Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for chemical conversion coating aluminum
In today’s competitive landscape, sourcing reliable chemical conversion coating for aluminum can pose a significant challenge for international B2B buyers. The need for effective corrosion resistance and enhanced surface integrity is paramount across various industries, including aerospace, defense, and electronics. This guide offers a comprehensive overview of chemical conversion coatings, particularly focusing on the widely recognized Alodine and chromate conversion processes.
Within these pages, we delve into the different types and classes of coatings, their applications in diverse sectors, and the critical considerations for supplier vetting. Buyers will gain insights into cost factors, compliance with international standards such as MIL-DTL-5541, and the environmental implications of hexavalent chromium alternatives.
By equipping decision-makers from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe—including key markets like Vietnam and Germany—with the essential knowledge to navigate the global market for chemical conversion coating aluminum, this guide empowers informed purchasing decisions. Whether you’re looking to enhance corrosion protection, improve paint adhesion, or ensure regulatory compliance, our expert insights will help you make strategic choices that align with your operational needs and sustainability goals.
Understanding chemical conversion coating aluminum Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Type 1 (Hexavalent Chromium) | Contains hexavalent chromium; typically gold or brown in color; provides high corrosion resistance. | Aerospace, military, automotive, and industrial sectors. | Pros: Excellent corrosion resistance, durable. Cons: Environmental concerns due to hexavalent chromium. |
| Type 2 (Trivalent Chromium) | Contains no hexavalent chromium; often clear in appearance; compliant with stricter environmental regulations. | Aerospace, electronics, and automotive industries. | Pros: Environmentally friendly, good corrosion resistance. Cons: May have slightly lower performance compared to Type 1. |
| Class 1A | Offers maximum corrosion protection; thicker coating suitable for final finish or pretreatment. | Military, aerospace, and high-performance applications. | Pros: Superior protection, ideal for harsh environments. Cons: Higher cost due to thickness and complexity. |
| Class 3 | Provides moderate corrosion protection; typically used for non-critical applications. | Commercial manufacturing and general industrial uses. | Pros: Cost-effective, sufficient for less demanding environments. Cons: Limited protection for critical components. |
| Iridite / Bonderite | A specific brand of chemical conversion coating; known for excellent adhesion and corrosion resistance. | Aerospace, defense, and electronics sectors. | Pros: Trusted brand, consistent quality. Cons: Brand-specific pricing may be higher. |
What Are the Key Characteristics of Type 1 (Hexavalent Chromium) Coatings?
Type 1 coatings are characterized by their inclusion of hexavalent chromium, providing robust corrosion resistance. They typically appear in a gold or brown hue, making them visually identifiable. This type is particularly suitable for demanding applications in aerospace and military sectors where durability is paramount. When purchasing, buyers should consider the environmental implications of hexavalent chromium and ensure compliance with local regulations.
How Does Type 2 (Trivalent Chromium) Differ from Type 1?
Type 2 coatings are free from hexavalent chromium, presenting a clear appearance that aligns with stricter environmental standards. They maintain good corrosion resistance and are increasingly adopted in aerospace and electronics industries. Buyers should weigh the benefits of compliance with environmental regulations against the potentially lower performance compared to Type 1 coatings, making this a suitable option for less critical applications.
Why Choose Class 1A for High-Performance Needs?
Class 1A coatings provide the highest level of corrosion protection, making them ideal for military and aerospace applications that face extreme conditions. Their thicker application ensures durability and reliability. Buyers should be prepared for a higher investment due to the complexity of application and the superior protection offered, which can be crucial in high-stakes environments.
What Applications Benefit from Class 3 Coatings?
Class 3 coatings offer moderate corrosion protection and are typically used in commercial manufacturing where budget considerations are critical. While they provide sufficient protection for less demanding applications, buyers should assess whether the level of corrosion resistance meets their operational needs, especially in environments that may expose components to moisture or corrosive agents.
How Do Iridite / Bonderite Coatings Stand Out?
Iridite and Bonderite coatings are recognized for their excellent adhesion properties and reliable corrosion resistance. Commonly used in aerospace and defense, these brand-specific coatings provide consistent quality. Buyers should consider the reputation and reliability of these brands, as well as the potential for higher costs, when making procurement decisions for specialized applications.
Key Industrial Applications of chemical conversion coating aluminum
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of chemical conversion coating aluminum | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Aerospace | Protective coatings for aircraft components | Enhances corrosion resistance and ensures compliance with military specifications. | Look for suppliers with MIL-DTL-5541 certification and experience in aerospace applications. |
| Defense | Coatings for military vehicles and equipment | Provides durable protection against harsh environments, extending the lifespan of components. | Ensure adherence to military standards and robust testing protocols. |
| Electronics Manufacturing | Surface treatment for electronic enclosures | Maintains electrical conductivity while preventing corrosion, crucial for functionality. | Source from vendors who can customize coatings for specific conductivity requirements. |
| Medical Devices | Coatings for surgical instruments and devices | Ensures biocompatibility and corrosion resistance, essential for safety and compliance. | Verify certifications for medical applications and stringent quality control processes. |
| Telecommunications | Coatings for communication equipment and towers | Protects against corrosion and environmental factors, ensuring reliable performance. | Consider suppliers with experience in outdoor applications and environmental testing. |
How is Chemical Conversion Coating Aluminum Used in Aerospace Applications?
