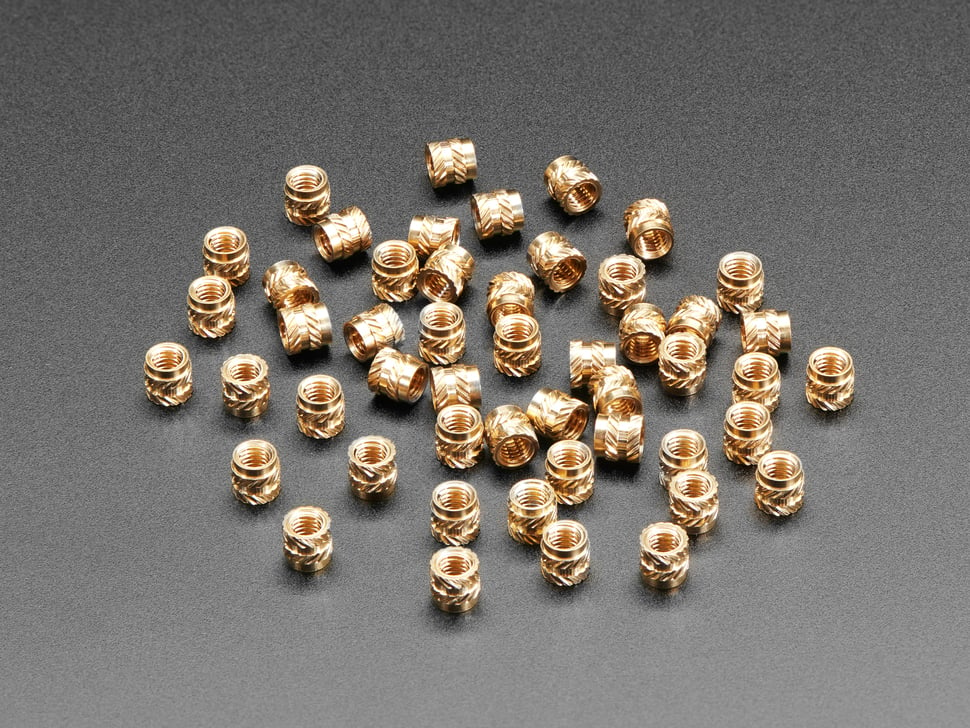
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for brass and heat
In an increasingly interconnected world, navigating the global market for brass and heat presents both opportunities and challenges for B2B buyers. Understanding the nuances of sourcing high-quality brass fittings and heat-resistant materials is crucial, especially when considering their specific applications across various industries. This comprehensive guide delves into essential aspects such as the types of brass and heat-resistant materials available, their applications in diverse sectors, effective supplier vetting strategies, and cost considerations.
By equipping international buyers from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe—including key markets like Nigeria and Saudi Arabia—with actionable insights, this guide empowers informed purchasing decisions. It addresses common challenges faced by buyers, such as identifying reliable suppliers, understanding material specifications, and managing costs effectively.
Moreover, the guide highlights the unique benefits of brass, including its malleability, durability, and exceptional thermal conductivity, which make it a preferred choice for various applications. With a focus on practical strategies and expert advice, this resource serves as a vital tool for businesses aiming to optimize their procurement processes and enhance operational efficiency. Whether you are exploring new suppliers or evaluating existing partnerships, this guide will help you navigate the complexities of the brass and heat market with confidence.
Understanding brass and heat Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Yellow Brass | Contains about 67% copper and 33% zinc; excellent corrosion resistance. | Plumbing, automotive parts, decorative items | Pros: Good machinability, moderate strength. Cons: Lower pressure rating than other types. |
| Red Brass | Higher copper content (up to 85%); superior corrosion resistance. | Marine applications, high-pressure systems | Pros: Excellent for harsh environments. Cons: More expensive than yellow brass. |
| Brass Alloys (C36000) | Highly machinable; often used for precision components. | Electronics, precision fittings | Pros: Exceptional machining characteristics. Cons: Not suitable for high-temperature applications. |
| Leaded Brass | Contains lead for improved machinability; used in high-speed machining. | Valves, fittings, and fasteners | Pros: Enhanced machinability, good for mass production. Cons: Toxicity concerns limit usage. |
| Brass with Nickel Coating | Offers enhanced corrosion resistance and aesthetic appeal. | Marine hardware, decorative applications | Pros: Improved durability and appearance. Cons: Higher cost due to additional coating process. |
What are the Characteristics of Yellow Brass for B2B Buyers?
Yellow brass, primarily composed of copper and zinc, is notable for its excellent corrosion resistance and moderate strength. This type is often used in plumbing, automotive parts, and decorative items, making it versatile for various industries. B2B buyers should consider yellow brass for applications where moderate pressure ratings are acceptable, as it typically supports pressures up to 3,000 psi. Its good machinability also makes it an appealing choice for manufacturers looking for ease of fabrication.
How Does Red Brass Compare in Terms of Suitability?
Red brass features a higher copper content, often exceeding 85%, which grants it superior corrosion resistance, particularly in marine environments. This makes it ideal for high-pressure systems and applications where exposure to harsh conditions is a concern. B2B buyers in industries such as shipbuilding or oil and gas should prioritize red brass for its durability, although its higher cost compared to yellow brass may be a consideration in budget-sensitive projects.
