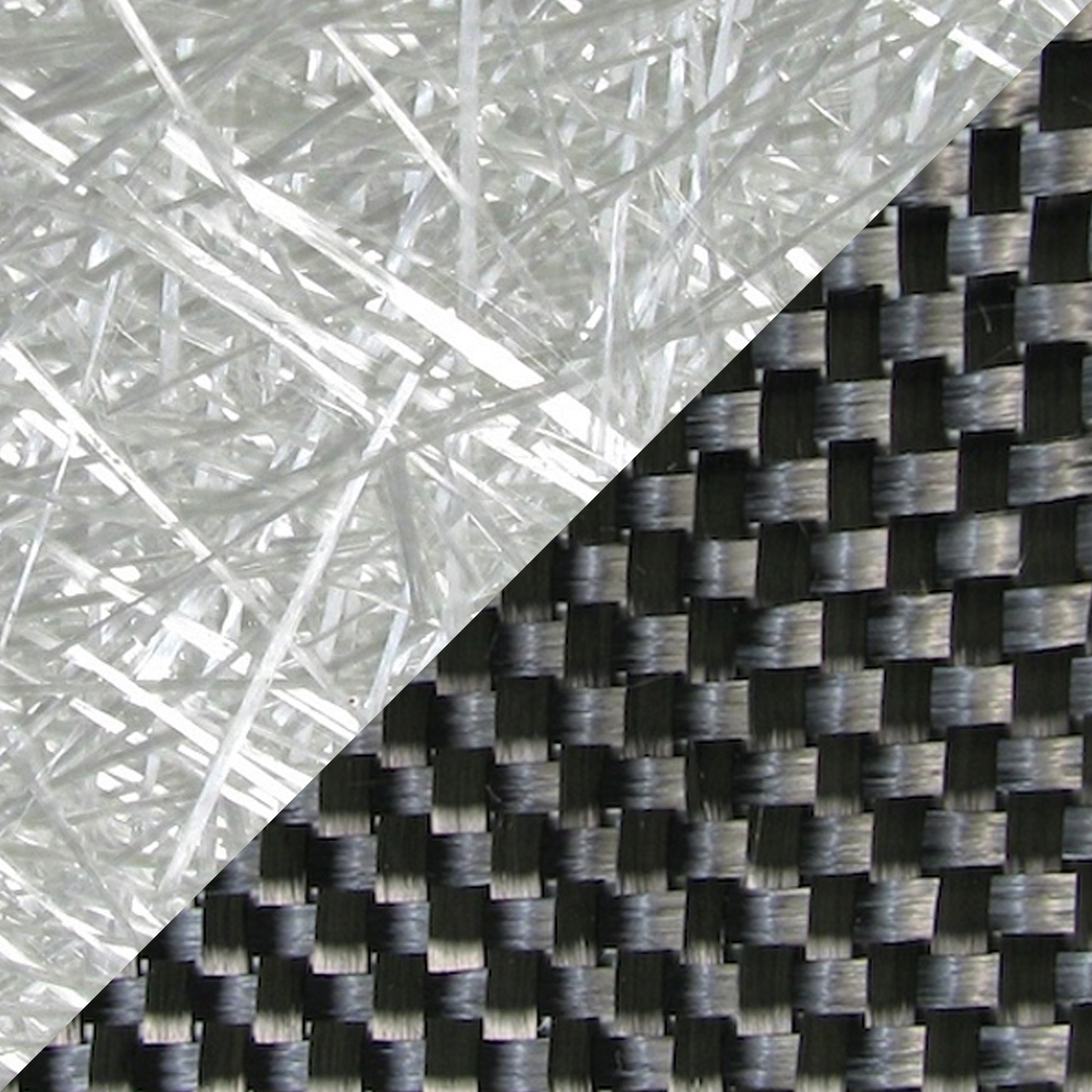
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for carbon fiber fiberglass
In today’s competitive landscape, sourcing high-performance materials like carbon fiber fiberglass poses significant challenges for international B2B buyers. These advanced composite materials are essential across various industries, including aerospace, automotive, and construction, where strength, weight, and durability are critical. However, navigating the complexities of material specifications, supplier reliability, and cost-effectiveness can be daunting, particularly for businesses operating in diverse markets such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe.
This comprehensive guide aims to demystify the global market for carbon fiber fiberglass by providing an in-depth exploration of its types, applications, and sourcing strategies. Readers will gain insights into the nuances of different carbon fiber materials, including woven fabrics, unidirectional sheets, and hybrid composites, along with their specific uses in enhancing product performance. Additionally, the guide emphasizes the importance of thorough supplier vetting, ensuring that buyers can identify trustworthy partners who meet their quality and compliance standards.
By equipping B2B buyers with actionable knowledge and tools, this guide empowers them to make informed purchasing decisions that align with their operational needs and strategic goals. Whether you are a manufacturer in Nigeria looking to reduce weight in your designs or a supplier in Saudi Arabia aiming to expand your product offerings, understanding the intricacies of carbon fiber fiberglass will be pivotal to your success in a rapidly evolving market.
Understanding carbon fiber fiberglass Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Woven Carbon Fiber Fabric | Made from interlaced fibers; high strength and flexibility | Aerospace, automotive, sporting goods | Pros: Excellent strength-to-weight ratio; Cons: More expensive than fiberglass. |
| Unidirectional Carbon Fiber | Fibers aligned in one direction; high tensile strength | Structural components, automotive parts | Pros: Superior strength along the fiber direction; Cons: Limited strength in other directions. |
| Carbon Fiber Reinforced Polymer | Composite material combining carbon fiber with resin | Marine, industrial applications, consumer goods | Pros: Enhanced mechanical properties; Cons: Requires careful resin selection for optimal performance. |
| Braided Carbon Fiber Sleeves | Braided structure provides flexibility and strength | Pipe reinforcement, aerospace applications | Pros: Good impact resistance; Cons: More complex manufacturing process. |
| Carbon Fiber Tapes | Thin, flexible strips used for repairs and reinforcement | General repairs, automotive, and aerospace applications | Pros: Easy to use and apply; Cons: Limited load-bearing capacity compared to thicker materials. |
What Are the Characteristics of Woven Carbon Fiber Fabric?
