Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for carbon coatings
In today’s rapidly evolving industrial landscape, sourcing effective carbon coatings presents a significant challenge for international B2B buyers. These advanced materials are essential for enhancing the performance and longevity of various applications, from automotive and aerospace to biomedical and electronics. However, understanding the nuances of different types of carbon coatings—such as ceramic coatings, graphene-based solutions, and specialized protective films—can be daunting. This guide aims to demystify the global market for carbon coatings by providing a comprehensive overview that covers types, applications, supplier vetting processes, and cost considerations.
International buyers from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe—specifically Brazil and Germany—will find this guide particularly beneficial. It empowers them to make informed purchasing decisions by highlighting key performance attributes, potential suppliers, and industry standards. By addressing common pain points and providing actionable insights, this resource equips B2B buyers with the knowledge needed to navigate the complexities of sourcing carbon coatings effectively. Whether you’re seeking to enhance product durability, reduce friction, or improve wear resistance, this guide serves as your essential roadmap in the global market for carbon coatings.
Understanding carbon coatings Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Ceramic Coatings | Durable, hydrophobic, and UV-resistant | Automotive, aerospace, and industrial tools | Pros: Excellent protection, easy maintenance. Cons: Higher initial cost. |
| Graphene Coatings | Superior strength, thermal conductivity, and corrosion resistance | Electronics, automotive, and manufacturing | Pros: Enhanced performance, lightweight. Cons: Limited availability and higher costs. |
| Diamond-Like Carbon (DLC) | Hard, wear-resistant, and low-friction properties | Medical devices, cutting tools, and optics | Pros: High durability, biocompatibility. Cons: Complex application processes. |
| Carbon Nanotube Coatings | Exceptional mechanical properties and electrical conductivity | Aerospace, electronics, and energy sectors | Pros: Lightweight and strong. Cons: Expensive production methods. |
| Carbon-Based Paints | Versatile applications, aesthetic finishes, and protective layers | Automotive, consumer goods, and decorative | Pros: Customizable, cost-effective. Cons: May require frequent reapplication. |
What Are the Key Characteristics of Ceramic Coatings?
Ceramic coatings are known for their durability and hydrophobic properties, which create a protective layer that repels water and contaminants. They are especially suitable for automotive and aerospace applications where resistance to UV rays and harsh weather conditions is essential. B2B buyers should consider the long-term benefits of reduced maintenance and enhanced aesthetics, despite the higher upfront investment.
How Do Graphene Coatings Stand Out in Performance?
Graphene coatings offer unmatched strength and thermal conductivity, making them ideal for high-performance applications in electronics and automotive industries. Their lightweight nature adds to their appeal, particularly in sectors where weight reduction is crucial. Buyers should weigh the advantages of enhanced performance against the potential for higher costs and limited availability in the market.
Why Choose Diamond-Like Carbon (DLC) Coatings?
DLC coatings provide exceptional hardness and wear resistance, making them perfect for medical devices and cutting tools that require longevity and precision. Their biocompatibility is a significant advantage in healthcare applications. However, B2B purchasers must consider the complexity of the application process, which may affect project timelines and costs.
What Are the Benefits of Carbon Nanotube Coatings?
Carbon nanotube coatings are recognized for their remarkable mechanical properties and electrical conductivity, making them suitable for aerospace and electronics applications. Their lightweight nature offers significant advantages in performance. Nevertheless, the production costs associated with these coatings can be a barrier for some buyers, necessitating a careful evaluation of their return on investment.
How Do Carbon-Based Paints Enhance Aesthetic and Functional Value?
Carbon-based paints are versatile and can be customized for aesthetic finishes while providing protective layers for various applications, including automotive and consumer goods. They are cost-effective and easy to apply but may require more frequent reapplication compared to other coating types. B2B buyers should consider the balance between cost, aesthetic appeal, and long-term maintenance when selecting carbon-based paints for their products.
Key Industrial Applications of carbon coatings
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of carbon coatings | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Aerospace | Protective coatings for aircraft components | Enhanced durability and reduced weight, improving fuel efficiency. | Compliance with aerospace standards and certifications. |
| Automotive | Engine components and exterior finishes | Increased wear resistance and aesthetic longevity, reducing maintenance costs. | Supplier reliability and coating performance under extreme conditions. |
| Biomedical | Coatings for dental implants and surgical instruments | Improved biocompatibility and reduced infection rates, enhancing patient outcomes. | Regulatory compliance and material safety certifications. |
| Energy | Coatings for fuel cell components | Enhanced conductivity and corrosion resistance, increasing energy efficiency. | Compatibility with existing manufacturing processes. |
| Industrial Manufacturing | Coatings for cutting tools and machinery parts | Reduced friction and wear, leading to longer tool life and lower operational costs. | Precision in coating thickness and uniformity. |
How Are Carbon Coatings Used in Aerospace Applications?
In the aerospace industry, carbon coatings are utilized on various components, including turbine blades and fuselage parts. These coatings provide superior protection against wear, corrosion, and high temperatures, which are critical for maintaining operational efficiency and safety. For international buyers, especially from Europe and the Middle East, understanding compliance with aerospace standards is crucial when sourcing these coatings. The ability to enhance durability while reducing weight can also lead to improved fuel efficiency, a significant consideration in the cost-sensitive aviation sector.
What Are the Benefits of Carbon Coatings in Automotive Applications?
