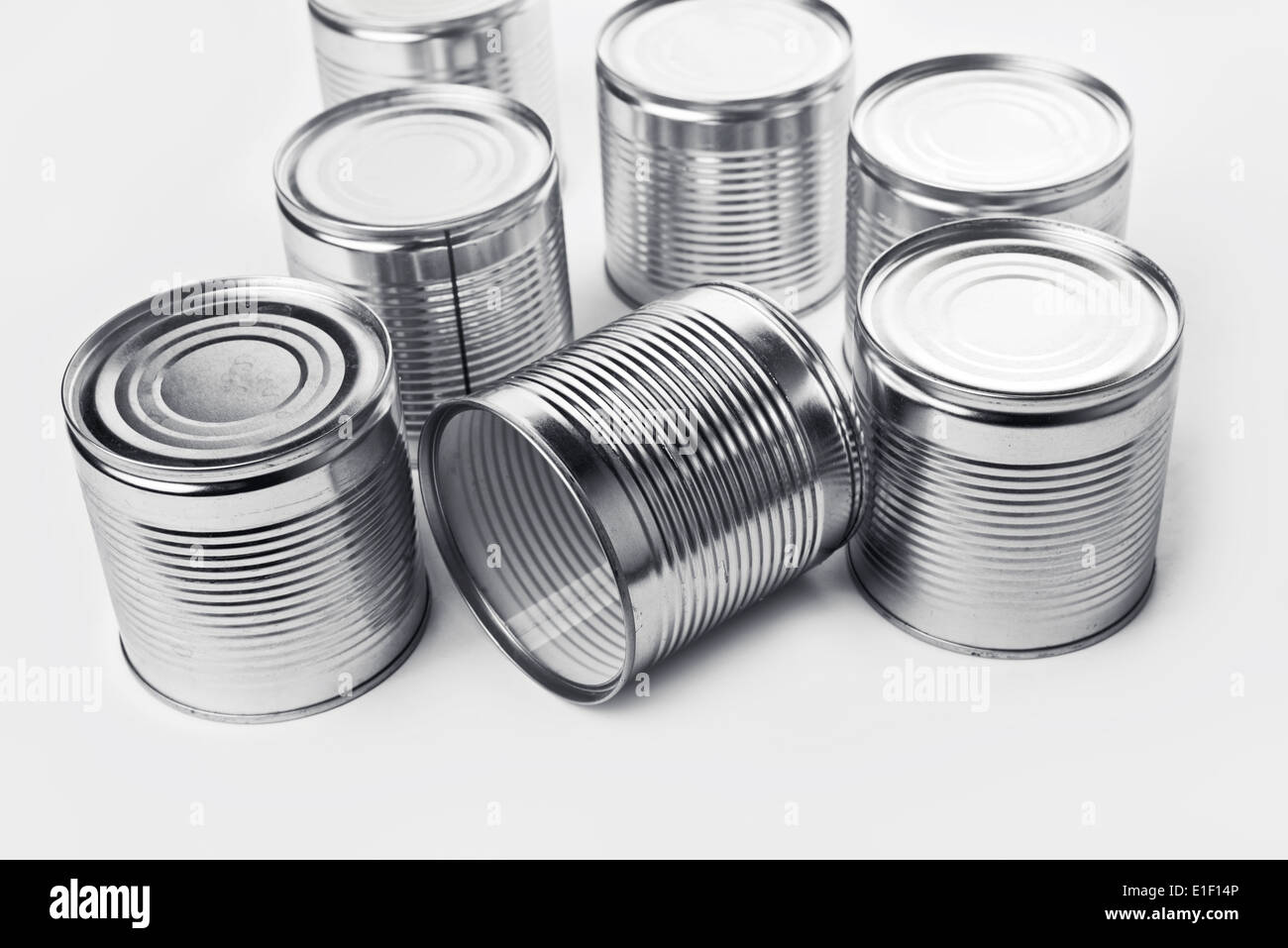
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for cheap aluminum
In today’s competitive landscape, sourcing cheap aluminum can pose significant challenges for international B2B buyers, particularly those operating in emerging markets across Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. The pressing need to find cost-effective solutions without compromising quality often leads to confusion and uncertainty. This guide aims to demystify the global market for aluminum by providing a comprehensive overview of various aluminum types, their applications, and effective supplier vetting strategies.
Buyers will gain insights into the diverse forms of aluminum available, such as alloys and wrought versus cast options, each tailored for specific industrial needs. Additionally, we will explore cost factors that influence pricing, including raw material availability and market demand fluctuations. Understanding these elements empowers buyers to make informed purchasing decisions that align with their operational requirements and budget constraints.
With a focus on practical solutions, this guide is designed to equip international B2B buyers from regions like Brazil and Vietnam with the knowledge necessary to navigate the complexities of sourcing cheap aluminum. By leveraging the actionable insights provided herein, businesses can enhance their procurement processes, ultimately driving efficiency and profitability in their operations.
Understanding cheap aluminum Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Pure Aluminum | High corrosion resistance, excellent ductility | Electrical components, packaging | Pros: Non-corrosive, lightweight. Cons: Lower strength compared to alloys. |
| 6061 Aluminum | Good weldability, medium strength, and corrosion resistance | Aerospace, automotive, construction | Pros: Versatile, easy to work with. Cons: Higher cost than some other alloys. |
| 5052 Aluminum | Excellent corrosion resistance, good workability | Marine applications, automotive parts | Pros: Durable in harsh environments. Cons: Limited to specific applications. |
| 3003 Aluminum | Good corrosion resistance, moderate strength | Chemical handling, food and beverage industry | Pros: Cost-effective, easy to fabricate. Cons: Lower strength than other alloys. |
| 7075 Aluminum | High strength, heat-treatable | Aerospace, military applications | Pros: Very strong, ideal for high-stress applications. Cons: Less corrosion resistance. |
What Are the Characteristics of Pure Aluminum for B2B Buyers?
