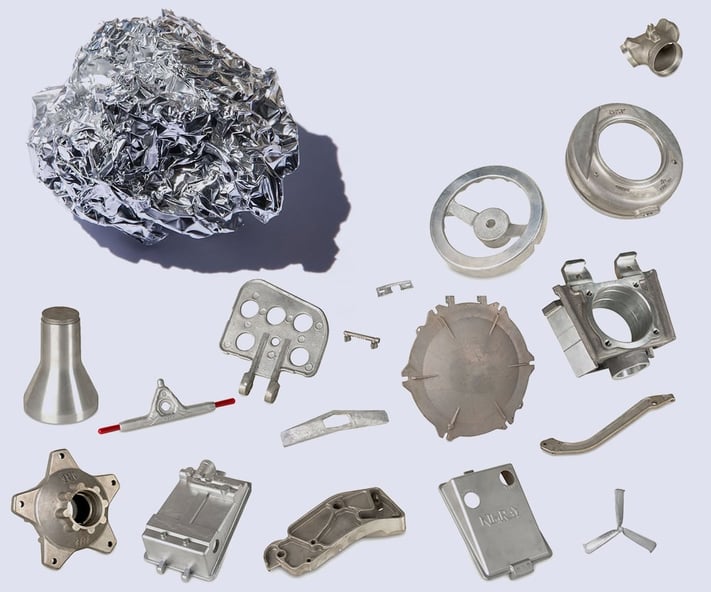
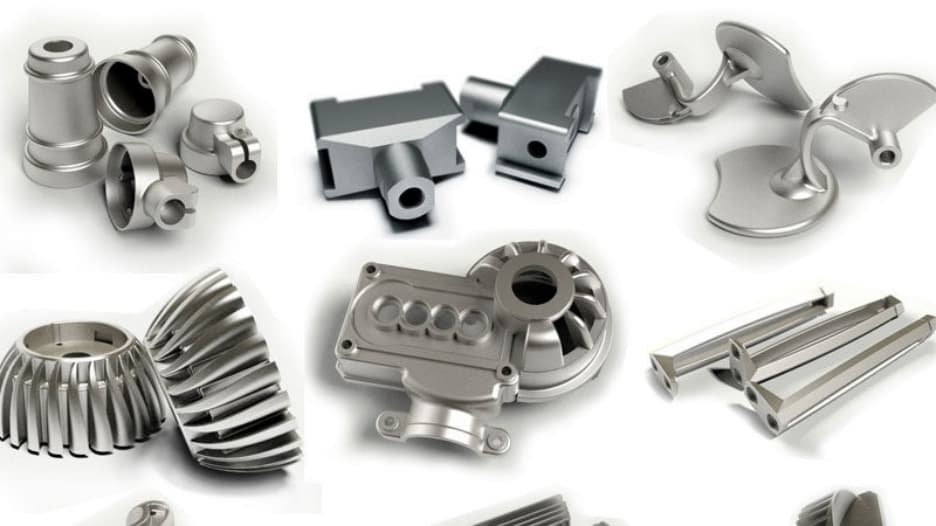
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for cast aluminum parts
Navigating the global market for cast aluminum parts presents a unique set of challenges for B2B buyers, especially when sourcing components that meet stringent quality and performance standards. With its lightweight properties, exceptional corrosion resistance, and versatility in design, cast aluminum is increasingly favored across various industries, from automotive to aerospace. However, identifying reliable suppliers, understanding the nuances of different casting processes, and evaluating the cost implications can complicate the purchasing process.
This guide provides a comprehensive overview of cast aluminum parts, detailing the various types and applications, the intricacies of supplier vetting, and strategies for optimizing cost-effectiveness. We explore the distinctions between casting methods such as die casting, sand casting, and permanent mold casting, empowering buyers to make informed decisions based on their specific project requirements. Additionally, the guide addresses market trends, regional considerations, and the importance of aligning with suppliers who adhere to international quality standards.
For international B2B buyers from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe—such as Nigeria and Brazil—this resource serves as a crucial tool. By equipping you with the knowledge to navigate the complexities of sourcing cast aluminum parts, this guide enables you to enhance your procurement strategies, reduce risks, and ultimately drive your business success in a competitive global marketplace.
Understanding cast aluminum parts Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Die Cast Aluminum Parts | High pressure injection into molds, excellent surface finish | Automotive, electronics, aerospace | Pros: High precision, good mechanical properties. Cons: Initial tooling costs can be high. |
| Sand Cast Aluminum Parts | Mold made from sand, lower dimensional accuracy | Construction, machinery, art | Pros: Cost-effective for low volume. Cons: Rough surface finish, requires post-processing. |
| Permanent Mold Cast Parts | Gravity-fed casting, better dimensional accuracy | Automotive, industrial components | Pros: Good surface finish, strong parts. Cons: Limited to lower complexity designs. |
| Investment Cast Parts | Uses a wax pattern for intricate shapes | Aerospace, medical devices | Pros: High precision, complex geometries. Cons: Longer lead times, higher costs. |
| Low-Pressure Cast Parts | Molten aluminum introduced under low pressure | Plumbing, HVAC, consumer products | Pros: Reduced porosity, good mechanical properties. Cons: Slower production rates. |
What Are the Characteristics of Die Cast Aluminum Parts?
Die cast aluminum parts are produced using a high-pressure injection process, which allows for high precision and excellent surface finishes. This method is particularly suited for mass production, making it ideal for industries like automotive and aerospace. Buyers should consider the initial tooling costs, which can be significant, but the long-term benefits of durability and consistency often justify the investment.
How Do Sand Cast Aluminum Parts Differ?
Sand cast aluminum parts are made using sand molds, which can accommodate large and complex shapes. This method is cost-effective for low-volume production runs, making it popular in construction and machinery applications. However, buyers should be aware that sand casting results in lower dimensional accuracy and a rougher surface finish, often necessitating additional post-processing to meet specific requirements.
What Are the Benefits of Permanent Mold Cast Parts?