Woven carbon fiber fabric is composed of interlaced fibers, providing a combination of high strength and flexibility. This type is particularly suitable for applications where both strength and weight considerations are critical, such as in aerospace and automotive sectors. B2B buyers should consider the weave pattern and fiber density, as these factors can significantly affect the fabric’s performance and cost. While this material offers an excellent strength-to-weight ratio, it is generally more expensive than fiberglass, which may impact budget considerations.
How Does Unidirectional Carbon Fiber Differ in Suitability?
Unidirectional carbon fiber features fibers aligned in a single direction, resulting in exceptional tensile strength along that axis. This property makes it ideal for structural components in automotive and aerospace applications, where maximum strength is required. Buyers should be aware that while unidirectional fiber excels in its aligned direction, it may lack strength in perpendicular directions. This characteristic can limit its versatility, so understanding the specific load requirements of the intended application is crucial.
What Are the Advantages of Carbon Fiber Reinforced Polymer?
Carbon fiber reinforced polymer (CFRP) combines carbon fibers with a resin matrix, creating a composite material that boasts enhanced mechanical properties. This type is widely used in marine, industrial, and consumer goods applications, where high performance is essential. When purchasing CFRP, B2B buyers should focus on the resin system used, as it plays a critical role in the composite’s overall performance. While CFRP offers superior strength and durability, it may require more careful handling and processing than traditional materials.
Why Choose Braided Carbon Fiber Sleeves?
Braided carbon fiber sleeves consist of interwoven fibers that provide both flexibility and strength. This type is particularly advantageous for applications like pipe reinforcement and aerospace components, where impact resistance is essential. Buyers should consider the complexity of the manufacturing process, which can influence lead times and costs. While braided sleeves offer a high degree of durability, their unique structure may also result in higher production costs compared to simpler forms of carbon fiber.
What Are the Key Features of Carbon Fiber Tapes?
Carbon fiber tapes are thin, flexible strips that are easy to apply for repairs and reinforcements in various applications, including automotive and aerospace. Their lightweight nature and ease of use make them a popular choice for quick fixes and enhancements. However, B2B buyers should recognize that while these tapes are convenient, they may not bear heavy loads as effectively as thicker materials. Understanding the specific application requirements will help buyers choose the right type of carbon fiber tape for their needs.
Key Industrial Applications of carbon fiber fiberglass
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of carbon fiber fiberglass | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Aerospace | Structural components in aircraft | Reduced weight leading to improved fuel efficiency | Compliance with aviation safety standards and certifications |
| Automotive | Lightweight body panels and frames | Enhanced performance and lower emissions | Compatibility with existing manufacturing processes |
| Marine | Hulls and structural reinforcements for boats and yachts | Increased durability and resistance to corrosion | Resistance to marine environment conditions |
| Sports Equipment | High-performance sporting goods like bicycles and fishing rods | Improved performance through weight reduction | Customization options for specific sports applications |
| Construction | Reinforcement in concrete and building materials | Enhanced strength and longevity of structures | Availability of local suppliers and logistics considerations |
How is Carbon Fiber Fiberglass Used in Aerospace Applications?
In the aerospace industry, carbon fiber fiberglass is utilized for structural components, such as wing spars and fuselage sections. Its lightweight nature significantly reduces the overall weight of aircraft, resulting in enhanced fuel efficiency and lower operational costs. For international buyers, particularly in regions like Africa and the Middle East, ensuring compliance with stringent aviation safety standards is crucial. Suppliers must provide documentation proving the material’s performance under rigorous conditions.
What Role Does Carbon Fiber Fiberglass Play in Automotive Manufacturing?
Automotive manufacturers increasingly adopt carbon fiber fiberglass for lightweight body panels and frames. This shift not only enhances vehicle performance but also contributes to lower emissions due to improved fuel efficiency. Buyers in South America and Europe must consider the compatibility of these materials with existing manufacturing processes, ensuring that they can seamlessly integrate carbon fiber components into their production lines without significant modifications.
How is Carbon Fiber Fiberglass Beneficial in Marine Applications?
In marine applications, carbon fiber fiberglass is used in constructing hulls and reinforcing structures of boats and yachts. Its resistance to corrosion and lightweight characteristics provide significant advantages in terms of durability and performance. For B2B buyers in coastal regions, understanding the specific marine environment and ensuring the material’s resistance to saltwater and UV exposure is essential when sourcing these products.
What Advantages Does Carbon Fiber Fiberglass Offer in Sports Equipment?
Carbon fiber fiberglass is widely used in high-performance sporting goods, such as bicycles and fishing rods, where its lightweight and strong properties enhance performance. For manufacturers, the ability to customize these materials for specific sports applications can lead to a competitive edge. Buyers must assess the availability of tailored solutions that meet their performance requirements while also considering the cost implications of sourcing high-quality carbon fiber products.
How is Carbon Fiber Fiberglass Transforming Construction Materials?
In construction, carbon fiber fiberglass is increasingly employed as a reinforcement material for concrete and other building materials. This application enhances the strength and longevity of structures, making them more resilient to environmental stresses. International buyers, particularly from developing markets in Africa and South America, should consider the availability of local suppliers to facilitate logistics and ensure timely project completion, as well as the material’s compliance with local building codes and regulations.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘carbon fiber fiberglass’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Understanding Material Specifications for Optimal Performance
The Problem: B2B buyers often grapple with the complexities of selecting the right specifications for carbon fiber fiberglass materials. In industries such as aerospace and automotive, where performance and safety are paramount, any oversight in material choice can lead to significant operational failures. Buyers may find it challenging to differentiate between the various types of carbon fiber fabrics, such as twill or unidirectional, and how these variations affect weight, strength, and flexibility. This confusion can lead to the procurement of unsuitable materials that do not meet project requirements, resulting in costly delays and safety risks.
