Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for bronze v copper
In the complex landscape of global sourcing, understanding the nuances between bronze and copper is essential for B2B buyers aiming to make informed decisions. The challenge often lies in not just recognizing the distinct properties and applications of these two metals, but also navigating the intricate supply chains that span continents, particularly for buyers from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. This guide is designed to illuminate the critical differences between bronze and copper, equipping you with insights into their various types, applications, and the factors influencing procurement costs.
As you delve into the specifics, you will discover how bronze, known for its hardness and corrosion resistance, stands apart from copper, celebrated for its excellent electrical conductivity and antimicrobial properties. We will explore supplier vetting processes, ensuring you select partners who meet stringent quality standards. Additionally, you’ll gain an understanding of market trends and pricing dynamics that affect sourcing decisions.
By the end of this guide, you will be empowered to navigate the complexities of sourcing bronze and copper, enabling you to optimize your purchasing strategy and enhance your operational efficiency. Whether you’re in construction, manufacturing, or art, having a solid grasp of these materials will be invaluable in meeting your project needs and ensuring long-term success.
Understanding bronze v copper Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Copper | Pure elemental metal with high electrical conductivity | Electrical wiring, plumbing, roofing | Pros: Excellent conductivity, antimicrobial properties. Cons: Lower hardness compared to alloys. |
| Bronze | Alloy primarily of copper and tin, harder than copper | Marine hardware, sculptures, bearings | Pros: Corrosion-resistant, low friction. Cons: More brittle than copper. |
| Phosphor Bronze | Contains tin and phosphorus for enhanced strength | Electrical connectors, springs, bushings | Pros: High fatigue resistance, excellent wear resistance. Cons: Higher cost due to alloying elements. |
| Aluminum Bronze | Contains aluminum for increased strength and corrosion resistance | Marine applications, pumps, valves | Pros: Strong and resistant to seawater. Cons: More challenging to machine than other bronzes. |
| Silicon Bronze | Contains silicon for improved strength and corrosion resistance | Valve components, pump parts | Pros: Good weldability and corrosion resistance. Cons: Limited availability compared to other alloys. |
What Are the Key Characteristics of Copper for B2B Buyers?
Copper is a highly ductile and malleable metal known for its excellent electrical and thermal conductivity. Its pure form is commonly used in electrical wiring, plumbing, and roofing applications due to its ability to resist corrosion and its antimicrobial properties. B2B buyers should consider the specific grades of copper available, such as oxygen-free copper, which is ideal for high-conductivity applications. However, its lower hardness compared to alloys may limit its use in more demanding environments.
How Does Bronze Differ from Copper in Industrial Applications?
Bronze, primarily an alloy of copper and tin, boasts enhanced hardness and corrosion resistance, making it suitable for applications in marine environments, sculptures, and bearings. Its unique properties allow it to withstand harsh conditions while minimizing metal-to-metal friction. Buyers should evaluate the specific type of bronze needed, as variations exist based on additional alloying elements. While bronze is more brittle than copper, its durability in demanding applications often justifies the trade-off.
What Advantages Does Phosphor Bronze Offer for Electrical Applications?
Phosphor bronze is a specialized alloy that includes tin and phosphorus, providing exceptional strength and fatigue resistance. This alloy is particularly advantageous in manufacturing electrical connectors, springs, and bushings, where durability and performance are critical. B2B buyers should assess the specific mechanical properties required for their applications, as the inclusion of phosphorus enhances wear resistance. However, the cost may be higher due to the complexity of alloying.
Why Choose Aluminum Bronze for Marine Applications?
Aluminum bronze is an alloy that incorporates aluminum to improve strength and corrosion resistance, especially in marine environments. Its resilience against seawater makes it ideal for applications such as marine hardware, pumps, and valves. Buyers in the maritime sector should consider the mechanical properties and corrosion resistance of aluminum bronze when making purchasing decisions. While it offers superior performance, it may present challenges during machining, which should be factored into project timelines and costs.
What Are the Benefits of Using Silicon Bronze in Manufacturing?
Silicon bronze is known for its high strength and excellent corrosion resistance, often used in valve components and pump parts. Its ability to be easily welded and its resistance to corrosion make it a preferred choice for various industrial applications. B2B buyers should look for silicon bronze when durability and performance are essential, especially in environments exposed to moisture. However, its availability may be limited compared to other more common alloys, which can impact procurement timelines.
Key Industrial Applications of bronze v copper
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of bronze v copper | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Electrical Engineering | Wiring and connectors | High conductivity ensures efficient energy transfer | Ensure compliance with international electrical standards |
| Marine Engineering | Ship fittings and propellers | Corrosion resistance enhances longevity in harsh environments | Verify alloy specifications for seawater compatibility |
| Construction | Plumbing and roofing materials | Durability and resistance to corrosion reduce maintenance costs | Source materials that meet local building codes |
| Arts and Culture | Sculptures and musical instruments | Aesthetic appeal and acoustic properties increase market value | Consider local artisanship and cultural relevance |
| Industrial Machinery | Bearings and bushings | Reduced friction improves operational efficiency | Assess load-bearing capacities and environmental conditions |
How is Copper Used in Electrical Applications and What Are the Benefits?
