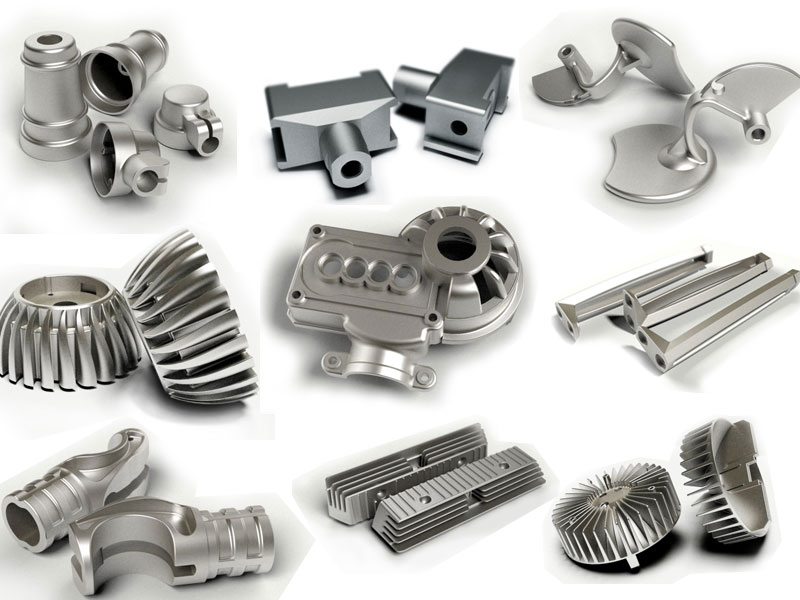
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for cast aluminum vs aluminum
In the competitive landscape of global sourcing, understanding the nuances between cast aluminum and aluminum is crucial for B2B buyers navigating diverse applications, from automotive components to outdoor furniture. This guide addresses the essential question: how do you choose between these two materials when sourcing products that meet your quality and cost expectations? Cast aluminum, known for its strength and intricate design capabilities, contrasts sharply with extruded aluminum, which offers lightweight versatility and cost-effectiveness.
This comprehensive resource delves into the various types of aluminum, their manufacturing processes, and the specific applications suited to each material. It also includes actionable insights on supplier vetting, cost considerations, and performance metrics to help you make informed purchasing decisions.
International buyers from regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe—including countries like Saudi Arabia and Germany—will find tailored recommendations that reflect regional market dynamics and procurement challenges. By leveraging the knowledge contained in this guide, you can enhance your sourcing strategies, ensuring that you select the right aluminum type for your business needs while optimizing both quality and cost efficiency.
Understanding cast aluminum vs aluminum Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Cast Aluminum | Solid structure, intricate designs, heavier weight | Automotive, aerospace, furniture | Pros: High durability, excellent design flexibility. Cons: Heavier, potentially higher shipping costs. |
| Extruded Aluminum | Hollow profiles, lightweight, customizable shapes | Construction, electronics, automotive parts | Pros: Lightweight, high strength-to-weight ratio. Cons: Limited design complexity compared to cast. |
| Die-Cast Aluminum | High precision, complex shapes, pressure-filled mold | Consumer products, automotive components | Pros: Excellent surface finish, efficient for high-volume production. Cons: Higher tooling costs, limited to smaller parts. |
| Sand-Cast Aluminum | Versatile, single-use molds, suitable for large parts | Industrial machinery, custom components | Pros: Cost-effective for low volumes, good for large components. Cons: Less precision, longer lead times. |
| Permanent Mold Aluminum | Reusable molds, good surface finish | High-volume production, automotive parts | Pros: Better mechanical properties, faster production. Cons: Higher initial investment in molds. |
What Are the Key Characteristics of Cast Aluminum for B2B Buyers?
Cast aluminum is renowned for its solid structure and ability to accommodate intricate designs, making it ideal for industries requiring durable, visually appealing components. Commonly used in automotive and aerospace applications, cast aluminum offers exceptional strength and weight efficiency. Buyers should consider the heavier weight of cast aluminum, which may influence shipping costs and logistics. However, its durability and design flexibility often justify these considerations, especially for high-end applications.
How Does Extruded Aluminum Differ in Suitability and Applications?
Extruded aluminum is characterized by its lightweight and customizable hollow profiles, making it a popular choice in construction and electronics. The extrusion process allows for the creation of complex shapes while maintaining a favorable strength-to-weight ratio. B2B buyers should prioritize extruded aluminum for projects requiring light structural components or intricate designs that need to be cost-effective. The trade-off is that extruded aluminum may not offer the same design complexity as cast aluminum, which could limit its applications in certain high-detail industries.
What Are the Advantages of Die-Cast Aluminum in Industrial Applications?
Die-cast aluminum is distinguished by its ability to produce high-precision components through a pressure-filling process. This method is particularly advantageous for consumer products and automotive parts, where a high-quality surface finish and dimensional accuracy are crucial. For B2B buyers, die-cast aluminum is efficient for high-volume production runs, though the initial tooling costs can be significant. Companies should assess their production needs to determine if the investment aligns with their long-term manufacturing goals.
Why Choose Sand-Cast Aluminum for Custom Components?
Sand-cast aluminum is versatile and well-suited for producing large, custom components, particularly in industrial machinery. The sand-casting process allows for low-volume production at a relatively low cost, making it an attractive option for businesses with specific needs. However, B2B buyers should note that sand-cast aluminum may not achieve the same precision as other methods, which can affect the performance of critical components. Lead times can also be longer, so planning is essential for timely project execution.
What Are the Benefits of Using Permanent Mold Aluminum in High-Volume Production?