In automotive applications, carbon coatings are applied to engine components, brake systems, and even the vehicle’s exterior. These coatings enhance wear resistance and provide a protective barrier against environmental factors, thus prolonging the life of parts and reducing maintenance costs. For B2B buyers in regions like South America and Africa, sourcing high-quality coatings that can withstand extreme conditions is essential. Additionally, aesthetic benefits such as improved shine and reduced cleaning frequency can significantly enhance the vehicle’s market appeal.
How Do Carbon Coatings Improve Biomedical Devices?
Carbon coatings are increasingly used in biomedical applications, particularly for dental implants and surgical instruments. These coatings enhance biocompatibility, minimizing the risk of infection and promoting better integration with human tissue. For buyers in the biomedical field, especially in Europe, ensuring that these coatings meet stringent regulatory requirements is paramount. The ability to improve patient outcomes through advanced materials makes carbon coatings a valuable investment in this sector.
What Role Do Carbon Coatings Play in Energy Sector Innovations?
In the energy sector, particularly in fuel cells, carbon coatings are applied to metallic bipolar plates to enhance conductivity and resist corrosion. This leads to improved energy efficiency and longevity of fuel cell systems, which is vital for sustainable energy solutions. International buyers from regions like Africa and South America should consider the compatibility of these coatings with existing manufacturing processes. Understanding the technological advancements in carbon coatings can provide a competitive edge in energy production and management.
How Are Carbon Coatings Beneficial in Industrial Manufacturing?
In industrial manufacturing, carbon coatings are extensively used on cutting tools and machinery parts. These coatings reduce friction and wear, significantly extending the lifespan of tools and decreasing operational costs. For B2B buyers, particularly in Europe and South America, sourcing coatings that ensure precision in thickness and uniformity is critical for maintaining quality standards in production. The reduction in downtime and maintenance enhances overall productivity, making carbon coatings a strategic investment in manufacturing efficiency.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘carbon coatings’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Difficulty in Choosing the Right Type of Carbon Coating for Specific Applications
The Problem: B2B buyers often struggle with selecting the appropriate type of carbon coating for their specific industrial applications. With various options available—such as diamond-like carbon (DLC), carbon nanotubes, and graphene coatings—the decision-making process can be overwhelming. Buyers may fear that choosing the wrong type could lead to inadequate performance, increased costs, or damage to the components they aim to protect, thus creating a significant barrier to making a timely purchase.
The Solution: To effectively navigate this complexity, buyers should begin by conducting a thorough needs assessment that includes understanding the specific requirements of their application, such as load-bearing capacity, environmental exposure, and friction characteristics. Engaging with manufacturers and suppliers who specialize in carbon coatings can provide valuable insights into which coating would best suit their needs. Additionally, utilizing detailed technical datasheets and case studies can help in comparing the performance of different coatings under similar conditions. It is also beneficial to request samples for testing prior to making a bulk purchase, allowing buyers to validate the performance claims in real-world scenarios.
Scenario 2: Concerns About the Longevity and Durability of Carbon Coatings
The Problem: Buyers often express concerns regarding the longevity and durability of carbon coatings, particularly in harsh environments. Industries such as automotive, aerospace, and manufacturing require coatings that can withstand extreme temperatures, corrosive substances, and physical wear and tear. Without assurance of a coating’s lifespan, buyers may hesitate to invest, fearing that frequent replacements could lead to increased operational costs and downtime.
The Solution: To address these concerns, buyers should seek coatings that come with comprehensive warranties and performance guarantees from reputable suppliers. Analyzing independent test results and certifications can also provide confidence in the coating’s durability. Furthermore, establishing a partnership with a coating specialist who can provide ongoing support and maintenance tips will help in extending the life of the coating. Implementing a regular inspection and maintenance schedule can identify potential issues early, allowing for timely interventions that prevent failures and prolong the performance of the coating.
Scenario 3: Challenges in Application and Integration of Carbon Coatings
The Problem: Integrating carbon coatings into existing manufacturing or maintenance processes can pose significant challenges for B2B buyers. Issues may arise from the complexity of the application process, the need for specialized equipment, or the requirement for trained personnel. Buyers may also worry about the potential disruption to production schedules if the coating application process is not streamlined.
The Solution: To mitigate these challenges, buyers should consider collaborating with specialized coating service providers who can offer comprehensive application solutions. Engaging in training programs for in-house staff can also enhance the team’s capability to handle carbon coating applications effectively. Additionally, investing in automated application systems can significantly reduce manual errors and speed up the process, minimizing production downtime. Establishing a clear timeline and project management plan prior to application can further ensure a smooth integration of carbon coatings into existing workflows, leading to improved efficiency and reduced operational disruptions.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for carbon coatings
What Are the Key Properties of Common Materials Used in Carbon Coatings?
When selecting materials for carbon coatings, it’s essential to understand their unique properties and how they align with specific application requirements. Here, we analyze four common materials used in carbon coatings: diamond-like carbon (DLC), graphite, graphene, and carbon nanotubes (CNTs).
How Does Diamond-Like Carbon (DLC) Perform in Carbon Coatings?
Diamond-like carbon (DLC) is known for its exceptional hardness and low friction properties. It typically exhibits a temperature tolerance of up to 300°C and is highly resistant to wear and corrosion. These properties make DLC ideal for applications in automotive and aerospace components, where durability and performance are paramount.
Pros: DLC coatings provide excellent surface protection, reducing wear and extending the lifespan of components. They also offer a low coefficient of friction, enhancing the efficiency of moving parts.