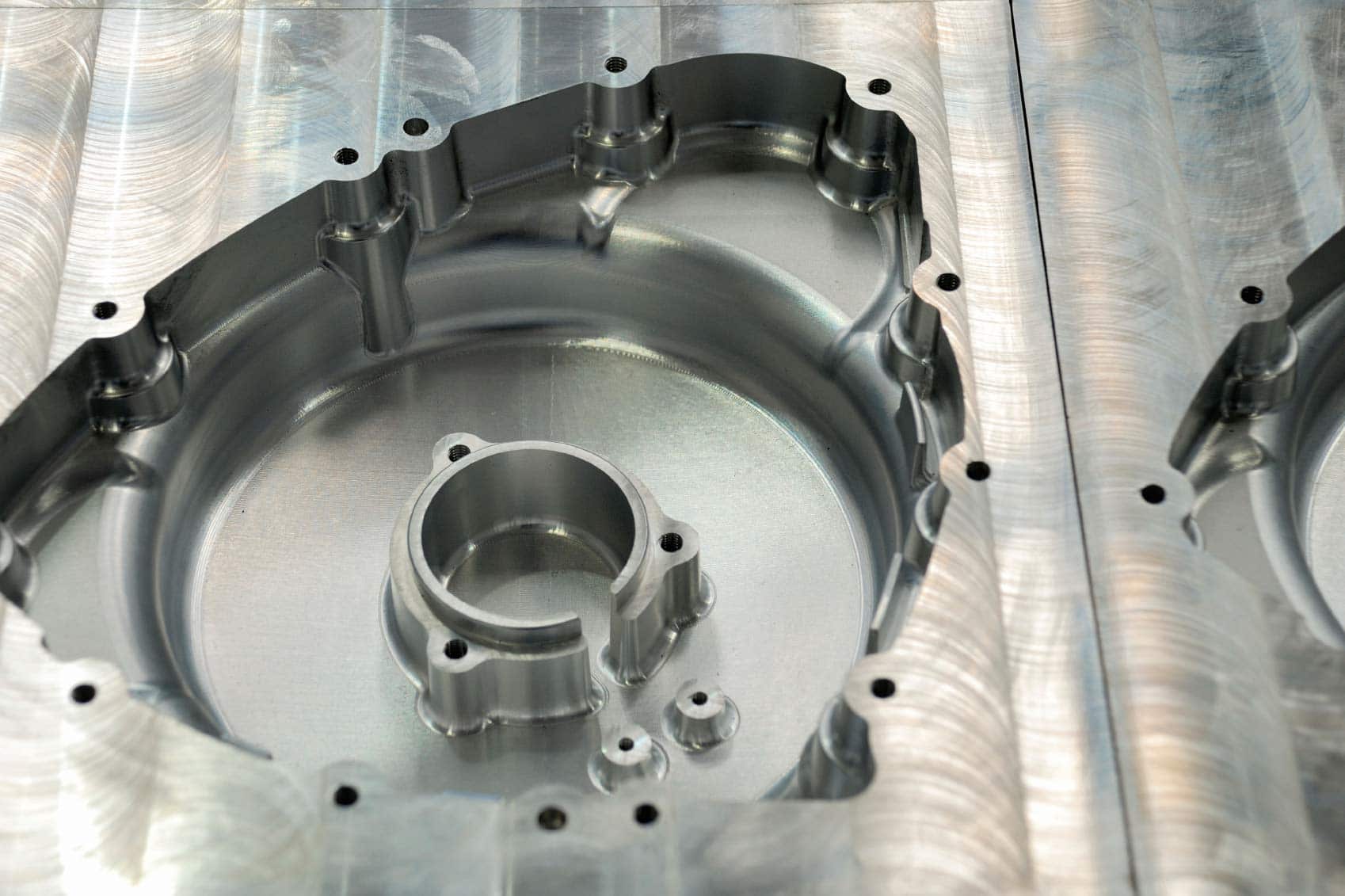
In the aerospace sector, chemical conversion coating aluminum is critical for protecting aircraft components from corrosion. The coatings enhance the surface integrity of aluminum parts while ensuring they meet stringent military specifications, such as MIL-DTL-5541. This is particularly important for international buyers who require reliable suppliers capable of providing consistent quality and compliance documentation. The coatings serve as an excellent primer for painting, ensuring long-lasting durability in high-stress environments.
What Benefits Does Chemical Conversion Coating Aluminum Offer for Defense Applications?
For defense applications, chemical conversion coatings provide robust protection for military vehicles and equipment exposed to extreme conditions. These coatings not only enhance corrosion resistance but also extend the operational lifespan of critical components. Buyers in this sector should prioritize sourcing from suppliers who adhere to military specifications and can demonstrate a proven track record in producing high-reliability coatings. This ensures that the coatings can withstand rigorous testing and real-world applications.
How is Chemical Conversion Coating Aluminum Applied in Electronics Manufacturing?
In electronics manufacturing, chemical conversion coating aluminum is used to treat electronic enclosures, ensuring both corrosion resistance and electrical conductivity. This dual functionality is vital for maintaining the performance of sensitive electronic components. International buyers should seek suppliers who can customize coatings based on specific conductivity needs while meeting industry standards. Additionally, the ability to provide thorough documentation and testing results is crucial for compliance and quality assurance.
What Role Does Chemical Conversion Coating Aluminum Play in Medical Device Manufacturing?
Chemical conversion coating aluminum is essential in the medical device sector, particularly for surgical instruments and other critical devices. These coatings ensure corrosion resistance and biocompatibility, addressing safety concerns in medical applications. Buyers from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe should prioritize suppliers with relevant certifications and rigorous quality control processes. This guarantees that the coatings meet health regulations and perform reliably in sterile environments.
How is Chemical Conversion Coating Aluminum Used in Telecommunications?
In telecommunications, chemical conversion coating aluminum is applied to communication equipment and towers, providing protection against corrosion and environmental factors. This is vital for ensuring the reliability and longevity of equipment in outdoor settings. Buyers should consider suppliers with experience in outdoor applications and robust environmental testing capabilities. This ensures that the coatings can withstand harsh weather conditions while maintaining performance standards.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘chemical conversion coating aluminum’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Challenges with Corrosion Resistance in Harsh Environments
The Problem: B2B buyers in sectors such as aerospace and defense often face significant challenges when it comes to ensuring that aluminum components can withstand extreme environmental conditions. Corrosion can compromise the integrity and functionality of critical parts, leading to costly failures and safety risks. The pressure to meet stringent regulations while maintaining performance can create stress, especially when traditional coatings do not provide adequate protection.
The Solution: To combat these issues, buyers should prioritize sourcing aluminum parts that are treated with high-performance chemical conversion coatings, specifically those adhering to MIL-DTL-5541 specifications. Opting for Class 1A coatings can provide maximum corrosion resistance, whether the parts are painted or left uncoated. It’s essential to work closely with suppliers to ensure that the chemical film application process meets all required standards. Furthermore, conducting regular inspections, including salt-spray tests, can validate the coating’s integrity and performance over time. Developing a robust maintenance schedule for these components will also aid in prolonging their lifespan and effectiveness in harsh environments.
