Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for chrome plating hardness
In the fast-evolving landscape of global manufacturing, sourcing high-quality chrome plating hardness solutions poses a significant challenge for B2B buyers across diverse industries. The durability and performance of components heavily rely on the right hardness specifications of chrome plating, particularly in high-wear applications. This comprehensive guide aims to equip international buyers, especially those from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, with the essential insights needed to make informed purchasing decisions.
We delve into the various types of chrome plating, including hard chrome plating, and their specific applications in industries such as agriculture, automotive, and heavy machinery. By exploring the critical factors influencing hardness—such as plating thickness and base material properties—we provide clarity on how to select the optimal solution for your operational needs. Furthermore, the guide addresses supplier vetting processes, cost considerations, and the importance of conducting field tests to ensure compatibility with real-world conditions.
By leveraging the knowledge presented in this guide, B2B buyers can navigate the complexities of sourcing chrome plating hardness more effectively, ultimately enhancing their product durability and operational efficiency while reducing maintenance costs. This empowers businesses to remain competitive in their respective markets, ensuring that every decision made aligns with both quality and cost-effectiveness.
Understanding chrome plating hardness Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Hard Chrome Plating | Hardness range of 66-72 HRC; applied thickness 0.001″ to 0.020″ | Heavy machinery, automotive components | Pros: Excellent wear resistance; cost-effective for base materials. Cons: Requires precise surface preparation. |
| Decorative Chrome Plating | Primarily aesthetic; lower hardness compared to hard chrome | Consumer goods, automotive trim | Pros: Enhances appearance; corrosion resistance. Cons: Limited protective qualities; not suitable for heavy wear. |
| Micro Chrome Plating | Very thin layer; typically less than 0.0005″ thick; high precision | Electronics, medical devices | Pros: Minimal impact on dimensions; ideal for tight tolerances. Cons: Limited wear resistance; not suitable for heavy-duty applications. |
| Chrome Oxide Coatings | Non-metallic; high hardness and corrosion resistance | Aerospace, marine applications | Pros: Excellent durability; withstands extreme conditions. Cons: More expensive; complex application process. |
| Flash Chrome Plating | Very thin layer; primarily for corrosion resistance; quick application | Fasteners, small components | Pros: Cost-effective; fast turnaround. Cons: Limited wear protection; not suitable for high-stress environments. |
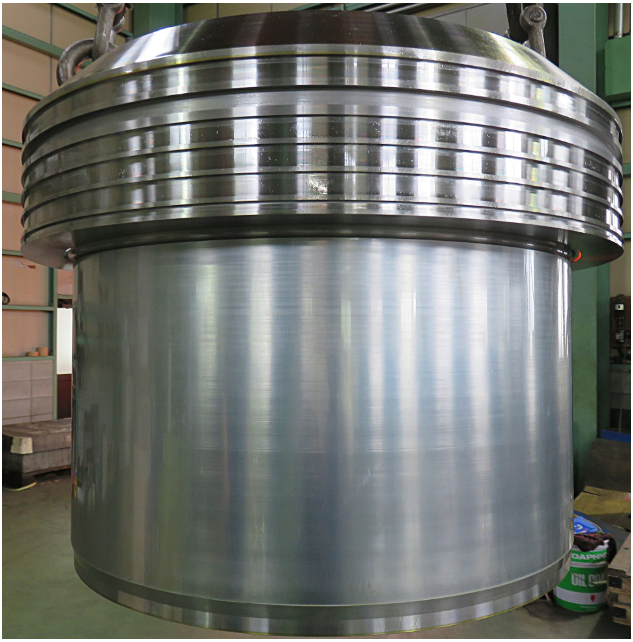
What are the Characteristics of Hard Chrome Plating?
Hard chrome plating is characterized by its hardness, typically ranging from 66 to 72 HRC, making it suitable for applications requiring significant wear resistance. It can be applied in various thicknesses, from 0.001″ to 0.020″, allowing for tailored solutions based on specific operational needs. This type of plating is ideal for heavy machinery and automotive components, where durability is paramount. Buyers should consider the preparation and post-plating processes required to achieve optimal adhesion and performance.
How Does Decorative Chrome Plating Differ?
Decorative chrome plating is primarily used for aesthetic purposes, offering a shiny finish to consumer goods and automotive trim. While it provides some level of corrosion resistance, its hardness is significantly lower than hard chrome plating. This type is suitable for applications where appearance is more critical than functionality. Buyers should weigh the visual appeal against the limited protective qualities when considering this option.
What is Micro Chrome Plating and Its Suitability?
Micro chrome plating involves applying a very thin layer of chrome, often less than 0.0005″ thick, making it suitable for high-precision applications like electronics and medical devices. This type of plating minimally affects the dimensions of components, which is critical for tight tolerances. However, its wear resistance is limited, so it’s best suited for environments where heavy wear is not a concern. B2B buyers should evaluate the specific requirements of their applications to determine if micro chrome plating is the right choice.
What Advantages Do Chrome Oxide Coatings Offer?
Chrome oxide coatings are non-metallic and provide excellent hardness and corrosion resistance, making them ideal for demanding environments such as aerospace and marine applications. This type offers durability and can withstand extreme conditions, which is a significant advantage for industries that require reliable performance. However, the application process can be complex and more expensive, so buyers must assess their budget against the benefits provided.
What is Flash Chrome Plating and When is it Used?
Flash chrome plating involves applying a very thin layer of chrome primarily for corrosion resistance. It is a cost-effective and quick solution often used for fasteners and small components. While it offers some protection against corrosion, it lacks the wear resistance needed for high-stress environments. B2B buyers should consider the trade-off between cost and performance when selecting flash chrome plating for their applications.