Cons: The manufacturing process for DLC can be complex and costly, which may deter some manufacturers, especially in regions where budget constraints are prevalent.
Impact on Application: DLC’s compatibility with various media, including oils and fuels, makes it suitable for a wide range of applications. However, buyers should consider the specific environmental conditions of their operations.
Considerations for International Buyers: Compliance with international standards such as ASTM or DIN is crucial. Buyers in regions like Europe and South America should verify the certification of DLC coatings to ensure they meet local regulations.
What Advantages Does Graphite Offer as a Carbon Coating Material?
Graphite is a widely used material for carbon coatings due to its excellent thermal and electrical conductivity. It can withstand high temperatures, making it suitable for applications in electronics and high-performance machinery.
Pros: Graphite coatings are relatively easy to apply and provide good lubrication properties, reducing friction and wear.
Cons: While graphite is cost-effective, it may not offer the same level of hardness and wear resistance as DLC or other advanced coatings, limiting its use in high-stress environments.
Impact on Application: Graphite’s compatibility with various lubricants makes it a versatile choice. However, its performance can be affected in corrosive environments, necessitating careful application selection.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should pay attention to the specific grades of graphite used, as different grades may comply with varying international standards.
How Does Graphene Enhance Carbon Coating Applications?
Graphene, a single layer of carbon atoms arranged in a two-dimensional lattice, has gained attention for its remarkable strength and conductivity. It is suitable for applications requiring lightweight and high-strength materials, such as in aerospace and automotive industries.
Pros: Graphene coatings provide exceptional mechanical strength and thermal stability, making them ideal for high-performance applications. They also enhance corrosion resistance.
Cons: The production of graphene can be expensive and complex, which may limit its widespread adoption in cost-sensitive markets.
Impact on Application: Graphene’s unique properties allow it to be used in various environments, including those with extreme temperatures or corrosive substances.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should ensure that graphene coatings meet specific international standards, as the technology is still evolving, and quality can vary significantly.
What Role Do Carbon Nanotubes (CNTs) Play in Carbon Coatings?
Carbon nanotubes (CNTs) are known for their high tensile strength and electrical conductivity. They are often used in composite materials to enhance mechanical properties.
Pros: CNTs improve the overall strength and durability of coatings while also providing excellent thermal and electrical conductivity.
Cons: The complexity of manufacturing CNTs can lead to higher costs, and their dispersion in coatings can be challenging.
Impact on Application: CNTs are particularly beneficial in applications where enhanced mechanical properties are essential, such as in aerospace and automotive sectors.
Considerations for International Buyers: International buyers should be aware of the regulatory landscape surrounding nanomaterials, as compliance can vary significantly across regions.
Summary Table of Carbon Coating Materials
| Material | Typical Use Case for carbon coatings | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Diamond-Like Carbon (DLC) | Automotive and aerospace components | Excellent hardness and wear resistance | Complex and costly manufacturing process | High |
| Graphite | Electronics and high-performance machinery | Good lubrication properties | Limited wear resistance in high-stress environments | Low |
| Graphene | Aerospace and automotive applications | Exceptional strength and corrosion resistance | Expensive and complex production | High |
| Carbon Nanotubes (CNTs) | Composite materials in aerospace and automotive | Enhanced mechanical properties | High manufacturing complexity | Med |
Understanding these materials and their properties allows B2B buyers to make informed decisions that align with their operational needs and compliance requirements.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for carbon coatings
What Are the Key Manufacturing Processes for Carbon Coatings?
The manufacturing processes for carbon coatings involve several critical stages that ensure the final product meets the specific requirements of various industries, including automotive, aerospace, and biomedical applications. The primary stages of manufacturing carbon coatings can be categorized into material preparation, forming, assembly, and finishing.
How Is Material Prepared for Carbon Coatings?
Material preparation is the initial step in the manufacturing process, where the substrate materials—often metals or ceramics—are thoroughly cleaned and prepped. This may involve surface treatments like sandblasting or chemical etching to enhance adhesion. The choice of substrate significantly influences the performance of the carbon coating, as different materials may require unique preparation methods.
Additionally, the selection of carbon-based materials—such as graphite, graphene, or carbon nanotubes—also plays a crucial role in determining the properties of the final coating. Suppliers often provide detailed specifications regarding the types and grades of carbon materials used, allowing B2B buyers to ensure compatibility with their applications.
What Techniques Are Used in Forming Carbon Coatings?
Forming carbon coatings generally utilizes advanced techniques to achieve the desired coating properties. The most common methods include:
-
Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD): This widely used technique involves the deposition of carbon atoms from gaseous precursors onto a substrate, forming a thin film. CVD can produce high-quality coatings with excellent adhesion and uniform thickness, making it ideal for critical applications in aerospace and electronics.
-
Physical Vapor Deposition (PVD): PVD techniques, such as sputtering and evaporation, are employed to create carbon coatings by vaporizing the material and condensing it onto the substrate. PVD is favored for its ability to produce coatings with superior hardness and wear resistance.
-
Plasma-Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition (PECVD): This method combines CVD with plasma technology to enhance the deposition process. PECVD is particularly effective for creating coatings with tailored properties, such as improved biocompatibility for medical applications.
Each of these techniques has its advantages and limitations, and the choice often depends on the specific requirements of the final product, such as thickness, composition, and intended use.
What Quality Control Measures Are Essential for Carbon Coatings?
Quality control (QC) is paramount in ensuring that carbon coatings meet international standards and customer expectations. Various QC measures are implemented throughout the manufacturing process, often aligned with international standards like ISO 9001 and industry-specific certifications.
