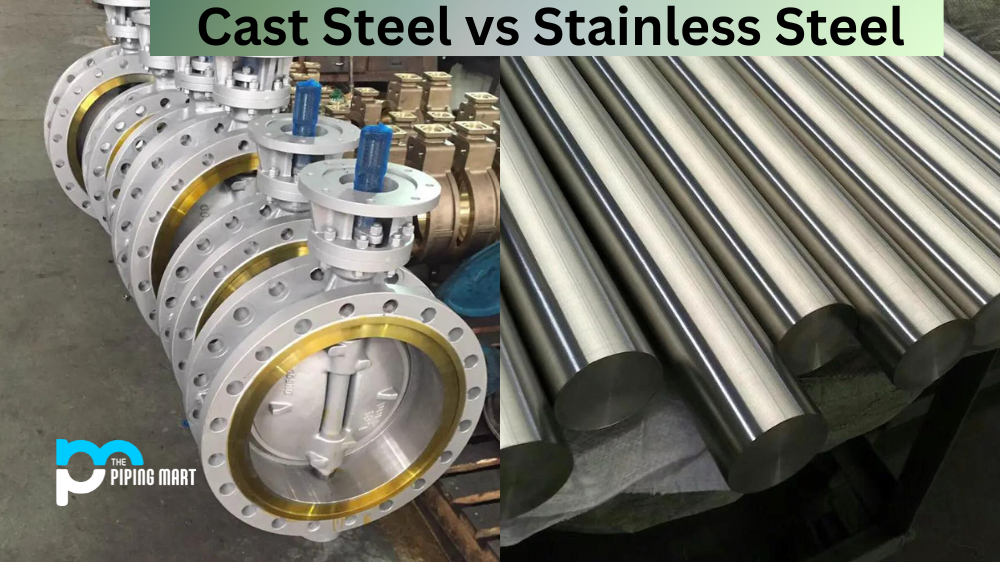
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for cast steel vs stainless steel
Navigating the complexities of sourcing cast steel versus stainless steel can be a daunting task for B2B buyers, particularly when considering factors such as application requirements, cost implications, and supplier reliability. This guide aims to demystify the differences between these two essential materials, providing a comprehensive analysis that spans their various types, applications across industries, and critical insights into supplier vetting processes. By understanding the unique properties of cast steel and stainless steel, buyers can make informed decisions that align with their operational needs and budget constraints.
In global markets, particularly in regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe—including countries such as Brazil and Nigeria—selecting the right material is crucial not only for product integrity but also for maintaining competitive advantage. This guide empowers international B2B buyers by offering actionable insights into the strengths and weaknesses of each material, helping them navigate the complexities of production timelines, cost considerations, and performance metrics. By equipping decision-makers with the knowledge needed to evaluate options critically, this resource fosters strategic procurement practices that enhance operational efficiency and drive long-term value. Whether you are looking for high-strength solutions for demanding applications or cost-effective options for intricate designs, this guide serves as your essential tool in making the best material choices for your business needs.
Understanding cast steel vs stainless steel Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Cast Stainless Steel | Complex shapes, good corrosion resistance | Valves, pumps, medical devices | Pros: Design flexibility, cost-effective; Cons: Lower strength than forged options. |
| Forged Stainless Steel | Enhanced strength and durability, uniform grain structure | Aerospace, automotive, heavy machinery | Pros: High tensile strength, reliability; Cons: Higher production costs. |
| Cast Carbon Steel | High carbon content, excellent wear resistance | Oil and gas, construction equipment | Pros: Cost-effective, good toughness; Cons: Prone to corrosion without treatment. |
| Alloy Steel | Combines various elements for enhanced properties | Manufacturing, tooling, heavy machinery | Pros: Versatile, tailored properties; Cons: Can be more expensive depending on alloy. |
| Ductile Iron | High tensile strength, malleable, and good impact resistance | Automotive components, pipes, machinery | Pros: Excellent durability, good for complex shapes; Cons: Heavier than steel alternatives. |
What Are the Characteristics of Cast Stainless Steel and Its Suitability for B2B Buyers?
Cast stainless steel is known for its ability to be molded into intricate designs, making it ideal for applications requiring precision, such as valves and pumps in the chemical and medical industries. Its inherent corrosion resistance allows it to perform well in harsh environments. B2B buyers should consider the cost-effectiveness of cast stainless steel when looking for components that require both aesthetic appeal and functionality, while also weighing its lower strength compared to forged alternatives.
How Does Forged Stainless Steel Stand Out in Industrial Applications?
Forged stainless steel is characterized by its superior strength and durability, achieved through a process that refines its grain structure. This makes it suitable for high-stress applications in industries like aerospace and automotive, where reliability is paramount. B2B buyers should prioritize forged stainless steel when their projects demand high tensile strength and resistance to fatigue, despite the higher costs associated with its production.
Why Choose Cast Carbon Steel for Your Industrial Needs?
Cast carbon steel features a higher carbon content, which enhances its wear resistance and toughness, making it a cost-effective choice for applications in oil and gas and construction equipment. However, it is susceptible to corrosion without proper treatment. For B2B buyers, understanding the balance between cost and long-term durability is crucial, especially in industries where equipment longevity is essential.
What Advantages Does Alloy Steel Offer to B2B Buyers?
Alloy steel incorporates various elements to enhance specific properties, making it versatile for manufacturing and tooling applications. It can be tailored to meet unique project requirements, which is a significant advantage for B2B buyers seeking customized solutions. However, the cost can vary depending on the alloying elements used, necessitating careful consideration of budget versus performance needs.
