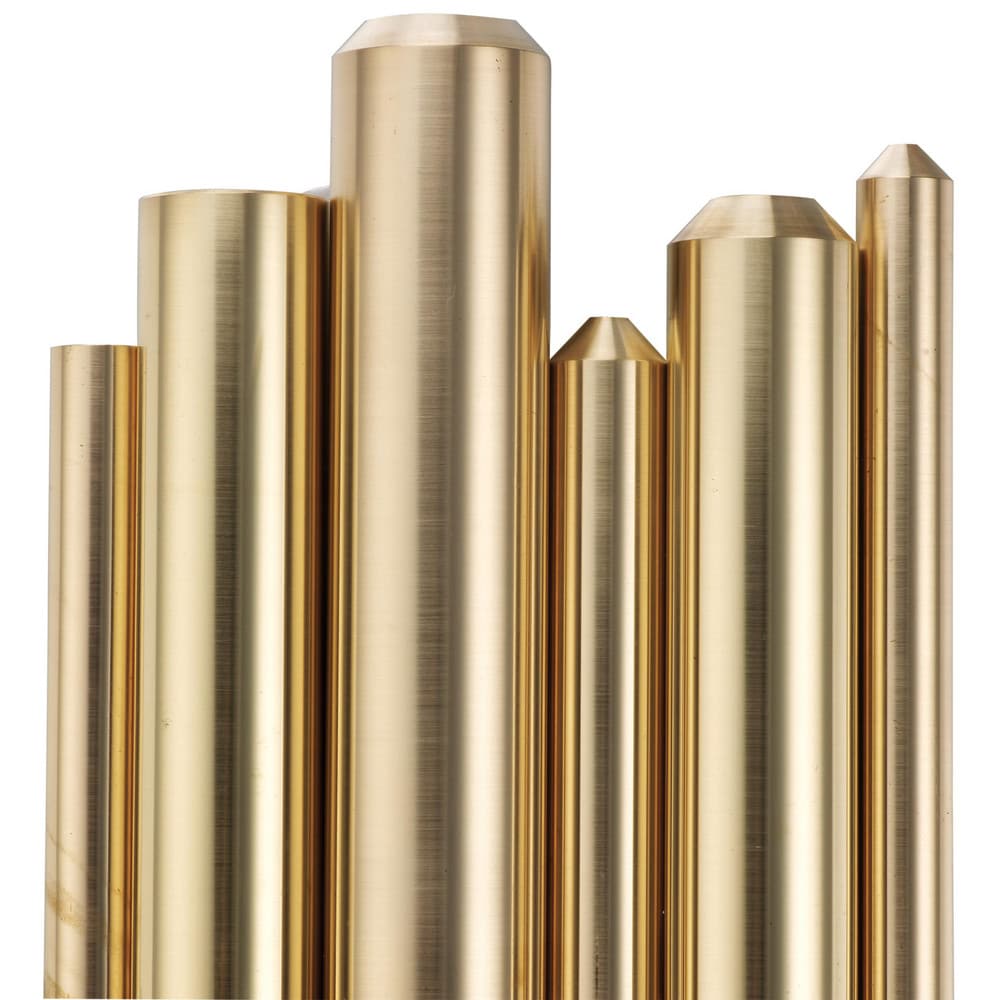
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for brass alloy 360
As global markets expand, B2B buyers face the critical challenge of sourcing high-quality brass alloy 360. This versatile and robust alloy, recognized for its superior machinability, corrosion resistance, and mechanical strength, serves a multitude of industries worldwide—from plumbing and automotive to electronics and architecture. In this guide, we explore the various aspects of brass alloy 360, offering insights into its chemical composition, mechanical properties, and broad applications. We delve into essential topics such as identifying reliable suppliers, understanding pricing structures, and evaluating material grades.
Designed specifically for international buyers from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe—especially Germany and Nigeria—this comprehensive guide empowers you to make informed purchasing decisions. By navigating the complexities of sourcing brass alloy 360, you can enhance your procurement strategies, reduce risk, and maximize operational efficiency. With the right knowledge at your fingertips, you can confidently select the best material to meet your unique project needs and ensure your applications achieve the highest performance standards. Prepare to dive deep into the intricate world of brass alloy 360 and elevate your supply chain management to new heights.
Understanding brass alloy 360 Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| C36000 | High copper content (61.5%), excellent machinability | Fasteners, plumbing components, actuators | Pros: Superior machinability, corrosion resistance; Cons: Lead content restricts some applications. |
| C360 Brass (CDA 360) | Identical to C36000, used interchangeably | Electrical connectors, valve stems | Pros: Consistent quality; widely available; Cons: Generally more expensive than other alloys. |
| C360003 | Slightly modified lead content for specific needs | Automotive parts, high-volume machining tasks | Pros: Enhanced machinability; Cons: Less common, may require custom orders. |
| CuZn36Pb3 | European designation for C360 brasses | Decorative fixtures, consumer goods | Pros: Meets European standards; Cons: Availability may be limited outside of Europe. |
| ISO CuZn36Pb3 (C360) | ISO specification ensuring quality and performance | Industrial machinery, aerospace components | Pros: Recognized international standard; Cons: Can have longer lead times due to specifications. |
What are the Key Characteristics of C36000 Brass for B2B Buyers?
C36000 brass stands out due to its exceptional machinability, rated at 100 on the machinability scale. This makes it ideal for high-precision applications like fasteners, plumbing components, and actuators. Its copper content ensures robust corrosion resistance, making it suitable for environments prone to moisture and chemical exposure. Buyers should consider its lead content, which enhances workability but may limit usage in applications where lead exposure is a concern.
Why Should Companies Consider C360 Brass (CDA 360)?
C360 brass, also known as CDA 360, is essentially a commercial variant of C36000 with no significant differences in chemical properties. Its popularity arises from consistent quality and availability across global markets, making it a reliable choice for electrical components and valve stems. When sourcing, buyers should prioritize suppliers with robust quality assurance programs to ensure consistency that meets their demands.