Permanent mold cast parts are produced using gravity to fill molds, resulting in better dimensional accuracy and a smoother finish compared to sand casting. This method is effective for producing medium to high volumes of parts, particularly in the automotive and industrial sectors. While it allows for more complex designs than some methods, it is generally limited to less intricate geometries.
Why Choose Investment Cast Parts?
Investment casting, also known as lost-wax casting, is ideal for creating intricate shapes and fine details. This method is frequently employed in the aerospace and medical device industries where precision is paramount. While investment casting offers high accuracy, buyers should consider the longer lead times and higher costs associated with this method, making it more suitable for specialized applications.
What Are the Advantages of Low-Pressure Cast Parts?
Low-pressure cast parts involve introducing molten aluminum into molds under low pressure, which helps to reduce porosity and improve mechanical properties. This technique is commonly used in plumbing and HVAC applications due to its reliability and efficiency. While it offers quality results, the production rates may be slower compared to other casting methods, which could impact time-sensitive projects.
Key Industrial Applications of cast aluminum parts
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of cast aluminum parts | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Aerospace | Aircraft components (e.g., brackets, housings) | Lightweight yet strong parts enhance fuel efficiency | Certification standards (e.g., AS9100), precision manufacturing capabilities |
| Automotive | Engine blocks and transmission cases | Improved performance and reduced weight lead to better fuel economy | Alloy specifications, heat treatment processes, and quality control measures |
| Industrial Machinery | Gearboxes and pumps | Enhanced durability and corrosion resistance ensure longer service life | Customization options, lead times, and post-processing capabilities |
| Consumer Electronics | Chassis and housings for electronic devices | Lightweight design improves portability and aesthetics | Surface finish options, thermal management properties, and cost-effectiveness |
| Energy Sector | Heat exchangers and turbine components | High thermal conductivity and resistance to corrosion optimize performance | Compliance with industry standards, alloy selection, and fabrication techniques |
How Are Cast Aluminum Parts Utilized in Aerospace Applications?
In the aerospace industry, cast aluminum parts are pivotal for manufacturing components such as brackets and housings that require a combination of strength and lightweight properties. These parts contribute to the overall fuel efficiency of aircraft, addressing the industry’s need for performance without compromising safety. Buyers in this sector must prioritize suppliers who meet stringent certification standards, such as AS9100, and can demonstrate precision manufacturing capabilities to ensure the reliability of critical components.
What Role Do Cast Aluminum Parts Play in the Automotive Sector?
Within the automotive sector, cast aluminum is commonly used for engine blocks and transmission cases. The lightweight nature of these parts directly translates to improved vehicle performance and enhanced fuel economy, which are crucial for competitive advantage. International buyers should focus on sourcing partners who can provide specific alloy specifications and robust heat treatment processes, ensuring that the components meet the demanding operational requirements of modern vehicles.
How Are Cast Aluminum Parts Beneficial for Industrial Machinery?
In industrial machinery, cast aluminum parts like gearboxes and pumps are favored for their durability and corrosion resistance. These properties ensure a longer service life and lower maintenance costs, which are significant factors for businesses looking to optimize operational efficiency. When sourcing these components, buyers should consider customization options and lead times, as well as the supplier’s ability to provide post-processing capabilities that may be necessary for their specific applications.
In What Ways Are Cast Aluminum Parts Used in Consumer Electronics?
Cast aluminum parts are increasingly utilized in consumer electronics, particularly for chassis and housings. Their lightweight design not only enhances portability but also contributes to the overall aesthetics of devices. For international buyers, it is essential to evaluate suppliers based on their surface finish options and thermal management properties, as these factors can significantly affect the performance and marketability of electronic products.
Why Are Cast Aluminum Parts Important in the Energy Sector?
In the energy sector, cast aluminum parts find applications in heat exchangers and turbine components due to their high thermal conductivity and corrosion resistance. These properties are essential for optimizing performance in demanding environments. Buyers in this sector must ensure that their sourcing partners comply with industry standards and can offer the right alloy selection and fabrication techniques to meet the unique challenges of energy applications.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘cast aluminum parts’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Quality Control Issues in Cast Aluminum Parts
The Problem: A common challenge faced by B2B buyers of cast aluminum parts is ensuring consistent quality across batches. Variability in casting processes, such as porosity or surface defects, can lead to significant issues in the final product, impacting performance and longevity. This inconsistency can result in increased rework or returns, jeopardizing project timelines and budget constraints. Buyers often feel frustrated when their suppliers do not meet the expected standards, leading to a breakdown in trust and reliability.
The Solution: To mitigate quality control issues, buyers should prioritize working with manufacturers that adhere to rigorous quality management systems (QMS) like ISO 9001. Before placing orders, conduct thorough supplier audits to evaluate their casting processes and quality assurance practices. Request samples from previous batches to assess dimensional accuracy and surface finish. Additionally, consider implementing a detailed quality checklist that includes parameters such as porosity levels, tensile strength, and surface roughness. Establish clear communication channels with your supplier to address concerns immediately and collaboratively refine production techniques as necessary.
Scenario 2: Difficulty in Selecting the Right Aluminum Alloy
The Problem: B2B buyers frequently struggle with selecting the appropriate aluminum alloy for their specific application. Each alloy has distinct properties, such as tensile strength, corrosion resistance, and thermal conductivity, which can significantly affect the performance of the final product. Making the wrong choice can lead to product failures or suboptimal performance, resulting in costly repairs or replacements. This dilemma is particularly pronounced in industries such as automotive or aerospace, where precise specifications are critical.
The Solution: To streamline the alloy selection process, buyers should invest time in understanding the specific requirements of their application. Collaborate closely with engineers or technical experts to define critical performance metrics, such as load-bearing capacity and environmental exposure. Utilize tools like alloy property databases or consult with suppliers who specialize in aluminum casting to gain insights into the best alloy choices for your needs. Additionally, consider running small-scale tests or prototypes using different alloys to evaluate performance before committing to larger production runs. This hands-on approach will help ensure the chosen alloy meets both performance and cost-effectiveness criteria.