How Does Ductile Iron Compare in Terms of Strength and Applications?
Ductile iron is recognized for its high tensile strength and malleability, making it suitable for automotive components and machinery. Its ability to be cast into complex shapes adds to its appeal in various industries. B2B buyers should evaluate ductile iron for projects requiring durable components that can withstand impact, while also considering its heavier weight compared to other steel options, which may affect logistics and handling.
Key Industrial Applications of cast steel vs stainless steel
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of cast steel vs stainless steel | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Oil & Gas | Cast steel components for pipelines and valves | High durability and resistance to extreme conditions | Verify compliance with international standards and certifications. |
| Automotive | Stainless steel parts for exhaust systems | Corrosion resistance and lightweight properties | Assess the material’s compatibility with specific vehicle models. |
| Construction | Cast steel structural components for buildings | Design flexibility and strength for load-bearing roles | Ensure availability of custom designs and rapid production capabilities. |
| Marine Engineering | Stainless steel fittings and fixtures | Enhanced corrosion resistance in seawater environments | Evaluate supplier’s experience with marine-grade materials. |
| Food Processing | Cast stainless steel equipment for processing plants | Hygiene and ease of cleaning while maintaining integrity | Confirm adherence to food safety regulations and certifications. |
How is Cast Steel Used in the Oil & Gas Industry?
In the oil and gas sector, cast steel is crucial for manufacturing pipelines, valves, and fittings that endure high pressures and corrosive environments. The durability of cast steel components ensures operational reliability even in harsh conditions, thus minimizing downtime and maintenance costs. For international buyers, especially in regions like Africa and the Middle East, sourcing cast steel requires careful consideration of local regulations and international compliance standards to ensure safety and efficiency.
What Role Does Stainless Steel Play in the Automotive Sector?
Stainless steel is widely used in the automotive industry for exhaust systems and structural components due to its excellent corrosion resistance and lightweight properties. These characteristics contribute to improved fuel efficiency and longevity of vehicle parts. B2B buyers from Europe and South America should focus on sourcing stainless steel that meets specific automotive standards and can withstand varying environmental conditions, ensuring that parts maintain performance over time.
Why is Cast Steel Important in Construction?
In construction, cast steel is favored for creating structural components such as beams and columns. Its strength-to-weight ratio allows for innovative architectural designs while ensuring safety and stability. Buyers, particularly in developing markets like Nigeria and Brazil, should prioritize suppliers who can offer customized solutions and rapid production to meet project timelines and specific design requirements.
How is Stainless Steel Utilized in Marine Engineering?
Stainless steel is a preferred choice for fittings and fixtures in marine engineering due to its superior corrosion resistance against seawater. This makes it ideal for applications in boats, ships, and offshore platforms, where exposure to harsh marine environments is a constant challenge. International buyers must assess suppliers’ expertise in marine-grade materials and their ability to provide products that meet rigorous marine industry standards.
What are the Benefits of Cast Stainless Steel in Food Processing?
In food processing, cast stainless steel is essential for equipment such as mixers, tanks, and conveyors due to its hygienic properties and resistance to corrosion. This material ensures that food safety standards are met while allowing for easy cleaning and maintenance. Buyers in regions with stringent food safety regulations, such as Europe and South America, should ensure that their suppliers comply with health and safety certifications to guarantee the integrity of their food processing equipment.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘cast steel vs stainless steel’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Choosing the Right Material for High-Pressure Applications
The Problem: A manufacturing company in Brazil is tasked with producing components for a high-pressure hydraulic system. The project manager faces the dilemma of selecting between cast steel and stainless steel for critical parts. The stakes are high; choosing the wrong material could lead to failures, increased costs, and safety risks. The project manager is particularly concerned about the strength, durability, and corrosion resistance of the materials under extreme conditions.
The Solution: To address this challenge, the project manager should conduct a thorough analysis of the application requirements. For high-pressure environments, forged stainless steel is often recommended due to its superior strength and uniform grain structure, which enhances durability. However, if cost and design complexity are also considerations, cast stainless steel may provide a balance of adequate strength and flexibility for intricate shapes. Collaborating with material specialists to assess stress factors, temperature variations, and corrosion potentials is vital. Additionally, sourcing materials from reputable suppliers who can guarantee compliance with industry standards will mitigate risks. Implementing a rigorous testing phase for prototypes can further ensure that the selected material performs adequately before full-scale production begins.
Scenario 2: Managing Corrosion Resistance in Harsh Environments
The Problem: An oil and gas company in Nigeria is expanding its operations and needs to choose between cast steel and stainless steel for offshore equipment. Given the corrosive marine environment, the procurement team is worried about the longevity and maintenance costs associated with each material. They face pressure to reduce downtime and maintenance while ensuring safety standards are met.
The Solution: To effectively tackle corrosion challenges, the procurement team should prioritize sourcing high-grade stainless steel that is specifically designed for harsh environments, such as duplex stainless steel, which offers enhanced corrosion resistance. Conducting a corrosion analysis that considers local environmental factors, such as salinity and temperature, is crucial. Additionally, they should evaluate the long-term lifecycle costs of both materials. While cast steel may be more affordable initially, its susceptibility to corrosion could result in higher maintenance costs over time. The team can also consider protective coatings or cathodic protection systems for cast steel components as an added measure. Partnering with experienced suppliers who can provide comprehensive data on the performance of materials in marine conditions will aid in making informed decisions.
