Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for casting metal at home
Navigating the complexities of the global market for casting metal at home presents unique challenges for B2B buyers seeking to source reliable suppliers and materials. The diverse landscape of metal casting processes—including methods such as sand casting, lost-wax casting, and die casting—offers immense potential for innovation and cost efficiency. However, understanding the nuances of each technique, along with the applications for various industries, can be daunting. This comprehensive guide aims to demystify the metal casting process, providing insights into the types of metals and alloys, supplier vetting criteria, and cost considerations essential for informed purchasing decisions.
For international B2B buyers from regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, including countries like Nigeria and Vietnam, this guide serves as a crucial resource. It empowers organizations to make strategic decisions in their metal casting endeavors, whether for manufacturing components, artistic creations, or custom tooling. With actionable insights and best practices, this guide not only enhances understanding but also fosters confidence in sourcing high-quality materials and services that meet specific production needs. As the demand for bespoke metal products continues to rise, mastering the art of casting metal at home becomes an invaluable asset in the global marketplace.
Understanding casting metal at home Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Sand Casting | Utilizes sand molds, easy to create, suitable for complex shapes | Automotive parts, machinery components | Pros: Cost-effective, versatile. Cons: Surface finish may require additional work. |
| Lost-Wax Casting | Involves creating a wax model, allows intricate designs | Jewelry, art sculptures, precision components | Pros: High detail, smooth finish. Cons: More time-consuming, higher material costs. |
| Die Casting | Uses high-pressure to inject metal into molds, reusable molds | High-volume production of parts, electronics | Pros: Excellent dimensional accuracy, fast production. Cons: Initial setup costs can be high. |
| Plaster Mold Casting | Employs plaster to create molds, good for fine details | Artistic objects, prototypes, low-volume runs | Pros: Great surface finish, complex shapes. Cons: Less durable for high-volume casting. |
| Investment Casting | Similar to lost-wax but uses metal molds for precision | Aerospace, automotive, medical devices | Pros: High accuracy, repeatability. Cons: High initial costs, lengthy process. |
What are the Characteristics of Sand Casting and Its B2B Applications?
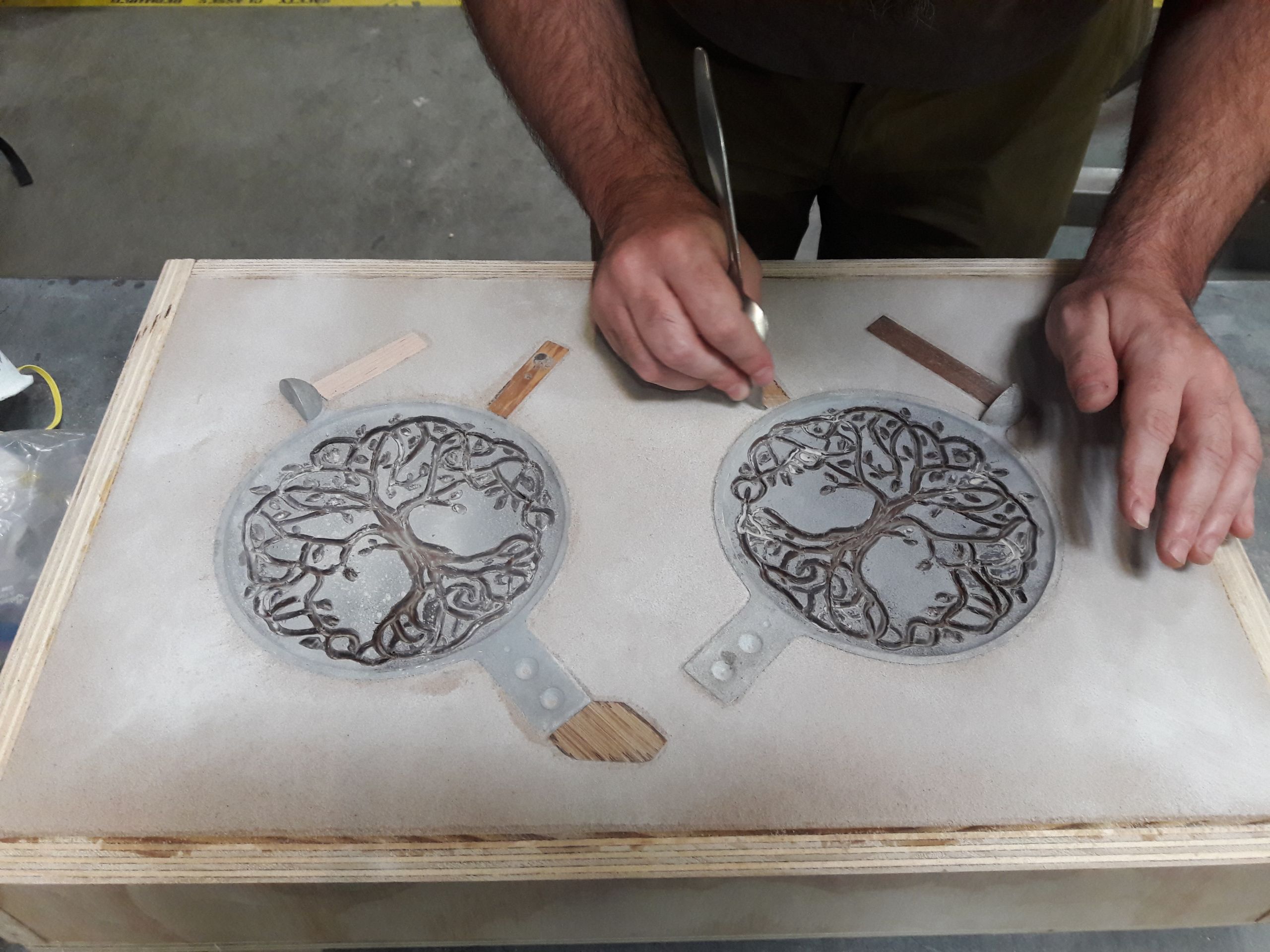
Sand casting is one of the oldest and most widely used metal casting techniques. It involves creating a mold from sand, allowing for the production of complex shapes and large parts. This method is particularly suitable for automotive parts and machinery components, making it a staple in industries requiring robust and cost-effective solutions. For B2B buyers, the key considerations include the ability to produce small to large quantities efficiently and the potential need for additional finishing processes to achieve desired surface quality.