Key Industrial Applications of chrome plating hardness
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of chrome plating hardness | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Mining and Construction | Wear protection for drill components | Extends equipment longevity and minimizes maintenance costs | Sourcing thickness should match application wear patterns; durability must withstand abrasive materials. |
| Agricultural Machinery | Treatment of hydraulic cylinders and rods | Reduces downtimes and increases operation efficiency | Evaluate corrosion resistance properties according to local soil conditions; consider local supply capabilities for timely delivery. |
| Automotive Manufacturing | Hard-chromed engine components | Enhances performance and resistance to wear, leading to longer part lifespans | Require certifications on hardness levels and surface finish; prioritize suppliers with established quality control processes. |
| Oil and Gas Industry | Coating for pumps and valves | Increases reliability under high-load conditions and extends life cycles | Assess chemical resistance to specific hydrocarbons; check compliance with local and international standards. |
| Aerospace | Hard chrome on landing gear and structural components | Improves safety and reliability while reducing maintenance intervals | Partner with suppliers who have aerospace-specific certifications; focus on precise hardness specifications for critical applications. |
Which Industries Benefit from Chrome Plating Hardness?
Mining and Construction: How is Chrome Plating Used in Heavy Equipment?
In mining and construction, chrome plating hardness is critical for wear protection on drill components, such as drill bits and augers. These parts often face extreme conditions, leading to wear and damage that can halt operations and escalate costs. By applying hard chrome plating, businesses can significantly extend the life of these components, allowing for reduced downtime and maintenance expenditures. Buyers should consider sourcing thicknesses tailored to specific wear patterns and ensure the durability can withstand abrasive materials commonly encountered at job sites.
What Role Does Chrome Plating Play in Agricultural Machinery?
In the agricultural sector, hard chrome plating is essential for hydraulic cylinders and rods that are pivotal in machinery such as tractors and harvesters. The increased hardness prevents premature wear from soil and crop interactions, improving the reliability and efficiency of farming operations. Buyers must evaluate the corrosion resistance properties to withstand varied soil conditions encountered in different regions and consider the capabilities of local suppliers to ensure timely delivery and service.
Why is Chrome-Plated Engine Components Vital for Automotive Manufacturing?
Automotive manufacturers utilize hard chrome plating on engine components to enhance performance and resistance to wear. This ensures that parts such as pistons and crankshafts can endure high stress without suffering damage, extending their operational lifespans. When sourcing these components, buyers should require certifications verifying hardness levels and surface finishes, as well as emphasize suppliers with robust quality control processes to maintain competitive advantages.
How Does Chrome Plating Improve Reliability in the Oil and Gas Industry?
In the oil and gas industry, hard chrome plating is applied to pumps, valves, and other critical equipment to increase reliability under high-load conditions. The enhanced hardness and wear resistance reduce the likelihood of failures that can lead to costly outages or hazardous incidents. Buyers should assess the chemical resistance of chrome plating against specific hydrocarbons and verify compliance with local and international industry standards to ensure safety and efficiency.
In What Ways is Chrome Plating Key to Aerospace Components?
Aerospace applications require the highest standards for safety and reliability, making hard chrome plating on landing gear and structural components indispensable. This maintenance solution minimizes wear and enhances part performance, thereby reducing service intervals and improving safety margins. Buyers must partner with suppliers who hold aerospace-specific certifications and focus on precise hardness specifications relevant to critical aerospace applications, ensuring compliance with stringent regulatory requirements.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘chrome plating hardness’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Inconsistent Hardness Levels Affecting Equipment Performance
The Problem: B2B buyers often encounter issues with inconsistent hardness levels in chrome plating. Variability in hardness can result from fluctuations in the plating bath parameters, leading to parts that don’t meet specifications. This inconsistency can affect the wear resistance of critical components, ultimately leading to premature failure, increased maintenance costs, and extended downtime. For manufacturers in sectors like mining or agriculture, where equipment reliability is paramount, these issues can significantly impact operational efficiency and profitability.
The Solution: To combat inconsistent hardness levels, it’s crucial to establish stringent quality control measures during the plating process. Buyers should partner with reputable suppliers who conduct regular testing and verification of hardness values using both Rockwell and Vickers scales. Specifying the desired hardness range during the procurement process is also vital. Buyers should request samples from the supplier and conduct their own tests to ensure the products meet their performance requirements. Additionally, engaging in a dialogue with suppliers about the specific environmental conditions and stressors the components will face can help tailor the plating thickness and hardness to better suit application needs.
Scenario 2: Challenges with Thickness Specification for Optimal Wear Protection
The Problem: Another common challenge faced by B2B buyers is determining the appropriate thickness of chrome plating for different applications. Excessive thickness can lead to issues like cracking or peeling, while insufficient thickness may not provide adequate wear protection. This dilemma is especially prevalent in industries such as manufacturing and construction, where equipment is subjected to heavy wear. Buyers often struggle with specifying the correct thickness to balance performance and cost, leading to either premature component failure or unnecessary expenses.
The Solution: To effectively specify chrome plating thickness, buyers should engage in thorough field testing to assess wear patterns and performance under real-world conditions. Collaboration with the supplier to conduct these tests can yield valuable insights into the optimal thickness needed for specific applications. Additionally, buyers can utilize a modular approach by plating only high-friction areas instead of the entire component. This targeted application can reduce costs while still ensuring adequate protection. Buyers should also consider the operational environment—factors such as temperature, pressure, and material interaction can all influence the ideal plating thickness. Documenting these parameters will aid in making informed decisions.
Scenario 3: Surface Preparation Issues Leading to Poor Adhesion
The Problem: Poor surface preparation before chrome plating can result in inadequate adhesion, leading to delamination and reduced effectiveness of the chrome layer. This issue is particularly concerning for B2B buyers in sectors such as automotive or aerospace, where precision and durability are critical. Components that fail due to poor adhesion can lead to significant costs related to repairs, recalls, or safety incidents, undermining trust in suppliers and damaging brand reputation.
