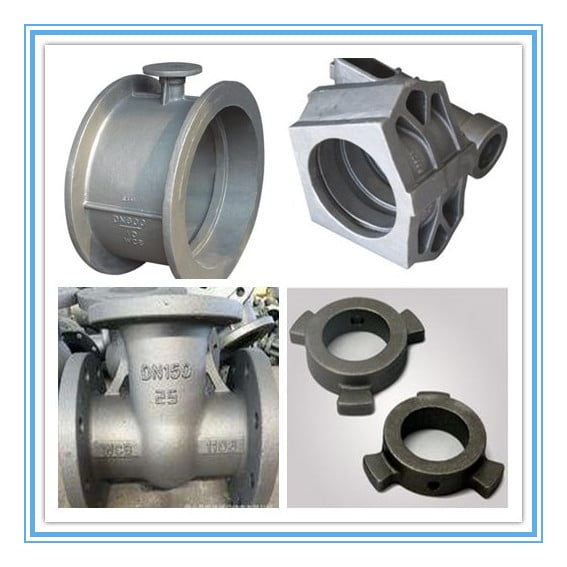
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for cast carbon steel
In the dynamic landscape of global manufacturing, sourcing cast carbon steel presents a unique challenge for B2B buyers, particularly those operating in diverse markets such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. With varying applications ranging from automotive components to industrial machinery, understanding the nuances of cast carbon steel—its composition, grades, and performance characteristics—becomes critical for informed purchasing decisions. This guide serves as an essential resource, offering a comprehensive overview of cast carbon steel, its types, and applications, alongside practical insights into supplier vetting and cost considerations.
As international buyers navigate this complex market, they face the dual challenge of identifying reliable suppliers while ensuring that the materials sourced meet specific operational needs and quality standards. This guide empowers B2B buyers by demystifying the procurement process, providing actionable strategies to evaluate potential suppliers, and highlighting key factors that influence pricing and availability. By equipping buyers with the knowledge necessary to make informed decisions, we aim to facilitate smoother transactions and foster lasting partnerships in the cast carbon steel supply chain.
As you explore the sections ahead, you will gain valuable insights that can enhance your procurement strategy, mitigate risks, and ultimately lead to successful sourcing outcomes in a competitive global market.
Understanding cast carbon steel Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Low Carbon Steel | Contains 0.05% to 0.25% carbon; excellent ductility | Automotive parts, structural components | Pros: Cost-effective, easy to weld. Cons: Lower strength compared to higher carbon steels. |
| Medium Carbon Steel | Contains 0.25% to 0.6% carbon; good balance of strength and ductility | Machinery, tools, and automotive components | Pros: Versatile; good wear resistance. Cons: Prone to brittleness if not heat-treated. |
| High Carbon Steel | Contains 0.6% to 2.1% carbon; high hardness and strength | Cutting tools, springs, and high-stress applications | Pros: Exceptional strength and wear resistance. Cons: Reduced ductility, more difficult to weld. |
| Alloyed Cast Carbon Steel | Contains additional alloying elements; enhanced properties | Aerospace components, specialized machinery | Pros: Tailored properties for specific applications. Cons: Higher cost due to alloying elements. |
| Ductile Cast Iron | Cast carbon steel with enhanced ductility; good impact resistance | Heavy machinery, automotive parts | Pros: High strength, good shock absorption. Cons: More expensive than standard cast iron. |
What are the Characteristics of Low Carbon Steel?
Low carbon steel typically contains a carbon content of 0.05% to 0.25%. This type is known for its excellent ductility, making it easy to form and weld. It is predominantly used in automotive parts and structural components where flexibility and ease of manufacturing are essential. For B2B buyers, the lower cost and ease of fabrication are significant advantages. However, its lower strength compared to higher carbon variants may limit its application in high-stress environments.
Why Choose Medium Carbon Steel for Your Applications?
Medium carbon steel contains between 0.25% and 0.6% carbon, striking a balance between strength and ductility. This type is widely used in machinery, tools, and automotive components due to its good wear resistance and versatility. B2B buyers should consider medium carbon steel for applications requiring a mix of toughness and strength. However, it may be prone to brittleness if not properly heat-treated, which should be factored into the purchasing decision.
What Makes High Carbon Steel Unique?
High carbon steel, with a carbon content ranging from 0.6% to 2.1%, is characterized by its exceptional hardness and strength. It is commonly used for cutting tools, springs, and applications subjected to high stress. For B2B buyers, the primary advantages lie in its superior wear resistance and strength. However, the reduced ductility and challenges in welding may necessitate careful consideration of application requirements before procurement.
How Do Alloyed Cast Carbon Steels Enhance Performance?
Alloyed cast carbon steels incorporate additional alloying elements to enhance specific properties, making them ideal for specialized applications such as aerospace components and advanced machinery. The tailored properties can significantly improve performance, but this comes at a higher cost. B2B buyers should evaluate the long-term benefits versus the initial investment to determine if the enhanced performance justifies the expense.
What are the Benefits of Ductile Cast Iron?
Ductile cast iron is a variation of cast carbon steel that offers enhanced ductility and impact resistance. It is often used in heavy machinery and automotive parts where high strength and shock absorption are critical. For B2B buyers, the benefits include better performance in demanding environments. However, it typically comes at a higher price point compared to standard cast iron, making cost considerations essential in the decision-making process.