Scenario 3: Challenges with Post-Processing and Machining
The Problem: Many buyers encounter difficulties with post-processing cast aluminum parts, which may require additional machining or finishing to achieve desired tolerances and surface finishes. This step can be resource-intensive and may lead to delays if not managed effectively. Buyers often find themselves frustrated when they discover that cast parts require more machining than initially anticipated, driving up costs and extending lead times.
The Solution: To address post-processing challenges, buyers should engage in early discussions with their suppliers about the expected tolerances and finishing requirements. When designing parts, incorporate features that minimize the need for extensive machining, such as adding generous fillets or avoiding sharp corners that complicate machining. Moreover, consider leveraging advanced casting techniques like die casting or permanent mold casting, which can yield parts with higher precision and better surface finishes right out of the mold. Lastly, establish a clear process for post-casting inspection and machining, including selecting a reliable machining partner experienced in working with cast aluminum. This proactive approach will enhance overall efficiency and reduce the likelihood of unexpected costs or delays.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for cast aluminum parts
What Are the Key Properties of Common Materials for Cast Aluminum Parts?
When selecting materials for cast aluminum parts, it is essential to consider the specific properties that influence performance in various applications. The most common materials used in casting aluminum parts include A356, A380, and A413 alloys, each with unique characteristics that cater to different industrial needs.
A356 Aluminum Alloy: What Makes It a Popular Choice?
A356 aluminum alloy is renowned for its excellent corrosion resistance and good mechanical properties. It has a temperature rating that allows it to perform well in moderately high-temperature applications, making it suitable for automotive and aerospace components. The alloy’s good casting fluidity enhances its ability to fill intricate molds, which is crucial for complex designs.
Pros: A356 offers high strength-to-weight ratios and good weldability, making it versatile for various applications. Its resistance to corrosion extends the lifespan of parts, particularly in harsh environments.
Cons: The primary limitation of A356 is its relatively higher cost compared to other aluminum alloys. Additionally, while it performs well under moderate temperatures, it may not be suitable for extremely high-temperature applications.
Impact on Application: A356 is ideal for parts exposed to moisture and corrosive environments, such as marine and automotive components. Its compatibility with various media makes it a preferred choice in these sectors.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers from regions like Africa and South America should ensure compliance with local standards, such as ASTM and ISO certifications, to guarantee quality and performance.
A380 Aluminum Alloy: Why Is It Favored for High-Volume Production?
A380 aluminum alloy is widely used in die casting due to its excellent fluidity and ability to produce intricate shapes with high dimensional accuracy. It has a good balance of strength and ductility, making it suitable for applications requiring complex geometries.
Pros: The primary advantage of A380 is its cost-effectiveness in high-volume production. It also exhibits good corrosion resistance and is suitable for a wide range of applications, including automotive parts and consumer electronics.
Cons: A380 has a lower tensile strength compared to A356, which may limit its use in high-stress applications. Additionally, its susceptibility to porosity can affect the integrity of the final product if not properly managed.
Impact on Application: A380 is ideal for components that require high production rates and complex shapes, such as housings and brackets in automotive and electronic devices.
Considerations for International Buyers: B2B buyers should be aware of the specific alloy grades and their certifications to ensure compliance with international standards, particularly in Europe and the Middle East.
A413 Aluminum Alloy: What Are Its Unique Benefits?
A413 aluminum alloy is characterized by its excellent casting characteristics and high corrosion resistance. It is often used in applications requiring good thermal conductivity, such as heat exchangers and electrical components.
Pros: The primary benefit of A413 is its ability to maintain dimensional stability during the casting process. Its high fluidity allows for the production of thin-walled sections, making it suitable for lightweight applications.
Cons: A413 is more expensive than A356 and A380, which can impact cost-sensitive projects. Additionally, its mechanical properties may not be as robust as those of other alloys, limiting its use in high-stress environments.
Impact on Application: A413 is particularly well-suited for applications in the aerospace and electronics sectors, where thermal management is critical.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should consider the availability of A413 in their local markets and ensure that suppliers can meet international quality standards, especially in regions with stringent regulations.
Summary Table of Common Materials for Cast Aluminum Parts
| Material | Typical Use Case for cast aluminum parts | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| A356 Aluminum Alloy | Automotive and aerospace components | Excellent corrosion resistance | Higher cost compared to other alloys | Medium |
| A380 Aluminum Alloy | High-volume production parts | Cost-effective for mass production | Lower tensile strength; susceptible to porosity | Low |
| A413 Aluminum Alloy | Heat exchangers and electrical components | High fluidity for thin-walled sections | More expensive; limited mechanical properties | High |
This strategic material selection guide provides international B2B buyers with essential insights into the properties, advantages, and limitations of common materials used for cast aluminum parts, enabling informed decision-making tailored to specific application needs.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for cast aluminum parts
What Are the Main Stages of Manufacturing Cast Aluminum Parts?
The manufacturing process for cast aluminum parts is intricate and consists of several key stages. Understanding these stages is crucial for B2B buyers who need to ensure that they are sourcing high-quality components.
Material Preparation: How Is Aluminum Prepared for Casting?
The first step in the manufacturing process is the preparation of aluminum materials. This involves selecting the appropriate aluminum alloy based on the desired properties of the final product, such as tensile strength, ductility, and corrosion resistance. The aluminum is then melted in a furnace, where temperature control is vital to prevent contamination and ensure uniformity.
Prior to pouring, the molten aluminum may undergo degassing to remove impurities and minimize porosity, a common defect in castings. Effective material preparation sets the foundation for a successful casting process, ensuring that the final product meets the necessary quality standards.
Forming: What Techniques Are Used to Shape Cast Aluminum Parts?
Once the aluminum is prepared, the next stage is forming, where the molten metal is poured into a mold. There are several casting techniques, each with its own advantages:
-
Die Casting: This is the most widely used method for high-volume production. In this technique, molten aluminum is injected under high pressure into a pre-made die. The result is a part with excellent surface finish and dimensional accuracy, making it suitable for industries like automotive and aerospace.