In electrical engineering, copper is predominantly used for wiring and connectors due to its exceptional electrical conductivity. This makes it an ideal choice for various applications, from residential wiring to large-scale industrial systems. For international buyers, particularly in regions like Africa and South America, it’s crucial to ensure that the copper sourced meets the required electrical standards and certifications to guarantee safety and efficiency. The ability of copper to resist corrosion also contributes to its longevity, reducing the need for frequent replacements and maintenance.
What Role Does Bronze Play in Marine Engineering?
Bronze is extensively utilized in marine engineering, particularly for ship fittings and propellers. Its inherent corrosion resistance makes it suitable for prolonged exposure to seawater, thereby enhancing the lifespan of marine equipment. For buyers in the Middle East and Europe, selecting the right bronze alloy is essential to ensure compatibility with specific marine environments and regulatory standards. This not only mitigates the risk of equipment failure but also supports sustainable practices by extending the service life of marine components.
How Does the Construction Industry Benefit from Bronze and Copper?
In the construction sector, both bronze and copper find applications in plumbing and roofing materials. Copper’s durability and corrosion resistance make it a preferred choice for piping systems, while bronze is often used in fixtures that require strength and aesthetic appeal. For B2B buyers in regions like Nigeria and Vietnam, sourcing materials that comply with local building regulations is vital. Additionally, the long-term cost savings associated with reduced maintenance and replacement needs can significantly enhance project profitability.
Why are Bronze and Copper Important in Arts and Culture?
Bronze is favored for creating sculptures and musical instruments due to its aesthetic qualities and acoustic properties. Its muted gold tone adds value to artistic creations, while its durability ensures that sculptures withstand the test of time. For international buyers, especially those in culturally rich markets, partnering with local artisans who understand the material’s properties can lead to unique and culturally relevant products. Sourcing considerations should include the alloy composition to achieve desired artistic effects while maintaining structural integrity.
What Are the Advantages of Using Bronze in Industrial Machinery?
In industrial machinery, bronze is commonly used for bearings and bushings, where its low metal-to-metal friction is a significant advantage. This property not only enhances the efficiency of machinery but also reduces wear and tear, leading to lower operational costs. For buyers in sectors like manufacturing, understanding the specific load-bearing capacities and environmental conditions where the bronze components will operate is critical. Ensuring that the sourced bronze meets these specifications can lead to improved machinery performance and extended service life.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘bronze v copper’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Confusion Over Material Properties for Specific Applications
The Problem: B2B buyers often grapple with the decision of whether to use bronze or copper for particular applications. For instance, a manufacturer might need a material for marine components that can withstand corrosion but is also strong enough to handle mechanical stress. The challenge arises when the buyer is unsure of the specific properties of each metal, leading to potential project delays or product failures due to incorrect material selection.
The Solution: To alleviate this confusion, it is crucial to conduct a comprehensive analysis of the required properties for the intended application. Buyers should collaborate closely with metallurgical experts to assess factors such as tensile strength, corrosion resistance, and thermal conductivity. For marine applications, bronze is typically the better choice due to its superior resistance to saltwater corrosion. Buyers can utilize detailed product specifications and performance data from reputable suppliers to make informed decisions. Additionally, creating a checklist of essential material properties tailored to each application can streamline the selection process and reduce the risk of material misapplication.
Scenario 2: Sourcing High-Quality Materials in a Competitive Market
The Problem: In international markets, particularly in regions like Africa and South America, the challenge of sourcing high-quality bronze or copper can be daunting. Buyers often encounter issues with inconsistent quality, fluctuating prices, and unreliable suppliers. This can result in project delays, increased costs, and ultimately, dissatisfaction with the final product quality.
The Solution: Establishing strong relationships with certified suppliers and conducting regular audits of their production processes can significantly mitigate these issues. Buyers should prioritize suppliers who adhere to international quality standards, such as ISO certifications, and who can provide traceability for their materials. Additionally, utilizing technology such as digital platforms to compare supplier offerings can ensure competitive pricing while securing the best quality. It’s also beneficial to engage in long-term contracts with reliable suppliers to stabilize pricing and ensure consistent material quality. Regular communication and feedback loops with suppliers can further enhance reliability and transparency in sourcing.
Scenario 3: Balancing Cost with Performance Requirements
The Problem: Many B2B buyers face the dilemma of balancing cost with the performance requirements of their projects. While copper may be less expensive upfront, its properties might not meet the rigorous demands of specific applications, leading to higher long-term costs due to maintenance or replacements. Conversely, while bronze may offer superior performance, the higher initial cost can strain budgets, especially for smaller businesses.
The Solution: To tackle this issue, buyers should perform a total cost of ownership (TCO) analysis for both materials, considering not just the purchase price but also maintenance, longevity, and performance over time. This analysis should include factors such as lifespan, corrosion resistance, and the potential costs associated with material failure. Engaging in pilot testing with small batches of both materials can provide valuable insights into their performance in real-world applications, helping to justify the investment in higher-quality materials like bronze. Furthermore, exploring bulk purchase agreements or cooperative buying strategies with other businesses can help offset costs while ensuring access to superior materials.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for bronze v copper
What Are the Key Properties of Copper?
Copper is renowned for its exceptional thermal and electrical conductivity, making it a preferred choice for applications in electrical wiring, telecommunications, and industrial machinery. Its resistance to corrosion, particularly in atmospheric conditions, enhances its longevity in various environments. Additionally, copper exhibits good machinability and retains its mechanical properties even at cryogenic temperatures. However, its relatively lower hardness compared to bronze can limit its use in high-stress applications.