Scenario 3: Cost vs. Performance Trade-offs for Custom Components
The Problem: A European machinery manufacturer is developing a new line of custom parts and faces a budget constraint while ensuring high performance. The design team is debating whether to use cast steel for its cost-effectiveness or stainless steel for its superior mechanical properties. The challenge lies in balancing budget limitations with the need for reliable, high-quality components.
The Solution: In this situation, the manufacturer should conduct a cost-benefit analysis that examines both upfront costs and long-term performance implications. If the design includes complex geometries that would benefit from the casting process, cast steel could be the better option, especially if the parts do not require extreme strength. However, for components that will face high wear or stress, investing in stainless steel may yield better performance and reduce future costs associated with replacements or failures. Engaging in discussions with both suppliers about potential compromises, such as using hybrid designs that incorporate both materials, can provide a tailored solution. Additionally, exploring bulk purchasing agreements or alternative suppliers may also yield cost savings without sacrificing quality. Implementing a prototype testing phase can ensure that the chosen material meets performance standards before full production, minimizing the risk of costly errors.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for cast steel vs stainless steel
What Are the Key Properties of Cast Steel and Stainless Steel?
When comparing cast steel and stainless steel, understanding their key properties is crucial for B2B buyers. Cast steel is known for its excellent strength and toughness, making it suitable for high-stress applications. It can withstand high temperatures and pressures, which is essential in industries such as oil and gas, construction, and heavy machinery. Conversely, stainless steel is renowned for its corrosion resistance, particularly in harsh environments. The addition of chromium provides a protective layer against rust and oxidation, making it ideal for applications in the food and beverage, pharmaceutical, and chemical sectors.
What Are the Pros and Cons of Cast Steel vs. Stainless Steel?
Cast Steel:
– Pros: Cast steel offers superior strength and durability, making it suitable for heavy-duty applications. Its manufacturing process allows for complex shapes, which can be advantageous in custom projects. Additionally, cast steel components can be produced at a lower cost compared to stainless steel.
– Cons: However, cast steel is generally heavier and may require additional machining to achieve the desired finish. It is also less resistant to corrosion compared to stainless steel, which can limit its use in certain environments.
Stainless Steel:
– Pros: Stainless steel is lightweight and offers excellent corrosion resistance, making it a preferred choice for applications exposed to moisture or chemicals. Its aesthetic appeal and ease of maintenance are also significant advantages, especially in consumer-facing industries.
– Cons: The primary drawback is its higher cost and the complexity of manufacturing processes, which can lead to longer lead times. Additionally, while stainless steel is strong, it may not withstand the same level of stress as cast steel in high-load applications.
How Do Material Choices Impact Application Performance?
The choice between cast steel and stainless steel significantly impacts application performance. For instance, cast steel is often used in heavy machinery components, where strength and durability are paramount. It is compatible with various media, including oils and gases, but may not perform well in corrosive environments. In contrast, stainless steel is frequently utilized in applications requiring hygiene and corrosion resistance, such as food processing equipment and medical devices. Its compatibility with a wide range of chemicals further enhances its suitability for diverse applications.
What Should International B2B Buyers Consider When Selecting Materials?
International B2B buyers, particularly those from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, must consider compliance with local and international standards such as ASTM, DIN, and JIS. Understanding the specific requirements and preferences of their markets is essential. For example, in regions with high humidity or saline environments, stainless steel may be favored due to its corrosion resistance. Additionally, buyers should assess the availability of materials and suppliers in their region to ensure timely delivery and support.
Summary Table of Material Comparison
| Material | Typical Use Case for cast steel vs stainless steel | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cast Steel | Heavy machinery components, construction equipment | Superior strength and toughness | Heavier and less corrosion-resistant | Medium |
| Stainless Steel | Food processing, medical devices, chemical handling | Excellent corrosion resistance | Higher cost and longer manufacturing lead time | High |
This guide provides a comprehensive overview of the strategic material selection process for cast steel and stainless steel, equipping international B2B buyers with the insights needed to make informed decisions tailored to their specific applications and regional requirements.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for cast steel vs stainless steel
What Are the Main Stages of Manufacturing Processes for Cast Steel and Stainless Steel?
The manufacturing processes for cast steel and stainless steel involve several critical stages, each with its own techniques and quality assurance measures. Understanding these stages can help B2B buyers make informed decisions when selecting suppliers.
Material Preparation: What Materials Are Used and How Are They Prepared?
The first stage in manufacturing involves the selection and preparation of raw materials. For both cast steel and stainless steel, the primary materials include iron ore, chromium, nickel, and carbon. In the case of stainless steel, the alloying elements are crucial as they enhance properties such as corrosion resistance and strength.
In this stage, suppliers typically conduct a thorough analysis of raw materials to ensure they meet industry standards. This includes chemical composition tests and impurity checks. B2B buyers should inquire about the sourcing of these materials, particularly in regions like Africa and South America, where material quality can vary significantly.
What Are the Key Techniques Used in Forming Cast and Stainless Steel?
The forming stage differs significantly between cast steel and stainless steel.
-
Cast Steel: The process begins with melting the prepared raw materials in an electric arc furnace. The molten steel is then poured into molds to create specific shapes, a process known as casting. After cooling, the cast components are removed from the molds. This method allows for complex geometries and intricate designs, making it suitable for specialized applications.
-
Stainless Steel: Manufacturing stainless steel often involves forging or rolling. In forging, heated steel is shaped under compressive forces, enhancing its mechanical properties. Alternatively, in rolling, the steel is passed through rollers to achieve the desired thickness and shape. Each method has its unique advantages; forging improves strength and ductility, while rolling is more efficient for mass production.