The Solution: To ensure optimal adhesion of chrome plating, buyers should prioritize rigorous surface preparation protocols. This includes ensuring that base materials are free of contaminants, such as rust, oil, or dirt, and that any weld spatter is removed. It’s advisable to work closely with the supplier to develop a tailored surface preparation plan that meets specific application needs. Techniques like abrasive blasting or chemical cleaning can significantly improve the surface condition prior to plating. Furthermore, post-plating processes such as baking to prevent hydrogen embrittlement should be employed when necessary. Buyers should also consider requesting adhesion testing as part of their quality assurance process to validate that the chromed components will perform reliably in service.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for chrome plating hardness
What Are the Key Properties of Common Materials for Chrome Plating Hardness?
When selecting materials for chrome plating hardness, several factors must be considered to ensure optimal performance in various applications. Below, we analyze four common materials used in conjunction with hard chrome plating, focusing on their key properties, advantages, disadvantages, and specific considerations for international B2B buyers.
1. Carbon Steel
Key Properties:
Carbon steel is known for its high tensile strength and good wear resistance. It typically has a hardness range of 40-50 HRC before plating, making it suitable for applications requiring toughness. Its corrosion resistance is moderate, which is enhanced significantly when coated with hard chrome.
Pros & Cons:
Pros include excellent machinability and lower cost compared to stainless steel. However, its susceptibility to rust and corrosion without adequate protection is a significant drawback, necessitating chrome plating for longevity.
Impact on Application:
Carbon steel is compatible with various media, including oils and water-based fluids. Its hardness after chrome plating (around 68-72 HRC) makes it ideal for heavy wear applications in industries such as agriculture and manufacturing.
Considerations for International Buyers:
Buyers should ensure compliance with ASTM standards for carbon steel, particularly ASTM A36 or A992. In regions like South America and Africa, where corrosion can be a concern, the added chrome layer is crucial for durability.
2. Stainless Steel
Key Properties:
Stainless steel offers excellent corrosion resistance and is available in various grades, such as 304 and 316. These grades exhibit hardness levels ranging from 30-40 HRC, which can be significantly improved with hard chrome plating.
Pros & Cons:
The primary advantage of stainless steel is its resistance to oxidation and staining, making it ideal for harsh environments. However, it is generally more expensive and can be challenging to machine compared to carbon steel.
Impact on Application:
Stainless steel is particularly suitable for applications involving corrosive media, such as chemicals and saline environments. The chrome plating enhances its wear resistance while maintaining its corrosion-resistant properties.
Considerations for International Buyers:
Compliance with international standards like ASTM A240 for stainless steel is essential. Buyers in the Middle East, where humidity is high, will find stainless steel with chrome plating particularly beneficial.
3. Aluminum
Key Properties:
Aluminum is lightweight and has good corrosion resistance, with a hardness typically around 15-25 HRC. While its base hardness is lower than steel, hard chrome plating can enhance its surface hardness significantly.
Pros & Cons:
The advantages of aluminum include its lightweight nature and excellent machinability. However, its lower strength compared to steel and potential for galling in high-friction applications are notable disadvantages.
Impact on Application:
Aluminum is compatible with various media, including water and mild chemicals. After chrome plating, it can be used in applications that require weight reduction without sacrificing performance, such as in aerospace and automotive industries.
Considerations for International Buyers:
Buyers should be aware of the specific grades of aluminum suitable for plating, such as 6061 or 7075. In Europe, adherence to EN standards for aluminum is crucial for ensuring quality.
4. Cast Iron
Key Properties:
Cast iron is known for its excellent wear resistance and ability to absorb vibrations. It typically has a hardness of 150-200 HB, which can be increased with hard chrome plating.
Pros & Cons:
The primary advantage of cast iron is its durability and cost-effectiveness. However, it is brittle and can crack under stress, which limits its application in high-impact environments.
Impact on Application:
Cast iron is often used in heavy machinery and automotive components. The addition of hard chrome plating enhances its wear resistance, making it suitable for high-load applications.
Considerations for International Buyers:
Buyers should ensure compliance with ASTM A48 for cast iron. In regions like Brazil, where heavy machinery is prevalent, the durability offered by chrome plating can be a significant selling point.
Summary Table
| Material | Typical Use Case for chrome plating hardness | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Carbon Steel | Heavy wear applications in manufacturing | Cost-effective and strong | Corrosion susceptibility | Low |
| Stainless Steel | Corrosive environments in food and chemical industries | Excellent corrosion resistance | Higher cost and machining difficulty | High |
| Aluminum | Aerospace and automotive lightweight components | Lightweight with good machinability | Lower strength compared to steel | Medium |
| Cast Iron | Heavy machinery and automotive components | Durable and cost-effective | Brittle and prone to cracking | Low |
This guide provides actionable insights for international B2B buyers, helping them make informed decisions regarding material selection for chrome plating hardness tailored to their specific needs and regional considerations.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for chrome plating hardness
What Are the Key Stages in the Manufacturing Process for Chrome Plating Hardness?
The manufacturing process for chrome plating involves several critical stages that ensure the final product meets the desired hardness and performance specifications. Each stage requires precise control and expertise to achieve optimal results.
Material Preparation: How Is the Base Material Prepped for Chrome Plating?
The first stage in chrome plating involves preparing the base material. This step is crucial as the quality of the surface directly affects the adhesion and performance of the chrome layer. The following actions are typically undertaken:
- Cleaning: The base material must be thoroughly cleaned to remove any surface contaminants, such as oils, dirt, or oxidation. This is often achieved through chemical baths or mechanical cleaning methods.
- Surface Conditioning: Depending on the material, it may require mechanical polishing or shot blasting to create a uniform surface. This process enhances the surface roughness, which promotes better adhesion of the chrome layer.
- Inspection: After cleaning and conditioning, the materials are inspected for any imperfections. Any defects at this stage can lead to issues later in the process, including poor adhesion or uneven plating.