Pros & Cons of Copper
Copper’s advantages include its excellent conductivity, ease of fabrication, and antimicrobial properties, making it suitable for medical and food processing industries. However, its susceptibility to wear and lower strength compared to bronze can be a drawback in demanding applications. Furthermore, copper is generally more expensive than some other metals, which can be a consideration for budget-sensitive projects.
Impact on Application
In applications requiring high conductivity, such as electrical connectors and wiring, copper’s properties are unmatched. However, when exposed to harsh environments, its corrosion resistance may not suffice, necessitating additional protective measures.
How Does Bronze Compare to Copper?
Bronze, primarily an alloy of copper and tin, offers enhanced hardness and corrosion resistance, particularly in marine environments. The incorporation of additional elements like aluminum or phosphorus can further improve its mechanical properties and wear resistance. Bronze is less malleable than copper but offers superior strength, making it suitable for applications such as bearings, bushings, and marine hardware.
Pros & Cons of Bronze
The primary advantage of bronze is its durability and resistance to corrosion, especially in seawater, making it ideal for maritime applications. However, bronze can be more challenging to manufacture due to its higher melting point and potential brittleness in certain alloys. Additionally, the cost of bronze can be higher than copper, particularly for high-grade alloys.
Impact on Application
Bronze’s unique properties make it particularly well-suited for applications in marine settings, where corrosion resistance is critical. Its low friction characteristics also make it a preferred choice for moving parts in machinery, enhancing operational efficiency.
What Specific Considerations Should International B2B Buyers Keep in Mind?
When sourcing materials like copper and bronze, international buyers, especially from regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, must consider compliance with local and international standards. Common standards such as ASTM (American Society for Testing and Materials), DIN (Deutsches Institut für Normung), and JIS (Japanese Industrial Standards) can significantly influence material selection. Additionally, understanding regional preferences and availability of materials can help in making informed purchasing decisions.
For instance, in markets like Nigeria and Vietnam, local suppliers may offer specific grades of copper and bronze that meet local standards, potentially impacting pricing and lead times. Buyers should also consider the logistics of transporting these materials, as bulk shipments can incur significant costs.
Summary Table of Material Comparisons
| Material | Typical Use Case for bronze v copper | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Copper | Electrical wiring, telecommunications | Excellent conductivity and antimicrobial properties | Lower hardness and wear resistance | Medium |
| Bronze | Marine hardware, bearings, sculptures | High corrosion resistance and durability | More complex manufacturing process | High |
| Brass | Plumbing fixtures, musical instruments | Good malleability and aesthetic appeal | Prone to dezincification in harsh environments | Medium |
| Phosphor Bronze | Electrical connectors, springs | High fatigue resistance and toughness | Limited availability in some regions | High |
This guide provides a comprehensive overview of the strategic material selection process for copper and bronze, enabling B2B buyers to make informed decisions based on their specific application needs and market conditions.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for bronze v copper
What Are the Key Stages in Manufacturing Copper and Bronze?
The manufacturing processes for copper and bronze involve several critical stages: material preparation, forming, assembly, and finishing. Each of these stages plays a vital role in ensuring the quality and performance of the final products.
Material Preparation: How Are Raw Materials Processed for Copper and Bronze?
In the material preparation stage, raw copper and alloying metals (such as tin for bronze) are sourced and processed. For copper, this often involves mining, smelting, and refining to achieve the desired purity levels. High-purity copper is essential for applications requiring excellent electrical and thermal conductivity.
For bronze, the process begins similarly but includes the careful selection of alloying elements. The combination of copper with tin or other metals is crucial, as it determines the final properties of the bronze. These materials are typically melted in a furnace, where precise temperature control is necessary to ensure homogeneity and prevent contamination.
Forming: What Techniques Are Used to Shape Copper and Bronze?
The forming stage encompasses various techniques, including casting, forging, rolling, and extrusion. For both copper and bronze, casting is a common method, where molten metal is poured into molds to create specific shapes. This method is particularly effective for producing complex geometries.
Forging is another prevalent technique, especially for high-strength applications. It involves shaping the metal through compressive forces, resulting in improved structural integrity due to grain refinement. Rolling and extrusion are employed to produce sheets, rods, or tubes, allowing for versatility in product dimensions.
How Is Assembly Conducted in Copper and Bronze Manufacturing?
Assembly processes may vary depending on the final product’s application. For electrical components, for instance, soldering or brazing is frequently used to join copper parts, leveraging its excellent thermal and electrical conductivity. In contrast, bronze components may be assembled using mechanical fastening methods due to their higher strength and hardness.
Quality assurance during assembly is crucial, as it ensures that the final product meets the required specifications. This may involve the use of jigs and fixtures to maintain precise tolerances throughout the assembly process.
What Finishing Techniques Are Employed for Copper and Bronze Products?
Finishing processes are essential for enhancing the aesthetic and functional properties of copper and bronze products. Common techniques include polishing, plating, and coating. Polishing not only improves the appearance but also reduces surface roughness, which can enhance corrosion resistance.
Plating may be used to apply a protective layer, especially for copper products in environments prone to oxidation. Coatings can also be applied to bronze components to enhance their resistance to environmental factors, particularly in marine applications.
