Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for camera pieces
Navigating the global market for camera pieces presents a unique set of challenges for B2B buyers, particularly those operating in diverse regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. The demand for high-quality camera components—ranging from lenses and sensors to image processors—has surged as photography continues to evolve into an essential tool for businesses across industries. However, sourcing reliable suppliers and understanding the intricacies of these components can be daunting.
This comprehensive guide is designed to empower international B2B buyers by providing in-depth insights into the various types of camera pieces, their applications, and the factors influencing their costs. It will also cover critical aspects such as supplier vetting processes and the latest market trends, enabling buyers to make informed purchasing decisions. By addressing common pain points and highlighting best practices for sourcing camera components, this guide serves as a vital resource for businesses looking to enhance their photography capabilities or expand their product offerings.
With a focus on actionable strategies and expert recommendations, readers will gain the knowledge necessary to navigate the complexities of the camera parts market effectively. Whether you’re a buyer in Germany seeking advanced imaging technology or a procurement manager in Nigeria looking for cost-effective solutions, this guide is tailored to meet your specific needs and elevate your purchasing strategy.
Understanding camera pieces Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Digital Single-Lens Reflex (DSLR) | Interchangeable lenses, optical viewfinder, larger image sensors | Professional photography, events, advertising | Pros: High image quality, versatility with lenses. Cons: Bulkier and heavier than other types. |
| Mirrorless Cameras | Compact design, electronic viewfinder, fast autofocus | Travel photography, videography | Pros: Lightweight, advanced video capabilities. Cons: Battery life can be shorter than DSLRs. |
| Compact Cameras | Fixed lens, user-friendly, lightweight | Casual photography, point-and-shoot | Pros: Easy to use, portable. Cons: Limited manual controls and lower image quality. |
| Action Cameras | Rugged build, wide-angle lens, waterproof capabilities | Adventure sports, outdoor events | Pros: Durable, versatile for different environments. Cons: Limited zoom and low-light performance. |
| Medium Format Cameras | Larger sensors, exceptional detail, and dynamic range | Commercial photography, high-end fashion | Pros: Superior image quality, great for large prints. Cons: Expensive and requires more skill to operate. |
What Are the Characteristics of Digital Single-Lens Reflex (DSLR) Cameras?
DSLR cameras are renowned for their interchangeable lenses and optical viewfinders, which provide a real-time view through the lens. They typically feature larger image sensors, allowing for superior image quality and performance in various lighting conditions. For B2B buyers, DSLRs are ideal for professional photography, events, and advertising campaigns due to their versatility and image quality. However, their bulkier design may be a consideration for businesses that prioritize portability.
How Do Mirrorless Cameras Differ From Traditional DSLRs?
Mirrorless cameras offer a compact design without the mirror mechanism found in DSLRs, utilizing electronic viewfinders instead. This enables faster autofocus and a lighter body, making them suitable for travel photography and videography. B2B buyers should consider mirrorless options for their advanced video capabilities and ease of use. However, they may face shorter battery life compared to DSLRs, which can be a drawback for extended shoots.
Why Are Compact Cameras Popular Among Casual Users?
Compact cameras are designed with a fixed lens and are user-friendly, making them ideal for casual photography and point-and-shoot scenarios. Their lightweight and portable nature appeals to businesses looking for simple solutions for everyday photography needs. However, B2B buyers should note that compact cameras often come with limited manual controls and may not deliver the same image quality as more advanced options.
What Makes Action Cameras Suitable for Adventure Sports?
Action cameras are built for rugged environments, featuring waterproof capabilities and wide-angle lenses. They are perfect for capturing adventure sports and outdoor events, making them a popular choice for businesses in the tourism and sports industries. While their durability and versatility are significant advantages, B2B buyers should be aware that these cameras often have limited zoom and may struggle in low-light conditions.
How Do Medium Format Cameras Stand Out in Commercial Photography?
Medium format cameras are distinguished by their larger sensors, which provide exceptional detail and dynamic range, making them a preferred choice for commercial photography and high-end fashion shoots. B2B buyers looking to produce large prints or require superior image quality should consider these cameras. However, their higher cost and the need for advanced photography skills can be barriers for some businesses.
Key Industrial Applications of camera pieces
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of camera pieces | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Security & Surveillance | High-resolution image sensors for CCTV systems | Enhanced image clarity for effective monitoring | Compatibility with existing systems and durability in various environments |
| Medical Imaging | Specialized lenses for endoscopic cameras | Improved precision in minimally invasive surgeries | Regulatory compliance and compatibility with medical equipment standards |
| Broadcast & Media | High-quality image processors for video production | Superior image quality for professional broadcasting | Supplier reliability and support for rapid technological advancements |
| Automotive Industry | Cameras for advanced driver-assistance systems (ADAS) | Increased safety and automated driving capabilities | Integration with existing vehicle systems and robustness to environmental conditions |
| Agriculture | Imaging sensors for precision farming tools | Data-driven insights for better crop management | Adaptability to various agricultural machinery and weather-resistant features |
How Are Camera Pieces Used in Security & Surveillance?
In the security and surveillance industry, high-resolution image sensors are critical for CCTV systems. These sensors capture clear images even in low-light conditions, enabling effective monitoring of premises. For B2B buyers, sourcing these components requires attention to compatibility with existing security infrastructures and the ability to withstand harsh environmental conditions. International buyers, particularly from regions with varying climates, must ensure that the camera pieces meet local regulatory standards and offer reliable performance over time.
What Role Do Camera Pieces Play in Medical Imaging?
Camera pieces, especially specialized lenses, are essential in medical imaging, particularly in endoscopic procedures. These lenses provide the clarity and precision needed for minimally invasive surgeries, allowing healthcare professionals to visualize internal organs without large incisions. Buyers in the medical sector must prioritize compliance with health regulations and ensure that the camera components are compatible with existing medical devices. This is particularly crucial in regions like Africa and South America, where healthcare standards may vary widely.