What Techniques Are Used in the Chrome Plating Process?
Once the base material is prepared, it enters the chrome plating stage. The primary technique used is electroplating, which involves the following steps:
- Electrolytic Bath Preparation: The base material is submerged in an electrolytic solution containing chromium salts. The chemical composition and temperature of this bath are critical in determining the hardness and quality of the chrome deposit.
- Electroplating: An electrical current is passed through the bath, causing chromium ions to deposit onto the surface of the base material. The thickness of the chrome layer can vary, typically ranging from 0.001 inches to 0.020 inches, depending on the application.
- Post-Plating Treatment: To enhance the hardness and durability of the chrome layer, post-plating treatments such as baking or polishing may be employed. This step can help mitigate issues like hydrogen embrittlement and improve the surface finish.
How Is Quality Assurance Implemented in Chrome Plating?
Quality assurance (QA) is paramount in the chrome plating process, ensuring that the final product meets industry standards and customer expectations. Various international and industry-specific standards guide these QA processes.
Which International Standards Are Relevant for Chrome Plating Quality Assurance?
Many international standards apply to chrome plating processes, with ISO 9001 being one of the most significant. This standard outlines quality management principles that help organizations ensure consistent quality in their products and services. Other relevant standards may include:
- ISO 13485: Particularly for applications in medical devices.
- CE Marking: Required for products sold in the European Economic Area.
- API Standards: Relevant for the oil and gas industry, ensuring that the materials used can withstand harsh environments.
What Are the Key Quality Control Checkpoints in the Chrome Plating Process?
Quality control (QC) checkpoints are integrated throughout the manufacturing process to catch any defects early. Common QC checkpoints include:
- Incoming Quality Control (IQC): Materials are inspected upon arrival to ensure they meet specified requirements before processing begins.
- In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): During the electroplating process, various parameters, such as bath chemistry and temperature, are continuously monitored to ensure optimal conditions are maintained.
- Final Quality Control (FQC): After plating, the finished products undergo rigorous testing to verify hardness, thickness, and surface quality. Common testing methods include Rockwell and Vickers hardness tests, as well as visual inspections for surface defects.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control Processes?
For international B2B buyers, especially those from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, verifying the quality control processes of suppliers is essential. Here are some effective methods:
- Supplier Audits: Conducting on-site audits of suppliers can provide firsthand insights into their manufacturing and quality assurance practices. This allows buyers to assess compliance with international standards.
- Quality Control Reports: Requesting documentation of quality control measures, including test results and process validation reports, can help buyers understand the reliability of a supplier’s QA practices.
- Third-Party Inspections: Engaging third-party inspection agencies can provide an unbiased assessment of the supplier’s quality control processes. This is particularly important for B2B buyers dealing with critical applications where failure could lead to significant costs.
What Are Common Testing Methods for Ensuring Chrome Plating Hardness?
To ensure that the chrome plating meets the required hardness specifications, several testing methods are commonly employed:
- Rockwell Hardness Test: This test is widely used due to its speed and ease of interpretation. It provides a direct measurement of hardness on the Rockwell C scale, which is particularly relevant for chrome plating.
- Vickers Hardness Test: Although slower and more costly, this method offers a more accurate measurement of hardness, making it suitable for applications with stringent quality requirements.
- Surface Roughness Testing: This assesses the texture of the chrome-plated surface, which can impact wear resistance and friction characteristics.
What Are the QC and Certification Nuances for International B2B Buyers?
For B2B buyers operating internationally, understanding the nuances of quality control and certification is vital. Different regions may have varying regulatory requirements that affect product certification and compliance. Buyers should consider:
- Local Regulations: Familiarizing themselves with local regulations in the target market can help ensure compliance and avoid potential legal issues.
- Language Barriers: Communication may pose challenges; thus, it is advisable to work with suppliers who can provide documentation and support in the buyer’s preferred language.
- Cultural Differences: Understanding cultural practices in business negotiations and quality assurance can facilitate smoother interactions with suppliers.
Conclusion
The manufacturing processes and quality assurance practices associated with chrome plating hardness are complex and critical for ensuring product performance and durability. B2B buyers must be diligent in evaluating suppliers’ capabilities, understanding international standards, and implementing effective verification methods to secure high-quality products tailored to their specific needs. By prioritizing these factors, businesses can enhance their operational efficiency, reduce costs, and maintain a competitive edge in their respective markets.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘chrome plating hardness’
Introduction
This guide provides a practical checklist for B2B buyers focused on procuring chrome plating services, specifically with an emphasis on hardness characteristics. Understanding the specifications and benefits of hard chrome plating is crucial for businesses aiming to enhance equipment durability and performance. This checklist will help streamline the sourcing process and ensure that you select the right supplier for your needs.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Begin by clearly outlining the technical requirements for your chrome plating project. This includes specifying the desired hardness level, which typically ranges from 66 to 72 Rockwell C (HRC) for industrial applications. Additionally, consider the thickness of the chrome layer, as this can impact wear resistance and overall performance.
Step 2: Research Industry Standards and Regulations
Understanding the relevant industry standards and regulations governing chrome plating is essential for compliance and quality assurance. Familiarize yourself with international standards such as ISO 9001 or local regulations that may apply in your region, particularly in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. Ensuring that your supplier adheres to these standards will help mitigate risks associated with quality and safety.
Step 3: Evaluate Potential Suppliers
Thoroughly vet potential suppliers to ensure they meet your technical and quality requirements. Request documentation such as company profiles, certifications, and case studies that demonstrate their experience in hard chrome plating. Pay particular attention to references from clients in similar industries or regions to gauge their reliability and quality of service.
Step 4: Assess Plating Technology and Equipment
Investigate the technology and equipment your potential suppliers use for chrome plating. Advanced equipment can provide more consistent results and better control over plating thickness and hardness. Inquire about their processes for quality control, as well as any surface preparation techniques they employ, such as removing surface impurities or optimizing base material uniformity.