How is C360003 Brass Used for Specialized Applications?
C360003 features a modified lead content, enhancing its already excellent machinability tailored for specific industrial applications, particularly in automotive parts and high-volume machining tasks. Despite being less commonly available, it offers buyers the advantage of elevated workability for intricate designs. Organizations looking to procure this variation should confirm that their suppliers can meet specific composition requirements, ensuring the material meets application demands.
What Distinguishes CuZn36Pb3 for International Buyers?
As the European designation for C360 brasses, CuZn36Pb3 is often sought after in regions adhering to strict quality standards. It’s commonly employed in decorative fixtures and consumer products due to its aesthetic appeal and durability. However, B2B buyers should be mindful of its availability, as sourcing this variant might be more complex outside Europe, potentially affecting lead times and costs.
Why is ISO CuZn36Pb3 (C360) Beneficial for Global Companies?
ISO CuZn36Pb3 is recognized internationally and guarantees adherence to rigorous quality controls. This makes it a prime choice for applications in industrial machinery and aerospace components where quality is paramount. Companies should be prepared for longer lead times, as compliance with ISO standards may necessitate additional processing. Nevertheless, the assurance of international recognition and conformity can justify the increased procurement efforts.
Key Industrial Applications of brass alloy 360
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of brass alloy 360 | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Plumbing | Plumbing fixtures, fittings, and valves | High corrosion resistance improves longevity and reduces maintenance. | Ensure compliance with local standards and specifications. |
| Electrical Components | Circuit board relays and connectors | Excellent electrical conductivity enhances performance reliability. | Verify quality certifications and conductivity ratings. |
| Automotive | Sensor bodies and fluid connectors | Lightweight yet strong materials improve fuel efficiency and performance. | Assess lead content for regulatory compliance in target markets. |
| General Manufacturing | Nuts, bolts, and pump shafts | Exceptional machinability speeds up production and reduces waste. | Consider machining service capabilities and delivery times. |
| Construction | Architectural components and hardware fittings | Aesthetic appeal combined with strength for both functionality and design. | Evaluate material certifications and aesthetic finish options. |
How is Brass Alloy 360 Utilized in Plumbing Applications?
Brass alloy 360 plays a vital role in plumbing systems, where it is commonly used for fixtures, fittings, and valves. Its high corrosion resistance ensures durability in environments with constant exposure to moisture and harsh chemicals, thereby increasing the lifespan of plumbing installations. For B2B buyers in emerging markets, such as Nigeria and South Africa, it’s crucial to ensure that the brass they source meets local plumbing standards to prevent future compliance issues.
What Are the Benefits of Brass Alloy 360 in Electrical Components?
In the electrical industry, brass alloy 360 is frequently utilized for circuit board connectors and relays due to its excellent electrical conductivity. This property ensures reliable performance in electronic devices, which is essential for industries relying on high-tech components. Buyers in Europe, especially in engineering hubs like Germany, should focus on sourcing materials that guarantee both conductivity and adherence to EU regulations regarding lead content, ensuring safety and compatibility with regional standards.
How is Brass Alloy 360 Applied in the Automotive Sector?
The automotive sector leverages brass alloy 360 for manufacturing sensor bodies and fluid connectors. Its high strength-to-weight ratio contributes to fuel efficiency without compromising on performance. For B2B buyers in South America and the Middle East, it’s essential to inquire about the alloy’s lead content and strength properties, especially given increasing regulatory pressure for sustainability in auto manufacturing.
What Advantages Does Brass Alloy 360 Offer in General Manufacturing?
In general manufacturing, brass alloy 360 is favored for producing nuts, bolts, and pump shafts, owing to its unmatched machinability, which enhances production efficiency. This characteristic allows manufacturers to achieve intricate designs with minimal waste, a critical factor for cost management. When sourcing this material, buyers should evaluate their suppliers’ machining capabilities and their delivery timelines to optimize their production schedules.
How is Brass Alloy 360 Beneficial in Construction Applications?
Brass alloy 360 is also significant in the construction industry, particularly for architectural components and hardware fittings. Its aesthetic appeal coupled with exceptional strength makes it a preferred choice for creating durable and visually appealing structures. For international buyers, especially in Europe and the Middle East, understanding the various finishes available (e.g., polished or brushed) will assist in selecting the right product to match architectural vision while meeting durability requirements.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘brass alloy 360’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Sourcing Quality Brass Alloy 360 Materials
The Problem: B2B buyers often face challenges when trying to source high-quality brass alloy 360. With a variety of suppliers offering different grades and specifications, it can be difficult to ascertain which products meet industry standards and customer requirements. Inconsistent quality leads to increased production costs and potential project delays, especially when tight deadlines are in play. Buyers may also experience anxiety about whether the alloy will perform reliably in their applications, given its critical role in structural integrity and functionality.
The Solution: To ensure quality sourcing, buyers should consider establishing partnerships with specialized suppliers who have a proven track record in supplying brass alloys. It’s essential to request detailed technical specifications and certifications for compliance with relevant industry standards, such as ASTM. Additionally, buyers should explore suppliers that offer transparent traceability of their materials, so they can track the provenance of their brass alloy 360. Engaging in direct communication with suppliers about technical requirements, machining strategies, and applications will create a relationship built on trust and reliability. Regular quality checks upon delivery can also mitigate risks associated with material inconsistencies.
Scenario 2: Machining Challenges for Complex Components
The Problem: B2B manufacturers find themselves grappling with machining challenges when working on complex components made from brass alloy 360. Despite its high machinability rating, problems like tool wear, breakage, and inconsistent finish quality can arise during precision machining. These obstacles not only increase operational costs but also lead to delays in project timelines, thereby affecting customer satisfaction and profitability.