How Do Camera Pieces Enhance Broadcast & Media Production?
In the broadcast and media sector, high-quality image processors are vital for video production. These processors ensure superior image quality, allowing broadcasters to deliver professional-grade content. For international B2B buyers, sourcing these processors involves assessing supplier reliability and their capacity to keep pace with rapid technological advancements. Buyers must also consider the compatibility of these components with various broadcasting equipment, especially in diverse markets across Europe and the Middle East.
Why Are Camera Pieces Important for the Automotive Industry?
Camera pieces, particularly those used in advanced driver-assistance systems (ADAS), play a significant role in enhancing vehicle safety. These cameras enable features such as lane-keeping assistance and collision avoidance, contributing to the growing trend of automated driving. B2B buyers in the automotive sector must focus on the integration capabilities of these camera systems with existing vehicle architectures and ensure that they can withstand challenging environmental conditions. This is particularly relevant for buyers in regions prone to extreme weather.
How Are Camera Pieces Utilized in Agriculture?
In agriculture, imaging sensors are increasingly used in precision farming tools to gather data on crop health and soil conditions. These sensors provide actionable insights that enable farmers to optimize their operations, leading to improved yields and reduced resource wastage. Buyers in this sector should look for camera pieces that can adapt to various agricultural machinery and are robust enough to handle different weather conditions. This is especially important in regions like Africa and South America, where agricultural practices and climates can vary significantly.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘camera pieces’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Navigating Compatibility Issues with Camera Lenses
The Problem:
B2B buyers in photography-related industries often face compatibility challenges when sourcing camera lenses. Different brands utilize proprietary lens mounts, leading to confusion over which lenses can be paired with specific camera bodies. For example, a buyer may invest in a high-end DSLR camera, only to discover that the lenses they purchased are not compatible due to differing mount specifications. This not only wastes financial resources but also hinders the ability to produce quality images, leading to frustration and potential delays in project timelines.
The Solution:
To effectively navigate these compatibility issues, buyers should prioritize thorough research before making purchases. It is crucial to check the lens mount specifications of the camera body and ensure that any additional lenses meet these requirements. Utilizing online resources, such as manufacturer websites or photography forums, can provide valuable insights into compatible lenses. Additionally, buyers should consider investing in third-party lenses that are specifically designed to fit multiple brands, as these often offer versatility without sacrificing quality. Partnering with reputable suppliers that provide clear compatibility information can also mitigate these issues, ensuring that buyers can confidently expand their lens collections without future conflicts.
Scenario 2: Managing the Learning Curve of Advanced Camera Features
The Problem:
As technology advances, many modern cameras come equipped with complex features that can overwhelm users, particularly those transitioning from basic to professional-level photography. B2B buyers who purchase high-end cameras may struggle to utilize features like manual exposure settings, autofocus modes, and image processing options. This learning curve can lead to underutilization of the equipment, resulting in subpar images that do not meet client expectations and potentially harming business reputations.
The Solution:
To overcome the learning curve associated with advanced camera features, B2B buyers should invest in comprehensive training and resources. Engaging in workshops or online courses focused on specific camera models can provide hands-on experience and practical insights into using advanced features effectively. Additionally, buyers should leverage manufacturer resources, such as user manuals and tutorial videos, which often cover essential functionalities in detail. Creating a supportive community among peers through forums or social media groups can also facilitate knowledge sharing and troubleshooting, allowing users to learn from each other’s experiences. Establishing a culture of continuous learning within the organization can lead to improved photography skills and better utilization of camera capabilities.
Scenario 3: Addressing Image Quality Concerns in Low Light Conditions
The Problem:
For B2B buyers in sectors like real estate, event photography, or product promotion, capturing high-quality images in low light conditions is often a significant challenge. Many cameras struggle to produce clear images without introducing noise or blurriness, which can adversely affect the quality of marketing materials or client portfolios. Buyers may find themselves frustrated when their equipment fails to deliver expected results, particularly in crucial business scenarios.
The Solution:
To address image quality concerns in low light conditions, buyers should focus on sourcing cameras equipped with larger image sensors and lenses with wide apertures (low f-stop numbers). These features allow more light to enter the camera, improving performance in dim settings. Additionally, investing in external lighting solutions, such as portable LED lights or on-camera flashes, can enhance image quality significantly. Buyers should also experiment with different camera settings, such as increasing ISO sensitivity, while being mindful of the trade-off between sensitivity and noise levels. Regular practice in low-light conditions, along with utilizing advanced post-processing software, can further enhance the final output, ensuring that the images produced meet professional standards even in challenging lighting situations.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for camera pieces
What Are the Key Materials Used in Camera Pieces?
When selecting materials for camera components, it is essential to consider their properties, advantages, disadvantages, and how they align with international standards and buyer preferences. Here, we analyze four common materials used in camera pieces: aluminum, plastic, glass, and magnesium alloy.
How Does Aluminum Benefit Camera Manufacturing?
Aluminum is widely utilized in camera construction due to its favorable strength-to-weight ratio and corrosion resistance. This metal can withstand varying temperatures and pressures, making it suitable for outdoor photography equipment. Its lightweight nature enhances portability, a crucial factor for photographers who travel frequently.
Pros: Aluminum is durable and resistant to corrosion, ensuring longevity in various environments. It is relatively easy to machine, allowing for intricate designs and precise tolerances.
Cons: While aluminum is cost-effective, it can be more expensive than some plastics. Additionally, it may not provide the same level of shock absorption as other materials, which could be a concern for high-impact applications.
Impact on Application: Aluminum is compatible with various media, including water and dust, making it ideal for rugged camera housings.
Considerations for International Buyers: Compliance with standards such as ASTM and DIN is crucial. Buyers in regions like Europe and the Middle East often prefer aluminum due to its established reputation for quality and durability.