Scenario 2: Difficulty in Achieving Consistent Coating Quality
The Problem: Many manufacturers encounter inconsistencies in the quality of chemical conversion coatings on aluminum parts, leading to variations in performance and compliance with specifications. This inconsistency can result from factors such as improper application techniques, lack of process validation, or variations in environmental conditions during coating. Such challenges can hinder production schedules and create complications during compliance audits, particularly for industries with strict regulatory requirements.
The Solution: To address these quality control issues, it is crucial to implement a standardized coating process that includes thorough training for personnel responsible for the application of chemical conversion coatings. Companies should invest in automated systems that can monitor coating thickness and adhesion, ensuring that each batch meets the required specifications. Additionally, establishing a process validation routine that includes regular checks on adhesion, corrosion resistance, and compliance with MIL-DTL-5541 can help maintain consistent quality. By creating a culture of quality assurance and investing in technology, manufacturers can significantly reduce the risk of inconsistencies and enhance overall production reliability.
Scenario 3: Environmental Concerns and Regulatory Compliance
The Problem: As environmental regulations evolve, B2B buyers face increasing pressure to adopt more sustainable practices. Many traditional chromate conversion coatings contain hexavalent chromium, which poses health and environmental risks. This raises concerns for companies aiming to meet compliance standards while still ensuring the performance and durability of their aluminum components. The challenge lies in finding alternative solutions that do not compromise on quality or effectiveness.
The Solution: Buyers should explore trivalent chromium alternatives that provide similar corrosion resistance without the associated environmental hazards of hexavalent chromium. These formulations are designed to meet or exceed the performance standards of traditional coatings while aligning with contemporary environmental regulations. When selecting suppliers, it’s essential to inquire about their compliance with ISO standards and sustainability practices. Additionally, conducting a thorough analysis of the long-term performance and cost-effectiveness of these alternatives will help in making an informed decision. Engaging with suppliers who are committed to sustainable practices can not only enhance compliance but also improve the company’s reputation in the market.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for chemical conversion coating aluminum
What Are the Key Materials Used in Chemical Conversion Coating for Aluminum?
Chemical conversion coatings, particularly chromate coatings, are essential in enhancing the durability and corrosion resistance of aluminum components. Below, we analyze several common materials used in chemical conversion coating processes, focusing on their properties, advantages, disadvantages, and considerations for international B2B buyers.
What Are the Key Properties of Hexavalent Chromium Coatings?
Hexavalent chromium coatings, commonly referred to as Type 1 coatings under MIL-DTL-5541 specifications, provide robust corrosion protection and are often used in aerospace and military applications. These coatings exhibit excellent adhesion properties, making them suitable for subsequent painting or powder coating.
Pros: They offer superior corrosion resistance and durability, making them ideal for high-stress environments. They also have a relatively lower application cost due to their widespread availability.
Cons: The primary drawback is the environmental and health concerns associated with hexavalent chromium, leading to stricter regulations in many regions. This can complicate compliance for manufacturers, especially in markets like Europe where RoHS and REACH regulations apply.
Impact on Application: Hexavalent chromium coatings are compatible with various media, including harsh chemicals, making them suitable for aerospace and defense applications.
International Considerations: Buyers in regions like Europe and South America should be aware of the environmental regulations governing hexavalent chromium usage. Compliance with standards such as ASTM and DIN is crucial.
How Do Trivalent Chromium Coatings Compare?
Trivalent chromium coatings, classified as Type 2 under MIL-DTL-5541, are an alternative to hexavalent coatings. They provide similar corrosion resistance without the associated health risks.
Pros: These coatings are less toxic and more environmentally friendly, making them increasingly popular in industries seeking sustainable practices. They also offer good adhesion properties and are effective as a primer for painting.
Cons: While they perform well, trivalent coatings may not provide the same level of corrosion resistance as hexavalent options, particularly in extreme conditions. Additionally, they can be more expensive due to the advanced technology required for their application.
Impact on Application: Trivalent coatings are suitable for a variety of applications but may require specific testing to ensure performance in aggressive environments.
International Considerations: Buyers should verify that trivalent coatings meet local and international standards, particularly in regions with stringent environmental regulations.
What Are the Benefits of Iridite Coatings?
Iridite coatings, often used as a proprietary brand for chromate conversion coatings, provide a unique balance of corrosion resistance and electrical conductivity. They are commonly used in electronics and telecommunications.
Pros: Iridite coatings enhance surface conductivity while offering corrosion protection, making them ideal for electronic components. They also have a low profile, which is beneficial for precision applications.
Cons: The application process can be complex and may require specialized equipment, increasing manufacturing complexity. Additionally, they may not provide as robust protection as traditional chromate coatings in extreme environments.
Impact on Application: Iridite coatings are particularly effective in applications where electrical continuity is critical, such as in circuit boards and connectors.
International Considerations: Buyers should ensure that Iridite coatings comply with relevant industry standards, such as ISO 9001, to guarantee quality and performance.
How Do Bonderite Coatings Fit Into the Landscape?
Bonderite coatings are another popular choice for chemical conversion coating, known for their versatility and effectiveness in various applications, including automotive and aerospace.
Pros: Bonderite coatings offer excellent corrosion resistance and can be tailored for specific applications, including those requiring enhanced paint adhesion. They are generally easier to apply than other coatings.
Cons: While effective, Bonderite coatings may not be as durable as hexavalent chromium coatings in extreme conditions. They can also be more expensive than traditional options.
Impact on Application: Bonderite coatings are suitable for a range of media, making them a versatile choice for many industries.
International Considerations: Buyers should ensure that Bonderite coatings meet the necessary compliance standards for their specific industry, particularly in regions with rigorous quality assurance processes.