How Does Lost-Wax Casting Work and Who Benefits from It?
Lost-wax casting is a precision technique that begins with a wax model coated in a ceramic shell. Once the shell is hardened, the wax is melted away, leaving a mold for molten metal. This method is ideal for producing intricate designs, making it popular in jewelry and art sculpture manufacturing. B2B buyers should consider the detail level required for their products, as well as the trade-off between higher material costs and the superior finish achieved through this method.
What Makes Die Casting a Preferred Choice for High-Volume Production?
Die casting involves forcing molten metal into reusable molds under high pressure, resulting in parts with excellent dimensional accuracy. This method is particularly favored in high-volume applications such as electronics and automotive components. B2B buyers should weigh the initial setup costs against the long-term benefits of rapid production and consistent quality, especially when planning large-scale manufacturing runs.
What are the Advantages of Plaster Mold Casting for Artistic Projects?
Plaster mold casting is known for its ability to produce fine details and smooth finishes, making it suitable for artistic objects and prototypes. The technique involves creating molds from plaster, which can capture intricate designs effectively. For B2B buyers, this method is advantageous for low-volume runs where aesthetic quality is paramount, though it may not be the best choice for high-volume production due to the durability of the molds.
Why is Investment Casting Considered High-Precision and Who Uses It?
Investment casting, akin to lost-wax casting, utilizes metal molds for high-precision applications. This method is widely used in industries such as aerospace, automotive, and medical devices, where accuracy and repeatability are critical. B2B buyers should consider the higher initial costs associated with this process against the long-term benefits of producing high-quality, complex components that meet stringent industry standards.
Key Industrial Applications of casting metal at home
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of casting metal at home | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Art and Sculpture | Custom metal sculptures and art pieces | Unique offerings that differentiate from competitors | Quality of metal, mold-making materials, and design capabilities |
| Automotive Repair | Fabrication of custom parts and tools | Cost-effective solutions for obsolete or rare parts | Specific metal alloys, precision in casting, and heat resistance |
| Jewelry Manufacturing | Creation of bespoke jewelry pieces | Personalization that enhances customer engagement | Precious metal sourcing, casting techniques, and finishing options |
| Construction | Production of decorative architectural elements | Enhances aesthetic appeal and functionality | Material durability, mold complexity, and compliance with standards |
| Agriculture | Custom tools and equipment for farming | Tailored solutions that improve efficiency | Metal strength, corrosion resistance, and adaptability to local conditions |
How Can Casting Metal at Home Benefit the Art and Sculpture Industry?
In the art and sculpture sector, casting metal at home allows artists to create unique, custom pieces tailored to their vision. This process not only provides artists with the ability to produce one-of-a-kind sculptures but also reduces reliance on external foundries, which can be costly and time-consuming. International buyers, especially from regions like Africa and South America, should consider sourcing high-quality metals and mold-making materials to ensure the durability and aesthetic appeal of their creations.
What Are the Advantages of Casting for Automotive Repair?
Casting metal at home enables automotive repair businesses to fabricate custom parts and tools, particularly for vintage or rare vehicles where replacement parts may be unavailable. This approach can significantly reduce costs and lead times associated with sourcing parts from manufacturers. Buyers in regions such as the Middle East must pay attention to the specific metal alloys required for durability and precision, ensuring that cast parts meet safety and performance standards.
Why is Jewelry Manufacturing Enhanced by Home Casting?
For jewelry manufacturers, casting metal at home allows for the creation of bespoke jewelry pieces that cater to individual customer preferences. This personalization enhances customer engagement and satisfaction, leading to increased sales and brand loyalty. Buyers should focus on sourcing high-quality precious metals and mastering various casting techniques, as the quality of the final product heavily relies on these factors. In markets like Europe and Africa, understanding local trends can further enhance product appeal.
How Does Home Casting Impact the Construction Sector?
In the construction industry, casting metal at home can be employed to produce decorative architectural elements, such as railings, gates, and fixtures. These custom pieces not only enhance the aesthetic appeal of buildings but also provide functional benefits, such as improved durability and resistance to environmental factors. Businesses should consider the durability of the materials used and ensure compliance with local construction standards, especially in regions prone to extreme weather conditions.
What Role Does Casting Play in Agriculture?
Casting metal at home serves the agricultural sector by enabling the production of custom tools and equipment tailored to specific farming needs. This flexibility allows farmers to create tools that enhance efficiency and productivity, providing a competitive edge. Buyers should prioritize sourcing metals with high strength and corrosion resistance, as these properties are critical for agricultural applications, particularly in humid or harsh environments often found in regions like South America and Southeast Asia.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘casting metal at home’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Difficulty in Material Sourcing for Home Casting Projects
The Problem: B2B buyers often face challenges in sourcing quality metal alloys suitable for home casting. In regions such as Africa and South America, local suppliers may not offer a consistent selection of ferrous and non-ferrous metals, leading to delays and quality issues in production. Additionally, the lack of understanding of alloy properties can result in the selection of inappropriate materials, which can compromise the integrity of the final product. This uncertainty can hinder businesses from fulfilling client demands or meeting project timelines.
The Solution: To effectively overcome material sourcing challenges, B2B buyers should establish relationships with reliable suppliers who specialize in metal alloys for casting. This involves conducting market research to identify suppliers that provide a range of ferrous (like steel and iron) and non-ferrous (such as aluminum and bronze) options. Buyers can also consider forming partnerships with international suppliers who have a track record of shipping quality materials to their regions. It is crucial to request material certifications and conduct small-scale trials before committing to larger orders. Additionally, investing in training for staff on alloy properties and appropriate applications can enhance decision-making and ensure that the right materials are used for specific casting projects, thereby improving overall production quality.