What Role Does Plastic Play in Camera Components?
Plastic is another common material used in camera production, particularly for internal components and casings. It offers excellent moldability and can be produced in various colors and finishes, enhancing aesthetic appeal.
Pros: Plastic is lightweight and cost-effective, making it a popular choice for budget-conscious manufacturers. Its ability to absorb shock helps protect sensitive components.
Cons: While durable, plastic may not offer the same level of heat resistance as metals. Over time, it can become brittle, especially under UV exposure, which may lead to cracking.
Impact on Application: Plastic is compatible with various media but may require additional treatments for enhanced UV resistance.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should ensure that the plastics used comply with regulations regarding environmental impact, such as REACH in Europe. In regions like Africa and South America, the cost-effectiveness of plastic can be a significant advantage.
How Does Glass Enhance Camera Performance?
Glass is primarily used for lenses and viewfinders in cameras. Its optical clarity and ability to refract light make it indispensable for high-quality imaging.
Pros: Glass provides superior optical performance, allowing for sharp images with minimal distortion. It is also highly resistant to scratching, maintaining clarity over time.
Cons: The fragility of glass can be a limitation, as it is prone to breaking under impact. Additionally, high-quality optical glass can be expensive, increasing overall production costs.
Impact on Application: Glass is essential for applications requiring high precision and clarity, such as professional photography and videography.
Considerations for International Buyers: Compliance with optical standards is critical, particularly in Europe, where regulations may dictate the quality of optical components.
Why is Magnesium Alloy Preferred in High-End Cameras?
Magnesium alloy is increasingly popular in high-end camera models due to its exceptional strength and lightweight properties. It offers a robust alternative to aluminum while maintaining a low profile.
Pros: Magnesium alloy provides excellent durability and resistance to corrosion. Its lightweight nature enhances portability without compromising structural integrity.
Cons: The manufacturing process for magnesium alloy can be more complex and costly compared to aluminum and plastic. Additionally, it may require specialized machining tools.
Impact on Application: Magnesium alloy is suitable for high-performance applications, particularly in professional photography where durability is paramount.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should be aware of specific compliance requirements for magnesium alloys, as they may vary by region. In markets like Germany, adherence to stringent quality standards is expected.
Summary Table of Material Selection for Camera Pieces
| Material | Typical Use Case for camera pieces | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Aluminum | Camera bodies, mounts | Durable and corrosion-resistant | Less shock absorption | Medium |
| Plastic | Internal components, casings | Lightweight and cost-effective | Can become brittle over time | Low |
| Glass | Lenses and viewfinders | Superior optical clarity | Prone to breaking | High |
| Magnesium Alloy | High-end camera bodies | Excellent strength-to-weight ratio | More complex manufacturing process | High |
This guide provides a comprehensive overview of the materials used in camera pieces, helping international B2B buyers make informed decisions based on performance, cost, and compliance with regional standards.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for camera pieces
What Are the Main Stages of Manufacturing Camera Pieces?
The manufacturing of camera components is a complex process that involves multiple stages to ensure precision and quality. The main stages include material preparation, forming, assembly, and finishing.
Material Preparation
Material preparation begins with selecting high-quality raw materials such as metals, plastics, and optical glass. For instance, aluminum and magnesium alloys are commonly used for camera bodies due to their lightweight and durable properties. The quality of these materials directly impacts the final product’s performance and longevity.
Once the materials are selected, they undergo processes such as cutting, machining, and polishing. Optical glass, for example, must be cut and polished to exact specifications to ensure clarity and minimize optical distortions. Advanced technologies like CNC (Computer Numerical Control) machining are often employed to achieve the desired precision in shaping components like lens mounts and viewfinders.
What Forming Techniques Are Commonly Used in Camera Manufacturing?
Forming techniques are essential for shaping the raw materials into usable components. Common methods include injection molding for plastics, die casting for metals, and glass molding for lenses.
-
Injection Molding: This technique is predominantly used for producing plastic parts such as buttons, casing, and internal components. It allows for high-volume production with consistent quality and intricate designs.
-
Die Casting: Metals are melted and poured into molds to create parts like the camera body or internal frames. This method is favored for its ability to produce complex shapes with high dimensional accuracy.
-
Glass Molding: This process is critical for lens manufacturing, where glass is heated to a malleable state and then formed into specific shapes. The precision of this process is vital for achieving the optical quality required in camera lenses.
How Is Assembly Conducted in Camera Manufacturing?
Assembly is a meticulous stage that requires skilled labor and precision tools. Components are carefully assembled to ensure that they fit together seamlessly. Automated assembly lines are often used for high-volume production, particularly for repetitive tasks like inserting sensors or attaching lens mounts.
Quality control checkpoints are integrated throughout the assembly process. For example, during the assembly of the image sensor, alignment and connectivity are checked to ensure proper functioning. Any misalignment can lead to significant issues in image quality, making this stage critical.
What Finishing Processes Are Applied to Camera Components?
Finishing processes enhance the aesthetic appeal and functionality of camera components. These processes can include surface treatments, painting, and coating. Anodizing is a popular method for metal parts, which not only improves corrosion resistance but also allows for various color options.
In addition, lens coatings are applied to reduce glare and enhance light transmission. These coatings are crucial for ensuring that the lenses deliver high-quality images under various lighting conditions.
How Does Quality Assurance Fit into Camera Manufacturing?
Quality assurance (QA) is integral to the manufacturing process of camera components. It ensures that each part meets specific standards before being assembled into a final product.
What International Standards Should B2B Buyers Look For?
B2B buyers should be aware of relevant international standards that govern manufacturing practices. ISO 9001 is one of the most recognized quality management system standards, ensuring that organizations consistently meet customer and regulatory requirements.