Pure aluminum (Al 99.5%) is recognized for its outstanding corrosion resistance and ductility, making it a preferred choice for various electrical applications, including wiring and components. Its lightweight nature facilitates ease of handling and installation. For B2B buyers, the key consideration is its lower strength compared to aluminum alloys; thus, it is best suited for applications where corrosion resistance is paramount over structural strength.
Why Choose 6061 Aluminum for Diverse Applications?
6061 aluminum is known for its exceptional weldability and medium strength, making it ideal for industries like aerospace and automotive. Its versatility allows it to be easily fabricated into various forms, which is advantageous for manufacturers needing customized solutions. Buyers should weigh its higher cost against its long-term benefits in durability and performance, especially in critical applications.
What Makes 5052 Aluminum Ideal for Marine Environments?
5052 aluminum stands out for its superior corrosion resistance, particularly in marine environments. This alloy is commonly used in boat hulls, marine hardware, and automotive fuel tanks due to its excellent workability and durability. B2B purchasers should consider the specific environmental conditions their products will face, as this alloy excels in harsh settings, although it may be limited to particular applications.
How Does 3003 Aluminum Provide Cost-Effective Solutions?
3003 aluminum is a versatile and cost-effective alloy that offers moderate strength and good corrosion resistance, making it suitable for applications in the chemical handling and food processing industries. Its ease of fabrication is a significant advantage for manufacturers looking for quick and efficient production processes. However, buyers should be mindful that its strength is lower compared to other aluminum alloys, which may limit its use in more demanding applications.
Why is 7075 Aluminum Preferred for High-Stress Applications?
7075 aluminum is highly regarded for its exceptional strength and is often used in aerospace and military applications where performance under stress is crucial. While it can be heat-treated to enhance its properties, it has lower corrosion resistance compared to other alloys, making it less suitable for marine environments. B2B buyers must evaluate the trade-off between strength and corrosion resistance when considering this alloy for their projects.
Key Industrial Applications of cheap aluminum
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of cheap aluminum | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Automotive | Lightweight vehicle components | Reduces fuel consumption and enhances performance | Ensure compliance with safety and performance standards |
| Construction | Structural framing and cladding | Offers durability and corrosion resistance | Assess local regulations and environmental impact |
| Electrical & Electronics | Wiring and conductor materials | Provides excellent conductivity and lightweight design | Look for suppliers with quality certifications |
| Packaging | Food and beverage containers | Extends shelf life and reduces transportation costs | Focus on recyclability and compliance with food safety |
| Aerospace | Aircraft structural components | High strength-to-weight ratio improves fuel efficiency | Verify alloy specifications and international standards |
How is cheap aluminum used in the automotive industry, and what are the benefits?
In the automotive sector, cheap aluminum is extensively utilized for producing lightweight vehicle components such as frames, panels, and wheels. This application is critical as it significantly reduces the overall weight of vehicles, leading to improved fuel efficiency and lower emissions. For international B2B buyers, sourcing aluminum for automotive parts requires adherence to stringent safety and performance standards, which vary by region. It’s essential to partner with suppliers who understand these regulations and can provide materials that meet the necessary certifications.
What role does cheap aluminum play in construction?
In construction, cheap aluminum is favored for structural framing and cladding due to its durability and resistance to corrosion. It is often used in building facades, window frames, and roofing systems, providing both aesthetic appeal and structural integrity. For buyers in regions like Africa and South America, it is vital to consider local regulations regarding material specifications and environmental impact. Ensuring that the sourced aluminum can withstand local weather conditions is also crucial for long-term performance.
How does cheap aluminum benefit the electrical and electronics sectors?
Cheap aluminum is a popular choice in the electrical and electronics industries for applications such as wiring and conductors. Its excellent electrical conductivity and lightweight nature make it ideal for reducing energy losses and improving efficiency in electrical systems. B2B buyers should prioritize suppliers who can guarantee high-quality aluminum that meets international standards. Additionally, understanding the specific alloy requirements is essential for ensuring compatibility with various electrical applications.
Why is cheap aluminum important for packaging?
In the packaging industry, cheap aluminum is commonly used for food and beverage containers due to its ability to extend shelf life while being lightweight. This not only helps in reducing transportation costs but also enhances product protection. International buyers should focus on sourcing aluminum that meets food safety regulations and offers recyclability, as sustainability is increasingly important in packaging solutions. Collaborating with suppliers who emphasize eco-friendly practices can also enhance brand reputation.
How is cheap aluminum utilized in aerospace applications?
In aerospace, cheap aluminum is utilized for manufacturing structural components of aircraft, where its high strength-to-weight ratio is a significant advantage. This property contributes to improved fuel efficiency and overall performance. For B2B buyers in this sector, it is critical to verify that the aluminum alloys meet specific aerospace standards and certifications. Additionally, understanding the nuances of heat-treatable versus non-heat-treatable alloys can influence sourcing decisions, especially when considering the specific performance requirements of aircraft components.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘cheap aluminum’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Quality Concerns with Cheap Aluminum Products
The Problem: B2B buyers often face significant challenges when sourcing cheap aluminum due to the inconsistency in quality. Inexpensive aluminum may not meet the required mechanical properties or corrosion resistance specifications for various applications, leading to potential failures or safety hazards. This concern is particularly acute for industries such as construction and manufacturing, where the integrity of aluminum components is critical. Buyers may find themselves in a situation where they need to replace subpar materials, resulting in increased costs and project delays.
The Solution: To mitigate quality concerns, buyers should prioritize sourcing from reputable suppliers who provide detailed product specifications and certifications. It is essential to request material test reports (MTRs) that confirm the aluminum’s properties align with your project requirements. Additionally, consider utilizing a quality assurance process, including sampling and testing of materials upon delivery. Engaging with suppliers that offer a variety of aluminum grades allows buyers to select the most suitable alloy for their specific application, ensuring a balance between cost and performance.