The Solution: To combat these machining challenges, manufacturers can optimize their processes by employing advanced machining techniques tailored for brass alloy 360. For example, utilizing high-speed machining tools with appropriate cutting speeds can minimize tool wear. Furthermore, implementing the right type of coolant or lubricant during the machining process enhances cutting performance and surface finish by reducing thermal buildup. Regular staff training on specific machining practices for brass alloy 360, including the use of appropriate speeds and feeds, can significantly improve yields and decreases waste. Investing in CNC equipment specifically calibrated for brass will also yield better precision and efficiency.
Scenario 3: Understanding Certification Requirements for Brass Alloy 360
The Problem: B2B buyers often struggle with the certification requirements necessary for brass alloy 360, particularly in sectors like automotive and aerospace where compliance is non-negotiable. Buyers may find themselves overwhelmed by the myriad of standards and regulations that pertain to material specifications. This leaves them at risk of selecting materials that do not meet required safety or quality standards, leading to costly recalls or failures in the field.
The Solution: To navigate the complexities of certification, it’s crucial for buyers to educate themselves on industry-specific standards that apply to their use of brass alloy 360. Partnering with suppliers who offer comprehensive certification documentation can streamline this process. Buyers should inquire about compliance with standards such as AS9100 for aerospace applications or ISO 9001 for general quality management. Utilizing tools like supplier audits and factory visits can further provide insight into the quality control measures in place. Organizing workshops or attending seminars focused on certification in the brass materials sector can also enhance understanding and provide updates on recent changes in regulatory requirements, enabling informed decision-making.
In conclusion, each scenario presents unique challenges, but with proactive strategies and a focus on quality sourcing, process optimization, and regulatory compliance, B2B buyers can effectively mitigate risks associated with using brass alloy 360.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for brass alloy 360
When considering brass alloy 360, also known for its excellent machinability and corrosion resistance, it is crucial for international B2B buyers to understand the specific types of products available, their properties, advantages, disadvantages, and overall impact on their applications. This knowledge is particularly valuable in diverse markets across Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, including countries such as Germany and Nigeria.
What Are the Key Properties of Brass Alloy 360?
Mechanical Properties
Brass alloy 360 is notable for its impressive tensile strength, which ranges from 49,000 to 68,000 psi, ensuring durability under stress. Its yield tensile strength is significant, varying from 18,000 to 45,000 psi, making it an excellent choice for high-stress applications. Machinability is rated at 100, making it highly workable, which is ideal for precision manufacturing. Brass 360 performs well across a range of temperatures with a melting point of approximately 1,630°F to 1,650°F, ensuring stability in varying conditions.
Corrosion Resistance
One of the standout features of brass 360 is its high resistance to corrosion due to its substantial copper and zinc content. This characteristic is essential for applications exposed to moisture or corrosive environments, making it suitable for plumbing and marine applications.
Benefits and Drawbacks: What Should Buyers Consider?
Benefits
– Durability: Brass 360 is robust, maintaining structural integrity even in rugged conditions.
– Excellent Machinability: The high machinability allows for cost-effective processing and complex designs without extensive tooling requirements.
– Versatility: Brass 360 can be used in a variety of applications from plumbing fittings to electronic components.
Drawbacks
– Lead Content: While the lead improves machinability, it may pose health and environmental concerns in regions with stringent regulations.
– Cost Considerations: Brass can be more expensive than alternative metals such as steel, which may impact budget-conscious projects.
– Welding Limitations: The alloy is not ideal for welding processes, which may limit its use in certain fabrications.
How Does Brass Alloy 360 Impact Different Applications?
Brass alloy 360 is commonly deployed in various sectors, including plumbing, automotive, and electrical industries. Its compatibility with different media—especially water and thermal fluids—ensures reliable performance in plumbing fixtures and pump components. However, understanding compliance with regional standards is essential, particularly in Europe, where DIN or EN standards may apply, while ASTM standards may be more prevalent in North America and other regions.
What Should International Buyers Consider?
When procuring brass alloy 360, international buyers must factor in compliance with local regulations surrounding lead content, as regions such as Europe enforce tighter control measures than others. Buyers in Africa and South America may find variances in local manufacturing capabilities impacting delivery timelines and costs. Knowledge of regional supply chains, tariffs, and standards will be critical to making informed decisions.
Below is a summary table encapsulating the characteristics of brass alloy 360 relevant for B2B buyers:
| Material | Typical Use Case for brass alloy 360 | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| C36000 Brass | Plumbing fittings, screw machine parts | High machinability, excellent corrosion resistance | Lead content raises health concerns, higher cost than alternatives | Medium |
| Free-Cutting Brass | Electronic components, automotive sensors | Durable under stress, versatile applications | Not ideal for welding, potential sourcing challenges | Medium |
| CDA 360 Brass | Marine components, valve stems | Maintains structural integrity despite harsh environments | Higher initial investment, lead regulatory compliance | Medium |
| H02 Temper Brass | Interior architectural hardware | Suitable for precision machining and aesthetic applications | Limited recyclability compared to other metals | Medium |
This table aims to assist international B2B buyers in making nuanced decisions regarding the procurement of brass alloy 360 based on their specific needs and regional regulations. Understanding these factors is essential for optimizing material selection in manufacturing and assembly processes.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for brass alloy 360
What Are the Key Stages in the Manufacturing Process of Brass Alloy 360?
The production of brass alloy 360, also known as C36000 or free-machining brass, involves several critical manufacturing stages that ensure the material meets stringent quality requirements. The primary stages in this process include material preparation, forming, assembly, and finishing.
How Is Material Prepared for Brass Alloy 360 Production?
Material preparation is the first step where raw materials—primarily copper and zinc—are sourced based on quality specifications. The composition of 360 brass typically includes 61.5% copper, 35.5% zinc, and 3% lead. Sourcing high-quality raw materials is crucial, as impurities can affect the mechanical properties of the final product.
Once the raw material is procured, it undergoes melting in a controlled environment to create a homogenous alloy. This melting process is vital as it ensures that the components are uniformly mixed, thus contributing to the alloy’s desired properties such as corrosion resistance and machinability.