Permanent mold aluminum combines the advantages of reusable molds with the ability to produce components with good mechanical properties and surface finishes. This method is particularly effective for high-volume production in the automotive sector. B2B buyers should consider permanent mold aluminum for projects that demand consistent quality and faster production rates. The initial investment in molds may be higher, but the long-term savings and efficiency gains can make it a worthwhile consideration for manufacturers looking to scale operations.
Key Industrial Applications of cast aluminum vs aluminum
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of cast aluminum vs aluminum | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Automotive | Engine components (e.g., cylinder heads, transmission cases) | Improved fuel efficiency and performance due to lightweight yet strong material | Ensure compliance with industry standards and specifications for safety and durability |
| Aerospace | Aircraft components (e.g., fuselage frames, landing gear) | Weight reduction leading to fuel savings and enhanced payload capacity | Look for suppliers with certifications for aerospace-grade materials |
| Construction | Structural elements (e.g., window frames, roofing) | Corrosion resistance and longevity reduce maintenance costs | Consider local regulations and climate impact on material choice |
| Electronics | Housings for electrical components and devices | Enhanced thermal conductivity and lightweight design improve device efficiency | Source from manufacturers with experience in electronic-grade aluminum |
| Furniture | Outdoor furniture (e.g., chairs, tables) | Aesthetic appeal combined with durability and weather resistance | Evaluate design options and customization capabilities for diverse markets |
How is Cast Aluminum Utilized in the Automotive Sector?
In the automotive industry, cast aluminum is extensively used for manufacturing engine components, such as cylinder heads and transmission cases. The casting process allows for complex shapes that contribute to weight reduction, ultimately enhancing fuel efficiency and vehicle performance. For international buyers, particularly in regions with stringent automotive regulations, sourcing cast aluminum requires ensuring compliance with safety standards and specifications. Additionally, selecting suppliers with a track record of quality can mitigate risks associated with defective components.
What Role Does Aluminum Play in Aerospace Applications?
In aerospace, cast aluminum is favored for its strength-to-weight ratio, which is crucial for components like fuselage frames and landing gear. The casting process enables the production of intricate designs that meet the rigorous demands of the industry. Buyers in the aerospace sector must prioritize suppliers who possess the necessary certifications for aerospace-grade materials, ensuring compliance with safety and performance standards. Furthermore, understanding the specific alloy compositions and their properties can aid in selecting the right materials for different applications.
Why is Aluminum Important for the Construction Industry?
Aluminum is increasingly utilized in the construction sector for structural elements such as window frames and roofing. Its inherent corrosion resistance and lightweight nature contribute to longer-lasting structures with reduced maintenance costs. For B2B buyers in Africa, South America, and the Middle East, it is essential to consider local regulations and environmental factors when sourcing aluminum. Engaging with suppliers who understand the regional climate can lead to better material choices that enhance durability and performance.
How is Aluminum Used in Electronics Manufacturing?
In the electronics industry, aluminum is commonly used for housings of electrical components and devices. Its lightweight properties and enhanced thermal conductivity improve device efficiency and performance. International buyers should focus on sourcing from manufacturers experienced in producing electronic-grade aluminum to ensure compatibility with various applications. Additionally, verifying the supplier’s quality assurance processes can help mitigate potential issues with material integrity.
What are the Benefits of Cast Aluminum in Outdoor Furniture?
Cast aluminum is a popular choice for outdoor furniture, combining aesthetic appeal with durability and resistance to weather elements. The casting process allows for intricate designs that enhance the visual appeal of outdoor spaces. For B2B buyers, especially those in regions with varying climates, evaluating design options and customization capabilities is crucial. Sourcing from manufacturers who can provide tailored solutions ensures that the furniture meets both functional and aesthetic requirements for diverse markets.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘cast aluminum vs aluminum’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Difficulty in Selecting the Right Aluminum Type for Specific Applications
The Problem: B2B buyers often struggle with the decision of whether to choose cast aluminum or hollow aluminum for their projects. This challenge can stem from a lack of understanding of the properties and applications of each type. For instance, a manufacturer in the automotive sector might be unsure whether to use cast aluminum for engine components due to its weight and strength characteristics, or hollow aluminum for weight-saving benefits. This indecision can lead to costly mistakes, delays in production, and potential performance issues in the final product.
The Solution: To navigate this challenge, buyers should conduct a thorough needs assessment that considers the specific requirements of their application, including strength, weight, and design complexity. Buyers can create a decision matrix that evaluates the key characteristics of cast versus hollow aluminum against their project specifications. For example, if intricate designs and high durability are paramount, cast aluminum might be the better choice. Conversely, if weight reduction is critical and the design is straightforward, hollow aluminum should be prioritized. Furthermore, collaborating with suppliers who can provide material samples and technical data sheets can enhance decision-making, ensuring that the selected aluminum type meets both performance and budgetary constraints.
Scenario 2: Misunderstanding Cost Implications of Different Aluminum Types
The Problem: Many B2B buyers mistakenly assume that cast aluminum is always more expensive due to its manufacturing process. This misconception can lead to over-budgeting for projects, as buyers may overlook the potential cost savings that hollow aluminum can provide, particularly in large-scale production. A construction company planning to use aluminum for window frames might choose cast aluminum solely based on perceived quality, resulting in significant overspending without realizing that hollow aluminum would have sufficed at a lower cost.
The Solution: Buyers should engage in a comprehensive cost analysis that factors in not just the initial material costs but also production volumes, potential waste, and long-term performance benefits. Requesting quotes from multiple suppliers for both types of aluminum can reveal surprising price differences. Additionally, buyers should consider lifecycle costs; hollow aluminum may be more cost-effective in terms of transport and installation due to its lighter weight, while cast aluminum may provide longevity and lower maintenance costs over time. By evaluating total cost of ownership rather than just upfront expenses, buyers can make more informed financial decisions.