-
Sand Casting: In this more traditional method, a sand mold is created, into which the molten aluminum is poured. While sand casting is versatile and cost-effective for low-volume production, it typically results in a rough surface finish and may require post-processing.
-
Permanent Mold Casting: This method uses reusable molds, allowing for better surface quality and dimensional accuracy compared to sand casting. Gravity is used to fill the mold, which can lead to less turbulence and porosity issues.
Each of these techniques has its own applications and suitability based on the complexity and volume of the parts being produced.
Assembly: How Are Cast Aluminum Parts Assembled?
In many cases, cast aluminum parts may need to be assembled with other components to form a final product. This can involve machining processes such as CNC milling or drilling to achieve precise dimensions and fit. Depending on the complexity, assembly may also require welding or fastening methods. Proper assembly is critical for the functionality and longevity of the final product, making it essential for manufacturers to adhere to stringent quality practices.
Finishing: What Are the Common Finishing Techniques for Cast Aluminum Parts?
Finishing processes enhance the aesthetic and functional properties of cast aluminum parts. Techniques such as anodizing, powder coating, and painting not only improve the appearance but also add a layer of protection against corrosion. Polishing and machining may also be applied to achieve tighter tolerances and smoother surfaces. The choice of finishing technique often depends on the application and environmental conditions the parts will face.
How Is Quality Assurance Implemented in the Manufacturing of Cast Aluminum Parts?
Quality assurance (QA) is critical in the manufacturing of cast aluminum parts, ensuring that products meet international standards and customer specifications.
What International Standards Should B2B Buyers Be Aware Of?
International standards such as ISO 9001 are essential for maintaining quality management systems. These standards provide a framework for manufacturers to ensure consistent quality in their processes. For specific industries, additional certifications like CE (Conformité Européenne) for European markets or API (American Petroleum Institute) for oil and gas applications may be required. B2B buyers should verify that their suppliers are compliant with these standards to ensure product reliability.
What Are the Key Quality Control Checkpoints?
Quality control checkpoints are integrated throughout the manufacturing process to identify and rectify issues early. The primary checkpoints include:
-
Incoming Quality Control (IQC): This involves inspecting raw materials before they enter the production line. Ensuring that materials meet specifications prevents defects in the final product.
-
In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): During manufacturing, various checks are conducted to monitor the process parameters and part dimensions. This stage is crucial for catching defects before they become larger issues.
-
Final Quality Control (FQC): After the parts are produced, a thorough inspection is conducted to ensure they meet the required specifications. This may include dimensional checks, visual inspections, and performance testing.
What Common Testing Methods Are Used in Quality Control?
To guarantee the integrity of cast aluminum parts, several testing methods are commonly employed:
-
Non-Destructive Testing (NDT): Techniques such as ultrasonic testing, X-ray inspection, and dye penetrant testing help identify internal defects without damaging the parts.
-
Mechanical Testing: Tensile strength, hardness, and impact tests are performed to verify that the material properties meet the specified standards.
-
Visual Inspection: A thorough visual examination is conducted to check for surface defects, such as cracks or porosity, that could affect performance.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control Practices?
B2B buyers must take proactive steps to ensure their suppliers maintain robust quality control systems. Here are some strategies:
-
Supplier Audits: Conducting on-site audits allows buyers to evaluate the supplier’s manufacturing processes, quality control systems, and compliance with international standards.
-
Requesting Quality Reports: Suppliers should provide documentation of their quality control processes, including inspection reports and certifications. This transparency is critical for building trust.
-
Engaging Third-Party Inspectors: Utilizing independent inspection services can provide an unbiased assessment of the supplier’s quality practices and the products being manufactured.
What Nuances Should International B2B Buyers Consider Regarding Quality Control?
International buyers, particularly from regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, should be aware of potential challenges in verifying quality standards. Differences in regulations, cultural practices, and market expectations can influence supplier performance. Therefore, it is vital to establish clear communication regarding quality expectations and to be familiar with the specific regulations applicable in the supplier’s country.
Additionally, understanding local market dynamics can provide insights into the reliability and reputation of suppliers. Engaging with local trade associations or industry networks can also aid in gathering valuable information about potential partners.
In conclusion, by comprehensively understanding the manufacturing processes and quality assurance measures in the production of cast aluminum parts, B2B buyers can make informed decisions, ensuring they source high-quality components that meet their specific needs.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘cast aluminum parts’
To effectively source cast aluminum parts, B2B buyers must follow a structured approach that ensures the procurement of high-quality components that meet their specific needs. This checklist provides a clear, actionable framework for navigating the sourcing process.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Before initiating your search for suppliers, clearly outline the technical specifications of the cast aluminum parts you require. This includes dimensions, weight, alloy type, and any special requirements such as surface finishes or heat treatments. Well-defined specifications help in communicating your needs and ensuring that potential suppliers can meet your requirements.
- Consider: The intended application of the parts and any industry standards they must comply with.
- Document: Create detailed drawings or CAD models to facilitate discussions with suppliers.
Step 2: Research Potential Suppliers
Conduct thorough research to identify suppliers with a proven track record in manufacturing cast aluminum parts. Look for companies that specialize in the specific casting process relevant to your needs, whether it’s die casting, sand casting, or permanent mold casting.
- Utilize: Online directories, industry associations, and trade shows to gather a list of potential suppliers.
- Assess: Consider factors such as location, production capabilities, and industry experience.
Step 3: Evaluate Supplier Certifications
Before moving forward, verify that potential suppliers hold relevant certifications, such as ISO 9001 for quality management or specific industry-related certifications. These certifications indicate a commitment to quality and adherence to international standards.
- Inquire about: Their quality control processes and the testing methods they use for their cast aluminum parts.
- Review: Any additional certifications that may be relevant to your industry, such as automotive or aerospace standards.
Step 4: Request Samples and Prototypes
To assess the quality of a supplier’s products, request samples or prototypes of their cast aluminum parts. This step is crucial for evaluating the supplier’s manufacturing capabilities and the suitability of their products for your application.