Which Techniques Are Used to Form Brass Alloy 360?
The forming stage employs various methods to achieve the desired shape of brass components. Common techniques include:
-
Casting: This is often used for producing complex shapes. The molten brass is poured into molds and allowed to cool, resulting in solidified products ready for further processing.
-
Extrusion: This process forces heated brass through a die to create long shapes like rods and bars. It enhances the mechanical properties through controlled deformation.
-
Machining: Given its high machinability rating, many components of brass 360 undergo machining to achieve precise dimensions and finishes. Techniques such as turning, milling, and drilling are employed to refine parts to exact specifications.
These forming techniques enable manufacturers to produce a range of components, from plumbing fittings to electrical connectors, tailored to various industries.
How Is Assembly Conducted in Brass Alloy 360 Production?
In the assembly phase, individual components fabricated from brass 360 are brought together to create finished products or subassemblies. This stage is critical for ensuring both functionality and aesthetic appeal.
Quality control measures are often put in place during assembly to check for alignment, fit, and overall durability. Assembly may require additional processes such as threading or knurling, which add to the functionality of brass components.
What Finishing Techniques Are Used on Brass Alloy 360 Products?
Finishing is the final stage of manufacturing wherein surface treatment processes are applied to enhance the aesthetic and functional properties of the brass components. Common finishing methods for brass alloy 360 include:
-
Polishing: This technique improves the surface finish, giving components a shiny, appealing look.
-
Plating: Sometimes, products are plated or coated with additional corrosion-resistant materials to extend longevity in harsh conditions.
-
Passivation: This process helps in removing any contaminants from the surface, improving corrosion resistance further.
These finishing techniques not only improve the aesthetics of the final product but also help in maintaining quality throughout its lifespan.
What International Quality Standards Are Relevant in Brass Alloy 360 Production?
Quality assurance (QA) in manufacturing brass 360 is governed by several international standards, most notably ISO 9001, which sets out the criteria for quality management systems. This standard is critical for ensuring reliability and consistency in the manufacturing process, making it essential for international B2B buyers.
Which QC Checkpoints Are Essential for Quality Assurance?
The quality control process in brass manufacturing typically involves three key checkpoints:
-
Incoming Quality Control (IQC): Raw materials are inspected before entering the production line for impurities or deviations from specified standards.
-
In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): Throughout the manufacturing phases, components are regularly checked for adherence to physical and chemical property requirements.
-
Final Quality Control (FQC): Once the products are finished, they undergo rigorous testing to confirm their meeting the predefined standards, including dimensions, strength, and aesthetic qualities.
These checkpoints help in minimizing defects and ensuring that the final products perform reliably in their intended applications.
What Common Testing Methods Are Used for Brass Alloy 360 Quality Assurance?
Various testing methods are employed to ensure the quality of brass alloy 360. Some of the most common methods include:
-
Tensile Testing: Measures the strength and elongation of the material to ensure it can withstand applied stresses.
-
Hardness Testing: Evaluates the material’s hardness to predict its machinability and wear resistance.
-
Corrosion Testing: Assesses the alloy’s resistance to environmental factors and chemical exposures.
Implementing these testing methods helps suppliers guarantee that their products meet both international and industry-specific standards.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify a Supplier’s Quality Control Processes?
For international B2B buyers, particularly those sourcing from regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, confirming the integrity of a supplier’s quality control processes is crucial. Here are some effective methods for verification:
-
Audits: Conducting onsite audits or requesting third-party inspections can provide insights into a supplier’s practices and compliance with industry standards.
-
Certificates and Reports: Suppliers should provide certifications that validate their compliance with standards like ISO 9001, along with detailed quality reports on batches shipped.
-
References and Reviews: Gaining feedback from previous clients can further inform on the reliability and quality assurance practices of the supplier.
What Quality Control and Certification Nuances Should International B2B Buyers Be Aware Of?
International buyers should also be aware of specific nuances related to quality control and certification when sourcing brass alloy 360. For instance, different regions may have varying regulations and certifications that impact quality expectations.
In markets like Europe, compliance with CE marking directives is critical, while in the American market, adherence to ASTM standards may be required. Thus, understanding these regional requirements is essential for buyers to make well-informed purchasing decisions.
In conclusion, the manufacturing processes and quality assurance frameworks associated with brass alloy 360 encompass a detailed and rigorous pathway tailored to produce high-quality components. B2B buyers must leverage both due diligence and a nuanced understanding of these processes to ensure that their procurement meets international standards and operational specifications.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘brass alloy 360’
Introduction
Navigating the procurement of brass alloy 360, also known as C36000 brass, requires a thoughtful approach to ensure that the material meets your project’s specific needs. This guide outlines essential steps for B2B buyers to effectively source this versatile copper-zinc-lead alloy known for its exceptional machinability, corrosion resistance, and strength. Following this checklist will help you streamline the sourcing process and make informed decisions.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Understanding your project requirements is paramount. Articulate the exact composition, physical properties, and applications needed for brass alloy 360. These specifications will guide your supplier discussions and help you identify the right product for your needs.
– Consider tensile strength and hardness: Ensure the alloy’s mechanical properties align with project demands.
– Identify corrosion resistance needs: Assess if the operational environment requires enhanced resistance.
Step 2: Research and Identify Reliable Suppliers
Conduct thorough research to create a shortlist of potential suppliers. Look for established manufacturers and distributors with experience in brass alloys. An extensive supplier network not only increases your chances of finding the best material but also provides options for price and delivery flexibility.
– Utilize industry directories and online platforms: Resources like Metal Supermarkets or Sequoia Brass & Copper can help you find viable options.
– Check reviews and testimonials: Verified customer feedback will provide insights into the quality and reliability of the suppliers.