Scenario 2: Difficulty in Sizing and Customization of Cheap Aluminum
The Problem: Many B2B buyers struggle with the limitations of standardized aluminum sizes, which can lead to excess waste or inadequate materials for specific projects. This is especially true for industries that require customized shapes and dimensions for unique applications. When working with cheap aluminum, the inability to find the right size can result in operational inefficiencies and increased production costs due to the need for additional machining or alterations.
The Solution: Buyers should seek out suppliers that offer cut-to-size services and customizable options for aluminum products. This capability allows businesses to order exact dimensions based on project needs, minimizing waste and optimizing material usage. When placing orders, provide detailed specifications, including thickness, width, length, and any specific finishing requirements. Additionally, discussing your project’s needs with suppliers can lead to expert recommendations on the best aluminum products to use, ensuring that you receive materials tailored precisely to your operational requirements.
Scenario 3: Misunderstanding the Alloys and Their Applications
The Problem: A common pain point for B2B buyers is the lack of understanding regarding the different aluminum alloys and their specific applications. Cheap aluminum may come in various forms and alloys, such as 6061, 5052, or 7075, each suited for different purposes. Misapplying these alloys can lead to inadequate performance in critical applications, potentially resulting in project failures, safety issues, or costly reworks.
The Solution: To navigate the complexities of aluminum alloys, buyers should invest time in educating themselves about the properties and applications of each alloy. Engaging with knowledgeable suppliers can provide invaluable insights into which aluminum types are best suited for specific applications. Creating a clear specification document that outlines the intended use of the aluminum, environmental conditions, and mechanical requirements can facilitate better communication with suppliers. Furthermore, attending workshops or industry seminars focused on material science can enhance understanding and help buyers make informed decisions, ultimately ensuring that the right aluminum alloy is utilized for each project.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for cheap aluminum
What Are the Key Properties of Common Aluminum Alloys for B2B Applications?
When selecting aluminum materials for cost-sensitive applications, it’s essential to consider specific alloys that balance performance, cost, and suitability for various environments. Below, we analyze four common aluminum alloys that are often regarded as “cheap aluminum” options in the B2B market.
1. 3003 Aluminum Alloy: What Makes It a Popular Choice?
3003 aluminum is a widely used alloy known for its excellent workability and moderate strength. It offers good corrosion resistance and is non-heat-treatable, making it easy to form and weld. The alloy is rated for temperatures up to 150 °C (302 °F), which is suitable for many applications.
Pros:
– Excellent corrosion resistance, particularly in marine environments.
– Good formability and weldability, making it suitable for various manufacturing processes.
– Cost-effective for applications that do not require high strength.
Cons:
– Lower strength compared to other alloys, limiting its use in high-stress applications.
– Not suitable for applications requiring high-temperature performance.
Impact on Application:
3003 aluminum is commonly used in cooking utensils, chemical equipment, and storage tanks. Its resistance to corrosion makes it ideal for food processing and marine applications.
Considerations for International Buyers:
Buyers should ensure compliance with local standards such as ASTM or DIN. In regions like Africa and South America, the availability of 3003 may vary, so sourcing from reliable suppliers is crucial.
2. 5052 Aluminum Alloy: How Does It Stand Out?
5052 aluminum alloy is known for its high corrosion resistance and good weldability. It can withstand temperatures up to 65 °C (149 °F) and is particularly effective in marine environments due to its resistance to saltwater corrosion.
Pros:
– High fatigue strength and excellent corrosion resistance.
– Good workability and weldability, making it suitable for complex shapes.
– Ideal for marine and architectural applications.
Cons:
– More expensive than 3003 and may not be suitable for all budget-conscious projects.
– Limited to lower temperature applications.
Impact on Application:
5052 is often used in marine applications, automotive fuel tanks, and pressure vessels. Its durability makes it a preferred choice for products exposed to harsh environments.
Considerations for International Buyers:
Buyers should verify compliance with international standards and consider local manufacturing capabilities. In Europe, for instance, adherence to EN standards is essential.
3. 6061 Aluminum Alloy: What Are Its Advantages?
6061 aluminum alloy is a heat-treatable alloy known for its excellent mechanical properties and versatility. It can withstand temperatures up to 160 °C (320 °F) and is often used in structural applications.
Pros:
– High strength-to-weight ratio and good corrosion resistance.
– Excellent weldability and machinability, making it suitable for various applications.
– Versatile, used in aerospace, automotive, and construction.
Cons:
– More expensive than non-heat-treatable alloys like 3003.
– Requires careful handling during heat treatment to avoid warping.
Impact on Application:
6061 is commonly used in structural components, automotive parts, and marine applications where strength and durability are critical.
Considerations for International Buyers:
Buyers should be aware of the specific alloy designation and ensure that suppliers meet ASTM or JIS standards. This is particularly important for buyers in the Middle East and Europe.
4. 7075 Aluminum Alloy: Is It Worth the Investment?
7075 aluminum is known for its high strength and is often used in aerospace and military applications. It can withstand temperatures up to 120 °C (248 °F) and is one of the strongest aluminum alloys available.
Pros:
– Exceptional strength-to-weight ratio, making it ideal for high-stress applications.
– Good fatigue resistance and durability.
Cons:
– Higher cost compared to other aluminum alloys.
– Poor corrosion resistance compared to 5052 and 3003.
Impact on Application:
7075 is primarily used in aerospace components, military applications, and high-performance sporting equipment. Its strength makes it suitable for critical applications.
Considerations for International Buyers:
Due to its specialized nature, buyers should ensure that 7075 aluminum is sourced from certified suppliers who comply with international standards, especially in regions with strict aerospace regulations.
