Contents
Manufacturing Insight: Carbon Steels

Carbon Steels: Precision Machining for Demanding Applications
Carbon steels remain a cornerstone material in industrial manufacturing due to their exceptional balance of strength, weldability, cost efficiency, and machinability. Grades such as AISI 1018, 1045, and 4140 offer tailored mechanical properties for structural components, automotive parts, tooling, and machinery elements. Their predictable behavior under CNC machining—excellent chip formation, thermal stability, and surface finish potential—makes them ideal for high-precision prototyping and low-to-medium volume production runs where dimensional accuracy and repeatability are non-negotiable.
At Honyo Prototype, we leverage advanced 3-, 4-, and 5-axis CNC milling and turning centers to transform carbon steel billets into mission-critical components with tolerances down to ±0.0002 inches. Our engineering team optimizes toolpaths, cutting parameters, and fixturing specifically for carbon steel’s material characteristics, ensuring minimal thermal distortion, superior surface integrity, and adherence to stringent geometric dimensioning and tolerancing (GD&T) requirements. From complex geometries requiring tight positional tolerances to high-volume runs demanding consistent throughput, our ISO 9001-certified processes deliver parts ready for immediate integration into your assembly.
Accelerate your development cycle with Honyo’s Online Instant Quote platform. Upload your CAD file (STEP, IGES, or native formats), specify material grade and finish requirements, and receive a detailed manufacturability analysis alongside a competitive price within hours—not days. This seamless integration of engineering expertise and digital efficiency ensures your carbon steel components progress from concept to certified production faster, without compromising on quality or precision. Partner with Honyo to streamline your prototyping and production workflows with carbon steels engineered to perform.
Technical Capabilities

Carbon steels are widely used in precision machining applications due to their strength, durability, and machinability. When processing carbon steels—especially in 3-axis, 4-axis, and 5-axis milling as well as turning operations—specific technical considerations must be addressed to achieve tight tolerances (typically ±0.0005″ to ±0.005″, depending on part geometry and application). These include tool selection, cutting speeds and feeds, thermal management, and fixturing strategies.
While the focus is on carbon steels, comparative insights with other commonly machined materials—such as aluminum, alloy steels, ABS, and nylon—are useful for process optimization in high-precision environments.
Below is a comparative technical specification table highlighting key properties and machining parameters relevant to tight-tolerance CNC operations:
| Material | Tensile Strength (MPa) | Hardness (HRC) | Thermal Conductivity (W/m·K) | Machinability Rating (%) | Typical Tolerance (± in) | Recommended Tooling | Coolant Requirement | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Low Carbon Steel (e.g., 1018) | 440–550 | 10–15 | 51 | 70 | 0.001–0.005 | Carbide end mills, HSS | Yes (flood) | Good for turning and milling; weldable; moderate tool wear |
| Medium Carbon Steel (e.g., 1045) | 570–700 | 18–25 | 48 | 55 | 0.001–0.003 | Coated carbide | Yes (flood) | Higher strength; requires rigid setup for tight tolerances |
| High Carbon Steel (e.g., 1095) | 760–1000 | 30–45 | 46 | 40 | 0.0005–0.003 | Polycrystalline cubic boron nitride (PCBN) | Yes (high-pressure) | High tool wear; pre-heat and stress-relieve before machining |
| Aluminum 6061-T6 | 310 | 15–16 | 167 | 90 | 0.0005–0.002 | Carbide with high rake angle | Yes (mist or flood) | Excellent for 5-axis; low cutting forces; high feed rates |
| Alloy Steel (e.g., 4140) | 655–965 | 25–32 | 42 | 50 | 0.001–0.003 | TiAlN-coated carbide | Yes (flood) | Used in high-stress applications; pre- and post-machining heat treat may be needed |
| ABS (Thermoplastic) | 40–50 | < 10 | 0.1–0.2 | 95 | 0.002–0.005 | Sharp high-speed steel | Optional (air blast) | Low melting point; prone to chatter; use sharp tools and high RPM |
| Nylon 6/6 | 70–90 | 8–12 | 0.25 | 85 | 0.002–0.005 | Polished HSS or carbide | Optional (air) | Hygroscopic; pre-dry before machining; low dimensional stability |
Notes on Machining Strategy for Tight Tolerance Work:
For carbon steels in multi-axis milling and turning, achieving tight tolerances requires stable tool paths, minimized tool deflection, and consistent thermal control. 5-axis machining allows for complex geometries with fewer setups, improving dimensional accuracy. High-pressure coolant delivery is critical when machining medium to high carbon steels to manage heat and extend tool life.