Key Industrial Applications of cast carbon steel
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of cast carbon steel | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Construction & Infrastructure | Structural components for buildings | High strength and durability for load-bearing applications | Ensure compliance with local building codes and standards |
| Automotive | Engine blocks and components | Enhanced impact resistance and wear resistance | Look for suppliers with certifications in quality and safety |
| Oil & Gas | Pipeline fittings and valves | Corrosion resistance and ability to withstand high pressures | Verify material specifications and performance standards |
| Mining & Heavy Machinery | Equipment parts and machinery components | Ability to endure extreme conditions and heavy loads | Consider suppliers with experience in heavy-duty applications |
| Agriculture | Agricultural machinery parts | Durability and resistance to wear and tear | Assess availability of custom manufacturing options |
How is Cast Carbon Steel Used in Construction & Infrastructure?
In the construction and infrastructure sector, cast carbon steel is predominantly utilized for structural components such as beams, columns, and frames. Its high strength-to-weight ratio makes it ideal for load-bearing applications, ensuring safety and stability in buildings. International buyers, especially from regions like Africa and South America, should prioritize suppliers that adhere to local building codes and standards, ensuring compliance and quality assurance for their projects.
What Role Does Cast Carbon Steel Play in the Automotive Industry?
In the automotive industry, cast carbon steel is critical for manufacturing engine blocks, transmission cases, and other components that require significant durability and impact resistance. Its ability to withstand high temperatures and mechanical stresses makes it a preferred choice. Buyers must ensure that suppliers have appropriate quality certifications and experience in producing automotive-grade components to meet stringent industry standards.
How is Cast Carbon Steel Essential for Oil & Gas Applications?
The oil and gas sector relies on cast carbon steel for producing pipeline fittings, valves, and other critical components that must endure harsh environments and high pressures. The material’s inherent corrosion resistance is essential for maintaining the integrity of pipelines. International buyers should verify material specifications and performance standards to ensure the products meet the demanding requirements of this industry.
Why is Cast Carbon Steel Important for Mining & Heavy Machinery?
In mining and heavy machinery applications, cast carbon steel is used for manufacturing equipment parts, such as gear housings, frames, and support structures. The material’s ability to withstand extreme conditions and heavy loads is crucial for operational efficiency. Buyers should consider suppliers with proven experience in heavy-duty applications to ensure reliability and performance in challenging environments.
How Does Cast Carbon Steel Benefit Agricultural Machinery?
In agriculture, cast carbon steel is utilized for parts in machinery such as tractors and harvesters, where durability and resistance to wear and tear are critical. This material helps enhance the longevity and efficiency of agricultural equipment, ultimately benefiting productivity. Buyers should assess the availability of custom manufacturing options to meet specific machinery requirements, ensuring that they can source tailored solutions for their operations.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘cast carbon steel’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Difficulty in Choosing the Right Grade of Cast Carbon Steel
The Problem: Many B2B buyers struggle to select the appropriate grade of cast carbon steel for their specific applications. With various grades available, each possessing distinct mechanical properties and carbon content, buyers often find themselves overwhelmed. For instance, a manufacturing company might need steel that can withstand high stress but is also resistant to wear and tear. Without proper guidance, this can lead to costly mistakes, such as selecting a grade that either fails under pressure or deteriorates prematurely.
The Solution: To effectively choose the right grade, buyers should start by conducting a thorough analysis of their project requirements. This includes understanding the load conditions, environmental factors, and any potential impact scenarios. Consulting with a knowledgeable supplier or engineer can provide insights into which grades, such as low, medium, or high carbon steels, would best suit their needs. Additionally, creating a detailed specification document that outlines required mechanical properties—like tensile strength, ductility, and hardness—can streamline the sourcing process. Suppliers often have extensive experience and can recommend the most suitable materials based on application-specific data.
Scenario 2: Challenges in Sourcing Quality Cast Carbon Steel
The Problem: B2B buyers frequently encounter issues related to sourcing high-quality cast carbon steel, especially in regions where the supply chain is fragmented. Quality inconsistencies can arise from poor manufacturing processes or inadequate quality control measures, leading to unreliable materials that can jeopardize the integrity of their products. This is particularly concerning for industries like construction and automotive, where material failure can have severe consequences.
The Solution: To mitigate sourcing challenges, buyers should prioritize partnerships with reputable suppliers who adhere to international quality standards, such as ISO certifications. Conducting site visits or audits can further ensure that the foundry implements strict quality control measures. Buyers can also request material certifications and test reports for the cast carbon steel they intend to purchase. Establishing a long-term relationship with a trusted supplier can lead to more favorable terms and consistent quality, which ultimately enhances the reliability of their own products.
Scenario 3: Insufficient Knowledge on Maintenance and Longevity of Cast Carbon Steel Products
The Problem: After procurement, many B2B buyers lack a comprehensive understanding of how to maintain cast carbon steel products effectively. This can lead to premature wear and tear, resulting in unexpected downtime and increased operational costs. For example, a manufacturing plant that uses cast carbon steel components may face frequent replacements due to corrosion or fatigue, which can disrupt production schedules and lead to financial losses.
The Solution: Buyers should invest in training and resources that educate their teams on the best practices for maintaining cast carbon steel products. This includes regular inspections, proper lubrication, and protective coatings to enhance corrosion resistance. Implementing a scheduled maintenance plan can significantly extend the lifespan of steel components. Additionally, working closely with suppliers to understand the specific environmental conditions and load factors will help inform maintenance strategies. Suppliers may also offer guidance on effective corrosion protection methods, such as galvanization or painting, tailored to the specific application and operational environment.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for cast carbon steel
What Are the Key Properties of Cast Carbon Steel Materials?