Which International Standards Should B2B Buyers Consider?
B2B buyers must be aware of relevant international standards that govern the quality of carbon coatings. ISO 9001, which focuses on quality management systems, is fundamental for suppliers aiming to demonstrate their commitment to quality and continuous improvement. Additionally, industry-specific standards such as CE marking for European markets and API standards for the oil and gas sector provide further assurance of compliance and quality.
What Are the Key QC Checkpoints in the Manufacturing Process?
Quality control checkpoints are strategically placed throughout the manufacturing process to monitor and ensure quality. These typically include:
-
Incoming Quality Control (IQC): This initial checkpoint involves inspecting raw materials and components for compliance with specifications before they enter the production line.
-
In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): During production, IPQC monitors the manufacturing processes to identify and rectify any deviations from established parameters. Techniques such as visual inspections, thickness measurements, and adhesion tests are commonly employed.
-
Final Quality Control (FQC): At the end of the production line, FQC ensures that the finished carbon coatings meet all technical and customer specifications. This may involve comprehensive testing, including wear resistance tests, corrosion resistance evaluations, and surface roughness measurements.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control?
For B2B buyers, verifying the quality control processes of potential suppliers is crucial. Several methods can be employed to ensure a supplier’s QC practices are robust:
-
Supplier Audits: Conducting audits of potential suppliers can provide insight into their quality management systems, manufacturing processes, and adherence to international standards. Audits can be performed by the buying company or through third-party organizations.
-
Quality Reports: Requesting quality control reports and documentation from suppliers can help buyers assess their compliance with industry standards. This may include certificates of conformity, test reports, and records of quality inspections.
-
Third-Party Inspections: Engaging third-party inspection agencies can provide an unbiased evaluation of a supplier’s manufacturing capabilities and quality assurance practices. This is particularly important for international buyers who may not have the resources to conduct on-site inspections.
What Are the QC Nuances for International B2B Buyers?
International B2B buyers, especially those from regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, should be aware of specific nuances in quality control when sourcing carbon coatings.
-
Regulatory Compliance: Different regions have distinct regulatory requirements that impact the acceptance of carbon coatings. Buyers must ensure that suppliers comply with local regulations, which may include environmental and safety standards.
-
Cultural Considerations: Understanding cultural differences in business practices can facilitate smoother negotiations and foster stronger relationships with suppliers. Buyers should be mindful of communication styles and negotiation techniques that vary across regions.
-
Logistical Challenges: International shipping and logistics can introduce additional risks to quality. Buyers must consider the impact of transportation on the coatings’ integrity and should work closely with suppliers to establish proper handling and shipping procedures.
In conclusion, a thorough understanding of the manufacturing processes and quality assurance protocols for carbon coatings is essential for B2B buyers. By focusing on these critical aspects, buyers can make informed decisions, ensuring that they source high-quality carbon coatings that meet their specific industrial needs.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘carbon coatings’
Introduction
This practical sourcing guide serves as a comprehensive checklist for B2B buyers looking to procure carbon coatings. Given the diverse applications and technological advancements in carbon-based materials, it is essential to approach sourcing with a clear strategy. This guide outlines the key steps to ensure you select the right carbon coating solutions that meet your specific needs.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Before initiating the sourcing process, establish clear technical specifications for the carbon coatings you require. Consider factors such as the intended application, environmental conditions, and performance requirements.
– Key considerations: Determine the desired properties, such as wear resistance, corrosion resistance, and thermal stability.
– Documentation: Prepare a detailed specification sheet that can be shared with potential suppliers.
Step 2: Research Supplier Capabilities
Conduct thorough research on potential suppliers to gauge their capabilities in providing carbon coatings. This step is critical to ensure that the suppliers can meet your technical specifications.
– Look for experience: Investigate their history in the industry, focusing on their experience with similar projects or applications.
– Check production capacity: Ensure that they have the necessary facilities and technology to handle your order volume and delivery timelines.
Step 3: Evaluate Potential Suppliers
Before making a commitment, it’s vital to vet suppliers thoroughly. Request company profiles, case studies, and references from buyers in similar industries or regions.
– Supplier credentials: Verify any relevant certifications or quality assurance processes they have in place.
– Customer feedback: Seek testimonials or reviews that demonstrate the supplier’s reliability and product quality.
Step 4: Request Samples and Conduct Testing
Once you’ve shortlisted potential suppliers, request samples of their carbon coatings for testing. This step is essential to assess the actual performance of the coatings in real-world conditions.
– Testing criteria: Define the parameters for testing, such as adhesion, durability, and resistance to environmental factors.
– Evaluation metrics: Use standardized tests to ensure a fair comparison between different suppliers’ products.
Step 5: Negotiate Terms and Pricing
Engage in negotiations regarding pricing, delivery schedules, and payment terms. This step can significantly impact your overall procurement costs and project timelines.
– Price comparisons: Compare quotes from multiple suppliers to ensure competitive pricing while considering the total cost of ownership.
– Terms of service: Clarify warranty conditions, return policies, and service agreements to avoid future disputes.
Step 6: Finalize Contracts and Place Orders
After agreeing on terms, finalize contracts and place your orders. Ensure all details, including specifications, pricing, and delivery timelines, are clearly documented.
– Contract review: Have legal counsel review contracts to safeguard your interests and ensure compliance with industry regulations.
– Order confirmation: Request a formal confirmation of the order, including expected delivery dates and tracking information.