Scenario 3: Challenges with Sourcing and Supply Chain Reliability
The Problem: B2B buyers often face significant challenges in sourcing either cast or hollow aluminum due to supply chain disruptions, especially in regions experiencing economic fluctuations or trade restrictions. For instance, a company in South America may find it increasingly difficult to secure a consistent supply of cast aluminum for manufacturing machinery parts, leading to production delays and missed deadlines. This unpredictability can strain relationships with clients and ultimately harm business reputation.
The Solution: To mitigate sourcing issues, buyers should diversify their supplier base and consider partnering with local manufacturers who can provide more reliable and timely deliveries. Establishing long-term contracts with suppliers can also ensure a steady supply of materials, reducing the risk of disruptions. Additionally, leveraging technology such as inventory management systems can help track material availability and forecast needs more accurately. This proactive approach not only enhances supply chain resilience but also fosters stronger relationships with suppliers, ultimately leading to a more streamlined production process.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for cast aluminum vs aluminum
What Are the Key Properties of Cast Aluminum and Aluminum?
When comparing cast aluminum and extruded aluminum, it’s essential to understand their distinct properties that influence product performance across various applications.
Cast Aluminum is created by pouring molten aluminum into molds, allowing for intricate designs and shapes. This process results in a material that boasts excellent strength-to-weight ratios, making it ideal for applications in automotive and aerospace industries. Cast aluminum also exhibits superior corrosion resistance, particularly beneficial in environments exposed to moisture and salt. Its ability to withstand high temperatures makes it suitable for parts like engine components.
Extruded Aluminum, on the other hand, is produced by forcing aluminum through a die to create specific shapes. This method yields a lightweight material that maintains good strength, especially when heat-treated. Extruded aluminum is often used in construction and manufacturing due to its versatility and ease of fabrication. However, it may not achieve the same level of detail in design as cast aluminum.
What Are the Pros and Cons of Each Material?
Pros and Cons of Cast Aluminum:
– Durability: Cast aluminum is robust and can withstand harsh conditions, making it ideal for outdoor furniture and heavy-duty applications.
– Cost-Effectiveness: While the initial investment may be higher due to the mold creation, the long-term benefits in durability and low maintenance costs can offset this.
– Manufacturing Complexity: The casting process can be complex and requires skilled labor, which may lead to longer lead times.
– End-Product Suitability: Best suited for applications requiring intricate designs and high strength.
Pros and Cons of Extruded Aluminum:
– Lightweight: Easier to handle and transport, making it suitable for applications where weight is a concern.
– Versatility: Can be easily machined and fabricated into various shapes, allowing for customization.
– Lower Initial Costs: Generally, the extrusion process is less expensive than casting, especially for large production runs.
– Design Limitations: While it can be shaped into many forms, it may lack the detailed designs achievable with cast aluminum.
How Do These Materials Impact Applications?
In terms of application impact, cast aluminum is often favored in industries where durability and design intricacy are paramount, such as automotive parts and decorative furniture. Its ability to resist corrosion and withstand high temperatures makes it particularly suitable for components exposed to extreme conditions.
Conversely, extruded aluminum is commonly used in construction, automotive, and consumer goods where lightweight and cost-effective solutions are needed. Its compatibility with various media, including chemicals and moisture, makes it a popular choice for a wide range of applications.
What Should International B2B Buyers Consider?
For international B2B buyers, particularly in regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, several considerations are crucial:
- Compliance and Standards: Familiarity with local and international standards (e.g., ASTM, DIN, JIS) is essential to ensure product quality and safety.
- Material Preferences: Different regions may have specific preferences based on climate and application needs. For example, buyers in coastal areas may prioritize corrosion resistance.
- Supply Chain Logistics: Understanding the manufacturing capabilities and lead times in different regions can help in planning and cost management.
- Cost Variability: Prices can fluctuate based on local market conditions, so it’s important to evaluate total cost of ownership rather than just initial purchase price.
Summary Table
| Material | Typical Use Case for cast aluminum vs aluminum | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cast Aluminum | Automotive components, decorative furniture | Excellent strength-to-weight ratio | Higher initial costs due to mold creation | Medium |
| Extruded Aluminum | Construction, consumer goods | Lightweight and versatile | Limited design detail compared to casting | Low |
| Cast Aluminum | Aerospace parts, high-temperature applications | Superior corrosion resistance | Complex manufacturing process | Medium |
| Extruded Aluminum | Electrical enclosures, frames | Easier to fabricate and machine | May not withstand extreme conditions | Low |
This analysis provides a comprehensive overview for B2B buyers, aiding in informed material selection based on specific project requirements and market conditions.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for cast aluminum vs aluminum
What Are the Main Manufacturing Processes for Cast Aluminum and Aluminum?
Understanding the manufacturing processes for cast aluminum and extruded aluminum is essential for B2B buyers looking to make informed decisions. Each process has its unique stages, techniques, and applications that can significantly impact the final product’s quality, cost, and suitability for specific industries.
How Is Cast Aluminum Manufactured?
The manufacturing process for cast aluminum typically involves several key stages:
-
Material Preparation:
– The initial step in producing cast aluminum involves selecting and preparing the appropriate aluminum alloy. This often includes melting aluminum scrap or ingots in a furnace until it reaches a molten state. -
Forming:
– Casting Techniques: The molten aluminum is poured into molds made from various materials such as sand, metal, or ceramic. Common casting methods include:- Sand Casting: A cost-effective method where sand molds are created and then discarded after use.
- Die Casting: Involves forcing molten aluminum into a steel mold under high pressure, allowing for high precision and repeatability.
- Permanent Mold Casting: Utilizes reusable metal molds to produce multiple parts, enhancing production efficiency.
