the passivation process, including the precise concentrations of citric acid, temperature ranges, and immersion times as outlined in ASTM A967. Additionally, investing in training for staff on proper handling and application of citric acid solutions can further enhance compliance and operational efficiency. Regular audits and testing of treated parts against industry standards will help maintain quality assurance and demonstrate commitment to regulatory compliance.
Scenario 3: Addressing Performance Reliability Issues
The Problem:
B2B buyers in manufacturing sectors often report performance reliability issues with stainless steel components, particularly in corrosive environments. These challenges can arise when the passivation process fails to adequately remove free iron or form a proper passive oxide layer, leading to premature corrosion and product failure. This can be particularly concerning for companies supplying critical components to industries like oil and gas or food processing.
The Solution:
To enhance the reliability of citric passivation processes, buyers should prioritize the selection of high-performance citric acid products like CitriSurf that are specifically formulated to optimize the removal of free iron and facilitate the formation of a robust passive layer. Additionally, implementing a rigorous pre-cleaning protocol to eliminate contaminants before the passivation stage is crucial. This includes using alkaline cleaners and deionized water for rinsing, which ensures that the citric acid can effectively interact with the stainless steel surface. Regular monitoring and testing of the passivation process, including salt spray tests and other industry-standard evaluations, will help ensure that the process consistently meets performance expectations. By adopting these practices, companies can significantly improve the longevity and reliability of their stainless steel products, thereby enhancing customer satisfaction and reducing warranty claims.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for citric passivation of stainless steel
What are the Key Materials for Citric Passivation of Stainless Steel?
When considering citric passivation of stainless steel, several materials play a critical role in the effectiveness and efficiency of the process. This guide analyzes four common materials used in citric acid passivation, focusing on their properties, advantages, disadvantages, and implications for international B2B buyers.
1. Citric Acid
Key Properties:
Citric acid is a weak organic acid with excellent chelating properties. It operates effectively within a pH range of 2-3, typically in concentrations of 4-10% by weight. Its low toxicity and biodegradability make it suitable for various applications, especially in industries with stringent environmental regulations.
Pros & Cons:
The primary advantage of citric acid is its safety profile compared to traditional nitric acid, which poses significant health and environmental risks. It effectively removes free iron from stainless steel surfaces, enhancing corrosion resistance. However, its effectiveness can be temperature-dependent, requiring careful control during the passivation process.
Impact on Application:
Citric acid is particularly effective in environments where corrosion resistance is critical, such as in medical devices and aerospace components. Its ability to form a protective oxide layer significantly reduces the risk of corrosion in harsh conditions.
Considerations for International Buyers:
B2B buyers from regions like Africa and South America should be aware of local regulations regarding chemical handling and disposal. Compliance with standards such as ASTM A967 is essential for ensuring product quality and safety.
2. Deionized Water
Key Properties:
Deionized (DI) water is free from dissolved salts and impurities, making it ideal for rinsing stainless steel after the citric acid passivation process. It helps prevent recontamination of the metal surface.
Pros & Cons:
Using DI water minimizes the risk of introducing contaminants that could compromise the passivation layer. However, it can be more expensive than regular water sources and requires specific infrastructure for production.
Impact on Application:
In high-precision industries, the use of DI water is crucial to maintain the integrity of the passivated surface, especially in components that will be exposed to corrosive environments.
Considerations for International Buyers:
Buyers should assess the availability and cost of DI water in their region. In areas with limited access to clean water, alternative rinsing methods may need to be considered.
3. Biocides
Key Properties:
Biocides are chemical agents used to prevent the growth of microorganisms in the citric acid solution. They enhance the stability of the passivation process by preventing organic growth that can interfere with the effectiveness of citric acid.
Pros & Cons:
The use of biocides significantly improves the longevity and reliability of the passivation solution. However, they may introduce additional regulatory considerations, especially in regions with strict environmental laws.
Impact on Application:
In industries where cleanliness is paramount, such as pharmaceuticals and food processing, the presence of biocides ensures that the passivation process remains uncontaminated and effective.
Considerations for International Buyers:
B2B buyers must ensure compliance with local regulations regarding biocide usage, particularly in regions like the Middle East, where environmental laws can be stringent.
4. Stainless Steel Alloys
Key Properties:
Different grades of stainless steel, such as 304 and 316, have varying compositions that affect their corrosion resistance and suitability for passivation. The presence of chromium and nickel enhances the formation of the passive oxide layer.
Pros & Cons:
Stainless steel alloys provide excellent durability and corrosion resistance, making them ideal candidates for citric passivation. However, the cost of high-grade alloys can be significant, impacting overall project budgets.
Impact on Application:
Specific alloys may be preferred in industries like oil and gas, where exposure to harsh environments is common. The choice of alloy directly influences the effectiveness of the passivation process.
Considerations for International Buyers:
Buyers should consider the availability and cost of specific stainless steel alloys in their local markets. Compliance with international standards such as ASTM and DIN is crucial for ensuring product performance.