What Quality Assurance Standards Are Relevant for Copper and Bronze Manufacturing?
Quality assurance (QA) is a critical aspect of manufacturing copper and bronze products. International standards such as ISO 9001 provide a framework for establishing an effective quality management system (QMS). This standard ensures that manufacturers consistently produce products that meet customer and regulatory requirements.
For industry-specific applications, additional certifications may be necessary. For example, the European CE marking indicates compliance with safety and environmental protection requirements, while the American Petroleum Institute (API) certification is essential for products used in the oil and gas sector.
What Are the Key QC Checkpoints in the Manufacturing Process?
Quality control (QC) checkpoints throughout the manufacturing process help ensure that products meet stringent quality standards. Common checkpoints include:
-
Incoming Quality Control (IQC): Raw materials are inspected upon arrival to ensure they meet specified standards. This includes checking for purity levels in copper and the correct alloy composition in bronze.
-
In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): During manufacturing, processes are monitored to detect any deviations from established parameters. This may involve real-time testing of temperature, pressure, and material properties.
-
Final Quality Control (FQC): The completed products undergo rigorous testing to ensure they meet all specifications. This may include dimensional checks, mechanical property testing, and corrosion resistance assessments.
Which Testing Methods Are Commonly Used in Copper and Bronze Manufacturing?
Several testing methods are employed to verify the quality of copper and bronze products. Common methods include:
-
Spectroscopy: Used to analyze the composition of alloys and ensure they meet required specifications.
-
Tensile Testing: Assesses the strength and ductility of the material, crucial for applications requiring specific mechanical properties.
-
Corrosion Testing: Evaluates the material’s resistance to environmental factors, particularly important for marine applications.
-
Electrical Conductivity Testing: Measures the efficiency of copper and bronze in electrical applications, ensuring they meet industry standards.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control Practices?
B2B buyers must ensure that their suppliers adhere to rigorous quality control practices. Here are some actionable steps:
-
Conduct Supplier Audits: Regular audits can help assess a supplier’s adherence to quality standards and processes. This can include site visits to evaluate manufacturing practices and QC measures.
-
Request Quality Reports: Suppliers should provide documentation detailing their QC procedures, test results, and compliance with international standards.
-
Engage Third-Party Inspectors: Utilizing independent inspectors can offer unbiased assessments of product quality, providing additional assurance of compliance with specifications.
-
Check Certifications: Ensure that suppliers hold relevant certifications (ISO, CE, API) and verify their validity through the issuing bodies.
What Are the QC and Certification Nuances for International Buyers?
International B2B buyers, particularly from regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, must navigate various certification and quality assurance nuances. Differences in local regulations, standards, and certification bodies can complicate procurement.
-
Understanding Regional Standards: Buyers should familiarize themselves with regional standards and certifications that may apply to their products, as these can differ significantly from international norms.
-
Navigating Import Regulations: Compliance with local import regulations is crucial. Buyers should ensure that their suppliers can provide the necessary documentation to facilitate smooth customs clearance.
-
Building Relationships with Local Inspectors: Establishing relationships with local quality assurance professionals can provide valuable insights into regional compliance requirements and help navigate potential challenges.
By understanding these manufacturing processes and quality assurance practices, B2B buyers can make informed decisions when sourcing copper and bronze products. This knowledge not only enhances product reliability but also fosters long-term partnerships with suppliers committed to quality excellence.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘bronze v copper’
In the competitive landscape of B2B procurement, understanding the differences between bronze and copper is essential for making informed purchasing decisions. This guide offers a practical checklist for international buyers looking to source these metals effectively, ensuring that you choose the right material for your specific application.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Before reaching out to suppliers, clearly outline your project requirements. Determine the specific properties you need from either bronze or copper, such as corrosion resistance, thermal or electrical conductivity, and mechanical strength. Knowing these specifications will help you narrow down your options and communicate effectively with potential suppliers.
Step 2: Assess Application Requirements
Consider the end-use of the material. For instance, if your project involves marine applications, bronze may be preferable due to its superior corrosion resistance in seawater. In contrast, if electrical conductivity is paramount, copper might be the more suitable choice. Understanding these distinctions will guide you toward the appropriate metal.
Step 3: Evaluate Potential Suppliers
Thoroughly vet potential suppliers to ensure they meet your quality and reliability standards. Request detailed company profiles, product catalogs, and certifications that demonstrate their compliance with international standards. Look for reviews or case studies from other businesses in your sector to gain insight into their performance and reliability.
Step 4: Request Material Samples
Before making a bulk order, always request samples of the metal you intend to procure. This allows you to evaluate the quality, finish, and physical properties firsthand. Pay attention to aspects such as surface texture and color, as these can impact both performance and aesthetics, especially in decorative applications.
Step 5: Verify Supplier Certifications
Ensure that your chosen suppliers hold relevant certifications, such as ISO 9001 or specific metal quality standards. These certifications provide assurance of their commitment to quality management and product consistency. Additionally, inquire about their supply chain practices to ensure ethical sourcing of raw materials.
Step 6: Compare Pricing and Payment Terms
Gather quotes from multiple suppliers to compare pricing structures. Be mindful of the total cost of ownership, which includes not just the price per unit but also shipping fees, taxes, and any potential tariffs. Negotiate favorable payment terms, ensuring they align with your budget and cash flow requirements.