The Solution: To overcome this challenge, buyers should engage in thorough research and utilize comprehensive material datasheets from reputable suppliers. These datasheets should detail the mechanical properties, weight, and intended applications of each type of carbon fiber fabric. Additionally, buyers can consult with material engineers or experts to understand the specific requirements of their projects. Implementing a prototyping phase using sample materials can also aid in identifying the most suitable fabric for their applications. By ensuring that they have a clear understanding of the specific performance characteristics needed, B2B buyers can make informed decisions that enhance the quality and safety of their products.
Scenario 2: Managing Costs While Ensuring Quality
The Problem: Cost management is a critical concern for B2B buyers, especially in regions with fluctuating currencies and economic instability. Carbon fiber fiberglass, while offering superior performance, often comes at a premium price compared to traditional materials. Buyers may feel pressured to cut costs, leading them to consider lower-quality alternatives that compromise strength and durability. This decision can have long-term repercussions, including increased maintenance costs and product failures, which ultimately affect the bottom line.
The Solution: To effectively manage costs without sacrificing quality, buyers should consider sourcing carbon fiber fiberglass directly from manufacturers or trusted distributors who offer bulk purchasing options. Establishing long-term relationships with suppliers can also facilitate negotiations for better pricing or exclusive discounts. Furthermore, buyers should prioritize investing in high-quality materials that provide a better return on investment through durability and performance, even if the initial costs are higher. Utilizing lifecycle cost analysis can help quantify the benefits of investing in quality materials versus cheaper alternatives, making it easier to justify expenditure to stakeholders.
Scenario 3: Addressing Compatibility Issues with Resin Systems
The Problem: A common pain point for manufacturers using carbon fiber fiberglass is the compatibility between the fiber and resin systems. Inadequate bonding due to mismatched materials can lead to structural weaknesses and failures in finished products. This is particularly critical in industries such as marine and aerospace, where safety is non-negotiable. Buyers may encounter difficulties in identifying the right resin system that complements their chosen carbon fiber, resulting in trial and error that wastes time and resources.
The Solution: To mitigate compatibility issues, buyers should select resin systems that are specifically formulated for use with carbon fiber fiberglass. Consulting technical datasheets and supplier recommendations is essential in this process. Buyers should also consider conducting preliminary tests to evaluate the bond strength and performance of different resin-fiber combinations before finalizing their choice. Collaborating with suppliers who provide technical support and application guidance can further streamline this process. By investing time in ensuring proper compatibility, manufacturers can significantly enhance the reliability and longevity of their products, thereby reinforcing their market position.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for carbon fiber fiberglass
What Are the Key Materials Used in Carbon Fiber Fiberglass?
When selecting materials for carbon fiber fiberglass applications, it is essential to consider various options that can influence the performance, durability, and cost-effectiveness of the end product. Below is an analysis of three common materials used in conjunction with carbon fiber, highlighting their key properties, advantages, limitations, and considerations for international B2B buyers.
1. Epoxy Resin
Key Properties:
Epoxy resins are known for their excellent adhesion, chemical resistance, and mechanical properties. They can withstand high temperatures, typically rated up to 150°C (302°F) or higher, depending on the formulation. This makes them suitable for applications in aerospace and automotive industries where temperature fluctuations are common.
Pros & Cons:
The primary advantage of epoxy resin is its superior mechanical strength and durability, which enhances the performance of carbon fiber composites. However, it can be relatively expensive compared to other resin systems, and the manufacturing process can be complex, requiring precise mixing and curing conditions.
Impact on Application:
Epoxy resins are compatible with a wide range of media, making them versatile for various applications, including structural components and high-stress environments.
Considerations for International Buyers:
B2B buyers in regions like Africa and the Middle East should ensure compliance with local regulations and standards (e.g., ASTM D638 for tensile properties). Understanding the specific requirements for temperature resistance and chemical compatibility is crucial for successful applications.
2. Vinyl Ester Resin
Key Properties:
Vinyl ester resins offer excellent corrosion resistance and are often used in marine applications. They can withstand temperatures up to 120°C (248°F) and are known for their toughness and flexibility.
Pros & Cons:
The key advantage of vinyl ester resins is their cost-effectiveness compared to epoxy systems while still providing good mechanical properties and resistance to environmental factors. However, they may not achieve the same level of performance as epoxy resins in high-stress applications.
Impact on Application:
Vinyl ester is particularly suited for applications exposed to harsh environments, such as chemical processing and marine industries, due to its corrosion resistance.
Considerations for International Buyers:
Buyers in South America and Europe should consider the local standards for marine and chemical applications, as compliance with regulations such as ISO 9001 can influence product acceptance in the market.
3. Polyurethane Resin
Key Properties:
Polyurethane resins are known for their flexibility, resilience, and impact resistance. They typically have a lower temperature tolerance than epoxy and vinyl ester, with ratings around 80-100°C (176-212°F).
Pros & Cons:
The flexibility of polyurethane resins makes them ideal for applications requiring high impact resistance. However, they may not provide the same level of strength or thermal stability as epoxy or vinyl ester resins, which could limit their use in high-performance applications.
Impact on Application:
Polyurethane is suitable for applications where flexibility and resilience are critical, such as in sporting goods and consumer products.
Considerations for International Buyers:
B2B buyers in regions like Nigeria and Saudi Arabia should be aware of the performance requirements for specific applications, ensuring that the selected polyurethane resin meets local industry standards.
Summary Table of Material Selection
| Material | Typical Use Case for carbon fiber fiberglass | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Epoxy Resin | Aerospace and automotive components | Superior mechanical strength | Higher cost and complex manufacturing | High |
| Vinyl Ester Resin | Marine and chemical processing applications | Excellent corrosion resistance | Lower performance in high-stress | Medium |
| Polyurethane Resin | Sporting goods and consumer products | High flexibility and impact resistance | Limited thermal stability | Medium |
This guide provides a comprehensive overview of the strategic material selection process for carbon fiber fiberglass, enabling international B2B buyers to make informed decisions based on their specific needs and regional considerations.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for carbon fiber fiberglass
What Are the Key Stages in the Manufacturing Process of Carbon Fiber Fiberglass?