In addition to ISO standards, industry-specific certifications like CE (Conformité Européenne) and API (American Petroleum Institute) may also be relevant, particularly for specialized applications. These certifications indicate compliance with safety and performance standards that can be critical in certain markets.
What Are the Key Quality Control Checkpoints in Camera Manufacturing?
Quality control checkpoints are established at various stages of the manufacturing process, including:
-
Incoming Quality Control (IQC): Raw materials and components are inspected upon arrival to ensure they meet specified standards.
-
In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): This occurs during the manufacturing process, where ongoing inspections and tests are conducted to identify defects early.
-
Final Quality Control (FQC): Before products are shipped, they undergo a comprehensive inspection to verify that they meet all quality standards and specifications.
Common testing methods used in quality control include functional testing, stress testing, and optical performance assessments. These tests are crucial for ensuring that the final product performs as expected in real-world conditions.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control?
B2B buyers must take proactive steps to ensure the suppliers they choose uphold stringent quality control standards. Here are some methods to verify supplier QC:
What Should Buyers Look for in Supplier Audits and Reports?
Conducting supplier audits is an effective way to assess a manufacturer’s quality control processes. Buyers can request documentation related to their quality management systems, such as ISO certifications and internal audit reports.
Additionally, buyers should inquire about the supplier’s history of compliance with international standards and any third-party inspections they may have undergone. Reliable suppliers will be transparent about their quality control processes and willing to share relevant documentation.
How Do Third-Party Inspections Work?
Third-party inspections are conducted by independent organizations that evaluate the supplier’s manufacturing practices and quality standards. These inspections provide an objective assessment of the supplier’s capabilities and compliance with international standards.
Buyers can request inspection reports to gain insights into the supplier’s quality assurance processes and any areas that require improvement. This can be especially valuable for buyers operating in regions like Africa and South America, where local manufacturing practices may vary.
What Are the Quality Control Nuances for International B2B Buyers?
International B2B buyers, especially from diverse regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, face unique challenges when navigating quality control in camera manufacturing. Understanding the regional differences in manufacturing standards and practices is crucial.
Buyers should be aware of the specific certifications required in their target markets. For example, while CE certification may be sufficient for European markets, additional certifications may be necessary for African or Middle Eastern markets.
Furthermore, cultural differences can impact supplier relationships. Establishing clear communication regarding quality expectations and standards is essential to foster a mutually beneficial partnership.
In conclusion, a comprehensive understanding of the manufacturing processes and quality assurance practices in camera piece production is vital for B2B buyers. By focusing on the key stages of manufacturing, relevant international standards, and effective verification methods, buyers can make informed decisions that ensure they source high-quality camera components.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘camera pieces’
Introduction
This sourcing guide serves as a practical checklist for B2B buyers looking to procure essential camera pieces. Understanding the intricacies of camera components is critical for ensuring the quality and compatibility of your photography equipment. This guide will help you navigate the procurement process effectively, enabling you to make informed decisions that enhance your business operations.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Before initiating the sourcing process, clearly outline the technical specifications required for the camera pieces. This includes factors such as resolution, sensor type, and lens compatibility. Having specific requirements helps in shortlisting suppliers who can meet your exact needs, ensuring that the equipment performs optimally for your business.
Step 2: Research and Identify Reputable Suppliers
Conduct thorough research to identify suppliers with a strong reputation in the camera equipment industry. Look for suppliers with positive reviews, established track records, and industry recognition. Engage with online forums and industry groups to gather insights from other businesses, which can guide you towards trustworthy suppliers.
Step 3: Evaluate Product Quality and Compatibility
Assess the quality of the camera pieces offered by potential suppliers. Request product samples or detailed specifications to understand the materials used, build quality, and performance metrics. Additionally, ensure that the components are compatible with your existing equipment, which can save you time and costs associated with returns or replacements.
Step 4: Verify Supplier Certifications and Compliance
It is crucial to verify that your suppliers hold relevant certifications and comply with industry standards. Look for certifications such as ISO 9001 for quality management systems or CE marking for compliance with European safety standards. This step ensures that you are sourcing from suppliers who adhere to best practices, which can directly impact the reliability of the camera pieces.
Step 5: Request Detailed Pricing and Terms
Gather detailed pricing information from shortlisted suppliers, including unit costs, bulk purchase discounts, and shipping fees. Clarify payment terms, lead times, and warranty policies to avoid any misunderstandings later. Transparent pricing and clear terms can help you manage your budget effectively and make informed purchasing decisions.
Step 6: Assess After-Sales Support and Service
Consider the after-sales support and service provided by the supplier. A reliable supplier should offer technical support, warranty services, and easy returns. Strong after-sales support can significantly enhance your operational efficiency and ensure that any issues with the camera pieces are resolved promptly.
Step 7: Make an Informed Decision and Place Your Order
After completing your evaluations, compile all findings and make an informed decision. Weigh the pros and cons of each supplier based on product quality, pricing, and support. Once you have chosen a supplier, place your order while confirming all details, including delivery timelines and payment agreements, to ensure a smooth transaction.
By following these steps, B2B buyers can effectively navigate the sourcing process for camera pieces, ensuring that they obtain high-quality equipment that meets their operational needs.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for camera pieces Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components in Camera Parts Sourcing?
When sourcing camera pieces, understanding the cost structure is essential for effective budgeting and decision-making. The primary cost components include materials, labor, manufacturing overhead, tooling, quality control (QC), logistics, and profit margin.
-
Materials: The choice of materials significantly impacts pricing. High-quality glass for lenses, advanced sensors, and durable plastics or metals for the body can lead to higher costs. Buyers should consider the long-term benefits of investing in higher-grade materials that enhance the durability and performance of the camera.
-
Labor: Labor costs vary based on geographical location and the complexity of the manufacturing process. Regions with lower labor costs might seem attractive; however, this can affect the quality and consistency of the final product.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This encompasses all indirect costs involved in production, such as utilities, rent, and administrative expenses. Efficient factories may reduce overhead costs, which can be passed on to buyers.