When selecting cast carbon steel for industrial applications, understanding the key properties of various materials is crucial. Cast carbon steel typically contains carbon as the principal alloying element, which contributes to its strength and durability. Here are three common materials used in cast carbon steel, along with their properties, advantages, disadvantages, and considerations for international B2B buyers.
1. Low Carbon Steel (0.05% – 0.25% Carbon)
Key Properties: Low carbon steel offers good ductility and weldability, making it suitable for applications requiring extensive forming. It typically has a tensile strength of around 400 MPa and can withstand moderate temperatures and pressures.
Pros & Cons: The primary advantage of low carbon steel is its ease of fabrication and lower cost, making it an economical choice for large-scale production. However, its lower hardness means it may not perform well in high-stress applications, leading to potential deformation under heavy loads.
Impact on Application: Low carbon steel is often used in automotive components and structural applications where flexibility is required. It is not ideal for high-pressure environments or corrosive media.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers from regions like Africa and South America should ensure compliance with local standards such as ASTM A36. Understanding regional preferences for material specifications can also aid in procurement.
2. Medium Carbon Steel (0.25% – 0.60% Carbon)
Key Properties: Medium carbon steel strikes a balance between strength and ductility, with tensile strengths ranging from 600 to 800 MPa. It can withstand higher temperatures and pressures compared to low carbon steel.
Pros & Cons: This material is well-suited for applications requiring a combination of strength and toughness, such as in machinery components and automotive parts. However, it may require heat treatment to enhance its properties, which can increase manufacturing complexity and costs.
Impact on Application: Medium carbon steel is commonly used in the manufacturing of gears, axles, and other components that experience significant stress. Its performance in moderate to high-pressure environments makes it a versatile choice.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers in Europe and the Middle East should be aware of compliance with standards like DIN EN 10083. Additionally, understanding the local market for heat treatment services can influence the overall cost and lead time.
3. High Carbon Steel (0.60% – 2.0% Carbon)
Key Properties: High carbon steel is known for its exceptional hardness and strength, with tensile strengths exceeding 1000 MPa. It is suitable for applications requiring high wear resistance and can withstand extreme temperatures.
Pros & Cons: The major advantage of high carbon steel is its durability and resistance to wear, making it ideal for cutting tools and heavy-duty applications. However, its brittleness can be a significant disadvantage, leading to potential failure under impact or shock loading.
Impact on Application: High carbon steel is often used in manufacturing blades, springs, and high-strength structural components. Its ability to handle harsh conditions makes it suitable for demanding applications.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers from regions like Vietnam and Brazil should consider the availability of high carbon steel and its compliance with international standards such as JIS G3101. Understanding local sourcing options can help mitigate supply chain risks.
Summary Table of Cast Carbon Steel Materials
| Material | Typical Use Case for cast carbon steel | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Low Carbon Steel | Automotive components, structural parts | Economical and easy to fabricate | Lower hardness and strength | Low |
| Medium Carbon Steel | Gears, axles, machinery components | Good balance of strength and ductility | Requires heat treatment | Medium |
| High Carbon Steel | Cutting tools, springs, heavy-duty parts | Exceptional hardness and durability | Brittle under impact | High |
This analysis provides B2B buyers with a comprehensive understanding of the different types of cast carbon steel materials available, their properties, and their suitability for various applications. By considering these factors, international buyers can make informed decisions that align with their specific needs and regional standards.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for cast carbon steel
What Are the Key Stages in the Manufacturing Process of Cast Carbon Steel?
The manufacturing of cast carbon steel involves several critical stages, each essential for producing high-quality materials that meet industry specifications. Understanding these stages can help B2B buyers from regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe make informed decisions when sourcing cast carbon steel products.
1. Material Preparation: What Are the Initial Steps for Cast Carbon Steel Production?
Material preparation is the foundational stage in the manufacturing process. It begins with the selection of raw materials, primarily iron and carbon, along with additional alloying elements like manganese and silicon, which enhance the material’s properties. The chosen materials undergo rigorous screening to ensure they meet specified chemical compositions and mechanical properties.
Once the materials are selected, they are melted in a furnace. There are various types of furnaces used, including electric arc furnaces (EAF) and induction furnaces, depending on the scale of production and specific requirements. The molten metal must be carefully monitored for temperature and composition, ensuring uniformity before proceeding to the next stage.
2. How Is the Forming Process Conducted in Cast Carbon Steel Manufacturing?
The forming process for cast carbon steel typically involves pouring the molten metal into molds. This can be achieved through various casting techniques, including sand casting, investment casting, and permanent mold casting. Each method has its advantages and is chosen based on the complexity of the part, desired finish, and volume of production.
Once the molten metal is poured into the molds, it is allowed to cool and solidify. The cooling rate can significantly impact the mechanical properties of the finished product. After solidification, the casting is removed from the mold, often requiring some initial cleaning to remove any residual sand or impurities.
3. What Is the Role of Assembly in the Production of Cast Carbon Steel Components?
In cases where the final product comprises multiple components, the assembly stage becomes critical. This involves fitting together various cast parts, which may require machining for precise dimensions. Techniques such as welding, riveting, or bolting can be employed to join components, depending on the design specifications.