- Evaluate: The physical properties, finish, and dimensional accuracy of the samples.
- Test: If possible, subject the samples to performance testing relevant to your application.
Step 5: Discuss Lead Times and Pricing
Once you have shortlisted suppliers, engage them in discussions about lead times and pricing structures. Understanding the production timeline is essential to ensure that the supplier can meet your project deadlines.
- Negotiate: Be clear about your budget constraints and explore options for bulk pricing or long-term contracts if applicable.
- Consider: The total cost of ownership, including shipping and any potential tariffs, especially if sourcing internationally.
Step 6: Check References and Past Performance
Before finalizing your supplier choice, check references from other clients, particularly those in similar industries or regions. This step provides insight into the supplier’s reliability, product quality, and customer service.
- Ask for: Case studies or testimonials that highlight their experience with similar projects.
- Evaluate: Any feedback regarding delivery performance and responsiveness to issues.
Step 7: Finalize Contractual Agreements
Once you have selected a supplier, finalize the contractual agreements, ensuring that all terms regarding quality, delivery, and payment are clearly articulated. This agreement should also include terms for handling defects or quality issues that may arise post-delivery.
- Include: Clear specifications for penalties or remedies in case of non-compliance.
- Review: Ensure that both parties have a mutual understanding of the terms to avoid future disputes.
By following this checklist, B2B buyers can streamline their sourcing process for cast aluminum parts, ensuring they partner with reliable suppliers who can deliver high-quality components tailored to their specific needs.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for cast aluminum parts Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components in Sourcing Cast Aluminum Parts?
When considering the sourcing of cast aluminum parts, it’s essential to break down the cost structure into key components. These include:
-
Materials: The primary cost driver in cast aluminum parts is the raw materials. Aluminum alloys, which are often used for casting, can vary significantly in price based on market conditions and alloy specifications. Special alloys may incur additional costs due to their unique properties.
-
Labor: Labor costs encompass the workforce required for the casting process, including skilled labor for operating machinery and quality control personnel. Labor costs can fluctuate based on the region, with countries in Africa and South America often facing different wage structures compared to Europe or the Middle East.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes costs associated with utilities, equipment maintenance, and facility management. Efficient manufacturing processes and advanced technologies can reduce overhead costs, impacting overall pricing.
-
Tooling: Tooling costs are critical, especially for processes like die casting, where molds can be expensive to produce. The complexity of the design and the number of parts produced can significantly influence tooling costs.
-
Quality Control (QC): Ensuring that cast aluminum parts meet specific standards requires rigorous quality control processes. This includes testing for porosity, dimensional accuracy, and compliance with industry certifications. Investment in quality assurance can elevate costs but is essential for maintaining product integrity.
-
Logistics: Shipping and handling costs are vital, particularly for international transactions. Factors such as distance, freight method, and Incoterms (International Commercial Terms) can significantly impact logistics expenses.
-
Margin: Suppliers typically add a margin to cover their operational costs and profit. This margin can vary based on supplier reputation, market demand, and the level of customization required by the buyer.
How Do Price Influencers Affect the Cost of Cast Aluminum Parts?
Several factors influence the pricing of cast aluminum parts, and understanding these can help buyers make informed decisions:
-
Volume/MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity): Larger orders often lead to reduced prices per unit due to economies of scale. Buyers should consider their needs and negotiate for better pricing on larger quantities.
-
Specifications and Customization: Custom parts often incur higher costs due to the additional labor and tooling required. Standardized designs can help keep costs down.
-
Materials and Quality Certifications: The choice of materials significantly affects pricing. Higher-grade alloys or those with specific certifications may command premium prices. Buyers should balance cost with the necessary quality standards.
-
Supplier Factors: The reputation and reliability of the supplier can influence pricing. Established suppliers may charge more due to their proven track record in quality and delivery.
-
Incoterms: Understanding Incoterms can help buyers manage logistics costs effectively. Terms such as FOB (Free on Board) or CIF (Cost, Insurance, and Freight) dictate the responsibilities of buyers and sellers, impacting overall costs.
What Buyer Tips Can Help Optimize Sourcing Costs?
For B2B buyers, particularly those in regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, several strategies can optimize sourcing costs:
-
Negotiate Terms: Engage in negotiations not just on price but also on payment terms, delivery schedules, and warranties. Building long-term relationships with suppliers can also yield better pricing over time.
-
Focus on Cost-Efficiency: Evaluate the Total Cost of Ownership (TCO) rather than just the upfront price. This includes considering durability, maintenance, and potential downtime associated with lower-quality parts.
-
Be Aware of Pricing Nuances: Different regions may experience fluctuations in material costs due to local economic conditions. Staying informed about these trends can help buyers time their purchases strategically.
-
Consider Local Suppliers: Sourcing from local manufacturers can reduce logistics costs and lead times. Additionally, local suppliers may better understand regional regulations and requirements.
Disclaimer on Indicative Prices
It’s important to note that the prices for cast aluminum parts can vary widely based on the factors outlined above. Buyers should conduct thorough market research and obtain multiple quotes to ensure they are receiving competitive pricing.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing cast aluminum parts With Other Solutions
Understanding Alternative Solutions to Cast Aluminum Parts
When evaluating manufacturing materials and techniques, it’s essential for B2B buyers to consider various options that can achieve similar performance objectives. Cast aluminum parts are widely recognized for their lightweight, strength, and versatility; however, alternatives such as cast iron, wrought aluminum, and plastic injection molding may also offer viable solutions depending on the specific requirements of a project. This section provides a comprehensive comparison of these alternatives, helping buyers make informed decisions.