The manufacturing of carbon fiber fiberglass involves several critical stages, each designed to ensure the optimal quality and performance of the final product. Understanding these stages can help B2B buyers make informed decisions when sourcing these materials.
1. Material Preparation: How Are Carbon Fibers and Resins Processed?
The first step in manufacturing carbon fiber fiberglass is the preparation of raw materials. Carbon fibers are produced from precursor materials, typically polyacrylonitrile (PAN). This involves several processes, including spinning the PAN into fibers, stabilizing these fibers through chemical treatment, and then carbonizing them through high-temperature heating. This multi-step process results in the formation of long, thin fibers that exhibit exceptional strength and rigidity.
Simultaneously, fiberglass is produced by heating silica sand, limestone, and soda ash to create molten glass, which is then drawn into fine strands. This fiber is often combined with resin systems, typically epoxy, to enhance its properties. The resin acts as a matrix that binds the fibers together, resulting in a composite material that boasts the strengths of both carbon fiber and fiberglass.
2. Forming: What Techniques Are Used to Shape Carbon Fiber Fiberglass?
Once the materials are prepared, the next stage is forming. This involves various techniques, including:
-
Layup: In this process, layers of carbon fiber fabric are laid into a mold, which can be done manually or using automated systems. This technique allows for intricate designs and is commonly used in industries such as aerospace and automotive.
-
Pultrusion: A continuous process where raw materials are pulled through a heated die, resulting in a uniform cross-section of composite material. This method is efficient for producing long sections of carbon fiber fiberglass profiles.
-
Filament Winding: This technique involves winding continuous strands of carbon fiber around a mandrel to create hollow shapes, such as tubes and tanks. Filament winding is ideal for applications requiring high strength and lightweight characteristics.
3. Assembly: How Are Different Components Joined Together?
The assembly stage typically involves combining various components, such as integrating different fiber orientations or adding reinforcing materials. Techniques used in this stage include:
-
Adhesive Bonding: High-performance adhesives are used to bond different components of the composite structure. This is particularly important in applications where mechanical fasteners might add unwanted weight.
-
Mechanical Fastening: In some cases, mechanical fasteners may be used, although this is less common due to the potential for increased weight and stress concentration.
4. Finishing: What Steps Ensure the Final Product Meets Quality Standards?
Finishing processes are crucial for enhancing the aesthetic and functional properties of carbon fiber fiberglass products. This stage may include:
-
Trimming and Machining: This involves cutting the composite to precise dimensions and machining surfaces to achieve the desired finish.
-
Surface Treatment: Various treatments, such as sanding, painting, or applying surface coatings, are applied to improve durability and appearance.
How Is Quality Assurance Implemented in Carbon Fiber Fiberglass Manufacturing?
Quality assurance is paramount in ensuring that carbon fiber fiberglass products meet international standards and specific industry requirements. B2B buyers should be aware of the various quality control (QC) measures that manufacturers undertake.
What International Standards Are Relevant for Carbon Fiber Fiberglass?
Manufacturers of carbon fiber fiberglass often adhere to several international standards, such as:
-
ISO 9001: This standard outlines the criteria for a quality management system, ensuring consistent quality in products and services. Compliance with ISO 9001 indicates a commitment to quality and customer satisfaction.
-
CE Marking: For products sold within the European Economic Area, CE marking signifies compliance with health, safety, and environmental protection standards.
-
API Standards: For applications in the oil and gas industry, adherence to American Petroleum Institute (API) standards can be critical, especially for products used in harsh environments.
What Are the Key QC Checkpoints in the Manufacturing Process?
Quality control is implemented at various checkpoints throughout the manufacturing process:
-
Incoming Quality Control (IQC): This stage involves inspecting raw materials and components before they enter the production process. Ensuring that materials meet specified standards is essential for the integrity of the final product.
-
In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): During manufacturing, various checks are conducted to monitor the production process. This includes verifying the curing times, fiber orientation, and the application of resin.
-
Final Quality Control (FQC): After the product is completed, a comprehensive inspection is performed. This may involve visual inspections, dimensional checks, and performance testing to ensure that the product meets all specifications.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control?
B2B buyers can take several steps to verify the quality control processes of their suppliers:
-
Conducting Audits: Regular audits of suppliers can help assess their adherence to quality standards and manufacturing processes. This can include on-site inspections of manufacturing facilities.
-
Requesting Quality Reports: Suppliers should provide documentation of their quality control measures, including test results and compliance certificates.
-
Engaging Third-Party Inspectors: Utilizing independent third-party inspectors can provide an unbiased assessment of the supplier’s quality control processes and product quality.
What Are the Quality Control Nuances for International B2B Buyers?
For international buyers, particularly those from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, understanding the nuances of quality control is crucial. These may include:
-
Cultural Differences in Quality Expectations: Different regions may have varying expectations regarding quality. Buyers should communicate their specific quality requirements clearly.
-
Regulatory Compliance: Buyers must be aware of local regulations regarding imported materials and products. Ensuring that suppliers comply with these regulations can prevent delays and additional costs.
-
Logistical Considerations: Transporting carbon fiber fiberglass across international borders can introduce risks, including damage during shipping. Buyers should work with suppliers that have robust packaging and shipping protocols to mitigate these risks.
In conclusion, understanding the manufacturing processes and quality assurance measures for carbon fiber fiberglass is essential for B2B buyers. By focusing on the key stages of production and the relevant quality control standards, buyers can make informed decisions that align with their needs and ensure the reliability of their supply chains.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘carbon fiber fiberglass’
To assist B2B buyers in successfully procuring carbon fiber fiberglass, this guide provides a structured checklist that outlines key steps to ensure a thorough sourcing process. This checklist is essential for companies seeking to leverage the unique properties of carbon fiber fiberglass for various applications, including automotive, aerospace, and construction.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Establishing clear technical specifications is crucial for identifying the right carbon fiber fiberglass products for your needs. Consider factors such as tensile strength, weight requirements, thermal expansion properties, and compatibility with resins. This clarity will guide your supplier discussions and help ensure you receive products that meet your performance criteria.