Summary Table
| Material | Typical Use Case for citric passivation of stainless steel | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Citric Acid | Medical devices, aerospace components | Environmentally friendly and safe | Temperature-dependent effectiveness | Medium |
| Deionized Water | High-precision industries | Prevents contamination | Higher cost than regular water | High |
| Biocides | Pharmaceuticals, food processing | Enhances solution stability | Regulatory considerations may complicate usage | Medium |
| Stainless Steel Alloys | Oil and gas, chemical processing | Excellent durability and corrosion resistance | Higher initial material costs | High |
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for citric passivation of stainless steel
What Are the Main Stages in the Manufacturing Process for Citric Passivation of Stainless Steel?
The manufacturing process for citric passivation of stainless steel involves several critical stages that ensure the material’s durability and resistance to corrosion. Understanding these stages can help B2B buyers make informed decisions when selecting suppliers.
1. Material Preparation: Ensuring Cleanliness and Integrity
Before any passivation treatment, the stainless steel parts must undergo thorough cleaning to remove contaminants such as oils, dirt, and other residues. This is typically achieved through alkaline cleaning processes using detergents like Micro90 or Simple Green. The effectiveness of this stage is crucial because any residual contaminants can interfere with the passivation process, potentially leading to inadequate corrosion resistance.
2. Forming: Shaping the Stainless Steel Parts
Once cleaned, the stainless steel parts are shaped according to specifications. This forming process may include machining, welding, or fabrication, depending on the end application. Ensuring precision during this stage is critical, particularly for industries such as aerospace and medical devices where tight tolerances are essential.
3. Assembly: Integrating Components
For products that require multiple components, the assembly stage involves the integration of these parts. Proper assembly is essential for the overall functionality of the final product. This stage should be monitored for quality, ensuring that all components fit correctly and function as intended.
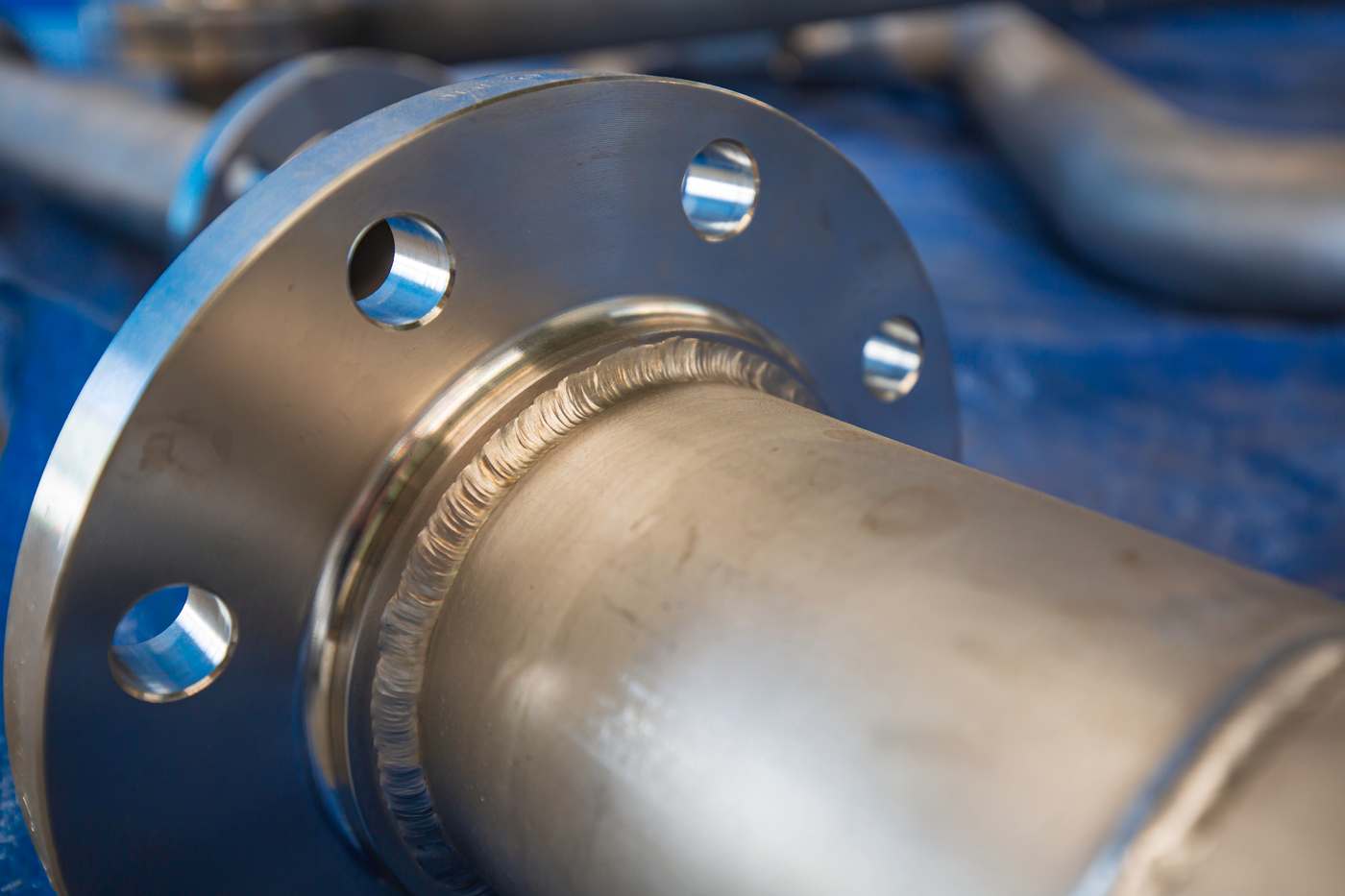
4. Finishing: The Passivation Process
The final stage is where citric passivation occurs. Stainless steel parts are immersed in a citric acid solution, often referred to as CitriSurf. This process effectively removes free iron from the surface and forms a protective oxide layer. The immersion time and temperature can vary, but adherence to standards like ASTM A967 ensures that the passivation is effective.