Comparison of Cast Aluminum Parts and Alternatives
| Comparison Aspect | Cast Aluminum Parts | Cast Iron | Wrought Aluminum | Plastic Injection Molding |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | High strength-to-weight ratio, excellent corrosion resistance | Good strength, brittle, heavy | High tensile strength, excellent machinability | Good for complex shapes, limited temperature resistance |
| Cost | Moderate, cost-effective for large volumes | Generally lower, but machining can be costly | Higher due to processing | Lower for mass production, tooling costs can be high |
| Ease of Implementation | Relatively easy, established processes | More complex due to brittleness | Requires specialized machining | Requires specific molds, longer lead times |
| Maintenance | Low maintenance, corrosion-resistant | Requires protective coatings | Moderate, dependent on application | Low, but can degrade over time |
| Best Use Case | Aerospace, automotive, consumer goods | Heavy machinery, automotive blocks | Structural components, high-stress applications | Consumer products, automotive parts with intricate designs |
Exploring the Pros and Cons of Each Alternative
Cast Iron: What Are Its Benefits and Drawbacks?
Cast iron is known for its excellent wear resistance and ability to absorb vibration, making it a suitable choice for heavy machinery and automotive applications. Its initial cost tends to be lower than that of cast aluminum; however, the brittleness of cast iron can lead to challenges in machining and increased risk of breakage. Additionally, cast iron parts often require protective coatings to prevent rust, which adds to maintenance needs.
Wrought Aluminum: Is It a Viable Option?
Wrought aluminum is favored for its superior tensile strength and excellent machinability, making it ideal for applications requiring precise dimensions and durability. While it offers high performance, the cost is generally higher than cast aluminum due to the more complex manufacturing processes involved. Wrought aluminum is often used in structural components and high-stress applications, but it may not be the best option for projects with intricate designs.
Plastic Injection Molding: When Should It Be Considered?
Plastic injection molding is a cost-effective alternative for high-volume production of complex shapes. It excels in applications where weight is a critical factor and offers good design flexibility. However, the material’s temperature resistance is limited compared to metals, and the initial tooling costs can be significant. This method is commonly used for consumer products and automotive parts where intricate designs are required but may not be suitable for high-stress applications.
Making the Right Choice: How Should B2B Buyers Decide?
In selecting the appropriate manufacturing solution, B2B buyers should carefully consider their specific requirements, including performance expectations, budget constraints, and project timelines. While cast aluminum parts offer a blend of lightweight durability and corrosion resistance, alternatives like cast iron, wrought aluminum, and plastic injection molding each have unique advantages and drawbacks. Assessing the intended application and the environmental conditions that the final product will face will guide buyers in making an informed choice that aligns with their operational needs and long-term goals.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for cast aluminum parts
What Are the Key Technical Properties of Cast Aluminum Parts?
Understanding the essential technical properties of cast aluminum parts is crucial for B2B buyers, especially when making informed purchasing decisions. Here are some critical specifications:
1. Material Grade
Material grade defines the specific alloy composition of the aluminum used in casting. Common grades include A356, A380, and A413, each offering different mechanical properties. For instance, A356 is known for its excellent corrosion resistance and weldability, making it suitable for automotive applications. Selecting the right material grade ensures that the cast parts meet the required performance standards for specific applications.
2. Dimensional Tolerance
Dimensional tolerance refers to the allowable variations in the dimensions of the cast parts. It is crucial for ensuring that parts fit together correctly in assemblies, particularly in precision industries like aerospace and automotive. Tighter tolerances often lead to higher manufacturing costs, so understanding the necessary tolerances for your application can help manage budgets effectively.
3. Ultimate Tensile Strength (UTS)
Ultimate tensile strength indicates the maximum amount of tensile stress that a material can withstand before failure. For cast aluminum, UTS values can vary significantly depending on the alloy and casting process used. For example, while pure aluminum has a UTS of about 90 MPa, some casting alloys can reach UTS values above 200 MPa. This property is vital for applications requiring high strength-to-weight ratios, such as in the transportation sector.
4. Porosity
Porosity describes the presence of voids or cavities within the cast aluminum structure, which can weaken the material. High porosity levels often result from less controlled casting processes. Understanding the porosity levels of cast parts is essential for industries where structural integrity is critical, as excessive porosity can lead to failure in operational conditions.
5. Corrosion Resistance
Aluminum naturally develops a protective oxide layer that enhances its resistance to corrosion. However, the degree of corrosion resistance can vary based on the alloy composition and surface treatments. For B2B buyers in industries exposed to harsh environments (like marine applications), selecting the right alloy with adequate corrosion resistance is imperative to ensure product longevity.
6. Thermal Conductivity
Thermal conductivity refers to the material’s ability to conduct heat. Cast aluminum exhibits excellent thermal conductivity, making it suitable for applications that require efficient heat dissipation, such as in electronic housings. Understanding this property helps buyers select materials that align with the thermal management requirements of their products.
What Are the Common Trade Terms Used in the Cast Aluminum Industry?
Familiarizing yourself with industry jargon can significantly enhance communication with suppliers and partners. Here are some essential terms:
1. OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
An OEM refers to a company that produces parts or equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer. In the context of cast aluminum parts, understanding OEM relationships helps buyers identify who is responsible for the quality and specifications of the components they are sourcing.
2. MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
Minimum Order Quantity is the smallest number of units a supplier is willing to sell. Knowing the MOQ is crucial for budget planning and inventory management, especially for small to medium-sized enterprises that may not require large quantities.
3. RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a document sent to suppliers requesting pricing, specifications, and terms for a specific product or service. Crafting a comprehensive RFQ can streamline the procurement process and ensure that buyers receive competitive offers tailored to their needs.
4. Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
Incoterms are standardized trade terms that define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in international transactions. Understanding these terms is essential for B2B buyers to manage logistics, costs, and risks associated with shipping cast aluminum parts across borders.
5. Lead Time
Lead time refers to the amount of time it takes from placing an order until it is delivered. For buyers, understanding lead times is vital for project planning and maintaining supply chain efficiency.
6. Surface Finish
Surface finish describes the texture and quality of the surface of the cast part. This property can affect both aesthetics and functionality. Knowing the required surface finish helps buyers specify their needs clearly, ensuring that the final product meets their quality standards.