Scenario 2: Challenges in Mold Creation and Design for Effective Casting
The Problem: Many B2B buyers struggle with creating effective molds for metal casting at home. Inadequate knowledge of mold design can lead to issues such as air pockets, improper flow of molten metal, and difficulties in mold release, resulting in defects in the cast products. For businesses that rely on precision parts, these challenges can be particularly detrimental, affecting both quality and profitability.
The Solution: To address mold creation challenges, buyers should invest in comprehensive training that covers advanced mold-making techniques, including the use of CAD software for design and the selection of appropriate mold materials (like sand, resin, or metal). Collaborating with experienced metallurgists or mold-making professionals can provide invaluable insights into best practices. Additionally, utilizing 3D printing technology to create prototype molds can streamline the design process and reduce errors. Regularly evaluating mold performance and implementing adjustments based on feedback can also help improve mold efficacy over time, ensuring that production standards are consistently met.
Scenario 3: Safety and Compliance Issues in Metal Casting Operations
The Problem: Safety and compliance are critical concerns for B2B buyers involved in home metal casting. Many businesses may lack proper safety protocols or knowledge about local regulations regarding the handling of molten metals and hazardous materials. This oversight can lead to workplace accidents, legal liabilities, and damage to company reputation, particularly in regions with stringent safety regulations.
The Solution: To mitigate safety and compliance issues, it is essential for B2B buyers to develop and implement a comprehensive safety plan that includes training programs on handling molten metal, personal protective equipment (PPE) requirements, and emergency response procedures. Engaging with local regulatory bodies to understand the specific requirements for metal casting operations is crucial. Buyers should also consider investing in high-quality ventilation systems and protective gear to minimize exposure to hazardous fumes and heat. Regular safety audits and feedback mechanisms can further enhance workplace safety and compliance, fostering a culture of safety that protects both workers and the business. By prioritizing these aspects, companies can not only comply with regulations but also build trust with clients and stakeholders.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for casting metal at home
What Are the Key Materials for Casting Metal at Home?
When considering materials for casting metal at home, several options stand out based on their properties, costs, and suitability for various applications. Below, we analyze four common materials used in metal casting, focusing on their key properties, advantages, disadvantages, and considerations for international B2B buyers.
1. Aluminum Alloys
Key Properties: Aluminum alloys are lightweight, have excellent corrosion resistance, and can withstand temperatures up to 660°C (1220°F). They also exhibit good thermal and electrical conductivity.
Pros & Cons: The primary advantage of aluminum alloys is their low weight and good strength-to-weight ratio, making them ideal for applications in automotive and aerospace industries. They are relatively easy to cast, allowing for complex shapes. However, the initial cost of aluminum can be higher than other metals, and the casting process requires careful temperature control to avoid defects.
Impact on Application: Aluminum is compatible with a variety of media, including water and many chemicals, making it suitable for diverse applications, from automotive parts to kitchenware.
Considerations for International B2B Buyers: Compliance with international standards such as ASTM and ISO is crucial. Buyers from regions like Africa and South America should consider local availability and cost fluctuations of aluminum, which can impact overall project budgets.
2. Bronze Alloys
Key Properties: Bronze alloys, primarily composed of copper and tin, exhibit excellent corrosion resistance and can withstand high temperatures (up to 950°C or 1742°F). They also have good wear resistance.
Pros & Cons: The key advantage of bronze is its durability and aesthetic appeal, making it a popular choice for artistic sculptures and functional items like bearings. However, bronze can be more expensive than aluminum and requires a more complex casting process, which may not be suitable for all home casters.
Impact on Application: Bronze is particularly compatible with marine environments due to its resistance to seawater corrosion, making it ideal for maritime applications and decorative items.
Considerations for International B2B Buyers: Buyers should ensure that bronze alloys meet local and international standards, such as JIS and DIN, especially for industrial applications. The higher cost may be a limiting factor for buyers in developing regions.
3. Cast Iron
Key Properties: Cast iron is known for its excellent castability, high wear resistance, and ability to withstand high temperatures (up to 1200°C or 2192°F). It has good compressive strength but is brittle under tension.
Pros & Cons: The primary advantage of cast iron is its durability and low cost, making it suitable for heavy machinery and automotive components. However, its brittleness can lead to cracking, and the casting process can be more complex due to the need for precise temperature control.
Impact on Application: Cast iron is compatible with high-stress applications, such as engine blocks and heavy equipment, but may not be suitable for applications requiring high tensile strength.
Considerations for International B2B Buyers: Compliance with standards like ASTM is essential, particularly for buyers in Europe and the Middle East. The availability of scrap iron for recycling into new castings can be a cost-effective option in these regions.
4. Steel Alloys
Key Properties: Steel alloys offer high tensile strength and can withstand temperatures up to 1500°C (2732°F). They also have good ductility and toughness, making them versatile for various applications.
Pros & Cons: The key advantage of steel is its strength and versatility, suitable for a wide range of industrial applications. However, the casting process can be complex and requires specialized equipment, making it less accessible for home casters.
Impact on Application: Steel is widely used in construction, automotive, and machinery applications due to its strength and durability.
Considerations for International B2B Buyers: Buyers must consider compliance with international standards, such as ISO and ASTM, especially in regions with stringent quality regulations. The cost of steel can vary significantly based on local market conditions.
Summary Table of Materials for Casting Metal at Home
| Material | Typical Use Case for casting metal at home | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Aluminum Alloys | Automotive parts, kitchenware | Lightweight and corrosion-resistant | Higher initial cost | Medium |
| Bronze Alloys | Sculptures, marine applications | Durable and aesthetically appealing | More expensive, complex casting | High |
| Cast Iron | Engine blocks, heavy machinery | Durable and low cost | Brittle, requires precise control | Low |
| Steel Alloys | Construction, automotive components | High strength and versatility | Complex casting process | Medium |
This guide provides a comprehensive overview of materials suitable for casting metal at home, enabling international B2B buyers to make informed decisions based on their specific needs and regional considerations.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for casting metal at home
What Are the Main Stages in the Manufacturing Process of Casting Metal at Home?