-
Tooling: Initial tooling costs for specialized equipment can be substantial but are often amortized over large production runs. For custom pieces, these costs can be significant and should be factored into the total cost.
-
Quality Control: Rigorous QC processes ensure that the camera parts meet the required standards and specifications. While this adds to costs, it is crucial for maintaining quality and reducing returns or failures.
-
Logistics: Transportation and storage costs are also key components. Global sourcing may involve complex logistics, including import duties and shipping fees, which need to be calculated to determine the total cost.
-
Margin: Suppliers typically add a profit margin to their costs, which can vary significantly between manufacturers. Understanding the competitive landscape and negotiating effectively can help buyers achieve better pricing.
How Do Price Influencers Affect Camera Parts Sourcing?
Several factors can influence the price of camera components, impacting the overall cost to buyers:
-
Volume and Minimum Order Quantity (MOQ): Bulk purchasing can lead to lower per-unit costs. Buyers should negotiate MOQs that align with their needs while maximizing cost-efficiency.
-
Specifications and Customization: Custom parts or those with advanced specifications generally cost more. Buyers should evaluate whether customization is necessary for their target market.
-
Material Quality and Certifications: Higher quality materials often come with certifications that ensure reliability and performance. These certifications can justify higher prices but may also be essential for meeting market demands.
-
Supplier Factors: Supplier reputation, reliability, and experience can influence pricing. Established suppliers may charge a premium, but their reliability can reduce risks associated with production delays and quality issues.
-
Incoterms: Understanding Incoterms is critical for international transactions as they define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers regarding shipping, insurance, and tariffs. This knowledge can help buyers manage costs effectively.
What Are Some Effective Buyer Tips for Sourcing Camera Parts?
-
Negotiation Strategies: Engage suppliers in discussions about pricing and be prepared to negotiate terms. Highlight your purchasing potential to leverage better deals.
-
Focus on Cost-Efficiency: Assess the Total Cost of Ownership (TCO), which includes not just the purchase price but also long-term costs related to maintenance, warranty, and performance.
-
International Pricing Nuances: Be aware of fluctuations in currency exchange rates and how they can affect pricing. Additionally, consider the impact of local regulations and tariffs on overall costs when sourcing from different regions, particularly in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe.
-
Research and Benchmarking: Conduct thorough market research to understand competitive pricing and product offerings. This will empower buyers to make informed decisions and negotiate effectively.
Conclusion
Sourcing camera pieces requires a comprehensive understanding of cost structures and price influencers. By being informed and strategic, international B2B buyers can navigate the complexities of the market, ensuring they secure quality products at competitive prices while optimizing their total cost of ownership.
Disclaimer: Prices mentioned are indicative and may vary based on market conditions and supplier negotiations.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing camera pieces With Other Solutions
Understanding the Alternatives to Camera Pieces in Photography Solutions
In the rapidly evolving landscape of photography and imaging technology, businesses must evaluate various solutions to capture high-quality images. While traditional camera pieces provide specific advantages, alternative solutions may offer different benefits suited to particular needs. This analysis compares camera pieces against advanced smartphone cameras and drone photography, enabling B2B buyers to make informed decisions based on performance, cost, and application.
Comparison Table
| Comparison Aspect | Camera Pieces | Smartphone Cameras | Drone Photography |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | High-quality images with interchangeable parts; offers manual controls for professionals. | Good image quality; convenient but limited manual control. | Excellent for aerial shots; high resolution, but can vary with model. |
| Cost | Typically high due to multiple components; initial investment can be significant. | Generally lower; integrated into smartphones, making them affordable. | Varies widely; from affordable models to premium drones, depending on features. |
| Ease of Implementation | Requires knowledge of settings and components; may need training for optimal use. | User-friendly; most users can operate with minimal learning curve. | Moderate; requires basic piloting skills and understanding of regulations. |
| Maintenance | Regular maintenance needed for parts like lenses and sensors; potential repair costs. | Low maintenance; mainly software updates and occasional hardware care. | Moderate; battery maintenance and occasional repairs needed. |
| Best Use Case | Professional photography, events, and studios requiring high-quality images. | Casual photography, social media, and travel due to portability. | Aerial photography for real estate, events, and landscape shots; unique perspectives. |
What Are the Benefits and Drawbacks of Smartphone Cameras?
Smartphone cameras have revolutionized photography by integrating advanced imaging technology into a portable device. They are user-friendly, allowing even novices to capture decent images without extensive knowledge of photography. However, while smartphone cameras are great for casual use, they typically lack the advanced features that professional photographers might require, such as interchangeable lenses and precise manual controls. Their performance can also be hindered in low-light situations compared to traditional camera pieces.
How Does Drone Photography Compare to Camera Pieces?
Drone photography offers unique advantages, particularly for capturing aerial shots and expansive landscapes. Drones equipped with high-resolution cameras can provide stunning images from angles and perspectives that are difficult to achieve with traditional camera setups. However, piloting a drone requires some skill and knowledge of local regulations, which may pose a barrier for some users. Additionally, drones can be more susceptible to environmental conditions, such as wind and rain, which may affect performance and image quality.
Conclusion: Which Photography Solution Is Right for Your Business?
When choosing between camera pieces and alternative solutions like smartphone cameras or drone photography, businesses should assess their specific needs and objectives. For high-quality, professional photography, investing in camera pieces remains the best option. Conversely, if the goal is to capture casual moments or conduct real estate shoots from unique angles, smartphone cameras and drones may provide adequate solutions at a lower cost and with greater convenience. Understanding these alternatives ensures that B2B buyers can select the right tools to meet their photography requirements effectively.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for camera pieces
What Are the Key Technical Properties of Camera Pieces?