Step 5: Request Samples and Conduct Field Tests
Before finalizing your order, request samples of the chrome-plated parts or conduct field tests under real-world conditions. Testing various thicknesses and hardness levels can help identify the optimal specifications for your application. This step is vital for ensuring that the plating performs as expected in your specific operational environment.
Step 6: Understand Cost Implications
Analyze the cost structure associated with chrome plating services. Be aware that while hard chrome plating can be more expensive upfront, its durability and wear resistance may lead to lower maintenance costs over time. Consider asking suppliers for a detailed breakdown of costs, including any additional charges for custom thicknesses or expedited services.
Step 7: Establish Clear Communication Channels
Once you have selected a supplier, establish clear communication channels to facilitate ongoing collaboration. Regular updates regarding production timelines, quality checks, and any potential issues will ensure that your project runs smoothly. Open lines of communication can also help address any adjustments required during the plating process.
By following this checklist, B2B buyers can make informed decisions when sourcing chrome plating services, ensuring they achieve optimal hardness and durability for their applications.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for chrome plating hardness Sourcing
In navigating the complex landscape of chrome plating hardness sourcing, understanding the cost structure and pricing dynamics is crucial for international B2B buyers. This analysis highlights the primary cost components, influential price factors, and offers strategic buyer tips tailored for markets in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe.
What are the Key Cost Components in Chrome Plating Hardness?
-
Materials
The primary raw material is chromium, which has fluctuating prices driven by global supply and demand. Secondary materials such as base metals (e.g., steel or aluminum substrates) contribute to the overall cost. The quality of these materials directly influences the final product’s hardness and performance. -
Labor
Labor costs can vary significantly based on geographic location, skill levels, and local wage rates. Countries with advanced manufacturing capabilities may command higher wages, but the quality and efficiency may offset these costs. Skilled operators are vital for achieving the desired plating thickness and quality. -
Manufacturing Overhead
Expenses related to facility maintenance, equipment, and utilities add to the overhead costs. Keeping the production environment optimal for plating processes is critical, especially for achieving consistent hardness values, which typically range from 66 to 70 on the Rockwell C scale. -
Tooling
The investment in tooling for preparation and processing adds to the initial costs. This includes both equipment for surface preparation and fixtures needed for handling components during plating. -
Quality Control (QC)
Ensuring quality through rigorous testing and inspection is essential. The QC process verifies that hardness, thickness, and surface finish specifications are met, contributing to the cost structure while minimizing post-production failures. -
Logistics
Effective logistics cover raw material procurement and the final delivery of plated products. International shipping costs, customs duties, and handling fees can be significant, especially for buyers located far from manufacturing sites. -
Margin
Suppliers will include a margin that reflects their operational efficiency, market conditions, and risk. This margin often varies based on volume commitments and competitive pressures in different regions.
How Do Price Influencers Impact Chrome Plating Costs?
-
Volume and Minimum Order Quantity (MOQ)
Larger orders generally lead to lower per-unit costs due to economies of scale. Suppliers are more inclined to offer discounts for bulk purchases, which is a critical aspect for buyers looking to manage costs effectively. -
Specifications and Customization
Custom specifications, such as particular hardness requirements or specific plating thickness, can lead to increased costs due to the need for specialized equipment and processes. Standard specifications may enjoy lower pricing due to established processes. -
Material Quality and Certification
The demand for high-quality base metals and certified plating processes influences pricing. Products that require strict regulatory compliance or industry certifications, such as aerospace or automotive standards, might incur higher costs. -
Supplier Factors
Supplier reputation, reliability, and historical performance will affect pricing. Established suppliers with proven track records can often justify higher prices through demonstrated quality assurance, reliability, and quicker turnaround times. -
Incoterms
Understanding Incoterms is vital for calculating total costs. The chosen Incoterm (e.g., FOB, CIF) dictates who is responsible for shipping charges, insurance, and other logistical considerations, impacting the final pricing landscape.
What Strategies Should Buyers Consider for Negotiation and Cost Efficiency?
-
Negotiate Volume Discounts: Leverage purchasing power by committing to larger orders or long-term contracts, which can lead to substantial price reductions.
-
Evaluate the Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Consider not just the unit price, but the long-term costs associated with durability, maintenance, and potential operational downtime due to equipment failures affected by coating quality.
-
Conduct Market Research: Benchmark pricing across different suppliers and regions to negotiate better terms. Insights from markets similar to yours can provide additional context on standard pricing and practices.
-
Be Aware of Regional Nuances: International buyers facing currency fluctuations, trade agreements, and varying regulations should factor these challenges into negotiation strategies.
Conclusion
This analysis provides a foundational understanding for international B2B buyers to effectively navigate the cost and pricing landscape of chrome plating hardness. By recognizing the interconnected components of cost, influencing factors, and employing strategic negotiation techniques, buyers can make informed decisions that will contribute to their overall operational efficiency and profitability in diverse markets. Always consider working with reliable suppliers who are transparent about their pricing models and can support your specific requirements, which can lead to successful business outcomes.