Why Choose Brass Alloys Like C36000 for Precision Applications?
Brass alloys, particularly C36000, are highly regarded for their exceptional machinability, making them perfect for producing precision components in electronics and fittings. These alloys allow for detailed and intricate designs, which are crucial in industries demanding high standards. However, buyers should be aware that while C36000 is excellent for machining, it may not perform as well under high-temperature conditions, limiting its use in specific applications.
What are the Advantages and Disadvantages of Leaded Brass?
Leaded brass is known for its improved machinability due to the inclusion of lead, making it suitable for high-speed machining processes. This type is commonly used in valves, fittings, and fasteners, where mass production is essential. However, the presence of lead raises toxicity concerns, leading to regulatory limitations in some regions. B2B buyers should weigh the benefits of efficiency against potential compliance challenges when considering leaded brass for their projects.
How Does Nickel Coating Enhance Brass for Buyers?
Brass with a nickel coating provides enhanced corrosion resistance and an aesthetically pleasing finish, making it a popular choice for marine hardware and decorative applications. This coating improves the longevity and durability of brass components, which is vital for industries that require reliable performance in challenging environments. While the initial investment may be higher due to the coating process, the long-term benefits often justify the cost for B2B buyers looking for durability and visual appeal.
Key Industrial Applications of brass and heat
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of brass and heat | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Automotive | Engine components and fittings | High thermal conductivity improves engine efficiency | Ensure compliance with international automotive standards |
| Oil & Gas | Valve and piping systems | Corrosion resistance enhances system longevity | Verify suitability for high-pressure and corrosive environments |
| HVAC (Heating, Ventilation, Air Conditioning) | Heat exchangers and fittings | Efficient heat transfer reduces energy costs | Look for high-quality brass alloys to withstand temperature fluctuations |
| Construction | Plumbing systems and fixtures | Durable and malleable for custom installations | Source from reputable suppliers to ensure quality and compliance |
| Electronics | Connectors and electrical components | Excellent conductivity enhances performance | Assess for compatibility with various electrical systems |
How is Brass and Heat Used in the Automotive Industry?
In the automotive sector, brass is extensively used for engine components and fittings due to its exceptional thermal conductivity, which aids in efficient heat dissipation. This property helps maintain optimal engine temperatures, ultimately enhancing performance and fuel efficiency. Buyers should prioritize sourcing brass that meets international automotive standards, particularly in regions like Europe and South America, where compliance is critical for market entry.
What Role Does Brass Play in Oil & Gas Applications?
Brass fittings and valves are vital in oil and gas applications, where they are utilized in piping systems. The material’s high resistance to corrosion makes it suitable for environments where exposure to chemicals and harsh conditions is inevitable. For buyers in the Middle East and Africa, it is essential to ensure that the brass sourced is capable of withstanding high-pressure systems, as well as the specific corrosive elements present in their operational environments.
How is Brass Utilized in HVAC Systems?
In HVAC systems, brass is commonly employed for heat exchangers and various fittings. Its ability to conduct heat effectively allows for efficient thermal management, which can significantly reduce energy costs for businesses. Buyers should consider sourcing high-quality brass alloys that can endure temperature fluctuations, especially in regions with extreme climates, such as parts of Africa and Europe, where HVAC efficiency is paramount.
Why is Brass Important in Construction Plumbing?
Brass is a preferred material in plumbing systems and fixtures within the construction industry due to its durability and malleability, allowing for custom installations. Its corrosion resistance is also a significant advantage, ensuring long-lasting performance in water supply systems. For international buyers, particularly in developing regions, sourcing from reputable suppliers is crucial to ensure compliance with local building codes and quality standards.
What is the Significance of Brass in Electronics?
In the electronics industry, brass is widely used for connectors and electrical components due to its excellent conductivity. This characteristic enhances the performance of electrical systems, making them more efficient. Buyers should assess the compatibility of brass components with various electrical systems, especially in international markets where specifications may vary, ensuring that they meet the necessary regulatory requirements for safety and performance.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘brass and heat’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Overcoming Corrosion Challenges in Harsh Environments
The Problem: B2B buyers in industries such as oil and gas or chemical processing often face significant challenges with equipment that must withstand harsh environmental conditions. Brass fittings, while known for their corrosion resistance, can still be vulnerable in certain high-acid or saltwater environments. This can lead to premature failures, increased maintenance costs, and operational downtime, which are critical concerns for businesses looking to maintain efficiency and profitability.
The Solution: To mitigate corrosion risks, it’s essential to select the right grade of brass for specific applications. B2B buyers should consider using brass alloys that include higher levels of zinc or special coatings that enhance corrosion resistance. Additionally, implementing a regular maintenance schedule that includes inspections for signs of wear or corrosion can help identify issues before they escalate. Educating staff on the proper installation techniques for brass fittings—such as avoiding over-tightening, which can create stress fractures—will also extend the lifespan of these components. Sourcing from reputable suppliers who provide detailed specifications and certifications can further ensure the quality and suitability of brass products for challenging environments.