-
Cooling and Solidification:
– Once the molten aluminum is poured into the mold, it is left to cool and solidify. This process can take anywhere from a few minutes to several hours, depending on the mold and part size. -
Finishing:
– After the aluminum has cooled, the cast pieces are removed from the molds. Finishing processes may include machining, sanding, or applying surface treatments to enhance appearance and performance. -
Assembly (if applicable):
– In certain applications, cast aluminum components may need to be assembled with other parts, requiring additional processes such as welding or fastening.
What Are the Key Techniques for Extruded Aluminum Manufacturing?
Extruded aluminum is produced using a different approach:
-
Material Preparation:
– Similar to cast aluminum, the process begins with selecting the appropriate aluminum alloy, which is then heated to a suitable temperature for extrusion. -
Extrusion:
– This process involves forcing the heated aluminum through a die, which shapes the aluminum into a continuous profile. The extrusion can be done in two ways:- Hot Extrusion: The aluminum is extruded while still hot, allowing for complex shapes and forms.
- Cold Extrusion: This method is used for less intricate shapes, typically at room temperature, resulting in higher strength and better surface finishes.
-
Cooling:
– After extrusion, the aluminum profiles are cooled, often using water or air, which helps to stabilize their shape. -
Cutting and Finishing:
– The extruded aluminum is cut to length and may undergo various finishing processes, including anodizing or painting, to enhance durability and aesthetics. -
Assembly (if needed):
– Extruded components may also be assembled into larger structures or products, depending on the application.
What Quality Assurance Standards Should B2B Buyers Consider?
Quality assurance is crucial in the manufacturing of aluminum products, and understanding the relevant international standards can help B2B buyers ensure that they are sourcing high-quality materials.
Which International Standards Are Relevant?
-
ISO 9001:
– This standard focuses on quality management systems and is widely recognized across industries. Compliance indicates that a manufacturer has met high-quality production standards. -
CE Marking:
– Particularly relevant in the European market, CE marking signifies that products meet EU safety, health, and environmental protection requirements. -
API Standards:
– For industries such as oil and gas, the American Petroleum Institute (API) provides specifications that ensure products meet rigorous quality and safety standards.
What Are the QC Checkpoints During Manufacturing?
Quality control is integral to the manufacturing process, with several key checkpoints to ensure product integrity:
-
Incoming Quality Control (IQC):
– Before production begins, raw materials are inspected to ensure they meet specified standards. This step prevents defects from entering the production line. -
In-Process Quality Control (IPQC):
– During manufacturing, periodic inspections are conducted to monitor various processes, ensuring that production parameters remain within acceptable limits. -
Final Quality Control (FQC):
– After manufacturing, finished products undergo thorough inspections and testing to confirm that they meet all quality and performance specifications.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control?
To ensure that suppliers adhere to stringent quality standards, B2B buyers can take several proactive steps:
-
Supplier Audits:
– Conducting regular audits of suppliers can help verify compliance with industry standards and assess their manufacturing processes. -
Quality Assurance Reports:
– Requesting detailed quality assurance reports can provide insights into the supplier’s QC practices and any certifications they hold. -
Third-Party Inspections:
– Engaging third-party inspection services can offer an unbiased evaluation of product quality and adherence to specifications.
What Are the Quality Control Nuances for International Buyers?
International B2B buyers, particularly from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, should be aware of several nuances in quality control:
-
Understanding Regional Standards:
– Different countries may have varying quality standards. Buyers should familiarize themselves with local regulations and certifications relevant to their market. -
Cultural Considerations:
– Communication styles and business practices may differ across regions. Building strong relationships and understanding local customs can enhance collaboration and quality assurance. -
Logistics and Supply Chain:
– International shipping can introduce risks related to product damage or discrepancies. Ensuring proper packaging and handling procedures are in place is vital for maintaining product integrity during transit.
By understanding the manufacturing processes and quality assurance standards for both cast aluminum and extruded aluminum, B2B buyers can make informed decisions that align with their project requirements and industry standards. This knowledge not only enhances product quality but also fosters strong supplier relationships and mitigates risks in the supply chain.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘cast aluminum vs aluminum’
Introduction
This sourcing guide provides a practical checklist for B2B buyers considering the procurement of cast aluminum or aluminum products. Understanding the nuances between these materials is essential for making informed purchasing decisions that can affect product performance, cost-efficiency, and overall satisfaction. This checklist will guide you through critical steps to ensure you select the right material and supplier for your specific needs.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Begin by outlining the specific requirements for your project, including dimensions, weight tolerance, and design complexity. Clearly defined specifications help in determining whether cast aluminum or extruded aluminum is more suitable for your application. Consider factors such as strength, durability, and aesthetic preferences, as these will influence your material choice.
Step 2: Assess Application Requirements
Evaluate the intended use of the aluminum products. Different applications may necessitate different properties. For instance, if weight reduction is critical for your project, hollow aluminum (extruded) might be preferable due to its strength-to-weight ratio. Conversely, if intricate designs and robust durability are paramount, cast aluminum would be more suitable.
Step 3: Evaluate Potential Suppliers
Before making a commitment, it’s crucial to vet suppliers thoroughly. Request company profiles, case studies, and references from buyers in similar industries or regions. Look for suppliers that have a proven track record in delivering high-quality aluminum products and can provide transparency in their manufacturing processes.
- Check Certifications: Ensure that potential suppliers hold relevant industry certifications, such as ISO or ASTM standards, which indicate their commitment to quality.
- Review Production Capabilities: Inquire about the supplier’s manufacturing techniques, as the method (e.g., sand casting vs. die casting) can significantly impact the product’s properties.
Step 4: Analyze Cost Structures
Understanding the cost implications of both cast aluminum and hollow aluminum is vital. While cast aluminum may have a higher upfront cost due to its complex manufacturing process, it may offer long-term savings through durability and lower maintenance. Request detailed quotations that break down material, labor, and shipping costs to make an informed comparison.