Step 3: Evaluate Potential Suppliers
Before committing, it’s crucial to vet suppliers thoroughly. Request company profiles, product certifications, and references from buyers within your industry or region. A deeper understanding of a supplier’s capabilities will significantly mitigate risks associated with quality and delivery.
– Look for certifications: Check if the supplier meets relevant international standards for brass alloy production.
– Inquire about lead times: Assess their capacity to meet your project’s timeline.
Step 4: Request Material Specifications and Certificates
Ensure that suppliers provide detailed specifications and testing certificates. This documentation should confirm the brass alloy’s composition, mechanical properties, and compliance with industry standards.
– Verify metallurgical reports: These documents will help you assess the quality consistency of the materials.
– Ask for a test sample if possible: This allows you to physically evaluate the brass before placing a bulk order.
Step 5: Negotiate Pricing and Terms
Engage in discussions to secure favorable pricing and contract terms. Pricing can vary widely based on order size, delivery schedules, and market demand, so negotiation can lead to significant savings.
– Be transparent about your budget: Clear communication can help suppliers offer tailored solutions.
– Consider total cost of ownership: Factor in potential shipping, taxes, and import duties specific to your region.
Step 6: Confirm Logistic Arrangements
Discuss delivery options and packaging to ensure safe transport of your materials. The logistics aspect is crucial for efficient supply chain management and can impact project timelines.
– Assess shipping methods based on urgency: Longer lead times may require bulk shipping, while urgency might demand expedited services.
– Inquire about packaging standards: Proper packaging minimizes the risk of material damage during transit.
Step 7: Establish Quality Control Measures
Plan for an evaluation phase upon material receipt. Implement a quality control process that includes inspection, testing, and approval to confirm that the brass alloy meets the agreed specifications.
– Develop an acceptance criteria checklist: This should be based on your initial specifications to simplify the evaluation.
– Consider third-party inspection services: External validation can provide an unbiased quality perspective.
By observing these steps, international B2B buyers can ensure they procure brass alloy 360 that meets both quality standards and project needs while building a reliable supply chain network.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for brass alloy 360 Sourcing
Analyzing the cost structure and the pricing of brass alloy 360 is vital for B2B buyers aiming to optimize their sourcing strategies. Understanding the underlying cost components and the factors influencing price can significantly enhance decision-making.
What Are the Key Cost Components for Brass Alloy 360?
When evaluating the cost of brass alloy 360, several components come into play:
-
Raw Materials: The primary constituents—copper, zinc, and lead—are subject to price fluctuations based on global market conditions. Copper and zinc prices can be particularly volatile, affecting overall costs.
-
Labor Costs: Labor is integral to the manufacturing process. Costs vary depending on location; suppliers in regions with higher labor rates will likely charge more. Additionally, skilled labor may be necessary for processing and finishing brass items, further impacting labor costs.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes expenses related to utilities, rent, and maintenance of manufacturing facilities. Efficient manufacturing processes can reduce overhead expenses, contributing to a more favorable cost structure.
-
Tooling Expenses: Specific tooling is often required for machining brass alloy 360, which can influence initial production costs. Tooling options like customized molds can increase setup times and costs.
-
Quality Control (QC): Ensuring that products meet industry standards incurs costs. Implementing effective QC processes may involve additional testing or certifications, especially for markets that demand high quality or specific compliance (e.g., European Union regulations).
-
Logistics and Transportation: Freight costs, particularly for international shipments, can escalate due to distance and regulatory requirements. Incoterms also determine responsibility for shipping costs and risks.
-
Profit Margins: Suppliers typically include a profit margin in their pricing. This margin can vary based on supplier market positioning and competitive factors.
Which Factors Influence Brass Alloy 360 Pricing?
The pricing of brass alloy 360 is influenced by multiple factors:
-
Order Volume/Minimum Order Quantity (MOQ): Higher purchase volumes can lead to discounts, making bulk purchasing beneficial. Understanding MOQ can aid in reducing per-unit costs.
-
Specifications and Customization: Custom specifications dictate production complexity, impacting lead time and costs. Specifying unique dimensions or additional treatments may involve extra costs.
-
Quality and Certifications: Materials tested to specific standards or featuring certifications typically command higher prices. Certifications can be crucial for industries requiring stringent compliance, enhancing buyer assurance.
-
Supplier Variability: Supplier experience, reputation, and reliability can affect pricing. Established suppliers with robust quality assurance systems may charge more but offer better consistency.
-
Incoterms: The chosen Incoterms will define who is responsible for shipping and insurance costs, affecting overall pricing. For international buyers, understanding incoterms such as FOB (Free On Board) or CIF (Cost, Insurance, and Freight) is critical.
What Tips Can Optimize Costs for Buyers in Different Regions?
-
Negotiation Strategies: Developing strong relationships with suppliers can foster better negotiation opportunities. Emphasizing long-term partnerships and repeat orders can lead to favorable pricing.
-
Assessing Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Beyond purchase price, consider factors like operational efficiency, product lifespan, and maintenance requirements. Choosing high-quality brass can result in lower wear and tear, reducing long-term costs.
-
Local Sourcing Considerations: For buyers in regions like Africa or South America, sourcing locally can mitigate logistics costs and lead times. However, ensuring quality standards must remain a priority.
-
Awareness of Pricing Nuances: Understanding regional economic conditions, currency fluctuations, and tariffs can inform purchasing decisions. In countries like Nigeria, for instance, local materials may be cheaper, but quality assurance must not be compromised.
-
Flexibility in Specifications: If time permits, opting for stock products or more standardized components can minimize costs incurred from custom orders, streamlining sourcing.
In conclusion, the sourcing of brass alloy 360 requires a keen understanding of cost implications and price influencers. Buyers need to analyze these factors meticulously to make informed, cost-efficient decisions. Remember that indicative prices are subject to change based on market conditions, ensuring constant reevaluation of sourcing strategies.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing brass alloy 360 With Other Solutions
When sourcing materials for manufacturing operations, business-to-business (B2B) buyers must evaluate various options, including brass alloy 360 and its alternatives. Understanding different alloys or materials can significantly affect production efficiency, cost management, and overall product performance.