Understanding the essential technical properties of camera components is crucial for B2B buyers in the photography industry. Here are some critical specifications that can impact performance and compatibility.
1. Material Grade
Material grade refers to the quality and type of materials used in manufacturing camera components, such as aluminum, plastic, or glass. For instance, high-grade aluminum is often used for camera bodies due to its lightweight and durable properties. In B2B transactions, material grade affects product lifespan and maintenance costs, making it vital to assess when sourcing components.
2. Tolerance Levels
Tolerance levels indicate the allowable deviations in dimensions during the manufacturing process. For camera parts like lens mounts and shutter mechanisms, precise tolerances are necessary to ensure proper fit and function. Inaccurate tolerances can lead to poor performance or failure, impacting customer satisfaction. Understanding these specifications helps buyers select reliable suppliers who can meet stringent quality requirements.
3. Sensor Resolution
Sensor resolution is measured in megapixels (MP) and determines the detail captured in an image. A higher resolution offers better image quality, essential for professional photography. Buyers must consider the intended use of the camera pieces; for instance, commercial photographers may prioritize higher resolutions, while casual users might not require such specifications. This understanding helps in making informed purchasing decisions based on market demands.
4. Aperture Range
The aperture range of a camera lens indicates its ability to open and close, affecting light intake and depth of field. Measured in f-stops, a lens with a lower f-stop number can achieve wider openings, suitable for low-light conditions. In B2B contexts, specifying the desired aperture range ensures that suppliers provide products tailored to specific photography needs, enhancing overall user experience.
5. Compatibility Standards
Compatibility standards refer to the specifications that ensure various camera components work seamlessly together. This includes lens mounts, communication protocols, and power supply specifications. Buyers must verify compatibility to avoid issues related to interoperability, which can lead to increased operational costs and delays in production.
What Are Common Trade Terms in the Camera Industry?
Familiarity with industry-specific jargon is vital for effective communication and negotiation in B2B transactions. Here are some common terms related to camera pieces:
1. OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
OEM refers to companies that produce parts or equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer. In the camera industry, an OEM might supply lenses or sensors to a brand that assembles complete cameras. Understanding OEM relationships is crucial for buyers looking to source quality components without compromising brand integrity.
2. MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ is the smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell. This term is essential for buyers as it directly impacts inventory management and cash flow. Knowing the MOQ allows businesses to plan their purchases strategically, ensuring they meet market demands without overcommitting resources.
3. RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a document that buyers send to suppliers to request pricing for specific products or services. In the camera industry, an RFQ helps buyers compare costs and terms from multiple suppliers, facilitating better purchasing decisions. A well-structured RFQ can lead to more accurate quotes and ultimately better pricing.
4. Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
Incoterms are a set of rules that define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in international trade transactions. These terms clarify who is responsible for shipping costs, insurance, and liability. For B2B buyers in the camera industry, understanding Incoterms helps mitigate risks and avoid misunderstandings in cross-border transactions.
5. Lead Time
Lead time refers to the time taken from placing an order to receiving the product. In the camera industry, lead times can vary significantly based on manufacturing processes and supply chain logistics. Buyers should consider lead times when planning product launches or inventory replenishment to ensure they meet customer expectations.
By grasping these technical properties and trade terms, B2B buyers can navigate the complex landscape of camera components more effectively, ensuring they make informed decisions that align with their business objectives.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the camera pieces Sector
What Are the Current Trends Influencing the Camera Pieces Market?
The global camera pieces market is experiencing dynamic shifts driven by technological advancements, evolving consumer preferences, and the rising demand for high-quality imaging solutions. With the proliferation of social media and digital content creation, there is a significant increase in demand for advanced camera components, particularly from international B2B buyers in regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. Key trends include the integration of artificial intelligence (AI) in camera functionalities, such as enhanced autofocus systems and smart image processing. These technologies enable photographers and videographers to achieve superior results with minimal effort, making them essential for both professional and amateur users.
Moreover, sustainability is becoming a crucial factor in sourcing decisions. Buyers are increasingly seeking suppliers that prioritize eco-friendly materials and practices, reflecting a broader trend toward responsible consumption. Additionally, the growth of e-commerce platforms is transforming the sourcing landscape, allowing buyers to access a wider array of camera components directly from manufacturers and distributors worldwide. This has made it easier for international buyers, particularly from emerging markets, to find competitive pricing and innovative products.
The shift towards modular camera systems is also notable, as it allows users to customize their setups according to specific needs. This trend not only enhances user experience but also opens new avenues for B2B partnerships in the supply chain, as manufacturers and suppliers collaborate to offer interchangeable parts that meet diverse consumer demands.
How Is Sustainability Shaping Sourcing Practices in the Camera Pieces Sector?
Sustainability and ethical sourcing have emerged as critical considerations for B2B buyers in the camera pieces market. The environmental impact of manufacturing processes, including the extraction of raw materials and energy consumption, is under scrutiny. International buyers are increasingly aware of the carbon footprint associated with camera production and are looking for suppliers who adopt sustainable practices. This includes the use of recycled materials, energy-efficient production methods, and waste reduction strategies.
Furthermore, ethical supply chains are gaining traction, with buyers prioritizing manufacturers that uphold labor rights and fair trade principles. Certifications such as ISO 14001 for environmental management and Fair Trade certification are becoming essential for suppliers aiming to establish credibility in the B2B market. By aligning with suppliers who adhere to these standards, buyers can mitigate risks associated with unethical practices and enhance their brand reputation.
Incorporating ‘green’ certifications and materials into product offerings not only fulfills regulatory requirements but also appeals to environmentally conscious consumers. As the demand for sustainable products grows, suppliers who can demonstrate their commitment to sustainability will likely see a competitive advantage in the market.
What Historical Developments Have Influenced the Camera Pieces Market?