What Are the Key Quality Control Checkpoints in Citric Passivation?
Quality control (QC) is an integral part of the manufacturing process for citric passivation of stainless steel. B2B buyers should be aware of the relevant international standards and industry-specific requirements to ensure product reliability.
Relevant International Standards for Quality Assurance
Manufacturers should comply with various international standards, such as ISO 9001, which outlines quality management systems. Additionally, industry-specific standards, such as CE marking for European markets or API specifications for the oil and gas industry, may also be relevant. Compliance with these standards assures buyers that the manufacturer adheres to established quality practices.
Key QC Checkpoints: IQC, IPQC, and FQC
-
Incoming Quality Control (IQC): This initial checkpoint assesses the quality of raw materials upon arrival. It ensures that the stainless steel meets specified standards before processing begins.
-
In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): During manufacturing, IPQC monitors the production process to detect and correct any deviations in real time. This might include checking the concentration of the citric acid solution and monitoring immersion times.
-
Final Quality Control (FQC): Once the passivation process is complete, FQC involves rigorous testing of the finished product. Common tests include salt spray tests, copper sulfate tests, and humidity tests, which evaluate the effectiveness of the passivation layer.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control Practices?
B2B buyers, particularly those operating in diverse international markets, should take proactive steps to verify the quality control measures of their suppliers.
Conducting Supplier Audits
Regular audits of suppliers can provide insights into their quality control processes. Buyers should consider scheduling on-site visits to assess the manufacturing environment, equipment, and adherence to safety and quality standards.
Requesting Quality Reports
Suppliers should be able to provide documentation detailing their quality control practices, including inspection reports and certifications. These documents should demonstrate compliance with relevant standards and outline the results of various testing methods conducted during the manufacturing process.
Utilizing Third-Party Inspection Services
Engaging third-party inspection services can further enhance the verification process. These independent entities can conduct unbiased assessments of the supplier’s products and processes, ensuring that they meet industry standards and buyer specifications.
What Are the Nuances in Quality Control for International B2B Buyers?
When engaging with suppliers from different regions, B2B buyers need to consider specific nuances in quality control and certification processes.
Regional Standards and Compliance
Different regions may have varying standards for quality assurance. For example, European manufacturers must comply with CE marking requirements, while companies in the Middle East may follow different local regulations. Buyers should familiarize themselves with these regional requirements to ensure compliance.
Language and Cultural Barriers
Communication can pose challenges when dealing with international suppliers. Language barriers may lead to misunderstandings regarding quality expectations. Buyers should ensure that specifications and requirements are clearly articulated and understood by all parties involved.
Logistics and Supply Chain Considerations
International logistics can impact the quality of products. Factors such as transportation methods, environmental conditions during shipping, and local handling practices can all affect the integrity of the stainless steel parts. Buyers should work closely with suppliers to establish robust logistics plans that maintain product quality throughout the supply chain.
Conclusion
Understanding the manufacturing processes and quality assurance measures for citric passivation of stainless steel is essential for B2B buyers. By focusing on material preparation, forming, assembly, and finishing stages, along with rigorous quality control checkpoints, buyers can ensure they receive high-quality products that meet their specifications. Additionally, by actively verifying supplier practices through audits, reports, and third-party inspections, buyers can mitigate risks and enhance their procurement strategies in a competitive international market.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘citric passivation of stainless steel’
In today’s competitive manufacturing landscape, ensuring the durability and corrosion resistance of stainless steel components is paramount. This practical sourcing guide offers a step-by-step checklist for B2B buyers seeking to procure citric passivation services for stainless steel. By following these steps, you can ensure a successful partnership with suppliers that meet your specific requirements.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Establish clear technical specifications for the citric passivation process tailored to your products. This includes the desired level of corrosion resistance, the specific grades of stainless steel being treated, and any industry standards that must be met (such as ASTM A967 or AMS 2700). Defining these parameters upfront will streamline the sourcing process and ensure suppliers can meet your needs effectively.