Step 2: Research and Identify Potential Suppliers
Conduct comprehensive research to identify suppliers specializing in carbon fiber fiberglass. Look for companies with a proven track record in your industry and those that offer a variety of products, including woven fabrics, unidirectional sheets, and hybrid materials. Utilize industry directories, trade shows, and online platforms to compile a list of potential suppliers.
Step 3: Evaluate Supplier Certifications
Before proceeding with any supplier, verify their certifications and quality standards. Look for ISO certifications, compliance with industry standards, and any relevant product testing reports. This step is vital to ensure that the materials you receive are of high quality and meet the necessary safety and performance regulations.
Step 4: Request Samples for Testing
Always request samples of the carbon fiber fiberglass products you are considering. Testing these samples in your specific application will provide valuable insights into their performance characteristics. Pay attention to aspects such as flexibility, strength, and compatibility with resins to ensure they align with your project requirements.
Step 5: Review Pricing and Terms of Sale
Once you have shortlisted potential suppliers, compare their pricing structures and terms of sale. Look beyond the initial cost; consider factors such as minimum order quantities, lead times, and shipping costs. A comprehensive understanding of these elements will help you make a cost-effective decision that aligns with your budget and timelines.
Step 6: Assess Customer Support and Communication
Effective communication and customer support are essential for a smooth procurement process. Evaluate how responsive and knowledgeable the suppliers are regarding your inquiries. Strong customer support can be a significant advantage, particularly if you encounter issues during the sourcing or implementation phases.
Step 7: Establish Long-term Relationships
Finally, consider the potential for long-term partnerships with your chosen suppliers. Building a strong relationship can lead to better pricing, priority access to new products, and collaborative opportunities for innovation. Engage in regular communication and express your future needs to foster a mutually beneficial partnership.
By following this checklist, B2B buyers can navigate the complexities of sourcing carbon fiber fiberglass with confidence, ensuring they select the right materials and suppliers for their specific applications.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for carbon fiber fiberglass Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components in Carbon Fiber Fiberglass Sourcing?
When sourcing carbon fiber fiberglass, understanding the cost structure is crucial for B2B buyers. The primary cost components include materials, labor, manufacturing overhead, tooling, quality control, logistics, and profit margins.
-
Materials: The cost of raw materials, such as carbon fibers and resin systems, represents a significant portion of the total cost. High-quality fibers, such as 12K or 3K fabrics, typically command higher prices due to their enhanced strength and durability.
-
Labor: Labor costs can vary widely based on the complexity of the manufacturing process and the region where production occurs. Skilled labor is essential for handling advanced composite materials, which can increase costs.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes expenses related to factory operation, utilities, and maintenance of machinery. Efficient production processes can help minimize overhead costs.
-
Tooling: Initial tooling costs can be substantial, especially for custom or specialized parts. Buyers should consider these costs when evaluating suppliers, as they can significantly impact the overall pricing.
-
Quality Control (QC): Ensuring the product meets industry standards requires investment in QC processes. This is especially important in sectors like aerospace and automotive, where safety and performance are critical.
-
Logistics: Transportation and shipping costs can fluctuate based on distance, shipping methods, and local tariffs. Understanding Incoterms is essential to accurately assess these costs.
-
Margin: Suppliers often factor in profit margins based on their cost structure, market demand, and competition. Buyers should be aware that margins can vary significantly between suppliers.
How Do Price Influencers Affect Carbon Fiber Fiberglass Costs?
Several factors can influence the pricing of carbon fiber fiberglass:
-
Volume/MOQ: Minimum order quantities (MOQ) can significantly affect pricing. Larger orders often lead to lower per-unit costs due to economies of scale.
-
Specifications and Customization: Customization requests can lead to higher costs. Specifications that require unique materials or manufacturing processes may incur additional fees.
-
Quality and Certifications: Products with higher quality or specific certifications (e.g., ISO, ASTM) typically come at a premium. Buyers should assess the importance of these certifications against their project requirements.
-
Supplier Factors: The supplier’s reputation, production capacity, and experience can impact pricing. Established suppliers may charge more but offer better reliability and quality assurance.
-
Incoterms: Understanding Incoterms is crucial for international buyers. Terms such as FOB (Free on Board) or CIF (Cost, Insurance, and Freight) determine who bears the risk and costs at various stages of the supply chain.
What Are Effective Buyer Tips for Negotiating Carbon Fiber Fiberglass Prices?
International B2B buyers should employ strategic approaches to enhance cost-efficiency:
-
Negotiation: Engage in open discussions about pricing, especially for larger orders. Suppliers may be willing to offer discounts for bulk purchases or long-term contracts.
-
Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Evaluate the TCO, which includes purchase price, maintenance, and operational costs over the product’s lifecycle. This approach can lead to better investment decisions.
-
Pricing Nuances for International Buyers: Be aware of currency fluctuations, import duties, and local taxes that may affect the final cost. Understanding the economic landscape in regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe can inform negotiation strategies.
-
Market Research: Conduct thorough research on market trends, competitor pricing, and supplier capabilities. This knowledge can empower buyers during negotiations and help in identifying the best value options.
-
Supplier Relationships: Building strong relationships with suppliers can lead to better pricing and service. Regular communication and collaboration can foster trust and encourage favorable terms.