Assembly must be executed with precision to ensure that the final product functions as intended. This stage often includes alignment checks and adjustments to maintain tolerances, especially in applications where high strength and accuracy are paramount.
4. What Finishing Techniques Are Commonly Used for Cast Carbon Steel Products?
Finishing is the final stage of the manufacturing process, aimed at enhancing the material’s surface quality and protective characteristics. Common techniques include machining, grinding, and polishing, which help achieve the desired surface finish and dimensional accuracy.
Additionally, surface treatments such as galvanizing, painting, or applying protective coatings can be implemented to improve corrosion resistance and overall durability. These treatments are especially important for components exposed to harsh environments, ensuring longevity and performance.
How Is Quality Assurance Integrated Throughout the Manufacturing Process?
Quality assurance (QA) is a critical component in the manufacturing of cast carbon steel, ensuring that products meet both international and industry-specific standards. This commitment to quality helps build trust with B2B buyers and minimizes the risk of defects in finished products.
1. What Are the International Standards Relevant to Cast Carbon Steel Quality Assurance?
Several international standards govern the quality assurance processes for cast carbon steel. Among these, ISO 9001 is a widely recognized standard that outlines the criteria for a quality management system. Adherence to ISO 9001 demonstrates a manufacturer’s commitment to consistent quality and customer satisfaction.
In addition to ISO 9001, industry-specific standards such as CE marking for European markets and API standards for the oil and gas sector are vital. These certifications signify compliance with safety, health, and environmental protection regulations, which are crucial for B2B buyers in various industries.
2. What Are the Key Quality Control Checkpoints During Manufacturing?
Quality control (QC) checkpoints are strategically integrated throughout the manufacturing process to ensure product integrity. Key checkpoints include:
-
Incoming Quality Control (IQC): This involves inspecting raw materials upon arrival to verify compliance with specifications.
-
In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): Continuous monitoring during the manufacturing stages, including temperature checks during melting and dimensional checks during forming and assembly.
-
Final Quality Control (FQC): Comprehensive testing of finished products, including mechanical property tests, non-destructive testing (NDT) such as ultrasonic and radiographic tests, and visual inspections.
These checkpoints help identify potential defects early in the process, reducing waste and ensuring that only high-quality products reach the market.
3. What Testing Methods Are Commonly Used to Ensure Cast Carbon Steel Quality?
Several testing methods are employed to evaluate the mechanical and chemical properties of cast carbon steel. Common techniques include:
-
Tensile Testing: Measures the material’s strength and ductility.
-
Hardness Testing: Assesses the material’s resistance to deformation.
-
Impact Testing: Evaluates the material’s toughness, particularly important for applications subject to sudden forces.
-
Chemical Analysis: Ensures that the material composition meets specified standards.
These tests are essential for verifying that the products are suitable for their intended applications and comply with industry regulations.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Assurance Practices?
For B2B buyers, especially those from diverse international markets, verifying a supplier’s quality assurance practices is crucial. Here are several methods to ensure supplier credibility:
-
Audits: Conducting regular audits of suppliers can provide insights into their manufacturing processes and quality control measures. This includes reviewing documentation related to ISO certifications and compliance with industry standards.
-
Reports: Requesting detailed QC reports, including results from mechanical and chemical tests, can help buyers assess product quality before making purchasing decisions.
-
Third-Party Inspections: Engaging third-party inspection services can provide an unbiased evaluation of the manufacturing processes and quality control measures in place. This is particularly valuable for international buyers who may not have direct oversight of production facilities.
What Are the Quality Control Nuances for International B2B Buyers?
International B2B buyers must navigate various quality control nuances when sourcing cast carbon steel. These include understanding regional standards, compliance requirements, and the impact of local regulations on manufacturing practices. Buyers should also consider the logistical aspects of transporting goods across borders, which may affect the condition and quality of the materials upon arrival.
Building strong relationships with suppliers who prioritize quality assurance can lead to better communication and a more reliable supply chain. Additionally, staying informed about global trends in quality management and manufacturing processes will empower buyers to make strategic sourcing decisions that align with their business goals.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘cast carbon steel’
To effectively procure cast carbon steel, B2B buyers must navigate a series of steps to ensure they meet their technical requirements and secure reliable suppliers. This guide provides a structured checklist to streamline the sourcing process, emphasizing the critical aspects necessary for successful procurement.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Clarifying your requirements is crucial. Determine the specific grades of cast carbon steel you need based on your application, including carbon content, mechanical properties, and any required certifications. This clarity helps suppliers understand your needs and ensures that the materials meet industry standards and performance expectations.
Step 2: Research Market Trends and Pricing
Understanding market dynamics is essential for informed purchasing. Investigate current trends in cast carbon steel pricing and availability, especially in your target regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. This knowledge can help you negotiate better prices and anticipate fluctuations that may affect your sourcing strategy.
Step 3: Evaluate Potential Suppliers
Thoroughly vetting suppliers is vital for quality assurance. Look for suppliers with a proven track record in producing cast carbon steel. Request company profiles, case studies, and references from clients in similar industries or geographical areas to gauge reliability and quality. It’s beneficial to assess their production capabilities and quality control processes.
Step 4: Verify Supplier Certifications
Certifications can indicate a supplier’s commitment to quality. Ensure that potential suppliers have relevant certifications such as ISO 9001 or ASTM standards. These certifications reflect adherence to international quality standards and can significantly reduce the risk of receiving subpar materials.