Scenario 2: Managing High Temperatures in Industrial Applications
The Problem: In high-temperature applications, such as those found in power generation or manufacturing, brass components can be at risk of losing their integrity. Many buyers have reported that, despite brass’s initial heat resistance, prolonged exposure to temperatures exceeding 400°F can lead to deformation or weakening of fittings. This not only jeopardizes the safety of operations but also necessitates costly replacements and downtime.
The Solution: To effectively manage high temperatures, buyers should consider integrating brass components specifically engineered for high-heat applications. These include brass alloys with enhanced thermal stability or even exploring hybrid solutions that combine brass with other materials designed to withstand higher temperatures, such as stainless steel. It’s also vital to monitor the operating temperatures closely using thermocouples or infrared thermometers to ensure they remain within safe limits. When sourcing brass components, request detailed thermal performance data from manufacturers to verify their suitability for your specific application. Implementing cooling systems or heat shields can also help protect brass fittings from excessive heat exposure, thereby prolonging their lifespan.
Scenario 3: Ensuring Precision in Machining and Fabrication
The Problem: B2B buyers in manufacturing sectors often encounter difficulties when machining brass components. Brass is highly malleable and machinable, but when not handled correctly, it can lead to issues such as work hardening or improper tolerances. This can result in defective parts that do not meet specifications, leading to increased scrap rates and wasted resources.
The Solution: To ensure precision during machining, buyers should invest in the right tooling and techniques tailored for brass. Utilizing sharp cutting tools with appropriate coatings can minimize friction and heat generation, reducing the risk of work hardening. It’s also important to implement a systematic approach to temperature management during machining—keeping components cool with the use of cutting fluids or air blasts can help maintain integrity. Additionally, thorough training for machinists on brass properties and best practices will lead to better outcomes. Collaborating with suppliers who offer technical support and guidance on machining brass can also provide valuable insights into optimizing processes, ultimately improving product quality and reducing waste.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for brass and heat
What Are the Key Properties of Brass in High-Temperature Applications?
Brass is an alloy primarily composed of copper and zinc, known for its excellent malleability and thermal conductivity. It typically withstands temperatures up to 400°F (204°C) and has a moderate pressure rating of around 3,000 psi. This makes it suitable for applications in hydraulic and pneumatic systems where heat and pressure are significant factors. Brass exhibits good corrosion resistance against many chemicals, making it ideal for environments that may include water, slurries, or other corrosive substances.
What Are the Advantages and Disadvantages of Using Brass?
The primary advantage of brass is its machinability, allowing for the creation of precise components. Its malleability enables it to be shaped easily, which is beneficial for custom fittings. However, brass has limitations, particularly in high-pressure applications where stainless steel may be preferable. Additionally, while brass is generally less expensive than stainless steel, it may not perform as well in highly acidic or saline environments.
How Does Brass Impact Specific Applications?
Brass is particularly effective in applications that require good thermal and electrical conductivity. It is often used in plumbing fittings, valves, and connectors where moderate pressure and temperature resistance are required. However, its performance may diminish in extreme conditions, such as high-pressure environments or prolonged exposure to harsh chemicals. International buyers should consider these factors when selecting brass for specific applications.
What Should International B2B Buyers Consider When Selecting Brass?
For international B2B buyers, especially those in regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, compliance with local standards is crucial. Common standards such as ASTM, DIN, and JIS should be adhered to, ensuring that the materials meet regional quality and safety requirements. Buyers should also be aware of the specific media compatibility of brass in their applications, as improper selection can lead to failures and increased costs.
Summary Table of Material Selection for Brass and Heat
| Material | Typical Use Case for brass and heat | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Brass | Hydraulic fittings and plumbing components | Excellent machinability and corrosion resistance | Limited performance in extreme pressure and acidic environments | Low |
| Stainless Steel | High-pressure hydraulic systems | Superior strength and longevity | Higher cost and lower machinability | High |
| Copper | Electrical connectors and heat exchangers | High thermal and electrical conductivity | Prone to corrosion and less durable than brass | Medium |
| Bronze | Marine applications and heavy-duty fittings | Excellent corrosion resistance in seawater | More expensive and less malleable than brass | High |
This guide provides a comprehensive overview of the strategic material selection process for brass and heat applications, helping B2B buyers make informed decisions based on their specific needs and regional considerations.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for brass and heat
What Are the Key Stages in the Manufacturing Process of Brass Components?
The manufacturing of brass components involves several critical stages, each requiring precision and adherence to quality standards. Understanding these stages can help B2B buyers ensure they are partnering with suppliers that maintain high manufacturing standards.
Material Preparation: What Steps Are Involved?
The first step in the manufacturing process is material preparation, where high-quality raw brass is sourced. Brass is an alloy primarily composed of copper and zinc, and its composition can vary to achieve desired properties. Suppliers often conduct thorough inspections of incoming materials to ensure they meet specific chemical and physical standards. This can include checking for impurities and verifying the alloy composition through spectrometry or chemical analysis.
How Is Brass Formed into Components?
After material preparation, the next stage is forming. Techniques such as forging, extrusion, and machining are commonly employed.
- Forging involves shaping brass using compressive forces, resulting in stronger, more durable components due to the alignment of the metal’s grain structure.