Summary Table of Material Selection for Chemical Conversion Coating Aluminum
| Material | Typical Use Case for chemical conversion coating aluminum | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hexavalent Chromium | Aerospace, military components | Superior corrosion resistance | Environmental and health concerns | Medium |
| Trivalent Chromium | Automotive, general manufacturing | Environmentally friendly | May offer lower corrosion resistance | High |
| Iridite | Electronics, telecommunications | Enhances electrical conductivity | Complex application process | Medium |
| Bonderite | Automotive, aerospace, general manufacturing | Excellent paint adhesion | Less durable in extreme conditions | Medium |
This guide provides valuable insights for B2B buyers seeking to select the appropriate chemical conversion coating material for aluminum, ensuring compliance with international standards while meeting performance requirements.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for chemical conversion coating aluminum
What Are the Key Stages in the Manufacturing Process of Chemical Conversion Coating for Aluminum?
The manufacturing process for chemical conversion coating aluminum typically involves several critical stages, each essential for achieving the desired surface characteristics and ensuring compliance with industry standards.
1. Material Preparation: Ensuring Clean Surfaces
Material preparation is the first step in the process. Aluminum components must be thoroughly cleaned to remove any contaminants, oils, or oxidation that could interfere with the coating adhesion. This is often accomplished through methods such as:
- Degreasing: Using solvents or alkaline solutions to eliminate grease and oil.
- Acid Etching: Employing acidic solutions to remove oxides and create a chemically reactive surface.
- Rinsing: Following cleaning processes with deionized water to prevent any residual contaminants from affecting the coating.
Effective material preparation is vital, as any contaminants left on the surface can compromise the coating’s integrity and performance.
2. Forming: Shaping Components to Specifications
Forming involves shaping the aluminum into the required dimensions and configurations. Techniques such as extrusion, stamping, or machining are commonly employed to produce parts that meet specific design requirements. Precision during this stage is crucial, as it determines the fit and function of the final product.
3. Assembly: Bringing Components Together
In cases where multiple aluminum parts are involved, assembly may be necessary. This can include welding, riveting, or using adhesives to join components. Ensuring that assembly processes do not introduce contaminants is essential, as any foreign materials can affect the subsequent coating process.
4. Finishing: Applying the Chemical Conversion Coating
The actual application of the chemical conversion coating follows assembly. This process, known as chromating, involves immersing the cleaned aluminum in a chemical solution that reacts with the surface to form a protective layer. Key techniques include:
- Immersion Coating: Parts are submerged in a bath of the chromate solution, ensuring even coverage.
- Spray Application: In some cases, spraying the solution onto the aluminum surface may be used for larger or complex geometries.
- Controlled Environment: Maintaining a controlled environment (temperature, humidity) during application is critical to ensure consistent coating quality.
The resulting film enhances corrosion resistance and prepares the surface for subsequent treatments, such as painting or powder coating.
What Are the Quality Control Standards and Checkpoints for Chemical Conversion Coating?
Quality control (QC) is integral to the manufacturing process, ensuring that the finished products meet both functional and regulatory requirements. Various international and industry-specific standards guide these QC measures.
Relevant International Standards: What to Look For
For B2B buyers, understanding the relevant quality standards is crucial. The following are key standards applicable to chemical conversion coating:
- ISO 9001: This standard outlines the requirements for a quality management system (QMS) that organizations must meet to ensure consistent quality in products and services.
- MIL-DTL-5541: Specific to chemical conversion coatings for aluminum, this military specification provides guidelines for application and testing methods.
- ISO 8081: The international equivalent to MIL-DTL-5541, it addresses chemical conversion coatings, ensuring global compliance.
What Are the Key Quality Control Checkpoints?
Quality control checkpoints throughout the manufacturing process include:
- Incoming Quality Control (IQC): Verification of raw materials and components upon receipt to ensure they meet specified requirements.
- In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): Monitoring of the manufacturing process at various stages to identify and rectify any deviations from quality standards.
- Final Quality Control (FQC): Assessment of finished products against specifications before delivery, including testing for coating thickness, adhesion, and corrosion resistance.
Common testing methods include:
- Adhesion Testing: To evaluate the bond strength between the coating and aluminum substrate.
- Salt Spray Testing: A standard method to assess corrosion resistance under accelerated conditions.
- Thickness Measurement: Utilizing tools like micrometers or non-destructive testing methods to verify coating thickness.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control Processes?
B2B buyers must take proactive steps to verify the quality control processes of their suppliers. This can be achieved through several methods:
1. Conducting Supplier Audits
Regular audits of suppliers can provide insights into their manufacturing processes and quality control measures. During these audits, buyers should assess:
- Compliance with international and industry-specific standards.
- Documentation practices, including records of inspections and testing results.
- Training programs for personnel involved in the coating process.
2. Requesting Quality Reports
Buyers should not hesitate to request quality reports from suppliers. These reports should detail:
- Results of quality control tests conducted during production.
- Information on past performance, including any non-conformities and corrective actions taken.
- Certifications that demonstrate compliance with relevant standards.
3. Engaging Third-Party Inspectors
Utilizing third-party inspection services can add an extra layer of assurance. These independent organizations can conduct thorough evaluations of the supplier’s processes and the quality of the final products, providing an unbiased assessment of quality assurance measures.
What Are the Quality Control and Certification Nuances for International B2B Buyers?
For international B2B buyers, especially those from diverse regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, understanding the nuances of quality control and certification is essential.
- Regional Standards Compliance: Buyers should be aware that different regions may have varying standards and regulations. For instance, European buyers might prioritize CE marking, while those in the U.S. may focus on MIL-spec compliance.
- Cultural and Regulatory Differences: Understanding the local regulations and cultural practices regarding quality assurance can help buyers navigate supplier relationships more effectively.
- Traceability and Documentation: Ensuring that suppliers maintain comprehensive documentation for traceability is crucial for compliance and quality assurance, particularly in industries such as aerospace and defense.
By being diligent in verifying quality control measures and understanding the manufacturing processes, B2B buyers can secure high-quality chemical conversion coated aluminum products that meet their specific needs and regulatory requirements.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘chemical conversion coating aluminum’
This guide aims to assist B2B buyers in effectively sourcing chemical conversion coating for aluminum. It outlines a structured approach to ensure that the procurement process meets industry standards and addresses specific requirements for performance, compliance, and supplier reliability.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Establishing clear technical specifications is essential for aligning your needs with the capabilities of potential suppliers. Consider factors such as the type of coating (hexavalent or trivalent), the required corrosion resistance class, and any specific industry certifications necessary for your application. This clarity helps streamline the sourcing process and ensures that the coatings meet your operational demands.