Summary Table of Aluminum Alloys
| Material | Typical Use Case for cheap aluminum | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 3003 | Cooking utensils, chemical equipment | Excellent corrosion resistance | Lower strength for high-stress use | Low |
| 5052 | Marine applications, fuel tanks | High fatigue strength | More expensive than 3003 | Medium |
| 6061 | Structural components, automotive | High strength-to-weight ratio | Requires careful heat treatment | Medium |
| 7075 | Aerospace, military applications | Exceptional strength | Poor corrosion resistance | High |
This guide provides a comprehensive overview of common aluminum alloys, their properties, and considerations for international B2B buyers, enabling informed decision-making in material selection.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for cheap aluminum
What Are the Main Stages of Manufacturing Cheap Aluminum?
The manufacturing process for cheap aluminum involves several critical stages that ensure the material’s quality and suitability for various applications. Understanding these stages can help B2B buyers make informed decisions when sourcing aluminum products.
Material Preparation: How Is Aluminum Sourced and Prepared?
The first step in the manufacturing process is material preparation, which includes sourcing raw aluminum and preparing it for further processing. Aluminum is typically derived from bauxite ore, which undergoes refining to produce alumina. The alumina is then reduced to aluminum metal through the Hall-Héroult process, a method that involves electrolysis.
Once the aluminum is obtained, it is cast into ingots or billets, which serve as the primary form for subsequent processing. The quality of the raw materials is crucial, as impurities can affect the aluminum’s mechanical properties. Suppliers often conduct chemical analyses to ensure that the aluminum meets industry standards.
What Forming Techniques Are Used in Aluminum Manufacturing?
The forming stage encompasses various techniques to shape the aluminum into desired products. Common methods include:
-
Extrusion: Aluminum billets are heated and forced through a die to create long shapes, such as pipes, bars, and profiles. This method is particularly efficient for producing complex cross-sections and is widely used in construction and automotive applications.
-
Rolling: In this process, aluminum sheets are created by passing the metal through a series of rollers. This technique can produce sheets of varying thicknesses and is essential for applications requiring flat aluminum products.
-
Forging: This involves shaping aluminum through the application of localized compressive forces. Forging enhances the mechanical properties of aluminum and is often used for parts that require high strength.
How Is Assembly Managed in Aluminum Manufacturing?
Assembly in aluminum manufacturing may involve welding, riveting, or fastening components together to create a finished product. Depending on the application, specific alloys may be chosen to enhance the weldability or corrosion resistance of the assembly. For instance, 6061 aluminum is often preferred in aerospace applications due to its excellent weldability and strength.
Effective assembly processes are crucial for ensuring the structural integrity of the final product. Manufacturers often employ automated systems for precision and efficiency, especially in high-volume production scenarios.
What Finishing Processes Enhance the Quality of Aluminum Products?
The finishing stage adds protective coatings, surface treatments, or aesthetic features to aluminum products. Common finishing techniques include:
-
Anodizing: This electrochemical process enhances the natural oxide layer on aluminum, improving corrosion resistance and allowing for various color finishes.
-
Powder Coating: A dry finishing process that provides a durable and aesthetically pleasing surface. Powder coating can help protect aluminum from environmental factors, making it ideal for outdoor applications.
-
Painting: Traditional painting methods can also be used, though they may not provide the same level of protection as anodizing or powder coating.
Each finishing technique can be tailored to meet specific customer requirements and industry standards.
What Quality Assurance Practices Are Essential for Cheap Aluminum Manufacturing?
Quality assurance (QA) is a critical aspect of aluminum manufacturing, ensuring that products meet specific standards and regulations. For B2B buyers, understanding QA practices can help in selecting reliable suppliers.
Which International Standards Should B2B Buyers Be Aware Of?
International standards such as ISO 9001 play a significant role in quality assurance for aluminum manufacturers. ISO 9001 provides a framework for consistent quality management systems, focusing on continuous improvement and customer satisfaction.
In addition to ISO standards, industry-specific certifications such as CE (Conformité Européenne) for European markets and API (American Petroleum Institute) for oil and gas applications are essential. These certifications indicate that the products meet specific safety and performance requirements.
What Are the Key Quality Control Checkpoints in Aluminum Manufacturing?
Quality control (QC) checkpoints are integrated throughout the manufacturing process to ensure that products meet established standards. Key checkpoints include:
-
Incoming Quality Control (IQC): This initial inspection focuses on the quality of raw materials upon arrival at the manufacturing facility. Suppliers should verify that the aluminum meets specified chemical and physical properties.
-
In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): Continuous monitoring during the manufacturing process helps identify defects early. Techniques such as visual inspections, dimensional checks, and non-destructive testing (NDT) are commonly employed.
-
Final Quality Control (FQC): The final inspection ensures that the finished products meet all specifications before shipment. This stage often includes performance testing and compliance checks.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control?
B2B buyers can take several steps to verify a supplier’s quality control processes:
-
Supplier Audits: Conducting on-site audits allows buyers to assess the manufacturing environment, quality management systems, and compliance with international standards.
-
Quality Reports: Requesting detailed quality reports can provide insights into the supplier’s QC processes and any issues encountered during production.
-
Third-Party Inspections: Engaging third-party inspection services can offer an unbiased assessment of product quality. This practice is especially beneficial when dealing with suppliers in different countries, where regulations and standards may vary.
What QC and Certification Nuances Should International B2B Buyers Consider?
For international buyers, particularly those from regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, understanding the nuances of quality control and certification is essential.
-
Regulatory Compliance: Different regions have specific regulations regarding aluminum products. Buyers should familiarize themselves with local requirements to ensure compliance.
-
Cultural Considerations: Cultural differences may influence communication and expectations around quality. Establishing clear guidelines and maintaining open lines of communication can help bridge these gaps.
-
Logistics and Shipping: Quality assurance does not end with production. Proper handling and transportation are critical to maintaining product integrity. Buyers should work closely with suppliers to ensure that products are shipped in a manner that protects them from damage.