Both processes require precision and expertise to ensure that the final products meet the necessary specifications.
How Is Assembly Conducted in the Manufacturing of Cast and Stainless Steel?
After forming, the assembly stage focuses on integrating various components into a final product. For cast steel, this may involve welding or bolting together different cast pieces, particularly in large machinery or structural applications. For stainless steel, components may be assembled using similar techniques, but the emphasis is often on achieving a clean, aesthetically pleasing finish due to the material’s visibility in applications like architecture and kitchenware.
B2B buyers should consider suppliers’ capabilities in assembly, particularly for custom projects, as this can significantly impact lead times and overall product quality.
What Finishing Techniques Are Commonly Used for Cast and Stainless Steel?
Finishing is crucial in both processes to enhance the appearance and performance of the final product. Typical finishing techniques include:
-
For Cast Steel: This often involves sandblasting or grinding to remove imperfections and improve surface finish. Coatings may also be applied for additional corrosion resistance.
-
For Stainless Steel: Finishing techniques often include polishing, passivation, and coating. Polishing enhances the aesthetic appeal, while passivation improves corrosion resistance by removing free iron from the surface.
B2B buyers should assess the finishing options offered by suppliers to ensure they align with their specific requirements.
How Do Quality Assurance Processes Ensure High Standards in Manufacturing?
Quality assurance (QA) is critical in the manufacturing of both cast and stainless steel. Adhering to international standards is essential for maintaining product integrity and reliability.
What Are the Relevant International Standards for Quality Assurance?
International standards such as ISO 9001 set the framework for quality management systems, ensuring that manufacturers maintain consistent quality in their processes. Additionally, industry-specific certifications like CE (Conformité Européenne) for products sold in Europe and API (American Petroleum Institute) standards for oil and gas applications play a significant role in ensuring product reliability.
B2B buyers should verify that their suppliers hold relevant certifications to ensure compliance with these standards.
What Are the Key Quality Control Checkpoints in Manufacturing?
Quality control (QC) checkpoints are strategically placed throughout the manufacturing process to monitor quality at various stages:
-
Incoming Quality Control (IQC): This phase involves inspecting raw materials upon receipt to ensure they meet specifications.
-
In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): During production, ongoing checks are performed to monitor processes and identify any deviations from quality standards.
-
Final Quality Control (FQC): Once production is complete, a thorough inspection of the finished product is conducted. This may involve dimensional checks, visual inspections, and performance testing.
B2B buyers should engage suppliers in discussions about their QC processes and the frequency of these inspections to ensure that quality is prioritized.
What Common Testing Methods Are Used in Quality Assurance?
Several testing methods are employed to verify the quality of cast and stainless steel products:
-
Mechanical Testing: This includes tensile tests, hardness tests, and impact tests to determine strength and durability.
-
Non-Destructive Testing (NDT): Techniques such as ultrasonic testing and radiography are used to detect internal defects without damaging the product.
-
Corrosion Testing: This assesses the material’s resistance to corrosive environments, which is crucial for stainless steel applications.
B2B buyers should request detailed reports on testing methods and results from suppliers to ensure product reliability.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control Practices?
Verifying a supplier’s quality control practices is essential for maintaining product standards. Here are several strategies B2B buyers can employ:
What Audits and Reports Should Buyers Request from Suppliers?
Buyers should request access to quality management system audits and reports. This includes ISO 9001 certifications and any relevant industry-specific certifications. Regular audits by third-party organizations can provide additional assurance of compliance with quality standards.
How Can Third-Party Inspection Services Enhance Quality Assurance?
Engaging third-party inspection services can provide an unbiased assessment of a supplier’s manufacturing processes and quality control measures. These services can conduct audits, oversee production, and verify compliance with international standards, offering peace of mind to B2B buyers.
What Are the Quality Control and Certification Nuances for International Buyers?
For international buyers, particularly from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, understanding the nuances of quality control and certification is vital. Factors such as local regulations, import standards, and certification requirements can vary significantly between regions. Buyers should familiarize themselves with these requirements and ensure that their suppliers can meet them to avoid delays and compliance issues.
In conclusion, understanding the manufacturing processes and quality assurance measures for cast steel and stainless steel is crucial for B2B buyers looking to make informed purchasing decisions. By thoroughly evaluating suppliers’ capabilities, certifications, and quality control practices, buyers can ensure they receive high-quality products that meet their specific needs.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘cast steel vs stainless steel’
Introduction
Navigating the decision between cast steel and stainless steel for your procurement needs can significantly impact the success of your projects. This guide provides a practical checklist to help international B2B buyers, particularly from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, make informed decisions. By following these steps, you can ensure that your sourcing aligns with your technical requirements and business objectives.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Before engaging with suppliers, clearly outline your project’s technical requirements. Consider factors such as strength, corrosion resistance, and design complexity. Understanding these specifications will guide your selection of materials, ensuring you choose between cast steel and stainless steel based on their unique properties.
Step 2: Assess Application Requirements
Evaluate the specific applications for which you need the materials. Cast steel is often preferred for intricate designs and shapes, while stainless steel is suitable for high-stress environments due to its superior strength. Identifying the primary use cases will help narrow down your material choices.
Step 3: Compare Cost and Production Time
Analyze the cost-effectiveness and production timelines for both materials. Cast steel generally offers a quicker turnaround and lower costs for complex shapes, whereas stainless steel, while more expensive, provides enhanced durability and longevity. Factor these elements into your budgeting and project timelines.