By grasping these technical properties and trade terminologies, B2B buyers can make more informed decisions when sourcing cast aluminum parts, ultimately leading to better product outcomes and stronger supplier relationships.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the cast aluminum parts Sector
What Are the Current Market Dynamics and Key Trends in the Cast Aluminum Parts Sector?
The global market for cast aluminum parts is witnessing significant growth, driven by the increasing demand for lightweight and durable materials across various industries. Key sectors, including automotive, aerospace, and consumer electronics, are leading this trend as manufacturers seek to improve fuel efficiency and reduce emissions. Moreover, the expanding construction and infrastructure projects in regions like Africa and South America are creating substantial opportunities for cast aluminum applications.
Emerging technologies are reshaping sourcing trends in this sector. For instance, the adoption of Industry 4.0 technologies, such as IoT and AI, is enhancing supply chain transparency and operational efficiency. B2B buyers are increasingly leveraging these technologies to optimize inventory management, forecast demand more accurately, and streamline procurement processes. Furthermore, the integration of additive manufacturing techniques with traditional casting processes is enabling the production of complex geometries, thus expanding the design capabilities for international buyers.
Another critical trend is the shift towards local sourcing. International buyers are re-evaluating their supply chains to mitigate risks and enhance responsiveness. This is particularly relevant for buyers in regions like Nigeria and Brazil, where local suppliers can offer more agile solutions compared to distant manufacturers. As such, understanding regional market dynamics and establishing partnerships with local foundries can provide strategic advantages.
How Is Sustainability Shaping the Sourcing of Cast Aluminum Parts?
Sustainability is becoming a cornerstone of sourcing strategies in the cast aluminum parts sector. With increasing global awareness of environmental issues, companies are prioritizing ethical sourcing and reducing their carbon footprints. The production of cast aluminum parts has a relatively lower environmental impact compared to other materials, thanks to aluminum’s recyclability and durability. For B2B buyers, this means seeking suppliers who implement sustainable practices throughout their operations.
Ethical supply chains are now a focus for many international buyers, particularly in Europe and the Middle East, where regulations around environmental standards are stringent. Buyers should look for suppliers that are certified for their sustainability efforts, such as ISO 14001 for environmental management and other green certifications. Furthermore, sourcing recycled aluminum can significantly reduce energy consumption and greenhouse gas emissions associated with production.
In addition to certifications, buyers should evaluate the use of eco-friendly materials and processes in the manufacturing of cast aluminum parts. This includes the adoption of cleaner production technologies and the implementation of waste reduction strategies. By aligning sourcing decisions with sustainability goals, companies can enhance their brand reputation and meet the growing demand for environmentally responsible products.
What Is the Historical Context of Cast Aluminum Parts and Its Relevance Today?
The use of aluminum in casting dates back over a century, with its introduction driven by the material’s lightweight and corrosion-resistant properties. Initially, cast aluminum parts were limited to applications in the automotive and aerospace industries, where performance and weight savings were paramount. Over the decades, advancements in casting techniques, such as die casting and sand casting, have enabled manufacturers to produce more complex shapes and improve the overall quality of the parts.
Today, the relevance of cast aluminum parts has expanded beyond traditional sectors. The ongoing evolution in manufacturing technology and the increasing emphasis on lightweight materials have solidified aluminum’s position in various industries, including consumer goods and electronics. As B2B buyers look to innovate and enhance product performance, understanding the historical context of cast aluminum not only provides insights into its capabilities but also helps in making informed sourcing decisions that align with modern manufacturing needs.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of cast aluminum parts
-
How do I ensure the quality of cast aluminum parts from suppliers?
To ensure quality, begin by vetting suppliers through certifications such as ISO 9001, which indicates adherence to quality management systems. Request samples of their cast aluminum parts to assess their finish, dimensions, and structural integrity. Additionally, inquire about their quality assurance processes, including testing for porosity and adherence to industry standards. Establish clear quality expectations in your purchase agreements and consider on-site audits if possible to verify production practices. -
What is the best aluminum casting process for my specific application?
The best aluminum casting process depends on your project requirements, including complexity, volume, and budget. Die casting is ideal for high-volume production with complex shapes due to its precision and surface finish. Sand casting is more suitable for larger, simpler components but may require additional finishing work. Permanent mold casting offers a good balance of strength and surface quality for medium-volume applications. Assess your design intricacies and functional requirements to determine the most appropriate process. -
What are the typical lead times for sourcing cast aluminum parts internationally?
Lead times can vary significantly based on several factors, including the casting process, supplier location, and order volume. Generally, expect a lead time of 4 to 12 weeks for production, with additional time for shipping. For urgent needs, communicate your timelines clearly with suppliers, as some may offer expedited services at a premium. It’s also wise to account for potential delays in customs clearance and logistics, especially when sourcing from overseas. -
What are the common minimum order quantities (MOQs) for cast aluminum parts?
Minimum order quantities (MOQs) for cast aluminum parts vary by supplier and the casting process used. Typically, MOQs can range from 50 to several thousand units, depending on the complexity of the parts and production methods. Discuss your specific requirements with potential suppliers, as they may offer flexibility for first-time orders or prototypes. Understanding the MOQ is crucial for managing your inventory and production planning effectively. -
How can I customize cast aluminum parts to meet my specifications?
Customization of cast aluminum parts can be achieved through detailed specifications provided to your supplier. This includes dimensions, tolerances, surface finishes, and any specific alloy requirements. Engage in collaborative design discussions with the supplier to ensure they understand your needs. Many suppliers also utilize CAD software to create prototypes, allowing for adjustments before full production. Be clear about your customization requirements upfront to avoid misunderstandings during the manufacturing process. -
What payment terms should I expect when sourcing cast aluminum parts?
Payment terms can vary widely among suppliers, but common practices include a deposit upfront (usually 30-50% of the total order) with the balance due upon completion or delivery. Some suppliers may offer favorable terms for larger orders or established relationships. It’s important to clarify payment methods accepted (e.g., wire transfer, credit card) and any potential fees associated with international transactions. Always ensure that payment terms are detailed in your purchase agreement to prevent disputes. -
How do I handle logistics and shipping for cast aluminum parts from international suppliers?