The evolution of camera technology has been marked by significant milestones that have shaped the current landscape of the camera pieces market. Initially, photography relied on analog systems, which were limited in functionality and accessibility. The introduction of digital cameras in the late 20th century revolutionized the industry, allowing for instant image capture and editing. This shift not only democratized photography but also led to the development of advanced camera components such as image sensors, processors, and lenses.
As digital cameras became more sophisticated, the demand for high-quality camera pieces surged, prompting manufacturers to innovate continuously. The rise of mirrorless cameras and smartphones equipped with advanced imaging technology has further transformed consumer expectations, driving the need for specialized components that enhance performance and usability.
In recent years, the integration of connectivity features, such as Wi-Fi and Bluetooth, has enabled seamless sharing and editing of images, appealing to a generation of content creators. This historical context underscores the importance of adaptability and innovation in the camera pieces market, as international B2B buyers seek suppliers who can meet the evolving demands of a diverse and dynamic customer base.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of camera pieces
-
How do I solve issues with camera parts compatibility?
To address compatibility issues with camera parts, start by confirming the specific camera model and its lens mount type. Each camera manufacturer has unique specifications, so ensure that the parts you source are designed for your camera model. Establish a strong relationship with suppliers who can provide detailed product information and compatibility charts. Additionally, consider requesting samples or technical data sheets to verify that the components meet your requirements before placing a bulk order. -
What is the best type of lens for professional photography?
The best type of lens for professional photography depends on the specific needs of the photographer. For versatility, a standard zoom lens (e.g., 24-70mm) is an excellent choice, providing a range of focal lengths suitable for various situations. For portrait photography, a prime lens with a wide aperture (like 85mm f/1.8) can create stunning bokeh effects. Ensure that the lens you choose is compatible with your camera’s mount and meets your desired image quality and performance standards. -
What are the key factors to consider when vetting camera parts suppliers?
When vetting camera parts suppliers, prioritize factors such as their industry experience, product quality, and customer reviews. Look for suppliers that provide certifications and warranties for their products, as this indicates reliability. Assess their capacity to fulfill orders, including their minimum order quantities (MOQs) and lead times. Communication is vital; a responsive supplier will be easier to work with. Lastly, consider their geographical location to evaluate shipping times and costs, especially for international trade. -
What are common payment terms for international camera parts orders?
Common payment terms for international camera parts orders include options like advance payment, partial payment upon order confirmation, and balance payment before shipment. Letters of credit are often used for larger transactions to ensure security for both parties. It’s crucial to establish clear payment terms in your purchase agreement to avoid misunderstandings. Discussing these terms upfront can help build trust with your supplier and ensure a smooth transaction process. -
How can I customize camera components for my business needs?
To customize camera components, first communicate your specific requirements to potential suppliers. Many manufacturers offer customization options, such as unique colors, branding, or specialized features tailored to your business needs. Be prepared to provide detailed specifications and, if possible, prototypes to ensure your vision is accurately conveyed. Keep in mind that customization may affect lead times and costs, so plan accordingly in your procurement strategy. -
What quality assurance measures should I implement when sourcing camera parts?
Implement quality assurance measures by requiring your suppliers to provide product certifications, inspection reports, and samples for testing before large orders. Establish clear quality criteria based on your specific needs and ensure that suppliers understand these standards. Regular audits and quality checks during production can help mitigate issues. Additionally, consider a third-party inspection service to verify quality before shipment, especially for international orders where distance may complicate oversight. -
What logistics considerations should I keep in mind when importing camera parts?
When importing camera parts, logistics considerations include shipping methods, customs regulations, and potential tariffs. Choose a reliable freight forwarder with experience in handling electronic components to navigate the complexities of international shipping. Understand the customs duties applicable to your products and prepare all necessary documentation to facilitate a smooth clearance process. Additionally, factor in lead times and potential delays when planning your inventory management strategy. -
How do I handle returns and warranty claims for camera parts?
Handling returns and warranty claims requires a clear return policy established with your suppliers before purchase. Ensure that you understand the conditions under which returns are accepted and the process for submitting warranty claims. Maintain documentation for all transactions, including invoices and correspondence with suppliers, to streamline the claims process. Communicating effectively with your supplier about any issues can help resolve matters quickly and maintain a positive business relationship.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.