Step 4: Verify Supplier Certifications
Ensure that potential suppliers hold relevant certifications and adhere to international quality standards. Certifications such as ISO 9001 can indicate a supplier’s commitment to quality management. Request documentation that demonstrates compliance with industry standards, as this can affect material performance and reliability.
Step 5: Evaluate Supplier Experience and Reputation
Research the experience and reputation of suppliers in your industry. Look for testimonials, case studies, and references from other clients, particularly those who have similar needs. A supplier with a proven track record in your specific sector is more likely to understand your requirements and deliver quality materials.
Step 6: Request Samples for Quality Assessment
Always request material samples before making a bulk purchase. Analyzing samples allows you to assess the quality, finish, and performance of the materials in real-world conditions. This step is crucial for verifying that the materials meet your specifications and are suitable for your applications.
Step 7: Establish Clear Communication Channels
Set up effective communication with potential suppliers to ensure clarity on expectations, timelines, and any potential issues. Regular updates and open lines of communication can prevent misunderstandings and ensure that your project stays on track. Establishing these channels early in the process fosters a collaborative relationship, which is vital for successful sourcing.
By following this checklist, B2B buyers can make well-informed decisions when sourcing cast steel and stainless steel, ensuring that they select the best materials for their specific needs while fostering strong supplier relationships.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for cast steel vs stainless steel Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components in Sourcing Cast Steel vs. Stainless Steel?
When evaluating the cost structure for sourcing cast steel and stainless steel, several critical components come into play. Materials constitute a significant portion of the overall costs. Cast steel typically requires less expensive raw materials compared to stainless steel, which involves higher-grade alloys, particularly nickel and chromium.
Labor is another essential factor. The production of stainless steel often demands more skilled labor due to the complexities involved in the forging and finishing processes. Manufacturing overhead, including energy costs and equipment maintenance, tends to be higher for stainless steel due to the energy-intensive processes involved in its production. Furthermore, tooling costs for stainless steel can be elevated, particularly for custom designs, as the machinery needs to be more precise to handle the intricate properties of the material.
Quality control (QC) is critical in both cases, but particularly for stainless steel, where stricter adherence to specifications is required due to its applications in high-stress environments. Finally, logistics costs can vary based on the weight and volume of materials being transported; stainless steel is generally heavier, which can lead to higher shipping expenses.
How Do Price Influencers Affect the Cost of Cast Steel vs. Stainless Steel?
Several factors influence pricing in the B2B marketplace for cast steel and stainless steel. Volume and minimum order quantities (MOQs) play a crucial role; larger orders often come with discounts, making it beneficial for buyers to consolidate their purchasing needs.
Specifications and customization can also significantly affect pricing. Custom parts, particularly in stainless steel, require more time and resources to produce, thus increasing costs. Additionally, the quality of materials and certifications can drive prices up. Buyers looking for high-grade stainless steel with specific certifications for aerospace or medical applications will find that these materials command a premium.
Supplier factors, such as reputation, reliability, and location, can also influence pricing. Suppliers with a strong track record may charge more due to their perceived value. Lastly, Incoterms should not be overlooked; the choice of shipping terms can dramatically affect the final price, especially for international transactions.
What Are the Best Buyer Tips for Negotiating Costs?
When sourcing cast steel and stainless steel, international B2B buyers, particularly from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, should adopt several strategies to optimize costs. Negotiation is key; understanding the cost structure allows buyers to challenge prices effectively and seek better terms.
Focusing on cost-efficiency is crucial. Buyers should assess the Total Cost of Ownership (TCO), which includes not just the purchase price but also costs related to maintenance, durability, and potential failure rates. For instance, while cast steel may have a lower upfront cost, stainless steel’s durability and corrosion resistance could lead to lower long-term costs in certain applications.
Buyers should also be aware of pricing nuances related to international sourcing, such as fluctuating currency rates and import tariffs that can impact overall expenses. Understanding these factors can aid in securing better deals and managing budgets more effectively.
Disclaimer on Indicative Prices
It is important to note that prices for cast steel and stainless steel can vary widely based on market conditions, supplier pricing strategies, and specific project requirements. Therefore, any indicative prices should be viewed as such—potential buyers should conduct thorough market research and seek multiple quotes to ensure they receive the best value for their sourcing needs.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing cast steel vs stainless steel With Other Solutions
Exploring Alternatives: Evaluating Cast Steel vs Stainless Steel Against Other Solutions
In the world of industrial materials, choosing the right solution is critical for ensuring performance, durability, and cost-effectiveness. While cast steel and stainless steel are popular choices, various alternatives can also meet specific project requirements. This analysis provides a comparative overview of cast steel and stainless steel against two notable alternatives: aluminum alloys and carbon fiber composites.
Comparison Table
| Comparison Aspect | Cast Steel Vs Stainless Steel | Aluminum Alloys | Carbon Fiber Composites |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | High strength, good ductility, and impact resistance. Corrosion resistance varies by alloy type. | Lightweight, good strength-to-weight ratio, and excellent corrosion resistance. | Exceptional strength and rigidity, very lightweight, but can be brittle. |
| Cost | Generally higher due to production methods; cost-effective for large volumes. | Moderate cost; often lower than cast steel. | Higher initial cost, but can reduce overall project costs through weight savings. |
| Ease of Implementation | Requires specific machining and handling due to weight and hardness. | Easier to machine and fabricate, though specific techniques are needed for best results. | Complex manufacturing process; requires specialized knowledge for shaping and joining. |
| Maintenance | Low maintenance; corrosion resistance varies. | Generally low maintenance; excellent resistance to corrosion. | Low maintenance; however, repair can be complicated if damaged. |
| Best Use Case | Heavy-duty applications (e.g., construction, automotive parts) requiring strength. | Aerospace components, automotive frames, and applications needing a lightweight yet strong material. | High-performance applications (e.g., sports equipment, aerospace) where weight reduction is critical. |
Detailed Breakdown of Alternatives
Aluminum Alloys:
Aluminum alloys are increasingly utilized in various industries due to their impressive strength-to-weight ratio and excellent corrosion resistance. They are particularly advantageous in applications where weight savings are paramount, such as in the aerospace and automotive sectors. However, aluminum alloys may not match the strength of cast steel for heavy-duty applications, and their performance can be compromised at high temperatures. Their moderate cost and ease of machining make them an attractive alternative for many projects.