Casting metal at home involves a series of well-defined manufacturing processes that ensure high-quality results. The main stages include material preparation, forming, assembly, and finishing. Each stage plays a critical role in determining the overall quality of the final product.
How Is Material Prepared for Metal Casting?
Material preparation is the foundational step in the metal casting process. This involves selecting the appropriate metal alloy based on the desired properties of the final product. Common choices include ferrous alloys such as steel and non-ferrous alloys like aluminum and bronze.
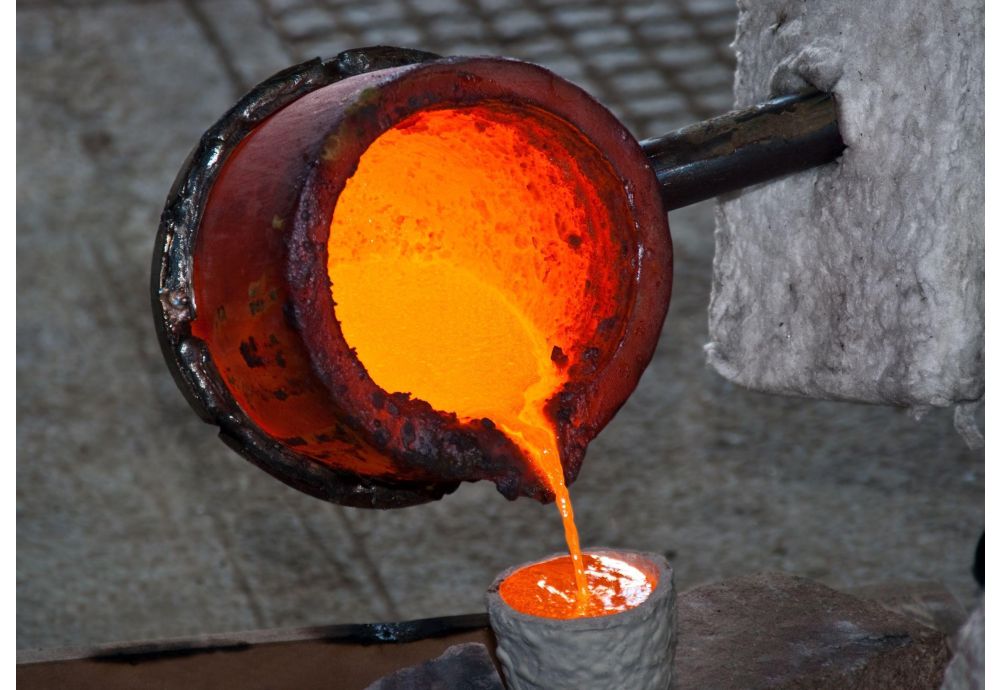
Once the alloy is chosen, the next step is to melt the metal. This is typically done in a crucible using a furnace or an open flame. The melting temperature varies by alloy, so it is crucial to monitor this closely to avoid impurities. After the metal is melted, it is allowed to cool slightly before pouring to ensure it reaches the right viscosity.
What Techniques Are Used in the Forming Stage of Metal Casting?
The forming stage involves creating a mold into which the molten metal will be poured. There are two main types of molds used in metal casting: expendable and non-expendable molds. Expendable molds, made from materials like sand or plaster, are single-use and best suited for low-volume production. Non-expendable molds, often made from metal, are reusable and ideal for mass production.
Creating a pattern is essential in this stage. The pattern represents the final shape of the cast and must account for the shrinkage of the metal as it cools. Techniques for creating patterns include 3D modeling and traditional sculpting methods. Proper design is critical to ensure the mold can be filled completely and to facilitate easy removal of the casting once it has cooled.
How Is the Assembly Process Managed in Metal Casting?
While assembly is not a traditional step in casting, it plays a role when multiple cast parts are required for a single product. In such cases, cast components may need to be welded or mechanically joined after the casting process. Ensuring proper fit and alignment is crucial to maintaining the integrity of the final product.
For B2B buyers, understanding how a supplier manages assembly—especially in complex designs—can inform decisions about sourcing. Suppliers should provide detailed information on their assembly capabilities and quality controls to ensure compatibility and performance.
What Finishing Techniques Are Commonly Used in Metal Casting?
Finishing involves refining the surface of the cast metal to meet specific aesthetic and functional requirements. Common techniques include machining, sanding, polishing, and coating. Each method is chosen based on the intended use of the final product. For instance, components used in high-stress environments may require additional surface treatments to enhance durability.
Quality assurance during finishing is vital. B2B buyers should inquire about the specific finishing processes used by suppliers and any certifications related to these processes.
How Is Quality Assurance Implemented in Metal Casting?
Quality assurance (QA) is a critical component of the metal casting process, ensuring that products meet international and industry-specific standards. For B2B buyers, understanding these QA measures can significantly influence supplier selection.
What International Standards Are Relevant for Metal Casting?
International standards such as ISO 9001 focus on quality management systems and provide a framework for consistent quality across processes. Compliance with these standards demonstrates a supplier’s commitment to quality and customer satisfaction. Additionally, industry-specific certifications like CE marking (for European markets) and API standards (for oil and gas) are also important indicators of quality.
B2B buyers should verify that suppliers possess relevant certifications and understand how these standards are applied in their manufacturing processes.
What Are the Key Quality Control Checkpoints in Metal Casting?
Quality control (QC) involves several checkpoints throughout the manufacturing process:
- Incoming Quality Control (IQC): This phase checks raw materials for compliance with specifications before they are used in production.