Step 2: Research Applicable Industry Standards
Familiarize yourself with relevant industry standards such as MIL-DTL-5541 for military applications or ISO 8081 for broader commercial use. Understanding these standards will inform your expectations for quality and performance, ensuring that the coatings not only protect against corrosion but also adhere to regulatory requirements. This knowledge is crucial for industries like aerospace, defense, and electronics, where compliance is paramount.
Step 3: Evaluate Potential Suppliers
Before committing to a supplier, conduct a thorough evaluation to ensure they meet your standards. Request detailed company profiles, including their experience in chemical conversion coatings, client references, and case studies from similar industries. Pay attention to their certifications, such as NADCAP or ISO certifications, which indicate their commitment to quality and reliability.
Step 4: Assess Production Capabilities
Investigate the supplier’s production capabilities to ensure they can meet your volume and timeline requirements. Consider factors such as their equipment, technology, and production processes, including whether they offer automated finishing systems for quality control. Suppliers that can demonstrate flexibility in their production methods will be better positioned to accommodate your specific needs.
Step 5: Request Samples and Conduct Testing
Before finalizing your supplier, request samples of their chemical conversion coatings for testing. Evaluate the samples for adhesion, corrosion resistance, and compliance with your technical specifications. Conducting tests such as salt-spray performance can provide insights into the durability and effectiveness of the coatings in real-world conditions.
Step 6: Verify Environmental and Safety Compliance
Ensure that the supplier adheres to environmental and safety regulations concerning the chemicals used in the coating process. Inquire about their waste disposal methods and whether they are transitioning to more sustainable practices, such as using trivalent chromium alternatives. This step is increasingly important due to growing environmental regulations and health considerations.
Step 7: Establish Clear Communication and Support
Once you select a supplier, establish open lines of communication to facilitate ongoing support and feedback. Discuss expectations regarding delivery schedules, quality assurance processes, and after-sales support. A strong partnership with your supplier will help address any issues that arise during the application of the coatings and ensure long-term satisfaction with the procurement process.
By following these steps, you will be better equipped to source chemical conversion coatings for aluminum that meet your specific requirements, ensuring optimal performance in your applications.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for chemical conversion coating aluminum Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components in Chemical Conversion Coating for Aluminum?
When sourcing chemical conversion coating for aluminum, understanding the cost structure is essential. The primary cost components include:
-
Materials: The chemicals used in the coating process, such as chromate compounds, are the most significant material costs. The choice between hexavalent and trivalent chromium can also influence pricing, as regulations increasingly favor the latter due to environmental concerns.
-
Labor: Skilled labor is required for the application of coatings, particularly in sectors demanding high precision, such as aerospace. Labor costs may vary based on the region and the complexity of the application process.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes utilities, facility costs, and equipment maintenance. Facilities must maintain compliance with environmental regulations, which can add to overhead costs.
-
Tooling: Specialized equipment may be necessary for certain applications, particularly for automated coating processes. The initial investment in tooling can be substantial but is often amortized over large production runs.
-
Quality Control (QC): Rigorous testing and inspection processes are vital to ensure coatings meet specified standards, such as MIL-DTL-5541. QC costs can vary based on the level of testing required.
-
Logistics: Transportation and handling of materials and finished products contribute to overall costs. International shipping can significantly impact pricing, especially with varying tariffs and import duties.
-
Margin: Suppliers typically incorporate a profit margin based on the complexity of the service and the market demand.
How Do Volume and Customization Affect Pricing for Chemical Conversion Coating?
Volume plays a critical role in determining pricing. Higher order quantities (MOQ) often lead to bulk discounts, which can substantially reduce the per-unit cost. Conversely, smaller orders may incur higher costs due to setup and processing time.
Customization, including specific color requirements or unique coating properties, can also influence pricing. Custom formulations may necessitate additional testing and development, leading to increased costs. Buyers should clearly communicate their specifications to ensure accurate quotes and avoid unexpected charges.
What Factors Should International Buyers Consider When Sourcing Chemical Conversion Coating?
Several price influencers are particularly relevant for international B2B buyers, including:
-
Quality and Certifications: Compliance with international standards, such as ISO 8081 or MIL-DTL-5541, often comes at a premium. Buyers should assess the certifications held by suppliers to ensure product reliability.
-
Supplier Factors: The reputation, reliability, and location of suppliers can affect pricing. Established suppliers with a track record of quality may charge more but provide better assurance of consistency and compliance.
-
Incoterms: Understanding the agreed terms of shipment is crucial. Different Incoterms (e.g., FOB, CIF) can alter the total landed cost, impacting overall pricing strategies.
What Negotiation Strategies Can Buyers Use to Achieve Cost Efficiency?
Effective negotiation can help buyers secure better pricing and terms. Here are some strategies:
-
Leverage Volume Discounts: Consider consolidating orders to meet MOQ thresholds, which can unlock significant savings.
-
Explore Long-term Contracts: Establishing a long-term relationship with suppliers can lead to favorable pricing and priority service.
-
Assess Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Evaluate all costs associated with the coating process, including maintenance and potential rework, to make informed purchasing decisions.
-
Stay Informed on Market Trends: Understanding fluctuations in raw material prices and industry demand can provide leverage during negotiations.
Are There Pricing Nuances Specific to Different Regions?
International buyers, particularly from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, should be aware of regional pricing nuances. Economic conditions, import/export tariffs, and local market competition can all influence the cost of chemical conversion coating. Additionally, currency fluctuations may affect pricing for buyers sourcing from different countries.