Step 2: Research and Identify Potential Suppliers
Conduct thorough research to identify suppliers specializing in citric acid passivation. Utilize industry directories, trade shows, and online platforms to compile a list of potential candidates. Pay particular attention to suppliers with a strong reputation in your geographical market, such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, or Europe, to ensure they understand regional compliance and market conditions.
Step 3: Evaluate Supplier Certifications
Before committing, verify that potential suppliers hold the necessary certifications relevant to citric passivation processes. Look for certifications that demonstrate compliance with environmental and safety standards, such as ISO 9001 or environmental management systems (ISO 14001). These certifications not only signify a commitment to quality but also indicate adherence to best practices in handling chemicals.
Step 4: Request Technical Documentation and Case Studies
Ask suppliers for technical documentation outlining their citric passivation procedures, including detailed material safety data sheets (MSDS) for the citric acid used. Additionally, request case studies or testimonials from previous clients in similar industries to assess their capability and reliability. This documentation will provide insights into their operational practices and success rates.
Step 5: Inquire About Waste Disposal Methods
Understand the supplier’s waste disposal methods post-passivation. Since citric acid is generally more environmentally friendly than traditional nitric acid, inquire how they manage waste disposal in compliance with local regulations. Ensure that they can safely dispose of effluent without incurring additional environmental liabilities for your company.
Step 6: Assess Lead Times and Capacity
Evaluate the supplier’s lead times and production capacity to ensure they can meet your timelines. Discuss their current workload and how they prioritize orders, especially if you require large volumes or expedited service. A supplier’s ability to deliver on time is crucial to maintaining your production schedules and customer commitments.
Step 7: Negotiate Terms and Establish a Trial Order
Once you’ve narrowed down your options, negotiate terms that align with your budget and operational needs. Consider placing a trial order to assess the quality of their passivation service before committing to a larger volume. This trial run can help validate their processes and ensure that they meet your expectations for quality and service.
By following this checklist, B2B buyers can effectively navigate the procurement of citric passivation services for stainless steel, ensuring they partner with suppliers that align with their technical and business requirements.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for citric passivation of stainless steel Sourcing
What are the Key Cost Components in Citric Passivation of Stainless Steel?
The cost structure for citric passivation of stainless steel encompasses several critical components that B2B buyers need to consider:
-
Materials: The primary material cost involves citric acid, which is typically less expensive than traditional nitric acid. Other materials may include detergents for pre-cleaning and water for rinsing. The quality of citric acid can influence price, as more purified forms may be required for high-performance applications.
-
Labor: Labor costs vary depending on the complexity of the passivation process and the level of expertise required. Skilled technicians are necessary to operate the passivation equipment and to ensure compliance with industry standards. Labor costs can also be impacted by geographic location and wage norms in different regions.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes the costs of utilities, maintenance of equipment, and depreciation. Facilities that comply with environmental regulations may incur higher overhead due to the need for waste management systems, even though citric acid is generally easier to dispose of compared to nitric acid.
-
Tooling: While the passivation process may not require extensive tooling, initial setup costs for immersion tanks and associated equipment can be significant. These costs should be amortized over production volume to determine their impact on per-unit pricing.
-
Quality Control (QC): Ensuring that the passivation process meets standards like ASTM A967 and AMS 2700 necessitates rigorous QC measures. This can involve testing for surface cleanliness and corrosion resistance, which adds to the overall cost.
-
Logistics: Transportation of both raw materials and finished products contributes to the total cost. Buyers must consider shipping logistics, especially when sourcing from international suppliers, as freight costs can vary widely.
-
Margin: Suppliers typically add a profit margin to cover risks and operational costs. Understanding the typical margins in your industry can aid in negotiations.
How Do Price Influencers Affect Citric Passivation Costs?
Several factors can significantly influence the pricing of citric passivation services:
-
Volume/MOQ: Larger orders often result in lower per-unit costs due to economies of scale. Buyers should negotiate minimum order quantities (MOQs) to leverage better pricing.
-
Specifications and Customization: Customized solutions that require unique formulations or processes can increase costs. Standardized solutions tend to be more economical.
-
Material Quality and Certifications: Higher quality materials or certifications can lead to increased costs but may be necessary for industries like aerospace or medical devices where compliance is critical.
-
Supplier Factors: The reputation and reliability of the supplier can impact pricing. Established suppliers with a proven track record may charge a premium, but they often offer better assurance of quality and service.
-
Incoterms: The chosen Incoterms (International Commercial Terms) can affect total costs. Buyers should understand who is responsible for shipping, insurance, and tariffs to avoid unexpected expenses.
What Tips Can Buyers Use to Optimize Costs in Citric Passivation?
B2B buyers, particularly in regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, can optimize their sourcing strategies by employing the following tips:
-
Negotiation: Engage suppliers in discussions about pricing, especially for bulk orders. Emphasize long-term relationships to negotiate better rates.