Step 7: Establish Ongoing Communication
After placing your order, maintain open lines of communication with your supplier. Regular updates can help address any issues that arise during production or delivery.
– Feedback loop: Provide feedback on product performance post-delivery to foster a mutually beneficial relationship.
– Future collaboration: Discuss potential future needs or projects to ensure your supplier understands your long-term goals.
By following this structured checklist, B2B buyers can navigate the complexities of sourcing carbon coatings effectively, ensuring a successful procurement process that aligns with their operational needs.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for carbon coatings Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components in Carbon Coatings Sourcing?
When sourcing carbon coatings, understanding the cost structure is crucial for B2B buyers. The primary cost components include:
-
Materials: The choice of raw materials significantly impacts pricing. High-quality carbon compounds and additives can elevate costs but also enhance performance. Buyers should consider the trade-off between cost and the technical specifications required for their applications.
-
Labor: Labor costs vary based on geographic location and the complexity of the coating application. Skilled technicians may command higher wages, particularly in regions with stringent quality requirements.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This encompasses utilities, facility maintenance, and administrative expenses. Overhead can fluctuate based on the scale of production and the efficiency of manufacturing processes.
-
Tooling: Initial setup costs for specialized tooling can be substantial, especially for customized applications. These costs should be amortized over the expected production volume.
-
Quality Control (QC): Rigorous QC processes are essential for ensuring the performance and reliability of carbon coatings. The costs associated with testing and certification can add a significant premium to the overall price.
-
Logistics: Transportation costs, including international shipping and customs duties, must be factored into the total cost. These can vary widely depending on the supplier’s location and the chosen shipping methods.
-
Margin: Suppliers typically apply a margin based on their operational costs and market demand. Understanding the competitive landscape can help buyers gauge whether the offered margin is reasonable.
How Do Price Influencers Affect Carbon Coating Costs?
Several factors influence the pricing of carbon coatings:
-
Volume/MOQ: Larger orders often result in lower per-unit costs due to economies of scale. Buyers should assess their projected needs to negotiate favorable terms.
-
Specifications and Customization: Customized solutions tailored to specific applications will typically incur higher costs. Buyers should clearly outline their requirements to avoid unexpected expenses.
-
Materials: The quality and type of carbon materials used can significantly affect price. High-performance coatings may come at a premium but offer better durability and resistance.
-
Quality and Certifications: Coatings that meet industry-specific certifications or quality standards may cost more. Buyers should ensure that any additional investment aligns with their operational needs.
-
Supplier Factors: The reputation and reliability of the supplier can impact pricing. Established suppliers with a track record of quality may charge more but can offer better assurance regarding performance.
-
Incoterms: The terms of trade (Incoterms) dictate shipping responsibilities and costs. Understanding these terms is essential for accurate cost estimation and negotiation.
What Are Effective Buyer Tips for Carbon Coating Sourcing?
To maximize cost efficiency when sourcing carbon coatings, consider the following tips:
-
Negotiate Terms: Leverage your purchasing volume to negotiate better pricing or payment terms. Building a long-term relationship with suppliers can also yield benefits.
-
Evaluate Total Cost of Ownership: Don’t focus solely on the initial purchase price; consider maintenance, operational efficiency, and product lifespan when assessing value.
-
Research Market Prices: Stay informed about market trends and competitor pricing to ensure you are getting a fair deal. This knowledge can empower you during negotiations.
-
Understand Pricing Nuances for International Purchases: Be aware of potential additional costs related to tariffs, shipping, and currency fluctuations when dealing with suppliers from different regions, especially in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe.
Conclusion
While the costs associated with carbon coatings can be complex, understanding the key components and influencers can empower buyers to make informed decisions. By strategically negotiating and evaluating the total cost of ownership, B2B buyers can optimize their sourcing strategies for carbon coatings, ultimately enhancing their operational efficiency and product performance.
Disclaimer: Prices mentioned in this analysis are indicative and can vary based on market conditions and specific supplier offerings.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing carbon coatings With Other Solutions
Introduction: Understanding Alternatives to Carbon Coatings
When considering protective solutions for various applications, carbon coatings stand out due to their unique properties, including durability, wear resistance, and hydrophobic characteristics. However, businesses often seek alternatives that may better suit their specific needs or budget constraints. This analysis compares carbon coatings with two viable alternatives: ceramic coatings and paint protection films (PPF). Each solution offers distinct advantages and disadvantages, making it essential for B2B buyers to understand these differences to make informed decisions.
Comparison Table
| Comparison Aspect | Carbon Coatings | Ceramic Coatings | Paint Protection Film |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | High wear and corrosion resistance; hydrophobic properties | Excellent UV protection; scratch-resistant | Self-healing properties; strong impact resistance |
| Cost | Moderate to high | High | Moderate |
| Ease of Implementation | Requires specialized application techniques | Requires careful surface preparation; can be complex | Generally straightforward; professional installation recommended |
| Maintenance | Low maintenance; easy to clean | Moderate; requires periodic inspection | Low; self-healing reduces upkeep |
| Best Use Case | Industrial applications, automotive, and aerospace | Automotive, aerospace, and biomedical applications | Consumer vehicles, luxury cars, and fleet management |
Detailed Breakdown of Alternatives
Ceramic Coatings
Ceramic coatings are renowned for their robust protection against UV rays and environmental contaminants. They provide a glossy finish that enhances the aesthetic appeal of vehicles while offering excellent scratch resistance. However, the initial cost can be relatively high, and the application process requires meticulous surface preparation to ensure optimal adhesion. While ceramic coatings demand moderate maintenance, they are generally regarded as a long-term investment due to their durability.