By understanding the manufacturing processes and quality assurance practices associated with cheap aluminum, B2B buyers can make informed decisions that align with their business needs. This knowledge not only aids in selecting reliable suppliers but also helps in negotiating better terms and fostering long-term partnerships.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘cheap aluminum’
Introduction
When sourcing cheap aluminum, particularly for international B2B transactions, a systematic approach is essential. This guide provides a practical checklist to help buyers navigate the complexities of procurement, ensuring they secure quality aluminum at competitive prices. By following these steps, you can streamline your sourcing process and mitigate risks associated with international purchases.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Clearly outline the specifications for the aluminum you need, including alloy type, thickness, dimensions, and finish. This step is vital as it ensures that you communicate your requirements effectively to suppliers, minimizing the risk of receiving incorrect materials. Consider the intended application to guide your specifications, whether for construction, automotive, or manufacturing.
Step 2: Research and Identify Potential Suppliers
Conduct thorough research to identify suppliers that specialize in aluminum products. Look for companies with a solid reputation in the industry and positive reviews from previous clients. Utilize online platforms and industry directories, and consider regional suppliers that understand local market conditions, especially if you are sourcing from Africa, South America, the Middle East, or Europe.
Step 3: Evaluate Supplier Certifications and Compliance
Ensure that potential suppliers hold relevant certifications, such as ISO 9001 for quality management and compliance with international aluminum standards. This step is crucial for guaranteeing that the materials meet quality and safety requirements. Additionally, inquire about their environmental practices, as sustainability is increasingly important in global trade.
Step 4: Request Samples for Quality Assurance
Before placing a bulk order, request samples of the aluminum you intend to purchase. This allows you to assess the quality, finish, and specific characteristics of the material firsthand. Evaluate the samples against your specifications to confirm that they meet your requirements for strength, corrosion resistance, and other critical factors.
Step 5: Negotiate Pricing and Terms
Engage in negotiations with selected suppliers to establish pricing and payment terms. Be prepared to discuss minimum order quantities and potential discounts for bulk purchases. This step is essential for ensuring that you secure the best possible deal while maintaining a good relationship with the supplier.
Step 6: Confirm Shipping and Logistics Arrangements
Once you’ve finalized your order, confirm the shipping terms, delivery timelines, and logistics arrangements. It’s important to understand the incoterms that will govern the transaction, as these dictate responsibilities for shipping costs and risks. Ensure that you have a clear plan for customs clearance and delivery to avoid unexpected delays.
Step 7: Establish a Quality Control Process
Implement a quality control process upon receiving the aluminum. Inspect the materials against your specifications to ensure they match what was agreed upon. Establishing a quality assurance protocol helps safeguard against defects and ensures that your procurement meets industry standards, thus protecting your business’s reputation and operational efficiency.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for cheap aluminum Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components in Cheap Aluminum Sourcing?
When evaluating the cost structure for sourcing cheap aluminum, several components contribute to the overall price. Understanding these elements is crucial for B2B buyers looking to optimize their procurement strategies.
-
Materials: The primary cost driver in aluminum pricing is the raw material itself. Prices can fluctuate based on global aluminum market trends, influenced by supply and demand dynamics, geopolitical factors, and production costs in primary producing countries. Buyers should monitor the London Metal Exchange (LME) for real-time pricing.
-
Labor and Manufacturing Overhead: Labor costs can vary significantly depending on the region and the complexity of the manufacturing processes involved. Overhead expenses related to facilities, utilities, and administrative costs also play a role. In regions with lower labor costs, such as parts of Africa and South America, buyers may find more competitive pricing.
-
Tooling and Quality Control (QC): Initial tooling costs for custom orders can be substantial, particularly for specialized aluminum shapes or alloys. Furthermore, quality control measures ensure that products meet international standards, which can add to the cost. Investing in quality assurance can prevent future costs associated with product failures.
-
Logistics: Shipping costs can significantly affect the total price of aluminum, especially for international shipments. Factors such as distance, mode of transport (air, sea, or land), and any potential tariffs or duties should be considered. Effective logistics management can mitigate these costs.
-
Margin: Suppliers typically include a margin to cover their risks and profits. This margin can vary based on the supplier’s market position, the competitiveness of the industry, and the relationship with the buyer.
How Do Price Influencers Impact Cheap Aluminum Sourcing?
Several factors can influence the pricing of cheap aluminum, and understanding these can help buyers negotiate better deals.
-
Volume and Minimum Order Quantity (MOQ): Generally, larger orders can lead to lower unit prices due to economies of scale. Suppliers often have minimum order quantities, and exceeding these can significantly reduce the cost per unit.
-
Specifications and Customization: Custom specifications such as thickness, alloy composition, and surface treatment can affect pricing. Standardized products typically cost less than customized solutions, so buyers should assess whether they require specific alterations.
-
Quality and Certifications: The quality of aluminum and the presence of certifications (e.g., ISO standards) can influence pricing. Higher-quality materials may command a premium but can result in lower total costs over time due to reduced failure rates and longer lifespans.
-
Supplier Factors: The supplier’s reputation, location, and relationship with the buyer can impact pricing. Established suppliers may offer better terms based on trust and reliability, while new suppliers may provide lower initial prices to attract customers.
-
Incoterms: The choice of Incoterms affects logistics and cost responsibilities between buyers and sellers. Terms like FOB (Free on Board) and CIF (Cost, Insurance, and Freight) can shift cost burdens and risks, impacting the final price.
What Negotiation Strategies Can Help in Sourcing Cheap Aluminum?
For international B2B buyers, particularly from diverse regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, effective negotiation is vital for achieving cost-efficiency.
-
Build Long-Term Relationships: Establishing a reliable relationship with suppliers can lead to better pricing and terms. Repeat business often results in loyalty discounts and preferential treatment.
-
Focus on Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Evaluate the full cost of aluminum procurement, including transport, storage, and potential waste. Sometimes, higher upfront costs can lead to lower TCO due to improved quality and durability.
-
Leverage Market Trends: Stay informed about market trends and fluctuations in aluminum pricing. Being knowledgeable can provide leverage during negotiations, especially if prices are expected to rise.