-
Cost-Efficiency: Evaluate the total cost of ownership (TCO) rather than just upfront costs. Consider long-term benefits of citric acid over nitric acid, including lower environmental compliance costs and reduced risks.
-
Understanding Pricing Nuances: Be aware of regional market dynamics. For instance, pricing may fluctuate based on local supply chains and availability of materials. Buyers in emerging markets like Nigeria or Brazil should factor in potential currency volatility.
-
Supplier Relationships: Establish strong relationships with reliable suppliers to gain insights into pricing trends and potential discounts for loyal customers.
Disclaimer
Prices indicated in this analysis are indicative and subject to change based on market conditions, supplier negotiations, and specific project requirements. Buyers should conduct thorough research and consult with multiple suppliers to obtain accurate pricing for their unique needs.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing citric passivation of stainless steel With Other Solutions
In the realm of corrosion resistance for stainless steel, citric passivation has emerged as a leading method. However, it’s essential for B2B buyers to explore various alternatives to determine the best solution tailored to their specific needs. This analysis will compare citric passivation with nitric acid passivation and electropolishing—two prevalent methods in the industry.
Comparison Table
| Comparison Aspect | Citric Passivation Of Stainless Steel | Nitric Acid Passivation | Electropolishing |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | Highly effective, creates a robust passive layer | Very effective, but may leave residual iron | Excellent surface finish, improves corrosion resistance |
| Cost | Generally lower operational costs | Higher due to waste treatment and safety measures | Higher initial setup costs, but may reduce maintenance costs |
| Ease of Implementation | Simple process, requires minimal training | Complex due to regulatory compliance | Requires specialized equipment and trained personnel |
| Maintenance | Low maintenance, eco-friendly disposal | High maintenance, hazardous waste disposal | Moderate maintenance, equipment upkeep necessary |
| Best Use Case | Medical devices, aerospace components | Heavy-duty industrial applications | High-precision components, aesthetic applications |
Detailed Breakdown of Alternatives
Nitric Acid Passivation
Nitric acid passivation has long been the industry standard for treating stainless steel. This method is highly effective in creating a protective oxide layer, but it comes with significant drawbacks. The process involves handling hazardous materials, which necessitates stringent safety measures and regulatory compliance. Additionally, waste treatment can be costly and complex, leading to higher overall operational expenses. While it may offer superior performance in certain heavy-duty applications, the risks and costs associated with nitric acid make it less appealing for companies prioritizing safety and environmental concerns.
Electropolishing
Electropolishing is an electrochemical process that removes material from the surface of stainless steel, resulting in a smooth and polished finish. This method not only enhances corrosion resistance but also improves the aesthetic quality of the metal. However, the initial setup costs can be high due to the need for specialized equipment and trained personnel. Furthermore, while electropolishing effectively reduces surface roughness, it may not be as effective as citric passivation in removing free iron and forming a passive layer. Electropolishing is best suited for high-precision components where appearance and cleanliness are critical, but it may not be the ideal choice for all applications.
Conclusion: How to Choose the Right Solution for Your Needs
When selecting a passivation method for stainless steel, B2B buyers should consider several factors, including performance requirements, cost implications, ease of implementation, maintenance needs, and the specific application. Citric passivation stands out as a safe, environmentally friendly, and effective solution, particularly for industries like medical devices and aerospace. However, depending on the specific operational context and desired outcomes, alternatives like nitric acid passivation or electropolishing may also be suitable. Ultimately, conducting a thorough analysis of each method’s strengths and weaknesses will enable buyers to make informed decisions that align with their business objectives and compliance requirements.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for citric passivation of stainless steel
What Are the Key Technical Properties of Citric Passivation for Stainless Steel?
Understanding the essential technical properties of citric passivation is crucial for B2B buyers, particularly when selecting materials and processes that ensure corrosion resistance and longevity in various applications. Here are the most critical specifications:
-
Material Grade: Stainless steel is categorized into various grades, primarily 300 and 400 series, each with distinct corrosion resistance properties. The selection of the appropriate grade is vital for applications in environments like food processing, aerospace, and medical devices, where corrosion could lead to product failure or contamination. Buyers must ensure that the chosen passivation method aligns with the specific grade to maximize performance.
-
Passivation Layer Thickness: The effectiveness of citric passivation lies in its ability to form a protective passive oxide layer. This layer’s thickness is crucial as it directly impacts the material’s resistance to corrosion. A thicker layer generally provides better protection, especially in corrosive environments, making it essential for manufacturers in sectors requiring high durability.
-
Tolerance Levels: Tolerance refers to the acceptable variation in dimensions during manufacturing. For industries that rely on precise engineering, such as aerospace and medical devices, maintaining tight tolerances is essential. Citric acid passivation is advantageous because it selectively removes free iron without affecting other alloying elements, thus preserving dimensional integrity.
-
Process Temperature and Time: The effectiveness of citric passivation is influenced by the temperature and duration of the immersion process. Higher temperatures and shorter treatment times can enhance the removal of free iron from the surface, contributing to a more robust passive layer. Understanding these parameters allows buyers to optimize their processes for better efficiency and results.