- In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): Continuous monitoring occurs during the casting process to identify defects early. This includes checking mold integrity and monitoring the pouring process.
- Final Quality Control (FQC): After the casting is complete, final inspections are conducted to ensure the product meets specifications. This may involve dimensional checks, surface quality inspections, and mechanical testing.
Which Testing Methods Are Commonly Used in Quality Assurance?
Common testing methods in metal casting include:
- Dimensional Inspection: Ensuring that the cast dimensions meet the required specifications.
- Non-Destructive Testing (NDT): Techniques such as ultrasonic testing or X-ray inspection to identify internal flaws without damaging the product.
- Mechanical Testing: Assessing the material properties, such as tensile strength and hardness, to ensure they meet performance criteria.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control?
For international B2B buyers, verifying a supplier’s quality control processes is essential. Here are some actionable steps:
- Conduct Supplier Audits: Regular audits of suppliers can provide insights into their quality control practices, adherence to standards, and overall manufacturing capabilities.
- Request Quality Reports: Suppliers should be able to provide documentation of their quality control processes, including test results and compliance certificates.
- Utilize Third-Party Inspections: Engaging third-party inspectors can provide an unbiased assessment of a supplier’s quality control measures, ensuring that they meet international standards.
What Are the Quality Control and Certification Nuances for International B2B Buyers?
International buyers, particularly those from regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, must consider local regulations and standards. Each region may have specific requirements for quality certifications and practices. Understanding these nuances can help buyers navigate the complexities of international trade and ensure compliance with local laws.
Additionally, cultural differences may influence supplier interactions and negotiations. Establishing clear communication and expectations regarding quality standards can mitigate misunderstandings and enhance supplier relationships.
In conclusion, the manufacturing and quality assurance processes involved in casting metal at home are intricate and require careful consideration. By understanding these processes, B2B buyers can make informed decisions, ensuring they partner with suppliers that prioritize quality and compliance.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘casting metal at home’
To assist international B2B buyers in successfully procuring the necessary materials and equipment for casting metal at home, this guide offers a clear, actionable checklist. These steps will ensure that you make informed decisions, optimize your sourcing process, and ultimately achieve high-quality metal casting results.
Step 1: Define Your Project Requirements
Establish the scope of your metal casting project by clearly defining the types of objects you wish to create. Consider factors such as size, complexity, and the type of metal alloy required. This step is crucial as it will guide your material selection and equipment needs, impacting both quality and cost.
- Key Considerations:
- Type of metal (ferrous vs. non-ferrous)
- Desired finish and durability of the final product
Step 2: Research and Identify Quality Suppliers
Conduct thorough research to identify potential suppliers of casting materials and equipment. Look for suppliers with a proven track record in the industry, particularly those that specialize in the type of metal you plan to use. This will ensure that you receive high-quality products suited to your specific requirements.
- What to Look For:
- Supplier certifications and industry experience
- Customer reviews and testimonials
Step 3: Request Samples and Product Specifications
Before making a bulk purchase, request samples of the materials and detailed product specifications from potential suppliers. This allows you to evaluate the quality of the metal, mold materials, and other components critical to your project.
- Important Aspects:
- Evaluate the physical properties of the metal (e.g., melting point, strength)
- Ensure mold materials are compatible with your casting methods
Step 4: Assess Production Capabilities and Lead Times
Understand the production capabilities of your suppliers, including their ability to meet your demand and lead times for delivery. This is essential for planning your project timeline and ensuring you have materials on hand when needed.
- Key Questions:
- What is the minimum order quantity?
- How quickly can the supplier deliver the materials?
Step 5: Verify Compliance and Safety Standards
Ensure that the materials and equipment you source comply with local regulations and international safety standards. This is particularly important in regions with strict manufacturing guidelines, as it protects your business from potential legal issues.
- Compliance Areas to Check:
- Material safety data sheets (MSDS)
- Certifications for environmental and workplace safety
Step 6: Negotiate Terms and Pricing
Once you have selected a supplier, engage in negotiations to secure favorable terms and pricing. Consider discussing bulk purchase discounts or payment plans that align with your budget and cash flow needs.
- Negotiation Tips:
- Be clear about your budget constraints
- Explore options for long-term partnerships for better pricing
Step 7: Establish a Quality Control Process
Implement a quality control process to monitor the materials and equipment received from suppliers. This ensures that you maintain high standards in your casting projects and can promptly address any issues that arise.
- Quality Control Measures:
- Regular inspections of incoming materials
- Feedback loops with suppliers for continuous improvement
By following this checklist, B2B buyers can effectively navigate the complexities of sourcing materials for home metal casting projects, ensuring successful outcomes and a strong return on investment.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for casting metal at home Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components for Casting Metal at Home?
In the metal casting industry, especially for small-scale home operations, understanding the cost structure is crucial for effective sourcing and pricing strategies. The primary cost components include:
-
Materials: The choice of metal significantly impacts costs. Ferrous metals like cast iron are generally cheaper than non-ferrous metals such as aluminum, bronze, or precious metals. Consider the volume needed, as bulk purchasing can reduce per-unit costs.
-
Labor: Skilled labor is essential in metal casting. The labor cost will vary based on the complexity of the casting process, the skill level required, and local wage rates. In regions like Africa and South America, labor costs may be lower, but the availability of skilled artisans can be a limiting factor.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes utility costs, rent, and equipment depreciation. Home-based operations may have lower overhead compared to larger foundries, but it’s important to account for all operational costs to avoid underpricing.
-
Tooling: Initial investments in molds and casting equipment can be significant. For home casting, reusable molds may reduce long-term costs, but single-use molds are cheaper upfront.
-
Quality Control (QC): Ensuring the quality of castings is essential, especially for B2B transactions. Implementing QC measures can add to costs but is necessary to maintain standards and avoid costly reworks.
-
Logistics: Shipping costs can be substantial, particularly when sourcing materials or delivering finished products internationally. Understanding Incoterms can help manage these logistics effectively.