Step 7: Establish Communication Channels
Develop clear lines of communication with your suppliers. Establishing a point of contact will facilitate smoother transactions and help resolve any issues that may arise during the procurement process. Regular updates on order status and delivery schedules can also enhance collaboration and trust.
By following this checklist, B2B buyers can navigate the complexities of sourcing bronze and copper with confidence, ensuring that they select the right materials for their specific needs while fostering strong supplier relationships.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for bronze v copper Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components in Sourcing Bronze and Copper?
When evaluating the cost structure for sourcing bronze versus copper, several key components come into play. The primary materials cost will vary significantly based on the alloying elements in bronze and the purity of copper. Copper is generally more expensive due to its high demand in electrical applications, while bronze, being an alloy, can fluctuate in price based on its tin content and other elements like aluminum or phosphorus.
Labor costs will depend on the complexity of manufacturing processes. Bronze often requires more intricate techniques for casting and machining, which can lead to higher labor costs compared to copper, which is more straightforward to work with. Manufacturing overhead, including utilities and facility maintenance, also plays a role, especially in regions with high energy costs. Tooling costs can be significant for both materials, particularly for custom designs or high-volume production runs.
Quality control (QC) is another essential component, particularly for international buyers who may require certifications for compliance with local regulations. The logistics of transporting these materials, especially from regions like Africa or South America to Europe or the Middle East, can add additional costs, influenced by shipping methods and tariffs. Lastly, the supplier’s margin will vary based on their market positioning and the exclusivity of their products.
How Do Price Influencers Affect Bronze and Copper Sourcing?
Several factors influence the pricing of bronze and copper, which international B2B buyers should consider. Volume and minimum order quantities (MOQ) can significantly impact pricing; larger orders typically benefit from economies of scale. Custom specifications can also affect price, as unique requirements for dimensions or alloy compositions necessitate specialized production processes.
The quality of materials is crucial; higher-grade copper or bronze alloys that meet specific certifications will command higher prices. Buyers should inquire about the supplier’s quality assurance practices and the certifications they hold. Supplier factors, such as reputation, reliability, and location, also play a role in pricing. For instance, sourcing from a well-established supplier may come at a premium but can reduce risks associated with quality inconsistencies.
International buyers should also consider Incoterms when negotiating prices, as they dictate the responsibilities of buyers and sellers regarding shipping, insurance, and tariffs, which can significantly affect the total cost.
What Buyer Tips Can Enhance Cost-Efficiency for Bronze and Copper?
To optimize sourcing costs for bronze and copper, buyers should engage in effective negotiation strategies. Understanding the supplier’s cost structure can provide leverage during discussions, particularly if the buyer can commit to larger volumes or long-term contracts. It’s essential to communicate specific needs clearly, as this can lead to more tailored pricing arrangements.
Considering the Total Cost of Ownership (TCO) is vital; this includes not just the purchase price but also costs associated with maintenance, durability, and potential resale value. For example, while bronze may have a higher upfront cost, its longevity and corrosion resistance might lead to lower maintenance costs in marine applications.
Pricing nuances are particularly relevant for international buyers. Understanding local market conditions, currency fluctuations, and geopolitical factors can help in making informed decisions. Buyers from regions like Nigeria or Vietnam should also be aware of local import regulations and potential tariffs, which can impact final pricing.
Disclaimer on Indicative Prices
While this analysis provides a framework for understanding the cost components and pricing influencers associated with bronze and copper sourcing, it is important to note that actual prices can vary widely based on market conditions, supplier negotiations, and specific project requirements. Buyers are encouraged to conduct thorough market research and obtain multiple quotes to ensure they are making well-informed purchasing decisions.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing bronze v copper With Other Solutions
Exploring Alternative Solutions to Bronze and Copper
When considering materials for industrial applications, the choice often boils down to the specific properties and performance characteristics required for the job. While bronze and copper are popular choices due to their excellent conductivity and corrosion resistance, there are alternative materials and technologies that may serve similar purposes. This analysis compares bronze and copper against two viable alternatives: aluminum and stainless steel.
| Comparison Aspect | Bronze V Copper | Aluminum | Stainless Steel |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | Excellent conductivity and corrosion resistance; bronze is harder and more wear-resistant than copper. | Good conductivity, lightweight, and resistant to corrosion, but less durable under heavy loads. | High strength, excellent corrosion resistance, but lower conductivity compared to copper. |
| Cost | Generally higher than aluminum; prices can vary based on alloy composition. | Typically lower than both bronze and copper, making it a cost-effective option. | Higher cost than aluminum but often comparable to bronze, depending on the grade. |
| Ease of Implementation | Can be easily soldered and brazed; requires specific techniques for casting. | Easy to work with and can be welded or machined with standard tools. | Requires specialized techniques for welding and forming due to its strength and hardness. |
| Maintenance | Low maintenance; resistant to many environmental factors, but can tarnish. | Requires minimal maintenance; can oxidize but often forms a protective layer. | Very low maintenance; resistant to rust and corrosion in a variety of environments. |
| Best Use Case | Ideal for marine applications, art, and high-stress mechanical components. | Best for lightweight applications, such as in the automotive and aerospace industries. | Suitable for structural applications, food processing, and environments requiring high hygiene standards. |
What Are the Pros and Cons of Aluminum as an Alternative to Bronze and Copper?