Conclusion
While sourcing chemical conversion coating for aluminum, understanding the intricate cost structure, influencing factors, and negotiation strategies is vital for maximizing value. Buyers should conduct thorough research and engage with suppliers to ensure they achieve competitive pricing while meeting their quality requirements. Remember, the pricing provided by suppliers may serve as a guideline, and it’s crucial to consider various factors to arrive at the total cost of ownership.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing chemical conversion coating aluminum With Other Solutions
When selecting a protective treatment for aluminum, businesses often consider various methods to ensure optimal performance and cost-effectiveness. Chemical conversion coating aluminum, known for its corrosion resistance and compatibility with other finishes, stands alongside several alternatives. This section delves into the comparative analysis of chemical conversion coating aluminum against other viable solutions.
| Comparison Aspect | Chemical Conversion Coating Aluminum | Anodizing | Powder Coating |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | Excellent corrosion resistance; maintains conductivity; adheres well to paints | Good corrosion resistance; enhances surface hardness | Superior durability; available in various colors; excellent resistance to chemicals |
| Cost | Generally low-cost, especially for high-volume applications | Moderate; costs can rise with thickness and complexity | Higher initial costs but cost-effective for large runs |
| Ease of Implementation | Requires specific chemical processes; can be automated | Requires specialized equipment and careful handling | Relatively simple application process; requires curing |
| Maintenance | Low maintenance; durable under various conditions | Moderate; may require touch-ups if damaged | Low; resistant to chipping and fading |
| Best Use Case | Aerospace, electronics, and military applications requiring tight tolerances | Automotive parts, architectural components, and consumer goods | General industrial applications, outdoor furniture, and appliances |
What Are the Pros and Cons of Anodizing as an Alternative?
Anodizing is an electrochemical process that converts the surface of aluminum into a durable, corrosion-resistant anodic oxide finish. This treatment enhances the aluminum’s surface hardness and aesthetic appeal.
Pros:
– Provides excellent corrosion resistance and wear resistance.
– Can be dyed for aesthetic purposes, offering a range of color options.
Cons:
– The process can be more complex and costlier, especially for thicker coatings.
– Anodized surfaces can become brittle if not handled carefully.
How Does Powder Coating Compare?
Powder coating involves applying a dry powder to the aluminum surface, which is then cured under heat to form a hard, protective layer. This method is popular in a variety of industrial applications due to its versatility.
Pros:
– Offers superior durability and resistance to impacts, chemicals, and UV light.
– Available in numerous colors and finishes, enhancing the visual appeal of the product.
Cons:
– Higher initial setup costs compared to chemical conversion coating.
– Requires curing ovens, which may not be feasible for all manufacturing setups.
Conclusion: How Should B2B Buyers Choose the Right Solution?
Selecting the appropriate protective coating for aluminum hinges on specific project requirements, including performance, cost, and application method. For high-precision applications like aerospace and electronics, chemical conversion coating aluminum may be the optimal choice due to its excellent adhesion and minimal impact on dimensions. In contrast, anodizing might be preferable for applications where enhanced surface hardness and aesthetic options are paramount. Powder coating serves well for a wide range of industrial uses where durability and color variety are desired. Ultimately, B2B buyers should evaluate their unique needs, industry standards, and budget constraints to make an informed decision on the best protective treatment for their aluminum components.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for chemical conversion coating aluminum
What Are the Key Technical Properties of Chemical Conversion Coating for Aluminum?
Understanding the essential technical properties of chemical conversion coatings for aluminum is critical for B2B buyers, particularly in industries such as aerospace, defense, and electronics. These properties not only ensure product performance but also compliance with industry standards.
1. Material Grade
Material grade refers to the specific classification of aluminum alloys used in conjunction with chemical conversion coatings. Different grades, such as 6061 or 7075, exhibit varying levels of strength, corrosion resistance, and workability. Selecting the appropriate grade is crucial for ensuring that the coated aluminum meets the specific performance requirements of applications, especially in demanding environments.
2. Coating Thickness
The thickness of the chemical conversion coating can significantly impact its protective qualities. Typically, coatings under MIL-DTL-5541 range from 0.0001 to 0.0003 inches. Thicker coatings (Class 1A) provide enhanced corrosion resistance and serve as a robust base for subsequent paint applications, while thinner coatings (Class 3) may be more suitable for applications requiring minimal dimensional change.
3. Corrosion Resistance
Corrosion resistance is a pivotal property of chemical conversion coatings. Under ASTM B117 salt spray testing, coatings are evaluated for their ability to withstand corrosive environments. High-performance coatings are essential for applications in marine, industrial, and aerospace sectors where exposure to harsh conditions is common. Ensuring adequate corrosion protection helps to prolong the lifespan of aluminum components, reducing maintenance costs.
4. Adhesion Strength
Adhesion strength measures how well the coating bonds to the aluminum substrate. A strong bond is vital for the durability of the coating, especially when used as a primer for paint or powder coating. Testing for adhesion strength ensures that the coating will not peel or flake during service, maintaining the integrity of the part throughout its lifecycle.
5. Electrical Conductivity
For applications requiring electrical conductivity, such as in the aerospace and electronics industries, the ability to maintain conductivity through the coating is critical. The process parameters can be adjusted to achieve either conductive or non-conductive properties in the chemical conversion coating, providing flexibility based on specific project requirements.
Which Trade Terms Should B2B Buyers Be Aware of When Sourcing Chemical Conversion Coatings?
Navigating the terminology in the chemical conversion coating industry is essential for effective communication and negotiation. Here are some commonly used terms that B2B buyers should understand:
1. OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
OEM refers to a company that produces parts or equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer. Understanding OEM relationships is crucial for B2B buyers, as it helps identify suppliers who can provide reliable and compliant coatings for their specific applications.
2. MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ is the smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell. Knowing the MOQ is important for buyers to assess whether a supplier’s offerings align with their purchasing needs, particularly in industries with fluctuating demands.
3. RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a document that buyers send to suppliers to request pricing and other details for specific products or services. For chemical conversion coatings, an RFQ helps buyers gather essential information about costs, lead times, and available options.
4. Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
Incoterms are internationally recognized rules that define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in international transactions. Familiarity with Incoterms is vital for B2B buyers to understand shipping responsibilities, risk transfer, and cost allocation related to chemical conversion coatings.
5. MIL-DTL-5541
This military specification outlines the requirements for chemical conversion coatings on aluminum and aluminum alloys. Compliance with MIL-DTL-5541 is often a prerequisite for suppliers serving industries such as aerospace and defense, making it a key term for buyers in these sectors.
By grasping these technical properties and trade terms, B2B buyers can make informed decisions when sourcing chemical conversion coatings, ensuring they select the right products that meet their operational needs and industry standards.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the chemical conversion coating aluminum Sector
What Are the Current Market Dynamics and Key Trends in Chemical Conversion Coating for Aluminum?