-
Margin: Setting a profit margin is vital for sustainability. This margin should reflect the quality of the product, market demand, and competition.
How Do Price Influencers Impact Metal Casting Costs?
Several factors influence pricing strategies in the metal casting sector:
-
Volume/MOQ: Minimum order quantities (MOQs) can affect pricing. Larger orders often lead to discounts, but they require an upfront investment in materials and production capacity.
-
Specifications and Customization: Custom designs or specific quality requirements can increase costs due to the need for specialized tooling or additional labor.
-
Material Selection: The choice of alloy impacts both the material cost and the complexity of the casting process. Non-ferrous alloys typically have higher costs but may offer superior properties for specific applications.
-
Quality and Certifications: Products requiring industry certifications (like ISO or ASTM) may incur additional costs related to compliance and testing. This is particularly relevant for sectors such as aerospace or automotive.
-
Supplier Factors: The reputation and reliability of suppliers can influence pricing. Established suppliers may charge a premium for their services, which can be justified by the assurance of quality and timely delivery.
-
Incoterms: Understanding shipping terms is crucial for international transactions. They dictate who bears the risk and costs at various stages of the shipping process, affecting the total cost.
What Tips Can Help Buyers Negotiate Better Prices for Metal Casting?
For international B2B buyers, particularly from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, effective negotiation and cost management strategies can significantly enhance profitability:
-
Negotiate Based on Volume: Leverage larger orders to negotiate better pricing or favorable payment terms. Suppliers are often more flexible with pricing for larger quantities.
-
Focus on Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Evaluate not just the purchase price but the total cost associated with sourcing, including logistics, potential quality issues, and lifecycle costs. This broader perspective can reveal more cost-effective options.
-
Understand Pricing Nuances: Be aware of regional price variations and market conditions that may influence costs. For instance, fluctuating material prices can impact overall expenses.
-
Build Relationships with Suppliers: Establishing long-term partnerships can lead to better terms and pricing flexibility over time.
-
Research Local Markets: Understanding the local market dynamics, including labor costs and material availability, can provide leverage in negotiations.
Disclaimer
Prices mentioned in this analysis are indicative and can vary widely based on location, market conditions, and specific requirements. It is advisable for buyers to conduct thorough market research and consult with multiple suppliers to obtain accurate pricing for their specific needs.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing casting metal at home With Other Solutions
Introduction
In the realm of metalworking, particularly for B2B buyers looking to optimize production processes, the option to cast metal at home presents an intriguing avenue. However, it’s essential to evaluate this method against other viable alternatives to ensure the best fit for specific operational needs. This analysis will compare home casting with two alternative solutions: outsourcing to a professional foundry and utilizing 3D printing for metal parts. Each method offers distinct advantages and challenges that can significantly impact production efficiency, cost, and suitability for various applications.
| Comparison Aspect | Casting Metal At Home | Outsourcing to a Professional Foundry | 3D Printing for Metal Parts |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | Variable, depends on skill and equipment | High, consistent quality | Moderate to high, depending on technology used |
| Cost | Low initial investment, variable material costs | Higher due to labor and overhead | Medium to high, depending on setup and material |
| Ease of Implementation | Moderate; requires knowledge and equipment | Easy; relies on external expertise | Moderate; requires specialized knowledge |
| Maintenance | Low; personal equipment maintenance only | None; dependent on foundry maintenance | Moderate; printer maintenance required |
| Best Use Case | Prototyping, small batch production | Large scale production, complex designs | Rapid prototyping, intricate designs |
What Are the Pros and Cons of Outsourcing to a Professional Foundry?
Outsourcing metal casting to a professional foundry offers several benefits, particularly in performance and consistency. Foundries are equipped with advanced technology and skilled labor, ensuring high-quality castings that meet industry standards. However, the cost can be prohibitive for small businesses or projects with limited budgets. Additionally, the reliance on external timelines can lead to delays if the foundry is busy or if communication issues arise. This method is ideal for companies looking to scale production or requiring complex castings that demand precision.
How Does 3D Printing for Metal Parts Compare?
3D printing has emerged as a modern alternative to traditional casting methods, offering the ability to create complex geometries that would be difficult or impossible to achieve through conventional casting. This method allows for rapid prototyping, enabling quicker iterations and adjustments to designs. However, the technology can be expensive, and the material costs for high-quality metal powders can add up. Additionally, not all 3D printing methods achieve the same level of structural integrity as traditional casting, making it less suitable for load-bearing applications. It is best suited for businesses focused on innovation and customization in their product offerings.
Conclusion
When determining the right solution for metal casting needs, B2B buyers must consider their specific requirements, including production volume, budget constraints, and the complexity of the desired components. Casting metal at home can be a cost-effective solution for small-scale projects or prototyping, while outsourcing to a professional foundry is ideal for larger, more complex production runs. On the other hand, 3D printing provides unique advantages in customization and rapid prototyping but may entail higher costs. By weighing these options carefully, businesses can make informed decisions that align with their operational goals and market demands.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for casting metal at home
What Are the Key Technical Properties in Metal Casting?
Understanding the critical technical properties of metal casting is essential for B2B buyers engaged in manufacturing or artistic endeavors. Here are some key specifications to consider:
1. Material Grade
Material grade refers to the classification of metals based on their composition and mechanical properties. Common grades include stainless steel, aluminum alloys, and bronze. Selecting the appropriate material grade is vital as it impacts the durability, strength, and corrosion resistance of the final product. Buyers should ensure that the chosen grade meets industry standards for their specific application, whether it’s for machinery, art, or consumer goods.
2. Tolerance
Tolerance is the permissible limit of variation in a physical dimension or measured value. In metal casting, tighter tolerances result in higher precision and better fitting components. Tolerance levels affect production costs and lead times; thus, understanding the required tolerances for specific applications helps buyers make informed decisions on mold design and manufacturing processes, ensuring compatibility and functionality in the final assembly.