Disclaimer: Prices mentioned in this analysis are indicative and subject to change based on market conditions. Always request formal quotations from suppliers for accurate pricing information.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing chrome plating hardness With Other Solutions
Exploring Alternatives to Chrome Plating Hardness
When considering surface treatment options for enhancing the hardness and durability of components, businesses have various alternatives to chrome plating. Each method offers unique benefits and challenges, making it essential for B2B buyers to assess their specific needs and application environments before making a decision. Below, we compare chrome plating hardness with two viable alternatives: Thermal Spray Coating and Induction Hardening.
| Comparison Aspect | Chrome Plating Hardness | Thermal Spray Coating | Induction Hardening |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | High hardness (68-72 HRC), excellent wear resistance, low friction | Good hardness, variable based on material used, moderate wear resistance | Very high hardness, excellent wear resistance, suitable for high-stress applications |
| Cost | Moderate initial cost, potential for long-term savings due to durability | Generally lower initial cost, but can vary based on materials | High initial cost due to equipment and processing, but cost-effective for high-volume production |
| Ease of Implementation | Requires surface preparation and post-treatment processes | Relatively easy to apply, adaptable to various shapes and sizes | Complex setup, requires specialized equipment and training |
| Maintenance | Low maintenance; long-lasting with proper application | Moderate maintenance; wear can occur over time depending on the coating material | Low maintenance; treated parts are highly durable |
| Best Use Case | Ideal for components with high wear and friction, such as hydraulic cylinders and shafts | Suitable for components with complex geometries or those requiring thermal barriers | Best for high-stress components in automotive, aerospace, and heavy machinery |
What are the Benefits and Drawbacks of Thermal Spray Coating?
Thermal spray coating involves the application of molten or heated materials to a substrate, creating a protective layer. One of the key advantages of this method is its versatility, as it can be applied to various shapes and sizes, making it suitable for intricate components. The initial cost is generally lower than chrome plating, making it appealing for companies on a budget. However, the hardness and wear resistance can vary significantly based on the materials used, and the maintenance requirements may increase over time due to wear.
How Does Induction Hardening Compare?
Induction hardening is a process that uses electromagnetic induction to heat specific areas of a metal part, followed by rapid cooling to increase hardness. This method provides very high hardness levels and is particularly effective for parts subjected to high stress, such as gears and crankshafts. While the initial setup costs can be considerable, the long-term benefits in durability and performance can justify the investment, especially for high-volume production runs. However, the complexity of the process and need for specialized equipment can be a barrier for smaller operations.
Making the Right Choice for Your Business Needs
Choosing the appropriate surface treatment solution depends on various factors, including the specific application, budget constraints, and desired performance characteristics. Chrome plating hardness stands out for its excellent wear resistance and low maintenance, making it ideal for many industrial applications. However, alternatives like thermal spray coating and induction hardening may offer better value or performance in specific contexts. Buyers should conduct thorough evaluations of their operational requirements and consider testing different methods under real-world conditions to determine the best fit for their needs.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for chrome plating hardness
What Are the Key Technical Properties of Chrome Plating Hardness?
1. Hardness Measurement (Rockwell C and Vickers)
The hardness of chrome plating is primarily measured using two methods: the Rockwell C scale (HRC) and the Vickers hardness test (HV). Hard chrome typically exhibits hardness values ranging from 65 to 72 HRC, which translates to approximately 940 to 1210 HV. Understanding these measurements is crucial for B2B buyers, as they indicate the wear resistance and durability of the plated components. Selecting materials with appropriate hardness levels ensures that parts can withstand the rigors of their operational environments, minimizing maintenance and replacement costs.
2. Plating Thickness
The thickness of the chrome plating is a critical specification, generally ranging from 0.001 to 0.020 inches, depending on the application. A minimum thickness of 0.001 inches is necessary for the chrome to achieve its full hardness potential over softer base materials. This specification is vital for buyers to consider, as thicker plating can enhance wear resistance, while thinner applications may suffice for less demanding environments. Customizing thickness based on operational needs can significantly impact the longevity and performance of components.
3. Coefficient of Friction
The coefficient of friction (CoF) is an essential property that quantifies the frictional force between two surfaces. Hard chrome plating has a low CoF, typically around 0.15 when dry, making it ideal for applications where reduced friction is critical. This property enhances the efficiency and service life of mechanical parts, reducing energy consumption and operational costs. Buyers should prioritize low-friction coatings to improve the performance of machinery and equipment in various industries.
4. Corrosion Resistance
Chrome plating inherently offers excellent corrosion resistance, which protects underlying metals from environmental degradation. This property is particularly important for components exposed to harsh conditions, such as moisture, chemicals, or salt. For B2B buyers, selecting chrome-plated parts can extend the lifespan of equipment, ensuring reliability and reducing the frequency of replacements.
5. Adhesion and Bonding
Effective adhesion of chrome plating to the substrate is critical for maintaining the integrity and performance of coated components. Poor adhesion can lead to delamination and premature failure. B2B purchasers should ensure that the plating process includes proper surface preparation and post-treatment measures, such as baking to prevent hydrogen embrittlement, which can compromise adhesion.
What Trade Terminology Should B2B Buyers Understand in Chrome Plating?
1. OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
OEM refers to companies that produce parts or equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer. Understanding OEM standards is essential for buyers seeking to ensure compatibility and quality in replacement parts or components.
2. MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ is the smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell. Knowing the MOQ helps B2B buyers plan their procurement strategies, manage inventory costs, and understand pricing structures, particularly in international markets.
3. RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a formal document requesting a price quote from suppliers for specific products or services. Buyers should utilize RFQs to compare costs, delivery times, and terms from multiple vendors, ensuring they make informed purchasing decisions.
4. Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
Incoterms define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in international transactions, covering aspects such as shipping, risk, and costs. Familiarity with Incoterms is crucial for B2B buyers to navigate logistics and avoid misunderstandings in cross-border transactions.
5. Surface Finish
Surface finish refers to the texture and quality of a surface after treatment. In chrome plating, a high-quality surface finish is essential for performance and aesthetics. Buyers should consider surface finish specifications to meet their operational requirements and customer expectations.
6. Hardness Testing Standards
These are established protocols to measure the hardness of materials, including Rockwell and Vickers tests. Understanding these standards helps buyers assess the quality and suitability of chrome-plated components for their specific applications.
By grasping these technical properties and trade terms, B2B buyers can make informed decisions about chrome plating hardness, ensuring they select the right materials and suppliers for their operational needs.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the chrome plating hardness Sector
What Are the Current Market Dynamics and Key Trends in the Chrome Plating Hardness Sector?