Disclaimer
Prices for carbon fiber fiberglass materials can vary widely based on market conditions, material specifications, and supplier factors. The information provided here is indicative and should be validated through direct communication with suppliers for accurate pricing tailored to specific needs.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing carbon fiber fiberglass With Other Solutions
Understanding Alternative Solutions to Carbon Fiber Fiberglass
When considering materials for industrial applications, it’s essential to evaluate not only carbon fiber fiberglass but also other viable alternatives. Each material has unique characteristics that may better suit specific project requirements. By comparing carbon fiber fiberglass with alternatives such as traditional fiberglass and aluminum, B2B buyers can make informed decisions based on performance, cost, and application suitability.
Comparison Table
| Comparison Aspect | Carbon Fiber Fiberglass | Traditional Fiberglass | Aluminum |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | High strength-to-weight ratio; excellent rigidity; low thermal expansion | Good strength; more flexible; lower weight-to-strength ratio | High strength; good thermal conductivity; heavier |
| Cost | Higher initial investment; long-term durability offsets cost | Lower cost; suitable for budget-conscious projects | Moderate cost; readily available |
| Ease of Implementation | Requires specialized handling and curing processes | Easier to handle and shape; more straightforward application | Familiar manufacturing processes; easy to work with |
| Maintenance | Minimal maintenance; resistant to corrosion | Moderate; susceptible to UV degradation | Low maintenance; corrosion-resistant coatings available |
| Best Use Case | Aerospace, high-performance automotive, and specialized industrial applications | General construction, boat manufacturing, and consumer goods | Structural components, automotive frames, and heat exchangers |
Detailed Breakdown of Alternatives
Traditional Fiberglass
Traditional fiberglass is a composite material made from woven glass fibers and a resin matrix. Its primary advantage lies in its cost-effectiveness and ease of use. For projects with budget constraints, fiberglass provides a suitable option, offering decent strength and flexibility. However, its lower strength-to-weight ratio compared to carbon fiber means it may require larger components to achieve similar performance levels. Additionally, while fiberglass is resistant to corrosion, it can degrade under prolonged UV exposure, necessitating additional protective measures in outdoor applications.
Aluminum
Aluminum is a widely used metal known for its excellent strength-to-weight ratio and thermal conductivity. It is generally more affordable than carbon fiber and offers good performance in structural applications. The ease of machining and forming aluminum makes it a popular choice in various industries, including automotive and construction. However, aluminum is heavier than carbon fiber and may not provide the same rigidity, which can be a disadvantage in applications where weight savings are crucial. Furthermore, aluminum can corrode if not properly treated, which may increase long-term maintenance costs.
Conclusion: How to Choose the Right Solution for Your Needs
Selecting the right material for your project depends on multiple factors, including performance requirements, budget constraints, and the specific application. Carbon fiber fiberglass stands out for high-performance applications where weight and rigidity are critical. In contrast, traditional fiberglass is ideal for cost-sensitive projects that do not compromise on basic strength and flexibility. Aluminum serves as a versatile option for structural integrity but may not meet the stringent requirements of specialized applications. By carefully assessing these alternatives, B2B buyers can align their material choices with their operational goals and project specifications.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for carbon fiber fiberglass
What Are the Key Technical Properties of Carbon Fiber Fiberglass?
Understanding the essential technical properties of carbon fiber fiberglass is crucial for B2B buyers aiming to make informed purchasing decisions. Here are some critical specifications to consider:
-
Material Grade
– Carbon fiber materials are available in various grades, often denoted by the number of filaments (e.g., 1K, 3K, 6K). The higher the number, the greater the strength and stiffness, making them suitable for high-performance applications. This is particularly important for industries such as aerospace and automotive, where structural integrity is paramount. -
Tensile Strength
– Measured in megapascals (MPa), tensile strength indicates how much pulling force a material can withstand before breaking. Carbon fiber typically boasts a tensile strength of around 4127 MPa, significantly higher than fiberglass. This property is crucial for applications requiring lightweight yet durable materials, allowing manufacturers to design thinner and lighter components without sacrificing strength. -
Weight-to-Strength Ratio
– This ratio measures the strength of a material relative to its weight, making it a vital specification for industries focused on performance and efficiency. Carbon fiber’s strength-to-weight ratio is approximately twice that of fiberglass, which translates into less material usage and cost savings during production, along with enhanced performance in end products. -
Thermal Expansion Coefficient
– Carbon fiber exhibits a negative coefficient of thermal expansion, meaning it shrinks when temperatures rise, in contrast to most materials that expand. This property is essential for applications where temperature fluctuations are common, as it helps maintain structural integrity without warping or deformation. -
Flexural Modulus
– This property indicates a material’s ability to resist deformation under load. A high flexural modulus in carbon fiber means it can withstand significant bending without breaking, making it suitable for structural applications where rigidity is required.
What Trade Terminology Should B2B Buyers Know About Carbon Fiber Fiberglass?
Navigating the terminology associated with carbon fiber fiberglass can be challenging. Here are some common terms that are essential for B2B buyers:
-
OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
– This term refers to companies that produce parts or equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer. Understanding OEM specifications can help in sourcing high-quality carbon fiber fiberglass components that meet specific industry standards. -
MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
– MOQ indicates the smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell. Knowing the MOQ is critical for B2B buyers to assess their purchasing power and inventory needs, especially when sourcing specialized materials like carbon fiber. -
RFQ (Request for Quotation)
– An RFQ is a document sent to suppliers requesting a price quote for specific products or services. This process is vital for buyers seeking competitive pricing and can lead to better negotiations when purchasing carbon fiber fiberglass. -
Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
– These are predefined commercial terms used in international trade to clarify the responsibilities of buyers and sellers. Familiarity with Incoterms such as FOB (Free on Board) or CIF (Cost, Insurance, and Freight) can help buyers understand shipping costs and risks associated with carbon fiber fiberglass procurement. -
Composite Materials
– Refers to materials made from two or more constituent materials with significantly different physical or chemical properties. Understanding composites is essential, as carbon fiber is often used in conjunction with resins to create stronger and lighter products. -
CFRP (Carbon Fiber Reinforced Polymer)
– This term describes a composite material consisting of carbon fibers embedded in a polymer matrix. Recognizing CFRP is crucial for B2B buyers, as it highlights the advanced properties of carbon fiber fiberglass, particularly in applications requiring enhanced performance and durability.