Aluminum is a lightweight metal known for its good conductivity and resistance to corrosion. It is often used in industries where weight is a critical factor, such as aerospace and automotive. One of its key advantages is its cost-effectiveness, as aluminum is generally cheaper than both bronze and copper. However, while it performs well under many conditions, aluminum is not as strong as bronze or copper under heavy loads, which may limit its applications in demanding environments.
How Does Stainless Steel Compare to Bronze and Copper?
Stainless steel is a highly durable material that offers excellent corrosion resistance and strength. It is particularly valued in industries that require stringent hygiene standards, such as food processing and pharmaceuticals. While stainless steel is more expensive than aluminum, it can be competitively priced against bronze depending on the specific grade. One downside is its lower electrical conductivity compared to copper, which may make it less suitable for electrical applications. However, its ability to withstand high temperatures and harsh environments makes it a formidable alternative for structural applications.
How Can B2B Buyers Choose the Right Material for Their Needs?
Selecting the appropriate material for your application involves a careful evaluation of various factors, including performance requirements, budget constraints, and environmental conditions. Buyers should assess the specific needs of their projects, considering not only the initial cost but also the long-term maintenance and operational performance of the material. For applications where conductivity and corrosion resistance are paramount, bronze or copper may be the best choice. In contrast, for lightweight and cost-sensitive applications, aluminum could be more suitable. Ultimately, understanding the unique properties of each material will enable B2B buyers to make informed decisions that align with their operational goals and industry standards.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for bronze v copper
What Are the Key Technical Properties of Bronze and Copper?
Understanding the technical properties of bronze and copper is essential for B2B buyers who need to select the right materials for their applications. Here are some critical specifications to consider:
-
Material Grades
Both copper and bronze come in various grades, which dictate their mechanical and physical properties. For instance, oxygen-free copper is known for its high conductivity and is ideal for electrical applications. In contrast, bronze grades like C95400 offer superior strength and corrosion resistance, making them suitable for marine applications. Choosing the right grade can significantly impact the durability and performance of the end product. -
Corrosion Resistance
Corrosion resistance is a pivotal property for both metals, especially in industries such as marine, construction, and plumbing. Copper resists corrosion well but can tarnish over time. Bronze, particularly aluminum bronze, excels in environments exposed to seawater, making it a preferred choice for ship fittings and underwater applications. Understanding corrosion resistance can help buyers select materials that enhance longevity and reduce maintenance costs. -
Thermal and Electrical Conductivity
Copper is renowned for its exceptional thermal and electrical conductivity, making it indispensable in electrical wiring and electronic applications. Bronze, while also conductive, does not match pure copper but offers improved strength and wear resistance, which is beneficial in electrical connectors and components. Buyers should assess the specific conductivity requirements of their applications to make informed material choices. -
Machinability and Fabricability
The ease with which materials can be machined and formed is crucial for production efficiency. Copper is highly malleable and ductile, allowing for intricate designs and complex shapes. Bronze, while less ductile, can still be cast and machined effectively, particularly in applications that require wear resistance. Understanding machinability can help buyers anticipate production costs and timelines. -
Tensile Strength
Tensile strength measures a material’s resistance to being pulled apart and is a key factor in applications involving mechanical stress. Bronze generally exhibits higher tensile strength than copper, making it suitable for load-bearing applications such as bearings and bushings. Buyers should evaluate the tensile requirements of their projects to ensure optimal performance. -
Melting Point
The melting point is crucial for applications involving high temperatures. Copper has a melting point of about 1,085°C, while bronze ranges from 900°C to 1,050°C, depending on its composition. Understanding melting points is important for processes like welding and casting, as exceeding these temperatures can affect material integrity.
What Are Common Trade Terms in the Bronze and Copper Industry?
Familiarity with industry jargon can streamline communication and negotiations for B2B buyers. Here are some common terms:
-
OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
An OEM refers to a company that produces parts or equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer. In the context of copper and bronze, OEMs often require specific material grades to meet performance standards in their products. -
MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ is the smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell. Understanding MOQs is critical for buyers to manage their inventory and budget effectively. Suppliers may set MOQs based on production costs and logistics. -
RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a document sent to suppliers to request pricing, terms, and conditions for specific products. In the copper and bronze market, an RFQ helps buyers gather competitive offers and make informed purchasing decisions. -
Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
Incoterms are a set of predefined commercial terms published by the International Chamber of Commerce (ICC) that define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in international trade. Familiarity with Incoterms is essential for B2B buyers to understand shipping, insurance, and delivery responsibilities. -
Lead Time
Lead time refers to the time taken from placing an order to the delivery of goods. It’s crucial for planning production schedules and inventory management. Buyers should inquire about lead times to ensure timely project execution. -
Certification
Certification indicates that a product meets specific industry standards or regulations. For copper and bronze materials, certifications can assure buyers of quality and compliance, which is especially important in sectors like construction and electronics.
By understanding these technical properties and trade terminologies, B2B buyers can make well-informed decisions when sourcing bronze and copper for their projects.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the bronze v copper Sector
What Are the Current Market Dynamics and Key Trends Influencing the Bronze and Copper Sourcing Landscape?