Carbon Fiber Composites:
Carbon fiber composites represent a cutting-edge alternative with exceptional strength and rigidity while being significantly lighter than both cast steel and aluminum. This makes them ideal for applications where weight is a critical factor, such as in aerospace and high-performance automotive sectors. However, the brittleness of carbon fiber can be a drawback, as it may not withstand impact as well as metals. The higher initial costs and complex manufacturing processes may deter some buyers, but the long-term benefits often justify the investment.
Conclusion: How to Choose the Right Solution for Your Needs
Selecting the appropriate material for your project requires a thorough understanding of your specific requirements, including performance needs, budget constraints, and ease of implementation. Cast steel and stainless steel offer robust solutions for heavy-duty applications, while aluminum alloys and carbon fiber composites provide compelling alternatives for projects prioritizing weight reduction and corrosion resistance. By carefully evaluating the strengths and weaknesses of each option, B2B buyers can make informed decisions that align with their operational goals and project specifications. Always consider consulting with material specialists to tailor the best solution for your unique challenges.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for cast steel vs stainless steel
What Are the Key Technical Properties of Cast Steel vs. Stainless Steel?
When evaluating cast steel and stainless steel for industrial applications, several critical technical properties must be considered. Understanding these specifications can significantly impact project outcomes, quality, and cost efficiency.
1. Material Grade
Material grade indicates the specific composition and mechanical properties of the steel. In the context of cast steel, common grades include ASTM A216 (WCB) for general applications and ASTM A352 for pressure-retaining components. For stainless steel, notable grades are 304 and 316, with 316 offering superior corrosion resistance due to its molybdenum content. Selecting the appropriate grade ensures compatibility with the intended application, balancing performance and cost.
2. Yield Strength
Yield strength refers to the maximum stress that a material can withstand while still maintaining its shape. Cast steel typically exhibits a yield strength ranging from 250 to 350 MPa, whereas stainless steel grades like 304 and 316 can exceed 200 MPa. High yield strength is essential in applications subjected to heavy loads and stress, such as in construction or heavy machinery.
3. Tensile Strength
Tensile strength measures the maximum amount of tensile (pulling) stress a material can endure before failure. Cast steel generally offers lower tensile strength compared to stainless steel. This property is crucial for applications where components experience dynamic loads, as it affects the material’s ability to resist deformation and potential failure.
4. Corrosion Resistance
Corrosion resistance is a defining characteristic that sets stainless steel apart from cast steel. Stainless steel is formulated with chromium, which forms a passive layer that protects against oxidation and corrosion. Cast steel, while durable, is more susceptible to rust and degradation when exposed to harsh environments. Industries such as oil and gas, where equipment faces corrosive substances, must prioritize this property in their material selection.
5. Machinability
Machinability refers to how easily a material can be cut, shaped, or otherwise manipulated during manufacturing. Stainless steel is often more challenging to machine than cast steel due to its hardness and toughness. Understanding machinability is vital for manufacturers to optimize production processes and minimize tooling costs.
What Are Common Trade Terms Related to Cast Steel and Stainless Steel?
In addition to technical properties, familiarizing yourself with industry terminology is essential for effective communication and negotiation in B2B transactions.
1. OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
An OEM is a company that produces parts or equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer. In the context of cast steel and stainless steel, OEMs often supply critical components for industries such as automotive and aerospace. Understanding OEM relationships can influence procurement strategies and sourcing decisions.
2. MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ refers to the smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell. This term is particularly relevant in B2B transactions, where bulk purchasing can lead to cost savings. Knowing the MOQ can help buyers plan their inventory and manage budgets effectively.
3. RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a formal request sent to suppliers to provide pricing for specific products or services. In the context of cast steel and stainless steel, issuing an RFQ allows buyers to compare offers and negotiate terms, ensuring they secure the best possible deal.
4. Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
Incoterms are a set of predefined international trade terms that clarify the responsibilities of buyers and sellers regarding shipping, insurance, and tariffs. Understanding Incoterms is crucial for international transactions, particularly when sourcing materials from different countries, as they define who bears the risk and costs during transportation.
5. Tolerance
Tolerance refers to the allowable variation in a material’s dimensions or properties. In manufacturing, understanding tolerance levels is essential for ensuring that parts fit together correctly and perform as expected. Different applications may require varying tolerance levels, making this a key consideration in procurement.
By grasping these technical properties and trade terms, B2B buyers can make informed decisions when selecting between cast steel and stainless steel, ultimately optimizing their operations and enhancing product quality.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the cast steel vs stainless steel Sector
What Are the Current Market Dynamics and Key Trends in the Cast Steel vs Stainless Steel Sector?