Step 5: Request Samples and Conduct Testing
Obtaining samples allows for practical evaluation. Request samples of the cast carbon steel to conduct your own tests or evaluations. Assess the samples for mechanical properties, durability, and compliance with your specifications. This step is essential to confirm that the supplier can meet your quality expectations before placing a larger order.
Step 6: Discuss Terms and Conditions
Clear agreements protect both parties. Before finalizing the purchase, discuss payment terms, delivery schedules, and any warranties or guarantees. Clear communication regarding these aspects helps prevent misunderstandings and establishes a solid foundation for a long-term relationship.
Step 7: Establish a Communication Plan
Effective communication is key to a successful partnership. Set up a communication plan with your chosen supplier to ensure ongoing updates about order status, shipping, and any potential issues. Regular check-ins can foster a strong relationship and help address any concerns proactively.
By following this step-by-step checklist, B2B buyers can enhance their sourcing strategy for cast carbon steel, ensuring they obtain high-quality materials that meet their specific needs while building reliable partnerships with suppliers.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for cast carbon steel Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components in Sourcing Cast Carbon Steel?
When sourcing cast carbon steel, understanding the cost structure is essential for effective budgeting and pricing negotiations. The primary cost components include:
-
Materials: The cost of raw materials, primarily iron and carbon, significantly impacts the overall price. Prices fluctuate based on global market conditions, with demand and supply dynamics influencing costs. Additional alloying elements like manganese and silicon can also affect material pricing.
-
Labor: Labor costs vary depending on the region and the expertise required for casting processes. Skilled labor is often more expensive, especially in regions with higher wages. The manufacturing process, whether it involves manual labor or advanced machinery, also influences this component.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes expenses related to facility maintenance, utilities, and administrative costs. Efficient operations can help minimize overhead, but high overhead costs can be a barrier for smaller manufacturers.
-
Tooling: The creation of molds and tools for casting can be a significant upfront investment. Costs vary based on the complexity and material of the tooling. Custom tooling for specific applications may raise initial costs but can lead to better product quality and lower per-unit costs over time.
-
Quality Control (QC): Maintaining high-quality standards incurs costs related to testing and inspections. Certifications, such as ISO or ASTM, can elevate costs but are often necessary to meet international standards and buyer specifications.
-
Logistics: Transportation and shipping costs are crucial, especially for international buyers. Factors such as distance, shipping mode, and Incoterms can significantly affect logistics expenses. Efficient logistics management can reduce costs and improve delivery times.
-
Margin: Suppliers often have specific margin expectations based on their operational costs and market positioning. Understanding these margins can aid in negotiation strategies.
How Do Price Influencers Affect Cast Carbon Steel Sourcing?
Several factors influence the pricing of cast carbon steel, and understanding these can aid buyers in making informed decisions:
-
Volume/MOQ: Bulk purchasing often leads to discounts. Suppliers may offer better rates for larger orders, making it beneficial for buyers to consolidate their sourcing needs.
-
Specifications and Customization: Custom specifications can lead to increased costs due to the need for specialized tooling or processes. Buyers should clearly define their requirements to avoid unexpected charges.
-
Quality and Certifications: Higher quality materials and specific certifications can increase costs. However, investing in quality can reduce long-term costs related to maintenance and replacements.
-
Supplier Factors: Supplier reputation, production capacity, and location can influence pricing. Established suppliers with a track record of reliability may charge a premium but can offer peace of mind.
-
Incoterms: The agreed terms of shipment can significantly affect total costs. Different Incoterms (like FOB, CIF, etc.) shift the responsibility and cost of logistics, impacting the overall price.
What Are the Best Buyer Tips for Sourcing Cast Carbon Steel?
For international B2B buyers, particularly from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, here are some actionable tips:
-
Negotiate Wisely: Leverage volume purchases and long-term partnerships to negotiate better pricing. Build relationships with suppliers to foster trust and improve negotiation outcomes.
-
Focus on Cost-Efficiency: Evaluate the Total Cost of Ownership (TCO) rather than just the purchase price. Consider maintenance costs, potential downtime, and the longevity of the materials.
-
Understand Pricing Nuances: Be aware of regional pricing variations and market conditions that may affect costs. Conduct thorough market research to ensure you are getting competitive pricing.
-
Request Quotes from Multiple Suppliers: Obtaining quotes from several suppliers can provide a clearer picture of the market rate and help in negotiations.
-
Stay Informed About Industry Trends: Keeping abreast of market trends, material availability, and global events can provide insights into potential price fluctuations.
Disclaimer: Prices for cast carbon steel can vary significantly based on the factors mentioned above. The information provided is indicative and should not be considered as fixed pricing. Always consult with suppliers for accurate quotes tailored to your specific needs.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing cast carbon steel With Other Solutions
Exploring Alternatives to Cast Carbon Steel: A Comparative Analysis
In the quest for optimal material solutions, B2B buyers often evaluate various options to meet their specific needs. Cast carbon steel, known for its strength, ductility, and impact resistance, is a popular choice in many applications. However, alternatives may offer distinct advantages depending on the context. This analysis compares cast carbon steel with two viable alternatives: cast iron and stainless steel.
| Comparison Aspect | Cast Carbon Steel | Cast Iron | Stainless Steel |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | High strength and ductility; excellent impact resistance | Good compressive strength; brittle under tension | High corrosion resistance; good tensile strength |
| Cost | Moderate cost; varies by grade and application | Generally lower cost; economical for bulk applications | Higher cost; premium pricing due to alloying elements |
| Ease of Implementation | Standard casting processes; versatile | Simple casting processes; widely used | More complex manufacturing; requires specialized processes |
| Maintenance | Requires regular maintenance to prevent corrosion | Lower maintenance but can corrode over time | Low maintenance; resistant to rust and corrosion |
| Best Use Case | Mechanical parts, structural applications | Heavy machinery, pipes, and fittings | Food processing, chemical, and marine applications |
What Are the Advantages and Disadvantages of Cast Iron?