The global market for bronze and copper is experiencing a renaissance driven by technological advancements, sustainability initiatives, and shifting economic landscapes. Key trends shaping the sector include the increasing demand for high-conductivity materials in electronics and renewable energy applications. With the proliferation of electric vehicles and the expansion of telecommunications infrastructure, the need for copper is surging, particularly in regions like Africa and South America, where infrastructure development is a priority.
Emerging B2B technologies such as blockchain for supply chain transparency and AI-driven analytics for demand forecasting are enhancing sourcing efficiency. Buyers are increasingly leveraging digital platforms to connect with suppliers, ensuring competitive pricing and quality assurance. In markets like Nigeria and Vietnam, where manufacturing capabilities are evolving, international buyers are keen to establish partnerships that offer not just materials but also technological support and expertise.
Moreover, geopolitical factors are influencing sourcing strategies. Trade policies, tariffs, and local regulations require B2B buyers to stay informed and agile. As companies increasingly prioritize local sourcing to mitigate risks, international buyers must navigate these complexities while ensuring they maintain supply chain resilience.
How Is Sustainability and Ethical Sourcing Shaping the Bronze and Copper Industry?
Sustainability has emerged as a critical focus in the bronze and copper sectors, driven by increasing regulatory pressures and consumer demand for ethical sourcing. The environmental impact of mining and processing metals necessitates a shift towards greener practices. Ethical supply chains are now paramount, with buyers seeking suppliers who demonstrate commitment to sustainable practices, including responsible sourcing of raw materials and energy-efficient production methods.
Certifications such as ISO 14001 for environmental management and the Responsible Minerals Initiative (RMI) are becoming vital for suppliers aiming to meet the growing expectations of international buyers. The use of recycled materials in the production of bronze and copper alloys is gaining traction, with companies actively promoting the benefits of circular economy practices. This not only reduces the environmental footprint but also appeals to buyers looking for sustainable solutions.
Furthermore, the integration of sustainability into procurement processes enhances brand reputation and fosters consumer loyalty. B2B buyers, particularly in Europe and the Middle East, are increasingly prioritizing partnerships with manufacturers that can demonstrate adherence to environmental standards and ethical sourcing practices.
What Is the Historical Context of Bronze and Copper in Global Trade?
The historical significance of bronze and copper cannot be overstated, as they have been foundational to human development and trade. Copper, one of the first metals utilized by humanity, dates back to ancient civilizations, where it was used for tools, currency, and ornamental items. The discovery of bronze—a durable alloy of copper and tin—marked a transformative era known as the Bronze Age, facilitating advances in agriculture, warfare, and artistry.
Throughout history, the trade of these metals has influenced economic relationships and cultural exchanges across continents. Today, the legacy of copper and bronze continues, as they remain integral to modern industries, from construction to electronics. Understanding this historical context allows B2B buyers to appreciate the enduring value of these materials and their evolving applications in contemporary markets.
In summary, navigating the dynamics of the bronze and copper sectors requires awareness of current trends, a commitment to sustainability, and an understanding of the historical context that shapes their usage. International buyers must leverage this knowledge to make informed sourcing decisions that align with both market demands and ethical considerations.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of bronze v copper
-
How do I choose between bronze and copper for my project?
Selecting between bronze and copper depends on the specific requirements of your project. Copper is known for its superior electrical and thermal conductivity, making it ideal for electrical applications, plumbing, and roofing. In contrast, bronze, being an alloy primarily of copper and tin, offers enhanced hardness and corrosion resistance, particularly in marine environments. Consider factors like environmental exposure, mechanical stress, and electrical requirements to determine the best material for your needs. -
What are the key properties of bronze and copper?
Copper is a ductile and malleable metal with excellent thermal and electrical conductivity, good corrosion resistance, and natural antimicrobial properties. It is suitable for electrical components and plumbing. Bronze, primarily made of copper and tin, is harder, more corrosion-resistant, and has low friction, making it ideal for bearings, sculptures, and marine applications. Understanding these properties helps in making informed decisions based on your project’s demands. -
How can I vet suppliers for bronze and copper materials?
When vetting suppliers, check for certifications that indicate adherence to quality standards, such as ISO or ASTM. Request samples to evaluate material quality and conduct thorough background checks, including reviews from previous customers. It’s also essential to verify their production capabilities, lead times, and experience in international shipping, particularly if you’re sourcing from regions like Africa, South America, or the Middle East. -
What are typical minimum order quantities (MOQs) for bronze and copper?
MOQs can vary significantly depending on the supplier and the specific alloy being ordered. Generally, for standard sizes and grades, MOQs can range from 100 kg to several tons. However, some suppliers may accommodate smaller orders, especially for custom projects. It’s advisable to discuss your needs directly with suppliers to find flexible options that suit your project scale. -
What payment terms should I expect when sourcing bronze and copper?
Payment terms can vary widely among suppliers but typically include options such as upfront payments, letters of credit, or installment plans. It’s common for suppliers to require a deposit (e.g., 30% upfront) before production, with the balance due upon delivery or prior to shipping. Always clarify payment terms during negotiations and ensure they align with your cash flow requirements. -
How can I ensure quality assurance (QA) for my bronze and copper orders?
To ensure quality assurance, request detailed documentation from your supplier, including material test reports and certificates of compliance. Establish clear quality standards before placing orders and consider conducting on-site inspections if feasible. Engaging third-party inspection services can also provide an unbiased assessment of material quality, which is especially useful for high-value orders. -
What are the logistics considerations when importing bronze and copper?