The global market for cast steel and stainless steel is driven by the increasing demand for durable, high-performance materials across various industries, including automotive, aerospace, and construction. In regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, buyers are witnessing a shift towards materials that not only offer superior strength but also adaptability to complex designs. Emerging trends include the growing adoption of digital sourcing technologies and supply chain management platforms that enhance transparency and efficiency. For instance, B2B platforms are enabling international buyers to connect directly with manufacturers, reducing costs and lead times.
Furthermore, the rise of Industry 4.0 technologies, such as IoT and AI, is influencing sourcing strategies. These technologies allow for better monitoring of production processes, ensuring quality control and timely deliveries. With increasing competition, buyers are also prioritizing suppliers who can offer value-added services, such as custom manufacturing and rapid prototyping. In particular, the stainless steel sector is experiencing a surge in demand for forged products, which are known for their superior mechanical properties, while cast steel is favored for applications requiring intricate designs and shapes.
How Is Sustainability and Ethical Sourcing Impacting the Cast Steel and Stainless Steel Markets?
Sustainability has become a pivotal concern for international B2B buyers in the cast steel and stainless steel sectors. The environmental impact of steel production, including high energy consumption and emissions, is pushing companies to seek eco-friendly materials and processes. Buyers are increasingly prioritizing suppliers who adhere to sustainable practices, such as using recycled materials and implementing energy-efficient production methods.
Ethical sourcing is also gaining prominence, with businesses demanding transparency in their supply chains. Certifications such as ISO 14001 for environmental management and ResponsibleSteel™ for ethical sourcing are becoming essential criteria for supplier selection. These certifications not only enhance a company’s reputation but also align with the growing consumer preference for sustainable products. Buyers from regions like Brazil and Nigeria are particularly focused on ensuring that their suppliers meet these standards, as they seek to comply with both local regulations and international sustainability benchmarks.
What Is the Evolution of the Cast Steel and Stainless Steel Industries in the B2B Context?
The evolution of the cast steel and stainless steel industries has been marked by significant technological advancements and changing market demands. Initially, the industry relied heavily on traditional manufacturing methods, with cast iron being the dominant material. However, the introduction of stainless steel in the early 20th century revolutionized the sector, thanks to its corrosion resistance and strength.
As industries evolved, so did the production techniques. The shift from basic casting methods to more sophisticated processes like precision casting and forging has allowed manufacturers to meet the increasing demands for high-quality, durable products. The globalization of supply chains has also enabled international buyers to source materials from diverse regions, promoting competition and innovation. Today, the focus is not just on the material properties but also on sustainability and ethical practices, reflecting the changing values of global consumers and businesses alike.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of cast steel vs stainless steel
-
How do I decide between cast steel and stainless steel for my manufacturing needs?
Choosing between cast steel and stainless steel largely depends on the specific requirements of your application. Cast steel is generally preferred for its strength and ability to be molded into complex shapes, making it ideal for components that require intricate designs. Stainless steel, known for its corrosion resistance, is better suited for environments exposed to moisture or corrosive substances. Assess factors such as mechanical properties, environmental conditions, and design requirements to make an informed decision. -
What are the key advantages of using cast steel over stainless steel?
Cast steel offers several advantages, particularly in terms of strength and flexibility in design. Its casting process allows for the creation of complex shapes and sizes, making it suitable for a wide range of applications, including machinery and structural components. Additionally, cast steel typically has lower production costs compared to stainless steel, making it an economical choice for large-scale projects. However, if corrosion resistance is a priority, stainless steel may be the better option. -
What factors should I consider when vetting suppliers for cast steel and stainless steel?
When vetting suppliers, consider their experience, reputation, and quality assurance processes. Look for suppliers who have certifications such as ISO 9001, indicating adherence to quality management standards. Additionally, assess their production capabilities, lead times, and ability to meet your specific requirements, including customization options. Request references from previous clients to gauge their reliability and service levels, especially for international transactions. -
What is the typical minimum order quantity (MOQ) for cast steel and stainless steel products?
MOQs can vary significantly based on the supplier and the complexity of the products. Generally, cast steel products may have lower MOQs due to their cost-effectiveness in mass production, while stainless steel products might have higher MOQs due to their more complex manufacturing processes. It’s advisable to discuss your specific needs with potential suppliers to negotiate suitable MOQs that align with your project requirements. -
What payment terms are commonly offered for international B2B transactions in cast steel and stainless steel?
Payment terms can vary by supplier and country. Common arrangements include upfront payments, letters of credit, and payment upon delivery. For large orders, suppliers may offer flexible payment plans to accommodate cash flow needs. It’s important to clearly establish and agree upon payment terms before finalizing contracts, ensuring both parties are protected against risks inherent in international trade. -
How do logistics and shipping impact the procurement of cast steel and stainless steel?
Logistics and shipping are critical factors in the procurement process, especially for international transactions. Consider the supplier’s location, shipping methods, and associated costs. Factors such as customs regulations, duties, and tariffs can significantly impact overall costs and delivery times. Collaborate with suppliers who have established logistics networks to ensure timely and cost-effective delivery, and always factor in potential delays due to geopolitical or economic conditions in the regions involved. -
What quality assurance measures should be in place for cast steel and stainless steel products?
Quality assurance is vital to ensure that the materials meet industry standards and specific application requirements. Suppliers should implement rigorous testing procedures, including tensile strength tests, corrosion resistance assessments, and dimensional inspections. Request documentation of these quality checks, including mill certificates and test reports, to verify the integrity of the materials before acceptance. Establishing clear quality standards in contracts can help mitigate risks associated with subpar materials. -
Can I customize cast steel and stainless steel products to meet my specific needs?