Comparison Table
| Comparison Aspect | Brass Alloy 360 | Aluminum Alloy 6061 | Stainless Steel 304 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | High machinability, good corrosion resistance, strength up to 68,000 psi | Good strength-to-weight ratio, medium corrosion resistance, not as machinable | Excellent corrosion resistance, durability, strength up to 70,000 psi |
| Cost | Moderate to high | Generally lower | Higher than brass and aluminum |
| Ease of Implementation | Highly machinable; complex shapes achievable easily | Moderate machinability; can require specialized tooling | Requires advanced techniques; welding and machining are more complex |
| Maintenance | Minimal maintenance needs; good longevity | Requires coatings for corrosion protection | Low maintenance; does not rust easily in many environments |
| Best Use Case | Precision parts in plumbing and electrical fittings | Structural components in lightweight applications | Heavy-duty applications requiring corrosion resistance, such as in marine environments |
Detailed Breakdown of Alternatives
Aluminum Alloy 6061
Aluminum 6061 is a popular alternative due to its favorable strength-to-weight ratio. It offers moderate machinability, though it may require more specific tooling compared to brass alloy 360. One key advantage of aluminum 6061 is its cost-effectiveness, making it an excellent choice for non-critical applications or those where weight is a primary concern. Nevertheless, its corrosion resistance is not as robust as that of brass 360 unless a hard anodized finish is applied.
Stainless Steel 304
Stainless steel 304 is another viable alternative, well-regarded for its outstanding corrosion resistance and overall strength, making it suitable for harsher environments. This alloy performs excellently in applications where durability is a concern, such as in marine or outdoor settings. However, the main disadvantages include higher costs and more complex machining requirements, which can translate to longer lead times and increased manufacturing costs.
Conclusion
When selecting the right alloy, B2B buyers must consider their specific application requirements, such as strength, cost, and environmental conditions. Brass alloy 360 is an optimal choice for applications requiring high machinability, good corrosion resistance, and precision engineering. However, alternatives like aluminum 6061 and stainless steel 304 may offer better cost efficiency or durability in particular situations. It is essential for buyers to assess their project parameters carefully to make the best-informed decision, balancing performance needs with budget constraints and manufacturing capabilities.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for brass alloy 360
What Are the Essential Technical Properties of Brass Alloy 360?
Brass alloy 360, also known as free-machining brass, is renowned for several technical properties that make it highly valuable for a wide range of applications in various industries. Understanding these properties is crucial for B2B buyers who need reliable materials for their manufacturing processes.
-
Chemical Composition: Why Does It Matter?
Brass alloy 360 consists of approximately 61.5% copper, 35.5% zinc, 3% lead, and 0.35% iron. This composition is pivotal as it contributes to the alloy’s stunning corrosion resistance and excellent machinability. The high copper content enhances strength, while the presence of lead improves workability, making it ideal for complex machining tasks. -
Tensile and Yield Strength: How Do They Impact Performance?
The tensile strength of brass alloy 360 ranges from 49,000 to 68,000 psi, with a yield strength between 18,000 and 45,000 psi, depending on the temper and diameter. These values indicate the alloy’s ability to withstand stress without deformation. For manufacturers, this translates to components that maintain structural integrity, even under demanding conditions. -
Machinability Rating: Why Is This Critical for Manufacturing?
Brass 360 boasts a machinability rating of 100, the highest among copper alloys, enabling efficient manufacturing processes. This property ensures that producers can swiftly cut, drill, and shape the material with minimal tooling wear, ultimately reducing production costs and lead times. -
Density and Thermal Properties: What Are the Implications?
With a density of 0.307 lb/in³, brass 360 strikes a balance between weight and strength. Additionally, it has a melting point ranging from 1,630°F to 1,650°F and an annealing point of 800°F to 1,100°F, crucial for processes that involve heat treatment. These characteristics are essential for applications requiring high durability, such as plumbing and electrical components. -
Corrosion Resistance: Why Should You Prioritize It?
The alloy’s exceptional resistance to corrosive environments makes it suitable for applications exposed to moisture and chemicals. This durability extends the lifespan of parts in demanding environments, vital for B2B buyers looking to minimize maintenance and replacement costs.
What Key Trade Terms Should B2B Buyers Know About Brass Alloy 360?
-
OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer): This term refers to companies that produce parts or equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer. Understanding OEM relationships is essential when sourcing brass alloy 360 for components used in various applications.
-
MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity): This specifies the minimum amount of a product that a supplier is willing to sell. For buyers, knowing the MOQ for brass 360 components helps in planning production runs and ensuring cost-effectiveness in bulk procurement.
-
RFQ (Request for Quotation): An RFQ is a document sent to suppliers to obtain pricing and terms for the supply of goods, such as brass alloy 360. This process allows buyers to compare offers and select suppliers who best meet their specifications and budget.
-
Incoterms (International Commercial Terms): These terms are critical in defining the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in international trade. Familiarity with Incoterms, like FOB (Free on Board) and CIF (Cost Insurance and Freight), can help buyers negotiate better shipping and logistics arrangements for their brass 360 purchases.
-
CDA (Copper Development Association) Designations: Brass alloys, including 360 brass, are often identified by CDA numbers. For instance, CDA 360 corresponds to brass 360. Knowing these designations helps buyers ensure they are sourcing the correct material for their specific requirements.
-
Lead Content and its Implications: Brass alloy 360 contains around 3% lead, influencing both machinability and regulatory considerations. It’s vital for buyers to understand lead restrictions in certain markets, especially in regions with strict environmental regulations.
By familiarizing themselves with these essential technical properties and industry jargon, B2B buyers can make informed decisions, optimizing their procurement and manufacturing strategies for brass alloy 360.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the brass alloy 360 Sector
What Are the Key Drivers and Trends Impacting the Brass Alloy 360 Market?