Logistics for importing bronze and copper involve understanding shipping regulations, tariffs, and customs procedures relevant to your country. Partnering with experienced freight forwarders can simplify the process, ensuring compliance with international trade laws. It’s also essential to factor in lead times for production and shipping, as these can vary based on the supplier’s location and your destination. -
What customization options are available for bronze and copper products?
Many suppliers offer customization options, including specific alloy compositions, dimensions, and finishes. When discussing your project with suppliers, clearly outline your requirements for factors such as size, shape, and application. Some suppliers may also provide prototype services, allowing you to test materials before committing to larger orders, which is particularly beneficial for specialized applications.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.
Top 7 Bronze V Copper Manufacturers & Suppliers List
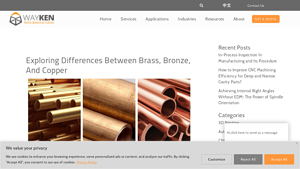
1. Metal Supermarkets – Copper and Brass
Domain: metalsupermarkets.com
Registered: 1996 (29 years)
Introduction: Copper: Pure elemental metal with reddish-brown hue, excellent thermal and electrical conductivity, used in electrical wiring and electronics. Brass: Alloy of copper and zinc, brighter yellowish appearance, enhanced strength and malleability, used in decorative arts, plumbing fixtures, and musical instruments. Bronze: Alloy of copper and tin, increased hardness and corrosion resistance, used in ma…
2. Wayken RM – Brass, Bronze & Copper Materials
Domain: waykenrm.com
Registered: 2013 (12 years)
Introduction: Brass, bronze, and copper are metallic materials known for high electric/thermal conductivity, corrosion resistance, and thermal resistance.
1. **Element Composition**:
– Copper: Natural metal, non-ferrous.
– Brass: Alloy of copper and zinc; may include lead, manganese, iron, aluminum, silicon.
– Bronze: Alloy of copper and tin; may include aluminum, nickel, phosphorus, zinc.
2. **…
3. Interstate Metal – Brass Alloys
Domain: interstatemetal.com
Registered: 2006 (19 years)
Introduction: Brass: Alloy of copper and zinc; characteristics include greater susceptibility to stress cracking, better malleability and formability, higher melting point. Applications: architectural elements, casings, electronics, musical instruments, plumbing. Available alloys: C26000, C26800, C27200, C33000, C36000, C38500, C46400 in round, hexagon, rectangular, square bar forms, and lead-free bars. Bronze:…
4. Reddit – Custom Pen Materials
Domain: reddit.com
Registered: 2005 (20 years)
Introduction: Brass, Bronze, Copper – Materials for custom pen fabrication. Bronze is the hardest, more scratch and dent resistant, and has inherent lubricity for smoother action. Copper forms a nice patina but may have a metallic scent. C110 copper is preferred over C145 for better machinability and aesthetic patina.
5. KDM Fab – Bronze and Copper Comparison
Domain: kdmfab.com
Registered: 2022 (3 years)
Introduction: Bronze and Copper Comparison:
1. **What is Bronze?**
– Composition: Primarily copper (about 88%) and tin (about 12%), with possible additions of nickel, zinc, lead, arsenic, and phosphorus.
– Historical Use: Discovered around 3500 BC.
– Applications: Varies based on alloy composition.
2. **What is Copper?**
– Composition: Naturally occurring metal with the chemical symbol Cu.
…
6. Tuofa – Copper Machining Solutions
Domain: tuofa-cncmachining.com
Registered: 2022 (3 years)
Introduction: Copper: One of the oldest metals used for various applications, extensively used in electrical components, heat exchangers, healthcare, and plumbing. Properties: Extremely ductile, good conductor of heat and electricity, density of 8.96 g/cm³, high melting point of 1085°C. Color: Bright metallic reddish-orange when polished, dull greenish-blue when aged due to copper carbonate formation. Copper Al…
7. AT Machining – Red Metals and Bronze Alloys
Domain: at-machining.com
Registered: 2014 (11 years)
Introduction: Bronze, brass, and copper are non-ferrous metals known as “red metals”. Bronze is a copper and tin-based alloy, often including aluminum, zinc, silicon, manganese, and phosphorus. It has low metal-to-metal friction, excellent ductility, corrosion resistance, and a high melting point. Common bronze alloys include Alloy 932 (high-leaded bronze for bushings and washers) and Alloy 954 (aluminum bronze…
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for bronze v copper
How Can B2B Buyers Navigate the Copper and Bronze Market Effectively?
In conclusion, the choice between bronze and copper hinges on understanding the specific requirements of your application. Copper excels in thermal and electrical conductivity, making it ideal for electronics and plumbing, while bronze offers superior hardness and corrosion resistance, particularly in marine environments and industrial applications. By strategically sourcing these materials, buyers can not only enhance product performance but also optimize costs and supply chain efficiency.
As international B2B buyers from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe look to source metals, it is essential to consider the unique properties of each alloy. Engage with suppliers who adhere to strict quality standards and can provide tailored solutions to meet your specific needs.
Looking ahead, the demand for both copper and bronze is expected to rise, driven by technological advancements and infrastructure development. Now is the time to forge strong partnerships with reliable suppliers to secure the best materials for your business. Explore your options today and position your company for future success in an evolving market.