- Extrusion allows for the creation of complex shapes by forcing heated brass through a die, which is particularly useful for creating pipes and fittings.
- Machining involves removing material to achieve precise dimensions, often using CNC (Computer Numerical Control) technology for high accuracy.
Each of these methods requires skilled operators and robust machinery to ensure that the final products meet the required specifications.
What Assembly Techniques Are Common in Brass Manufacturing?
In the assembly phase, various brass components are brought together to create finished products. This can involve soldering, welding, or using mechanical fasteners.
- Soldering is commonly used for creating leak-proof seals in plumbing fittings, while
- Welding offers a strong bond for more demanding applications.
Quality assurance during assembly is crucial, as improper joining techniques can lead to product failure. Thus, suppliers often employ visual inspections and non-destructive testing methods to verify the integrity of joints and connections.
What Finishing Processes Enhance the Quality of Brass Products?
The final stage in the manufacturing process is finishing. This includes processes like polishing, plating, and coating to enhance the aesthetic appeal and corrosion resistance of brass components.
- Polishing improves surface smoothness and shine, while
- Plating with materials like nickel or chrome can provide additional protection against corrosion.
Finishing not only affects the product’s appearance but also its functional properties, making it essential for suppliers to adhere to industry best practices.
Which International Standards Are Relevant for Quality Assurance in Brass Manufacturing?
Quality assurance in brass manufacturing is governed by several international standards. The ISO 9001 certification is widely recognized and ensures that organizations meet customer and regulatory requirements consistently.
In addition, industry-specific standards such as CE marking (for products sold in the European Economic Area) and API standards (for oil and gas applications) play a significant role in ensuring product safety and performance. These standards require manufacturers to have rigorous quality control systems in place.
What Are the Key Quality Control Checkpoints in Brass Manufacturing?
Quality control (QC) in brass manufacturing typically involves several checkpoints:
- Incoming Quality Control (IQC): This is the initial inspection of raw materials to ensure they meet specified standards.
- In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): During production, samples are taken to monitor the manufacturing process and ensure that specifications are being adhered to.
- Final Quality Control (FQC): After production, finished products undergo comprehensive testing to ensure they meet all quality and safety standards.
Common testing methods include tensile strength tests, hardness tests, and corrosion resistance evaluations, which are essential for verifying that the products can withstand their intended applications.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control Practices?
For international B2B buyers, verifying a supplier’s quality control practices is crucial. Here are several actionable steps:
- Conduct Supplier Audits: Regular audits can help assess compliance with quality standards and the effectiveness of the supplier’s QC processes.
- Request Quality Reports: Suppliers should provide documentation detailing their quality control procedures and any certifications they hold.
- Engage Third-Party Inspectors: Utilizing third-party inspection services can provide an unbiased assessment of the supplier’s quality practices, ensuring they meet international standards.
What Nuances Should International B2B Buyers Consider Regarding Quality Control?
When sourcing brass products from international suppliers, particularly in regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, several nuances should be considered:
- Cultural Differences: Understanding local manufacturing practices and quality expectations can help in evaluating supplier capabilities.
- Regulatory Compliance: Different regions may have specific regulations regarding material composition and safety standards. B2B buyers should be familiar with these to ensure compliance.
- Supply Chain Transparency: Establishing clear communication channels with suppliers regarding their QC practices and any potential issues is essential for building trust and ensuring product quality.
In conclusion, the manufacturing processes and quality assurance practices for brass components are multifaceted and require careful consideration from B2B buyers. By understanding these processes and implementing effective verification strategies, buyers can ensure they source high-quality brass products that meet their specific needs.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘brass and heat’
Introduction
This guide serves as a practical checklist for B2B buyers seeking to procure brass materials, particularly for applications involving heat resistance. Understanding the properties of brass and the nuances of sourcing it effectively can lead to better performance in your operations and ultimately, cost savings.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Before initiating the sourcing process, clearly outline the technical specifications required for your brass components. This includes considerations such as dimensions, alloy composition, temperature resistance, and pressure ratings. Accurate specifications ensure that you select materials that meet your operational needs, which is crucial for performance and safety.
Step 2: Research Potential Suppliers
Conduct thorough research to identify potential suppliers specializing in brass materials. Look for companies with a strong reputation in the industry, particularly those that have experience in your specific application area. Consider factors like their market presence, years in business, and customer reviews to gauge reliability.
Step 3: Evaluate Supplier Certifications
Ensure that your selected suppliers hold relevant certifications, such as ISO 9001, which indicates a commitment to quality management systems. Certifications not only reflect the quality of their products but also their adherence to industry standards. This step is vital to minimize risks associated with subpar materials and ensure compliance with regulatory requirements.
Step 4: Request Material Samples
Before making a bulk order, request samples of the brass materials you intend to purchase. This allows you to assess the quality, finish, and overall suitability of the materials for your specific applications. Evaluate the samples under actual working conditions to understand how they perform under heat and pressure.
Step 5: Inquire About Manufacturing Processes
Engage with suppliers to understand their manufacturing processes, especially concerning heat treatment and alloying techniques. Knowledge of these processes can provide insights into the material’s performance characteristics, such as tensile strength and thermal conductivity. Suppliers who are transparent about their production methods are often more reliable.