The global brass alloy market, particularly the C36000 segment, is witnessing robust growth driven by several factors. Increased industrialization in emerging markets such as Nigeria and Brazil is pushing demand for durable and highly machinable materials. Furthermore, the automotive and plumbing sectors are significantly investing in brass components due to their corrosion resistance and machinability. By offering high tensile strength and a favorable machinability rating, brass alloy 360 has become a choice material in applications ranging from screw machine parts to intricate plumbing fixtures.
Emerging B2B tech trends are revolutionizing the sourcing landscape. Digital supply chain platforms streamline procurement processes, making it easier for buyers from regions like Africa and Europe to source materials effectively. Furthermore, the integration of artificial intelligence and data analytics into supply chain management helps businesses forecast demand more accurately, manage inventory better, and establish stable supplier relationships. Sustainability is another critical trend that is shaping sourcing strategies; B2B buyers are increasingly focusing on suppliers who adhere to environmentally sustainable practices and ethical sourcing protocols.
How is Sustainability Influencing Sourcing Decisions in the Brass Alloy Sector?
The growing awareness of environmental impacts is steering B2B buyers towards more sustainable sourcing models for brass alloys. The traditional extraction and processing of metals, including brass, can lead to significant environmental degradation. Therefore, buyers are now prioritizing suppliers that practice responsible mining and processing techniques, which mitigate ecological harm and reduce carbon footprints.
Additionally, certifications such as ISO 14001 (Environmental Management) and compliance with REACH (Registration, Evaluation, Authorisation, and Restriction of Chemicals) are becoming essential criteria for many businesses when selecting suppliers. These certifications demonstrate a commitment to sustainability in production processes. Buyers looking for brass alloy 360 should also inquire about the availability of lead-free alternatives that maintain the desired properties while minimizing health risks, thus aligning with the broader industry trend towards “greener” materials.
What Is the Historical Context of Brass Alloy 360’s Adoption in B2B Industries?
The evolution of brass alloy 360 traces back to the early industrial era when engineers sought a material that combined strength, machinability, and resistance to corrosion. Initially used in mechanical applications, its unique composition of copper, zinc, and lead quickly proved advantageous in various sectors, including plumbing and automotive manufacturing. Over the decades, as manufacturing technologies evolved, so did the applications of brass alloy 360, expanding from basic fittings to sophisticated components in electronics and aerospace.
Today, the versatility of brass alloy 360 not only underscores its historical significance but also enhances its relevance in modern manufacturing, as industries seek efficient and reliable materials to meet contemporary demands. This historical adaptability positions 360 brass as a staple in many B2B sectors, continuing to meet the changing needs of global markets.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of brass alloy 360
-
What are the key properties of brass alloy 360 that make it suitable for B2B applications?
Brass alloy 360, also known as C36000, is celebrated for its excellent machinability, high corrosion resistance, and impressive strength. Comprising approximately 61.5% copper, 35.5% zinc, and 3% lead, this alloy boasts the highest machinability rating of all copper alloys, making it ideal for intricate components. It maintains structural integrity with a yield strength of 45,000 psi and tensile strength reaching up to 68,000 psi. Its durability and malleability make it suitable for applications ranging from plumbing fittings to intricate electronics. -
How can I evaluate potential suppliers of brass alloy 360 for my business?
When vetting suppliers, prioritize reliability, quality certifications, and industry expertise. Request samples of brass alloy 360 to assess specifications against project requirements. Look for suppliers who provide transparent information about their manufacturing processes, testing methods, and compliance with international standards. Additionally, evaluate their historical performance, customer reviews, and the ability to meet delivery timelines—critical factors for maintaining your production schedule. -
What are the common applications of brass alloy 360 in various industries?
Brass alloy 360 is widely used for its machinability and corrosion resistance. Common applications include manufacturing screw machine parts, nuts, bolts, connectors, couplings, and valve stems. Its golden appearance and smooth surface also make it popular for decorative elements in architecture and automotive components such as sensor bodies and fluid connectors. This versatility allows businesses across sectors to harness the benefits of this alloy in both functional and aesthetic applications. -
What minimum order quantities (MOQs) should I expect when sourcing brass alloy 360?
Minimum order quantities for brass alloy 360 can vary significantly depending on the supplier and the size or type of material requested. For larger suppliers, MOQs may range from 100 to 500 kg for bulk purchases. However, many suppliers are willing to accommodate smaller orders for custom applications. It’s essential to clarify MOQs early in your discussions to avoid potential delays and ensure that your needs align with the supplier’s capabilities. -
What payment terms are typically offered by suppliers of brass alloy 360?
Payment terms can vary between suppliers, but common practices include advance payments, net 30, or net 60 days, depending on the buyer’s creditworthiness and the supplier’s policies. Some suppliers might offer discounts for early payment or bulk orders. Before finalizing your sourcing agreement, it’s crucial to discuss and agree on payment terms that align with your cash flow and project timelines to maintain a healthy business relationship. -
How do I ensure quality assurance (QA) when sourcing brass alloy 360?
To guarantee quality assurance, request a Certificate of Compliance that verifies the alloy’s specifications against industry standards. Conduct regular inspections of the material upon reception and assess physical properties like hardness and machinability. Additionally, consider third-party testing if large quantities are involved or the parts are critical to your operations. Building a relationship with the supplier that promotes open communication about quality control processes can also enhance confidence in the materials received. -
What logistics considerations should I be aware of when importing brass alloy 360?
When importing brass alloy 360, consider shipping methods, customs regulations, and lead times impacting delivery schedules. Ensure you are aware of import duties and tariffs that may apply based on your location. Opt for suppliers with a reliable logistics partner to facilitate smoother shipping processes. Also, using Incoterms such as FOB (Free On Board) or CIF (Cost Insurance and Freight) can clarify responsibilities and costs during transportation. -
Can brass alloy 360 be customized to meet specific design requirements?