By grasping these technical properties and trade terms, B2B buyers can make more informed decisions, ensuring they select the right materials for their specific applications while optimizing cost-efficiency and performance.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the carbon fiber fiberglass Sector
What Are the Key Drivers and Trends in the Global Carbon Fiber Fiberglass Market?
The carbon fiber fiberglass market is witnessing significant growth driven by the increasing demand for lightweight and high-strength materials across various industries. The aerospace, automotive, and marine sectors are particularly influential, as they seek to enhance performance while reducing fuel consumption and emissions. In emerging markets like Africa and South America, local industries are beginning to adopt advanced composites for construction and infrastructure projects, leveraging the superior properties of carbon fiber.
Technological advancements in manufacturing processes, such as automated fiber placement and 3D printing, are reshaping sourcing trends. These innovations not only enhance production efficiency but also allow for greater customization in product design. As international B2B buyers, particularly from regions like Nigeria and Saudi Arabia, look for suppliers, the emphasis on quality and reliability is paramount. Buyers are increasingly prioritizing partnerships with manufacturers that can provide comprehensive technical support and demonstrate a commitment to quality assurance.
Moreover, the industry is witnessing a gradual shift towards digitization in the supply chain. E-commerce platforms are streamlining procurement processes, enabling buyers to compare products, pricing, and certifications easily. This trend is particularly relevant for buyers in Europe, where stringent regulations on material quality and performance are in place, necessitating reliable sourcing partners.
How Is Sustainability Reshaping the Sourcing of Carbon Fiber Fiberglass?
Sustainability is becoming a critical consideration in the sourcing of carbon fiber fiberglass. The environmental impact of manufacturing processes and materials is under scrutiny, prompting businesses to adopt more sustainable practices. Buyers are increasingly seeking suppliers that demonstrate a commitment to ethical sourcing and environmental stewardship. This includes using recycled materials in production and ensuring that their supply chains adhere to sustainable practices.
Certification schemes such as ISO 14001 for environmental management systems and certifications for recycled content are gaining traction. Buyers are encouraged to prioritize suppliers who can provide these certifications, as they reflect a commitment to reducing environmental footprints. Furthermore, the development of bio-based resins and materials presents opportunities for companies looking to enhance their sustainability credentials.
In regions like the Middle East, where environmental regulations are tightening, the demand for sustainable products is expected to rise. International buyers are advised to engage with suppliers who can not only meet performance requirements but also align with their sustainability goals, thereby enhancing their brand value and market competitiveness.
What Is the Historical Context Behind Carbon Fiber Fiberglass Development?
The evolution of carbon fiber fiberglass dates back to the mid-20th century, when the aerospace industry first recognized the potential of carbon composites for weight reduction and strength enhancement. Initially developed for military applications, the technology gradually found its way into commercial aviation and automotive sectors. By the 1970s and 1980s, advancements in manufacturing techniques led to more widespread adoption in sports equipment and consumer goods.
As the technology continued to advance, the introduction of various processing methods, such as pultrusion and filament winding, expanded its applications across multiple industries. Today, carbon fiber fiberglass is integral to modern engineering solutions, with ongoing research focused on improving material properties and reducing production costs. For B2B buyers, understanding this historical context can inform sourcing decisions, as it highlights the material’s proven track record and reliability across diverse applications.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of carbon fiber fiberglass
-
How do I select the right type of carbon fiber fiberglass for my application?
When selecting carbon fiber fiberglass, consider the specific requirements of your application, such as weight, strength, and flexibility. For high-strength applications, opt for unidirectional or woven fabrics with a high fiber count. If your project requires flexibility, consider fiberglass options that offer better toughness. Additionally, evaluate the environmental conditions, such as temperature and exposure to chemicals, to ensure compatibility with the chosen material. Collaborating with suppliers who can provide samples and technical specifications can also help make an informed decision. -
What are the advantages of using carbon fiber fiberglass over traditional materials?
Carbon fiber fiberglass offers several advantages, including a high strength-to-weight ratio, excellent rigidity, and resistance to corrosion. It is significantly lighter than metals like steel and aluminum, allowing for reduced weight in applications such as aerospace and automotive parts. Additionally, its thermal expansion properties make it suitable for environments with fluctuating temperatures. The ability to tailor the material properties through composite design further enhances its versatility for various industrial applications. -
What minimum order quantities (MOQs) should I expect when sourcing carbon fiber fiberglass?
Minimum order quantities for carbon fiber fiberglass can vary widely depending on the supplier and the specific product. Some manufacturers may have MOQs as low as 10 square meters for fabric, while others may require larger orders for custom or specialized products. It’s advisable to discuss your needs with suppliers early in the negotiation process to understand their MOQ policies and explore options for smaller orders or samples if necessary. -
What payment terms are typically offered by suppliers of carbon fiber fiberglass?
Payment terms can vary significantly among suppliers, often depending on the order size and the buyer’s creditworthiness. Common terms include net 30, net 60, or payment upon delivery. Some suppliers may also offer discounts for upfront payments or large orders. It is crucial to clarify payment expectations during negotiations and ensure that both parties agree on terms to avoid any misunderstandings later in the transaction. -
How can I ensure the quality of carbon fiber fiberglass products?
To ensure product quality, request certifications and quality assurance documentation from potential suppliers. Look for compliance with international standards such as ISO 9001 for manufacturing processes. Additionally, consider asking for samples to evaluate the material’s properties firsthand. Building a strong relationship with your supplier can also facilitate regular quality checks and updates on production processes, helping to maintain consistent standards. -
What logistics considerations should I be aware of when importing carbon fiber fiberglass?
When importing carbon fiber fiberglass, consider factors such as shipping costs, import tariffs, and delivery timelines. Ensure that your supplier can provide the necessary shipping documentation, including invoices, packing lists, and certificates of origin. Additionally, familiarize yourself with the import regulations in your country, as certain materials may require specific compliance or testing. Engaging a logistics provider with experience in international shipments can streamline the process and reduce delays. -
How do I vet suppliers of carbon fiber fiberglass effectively?