Handling logistics for international shipments involves selecting a reliable freight forwarder familiar with customs regulations in your country. Discuss shipping options with your supplier, including Incoterms, to understand who is responsible for shipping costs and risks. Ensure proper documentation is prepared for customs clearance to avoid delays. It’s also wise to track shipments closely and have contingency plans in place for unforeseen delays or issues during transit. -
What are the common applications for cast aluminum parts in various industries?
Cast aluminum parts are widely used across multiple industries due to their lightweight, strength, and corrosion resistance. Common applications include automotive components like engine blocks and transmission housings, aerospace parts such as brackets and housings, and consumer goods like cookware and appliances. Additionally, they are utilized in construction for window frames and structural components. Understanding the specific requirements of your industry will help in selecting the right materials and processes for your applications.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.
Top 8 Cast Aluminum Parts Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. Wayken – Cast Aluminum Solutions
Domain: waykenrm.com
Registered: 2013 (12 years)
Introduction: Cast aluminum is a lightweight part made from aluminum and/or other metals using various casting processes. Key details include: 1. **Properties**: Lightweight, durable, strong, corrosion-resistant due to aluminum oxide coating. 2. **Comparison with Cast Iron**: Lighter, better dimensional tolerance, higher thermal resistance. 3. **Comparison with Wrought Aluminum**: Higher carbon content, better …
2. Neway Precision – High Pressure Aluminum Die Casting Services
Domain: newayprecision.com
Registered: 2017 (8 years)
Introduction: High Pressure Aluminum Die Casting Services, Custom aluminum casting service from design to finished parts, Die Cast Aluminum Alloys: A356, A360, A383 (ADC12), A380, B390, Benefits: High Production Efficiency, Excellent Dimensional Accuracy, Superior Surface Finish, Material and Energy Efficiency, Applications: Aerospace (aircraft engine housings, avionics enclosures), Automotive (engine blocks, t…
3. Edelbrock – Cast Aluminum Parts
Domain: lsxmag.com
Registered: 2015 (10 years)
Introduction: Edelbrock produces a variety of cast aluminum parts including thermostat housings, heads, intake manifolds, water jackets, and valve covers. The manufacturing process utilizes advanced software called MAGMA (Magmasoft) for quality control, monitoring factors like thickness, temperature, and fill velocity. The casting process involves melting aluminum ingots, pouring molten aluminum into molds, and…
4. Scorchworks – One Day Aluminum Casting Solutions
Domain: scorchworks.com
Registered: 2013 (12 years)
Introduction: One Day Foundry – For Casting Aluminum
Key Product Details:
– Purpose: Aluminum casting for creating new items and replacement parts.
– Setup: Lightweight tools and materials for small casting projects.
– Timeframe: Capable of casting an aluminum part in less than one day.
Recommended Raw Materials:
– Two (2) eight-foot lengths of 2×2 lumber
– Fire clay (Hawthorn-50 recommended)
– Fine sand
– Ch…
5. Hobby Machinist – Clay Bricks & Aluminum Casting Supplies
Domain: hobby-machinist.com
Registered: 2010 (15 years)
Introduction: Natural clay bricks, clay-grafite crucible, charcoal briquettes, propane torch, aluminum sources (cast aluminum car wheels, extrusion aluminum, soda cans, aluminum chips), flux for aluminum casting.
6. Stahl Specialty – Engine Parts Solutions
Domain: stahlspecialty.com
Registered: 1996 (29 years)
Introduction: Cast Aluminum Engine Parts: Lightweight, improved fuel efficiency, excellent thermal conductivity, corrosion resistance, design flexibility. Cast Iron Engine Parts: Superior strength, long-term wear resistance, vibration dampening, cost-effective to cast and machine.
7. Batesville Products – A356 Aluminum Casting
Domain: batesvilleproducts.com
Registered: 1998 (27 years)
Introduction: Batesville Products specializes in aluminum casting, particularly using the A356 aluminum alloy, known for its castability, strength, weight, and corrosion resistance. They offer permanent mold casting, which is a gravity-fed process using reusable steel molds, ideal for moderate volume production runs (500-20,000 pieces per year). The company also provides engineering and design assistance, tooli…
8. Milwaukee Precision – Aluminum Investment Castings
Domain: milwaukeeprec.com
Registered: 1998 (27 years)
Introduction: Aluminum Investment Castings – A356 aluminum alloy used for critical parts such as pump impellers, housings, covers, and plates. Precision investment casting process with ±0.005 inch/inch linear tolerance. Heat treatment options include T2, T4, T5, T6, and T61 for strength and ductility. Benefits include lightweight, corrosion resistance, design flexibility, and smooth surface finish. Industries s…
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for cast aluminum parts
Why is Strategic Sourcing Crucial for Cast Aluminum Parts?
In the competitive landscape of global manufacturing, strategic sourcing for cast aluminum parts presents significant advantages for international B2B buyers. Understanding the diverse casting processes—such as die casting, sand casting, and permanent mold casting—enables companies to select the most suitable method based on their specific requirements for quality, cost, and application. The lightweight and durable nature of aluminum, coupled with its excellent corrosion resistance and thermal conductivity, makes it a preferred choice across various industries, from automotive to aerospace.
What Should International Buyers Consider for Future Procurement?
As markets in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe continue to evolve, leveraging strategic sourcing practices will become increasingly vital. Buyers should focus on building strong partnerships with suppliers who can provide high-quality cast aluminum parts while ensuring competitive pricing and reliable delivery. Emphasizing supplier diversity and sustainability can also enhance supply chain resilience.
How Can Buyers Prepare for Emerging Opportunities?
Looking ahead, international B2B buyers should remain proactive in exploring new technologies and innovations in aluminum casting. Engaging in continuous market research and fostering collaboration with manufacturers will be essential for staying ahead in this dynamic environment. By adopting these strategies, buyers can position themselves for success in sourcing cast aluminum parts that meet the demands of tomorrow’s manufacturing challenges.