Cast iron is often favored for its excellent compressive strength and castability. Its lower cost makes it an attractive option for large-scale applications such as pipes and heavy machinery components. However, cast iron is brittle, which limits its use in applications subject to tension or impact forces. While it requires less maintenance than cast carbon steel, it can corrode if not properly treated, leading to potential failure in critical applications.
How Does Stainless Steel Compare as an Alternative?
Stainless steel offers significant advantages, particularly in environments where corrosion resistance is paramount. Its high tensile strength and ductility make it suitable for a wide range of applications, from food processing to marine environments. However, the cost of stainless steel is generally higher due to the alloying elements involved, and its manufacturing processes can be more complex. For industries requiring stringent hygiene standards, stainless steel is often the preferred choice despite the higher initial investment.
Conclusion: How Should B2B Buyers Choose the Right Material?
Selecting the right material requires a careful assessment of specific application needs, budget constraints, and environmental factors. Buyers should consider the performance characteristics, cost implications, and maintenance requirements of each option. While cast carbon steel remains a reliable choice for many applications, alternatives like cast iron and stainless steel may offer unique benefits that align better with certain operational demands. Conducting a thorough analysis of these factors will empower B2B buyers to make informed decisions that enhance their operational efficiency and product quality.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for cast carbon steel
What Are the Key Technical Properties of Cast Carbon Steel?
Understanding the essential technical properties of cast carbon steel is crucial for B2B buyers looking to optimize their manufacturing processes. Here are several critical specifications that play a vital role in the selection and application of cast carbon steel:
-
Material Grade
Material grades indicate the chemical composition and mechanical properties of cast carbon steel. Common grades include ASTM A216 WCB, which has a carbon content between 0.2% and 0.3%, offering excellent strength and ductility. Choosing the right grade ensures that the material meets the specific demands of the application, such as load-bearing capacity and resistance to wear. -
Carbon Content
The carbon content in cast carbon steel typically ranges from 0.1% to 2.1%. This specification directly affects hardness and tensile strength; higher carbon content generally leads to increased hardness but reduced ductility. B2B buyers should assess their application needs—whether strength or flexibility is more critical—to choose the appropriate carbon level. -
Tensile Strength
Tensile strength is a measure of the material’s ability to withstand pulling forces without breaking. In cast carbon steel, this property is crucial for applications subjected to high stress and strain, such as structural components in construction or heavy machinery. Understanding tensile strength helps businesses ensure that the selected steel will perform reliably under operational conditions. -
Impact Resistance
Impact resistance refers to the ability of cast carbon steel to absorb energy during sudden impacts without fracturing. This property is particularly important in industries like automotive and aerospace, where components are subject to dynamic loads. Buyers should prioritize materials with high impact resistance to enhance the safety and durability of their products. -
Machinability
Machinability assesses how easily a material can be cut, shaped, or finished. Cast carbon steel is known for good machinability, which is essential for producing precision components. Understanding this property can help manufacturers reduce production costs and improve overall efficiency. -
Weldability
Weldability indicates how easily a material can be welded without compromising its integrity. Cast carbon steel generally has good weldability, making it suitable for applications that require assembly or repair. Buyers should consider this property when planning fabrication processes to ensure strong joints and structural integrity.
What Are Common Trade Terms Related to Cast Carbon Steel?
Familiarity with industry jargon is essential for effective communication and negotiation in the B2B landscape. Here are several common terms that buyers should understand:
-
OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
OEM refers to companies that produce parts or equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer. Buyers should be aware of OEM specifications to ensure compatibility with existing systems and components. -
MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ is the smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell. Understanding MOQ helps buyers negotiate better terms and manage inventory levels effectively, especially in regions with diverse demand patterns. -
RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a document sent to suppliers to request price estimates for specific products or services. It is a critical step in the procurement process, allowing buyers to compare offers and make informed purchasing decisions. -
Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
Incoterms are a set of internationally recognized rules that define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in international transactions. Familiarity with Incoterms helps B2B buyers understand shipping costs, risk, and delivery obligations, facilitating smoother cross-border trade. -
Lead Time
Lead time refers to the time taken from placing an order to receiving the product. Knowing lead times is essential for production planning, as it impacts project timelines and inventory management. -
Certification
Certification indicates that a material meets specific standards or regulations. Buyers should look for certifications relevant to their industry, such as ISO or ASTM, to ensure compliance and quality assurance in their supply chain.
By grasping these technical properties and trade terms, B2B buyers can make more informed decisions when sourcing cast carbon steel, ultimately leading to better project outcomes and enhanced operational efficiency.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the cast carbon steel Sector
What Are the Current Market Dynamics Influencing the Cast Carbon Steel Sector?
The global cast carbon steel market is currently experiencing robust growth, driven by a combination of industrial expansion, infrastructure development, and technological advancements. Key regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe are witnessing increased demand for cast carbon steel due to ongoing urbanization and industrialization efforts. Notably, countries like Vietnam and Brazil are ramping up their manufacturing capabilities, presenting significant opportunities for international B2B buyers to source high-quality materials.