Yes, brass alloy 360 can be customized to suit specific design needs. Many suppliers offer various forms, including bars, rods, and custom shapes based on your engineering specifications. Discuss your project requirements with the supplier, including dimensions, surface finishes, and any specific mechanical properties needed for your application. Customization services often include short lead times and flexibility to tweak designs based on evolving demands, making them ideal for innovative projects.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.
Top 9 Brass Alloy 360 Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. Sequoia – C36000 Brass
Domain: sequoia-brass-copper.com
Registered: 1998 (27 years)
Introduction: C36000 Brass (C360 Brass) is a copper-zinc-lead alloy known for its high machinability, strength, and corrosion resistance. Composition: 61.5% copper, 35.5% zinc, 3% lead, 0.35% iron. Material Properties: Tensile strength: 58,000 psi, Yield strength: 45,000 psi, Density: 0.307 lb/in.3, Elastic modulus: 17,000 ksi, Shear modulus: 5,370 ksi, Elongation at break: 53%, Poisson’s ratio: 0.34. Hardness …
2. McMaster – Brass Alloy 360
Domain: mcmaster.com
Registered: 1994 (31 years)
Introduction: This company, McMaster – Brass Alloy 360, is a notable entity in the market. For specific product details, it is recommended to visit their website directly.
3. Metal Supermarkets – Brass 360
Domain: metalsupermarkets.com
Registered: 1996 (29 years)
Introduction: Brass 360 – Grade Summary: Brass 360 is the most commonly used of the brass rod and bar items. The presence of lead creates a highly machinable material that can be cut, drilled and shaped easily. Applications include: Architecture (terrazzo strip), Automotive (sensor bodies, thermostat parts, fluid connectors, threaded inserts for plastic), Builders Hardware (lock bodies, fittings, hardware), Con…
4. Materials Plus – Brass Alloy 360 (C36000)
Domain: materialsplus.com
Registered: 2000 (25 years)
Introduction: Brass Alloy 360 (C36000) is composed of 61.5% copper, 35.4% zinc, and 3.1% lead. It is primarily used for continuous high-speed machining operations due to its high lead content, which results in short machined chips that minimize tool wear and breakage. The machinability index is rated at 100, making it the standard for comparison among copper alloys. C36000 has fair hot workability and can be ex…
5. Online Metals – 360 Brass (C36000)
Domain: onlinemetals.com
Registered: 1997 (28 years)
Introduction: 360 Brass (C36000) is a free machining brass known for its high machinability due to the presence of lead in the alloy. It resists corrosion well and has good strength, making it suitable for industrial applications. Common uses include plumbing products, fittings, adapters, shafts, valves, screw parts, machine parts, couplings, electrical components, circuit boards, and industrial hardware. Avail…
6. Sequoia – 360 Brass Tube 2.625 in x 36 in
Domain: catalog.sequoia-brass-copper.com
Registered: 1998 (27 years)
Introduction: {“Item Number”: “360RRD2625-36”, “Outer Diameter”: “2.625 in”, “Length”: “36 in”, “Temper”: “H02”, “Alloy”: “360”, “Product Weight”: “59.8121 lb”, “Price”: “$483.03”, “UNS Number”: “C36000”, “Trade Names”: [“FM Brass”, “Free-Machining Brass”], “Industry Standards”: “ASTM B16”}
7. Industrial Metal Supply – 360 Brass
Domain: industrialmetalsupply.com
Registered: 1999 (26 years)
Introduction: 360 Brass is a highly machinable metal known for its excellent corrosion resistance, making it suitable for soldering. Also referred to as free machining brass, alloy 360 is commonly used in plumbing products, gears, industrial components, bolts, couplings, and more. Available metal shapes include bars, and custom cutting options are offered to meet specific project requirements.
8. Lewis Brass – A360 Brass Alloy
Domain: lewisbrass.com
Registered: 1998 (27 years)
Introduction: A360 brass is a popular alloy known for its flexibility, corrosion resistance, and intricate casting applications. It falls into the alpha brass family with a composition of approximately 61-63% copper (Cu), 2.5-3.5% iron (Fe), 2-3% lead (Pb), and the remainder zinc (Zn). Key properties include excellent machinability, corrosion resistance, castability for detailed designs, and dimensional stabili…
9. Michlin Metals – 360 Brass (UNS C36000)
Domain: michlinmetals.com
Registered: 1999 (26 years)
Introduction: 360 Brass – UNS C36000 – AMS 4610
– Highly machinable due to approximately 3% lead content
– Machinability rating: 100% (basis for comparison with other copper alloys)
– Common uses: hardware, plumbing fixtures, and fittings
– Lead content restricts use in contact with potable water
Chemical Composition:
– Copper: 60% – 63%
– Lead: 2.5% – 3.7% (can be restricted to a maximum of 3.0% by environmen…
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for brass alloy 360
What Are the Key Takeaways for Sourcing Brass Alloy 360?
In conclusion, strategic sourcing of brass alloy 360 offers significant advantages for international buyers, particularly in regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. This exceptional copper-zinc-lead alloy is renowned for its unparalleled machinability, corrosion resistance, and impressive strength attributes, making it indispensable across various applications, from plumbing fixtures to automotive components. By prioritizing reliable suppliers that adhere to stringent quality standards, businesses can ensure the longevity and performance of their products while reducing potential risks associated with material sourcing.
How Can Strategic Sourcing Enhance Your Business Operations?
The value of strategic sourcing extends beyond mere cost savings; it encompasses building strong supplier relationships and enhancing supply chain resilience. As demand for high-quality brass components continues to grow globally, staying ahead in procurement strategies will allow businesses to capitalize on emerging market opportunities.
International B2B buyers are encouraged to explore the diverse offerings of brass alloy 360 available through reputable suppliers. Investing in this versatile material not only promises superior product performance but also positions your company as a leader in quality and innovation. Reach out today to discover how brass alloy 360 can elevate your projects and drive success in your marketplace.