Aluminum and plastics like ABS and nylon require different approaches due to lower thermal resistance and higher ductility or flexibility. While aluminum permits very tight tolerances with high-speed machining, plastics require careful fixturing and chip evacuation to prevent deformation.
In all cases, in-process inspection using CMM or on-machine probing is recommended to maintain tolerance compliance across production runs.
From CAD to Part: The Process
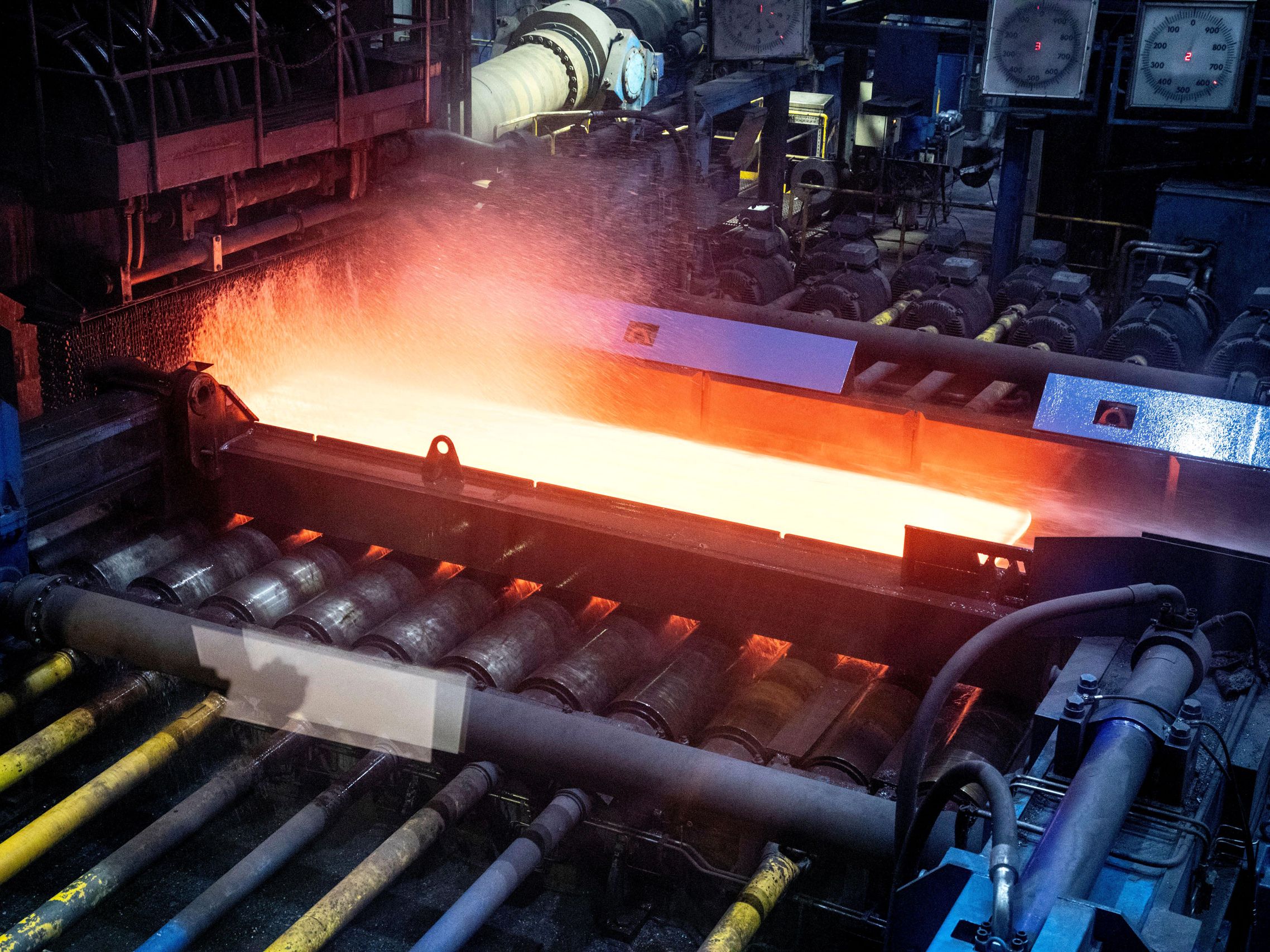
Honyo Prototype Carbon Steel Manufacturing Process Overview
Honyo Prototype executes carbon steel part production through a rigorously defined sequence optimized for speed, cost efficiency, and metallurgical integrity. The process begins with CAD Upload, where clients submit 3D models via our secure portal. Critical carbon steel specifications must be explicitly defined in the CAD file or associated documentation, including grade (e.g., AISI 1018, 1045, 4140), required heat treatment (annealed, normalized, quenched & tempered), and surface finish tolerances. Failure to specify these parameters triggers an automated validation hold until clarified, ensuring downstream accuracy.