Emerging B2B technologies are reshaping the sourcing landscape, with digital platforms facilitating easier access to suppliers and materials. The rise of Industry 4.0 technologies, including IoT and AI, is enhancing supply chain efficiencies and enabling better quality control in the production of cast carbon steel. Buyers are increasingly leveraging data analytics to make informed sourcing decisions, assess supplier reliability, and optimize inventory management.
Moreover, fluctuating raw material prices and geopolitical factors are creating volatility in the market. As a result, B2B buyers are urged to adopt flexible sourcing strategies, including diversifying their supplier base and considering long-term contracts to mitigate risks. Understanding local market dynamics, regulatory requirements, and cultural nuances in target regions is also crucial for successful sourcing.
How Can Sustainability and Ethical Sourcing Shape the Future of Cast Carbon Steel?
Sustainability is becoming a cornerstone of sourcing strategies for cast carbon steel, driven by both regulatory pressures and consumer demand for environmentally responsible products. The environmental impact of steel production, including carbon emissions and energy consumption, has prompted many manufacturers to adopt greener practices. International B2B buyers are increasingly seeking suppliers that prioritize sustainable production methods, such as using recycled materials and implementing energy-efficient technologies.
Ethical sourcing has emerged as a critical factor in supplier selection. Buyers are encouraged to conduct thorough due diligence on their supply chains to ensure compliance with labor laws and environmental standards. Certifications such as ISO 14001 for environmental management and responsible sourcing initiatives can serve as indicators of a supplier’s commitment to ethical practices.
In addition, innovations in green steel production, such as hydrogen-based processes and carbon capture technologies, are gaining traction. These advancements not only reduce the carbon footprint associated with cast carbon steel but also align with global efforts to combat climate change. As sustainability becomes a key differentiator, international buyers are advised to prioritize partnerships with suppliers that demonstrate a clear commitment to environmental stewardship.
What Is the Historical Context of Cast Carbon Steel in B2B Markets?
The history of cast carbon steel dates back to the late 19th century when advancements in metallurgy allowed for the development of stronger and more durable steel alloys. Initially used in heavy industries, cast carbon steel quickly became a staple material in construction, transportation, and manufacturing due to its excellent strength-to-weight ratio and impact resistance.
Over the decades, the evolution of casting techniques, including investment casting and continuous casting, has enhanced the efficiency and precision of producing cast carbon steel components. Today, this material is integral to various applications, from automotive parts to structural components in buildings. Understanding this historical context helps B2B buyers appreciate the reliability and versatility of cast carbon steel in meeting diverse industry demands.
As the market continues to evolve, staying informed about historical trends can offer valuable insights into future developments and opportunities within the cast carbon steel sector.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of cast carbon steel
-
How do I solve issues with the quality of cast carbon steel?
To address quality concerns with cast carbon steel, establish clear quality assurance (QA) protocols with your suppliers. Request detailed certifications and test reports that comply with international standards such as ASTM or ISO. Conduct regular audits and site visits to ensure adherence to manufacturing processes. Additionally, consider collaborating with suppliers who offer traceability and transparency in their production practices, which can help you monitor quality throughout the supply chain. -
What is the best grade of cast carbon steel for high-impact applications?
For high-impact applications, cast carbon steel grades with a carbon content of 0.1% to 0.5% are typically recommended. These grades provide an optimal balance of strength and ductility, allowing them to withstand sudden stress without breaking or deforming. Always consult with your supplier to determine the most suitable grade based on specific application requirements, including load-bearing capacity and environmental conditions. -
How do I determine the right supplier for cast carbon steel?
To find a reliable supplier for cast carbon steel, evaluate their experience in the industry, production capabilities, and quality certifications. Request references from past clients and assess their responsiveness to inquiries. It’s beneficial to choose suppliers who have a robust supply chain and can provide customization options. Additionally, consider their location and logistics capabilities to ensure timely delivery, especially if sourcing from international markets. -
What customization options are available for cast carbon steel products?
Customization options for cast carbon steel include variations in carbon content, alloying elements, and specific dimensions to meet your project requirements. Many suppliers offer tailored solutions such as different surface treatments, heat treatments, and finishes. When discussing your needs, provide detailed specifications and performance criteria to ensure that the final product aligns perfectly with your application. -
What are the minimum order quantities (MOQ) for cast carbon steel?
Minimum order quantities for cast carbon steel can vary significantly among suppliers, typically ranging from a few tons to several dozen tons. Factors influencing MOQ include production capabilities, material availability, and the complexity of the casting process. When negotiating with suppliers, clarify your requirements and explore options for smaller trial orders if you are just starting or testing a new application. -
What payment terms should I expect when sourcing cast carbon steel internationally?
Payment terms for international orders of cast carbon steel often involve upfront deposits, typically ranging from 30% to 50% of the total order value, with the balance due prior to shipping. Some suppliers may offer flexible terms like letters of credit or payment upon delivery. It’s crucial to discuss payment options in advance to ensure alignment with your financial processes and to mitigate risks associated with international transactions. -
How can I ensure timely logistics and delivery for my cast carbon steel orders?
To ensure timely logistics and delivery, work closely with your supplier to establish a clear timeline and shipping plan. Discuss available shipping methods and choose one that aligns with your urgency and budget. Consider using freight forwarders with experience in international shipments to handle customs clearance and documentation. Regular communication with your supplier throughout the process can help mitigate delays and ensure a smooth delivery. -
What are the common applications of cast carbon steel in various industries?