Step 5: Request Material Samples
Before finalizing your order, request samples of both cast aluminum and hollow aluminum. Physical samples allow you to assess the quality, finish, and weight firsthand. This step can be crucial in determining which material aligns best with your project specifications and aesthetic goals.
Step 6: Review Delivery and Lead Times
Understanding the supplier’s delivery capabilities is essential for project planning. Different manufacturing processes may have varying lead times. Confirm the expected delivery dates and ensure they align with your project timeline. This helps avoid costly delays and ensures that your supply chain remains uninterrupted.
Step 7: Implement Quality Control Measures
Once you’ve selected a supplier, establish quality control measures to monitor the production process and final products. This includes setting criteria for inspection and testing to ensure that the materials meet your specifications. Regular communication with your supplier during production can also help address any issues promptly, ensuring that the final product aligns with your expectations.
By following this checklist, B2B buyers can make informed decisions when procuring cast aluminum or aluminum products, ensuring alignment with their project goals and operational needs.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for cast aluminum vs aluminum Sourcing
Understanding the cost structure and pricing dynamics of cast aluminum versus extruded aluminum is essential for international B2B buyers, especially those operating in diverse markets such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. Below is a comprehensive analysis designed to help buyers navigate the complexities of sourcing these materials.
What Are the Key Cost Components for Cast Aluminum and Extruded Aluminum?
-
Materials: The primary cost driver in both cast and extruded aluminum is the raw aluminum itself. Prices can fluctuate based on global supply and demand, alloy specifications, and market conditions. Cast aluminum often requires higher-quality alloys to ensure durability and performance, which can increase costs.
-
Labor: Labor costs can vary significantly depending on the manufacturing process. Casting typically requires skilled labor for mold creation and pouring, leading to higher labor costs than extrusion, which can be more automated. For international buyers, understanding local labor rates is crucial.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes costs associated with running production facilities, such as utilities, maintenance, and facility depreciation. Cast aluminum production may incur higher overhead due to the complexity of the casting process.
-
Tooling: Tooling costs are significant for both processes. Cast aluminum requires molds, which can be expensive to create, particularly for intricate designs. In contrast, extrusion tooling is often more straightforward but still represents a significant upfront investment.
-
Quality Control (QC): Quality assurance measures are essential in both processes to ensure the final product meets specifications. However, cast aluminum may require more extensive QC due to the variability in casting quality.
-
Logistics: Shipping costs can vary based on the weight and volume of the product. Cast aluminum is generally heavier than extruded aluminum, leading to higher transportation costs. Additionally, international logistics can introduce complexities like tariffs and customs duties.
-
Margin: Suppliers will factor in their desired profit margin, which can vary widely based on market competition and the perceived value of the product. Cast aluminum often commands a premium price due to its durability and aesthetic appeal.
What Factors Influence Pricing for Cast Aluminum and Extruded Aluminum?
-
Volume/MOQ: Minimum order quantities (MOQ) can significantly impact pricing. Larger orders typically reduce per-unit costs due to economies of scale. Buyers should negotiate MOQs to achieve better pricing.
-
Specifications and Customization: Custom designs or specific alloy requirements can increase costs. Buyers should clearly communicate their needs to avoid unexpected expenses.
-
Quality and Certifications: Products that meet specific international standards or certifications may cost more. Buyers should weigh the importance of these certifications against their budget constraints.
-
Supplier Factors: The reputation and reliability of the supplier can influence price. Established suppliers may charge more due to their experience and quality assurance processes.
-
Incoterms: Understanding Incoterms (International Commercial Terms) is crucial for international transactions. They define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in the shipping process and can affect overall costs.
What Tips Can Help Buyers Optimize Costs in Sourcing Aluminum?
-
Negotiation: Engage suppliers in discussions about pricing, especially for large orders. Building a good relationship can lead to better terms and potential discounts.
-
Cost Efficiency: Consider the Total Cost of Ownership (TCO), which includes not just the purchase price but also maintenance, longevity, and performance. Cast aluminum may have a higher initial cost but can offer better durability and lower replacement rates.
-
Pricing Nuances for International Buyers: Buyers from regions like Africa and South America should be aware of currency fluctuations and regional economic conditions that can affect pricing. Additionally, understanding local market dynamics can provide leverage in negotiations.
-
Disclaimer on Prices: Prices for cast and extruded aluminum can vary widely based on numerous factors, including market conditions and supplier capabilities. Buyers should conduct thorough market research and obtain multiple quotes to ensure they are getting competitive pricing.
By considering these cost components and pricing influencers, B2B buyers can make informed decisions when sourcing cast aluminum and extruded aluminum, ultimately leading to better procurement strategies and enhanced operational efficiency.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing cast aluminum vs aluminum With Other Solutions
Understanding Alternatives to Cast Aluminum and Aluminum Solutions
When evaluating materials for various applications, particularly in B2B contexts, it’s essential to consider not just the primary options—cast aluminum and aluminum—but also viable alternatives. These alternatives may offer unique benefits or cater to specific needs that could enhance project outcomes, cost-efficiency, and overall performance. Below, we compare cast aluminum and aluminum with other potential solutions: stainless steel and carbon fiber composites.
| Comparison Aspect | Cast Aluminum Vs Aluminum | Stainless Steel | Carbon Fiber Composites |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | High strength-to-weight ratio; good corrosion resistance | Excellent strength; higher durability under stress | Superior strength-to-weight ratio; excellent fatigue resistance |
| Cost | Generally lower cost for mass production | Higher initial investment, but long-term durability can justify the price | High material cost; however, reduced maintenance can offset expenses |
| Ease of Implementation | Relatively easy to manufacture; versatile in design | Requires specialized welding and machining | Complex manufacturing process; requires skilled labor |
| Maintenance | Low maintenance; resistant to rust and corrosion | Moderate maintenance; can rust if not properly treated | Very low maintenance; resistant to environmental damage |
| Best Use Case | Ideal for intricate designs and furniture applications | Best for structural applications and environments exposed to high stress | Suitable for high-performance applications in aerospace and automotive industries |
In-Depth Analysis of Alternatives
Stainless Steel
Stainless steel is a robust alternative to cast aluminum and aluminum, particularly when high durability and corrosion resistance are required. Its strength makes it suitable for applications where structural integrity is paramount. However, stainless steel typically involves higher costs and requires specialized welding techniques, which can complicate implementation. While it can handle harsh environments, regular maintenance is necessary to prevent rusting, especially in coastal areas.