Paint Protection Films (PPF)
Paint protection films are designed to shield surfaces from physical damage such as scratches, chips, and road debris. Their self-healing properties allow minor abrasions to disappear over time, making them a popular choice for high-end vehicles. PPF installation is typically straightforward, although professional expertise is recommended to achieve seamless results. While the cost can be moderate, the long-term benefits of preserving the vehicle’s appearance often justify the expense, particularly for luxury or performance cars.
Conclusion: How Should B2B Buyers Choose the Right Solution?
When selecting the appropriate protective coating solution, B2B buyers must consider several factors, including application requirements, budget constraints, and desired performance characteristics. Carbon coatings excel in industrial and high-performance settings, offering exceptional durability and maintenance ease. In contrast, ceramic coatings and paint protection films cater to different needs, such as aesthetic appeal and damage prevention. By evaluating the specific use cases and operational contexts, businesses can make strategic choices that align with their goals, ensuring optimal protection and performance for their investments.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for carbon coatings
What Are the Key Technical Properties of Carbon Coatings?
When considering carbon coatings for various applications, several critical technical properties should be evaluated. Understanding these properties not only aids in selecting the right product but also ensures that it meets the specific requirements of your project or application.
-
Material Grade
– Material grade refers to the quality and composition of the carbon coating. Different grades have varying levels of hardness, wear resistance, and thermal stability. Selecting the appropriate grade is crucial for applications subjected to extreme conditions, such as aerospace or automotive industries, where durability is paramount. -
Thickness
– The thickness of a carbon coating can significantly influence its performance. Thicker coatings often provide enhanced protection against wear and corrosion but may also affect the weight and flexibility of the underlying material. B2B buyers should assess the required thickness based on environmental factors and operational demands. -
Adhesion Strength
– Adhesion strength measures how well the carbon coating bonds to the substrate material. High adhesion strength is essential for ensuring that the coating remains intact during use, particularly in high-stress environments. Poor adhesion can lead to delamination, affecting the longevity and effectiveness of the coating. -
Wear Resistance
– This property indicates the coating’s ability to withstand abrasion and friction. High wear resistance is critical in applications involving moving parts or contact with abrasive materials, such as in manufacturing tools or automotive components. Evaluating wear resistance helps in reducing maintenance costs and prolonging equipment life. -
Thermal Stability
– Thermal stability refers to the coating’s ability to maintain its properties at elevated temperatures. For applications in high-temperature environments, such as in aerospace or energy sectors, selecting a coating with excellent thermal stability is essential to prevent degradation and ensure performance consistency.
What Are Common Trade Terms in the Carbon Coatings Industry?
Familiarity with industry jargon is crucial for effective communication and negotiation in B2B transactions. Here are some common terms you may encounter in the carbon coatings market:
-
OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
– OEM refers to companies that produce parts or equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer. In the context of carbon coatings, understanding OEM relationships helps buyers identify reliable suppliers and manufacturers who can provide tailored solutions for specific applications. -
MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
– MOQ is the smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell. Understanding MOQ is essential for B2B buyers to manage inventory and minimize costs. Low MOQs can be advantageous for smaller businesses or specific projects, while higher MOQs may benefit larger scale operations. -
RFQ (Request for Quotation)
– An RFQ is a document issued by a buyer to solicit price offers from suppliers. It typically includes detailed specifications of the required carbon coatings, making it essential for ensuring competitive pricing and compliance with quality standards. Crafting a clear RFQ can streamline the procurement process. -
Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
– Incoterms are a set of predefined commercial terms published by the International Chamber of Commerce (ICC) that clarify the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in international transactions. Familiarity with Incoterms helps B2B buyers understand shipping, risk, and cost responsibilities, aiding in smoother logistics. -
Lead Time
– Lead time is the period between placing an order and receiving the product. In the carbon coatings industry, lead times can vary based on manufacturing processes and material availability. Understanding lead times is crucial for project planning and ensuring timely delivery of materials.
By grasping these essential properties and trade terms, B2B buyers can make informed decisions when procuring carbon coatings, ultimately enhancing their operational efficiency and product performance.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the carbon coatings Sector
What Are the Current Market Dynamics and Key Trends in the Carbon Coatings Sector?
The carbon coatings market is witnessing robust growth, driven by various global factors such as advancements in technology, increasing demand for durable and high-performance materials, and a shift towards sustainable solutions. Industries such as automotive, aerospace, and electronics are increasingly adopting carbon-based coatings due to their exceptional properties, including wear resistance, low friction, and corrosion protection. In regions like Africa and South America, where industrialization is rapidly advancing, the demand for high-quality carbon coatings is on the rise, particularly in sectors like manufacturing and automotive.
Emerging technologies such as chemical vapor deposition (CVD) and plasma-enhanced chemical vapor deposition (PECVD) are revolutionizing the sourcing landscape, enabling manufacturers to produce coatings with superior characteristics. Furthermore, the trend towards customization is gaining momentum, as international B2B buyers seek tailored solutions that meet specific application requirements. In Europe, particularly in Germany, the focus is on integrating carbon coatings into smart materials and energy-efficient applications, reflecting a broader trend of innovation and sustainability.