Step 6: Verify Delivery and Lead Times
Discuss delivery schedules and lead times with potential suppliers. Reliable suppliers should provide clear timelines for order fulfillment, which is critical for your project planning. Ensure they can accommodate your timelines, especially if you have urgent needs or are working on a time-sensitive project.
Step 7: Establish a Quality Assurance Plan
Develop a quality assurance plan that includes criteria for inspection and testing of the brass materials upon delivery. This may involve checking for compliance with your specifications, conducting mechanical tests, or ensuring the absence of defects. A robust QA plan helps mitigate risks and ensures that the materials meet your operational standards.
By following these steps, B2B buyers can effectively source brass materials suited for high-heat applications, ensuring both quality and performance in their operations.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for brass and heat Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components in Brass and Heat Sourcing?
When sourcing brass and heat products, understanding the cost structure is crucial for B2B buyers. The primary cost components include:
-
Materials: Brass prices fluctuate based on copper and zinc market trends, as these are the primary constituents. Quality and grade of brass can significantly impact pricing.
-
Labor: Labor costs vary widely depending on the region and skill level required. In countries with lower labor costs, buyers may find more competitive pricing.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes expenses related to production facilities, equipment maintenance, and utilities. Efficient manufacturing processes can help reduce overhead costs.
-
Tooling: Initial tooling costs for custom components can be high. However, these costs are amortized over large production runs, impacting the unit price favorably for bulk orders.
-
Quality Control (QC): Ensuring products meet specific standards incurs costs. Investments in quality assurance can prevent costly defects, making them a worthwhile expenditure.
-
Logistics: Transportation costs depend on distance, mode of shipping, and the complexity of delivery. Incoterms play a vital role in defining who bears these costs.
-
Margin: Suppliers typically add a margin to cover their costs and ensure profitability. The margin can vary based on competition, market demand, and relationship with the buyer.
How Do Price Influencers Affect Brass and Heat Sourcing?
Several factors influence pricing in the brass and heat market:
-
Volume/MOQ: Suppliers often offer discounts for larger orders. Understanding Minimum Order Quantities (MOQs) can help buyers leverage better pricing.
-
Specifications/Customization: Custom designs or specific material grades can increase costs. Buyers should be clear about their requirements to avoid unexpected expenses.
-
Materials Quality/Certifications: Higher quality materials and certifications (e.g., ISO standards) generally command higher prices. Buyers should assess the value of these certifications against their application needs.
-
Supplier Factors: The supplier’s reputation, reliability, and production capacity can influence pricing. Building long-term relationships can lead to more favorable terms.
-
Incoterms: The choice of Incoterms affects logistics costs and responsibilities. Familiarizing oneself with these terms can lead to more informed purchasing decisions.
What Are Essential Buyer Tips for Cost-Efficient Brass and Heat Sourcing?
Navigating the complexities of international sourcing requires strategic approaches:
-
Negotiation Strategies: Engage in open discussions with suppliers about pricing structures. Understanding their cost components can provide leverage during negotiations.
-
Focus on Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Instead of looking solely at initial prices, consider the total cost, including maintenance, replacement, and operational costs over the product’s lifecycle.
-
Pricing Nuances for International Buyers: Be aware of currency fluctuations, tariffs, and import duties that can affect the final cost. Collaborating with local distributors can help mitigate these challenges.
-
Market Research: Conduct thorough market analysis to understand regional pricing trends and supplier availability. This knowledge can empower buyers during negotiations.
-
Build Relationships: Establishing strong relationships with suppliers can lead to better pricing, priority in production, and enhanced service.
What Should Buyers Consider Regarding Pricing Disclaimer?
While indicative prices can be provided, they are subject to change based on market conditions, supplier policies, and economic factors. Buyers should always verify current pricing with suppliers before finalizing any agreements to ensure that they are making informed purchasing decisions.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing brass and heat With Other Solutions
Exploring Alternatives to Brass and Heat Solutions
In the evolving landscape of industrial materials and methods, understanding the alternatives to brass and heat is crucial for B2B buyers. Different applications may require specific properties such as durability, corrosion resistance, and cost-effectiveness. This section compares brass and heat against viable alternatives, providing insights that can assist businesses in making informed purchasing decisions.
| Comparison Aspect | Brass And Heat | Stainless Steel Fittings | Plastic Composites |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | High thermal and electrical conductivity; good for hydraulic systems | Excellent for high-pressure applications; superior in corrosive environments | Lightweight; suitable for low-pressure systems; good chemical resistance |
| Cost | Generally lower initial cost; moderate long-term durability | Higher initial investment; long-term cost savings due to durability | Low initial cost; often requires replacement more frequently |
| Ease of Implementation | Malleable and easy to work with; good machinability | Requires specialized tools for installation; heavier than brass | Easy to mold and install; lightweight and flexible |
| Maintenance | Moderate maintenance; can corrode in specific environments | Low maintenance; resistant to rust and corrosion | Limited maintenance; may degrade over time under UV exposure |
| Best Use Case | Ideal for hydraulic systems, plumbing, and low-pressure applications | Best for high-pressure systems and corrosive environments, such as offshore applications | Suitable for non-pressurized applications, food packaging, and electrical insulation |
Detailed Breakdown of Alternatives
Stainless Steel Fittings
Stainless steel is a robust alternative to brass, particularly in applications requiring high pressure and corrosion resistance. Its long lifespan, often exceeding 50 years, reduces the need for frequent replacements, making it a cost-effective choice in the long run. However, stainless steel fittings typically involve a higher upfront cost and require specialized tools for installation, which may increase labor expenses. Their superior performance in hostile environments, particularly against saltwater and acidic substances, positions them as the preferred choice for marine and chemical industries.