Carbon Fiber Composites
Carbon fiber composites represent a cutting-edge alternative that excels in terms of strength-to-weight ratio, making them ideal for high-performance applications in industries like aerospace and automotive. The lightweight nature of carbon fiber can significantly enhance fuel efficiency in transportation applications. However, the manufacturing process for carbon fiber is complex and costly, requiring specialized skills and equipment. Additionally, while maintenance is minimal, the initial investment can be a barrier for some businesses.
Making the Right Choice for Your B2B Needs
When selecting between cast aluminum, aluminum, and alternative materials, B2B buyers should assess their specific project requirements. Considerations such as performance needs, budget constraints, and the intended application environment are crucial. For example, if the project demands lightweight and high-strength materials, carbon fiber may be the best choice despite its higher cost. Conversely, for applications needing intricate designs with reasonable durability, cast aluminum could be the most cost-effective option. Ultimately, a thorough evaluation of each material’s properties and their alignment with project goals will guide buyers to the optimal solution.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for cast aluminum vs aluminum
What Are the Key Technical Properties of Cast Aluminum vs. Aluminum?
Understanding the technical properties of cast aluminum and aluminum is crucial for B2B buyers when selecting materials for various applications. Here are some essential specifications:
1. Material Grade
Material grade indicates the composition and quality of aluminum alloys used. Common grades for cast aluminum include A356 and A380, known for their excellent corrosion resistance and mechanical properties. For extruded aluminum, grades such as 6061 and 6063 are prevalent. Choosing the correct material grade affects the performance, durability, and cost of the final product, making it essential for buyers to align material specifications with project requirements.
2. Tolerance
Tolerance refers to the permissible limit of variation in a physical dimension of a part. In aluminum manufacturing, tighter tolerances (e.g., ±0.005 inches) are typically required for precision applications, such as aerospace components. Understanding tolerance specifications is critical for ensuring that parts fit together correctly and function as intended. Buyers should prioritize suppliers who can meet their tolerance requirements to avoid costly reworks or failures.
3. Density
Density, measured in grams per cubic centimeter (g/cm³), affects the weight and strength of aluminum products. Cast aluminum generally has a density of around 2.7 g/cm³, while hollow aluminum can be lighter due to its design. Knowing the density helps B2B buyers evaluate the structural integrity and weight efficiency of the materials, which is particularly important in industries such as automotive and aerospace.
4. Strength-to-Weight Ratio
This property is a measure of how much load a material can bear relative to its weight. Cast aluminum has a high strength-to-weight ratio, making it suitable for applications requiring lightweight yet strong components. For example, in automotive design, using materials with a favorable strength-to-weight ratio can lead to improved fuel efficiency and performance. Buyers should assess this ratio based on the intended use to optimize their products.
5. Corrosion Resistance
Both cast aluminum and aluminum exhibit excellent corrosion resistance, which is vital for applications exposed to harsh environments. However, cast aluminum often requires additional treatments to enhance this property further. Understanding the corrosion resistance of each type can influence material selection for outdoor or marine applications, where exposure to moisture and salt is common.
What Are Common Trade Terms Related to Cast Aluminum and Aluminum?
Familiarity with industry jargon is essential for effective communication in B2B transactions. Here are several key terms:
1. OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
OEM refers to companies that produce parts and equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer. In the context of aluminum products, an OEM may design and manufacture components for various industries, ensuring that specifications are met for quality and performance.
2. MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ is the smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell. Understanding MOQs helps buyers plan their purchasing strategies, especially when sourcing from international suppliers. Lower MOQs can be beneficial for smaller businesses or specific project needs.
3. RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a document issued by a buyer to solicit price bids from suppliers for specific products or services. This process allows companies to compare prices and select vendors based on their capabilities and cost-effectiveness, making it a crucial step in procurement.
4. Incoterms
Incoterms, or International Commercial Terms, are standardized trade terms used in international contracts. They define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers regarding shipping, insurance, and tariffs. Familiarity with Incoterms is critical for B2B buyers engaging in global trade, as they help clarify risk and responsibility during transportation.
5. Lead Time
Lead time refers to the amount of time it takes from placing an order to receiving the goods. Understanding lead times is essential for effective project planning and inventory management, particularly in industries where timing is critical.
By grasping these properties and terms, B2B buyers can make informed decisions, ensuring their projects are successful and cost-effective.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the cast aluminum vs aluminum Sector
What Are the Current Market Dynamics and Key Trends in the Cast Aluminum vs. Aluminum Sector?
The global aluminum market has seen significant evolution, driven by factors such as demand for lightweight materials in automotive and aerospace industries, sustainability initiatives, and technological advancements in manufacturing processes. In regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, international B2B buyers are increasingly focused on materials that offer both durability and efficiency. Cast aluminum, with its strength and ability to form intricate designs, is gaining traction in sectors requiring high-performance components, such as automotive and industrial machinery.