3. Shrinkage Rate
Shrinkage rate is the percentage decrease in volume that occurs as metal cools and solidifies. Different alloys exhibit varying shrinkage rates, which can significantly affect the final dimensions of a casting. Accurate calculations of shrinkage are crucial during the mold-making process to achieve the desired final dimensions. Buyers must communicate specific shrinkage characteristics to their suppliers to minimize discrepancies in the final products.
4. Surface Finish
Surface finish refers to the texture and smoothness of a metal casting. It is classified by grades, which can range from rough to mirror-like finishes. The surface finish impacts not only the aesthetic appeal but also the functional performance, such as wear resistance and the ability to paint or coat. Buyers should specify the required surface finish to align with their product standards, as it can influence both production techniques and costs.
5. Alloy Composition
Alloy composition defines the specific elements and their proportions within a metal alloy. Different combinations yield varying physical properties, such as strength, ductility, and thermal conductivity. For instance, aluminum alloys are often preferred for lightweight applications, while bronze is favored for its corrosion resistance. Buyers need to understand alloy compositions to ensure that the final products meet the required performance criteria for their intended applications.
What Are Common Terms Used in Metal Casting Trade?
Familiarity with industry jargon is essential for effective communication and negotiation in the metal casting sector. Here are some important terms:
1. OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
An OEM is a company that produces parts or equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer. In the context of metal casting, buyers often work with OEMs to create customized components that fit specific machinery or products. Understanding OEM relationships can help buyers streamline their supply chains and ensure quality control.
2. MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ refers to the smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell. For metal casting, MOQs can vary based on the complexity of the mold and the materials used. Buyers should be aware of MOQs to plan their inventory and purchasing strategies effectively, ensuring they meet production demands without excess stock.
3. RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a document sent to suppliers requesting a price quote for specific products or services. In metal casting, this is crucial for obtaining competitive pricing and understanding lead times. Buyers should provide detailed specifications in their RFQs to receive accurate and relevant quotes that meet their project requirements.
4. Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
Incoterms are a set of international trade rules that define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in shipping goods. They specify who is responsible for shipping, insurance, and tariffs during transit. Knowledge of Incoterms helps buyers navigate international transactions effectively, ensuring clarity in terms of delivery and risk management.
5. Foundry
A foundry is a facility where metal casting takes place. It encompasses the equipment and technology necessary for melting metal and producing castings. Buyers should consider the capabilities of a foundry, including their expertise in specific casting methods and materials, to ensure they partner with the right suppliers for their projects.
Understanding these technical properties and trade terminology empowers B2B buyers to make informed decisions in the metal casting industry, facilitating smoother transactions and higher-quality outcomes.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the casting metal at home Sector
What Are the Current Market Dynamics and Key Trends in the Casting Metal at Home Sector?
The global casting metal sector is experiencing a transformative phase driven by several key factors, particularly relevant for B2B buyers in regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. The rise of DIY culture and home-based manufacturing is reshaping the market, as businesses recognize the potential for localized production to meet specific customer needs. Technological advancements, including 3D printing and computer-aided design (CAD), are enabling more precise and efficient mold-making processes, which is crucial for small-scale operations. Additionally, the increasing demand for customized products has led to a surge in the use of expendable mold casting techniques that allow for unique designs without significant investment in permanent molds.
Moreover, B2B buyers are increasingly looking for suppliers who offer comprehensive support throughout the casting process, from mold design to alloy selection. This shift emphasizes the importance of supplier relationships and technical expertise in meeting the evolving needs of the market. International buyers, particularly those from developing regions, are also seeking affordable, high-quality materials that can withstand the rigors of casting while maintaining cost-effectiveness. As competition intensifies, businesses must navigate fluctuating raw material prices and supply chain disruptions, making strategic sourcing decisions critical for maintaining profitability.
How Is Sustainability and Ethical Sourcing Influencing the Casting Metal at Home Sector?
The growing emphasis on sustainability and ethical sourcing is significantly impacting the casting metal sector, with increasing pressure on businesses to adopt environmentally friendly practices. The environmental impact of metal casting, which includes energy consumption and emissions, is prompting companies to explore greener alternatives. This shift includes the use of recycled metals and eco-friendly materials that reduce the carbon footprint associated with production.
B2B buyers are now prioritizing suppliers who demonstrate a commitment to sustainability through certifications and transparent supply chains. Green certifications, such as ISO 14001 for environmental management, are becoming essential for companies aiming to differentiate themselves in a competitive market. Moreover, ethical sourcing practices are crucial for ensuring that materials are obtained responsibly, particularly in regions where mining and metal production can have significant socio-economic implications. By aligning their sourcing strategies with sustainability goals, businesses can not only enhance their brand reputation but also meet the growing consumer demand for ethically produced goods.
What Is the Brief Evolution of the Casting Metal Process Relevant to Today’s B2B Buyers?
The evolution of the metal casting process is deeply rooted in history, dating back over 7,000 years. Initially utilized for crafting tools and religious artifacts, metal casting has transformed significantly, especially with the advent of industrialization in the 19th century. The introduction of advanced casting techniques, such as sand casting and lost-wax casting, allowed for greater precision and versatility in production.
In recent decades, the advent of digital technology has revolutionized the sector, enabling the creation of complex designs through computer modeling and rapid prototyping. This evolution has made metal casting more accessible to small-scale producers and hobbyists, fostering a vibrant DIY community. For today’s B2B buyers, understanding this historical context is crucial, as it underscores the importance of innovation and adaptability in a rapidly changing market landscape. The ability to leverage modern technology while respecting traditional practices can provide a competitive edge in meeting diverse customer needs.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of casting metal at home
-
How do I select the right metal alloy for casting at home?
Choosing the right metal alloy depends on the intended application and desired properties of the final product. Common choices for home casting include aluminum for its lightweight and corrosion resistance, bronze for its durability and aesthetic appeal, and copper for its excellent conductivity. Evaluate factors such as melting temperature, mechanical properties, and compatibility with your casting process. It’s also essential to consider local availability and cost-effectiveness, particularly when sourcing materials internationally. -
What is the best casting process for beginners?