The global market for chemical conversion coatings on aluminum is experiencing robust growth, driven by increasing demand across industries such as aerospace, automotive, electronics, and defense. As international buyers from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe seek reliable suppliers, understanding the market dynamics becomes essential. Key trends include the shift towards advanced coating technologies that enhance corrosion resistance while maintaining electrical conductivity. The integration of automation in the coating process is also gaining traction, enabling manufacturers to achieve consistent quality and efficiency.
Emerging B2B technologies, such as AI and IoT, are transforming how chemical coatings are applied and monitored. Real-time data analytics can now optimize coating thickness and adhesion quality, ensuring compliance with stringent industry standards like MIL-DTL-5541. Additionally, the demand for trivalent chromium alternatives is rising as companies strive to meet environmental regulations while still achieving desired performance metrics. Such innovations not only fulfill compliance requirements but also offer cost-effective solutions, making them attractive to global buyers.
Moreover, the emphasis on supply chain transparency and traceability is becoming increasingly critical. Buyers are now prioritizing suppliers who can demonstrate adherence to international standards and provide documentation for quality assurance. This evolving landscape requires international B2B buyers to stay informed about technological advancements and sourcing trends to make well-informed purchasing decisions.
How Is Sustainability and Ethical Sourcing Shaping the Chemical Conversion Coating Aluminum Market?
Sustainability is a pivotal concern in the chemical conversion coating aluminum sector, influenced by growing environmental awareness and regulatory pressures. Manufacturers are increasingly recognizing the importance of ethical supply chains, focusing on minimizing environmental impacts throughout the production process. The traditional use of hexavalent chromium in coatings, known for its effectiveness but also for its health hazards, is being scrutinized. As a result, many companies are exploring trivalent chromium formulations that provide comparable performance with significantly reduced environmental risks.
In addition to regulatory compliance, the demand for ‘green’ certifications is on the rise. Buyers are looking for suppliers who can provide coatings that meet eco-friendly standards, such as ISO 14001. This shift not only aligns with corporate social responsibility goals but also enhances brand reputation in an increasingly eco-conscious market. Furthermore, the use of sustainable materials in the chemical conversion coating process is becoming a competitive advantage for suppliers, enabling them to differentiate their offerings.
Buyers are advised to assess potential suppliers based on their sustainability practices, including waste management, energy consumption, and sourcing of raw materials. Collaborating with suppliers who prioritize ethical sourcing can foster long-term relationships and ensure compliance with emerging global sustainability standards.
What Is the Historical Context of Chemical Conversion Coating for Aluminum?
Chemical conversion coatings have a rich history, dating back over five decades, primarily used in military and aerospace applications to enhance the corrosion resistance of aluminum. Initially dominated by hexavalent chromium-based processes, the industry has seen significant evolution driven by technological advancements and regulatory changes. The introduction of military specifications such as MIL-DTL-5541 has standardized the requirements for chemical conversion coatings, ensuring consistent quality and performance.
In recent years, the industry has shifted towards safer alternatives, reflecting broader trends in environmental responsibility and health awareness. This evolution not only illustrates the technological advancements in coating processes but also highlights the importance of adapting to changing market demands and regulatory landscapes. As international B2B buyers navigate this sector, understanding the historical context can provide valuable insights into current practices and future trends.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of chemical conversion coating aluminum
-
How do I ensure the quality of chemical conversion coatings for aluminum?
To ensure the quality of chemical conversion coatings, it’s crucial to partner with suppliers who adhere to established industry standards like MIL-DTL-5541. Request documentation that demonstrates compliance with these specifications, including test results for adhesion, corrosion resistance, and coating thickness. Regular audits and inspections should be part of your quality assurance process. Additionally, consider suppliers who utilize automated systems for coating verification to ensure consistency and reliability in their products. -
What is the best chromate conversion coating type for aerospace applications?
For aerospace applications, Type 1 chromate conversion coatings (which may contain hexavalent chromium) are generally recommended for their superior corrosion resistance and durability. However, with increasing environmental regulations, Type 2 coatings, which are free from hexavalent chromium, are also gaining traction. Choosing the right type often depends on specific project requirements, including environmental considerations and regulatory compliance. Discuss your specific needs with your supplier to determine the best fit. -
How can I customize chemical conversion coatings for my specific needs?
Customization options for chemical conversion coatings can include variations in thickness, color, and chemical composition to suit specific applications. Engage with your supplier early in the design process to discuss your requirements. Many suppliers offer tailored solutions that can enhance adhesion for subsequent coatings or meet specific corrosion resistance levels. Ensure that any customization complies with relevant industry standards to maintain product integrity. -
What are the minimum order quantities (MOQ) for chemical conversion coatings?
Minimum order quantities can vary significantly between suppliers based on their production capabilities and the specific coatings requested. Typically, MOQs range from a few hundred to several thousand units. It’s advisable to discuss your anticipated demand with potential suppliers to negotiate favorable terms. Some suppliers may offer flexibility for smaller orders, especially for prototyping or initial runs. -
What payment terms should I expect when sourcing chemical conversion coatings?
Payment terms can vary widely depending on the supplier and your location. Common terms include a percentage upfront with the balance due upon delivery or after a specified period. For international transactions, consider options like letters of credit or escrow services to safeguard your investment. Always clarify payment terms before finalizing agreements to avoid misunderstandings. -
How do I vet suppliers of chemical conversion coatings?
Vetting suppliers involves assessing their experience, certifications, and customer reviews. Request references from past clients and inquire about their adherence to industry standards like MIL-DTL-5541. Additionally, evaluate their production capabilities, quality assurance processes, and responsiveness to inquiries. Attending trade shows or industry events can also provide insights into potential suppliers’ reputations. -
What logistics considerations should I keep in mind when importing chemical conversion coatings?
When importing chemical conversion coatings, consider factors like shipping times, customs regulations, and storage requirements. Ensure your supplier can provide necessary documentation for customs clearance, including safety data sheets (SDS) and compliance certificates. Working with a logistics partner experienced in international trade can help streamline the process and mitigate potential delays. -
What are the environmental considerations for chemical conversion coatings?