-
Environmental Compliance: Citric acid is recognized for its eco-friendliness, being biodegradable and non-toxic. This is increasingly important for businesses aiming to meet stringent environmental regulations. Understanding the environmental impact of the materials and processes involved can help companies avoid potential liabilities and align with sustainability goals.
-
Performance Testing Standards: Compliance with industry standards such as ASTM A967 and AMS 2700 is crucial for validating the effectiveness of the citric passivation process. These standards outline the requirements for passivation treatments and acceptance criteria. Buyers should ensure that suppliers adhere to these standards to guarantee quality and performance in their applications.
What Are the Common Trade Terms in Citric Passivation of Stainless Steel?
Familiarity with trade terminology is vital for effective communication and negotiation in B2B transactions. Here are some common terms that buyers should know:
-
OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer): This term refers to companies that produce parts or equipment that are sold under another company’s brand name. Understanding OEM relationships is essential for buyers sourcing components that require citric passivation, as it impacts quality assurance and supply chain management.
-
MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity): MOQ defines the minimum quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell. This term is significant for buyers as it affects inventory management and budgeting. Knowing the MOQ can help buyers plan their orders effectively to minimize costs.
-
RFQ (Request for Quotation): An RFQ is a document sent to suppliers to solicit price quotes for specific products or services. In the context of citric passivation, buyers may use RFQs to compare costs and capabilities among different providers, ensuring they select the most competitive option.
-
Incoterms (International Commercial Terms): These are standardized trade terms that define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in international transactions. Knowledge of Incoterms helps buyers understand shipping logistics, risk management, and cost responsibilities, which is critical when sourcing materials from global suppliers.
-
Lead Time: Lead time refers to the period from placing an order to receiving the product. For buyers in industries with tight schedules, understanding lead times for citric passivation services is crucial for planning and ensuring timely delivery of materials.
-
Certification: This term indicates that a product or process meets specific industry standards or regulatory requirements. Buyers should ensure that their suppliers provide appropriate certifications for citric passivation processes to guarantee compliance and quality assurance.
In summary, understanding both the technical properties and trade terminology related to citric passivation of stainless steel enables B2B buyers to make informed decisions that enhance product performance and compliance while minimizing risks.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the citric passivation of stainless steel Sector
What Are the Current Market Dynamics and Key Trends in Citric Passivation of Stainless Steel?
The citric passivation of stainless steel is witnessing a paradigm shift driven by several global factors. The increasing demand for environmentally friendly and safer alternatives to traditional nitric acid passivation methods is a key driver. As industries prioritize sustainability, citric acid has emerged as a safer, biodegradable option that aligns with stringent environmental regulations. This trend is particularly relevant for international B2B buyers in regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, where regulatory compliance and environmental impact are critical considerations.
Technological advancements are also influencing sourcing strategies. Modern citric acid passivation systems, such as CitriSurf, are designed to enhance efficiency while meeting industry standards like ASTM A967 and AMS 2700. These systems not only improve corrosion resistance but also minimize the risk of surface contamination, making them attractive to manufacturers in high-stakes sectors like aerospace and medical devices. Buyers are increasingly looking for suppliers who can provide these innovative technologies to gain a competitive edge.
Additionally, the rise of digital platforms for sourcing and procurement is reshaping the landscape. Buyers can now access a broader range of suppliers and technologies, enabling more informed decisions. The integration of digital tools also facilitates better supply chain transparency, allowing B2B buyers to track the sustainability practices of their suppliers, thereby aligning with their corporate social responsibility goals.
How Is Sustainability Shaping Ethical Sourcing in Citric Passivation of Stainless Steel?
Sustainability is not just a buzzword; it has become a core principle guiding sourcing decisions in the citric passivation sector. The environmental impact of manufacturing processes is under scrutiny, prompting companies to adopt greener practices. Citric acid’s non-toxic and biodegradable properties align well with this trend, providing a safe alternative for passivation processes that minimizes harmful waste. This is particularly important for buyers in regions with strict environmental regulations, as non-compliance can lead to costly penalties and damage to reputation.
Ethical supply chains are increasingly prioritized by B2B buyers who seek to mitigate risks associated with environmental and social governance (ESG) issues. Suppliers offering certifications for sustainability, such as ISO 14001 for environmental management, are becoming more attractive. These certifications not only demonstrate a commitment to reducing environmental impact but also ensure that sourcing practices are socially responsible.
Moreover, the use of green materials in citric passivation processes can enhance a company’s brand image and appeal to environmentally conscious customers. Buyers are encouraged to engage with suppliers who prioritize sustainable practices, as this can lead to long-term partnerships and competitive advantages in their respective markets.
What Has Been the Evolution of Citric Passivation in the Stainless Steel Industry?
The evolution of citric passivation can be traced back to the need for safer alternatives to nitric acid, which has long been the traditional choice for passivating stainless steel. While effective, nitric acid poses significant health and environmental risks, leading to regulatory challenges. The introduction of citric acid as a passivation agent marked a significant turning point, driven by advancements in chemical technology that improved its efficacy and stability against organic growth.