Emerging trends include the adoption of advanced manufacturing technologies, such as 3D printing and automation, which enhance the efficiency of aluminum production. Additionally, the shift toward digital procurement platforms is streamlining sourcing processes, enabling buyers to access a wider range of suppliers and materials. Buyers are also paying more attention to the total cost of ownership rather than just the initial purchase price, which includes considerations for maintenance and lifecycle sustainability.
As the market expands, so does the importance of global supply chain resilience. Recent disruptions have prompted companies to seek diversified sourcing strategies, ensuring a steady supply of both cast and extruded aluminum products. International buyers must stay attuned to regional market conditions, fluctuating raw material prices, and geopolitical factors that could impact supply chains.
How Is Sustainability and Ethical Sourcing Impacting the Cast Aluminum vs. Aluminum Market?
Sustainability is increasingly at the forefront of the aluminum industry, with both cast and extruded aluminum recognized for their lower environmental impact compared to other metals. Aluminum is inherently recyclable, which significantly reduces energy consumption in production. B2B buyers are prioritizing ethical sourcing, looking for suppliers that adhere to environmental regulations and promote responsible mining practices. This focus not only enhances brand reputation but also aligns with consumer expectations for sustainability.
The availability of certifications, such as LEED (Leadership in Energy and Environmental Design) and ISO 14001, is becoming crucial for buyers. These certifications demonstrate a commitment to environmental management and sustainable practices throughout the supply chain. Suppliers that can provide ‘green’ materials, including those made from recycled aluminum, are positioned favorably in the marketplace.
Moreover, the trend towards circular economy principles is influencing purchasing decisions. Companies are seeking to minimize waste and maximize resource efficiency, leading to increased demand for suppliers who can offer closed-loop recycling solutions. This shift not only supports environmental goals but also contributes to cost savings, making it an attractive option for international B2B buyers.
What Is the Evolution of the Cast Aluminum vs. Aluminum Market?
The evolution of the cast aluminum and aluminum sector can be traced back to the early 20th century, when the versatility of aluminum was first recognized in various applications. Initially, aluminum was primarily used in lightweight applications, but advancements in casting technology, such as die casting and sand casting, expanded its use significantly.
By the late 20th century, as industries like automotive and aerospace began to prioritize weight reduction and fuel efficiency, cast aluminum components became essential. The growth of extruded aluminum further diversified the market, allowing for a broader range of applications in construction, electronics, and consumer goods.
In recent years, the emphasis on sustainability has transformed the landscape, pushing manufacturers to innovate and adopt more eco-friendly practices. The integration of smart technologies in manufacturing processes continues to shape the future of the aluminum sector, ensuring that it remains competitive and aligned with global sustainability goals. For international B2B buyers, understanding this evolution is key to making informed sourcing decisions that align with both market trends and environmental responsibilities.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of cast aluminum vs aluminum
-
How do I solve the issue of choosing between cast aluminum and hollow aluminum for my project?
Choosing between cast aluminum and hollow aluminum depends on your project requirements. Cast aluminum is ideal for applications requiring durability and intricate designs, as its solid structure allows for detailed mold creation. Conversely, hollow aluminum is lightweight and easy to handle, making it suitable for projects where mobility and ease of installation are priorities. Evaluate your specific needs regarding weight, design complexity, and the environmental conditions the product will face to make an informed choice. -
What is the best application for cast aluminum versus hollow aluminum?
Cast aluminum is best suited for applications where structural integrity and aesthetic detail are essential, such as decorative furniture or automotive parts. It excels in environments requiring resistance to corrosion and weather elements. Hollow aluminum is preferable in applications needing a high strength-to-weight ratio, like lightweight furniture or modular structures. Consider the operational demands and visual requirements of your project to determine which type will serve you best. -
How can I vet suppliers for cast aluminum and hollow aluminum products?
When vetting suppliers, consider their industry reputation, certifications, and production capabilities. Request samples to assess quality and consistency. Engage in discussions about their manufacturing processes, lead times, and customization options. Additionally, check for client testimonials and case studies relevant to your sector. This due diligence will help ensure you partner with a reliable supplier who meets your specific needs. -
What customization options should I expect when sourcing cast aluminum and hollow aluminum?
Most suppliers offer various customization options, including size, shape, finish, and alloy specifications. For cast aluminum, you can often request intricate designs due to the nature of the casting process. Hollow aluminum can be customized in terms of extrusion profiles and surface treatments. Discuss your specific requirements with suppliers to understand what they can accommodate and any additional costs associated with customization. -
What are the typical minimum order quantities (MOQs) for cast aluminum and hollow aluminum products?
Minimum order quantities can vary widely depending on the supplier and the complexity of the product. Generally, cast aluminum products may have higher MOQs due to the costs associated with mold creation and production setup. Hollow aluminum typically has lower MOQs since extrusion processes can be more flexible. Always clarify MOQs upfront to align your purchasing strategy with your project needs and budget constraints. -
What payment terms should I expect when sourcing aluminum products internationally?
Payment terms can vary based on supplier policies and the nature of your agreement. Common terms include upfront deposits, payment upon delivery, or net terms (e.g., net 30, net 60). For international transactions, consider using secure payment methods such as letters of credit or escrow services to mitigate risks. Negotiate terms that are favorable for both parties and ensure clarity in the contract to avoid potential disputes. -
How do I ensure quality assurance (QA) in my aluminum products?
To ensure quality assurance, request detailed specifications and compliance certifications from your supplier. Implement a quality control plan that includes inspections at various production stages, from raw material sourcing to final product delivery. Consider third-party inspections if necessary, particularly for large orders or critical applications. Establish clear communication channels with your supplier to address any QA concerns promptly. -
What logistics considerations should I keep in mind when sourcing aluminum products internationally?