The chrome plating hardness market is experiencing significant growth, driven by the increasing demand for durable and wear-resistant materials across various industries, including automotive, aerospace, and heavy machinery. International B2B buyers, particularly from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, are increasingly seeking hard chrome plating solutions to enhance the longevity and performance of their products. One of the key trends shaping this market is the customization of plating thickness to meet specific application needs. Companies are now able to deposit chrome selectively, applying it only to high-friction areas of components, thus optimizing material usage and reducing costs.
Additionally, advancements in electroplating technologies are enhancing the quality and efficiency of chrome plating processes. These innovations allow for better control over hardness levels and surface properties, enabling manufacturers to produce parts that exhibit superior wear resistance and reduced friction. As global supply chains evolve, international buyers are also placing greater emphasis on sourcing from suppliers who can offer quick turnaround times and flexible order quantities, thereby reducing inventory costs.
Another crucial dynamic is the increasing competition among suppliers. With a growing number of players entering the market, B2B buyers can benefit from more options and competitive pricing. However, this also necessitates thorough supplier evaluations to ensure reliability and product quality.
How Are Sustainability and Ethical Sourcing Impacting the Chrome Plating Hardness Sector?
Sustainability is becoming a pivotal concern in the chrome plating hardness sector, as companies are increasingly aware of their environmental impact. The chrome plating process traditionally involves the use of hazardous materials, leading to potential ecological and health risks. As a result, many businesses are now prioritizing ethical sourcing and sustainability in their procurement strategies. This shift is driving the demand for suppliers that adhere to environmental regulations and can provide ‘green’ certifications for their processes and materials.
B2B buyers are encouraged to consider suppliers that employ eco-friendly plating techniques, such as trivalent chromium processes, which are less harmful than traditional hexavalent chromium methods. Additionally, the implementation of closed-loop systems in chrome plating operations can significantly reduce waste and conserve water, aligning with global sustainability goals.
The importance of ethical supply chains cannot be overstated. Buyers are increasingly looking for transparency in sourcing practices, ensuring that their suppliers not only meet quality standards but also uphold ethical labor practices and environmental stewardship. By prioritizing suppliers with strong sustainability credentials, B2B buyers can enhance their brand reputation while contributing to a more sustainable industry.
How Has the Chrome Plating Hardness Sector Evolved Over Time?
The evolution of the chrome plating hardness sector can be traced back to its origins in the early 20th century, when chrome plating began to be utilized primarily for decorative purposes. However, as industries recognized the functional benefits of hard chrome plating—such as its exceptional hardness and wear resistance—the focus shifted towards industrial applications. Over the decades, the technology surrounding chrome plating has advanced significantly, with developments in electroplating techniques allowing for more precise control over hardness levels and surface finishes.
In recent years, the sector has adapted to meet the increasing demands for sustainability and efficiency, leading to innovations in eco-friendly plating processes and the ability to customize applications based on specific operational needs. This evolution reflects a broader trend in manufacturing toward greater efficiency, cost-effectiveness, and environmental responsibility, ensuring that the chrome plating hardness market remains a vital component of industrial production worldwide.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of chrome plating hardness
-
How do I choose the right hardness specification for chrome plating?
Choosing the appropriate hardness specification for chrome plating depends on the application and the materials involved. For most industrial applications, a hardness range of 65-70 Rockwell C is typical, but specific requirements may vary based on wear conditions, load, and environmental factors. Conducting field tests under real-world conditions can provide insights into the optimal thickness and hardness for your specific use case. Collaborating with suppliers who have experience in your industry can further guide you in selecting the best specifications. -
What is the best thickness for chrome plating in heavy wear applications?
The ideal thickness for chrome plating in heavy wear applications typically ranges from 0.002 inches to 0.020 inches. However, the specific thickness needed can vary based on the part’s design, the intensity of wear, and operational conditions. It’s advisable to consult with your chrome plating supplier to determine the best thickness based on empirical data and field tests. This ensures the coating provides adequate protection without unnecessarily increasing costs. -
How can I ensure the quality of chrome plating for my products?
To ensure high-quality chrome plating, verify that your supplier employs rigorous quality assurance (QA) processes. This includes pre-plating surface preparation, adherence to industry standards, and post-plating inspections. Look for suppliers who utilize advanced testing methods, such as Vickers and Rockwell hardness tests, to confirm the coating’s hardness and durability. Request documentation of quality tests and certifications to ensure compliance with international standards. -
What are the typical payment terms when sourcing chrome plating services internationally?
Payment terms for international chrome plating services can vary significantly by supplier and region. Common terms include advance payments, partial payments upon order confirmation, and balance due upon delivery. It is crucial to clarify payment methods accepted, such as wire transfers or letters of credit, and consider any currency fluctuations that may affect pricing. Establishing clear terms in the contract can help avoid misunderstandings and ensure smooth transactions. -
How do I vet suppliers for chrome plating services?
Vetting suppliers for chrome plating services involves several steps. First, research their reputation by checking customer reviews, case studies, and industry certifications. Request references from previous clients to gauge their reliability and quality. Additionally, evaluate their production capabilities, including equipment, technology, and experience with your specific industry. Finally, consider conducting site visits to inspect their facilities and processes firsthand. -
Can I customize the chrome plating process for my specific needs?
Yes, many suppliers offer customization options for the chrome plating process. This includes adjustments to plating thickness, hardness levels, and surface finishes tailored to specific applications. Discuss your requirements with potential suppliers to see how they can accommodate your needs, including any special treatments for enhanced performance. Customization can lead to better product performance and durability, especially in demanding environments. -
What logistics considerations should I keep in mind when sourcing chrome plating internationally?