For beginners, sand casting is often the most accessible and versatile method. It allows for the use of easily obtained materials and requires minimal specialized equipment. Sand casting is suitable for small to medium-sized projects and can produce complex shapes. Alternatively, lost-wax casting offers precision for intricate designs but may require more expertise and investment in materials. Evaluate your project needs and skill level to determine the best approach. -
What are the minimum order quantities (MOQ) for casting materials?
Minimum order quantities for casting materials can vary significantly based on the supplier and the type of metal. Generally, larger suppliers may have higher MOQs, while local or specialized suppliers may accommodate smaller orders. It is advisable to communicate directly with suppliers to negotiate MOQs that fit your business needs, especially if you are just starting or testing new designs. This flexibility is crucial for businesses in regions with varying demand. -
How do I vet suppliers for casting materials?
To vet suppliers, start by checking their certifications and industry reputation. Look for reviews and testimonials from other B2B buyers, and inquire about their quality assurance processes. Request samples of materials to assess their quality firsthand. Additionally, consider suppliers’ responsiveness and willingness to engage in discussions about your specific needs. For international suppliers, ensure they comply with local regulations and understand the logistics involved in shipping to your location. -
What payment terms should I expect when sourcing casting materials internationally?
Payment terms can vary widely among suppliers, but common options include advance payment, letters of credit, or payment upon delivery. It is essential to clarify payment terms upfront and ensure they align with your cash flow requirements. Some suppliers may offer discounts for bulk purchases or early payments. Be cautious with international transactions and consider using escrow services to protect your investment until the goods are received satisfactorily. -
How can I ensure quality assurance in my metal casting projects?
Quality assurance can be achieved by implementing standardized processes and conducting regular inspections throughout your casting operations. Work with suppliers who provide material certifications and conduct thorough testing on their alloys. Additionally, establish a quality control checklist for your projects, which includes checks for mold integrity, alloy composition, and final product specifications. Regular training and updates for your team on best practices in casting can further enhance quality assurance. -
What are the logistics considerations for international shipping of casting materials?
When shipping casting materials internationally, consider factors like shipping costs, customs regulations, and delivery timelines. Work with logistics partners experienced in handling metal shipments to ensure compliance with local and international regulations. Proper packaging is crucial to prevent damage during transit. Additionally, familiarize yourself with duties and taxes that may apply to your materials, which can affect overall costs and profitability. -
How can I customize my metal casting projects to meet specific business needs?
Customization begins with clear communication of your project requirements to your supplier. Discuss options for mold design, alloy selection, and finishing processes that align with your end-use applications. Many suppliers offer tailored services, including creating unique patterns or modifying existing designs. Collaborate closely with your supplier throughout the design and production phases to ensure the final product meets your specifications and quality standards.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.
Top 4 Casting Metal At Home Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. Reddit – Aluminum Melting Tools
Domain: reddit.com
Registered: 2005 (20 years)
Introduction: Tools needed for melting aluminum and casting: 1. Furnace (propane or charcoal) 2. Graphite crucible 3. Crucible tongs 4. Pouring tongs 5. Mold (graphite molds, petrabond sand, or green sand) 6. Borax (as flux) 7. Stirring rod 8. Skimming spoon 9. Temperature gun (capable of reaching aluminum’s melting point)
Safety equipment: 1. Respirator (for organic fumes) 2. Safety glasses 3. Face shield 4….
2. iForgeIron – Metal Casting Essentials
Domain: iforgeiron.com
Registered: 2001 (24 years)
Introduction: Overview of metal casting for beginners, including smelting, melting, foundry, and casting techniques. Key safety precautions include using proper safety equipment such as goggles, faceshields, thick leather jackets, welding gloves, jeans, and heavy leather boots. Emphasis on the dangers of molten metal and the importance of dry materials. Discussion on metals suitable for casting: Mild Steel (275…
3. WikiHow – DIY Metal Casting Guide
Domain: wikihow.com
Registered: 2004 (21 years)
Introduction: This article provides a DIY guide for metal casting, focusing on creating and filling a custom mold. Key details include: 1. **Mold Frame**: A 2-piece mold frame is required, made of wood, iron, or similar solid material, large enough to hold the object to be cast. 2. **Casting Object**: The object to be cast should be placed with its flattest side down in the mold frame. 3. **Parting Dust**: This…
4. Cloudy Nights – Sand Casting Solutions
Domain: cloudynights.com
Registered: 2000 (25 years)
Introduction: Tom Stock is interested in sand casting aluminum for projects like 6″ setting circles, as buying thick sheets of aluminum is not cost-effective. He plans to 3D print parts to use as patterns for sand casting. He mentions making a foundry from a 5-gallon steel paint bucket and sand plus fire clay, and is looking for an affordable source for fire clay. Other users discuss their experiences with sand…
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for casting metal at home
As the metal casting landscape evolves, B2B buyers are increasingly recognizing the strategic advantages of sourcing materials and processes for casting metal at home. Understanding the diverse casting methods—such as expendable and non-expendable molds—allows businesses to tailor their production strategies effectively. By leveraging local resources and expertise, companies can reduce costs and enhance supply chain resilience, particularly in regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe.
Investing in quality raw materials and innovative casting techniques not only ensures superior product outcomes but also positions businesses to capitalize on emerging market trends. For instance, the growing demand for customized metal products presents an opportunity for small to medium enterprises to differentiate themselves through unique offerings.
Looking ahead, the potential for growth in the home casting market is significant. International buyers are encouraged to engage with local suppliers, explore collaborative partnerships, and invest in training to refine their casting skills. By fostering a culture of innovation and quality, businesses can secure a competitive edge in a rapidly changing industry. Embrace the future of metal casting—strategically source your materials today to pave the way for tomorrow’s successes.