The competitive landscape is also evolving, with an increasing number of suppliers entering the market, which enhances options for B2B buyers. However, this also necessitates a strategic approach to sourcing to ensure quality and reliability. International buyers must stay informed about regional suppliers and technological advancements to leverage opportunities effectively.
How Can Sustainability and Ethical Sourcing Impact the Carbon Coatings Sector?
Sustainability has become a pivotal concern for B2B buyers in the carbon coatings sector. The environmental impact of manufacturing processes and the materials used is under scrutiny, prompting companies to adopt more sustainable practices. Ethical sourcing is not just a trend; it is a necessity that influences purchasing decisions. Buyers are increasingly looking for suppliers that adhere to environmental regulations and demonstrate a commitment to reducing their carbon footprint.
In this context, certifications such as ISO 14001 for environmental management and the use of green materials are becoming essential. Suppliers who can showcase their commitment to sustainability through transparent supply chains and eco-friendly practices will be more attractive to buyers seeking to align with responsible sourcing initiatives. Additionally, the integration of biocompatible and recyclable materials in carbon coatings is gaining traction, particularly in markets focused on innovation and sustainability.
As environmental regulations tighten globally, particularly in Europe, buyers must ensure that their suppliers are compliant with these standards. This not only mitigates risk but also enhances brand reputation in an increasingly eco-conscious market.
What Has Been the Evolution of Carbon Coatings in a B2B Context?
The evolution of carbon coatings can be traced back to their initial applications in specialized industries. Initially developed for aerospace and defense, these coatings have expanded into various sectors, including automotive, biomedical, and electronics. The introduction of advanced manufacturing techniques, such as CVD and PECVD, has significantly enhanced the performance and applicability of carbon coatings.
Over the years, the focus has shifted from simply providing protective coatings to developing multifunctional coatings that offer additional benefits such as thermal conductivity and energy efficiency. This evolution reflects the growing demand for materials that not only perform well but also contribute to overall sustainability goals.
As industries continue to innovate, carbon coatings are positioned to play a crucial role in the development of next-generation materials and technologies, making them a vital consideration for B2B buyers looking to stay competitive in their respective markets.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of carbon coatings
-
How do I select the right carbon coating for my application?
Choosing the appropriate carbon coating depends on several factors, including the specific application, environmental conditions, and desired properties. Assess the requirements such as wear resistance, corrosion protection, and thermal stability. For instance, if you’re in the automotive sector, look for coatings that offer high durability and UV resistance. Additionally, consult with suppliers to understand the technical specifications and performance metrics of their products, ensuring they align with your operational needs. -
What are the common applications of carbon coatings in various industries?
Carbon coatings are utilized across diverse sectors, including automotive, aerospace, electronics, and biomedical fields. They enhance surface properties such as hardness, wear resistance, and biocompatibility. For example, in the automotive industry, they protect parts from wear and corrosion, while in electronics, they improve conductivity and thermal management. Understanding your industry’s specific needs can help you identify the best carbon coating solutions for your products. -
What factors should I consider when vetting carbon coating suppliers?
When vetting suppliers, consider their manufacturing capabilities, quality control processes, and experience in your industry. Look for certifications (like ISO) that indicate adherence to quality standards. Additionally, evaluate their technical support and ability to customize coatings based on your requirements. Reviewing customer testimonials and case studies can also provide insights into their reliability and performance. -
What is the minimum order quantity (MOQ) for carbon coatings?
Minimum order quantities for carbon coatings can vary significantly among suppliers, typically ranging from a few liters for small-scale applications to several hundred liters for industrial orders. It’s essential to discuss your specific needs with potential suppliers to understand their MOQ policies. Some suppliers may offer flexibility based on your project scope or ongoing partnerships. -
What payment terms are commonly offered by carbon coating suppliers?
Payment terms can vary, but common practices include upfront payments, net 30, or net 60 days. Some suppliers may also offer discounts for early payments or bulk orders. It’s crucial to clarify these terms upfront and negotiate conditions that suit your cash flow and procurement strategies. Ensure that you understand the implications of different payment terms on your overall project budget. -
How do I ensure quality assurance for carbon coatings?
To ensure quality assurance, request detailed product specifications and compliance documentation from suppliers. Look for third-party testing or certifications that verify the coating’s performance metrics, such as adhesion, hardness, and resistance to environmental factors. Additionally, consider conducting your own quality checks upon receipt of the products, or work with suppliers who offer return policies or guarantees. -
What logistics considerations should I keep in mind when importing carbon coatings?
Logistics for importing carbon coatings involve understanding shipping regulations, customs duties, and transportation methods. Ensure that your supplier provides necessary documentation for customs clearance, such as material safety data sheets (MSDS) and certificates of origin. Additionally, assess the reliability of shipping partners to avoid delays, and consider potential storage solutions if you require large quantities. -
Can carbon coatings be customized for specific applications?
Yes, many suppliers offer customization options for carbon coatings to meet unique application requirements. This can include adjustments in composition, thickness, or performance characteristics. Discuss your specific needs with potential suppliers to explore available customization options and ensure that the coatings are tailored to enhance performance for your intended use.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.