Top 7 Camera Pieces Manufacturers & Suppliers List
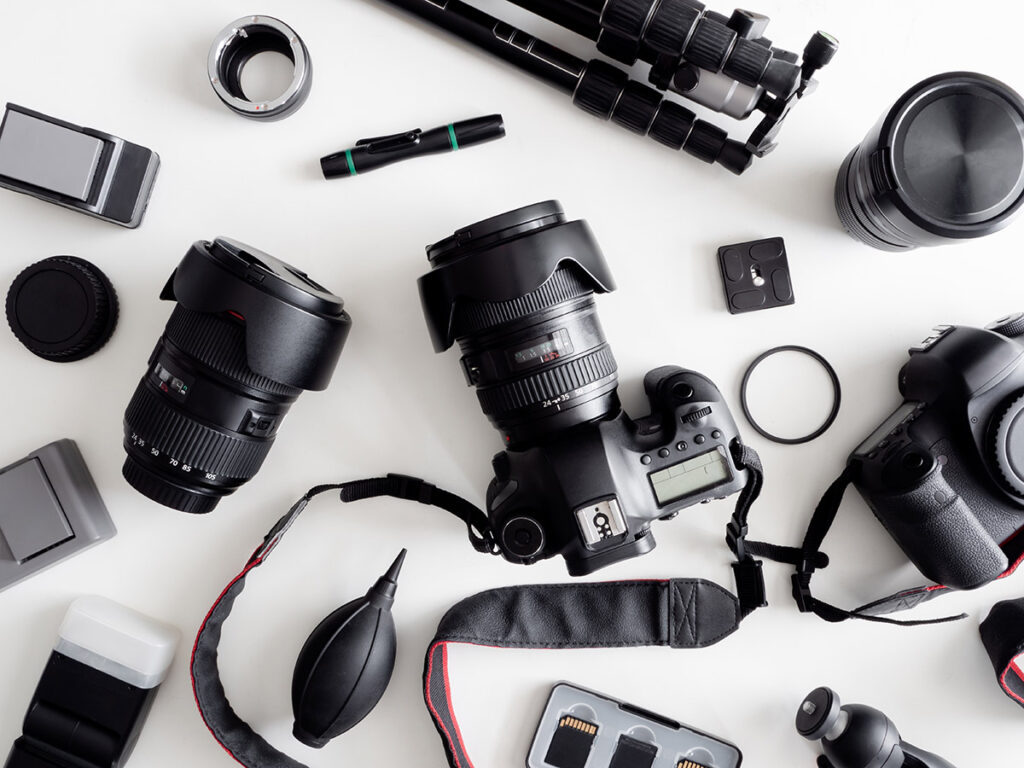
1. Adorama – Key Camera Components
Domain: adorama.com
Registered: 1996 (29 years)
Introduction: Viewfinder: Rectangular part at the back for framing subjects; may display shutter speed, aperture, and ISO. Pentaprism: Mirror at a 45-degree angle that projects light from the lens to the viewfinder, essential for SLR cameras. Built-in Flash: Produces a burst of light when triggered, fixed position on the camera. Flash Button: Forces the built-in flash to open and adjust intensity on some models…
2. Mefoto – Camera Accessories
Domain: mefoto.com
Registered: 2001 (24 years)
Introduction: 1. Viewfinder: A rectangular part on the camera’s back that allows you to frame subjects before taking a shot, can be digital with display settings.
2. Pentaprism: A mirror positioned at a 45° angle that reflects light from the lens to the viewfinder, essential for SLR cameras.
3. Built-in Flash: A small light that activates to illuminate subjects when taking a picture.
4. Flash Button: Opens the …
3. Wedio – Camera Essentials
Domain: wedio.com
Registered: 2003 (22 years)
Introduction: 1. Lens mount index: A mark on the lens mount to assist in attaching a lens to the camera body. 2. Mode dial: A small cogwheel on the top of the camera to switch between different camera modes. 3. Flash button: A button on the top of the camera to activate the flash and adjust its intensity, present only if the camera has a built-in flash. 4. Lens release button: A button located on the front of t…
4. Ace Photo – Digital Camera Parts
Domain: acephoto.net
Registered: 1999 (26 years)
Introduction: The best selection of Digital Camera Parts at Ace Photo includes parts for various brands such as Canon, Nikon, Olympus, Leica, and Vivitar. Key categories of digital camera parts offered are: Fuji Camera Parts, Hot Shoe Covers, Misc Screws, Battery Doors, Digital Camera Screen Protectors, Underwater Point and Shoot Accessories, Action and 360 Accessories, Digital Projectors, Digital Camera LCD Ho…
5. Camera Parts – Genuine Components
Domain: ebay.com
Registered: 1995 (30 years)
Introduction: Digital Camera Parts available for various brands including Canon, Nikon, Sony, GoPro, Fujifilm, Olympus, Panasonic, and more. Key compatible series include Canon EOS, Nikon D, Sony Alpha, and others. Products include genuine parts like rubber eye cups, circuit boards, and LCD screens. Items are available in new, used, and for parts condition. Price range varies, with options under $17, $17 to $30…
6. Lippert – Furrion Replacement Vision S Displays
Domain: lippert.com
Registered: 1996 (29 years)
Introduction: Furrion Replacement Vision S 7″ Display #C-FOS07TAPK-008 – $485.95; Furrion Replacement Vision S 5″ Display #C-FOS07TAPK-009 – $458.95; Furrion Replacement Vision S 4.3″ Display #C-FOS07TAPK-010 – $291.95; Lippert Insight™ Camera LCD Display Kit – $235.95; Furrion Vision S® 7-Way Adapter with Power Switch for RV Camera System #F2BC004XXBK – $65.95; Furrion Replacement Vision S Side Marker Light Co…
7. Clean Camera Support – Replacement Rangefinder Kip Handle
Domain: cleanscamerasupport.com
Registered: 2013 (12 years)
Introduction: {“products”:[{“name”:”REPLACEMENT Rangefinder Kip Handle”,”price”:”$25.00″},{“name”:”REPLACEMENT Rosie Adapters”,”price”:”$25.00″,”variants”:[“arri”,”flat”,”smallhd”]},{“name”:”REPLACEMENT Screw Rangefinder Fixed”,”price”:”$25.00″},{“name”:”REPLACEMENT dovetail screw”,”price”:”$10.00″},{“name”:”Thumbscrew”,”price”:”$30.00″},{“name”:”REPLACEMENT Spinner Plates”,”price”:”$125.00″,”rating”:”5.00″,”re…
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for camera pieces
How Can Strategic Sourcing Enhance Your Camera Piece Procurement?
In conclusion, a thorough understanding of camera components and their functionalities is essential for B2B buyers aiming to optimize their procurement strategies. Strategic sourcing not only ensures access to high-quality camera parts but also fosters relationships with reliable suppliers, which can lead to cost efficiencies and improved product offerings.
International buyers from diverse regions, including Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, should prioritize partnerships with manufacturers that provide comprehensive insights into their products. This approach allows for informed decision-making and enhances the overall value proposition of your camera offerings.
As the demand for advanced camera technology continues to grow, aligning your sourcing strategies with market trends will be crucial. Invest in suppliers who demonstrate innovation and adaptability to emerging technologies. By doing so, you will not only enhance your competitive edge but also position your business for future success. Embrace the opportunities ahead and take action to refine your sourcing strategies today. Your next breakthrough in camera technology could be just a partnership away.