-
Be Flexible with Specifications: If possible, maintain flexibility in product specifications. Suppliers may offer better pricing on standard products rather than customized ones.
-
Consider Alternative Suppliers: Exploring multiple suppliers can provide a comparative view of pricing and quality. This can enhance negotiation power and help identify the best value.
Disclaimer on Pricing
Pricing for aluminum can vary widely based on numerous factors, including market conditions and supplier agreements. The figures provided in this analysis are indicative and should be verified with suppliers for accurate and current pricing information.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing cheap aluminum With Other Solutions
Understanding Alternatives to Cheap Aluminum
In the competitive landscape of materials procurement, B2B buyers often explore various options to meet their needs. While cheap aluminum offers significant advantages such as lightweight, corrosion resistance, and versatility, several alternative materials can also serve similar purposes. This analysis compares cheap aluminum with two viable alternatives: galvanized steel and composite materials, allowing buyers to make informed decisions based on their specific requirements.
| Comparison Aspect | ‘Cheap Aluminum’ | Galvanized Steel | Composite Materials |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | High strength-to-weight ratio; excellent corrosion resistance | Strong but heavier; good corrosion resistance | Lightweight; variable strength based on composition |
| Cost | Generally low cost per unit | Moderate cost; higher than aluminum | Can be expensive; varies widely based on type |
| Ease of Implementation | Easy to cut and shape; widely available | Requires specialized tools for cutting | May require specific fabrication techniques |
| Maintenance | Low maintenance due to corrosion resistance | Moderate; may require periodic repainting | Low maintenance but can be sensitive to UV exposure |
| Best Use Case | Aerospace, automotive, and construction applications | Structural applications, automotive frames | Aerospace, marine, and architectural applications |
In-Depth Look at Alternatives
Galvanized Steel
Galvanized steel is a popular alternative known for its strength and durability. It undergoes a galvanization process, where a protective zinc coating is applied to prevent rusting. While it offers significant structural integrity, it is heavier than aluminum, which can be a drawback in applications where weight is a critical factor. Additionally, galvanized steel may require periodic maintenance, such as repainting, to maintain its corrosion resistance. It is ideal for construction and automotive applications where strength is prioritized over weight.
Composite Materials
Composite materials, often made from a combination of plastic and fiber, present a lightweight option with excellent strength-to-weight ratios. They are highly versatile and can be engineered for specific applications, making them suitable for aerospace and marine industries. However, the cost can be significantly higher than that of aluminum, and they may require specialized fabrication techniques, which can complicate the implementation process. Moreover, while composites are resistant to corrosion, they can be susceptible to UV damage, requiring careful consideration in outdoor applications.
Choosing the Right Solution for Your Needs
When selecting the appropriate material for your project, consider factors such as performance requirements, budget constraints, and ease of implementation. Cheap aluminum excels in applications that require lightweight and corrosion-resistant materials, making it a go-to choice for many industries. However, if your project demands higher strength or specific properties that aluminum cannot provide, alternatives like galvanized steel or composite materials may be more suitable.
Ultimately, understanding the strengths and weaknesses of each material will empower B2B buyers to make decisions that align with their operational goals and project specifications. By evaluating the unique characteristics of cheap aluminum and its alternatives, businesses can optimize their material selection process for maximum efficiency and cost-effectiveness.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for cheap aluminum
What Are the Key Technical Properties of Cheap Aluminum for B2B Buyers?
When considering cheap aluminum for various applications, understanding its critical technical properties is essential. Here are some key specifications that B2B buyers should be aware of:
1. Material Grade
Aluminum is categorized into different grades based on its composition and properties. Common grades include 1100, 3003, 5052, 6061, and 7075. Each grade possesses unique characteristics, such as strength, corrosion resistance, and weldability, which dictate its suitability for specific applications. For example, 6061 is often used in structural applications due to its good mechanical properties, while 5052 is favored in marine environments for its superior corrosion resistance. Selecting the appropriate grade ensures optimal performance and longevity in your products.
2. Tolerance
Tolerance refers to the permissible limits of variation in a material’s dimensions. In aluminum manufacturing, tight tolerances are crucial, especially in precision industries like aerospace and automotive. Understanding tolerance specifications helps ensure that components fit together correctly, reducing the risk of defects and improving overall product quality. Buyers should inquire about the manufacturer’s tolerance capabilities to align with their project requirements.
3. Yield Strength
Yield strength is the amount of stress a material can withstand before it deforms permanently. For aluminum, this property is vital in determining how much load a component can bear during its service life. Higher yield strength typically indicates a more robust material, which is essential for load-bearing applications. Buyers should assess yield strength to ensure that the aluminum they procure meets the demands of their specific applications.
4. Ductility
Ductility measures a material’s ability to deform under tensile stress without breaking. Aluminum is known for its excellent ductility, which allows it to be formed into various shapes without losing its integrity. This property is particularly important for manufacturers who require aluminum sheets or extrusions that can be bent or shaped without cracking. Understanding ductility helps buyers select materials that can be easily processed and fabricated into finished products.
5. Corrosion Resistance
Aluminum naturally forms a protective oxide layer that enhances its resistance to corrosion. This property is crucial for applications exposed to harsh environments, such as marine and industrial settings. Buyers should consider the corrosion resistance of different aluminum grades, especially when selecting materials for outdoor or corrosive applications. Enhanced corrosion resistance can lead to lower maintenance costs and increased product lifespan.
6. Melting Point
The melting point of aluminum is approximately 660 °C (1220 °F). This property is essential for manufacturers involved in processes like welding and casting. Knowing the melting point helps in selecting the right processes and equipment for fabrication, ensuring that the aluminum maintains its desired properties throughout manufacturing.
What Common Trade Terms Should B2B Buyers Know When Sourcing Cheap Aluminum?
Familiarity with industry jargon can significantly streamline the procurement process. Here are some common terms that B2B buyers should understand:
1. OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
OEM refers to a company that produces parts or equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer. In the aluminum industry, buyers often source aluminum products from OEMs to ensure compatibility with their existing systems. Understanding OEM relationships can help buyers identify reliable suppliers and ensure quality standards are met.
2. MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ is the smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell. For aluminum products, MOQs can vary based on the manufacturer and the type of aluminum being sourced. Knowing the MOQ is crucial for buyers to manage inventory levels effectively and avoid excess stock.
3. RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a document sent to suppliers to solicit pricing and terms for specific products. When sourcing cheap aluminum, submitting an RFQ helps buyers compare offers and negotiate better deals. Providing clear specifications in the RFQ can lead to more accurate quotes and streamlined procurement.
4. Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
Incoterms are standardized trade terms that define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in international transactions. These terms clarify who is responsible for shipping, insurance, and tariffs. Understanding Incoterms is vital for buyers engaged in global sourcing, as they impact total costs and logistics.
5. Lead Time
Lead time refers to the time it takes from placing an order to receiving the product. In the aluminum industry, lead times can vary based on the complexity of the order and the supplier’s capabilities. Buyers should consider lead times in their planning to ensure timely project execution.
6. Fabrication
Fabrication encompasses the processes involved in transforming raw aluminum into finished products. This can include cutting, bending, welding, and machining. Understanding fabrication capabilities is essential for buyers to ensure that their suppliers can meet their specific manufacturing needs.
By grasping these essential properties and terms, B2B buyers can make informed decisions when sourcing cheap aluminum, ultimately leading to better product outcomes and supplier relationships.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the cheap aluminum Sector
What Are the Key Market Dynamics and Trends Influencing the Cheap Aluminum Sector?
The global aluminum market is experiencing robust growth driven by increasing demand across various sectors, including automotive, aerospace, construction, and packaging. Cheap aluminum, characterized by its affordability and versatility, is particularly attractive to international B2B buyers from emerging markets in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. A significant driver of this trend is the shift towards lightweight materials, which enhance fuel efficiency and reduce emissions in transportation applications. Additionally, the growing urbanization in developing regions is spurring demand for aluminum in construction projects, further propelling market dynamics.
In terms of sourcing trends, technology is playing a pivotal role. The adoption of digital procurement platforms and e-commerce solutions is streamlining the sourcing process, allowing buyers to compare suppliers, prices, and product specifications efficiently. Innovations in supply chain management, such as blockchain technology, are enhancing transparency and traceability, which is crucial for ensuring quality and compliance in the sourcing of cheap aluminum. Moreover, the trend towards just-in-time inventory management is compelling suppliers to offer flexible, cut-to-size aluminum solutions that cater to specific project requirements, reducing waste and costs.
How Is Sustainability and Ethical Sourcing Impacting the Cheap Aluminum Industry?
Sustainability has emerged as a critical consideration in the aluminum sector, particularly in the context of cheap aluminum sourcing. The environmental impact of aluminum production is significant, with energy-intensive processes contributing to carbon emissions. As a result, buyers are increasingly prioritizing suppliers that adopt sustainable practices, such as using renewable energy sources and minimizing waste in their production processes.
Ethical sourcing is also gaining traction, with companies seeking to ensure that their supply chains are free from human rights abuses and environmental degradation. Certifications such as ISO 14001 (Environmental Management) and ASI (Aluminium Stewardship Initiative) are becoming essential for suppliers aiming to demonstrate their commitment to sustainability. B2B buyers are encouraged to consider these certifications when evaluating potential suppliers, as they reflect a commitment to responsible production practices. Furthermore, the use of recycled aluminum is becoming more prevalent, not only due to its lower environmental impact but also because it offers cost savings, making it an appealing option for budget-conscious buyers.
What Is the Historical Context of the Cheap Aluminum Market?
The aluminum industry has evolved significantly over the past century. Initially, aluminum was considered a luxury material due to its high production costs. However, advancements in extraction and processing technologies, particularly the Hall-Héroult process developed in the late 19th century, revolutionized aluminum production, making it more accessible and affordable. The post-World War II era saw an exponential increase in aluminum usage, driven by its lightweight and corrosion-resistant properties, leading to its widespread adoption across various industries.
Today, the cheap aluminum sector reflects a mature market with established supply chains and a growing emphasis on sustainability. As international B2B buyers continue to seek cost-effective solutions, the evolution of aluminum production methods and sourcing practices will remain pivotal in shaping the future landscape of this vital industry.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of cheap aluminum
-
How do I choose the right type of aluminum for my project?
Selecting the appropriate aluminum type hinges on your project’s specific requirements, such as strength, weight, corrosion resistance, and application. Common alloys like 6061 are excellent for structural applications due to their weldability and corrosion resistance, while 5052 is ideal for marine environments due to its high corrosion resistance. Consider the mechanical properties and environmental conditions the aluminum will face, and consult suppliers for expert guidance on the best alloy for your needs. -
What are the minimum order quantities (MOQs) for aluminum purchases?
Minimum order quantities can vary significantly depending on the supplier and the type of aluminum you require. Many suppliers cater to both small and large-scale orders, but MOQs often range from 100 kg to several tons. It’s advisable to communicate your specific needs with potential suppliers to negotiate MOQs that align with your project scale, especially if you’re sourcing from international suppliers. -
What payment terms should I expect when sourcing aluminum internationally?
Payment terms can differ based on supplier policies and your business relationship. Common terms include advance payment, letter of credit, or net 30/60 days after delivery. For international transactions, consider using secure payment methods like PayPal or escrow services to mitigate risk. Always ensure that payment terms are clearly outlined in the contract to avoid misunderstandings. -
How can I ensure the quality of aluminum products sourced from overseas?
Ensuring product quality begins with thorough supplier vetting. Request certifications such as ISO 9001 or specific alloy certifications to verify compliance with international standards. Consider conducting factory audits or requesting samples before placing large orders. Establishing clear quality assurance protocols in your contracts can also help maintain quality throughout the production and shipping processes. -
What is the importance of aluminum recycling in my supply chain?