Top 8 Carbon Coatings Manufacturers & Suppliers List
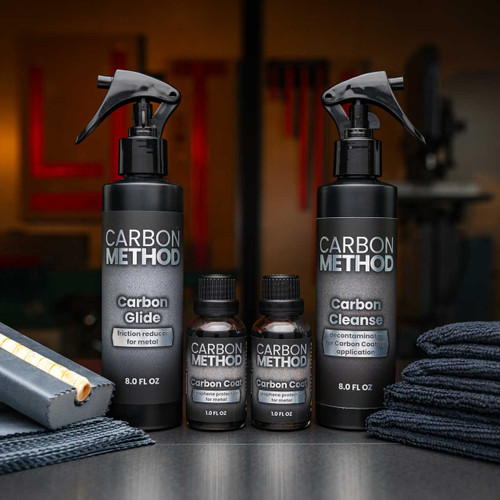
1. Carbon Method – Carbon Coating Kit
Domain: carbonmethod.com
Registered: 2014 (11 years)
Introduction: {“products”:[{“name”:”Carbon Coating Kit”,”price_range”:”$84.99 – $199.99″},{“name”:”Carbon Coating Prep Kit”,”price_range”:”$27.99 – $49.99″},{“name”:”Carbon Cleanse decontaminator for carbon coating application”,”price_range”:”$19.99 – $34.99″},{“name”:”Carbon Coat graphene protection for metal”,”price_range”:”$49.99 – $74.99″},{“name”:”Carbon Glide friction reducer for metal”,”price_range”:”$24…
2. ScienceDirect – Carbon-Based Coatings
Domain: sciencedirect.com
Registered: 1997 (28 years)
Introduction: Carbon-based coatings are bioinert materials that enhance the surface properties of medium-to-heavy load-bearing and wear parts. They offer elevated wear resistance, corrosion resistance, and reduced friction. These coatings have low protein adhesion and improved blood compatibility due to their blood-repelling surfaces. They are synthesized using methods such as physical vapor deposition, chemica…
3. IBC Coatings – DLC Coating
Domain: ibccoatings.com
Registered: 2000 (25 years)
Introduction: DLC Coating – Diamond-Like Carbon Coating – CeraTough™-D
– Type: Nanocomposite coating with properties similar to natural diamond.
– Key Characteristics:
– High hardness
– Low coefficient of friction (0.02 – 0.15)
– High corrosion resistance
– Great adhesion to substrate material
– Fretting resistance
– Adhesive wear resistance
– Self-lubrication in dry wear conditions
– Excellent…
4. Carbon Coatings – Ceramic Coating Solutions
Domain: carboncoatingsus.com
Registered: 2020 (5 years)
Introduction: Ceramic Coating: Long-lasting ceramic coating technology that creates a durable, hydrophobic shield resistant to UV rays, road grime, bird droppings, and harsh weather. Enhances depth and clarity, providing a deep, glossy finish that stays cleaner longer and simplifies maintenance. Suitable for daily commuters and exotic vehicles. Paint Protection Film: Specializes in STEK Paint Protection Film (P…
5. Encyclopedia.pub – Carbon Coating Method for Lithium-Ion Batteries
Domain: encyclopedia.pub
Registered: 2017 (8 years)
Introduction: The carbon coating method enhances the performance of cathode materials in lithium-ion batteries through three main mechanisms: modifying surface chemical stability, enhancing structural stability, and improving Li-ion diffusion. The methods can be categorized into wet chemical methods (such as hydrothermal/solvothermal, sol-gel, and chemical polymerization routes) and dry coating techniques (incl…
6. Vaportech – Diamond-Like Carbon Coatings
Domain: blog.vaportech.com
Registered: 1996 (29 years)
Introduction: Diamond-Like Carbon (DLC) is a range of amorphous carbon coatings that combine properties of both diamond and graphite. Key characteristics include: high hardness, low friction, wear resistance, corrosion resistance, and a distinctive dark gray appearance. DLC coatings can be customized through doping with elements like hydrogen, silicon, or metals to adjust color, conductivity, hardness, and othe…
7. Oerlikon – DLC Coatings
Domain: oerlikon.com
Registered: 1998 (27 years)
Introduction: DLC Coatings by Oerlikon Balzers are diamond-like carbon coatings that offer extreme hardness and low friction, making them ideal for demanding tribological applications. They are designed to withstand high loads and extreme friction, preventing issues such as pitting, galling, and seizing. Applications include performance automotive, racing, wind turbine shaft bearings, stainless steel cutting bl…
8. Edmund Optics – Diamond-Like Carbon Coatings
Domain: edmundoptics.com
Registered: 1999 (26 years)
Introduction: This company, Edmund Optics – Diamond-Like Carbon Coatings, is a notable entity in the market. For specific product details, it is recommended to visit their website directly.
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for carbon coatings
How Can Strategic Sourcing Enhance Your Carbon Coating Procurement?
As the demand for carbon coatings continues to grow across various industries, strategic sourcing plays a pivotal role in securing high-quality materials that deliver superior performance. Buyers must prioritize suppliers who offer advanced synthesis methods, such as chemical vapor deposition and plasma-enhanced techniques, ensuring the coatings exhibit optimal properties like high wear resistance, low friction, and biocompatibility. Establishing robust relationships with manufacturers that emphasize sustainability and innovation will further enhance your supply chain resilience.
The diverse applications of carbon coatings—from automotive to biomedical—highlight their versatility and the significant advantages they provide in protecting assets and improving operational efficiency. For B2B buyers in regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, understanding regional supply chains and potential local partnerships can lead to cost-effective sourcing strategies and improved product availability.
Looking ahead, the evolution of carbon coatings presents exciting opportunities for innovation and growth. Engage with leading suppliers to explore cutting-edge developments that can elevate your business operations. Act now to position your company at the forefront of this dynamic market and leverage the unique advantages offered by advanced carbon coatings.