Yes, many suppliers offer customization options for both cast steel and stainless steel products. This can include alterations in dimensions, finishes, and alloy compositions tailored to your project’s requirements. It’s important to communicate your specifications clearly and discuss potential design changes early in the procurement process. Collaborating with suppliers who have experience in custom manufacturing can lead to better results and ensure that the final products meet your expectations.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.
Top 8 Cast Steel Vs Stainless Steel Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. The Piping Mart – Cast Steel Solutions
Domain: blog.thepipingmart.com
Registered: 2022 (3 years)
Introduction: Cast Steel: A form of carbon steel alloyed with chromium, nickel, molybdenum, and manganese. Made by melting iron ore at high temperatures and pouring into a mold. Used in structural components due to superior strength-to-weight ratio. More affordable but requires frequent maintenance due to susceptibility to corrosion.
Stainless Steel: An alloy of iron containing at least 10.5% chromium, someti…
2. Titan Fittings – Forged and Cast Stainless Steel Solutions
Domain: titanfittings.com
Registered: 2014 (11 years)
Introduction: Forged stainless steel: stronger, more reliable, ideal for high-stress applications (aerospace, automotive, heavy machinery), enhanced tensile strength and toughness, more resistant to corrosion due to uniform structure. Cast stainless steel: excels in design flexibility and alloy versatility, suitable for intricate designs and custom parts, often used in medical devices and architecture, good cor…
3. Made in Cookware – Cast Iron Cookware
Domain: madeincookware.com
Registered: 2017 (8 years)
Introduction: Cast Iron:
– Material: Alloy of carbon and iron
– Heat Resistance: Withstands up to 1500F
– Cooking Styles: Excellent for low and slow cooking, high heat cooking, braising vegetables, searing meat, baking cornbread
– Surface: Naturally non-stick when seasoned or enameled
– Durability: Can last lifetimes with proper care, less likely to warp from heat
– Available Styles: Unfinished and enamel…
4. Razab – Cast Iron Cookware
Domain: razab.com
Registered: 2011 (14 years)
Introduction: Cast Iron Cookware:
– Benefits:
– Heat Retention: Retains heat for even cooking, ideal for slow-cooked dishes.
– Versatile: Can be used on stovetop, in the oven, and over a campfire.
– Durability: Long-lasting investment.
– Non-Stick: Develops a natural non-stick finish over time.
– Demerits:
– Heavy Weight: Can be cumbersome to handle.
– Maintenance: Requires regular seasoning…
5. Intercast – Stainless Steel and Cast Iron Solutions
Domain: intercast.com
Registered: 2000 (25 years)
Introduction: Stainless steel casting and cast iron are two popular materials used in manufacturing. Stainless steel is known for its corrosion resistance, strength, and durability, making it suitable for applications in harsh environments. It is often used in industries such as food processing, pharmaceuticals, and marine applications. Cast iron, on the other hand, is known for its excellent castability, wear …
6. Organic Authority – Cookware Essentials
Domain: organicauthority.com
Registered: 2004 (21 years)
Introduction: Carbon Steel: Lightweight, heats up quickly, ideal for searing, balances weight and heat retention, popular among chefs. Stainless Steel: Light, durable, versatile, excellent for browning, can go in the oven, indestructible, preferred type is tri-ply or fully-clad. Cast Iron: Excellent heat retention, great for browning and searing, heavy, may have a rough surface, can interact with acidic ingredi…
7. Zeenews – Cast Iron Cookware
Domain: zeenews.india.com
Registered: 1997 (28 years)
Introduction: Cast Iron Cookware:
– Material: Made from a mixture of carbon and iron
– Heat Retention: Excellent, retains heat well
– Maintenance: Requires seasoning, can rust if not maintained
– Reactivity: Reacts with acidic foods if not properly seasoned
– Price: Affordable
– Weight: Heavy
– Durability: Can last for generations with proper care
– Cooking Characteristics: Best for slow cooking, searin…
8. Stainless Steel Casting – Investment Casting Techniques
Domain: stainlesssteelcasting.net
Registered: 2019 (6 years)
Introduction: Stainless Steel Casting: 1. Casting Technique: Investment casting or lost wax casting process. 2. Common Grades: 304(L), 316(L), 17-4 PH, Duplex 2205. 3. Characteristics: Good corrosion resistance, heat resistance, higher melting point (around 2600˚F), better impact resistance, more difficult to machine than cast iron. 4. Applications: Suitable for parts requiring high strength and ductility. 5. M…
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for cast steel vs stainless steel
What Are the Key Takeaways for B2B Buyers in Choosing Between Cast Steel and Stainless Steel?
In the competitive landscape of B2B sourcing, understanding the distinct advantages of cast steel and stainless steel is crucial for making informed procurement decisions. Cast steel offers design flexibility and is ideal for complex components, making it a cost-effective solution for industries that prioritize intricate shapes. Conversely, stainless steel, particularly in its forged form, delivers superior strength and durability, which is essential for high-stress applications in sectors such as aerospace and automotive.
Strategic sourcing is not just about cost; it encompasses evaluating material properties, production timelines, and application suitability. Buyers from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe must consider local market conditions and supply chain dynamics when selecting the appropriate material for their needs.
As the global market continues to evolve, the demand for high-quality materials will only increase. Therefore, engaging with trusted suppliers and leveraging industry expertise will empower you to make choices that enhance your operational efficiency and product reliability. Embrace these insights as you navigate your sourcing strategy, ensuring you remain competitive in your industry.