Over the years, the citric passivation process has been refined, with modern formulations like CitriSurf offering enhanced performance and compliance with industry standards. This evolution has been crucial in industries where corrosion resistance is paramount, such as aerospace and medical devices. Today, citric acid passivation is recognized not only for its effectiveness but also for its environmental benefits, making it the preferred choice for many manufacturers globally. This historical context underscores the importance of adopting innovative and sustainable practices in the stainless steel industry, aligning with current market demands.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of citric passivation of stainless steel
-
How do I solve corrosion issues in stainless steel products?
Corrosion in stainless steel can be effectively mitigated through proper passivation processes, particularly using citric acid passivation. This method removes free iron ions from the surface, forming a protective oxide layer that enhances corrosion resistance. To implement this solution, ensure your stainless steel components undergo a thorough cleaning followed by immersion in a citric acid bath. This process not only addresses existing corrosion but also helps prevent future occurrences, making your products more durable and reliable. -
What is the best method for passivating stainless steel?
The preferred method for passivating stainless steel is citric acid passivation. Unlike traditional nitric acid methods, citric acid is environmentally friendly, non-toxic, and safer for workers. It effectively removes free iron from the surface, forming a stable passive oxide layer that provides long-lasting corrosion resistance. This method is particularly advantageous for industries requiring stringent compliance with safety and environmental standards, such as medical and aerospace sectors. -
How do I evaluate suppliers for citric passivation services?
When evaluating suppliers for citric passivation, consider their certifications and adherence to industry standards such as ASTM A967 and AMS 2700. Assess their experience in handling stainless steel and their ability to customize solutions based on your specific needs. Request samples or references from previous clients to gauge their service quality. Additionally, inquire about their waste disposal practices and environmental compliance to ensure they align with your corporate sustainability goals. -
What are the minimum order quantities (MOQ) for citric passivation services?
Minimum order quantities for citric passivation services can vary significantly among suppliers. Some may have a low MOQ, catering to smaller businesses or specific projects, while others might require larger quantities due to operational costs. It’s essential to communicate your needs upfront and negotiate terms that work for both parties. Establishing a clear understanding of MOQ can help in managing your production schedules and budgeting effectively. -
What payment terms should I expect when sourcing citric passivation?
Payment terms for citric passivation services typically range from upfront payments to net 30 or net 60 days, depending on the supplier’s policies and your business relationship. International buyers should also consider the implications of currency fluctuations and transfer fees. It’s advisable to negotiate favorable terms that align with your cash flow while ensuring the supplier feels secure in the transaction. Always review the contract thoroughly before finalizing any agreements. -
How do logistics and shipping impact citric passivation services?
Logistics and shipping play a crucial role in the timely delivery of passivated stainless steel products. Factors such as distance, customs regulations, and transportation methods can affect lead times and costs. When sourcing internationally, ensure that your supplier has experience with export regulations in your region. Additionally, consider using a logistics partner familiar with handling chemicals to avoid delays or compliance issues during transit. -
What quality assurance measures should I look for in a citric passivation supplier?
Quality assurance measures are vital for ensuring the effectiveness of citric passivation. Look for suppliers that conduct thorough inspections and testing in accordance with industry standards such as ASTM A967. They should have protocols for tracking passivation results, including salt spray tests and surface analysis. Request documentation demonstrating their quality control processes and ask about their approach to continuous improvement to ensure consistent service quality. -
Can citric passivation be customized for different grades of stainless steel?
Yes, citric passivation can be customized for different grades of stainless steel. Each grade may require specific treatment parameters such as temperature, concentration, and immersion time to achieve optimal results. Discuss your material specifications with potential suppliers to ensure they can tailor their passivation process to meet the unique needs of your products. Customization can enhance the effectiveness of corrosion resistance and ensure compliance with industry standards.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.
Top 10 Citric Passivation Of Stainless Steel Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. Best Technology Inc – Citric Acid Passivation for Stainless Steel
Domain: besttechnologyinc.com
Registered: 2001 (24 years)
Introduction: Citric Acid Passivation for Stainless Steel is a post-fabrication finishing process that uses citric acid to passivate stainless steel and other alloys, preventing corrosion by removing free iron ions and forming a protective passive oxide layer. Key benefits include: environmentally safe chemistry, low workplace hazard, compliance with industry standards (ASTM A967, AMS 2700), effective removal o…
2. CitriSurf – Citric Acid Passivation Products
Domain: citrisurf.com
Registered: 2001 (24 years)
Introduction: CitriSurf Stainless Steel Citric Acid Passivation products include: CitriSurf® 2050 (most cost effective for 300 series austenitic grades), CitriSurf® 2210 (thicker gel for vertical surfaces), CitriSurf® 2250 (increased pH for 400 series), CitriSurf® 2450 (higher pH for low chromium grades), CitriSurf® 3050 (low foaming for spraying), CitriSurf® 3250 (low foaming version), CitriSurf® 77 (liquid fo…
3. Reddit – Citric Acid for Stainless Steel Passivation
Domain: reddit.com
Registered: 2005 (20 years)
Introduction: Citric Acid is used for cleaning and passivating stainless steel fermenters in homebrewing. A 4% solution at 160-180°F for about an hour is recommended for effective passivation. It is noted that phosphoric acid does not effectively passivate stainless steel, while citric acid is preferred for its properties. Users have shared experiences with different brands of stainless steel equipment, such as…
4. Homebrew Talk – Citric Acid Passivation Solution
Domain: homebrewtalk.com
Registered: 2004 (21 years)
Introduction: Citric Acid for passivation of stainless steel kettles; recommended mixture is a 4% solution (40 grams per liter or 151 grams per gallon, equivalent to 5.32 oz per gallon); soak temperature should be around 180°F for approximately 30 minutes; alternative to StarSan for passivation; citric acid is environmentally friendly and cost-effective.