Plastic Composites
Plastic composites offer a lightweight and cost-effective alternative, especially for applications that do not require high-pressure capabilities. They are easy to mold and install, making them suitable for various industries, including food and beverage packaging. However, while they are resistant to many chemicals, their durability may be compromised over time when exposed to UV light or extreme temperatures. As a result, they may need more frequent replacement, which can offset their initial cost advantage in the long run.
Conclusion: How to Choose the Right Solution for Your Needs
When selecting between brass and heat versus its alternatives, B2B buyers should consider the specific requirements of their applications. Factors such as performance needs, budget constraints, and maintenance capabilities play a significant role in the decision-making process. For high-pressure and corrosive environments, stainless steel may be the best choice despite its higher cost. Conversely, for applications with lower pressure and budget constraints, brass or plastic composites could provide a more suitable solution. Understanding these nuances will enable businesses to select materials and methods that align with their operational goals and financial strategies.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for brass and heat
What Are the Key Technical Properties of Brass Relevant to B2B Buyers?
Understanding the essential technical properties of brass is crucial for B2B buyers, especially those involved in manufacturing, plumbing, and HVAC systems. Here are some critical specifications to consider:
-
Material Grade
Brass comes in various grades, typically classified by their alloy composition, such as C36000 (free-cutting brass) or C28000 (semi-red brass). The choice of grade affects machinability, corrosion resistance, and mechanical strength. Selecting the appropriate grade can enhance product performance and longevity, reducing the risk of system failures. -
Tensile Strength
This measures a material’s resistance to being pulled apart and is expressed in megapascals (MPa). Brass has a tensile strength ranging from 338 to 469 MPa, making it suitable for applications that require durability under pressure. Understanding tensile strength is vital when designing systems that may face high-stress conditions, ensuring safety and reliability. -
Thermal Conductivity
Brass has excellent thermal conductivity, approximately 15 times that of stainless steel. This property is essential for applications involving heat transfer, such as in heating systems or radiators. For B2B buyers, selecting materials with optimal thermal properties can lead to energy efficiency and improved system performance. -
Corrosion Resistance
Brass exhibits superior corrosion resistance in various environments, including exposure to water and certain chemicals. This makes it a preferred choice for plumbing and hydraulic fittings. Buyers should prioritize corrosion resistance to minimize maintenance costs and extend the lifespan of their systems. -
Machinability
The ease with which brass can be shaped and formed is a significant advantage for manufacturing precision components. Its malleability allows for intricate designs and custom fittings, which is crucial for companies requiring tailored solutions. Understanding machinability helps buyers gauge the potential for cost-effective production. -
Pressure Rating
Brass fittings typically have a pressure rating of up to 3,000 psi, while stainless steel can exceed this. This metric is critical for applications involving fluid management under pressure. Buyers must ensure the selected brass components can handle the expected operational pressures to prevent failures.
What Are Common Trade Terms in the Brass Industry?
Familiarity with industry jargon is essential for effective communication and negotiation in the brass supply chain. Here are some common terms:
-
OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
This refers to companies that manufacture products that are sold under another company’s brand name. Understanding OEM relationships can help buyers identify reliable suppliers who meet quality standards. -
MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ is the smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell. Knowing the MOQ is essential for budgeting and inventory management, especially for smaller businesses looking to minimize upfront costs. -
RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a document sent to suppliers requesting price quotes for specific products or services. This process is crucial for ensuring competitive pricing and understanding the market rates for brass components. -
Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
These are standardized terms used in international trade to define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers regarding shipping, insurance, and tariffs. Familiarity with Incoterms can streamline negotiations and clarify shipping responsibilities. -
Lead Time
This term refers to the time taken from placing an order to its delivery. Understanding lead times is vital for project planning and inventory management, ensuring that production schedules are met without delays. -
Certification Standards
Certifications such as ISO or ASTM indicate that products meet specific quality and safety standards. For B2B buyers, ensuring that suppliers adhere to these standards is crucial for compliance and product reliability.
By comprehending these technical properties and trade terms, B2B buyers can make informed decisions, ensuring they choose the right brass components for their applications while optimizing their supply chain operations.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the brass and heat Sector
Market Overview & Key Trends in the Brass and Heat Sector
The global brass and heat sector is currently experiencing robust growth driven by industrialization, technological advancements, and increasing demand for high-performance materials in various applications. Key drivers include the expanding automotive, aerospace, and construction industries, particularly in emerging markets in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. Countries like Nigeria and Saudi Arabia are investing heavily in infrastructure and manufacturing, which fuels demand for brass components due to their durability, corrosion resistance, and excellent thermal and electrical conductivity.