Logistics play a crucial role in international sourcing. Factor in shipping methods, costs, and transit times when planning your order. Understand the customs regulations in your country and the supplier’s country, as these can impact delivery schedules. Work with logistics partners experienced in handling international shipments to streamline the process. Additionally, confirm packaging standards to prevent damage during transportation and ensure compliance with international shipping regulations.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.
Top 9 Cast Aluminum Vs Aluminum Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. TFG USA – Cast Aluminum Solutions
Domain: tfgusa.com
Registered: 2008 (17 years)
Introduction: Cast aluminum is a lightweight, attractive metal used in a variety of products due to its strength, heat resistance, and affordability. It is created by heating aluminum to high temperatures, molding it into shapes, and cooling it. Common casting methods include die casting, sand casting, shell molds, permanent mold casting, ceramic molds, and plaster molds. Cast aluminum is widely used in cookwar…
2. Pioneer Family Pools – Aluminum Furniture Types
Domain: pioneerfamilypools.ca
Registered: 2000 (25 years)
Introduction: There are two types of aluminum furniture: Hollow (extruded) and Cast (solid). Hollow aluminum is shaped through a process called extrusion, resulting in lighter furniture that is easier to move but may dent or bend. Key quality differentiators include weight, support, powder-coating techniques, welding materials, and storage options. Cast aluminum is formed in molds, providing intricate designs a…
3. Howard Precision Metals – Cast and Wrought Aluminum Alloys
Domain: howardprecision.com
Registered: 1998 (27 years)
Introduction: Howard Precision Metals specializes in cast and wrought aluminum alloys. Key product details include: 1. Cast Aluminum Alloys: – Primary metal: Aluminum with alloying elements. – Characteristics: Low tensile strength, cost-efficient, good fluidity, low melting point, ability to control grain structure, good surface finish. – Negative aspects: Susceptible to shrinkage, low ductility, vulnerable to …
4. Cast Aluminum – CNC Parts Advantages
Domain: reddit.com
Registered: 2005 (20 years)
Introduction: Cast aluminum is being considered for CNC parts due to its advantages over 6061-T6 aluminum. Key details include: 1. Thickness tolerance of +-0.005″ which eliminates the need for additional machining. 2. Certain cast plate variants like Alca 5, K100-S, and ATP-5 have good anodizing properties despite common belief that cast aluminum cannot be anodized. 3. Pricing is comparable to 6061. 4. While 60…
5. Wonderffle – Cast Iron vs. Cast Aluminum Cookware
Domain: wonderffle.com
Registered: 2015 (10 years)
Introduction: Cast Iron: Durable, excellent heat retention, ideal for high-heat cooking, requires seasoning, heavy, can rust if not maintained. Cast Aluminum: Lightweight, good heat conductivity, often non-stick, easier to handle, may warp at high temperatures, generally less expensive.
6. Aluminum – Key Properties and Applications
Domain: linkedin.com
Registered: 2002 (23 years)
Introduction: Aluminum:
– Properties: High ductility, high strength-to-weight ratio, high corrosion resistance.
– Applications: Automotive, aerospace, marine industries.
– Pros:
– Low weight due to low density.
– Natural corrosion resistance, enhanced by anodizing.
– Good electrical conductivity, alternative to copper.
– High strength-to-weight ratio.
– Cons:
– Difficult to weld due to low melting …
7. Gabrian – Die Casting Solutions
Domain: gabrian.com
Registered: 2000 (25 years)
Introduction: Die Casting: 1. Process: Melting aluminum ingots, injecting into a die mold, solidifying. 2. Capable of complex geometries and larger products. 3. Generally not as strong as extruded products. 4. Potential for porosity. 5. Rough surface finish with seams. 6. High cost and time-consuming mold creation. 7. More expensive, suited for higher production runs.
Extrusion: 1. Process: Forcing heated alu…
8. The Piping Mart – Cast Aluminium Products
Domain: blog.thepipingmart.com
Registered: 2022 (3 years)
Introduction: Cast Aluminium: Made by pouring molten aluminium into a mould, resulting in strong and durable products with intricate designs. Ideal for applications like boat propellers and engine blocks due to its lightweight and corrosion-resistant properties. Aluminium: A naturally occurring metal, lightweight and corrosion-resistant, used in various applications. Cast aluminium is created by casting molten …
9. Eng-Tips – Cast 7075-T6 Aluminum Alloys Explained
Domain: eng-tips.com
Registered: 1997 (28 years)
Introduction: The discussion revolves around the properties and classifications of cast versus wrought aluminum alloys, specifically focusing on the ‘cast 7075-T6 aluminum.’ Key points include: 1. Cast aluminum alloys typically have designations like ‘AXX.Y,’ while wrought alloys use designations such as ‘2XXX’ or ‘3XXX,’ with ‘T-some number’ indicating heat treatment. 2. The term ‘cast 7075-T6’ may imply a cas…
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for cast aluminum vs aluminum
In the competitive landscape of international sourcing, understanding the distinctions between cast aluminum and hollow aluminum is essential for making informed purchasing decisions. Cast aluminum excels in durability and design flexibility, making it ideal for applications where strength and intricate aesthetics are paramount, such as in automotive or high-end furniture. Conversely, hollow aluminum offers a remarkable strength-to-weight ratio and cost-effectiveness, appealing to industries that prioritize lightweight components and sustainable practices.
Strategic sourcing is not merely a procurement process; it is a critical approach that can enhance your product offerings and operational efficiency. By aligning your sourcing strategy with the unique properties of each aluminum type, you can optimize costs while maintaining quality.
As you navigate the complexities of global supply chains, particularly in regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, consider leveraging local partnerships and innovative manufacturing processes to capitalize on the strengths of both materials. Embrace the opportunity to enhance your product portfolio and drive sustainable growth. The future of your sourcing strategy is not just about materials; it’s about making strategic choices that position your business for success in an evolving marketplace.