Cast carbon steel is widely used across multiple industries due to its strength and versatility. Common applications include structural components in construction, automotive parts, machinery, and heavy equipment. It’s also utilized in manufacturing tools, valves, and pumps. Understanding the specific demands of your industry will help you select the right grade and specifications of cast carbon steel for optimal performance in your projects.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.
Top 8 Cast Carbon Steel Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. EPCAST – Carbon Steel Casting
Domain: epcast.com
Registered: 1996 (29 years)
Introduction: Carbon Steel Casting is a steel alloy primarily containing carbon as the main alloying element. It is available in low carbon and mid carbon varieties. Low carbon steel is known for its ductility, weldability, and machinability, suitable for automotive and construction applications such as fasteners and bolts. Mid carbon steel offers good wear resistance and can be heat treated, commonly used in m…
2. Total Materia – Cast Carbon Steels
Domain: totalmateria.com
Registered: 2013 (12 years)
Introduction: Cast carbon steels are classified into three categories based on carbon content: low-carbon (<0.20% C), medium-carbon (0.20-0.50% C), and high-carbon (>0.50% C). Key mechanical properties include strength, hardness, ductility, toughness, and fatigue resistance, which are influenced by composition and heat treatment. Ultimate tensile strength levels range from 414 to 1724 MPa. Silicon content typic…
3. Intercast – Carbon Steel Solutions
Domain: intercast.com
Registered: 2000 (25 years)
Introduction: Carbon steel is a type of steel that contains carbon as the main alloying element, while cast steel is a type of steel that is melted and poured into a mold to create a specific shape. Carbon steel is known for its strength and durability, making it suitable for a wide range of applications, including construction and manufacturing. Cast steel, on the other hand, is often used for more complex sha…
4. Make It From – ASTM A27 Cast Carbon Steel Grades
Domain: makeitfrom.com
Registered: 2009 (16 years)
Introduction: ASTM A27 Cast Carbon Steel is a carbon steel formulated for casting, with five common variations. The grades include: ASTM A27 Grade 60-30 (415-205, J03000), ASTM A27 Grade 65-35 (450-240, J03001), ASTM A27 Grade 70-36 (485-250, J03501), ASTM A27 Grade 70-40 (485-275, J02501), and ASTM A27 Grade U-60-30 (415-205, J02500). Mechanical properties include: Elastic Modulus 190 GPa, Elongation at Break …
5. Kormax – Carbon Steel Casting Solutions
Domain: kormax.com
Registered: 1998 (27 years)
Introduction: Kormax offers cast carbon steel and alloy casting services, partnering with leading foundries to supply high-performance materials that meet strict industry benchmarks. Key features of their carbon steel alloys include high-temperature resistance, strength and toughness, pressure containment, and ferromagnetic properties. Common applications include valves, pumps, pressure vessels, heat exchangers…
6. Fisher Cast Steel – Stainless and Carbon Steel Castings
Domain: fishercaststeel.com
Registered: 1999 (26 years)
Introduction: Fisher Cast Steel specializes in stainless and carbon steel castings, offering both sand and investment casting services. They are ISO 9001:2015 certified and adhere to the PED (Pressure Equipment Directive) 97/23/EC. Their casting capabilities include:
– **Materials & Alloys**:
– Corrosion-Resistant Stainless Steel (Austenitic, Super Austenitic, Martensitic, Duplex, Precipitation Hardenable, …
7. Tanghai Valve – Carbon Steel vs. Cast Steel
Domain: tanghaivalve.com
Registered: 2016 (9 years)
Introduction: The text discusses the differences between carbon steel and cast steel, including classifications of carbon steel (low, medium, high carbon), and the processing methods (forged and cast). It highlights that cast steel valves are made through casting methods, while carbon steel valves can be made through rolling. The main differences between cast iron and cast steel valves are carbon content, stren…
8. Kicastings – Carbon Steel Casting Solutions
Domain: kicastings.com
Registered: 2019 (6 years)
Introduction: Carbon steel casting is a popular material option for steel castings due to its cost-effectiveness, wear resistance, and machinability. It is used in various industries including automotive, railway, and heavy equipment. Key benefits include: 1. Cost-effective mechanical parts, as carbon steel is cheaper than stainless steel and can be customized with alloying elements. 2. Multiple material grades…
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for cast carbon steel
What Are the Key Benefits of Strategic Sourcing for Cast Carbon Steel?
In conclusion, strategic sourcing of cast carbon steel is essential for businesses looking to enhance operational efficiency and product quality. By understanding the differences between cast steel and carbon steel, international B2B buyers can make informed decisions tailored to their specific applications. This knowledge allows companies to select the right grades that offer optimal impact resistance, durability, and corrosion resistance, ultimately leading to improved performance in mechanical and structural applications.
Furthermore, leveraging the expertise of suppliers with extensive industry experience ensures that businesses can access innovative alloys and cost-effective solutions. This collaboration can lead to long-term partnerships that support growth and sustainability across various sectors, particularly in emerging markets in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe.
As the demand for high-quality materials continues to rise, now is the time to invest in strategic sourcing initiatives. By doing so, you position your business not just for immediate success but also for future resilience in a competitive global marketplace. Reach out to trusted suppliers today to explore the potential of cast carbon steel in your projects and set the stage for sustained growth.