When sourcing chrome plating services internationally, logistics considerations are vital. Assess shipping costs, transit times, and customs regulations that may impact delivery schedules. Choose suppliers who can provide reliable shipping options and track your order from production to delivery. Additionally, understand any import duties or taxes that may apply in your country to avoid unexpected expenses. Planning for these logistics can help ensure a smooth supply chain process. -
What is the role of surface preparation in chrome plating hardness?
Surface preparation is critical in achieving the desired hardness and adhesion of chrome plating. Imperfections on the base material can affect the quality of the chrome layer, leading to premature wear or failure. Effective preparation methods include removing contaminants, polishing the surface, and ensuring uniformity. Discuss with your supplier the specific pre-treatment processes they employ to enhance the durability and performance of the chrome plating, as this can significantly impact the final product’s quality.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.
Top 8 Chrome Plating Hardness Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. Electro Coatings – Industrial Hard Chrome Plating
Domain: electro-coatings.com
Registered: 1996 (29 years)
Introduction: Industrial hard chrome plating has an average hardness range of 66 to 70 on the Rockwell C scale. A minimum thickness of 0.001 inches is required for chromium to exhibit its true hardness characteristics over unhardened base metals. The hardness values of various materials are compared, with chrome having a Moh’s value of 6.8, Knoop value of 775, and Rockwell C scale value of 62. The properties an…
2. US Chrome – Hard Chrome Properties
Domain: uschrome.com
Registered: 1999 (26 years)
Introduction: Physical and Chemical Properties of Hard Chrome: 1. Hardness: Average hardness range of 65-70 HRc or 940-1210 HV. Measured using Vickers (HV) and Rockwell C (HRc) tests. 2. Coefficient of Friction: Very low CoF, improving service life and performance of parts. Dry CoF for Chromium on Hard Steel is 0.15, and Oiled CoF is 0.03. 3. Coefficient of Linear Thermal Expansion (CTE): 8.1 X 10 -6 cm/cm/°C, …
3. HCS Plating – Hard Chrome Plating Solutions
Domain: hcsplating.com
Registered: 2005 (20 years)
Introduction: Hard chrome plating increases hardness, durability, and corrosion resistance of surfaces, creating a shiny and smooth finish that is easier to clean. It is suitable for harsh environments and can extend the wear life of base materials by 2 to 10 times. The process typically takes up to a day and is applicable to various metals including stainless steel, copper, and brass. Common applications inclu…
4. Chromplate – Hard Chrome Plating Services
Domain: chromplate.com
Registered: 2002 (23 years)
Introduction: Chromplate Company offers Flash Hard Chrome and Hard Chrome Plating services. Key details include: 1. Types of Hard Chrome: Flash Hard Chrome, Thin Dense Hard Chrome, Pure/Nodular Hard Chrome. 2. Specifications: AMS 2460, MIL QQ C 320. 3. Hard Chrome Plating Services: Standard Hard Chrome (hardness approx. 950-1050 Vickers or 68 Rockwell C) and Flash Hard Chrome (hardness approx. 1050-1150 Vickers…
5. TWI Global – Hard Chrome Plating Solutions
Domain: twi-global.com
Registered: 2006 (19 years)
Introduction: Hard chrome plating is an electroplating process where chromium is deposited from a chromic acid solution. The thickness of hard chrome plating ranges from 2 to 250µm. Types of hard chrome include micro-cracked chromium, micro-porous chromium, porous chromium, and crack-free chromium. Micro-cracked and porous coatings require a minimum thickness of 80-120µm for adequate corrosion resistance. Micro…
6. LinkedIn – Hard Chrome Plating
Domain: linkedin.com
Registered: 2002 (23 years)
Introduction: Hard chrome plating is a widely used process in various industries to provide a hard, wear-resistant coating to metal parts. The hardness of hard chrome plating is influenced by the thickness of the coating and the hardness of the base material. A thicker coating generally results in higher hardness, but excessive thickness can lead to internal stresses and cracking. Softer base materials can redu…
7. HTS Coatings – HVAF Thermal Spray vs. Hard Chrome Plating
Domain: htscoatings.com
Registered: 2017 (8 years)
Introduction: HVAF Thermal Spray (BTHC-0005) vs. Hard Chrome Plating: 1. **History**: Hard Chrome Plating has been used since the early 1800s, popular in industrial and automotive applications. 2. **Cost and Environmental Impact**: Rising costs and environmental regulations are prompting a reevaluation of hard chrome plating. 3. **Suitability**: Hard chrome is more suitable for small inside diameter parts (belo…
8. Armoloy – Thin Dense Chrome Plating
Domain: armoloy.com
Registered: 1997 (28 years)
Introduction: Thin Dense Chrome Plating Process Overview: 1. **Durability and Versatility**: Thin dense chrome is known for its durability and protective benefits, making it suitable for various industrial and commercial applications. 2. **Plating Processes**: The two main hard chrome plating processes are Hexavalent chromium plating and Trivalent chromium plating. Armoloy’s thin dense chrome is applied more sl…
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for chrome plating hardness
What Are the Key Insights for B2B Buyers on Chrome Plating Hardness?
In summary, chrome plating hardness is a critical consideration for industries seeking to enhance the durability and performance of their components. With hardness values typically ranging from 66 to 72 on the Rockwell C scale, hard chrome plating provides excellent wear resistance, reduces friction, and can significantly extend the lifespan of machinery and parts. For international B2B buyers, particularly in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, leveraging strategic sourcing can lead to substantial cost savings and operational efficiencies.
By selecting suppliers that specialize in hard chrome plating, businesses can tailor their coating solutions to specific applications, optimizing both performance and cost. This adaptability allows companies to utilize less expensive base materials while achieving high durability, ultimately enhancing competitiveness in the global market.
As industries continue to evolve, the demand for advanced chrome plating applications is expected to grow. B2B buyers are encouraged to engage with reliable suppliers who can provide customized solutions that meet unique operational challenges. By investing in quality chrome plating, organizations not only protect their investments but also position themselves for sustainable growth in an increasingly competitive landscape.