The AI Quote phase leverages our proprietary algorithm, trained on 12+ years of carbon steel machining data. It dynamically calculates cost drivers unique to carbon steels: material waste factors (e.g., 15-25% higher scrap rates for 4140 vs. 1018 due to hardenability), tool wear coefficients based on carbon content, and thermal deformation risks during milling/turning. Real-time scrap metal market data adjusts raw material costs, while geometric complexity metrics assess secondary operation needs like stress-relieving for thin-walled components. Quotes include explicit notes on carbon steel-specific constraints, such as minimum bend radii for sheet steel or chip evacuation challenges in deep drilling of high-carbon grades.
DFM Analysis is conducted by our metallurgy-specialized engineering team, not solely by AI. We focus on carbon steel-specific pitfalls: verifying adequate draft angles for cast/forged preforms to prevent tearing, confirming hole depth-to-diameter ratios to avoid drill whip in 1045, and validating heat treatment distortion allowances. For example, a 4140 part requiring HRC 28-32 will trigger a review of cross-sectional uniformity to prevent cracking during quenching. Clients receive a DFM report with actionable revisions, such as adding relief grooves near sharp corners in high-carbon steels to mitigate stress concentrations.
Production adheres to carbon steel-specific protocols. Material certificates (MTRs) are verified upon receipt against ASTM/ASME standards. Machining employs carbide tooling with geometries optimized for carbon steel’s gummy chip formation, using rigid setups to minimize chatter in low-carbon grades like 1006. Critical steps include:
Pre-heat treatment for 4140/4340 to 150-200°C before rough machining to reduce residual stress
Coolant selection tailored to carbon content (e.g., soluble oil for 1045 to prevent built-up edge)
In-process Rockwell hardness checks post-heat treatment
Vibration aging for welded assemblies to prevent distortion
Delivery encompasses carbon steel-specific quality assurance. All parts undergo final inspection per ASME Y14.5, with material traceability documented via serialized MTRs linked to the heat number. Protective oiling or VCI paper packaging is applied to prevent flash rust during transit. Shipments include a comprehensive package: dimensional CMM reports, hardness test results, surface roughness verification, and non-destructive testing records (e.g., MPI for critical 4140 weldments). Standard lead time for carbon steel prototypes is 7-12 business days, with expedited options for low-carbon grades (1008-1026) at 4-6 days due to faster machinability.
This integrated workflow ensures carbon steel components meet stringent mechanical property and dimensional requirements while minimizing iteration cycles through upfront metallurgical rigor.
Start Your Project

Looking for high-quality carbon steel solutions for your next project? Honyo Prototype offers precision manufacturing with fast turnaround times, leveraging our state-of-the-art facility in Shenzhen, China. As a trusted partner in rapid prototyping and low-volume production, we ensure material consistency, tight tolerances, and full traceability for all carbon steel components.
Contact Susan Leo today to discuss your requirements and get a competitive quote.
Email: [email protected]
With our in-house capabilities and strategic location in Shenzhen, we deliver reliable, cost-effective results—on time and to specification.
🚀 Rapid Prototyping Estimator
Estimate rough cost index based on volume.