5. Capital Weld Cleaners – Citric Acid Passivation Spray
Domain: capitalweldcleaners.com
Registered: 2008 (17 years)
Introduction: High-Quality Citric Acid Passivation – Clean & Passivate Stainless Steel. Price: $24.00 – $1,785.00. Product: Citric Acid Passivation Spray – Ready-to-Use Surface Treatment for Stainless Steel. Features: Ready-to-Use Citric Acid Formula, ASTM A967 / A380 Compliant, Non-Hazardous & Environmentally Friendly, Selective Iron Removal, Safe for Operators & Workspaces, Broad Alloy Compatibility. Applicat…
6. Brulin – Citric Acid Passivation Process
Domain: brulin.com
Registered: 1998 (27 years)
Introduction: Citric Acid Passivation Process: A common method for passivating stainless steel, using citric acid as a replacement for nitric acid. Key details include:
– Effective pH range: 1.7-2.2
– Importance of cleaning and soil removal prior to passivation
– Recommended use of a mild alkaline detergent for immersion/ultrasonic cleaning
– Typical concentration of aqueous detergent: 10%
– Benefits of us…
7. NE Electropolishing – Citric Acid Passivation
Domain: neelectropolishing.com
Registered: 1998 (27 years)
Introduction: Citric acid passivation is a process used to enhance the corrosion resistance of stainless steel and other alloys. It involves treating the metal surface with a citric acid solution, which removes free iron and other contaminants, leaving a protective oxide layer. This method is environmentally friendly and effective for improving the durability of metal components in various industries.
8. iForge Iron – Pickling and Passivation Solutions
Domain: iforgeiron.com
Registered: 2001 (24 years)
Introduction: 1. Pickling and Passivation Process: Used for stainless steel to enhance corrosion resistance. 2. Common Chemicals: Citric acid (10% solution preferred), nitric acid, aluminum sulfate (less common). 3. Application: Citric acid is biodegradable and safer than nitric acid. 4. Effectiveness: Passivation increases nickel and chromium concentration on the surface, removing free iron. 5. Appearance Post…
9. Chempoint – Anhydrous Citric Acid
Domain: chempoint.com
Registered: 1999 (26 years)
Introduction: Anhydrous citric acid is a naturally derived powder used for metal passivation, particularly for stainless steel surfaces. It provides a safer and environmentally friendly method to protect metal components from corrosion and rust. Key benefits include improved corrosion resistance, extended component lifetime, improved surface cleanliness, and increased quality and manufacturing consistency. Citr…
10. Practical Machinist – Citric Acid for Passivation
Domain: practicalmachinist.com
Registered: 2000 (25 years)
Introduction: Citric acid for passivation, typically used at concentrations of 6-10% and heated to around 140 degrees Fahrenheit. Available in powdered form from brewing shops or online, priced approximately $6-$10 per pound. Can be used in conjunction with alkaline cleaners to remove residues before passivation. Suitable for stainless steel parts, particularly 303 alloy, to create a protective chromium oxide l…
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for citric passivation of stainless steel
In conclusion, citric acid passivation presents a robust and environmentally friendly alternative to traditional nitric acid methods for treating stainless steel. This process not only enhances corrosion resistance by effectively removing free iron but also aligns with increasing global regulatory demands for safer chemicals. For B2B buyers, particularly in regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, the strategic sourcing of citric acid passivation solutions like CitriSurf can lead to improved product durability and compliance with industry standards such as ASTM A967 and AMS 2700.
Investing in citric passivation technology not only mitigates health risks and environmental concerns associated with nitric acid but also offers a cost-effective solution that can be integrated into existing manufacturing processes. As industries evolve, the demand for sustainable and efficient metal treatment solutions will continue to grow.
Now is the time for international buyers to embrace this innovative approach, ensuring their operations not only meet current standards but also pave the way for future advancements in material science. Engage with suppliers who prioritize safety, efficiency, and sustainability in their offerings, and position your business as a leader in responsible manufacturing practices.