As environmental regulations evolve, many industries are moving towards more sustainable practices. When sourcing chemical conversion coatings, inquire about the environmental impact of the materials used, particularly regarding hexavalent chromium. Suppliers may offer trivalent chromium alternatives that provide similar performance with reduced health and environmental risks. Understanding the ecological footprint of your chosen coatings is essential for compliance and corporate responsibility.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.
Top 9 Chemical Conversion Coating Aluminum Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. Best Technology Inc – Alodine Coating Solutions
Domain: besttechnologyinc.com
Registered: 2001 (24 years)
Introduction: Alodine, also known as chem film or chromate conversion coating, is a protective coating for aluminum and other metals that prevents corrosion. It is a type of chemical conversion coating that transforms the existing metal surface into a protective layer through a chemical reaction, rather than adding a new layer like plating. The primary benefits include corrosion protection, improved adhesion fo…
2. ENS Technology – MIL-DTL-5541F Chemical Conversion Coating
Domain: enstechnology.com
Registered: 2001 (24 years)
Introduction: MIL-DTL-5541F Chemical Conversion Coating for Aluminum and Aluminum Alloys. Approved for use by all departments and agencies of the United States Department of Defense (DoD). Used for corrosion resistance and as a primer for painting. Types: Type 1 (Hexavalent Chromium) – gold or brown color, Type 2 (No Hexavalent Chromium) – clear. Classes: Class 1A – maximum corrosion protection, Class 3 – low e…
3. Protocase – Chemical Conversion Coating
Domain: protocase.com
Registered: 2001 (24 years)
Introduction: Chemical Conversion Coating for Aluminum, also known as chem film, chromate coating, or yellow chromate coating. This process applies chromate to aluminum substrates, providing corrosion resistance, durability, and stable electrical conductivity. It protects enclosures and metal parts from corrosion and ensures reliable electrical connections. Protocase’s coating meets specifications Type II, Clas…
4. Anoplate – Chem Film Solutions
Domain: anoplate.com
Registered: 1996 (29 years)
Introduction: Chem film, also known as chemical film, is a chemical conversion coating primarily applied to aluminum using chromates. Key product details include: 1. Benefits: Enhanced corrosion protection, ideal primer for paints and adhesives, prevents fingerprinting on soft metals, quick application methods (immersion, spray, brush), fewer processing steps, reliable electrical connections, and a thin coating…
5. Henkel – Alodine 1201 Chromate Conversion Coating
Domain: chemical-supermarket.com
Registered: 2005 (20 years)
Introduction: {“Product Name”: “Henkel Alodine 1201 Chromate Conversion Coating”, “Price”: “$34.95”, “Chemical Name”: “Alodine 1201 Conversion Coating”, “Synonyms”: “Chromate Conversion Coating”, “Description”: “Alodine® 1201 is a chemical treatment process for aluminum providing corrosion protection and surface preparation for paint and adhesives. It contains hexavalent chromium and enhances organic coating bo…
6. Advanced Plating Tech – Aluminum Chromate Conversion Coatings
Domain: advancedplatingtech.com
Registered: 2013 (12 years)
Introduction: Aluminum Chromate Conversion Coatings per MIL-C-5541 (MIL-DTL-5541) and ASTM B449-93. Provides a clear iridescent to slightly golden iridescent film of low contact resistance. Improves corrosion resistance of wrought, heat treatable, and cast aluminum alloys. Excellent base for subsequent painting or powder coating. Coating thickness: 0.00001-0.00004 inches. Amorphous structure with self-healing c…
7. Finishing & Coating – Chromium Conversion Coatings
Domain: finishingandcoating.com
Registered: 2020 (5 years)
Introduction: Chromium conversion coatings for aluminum surface treatment, developed in 1946, promote adhesion of organic films and increase corrosion resistance. Common issues include uneven coatings, dull brown color, loose coatings, and salt spray failure. Key process steps involve cleaning, deoxidizing, conversion coating, rinsing, and drying. Effective cleaning methods include solvent wipes and alkaline cl…
8. Valence Surface Tech – Chemical Conversion Coatings
Domain: valencesurfacetech.com
Registered: 2014 (11 years)
Introduction: Chemical conversion coating is a surface treatment process used to protect metal substrates from corrosion and improve adhesion for subsequent coatings. It involves the application of a chemical solution containing reactive materials such as chromates, phosphates, or other proprietary substances. Key benefits include corrosion resistance, enhanced paint adhesion, and preservation of electrical con…
9. Jets MRO – Chemical Conversion Coating
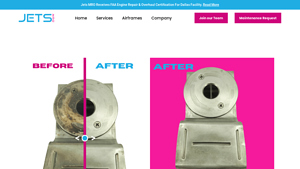
Domain: jetsmro.com
Registered: 2022 (3 years)
Introduction: Chemical conversion coating is a process used to enhance the corrosion resistance of metal surfaces, particularly aluminum. It creates a protective layer that improves adhesion for paints and other coatings. This process is essential for industries that require durable and long-lasting finishes, such as aerospace, automotive, and manufacturing. Benefits include increased durability, improved paint…
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for chemical conversion coating aluminum
In navigating the complexities of chemical conversion coatings for aluminum, international B2B buyers must prioritize strategic sourcing to ensure optimal product quality and compliance with industry standards. Understanding specifications like MIL-DTL-5541 is essential for selecting coatings that not only enhance corrosion resistance but also facilitate superior adhesion for subsequent finishes. The dual benefits of cost-effectiveness and reliability make chromate conversion coatings indispensable across various sectors, including aerospace, medical devices, and telecommunications.
Investing in high-quality chemical conversion coatings can yield significant long-term savings by reducing maintenance costs and extending the lifespan of aluminum components. Furthermore, as environmental regulations evolve, exploring trivalent chromium alternatives offers a sustainable path forward without compromising performance.
Looking ahead, the demand for innovative and efficient surface treatment solutions will only grow. B2B buyers are encouraged to engage with suppliers who demonstrate expertise and adaptability in this field. By fostering strong partnerships and staying informed about emerging technologies, businesses can enhance their competitive edge in the global marketplace. Connect with trusted manufacturers today to explore tailored solutions that meet your specific requirements.