Aluminum recycling is crucial not only for sustainability but also for cost savings. Recycled aluminum requires 95% less energy to produce than primary aluminum, reducing overall costs and environmental impact. By sourcing recycled aluminum, you can enhance your company’s sustainability profile, meet regulatory requirements, and appeal to environmentally conscious customers. Discuss recycling options with suppliers to integrate this into your supply chain effectively. -
How do logistics and shipping affect my aluminum procurement?
Logistics and shipping are vital components of your procurement strategy, especially for international sourcing. Consider factors such as shipping costs, lead times, and customs regulations in your planning. Collaborate with suppliers who have experience in international shipping to ensure timely delivery and compliance with import/export laws. Additionally, using a freight forwarder can help streamline the logistics process and mitigate potential delays. -
What customization options are available for aluminum products?
Many suppliers offer customization options, including cut-to-size sheets, specific alloy compositions, and surface treatments like anodizing or powder coating. When discussing your project requirements, be clear about your specifications and ask suppliers about their capabilities. Customization can enhance product performance and aesthetics, making it essential to identify a supplier who can meet your unique needs. -
How do I handle disputes with aluminum suppliers?
Disputes with suppliers can arise from quality issues, delivery delays, or payment disagreements. To handle such disputes effectively, maintain clear communication and document all transactions and agreements. If issues arise, try to resolve them amicably through direct negotiation. Should disputes escalate, refer to the terms outlined in your contract regarding conflict resolution, which may include mediation or arbitration clauses. Having a legal framework in place can help protect your interests.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.
Top 6 Cheap Aluminum Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. Online Metals – Aluminum Products
Domain: onlinemetals.com
Registered: 1997 (28 years)
Introduction: Aluminum products available for purchase, including various shapes and sizes such as sheets, plates, bars, and extrusions. Options for different grades and finishes are provided, along with specifications like thickness, width, and length. Pricing and availability are also included.
2. Metal Supermarkets – Aluminum
Domain: metalsupermarkets.com
Registered: 1996 (29 years)
Introduction: Aluminum is a silver-colored, low-density, non-ferrous metal used in various commercial applications. It has excellent strength-to-weight ratio, corrosion resistance, and versatility. Key grades available include 1100, 2011, 2024, 3003, 4017, 5052, 6061, 6063, and 7075. Common shapes include Angle, Bar Grating, Beam, Channel, Diamond Grip, Expanded Sheet, Flat Bar, Hexagon Bar, Perforated Sheet, P…
3. FastMetals – Aluminum Metal Stock Supply
Domain: fastmetals.com
Registered: 2013 (12 years)
Introduction: Aluminum Metal Stock Supply – Cut to Size – FastMetals.com. Products include: Aluminum Extruded Angle (6061 T6, 6063 T52), Aluminum Extruded Channel (6061 T6, 6063 T52), Aluminum Extruded Flat Bar (6061 T6511), Aluminum Extruded Hex Bar (6061 T6511), Aluminum Extruded I-Beam (6061-T6), Aluminum Pipe (6061 T6 Schedule 40, Schedule 80), Aluminum Plate (6061 T651), Aluminum Extruded Rectangular Tube …
4. Aluminum – Cost Variations
Domain: reddit.com
Registered: 2005 (20 years)
Introduction: Aluminum can be inexpensive in certain forms, such as soda cans, but can also be expensive when used in specialized applications like aluminum siding or automotive manufacturing. The cost varies based on the type and processing of aluminum.
5. Metals Depot – Aluminum Sheet Types
Domain: metalsdepot.com
Registered: 1999 (26 years)
Introduction: Aluminum Sheet Types: 3003-H14, 5052-H32, 6061-T6. 3003-H14: Excellent weldability and formability, good corrosion resistance, applications include fuel tanks, food & chemical handling, trailer siding & roofing. Mill Finish, Non-magnetic, Brinell = 40, Tensile = 22,000, Yield = 21,000. 5052-H32: Superior corrosion resistance, good weldability, excellent formability, applications include tanks, mar…
6. TNutz – EX-1010 Smooth T-Slotted Aluminum Extrusion
Domain: tnutz.com
Registered: 2007 (18 years)
Introduction: {“product_name”: “EX-1010 – 1\” x 1\” Smooth T-Slotted Aluminum Extrusion”, “sku”: “EX-1010”, “category”: “10 Series Extrusions”, “price_range”: “$0.22 – $21.62”, “length_options”: [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11, 12, 13, 14, 15, 16, 17, 18, 19, 20, 21, 22, 23, 24, 25, 26, 27, 28, 29, 30, 31, 32, 33, 34, 35, 36, 37, 38, 39, 40, 41, 42, 43, 44, 45, 46, 47, 48, 49, 50, 51, 52, 53, 54, 55, 56, 57,…
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for cheap aluminum
How Can Strategic Sourcing Enhance Your Aluminum Procurement?
In summary, the strategic sourcing of cheap aluminum offers significant advantages to international B2B buyers, particularly those in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. By understanding the diverse types of aluminum and their applications, businesses can make informed decisions that align with their specific needs, whether for construction, automotive, or electrical applications. The ability to procure aluminum in various forms—such as sheets, extrusions, and alloys—enables companies to optimize their supply chains and reduce costs effectively.
Moreover, leveraging relationships with reputable suppliers can enhance procurement efficiency, ensuring that quality aluminum is sourced at competitive prices. As aluminum continues to play a crucial role in industries around the globe, buyers are encouraged to adopt a proactive approach to sourcing. This involves not only evaluating current suppliers but also exploring new markets and innovative sourcing strategies.
Looking ahead, the demand for sustainable and cost-effective aluminum solutions will only grow. International buyers should seize this opportunity to refine their sourcing strategies now, ensuring they remain competitive in an evolving marketplace. Engage with suppliers who prioritize sustainability and innovation to position your business for future success in the aluminum sector.