Emerging B2B technology trends are reshaping sourcing practices within the sector. The adoption of advanced analytics and supply chain management software is enhancing transparency and efficiency, allowing buyers to make data-driven decisions. Additionally, digital platforms for sourcing are gaining traction, offering international buyers access to a wider range of suppliers, competitive pricing, and real-time inventory updates. This digital transformation is particularly beneficial for businesses in regions with less developed traditional supply chains, enabling them to connect with global markets more effectively.
Market dynamics also reflect an increasing focus on customization and rapid prototyping in brass fittings and components. Companies are leveraging 3D printing technologies to create tailored solutions that meet specific client needs, thereby reducing lead times and minimizing waste. As global competition intensifies, buyers are encouraged to stay abreast of these trends to optimize their procurement strategies and enhance their competitive edge in the marketplace.
Sustainability & Ethical Sourcing in B2B: Why It Matters in the Brass and Heat Sector
Sustainability has become a critical consideration in the brass and heat sector, with increasing pressure from consumers, regulatory bodies, and investors for environmentally responsible practices. The environmental impact of brass production, particularly in terms of energy consumption and emissions, necessitates a shift towards greener sourcing strategies. International B2B buyers must prioritize suppliers who demonstrate a commitment to sustainability through responsible sourcing of raw materials and energy-efficient manufacturing processes.
Ethical supply chains are equally important, as businesses face growing scrutiny regarding labor practices and community impacts. Buyers should seek out suppliers with certifications such as ISO 14001 for environmental management and Fair Trade standards, which ensure ethical labor practices. Additionally, adopting ‘green’ materials—like recycled brass—can significantly reduce the carbon footprint associated with production and sourcing.
Investing in sustainable sourcing not only aligns with corporate social responsibility goals but can also lead to cost savings in the long run. Efficient resource use, waste reduction, and energy savings translate to lower operational costs, making sustainability a financially sound strategy. By focusing on ethical sourcing, B2B buyers can enhance their brand reputation while contributing positively to the global community.
Brief Evolution/History of Brass and Its Applications in B2B
Brass, an alloy of copper and zinc, has been utilized for thousands of years, with its origins tracing back to ancient civilizations that recognized its unique properties. Historically, brass was favored for its workability and corrosion resistance, making it an ideal material for various applications, from decorative items to functional components in machinery.
In the industrial era, brass gained prominence in plumbing, electrical, and automotive applications due to its superior thermal and electrical conductivity compared to other materials. The evolution of manufacturing techniques, including advancements in casting and machining, has further expanded its applications in modern industries. Today, brass fittings and components are integral in hydraulic systems, HVAC applications, and more, underscoring its enduring significance in the B2B landscape.
As industries continue to evolve, the adaptability of brass remains a key asset, allowing it to meet the changing needs of international markets while maintaining its status as a trusted material for high-performance applications.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of brass and heat
-
How do I ensure the quality of brass fittings when sourcing internationally?
To ensure quality, conduct thorough supplier vetting by checking certifications, production processes, and past client reviews. Request samples to assess the material’s performance under your specific conditions. It’s also advisable to establish a quality assurance (QA) protocol that includes third-party inspections, especially for large orders. Collaborating with suppliers who have a history of exporting to your region can also be beneficial, as they are likely familiar with local standards and regulations. -
What is the best type of brass for high-temperature applications?
For high-temperature applications, select brass alloys with higher zinc content, such as C36000 or C37700. These alloys offer excellent thermal conductivity and can withstand temperatures up to 400°F. It’s essential to consider the specific requirements of your application, including pressure and corrosion resistance, as different brass alloys may perform variably under extreme conditions. Consult with your supplier to identify the most suitable alloy for your needs. -
What are the common payment terms for brass and heat suppliers?
Payment terms can vary widely based on the supplier and the nature of the transaction. Common terms include 30% upfront and 70% upon delivery or net 30 days after receipt of goods. It’s crucial to negotiate terms that align with your cash flow and project timelines. Additionally, consider using escrow services for large orders to mitigate risk, especially when working with new suppliers or those in different countries. -
How can I customize brass components for my specific needs?
Customization options typically include varying sizes, shapes, and finishes. Discuss your specifications with potential suppliers to determine their capabilities. Many manufacturers offer design services, allowing you to create prototypes before mass production. When sourcing internationally, ensure that the supplier can meet your customization requirements while adhering to quality standards and delivery timelines. -
What should I consider when evaluating minimum order quantities (MOQs)?
When evaluating MOQs, consider your production needs, storage capabilities, and budget constraints. Suppliers often set MOQs based on production efficiency, but it may be negotiable, especially if you’re a first-time buyer. Assess whether the MOQ aligns with your demand forecasts and whether the cost savings from bulk purchasing outweigh the risks of overstocking. -
What logistics challenges should I expect when importing brass fittings?
Logistics challenges can include customs clearance, shipping delays, and fluctuations in freight costs. Ensure that your supplier is experienced in international shipping and can provide necessary documentation for customs. It’s advisable to work with a freight forwarder who understands the regulations in your country and can assist with navigating any logistical hurdles. -
How do I handle disputes with international brass suppliers?