To vet suppliers, start by researching their reputation and customer reviews online. Request references from previous clients to gain insights into their reliability and product quality. Assess their manufacturing capabilities by asking about production processes, quality control measures, and lead times. If possible, visit their facilities or arrange for third-party inspections to verify their operations. Establishing clear communication and understanding their responsiveness can also be indicative of a reliable partnership. -
Can I customize carbon fiber fiberglass products to meet my specifications?
Yes, many suppliers of carbon fiber fiberglass offer customization options to meet specific requirements. This can include tailoring the fiber type, weave patterns, thickness, and even resin systems used in composites. Discuss your project needs with potential suppliers to understand their capabilities for custom orders. Providing detailed specifications and collaborating closely during the design process can ensure that the final product meets your exact expectations.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.
Top 7 Carbon Fiber Fiberglass Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. Fibreglast – Carbon Fiber Materials
Domain: fibreglast.com
Registered: 1995 (30 years)
Introduction: All Carbon Fiber Materials, Certified & Traceable Products, Same-Day Shipping if ordered by 2:30pm ET, includes Carbon Fiber Fabrics, Tapes, Tow, & Sleeves, Carbon/KEVLAR Hybrid Fabric, Classic and Contemporary Carbon Fiber Styles, Sample Packs, Fabric Racks & Workstations.
2. Reddit – Carbon Skinning Fiberglass Parts
Domain: reddit.com
Registered: 2005 (20 years)
Introduction: The user is interested in carbon skinning fiberglass parts, specifically for a car side mirror cowl, to enhance durability. They are seeking advice on whether the epoxy used for carbon fiber will damage the fiberglass. Responses indicate that it is possible to skin fiberglass parts with carbon fiber, using the same resin as the fiberglass. It is noted that no resin will eat away at composite fabri…
3. Goodwinds – Carbon Fiber Composite Rods and Tubes
Domain: goodwinds.com
Registered: 2006 (19 years)
Introduction: Carbon Fiber Composite Rods and Tubes:
– Diameter: 5 to 10 micrometers (carbon fibers)
– Modulus of Elasticity: ~250 GPa
– Tensile Strength: 3 to 7 GPa
– Density: 1.15g/cm3 to 2.25g/cm3
– Fatigue Resistance: High, enhanced by resin choice and layup design
– Corrosion Resistance: Inert to environmental degradation, does not rust or corrode
– Temperature Resistance: Glass transition temperatu…
4. Rock West Composites – Carbon Fiber Fabric
Domain: rockwestcomposites.com
Registered: 2009 (16 years)
Introduction: Carbon Fiber Fabric available by the yard or roll, sourced from leading manufacturers like Toray and Hexcel. Key features include:
– Tensile Strength: Min 0.000 Ksi, Max 700.000 Ksi
– Patterns: 12k 2X2 Twill Weave, 1k Plain Weave, 3k 2X2 Twill Weave, 3k Plain Weave, Braided, Chip Fiber (particle board), Diamond Weave, Tri-Axial Weave, Unidirectional
– Tensile Modulus: Min 0.000 Msi, Max 33.000 …
5. Spartec Composites – Carbon Fiber and Fiberglass Solutions
Domain: sparteccomposites.com
Registered: 2003 (22 years)
Introduction: Spartec Composites specializes in the design and manufacturing of carbon fiber, fiberglass, and other composite materials for over 40 years. Carbon fiber is made from strands of carbon atoms and is stronger, lighter, and more expensive to produce than fiberglass, which is made from melted strands of glass. Carbon fiber can be up to 15% lighter and more than 20% stronger than fiberglass, making it …
6. U.S. Composites – Composite Materials & Resins
Domain: uscomposites.com
Registered: 2000 (25 years)
Introduction: U.S. Composites, Inc. offers a wide range of composite materials including Fiberglass, Epoxy, Composites, Urethane Molding Rubbers, Carbon Fiber, and Urethane Foam. They specialize in carbon fiber, fiberglass, and KEVLAR® woven fabrics, as well as high-performance epoxy and polyester resins. Key products include Carbon & KEVLAR® Cloths, Table Top Epoxy for clear coating, Expanding Urethane Foam, E…
7. Instructables – Essential Materials for DIY Projects
Domain: instructables.com
Registered: 2005 (20 years)
Introduction: Materials: Clear packing tape, Blue foam insulation, Laminating resin (polyester and epoxy), Acetone, Paint brushes, Mold release paste wax, Woven fiberglass cloth, Chopped strand mat (CSM), Woven carbon fiber cloth, 3M Super 77 spray glue (optional), Rubber gloves, Filtering mask. Methods: 1. Creating a Mold and Pulling a Positive – involves using blue foam, clear packing tape, and fiberglass clo…
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for carbon fiber fiberglass
As the demand for advanced materials like carbon fiber continues to rise across various industries, strategic sourcing becomes crucial for international buyers aiming to enhance their product offerings. Carbon fiber’s exceptional strength-to-weight ratio, rigidity, and resistance to environmental factors make it a superior choice for applications in aerospace, automotive, and construction, particularly when compared to traditional materials like fiberglass.
For buyers in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, understanding the nuances of carbon fiber sourcing can lead to significant competitive advantages. By collaborating with reputable suppliers and leveraging innovative composite technologies, businesses can optimize their production processes, reduce material costs, and improve product performance.
Looking ahead, the global market for carbon fiber is poised for growth, driven by technological advancements and increasing applications in high-performance sectors. Companies should proactively seek partnerships with manufacturers who prioritize quality and sustainability, ensuring they are well-positioned to meet the evolving demands of the market.
Investing in strategic sourcing today not only prepares businesses for future challenges but also unlocks new opportunities for innovation and expansion. Take the next step in your sourcing strategy and explore the vast potential that carbon fiber offers for your business.