Establish clear communication channels and documentation practices to minimize disputes. If issues arise, attempt to resolve them amicably through direct negotiation. If necessary, refer to the terms outlined in your purchase agreement, including dispute resolution clauses. Consider involving a third party, such as a mediator, if negotiations stall. Having a clear contract can help protect your interests in case of disputes. -
What are the advantages of using brass over other materials like stainless steel?
Brass is often preferred for applications requiring high malleability and excellent machinability, making it suitable for intricate designs. Its superior corrosion resistance in many environments, along with good thermal and electrical conductivity, makes brass ideal for plumbing and electrical applications. While stainless steel offers durability in highly acidic environments, brass is typically more cost-effective and easier to work with for many B2B applications.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.
Top 7 Brass And Heat Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. Brass Safety – Heating Guidelines
Domain: reddit.com
Registered: 2005 (20 years)
Introduction: Brass can emit fumes when heated, particularly due to the loss of zinc through a process called ‘dezincification’. This reaction produces zinc oxide, which is not highly toxic but can cause metal fume fever. Users are advised to heat brass in an open environment and rinse it with water afterward to ensure cleanliness.
2. Metal Supermarkets – Thermal Conductivity Overview
Domain: metalsupermarkets.com
Registered: 1996 (29 years)
Introduction: Copper: Thermal Conductivity 223 BTU/(hr·ft⋅°F) – Excellent conductor, suitable for heat exchangers, heat sinks, cookware. Aluminum: Thermal Conductivity 118 BTU/(hr·ft⋅°F) – Good conductor, cost-effective alternative for heat exchangers. Brass: Thermal Conductivity 64 BTU/(hr·ft⋅°F). Steel: Thermal Conductivity 17 BTU/(hr·ft⋅°F) – Poor conductor, ideal for high-temperature environments. Bronze: T…
3. BladeForums – Solid Brass Fasteners
Domain: bladeforums.com
Registered: 1998 (27 years)
Introduction: Solid brass chicago screws and solid brass rivets used in leather work, refinished to a matte finish using high-speed abrasives. Concerns about overheating affecting strength, with discussions on temperatures and work hardening. Users suggest that heating does not harden brass but can soften it, and recommend testing for strength after refinishing. The refinishing process involves using 320 grit s…
4. Canadian Hobby Metalworkers – Heat Sink Solutions
Domain: canadianhobbymetalworkers.com
Registered: 2015 (10 years)
Introduction: Heat Sink for Bicycle Seat Tube; Material Options: Brass, Bronze, Copper; Brass: 100% machinable, easier to locate, cheaper than bronze; Bronze: bearing bronze (leaded) is machinable, surface finish is good; Copper: best for heat wicking, similar price to brass, challenging to machine; Air fitting for back purging argon; Wall thickness of chromoly tubing: 0.035″; Drilling: 1/2″ through-hole, 4-5″ …
5. Model Engineer – Brass & Bending Techniques
Domain: model-engineer.co.uk
Registered: 2006 (19 years)
Introduction: Brass, 3 mm diameter; various grades of brass (e.g., Naval Brass, Cartridge Brass, Jewellery Brass); Nickel (German Silver); bending techniques (hot, warm, cold); annealing temperatures (300 to 700°F, common brass at about 450°F); bending methods (heating to red heat, using salt bath of Potassium Nitrate/Sodium Nitrite at 350 to 400°C); applications for model engineering (drain cocks, actuating st…
6. Practical Machinist – Heat Relieving Ovens for Brass
Domain: practicalmachinist.com
Registered: 2000 (25 years)
Introduction: Oven for heat relieving brass: Recommended temperature is at least 500F for 1 hour of heating and slow cooling. Types of ovens discussed include conventional ovens, convection ovens, and the possibility of using a propane BBQ grill or a pottery kiln with digital controllers for precise temperature control. Concerns about using a kitchen oven include potential contamination and damage to the oven. …
7. Classic Pressure Lamps – Brass Restoration Techniques
Domain: classicpressurelamps.com
Registered: 2010 (15 years)
Introduction: Brass can be heated and worked to remove dents, but it is important to heat and quench the metal before working it to avoid cracking. The recommended heating temperature is around 650C, as brass melts at approximately 800C. Quenching is advised to soften the brass, while slow cooling can also anneal it. Care must be taken with soldered joints, as heating can compromise them. Using tools like a woo…
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for brass and heat
In the evolving landscape of brass and heat applications, strategic sourcing emerges as a critical component for international B2B buyers seeking to optimize performance and cost efficiency. Brass fittings, with their superior malleability, corrosion resistance, and thermal conductivity, are ideal for various applications across industries, especially in harsh environments. Understanding the specific advantages of brass over other materials, such as stainless steel, allows buyers to make informed decisions tailored to their unique operational needs.
As markets in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe continue to grow, the demand for high-quality brass components is expected to rise. Buyers should focus on building strong relationships with reliable suppliers who can provide not only competitive pricing but also valuable insights into material properties and application suitability.
Looking ahead, the emphasis on sustainability and innovation in manufacturing processes will shape the future of brass sourcing. By aligning with suppliers that prioritize environmentally friendly practices, B2B buyers can enhance their brand reputation while meeting regulatory standards. Take action now to evaluate your sourcing strategies and embrace the opportunities that brass and heat technologies present in the global market.