Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for black oxide vs black phosphate
In today’s competitive landscape, sourcing the right metal finishing solutions, such as black oxide and black phosphate coatings, is crucial for B2B buyers aiming to enhance the durability and performance of their products. With distinct characteristics and applications, understanding these two coating processes is essential for making informed procurement decisions. This comprehensive guide delves into the nuances of black oxide and black phosphate coatings, exploring their respective processes, benefits, and ideal uses across various industries.
International buyers, particularly from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe—including Vietnam and Brazil—face unique challenges in selecting the right coating for their specific needs. This guide not only outlines the technical differences and advantages of each coating type but also provides actionable insights on supplier vetting, cost considerations, and best practices for implementation.
By equipping B2B purchasers with the necessary knowledge and tools, this resource empowers them to navigate the complexities of the global market confidently. Whether your focus is on enhancing corrosion resistance, improving aesthetic appeal, or ensuring optimal performance in demanding environments, this guide serves as a vital tool in your decision-making process, helping you choose the right metal finishing solution for your business needs.
Understanding black oxide vs black phosphate Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Black Oxide | Chemical conversion to magnetite, provides a matte finish. | Firearms, precision instruments, decorative hardware | Pros: Aesthetic appeal, minimal thickness. Cons: Limited corrosion resistance without post-treatment. |
| Manganese Phosphate | Forms a hard, crystalline layer, excellent for lubrication. | Automotive parts, industrial machinery | Pros: High corrosion resistance, improves lubricity. Cons: Dimensional changes due to thickness. |
| Zinc Phosphate | Offers a protective layer, enhances paint adhesion. | Construction, automotive undercarriages | Pros: Excellent paint base, good corrosion resistance. Cons: Typically requires an oil treatment for best results. |
| Iron Phosphate | Less common, provides a moderate protective coating. | Metalworking, general manufacturing | Pros: Cost-effective, good adhesion properties. Cons: Weaker corrosion resistance compared to manganese or zinc. |
| Copper Phosphate | Specialized for copper and its alloys, provides a distinct finish. | Electrical components, decorative items | Pros: Effective for corrosion protection in electronics. Cons: Limited applications outside copper-based materials. |
What are the Characteristics and Suitability of Black Oxide Coating for B2B Buyers?
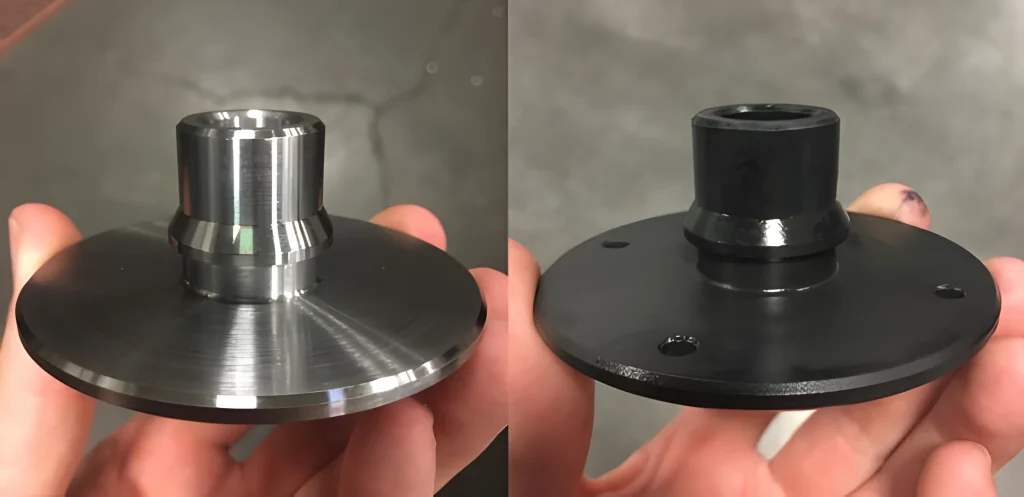
Black oxide coating is a chemical conversion process that transforms the surface of metals into magnetite, resulting in a sleek, matte finish. This coating is primarily applied to steel, stainless steel, copper, and zinc, making it suitable for precision instruments and decorative hardware. B2B buyers favor black oxide for its aesthetic appeal and minimal thickness, which preserves tight tolerances. However, it offers limited corrosion resistance unless treated with oils or waxes, making it less durable in harsh environments.
How Does Manganese Phosphate Coating Stand Out in Industrial Applications?
Manganese phosphate coating is known for its hard, crystalline structure that enhances wear resistance and lubrication. This coating is primarily used in automotive parts and industrial machinery, where it excels in corrosion resistance, especially when oil-impregnated. For B2B buyers, the key advantage lies in its ability to reduce friction, thus prolonging the lifespan of components. However, its thicker application can lead to dimensional changes, necessitating careful consideration of tolerances in manufacturing.
What are the Advantages of Zinc Phosphate Coating for Construction and Automotive Industries?
Zinc phosphate coating creates a protective layer that not only offers corrosion resistance but also significantly enhances paint adhesion. Commonly used in construction and automotive undercarriages, this coating is particularly advantageous for B2B buyers looking to ensure longevity and durability in their products. While it provides excellent protection, it typically requires an oil treatment to achieve optimal results, which may add to the processing time and cost.
How Does Iron Phosphate Coating Compare in Terms of Cost-Effectiveness?
Iron phosphate coating is a less common option, known for its moderate protective capabilities. Its cost-effectiveness makes it appealing for general manufacturing and metalworking applications. B2B buyers appreciate its good adhesion properties, which can be beneficial for further coatings. However, it does not provide the same level of corrosion resistance as manganese or zinc phosphate, which may limit its use in more demanding environments.
What are the Unique Benefits of Copper Phosphate Coating for Electrical Components?
Copper phosphate coating is specifically designed for copper and its alloys, offering effective corrosion protection, particularly in electrical components. This specialized coating is suitable for decorative items as well. B2B buyers benefit from its unique properties that cater to the electronics sector, but its applications are limited primarily to copper-based materials, which may restrict its broader utility in other manufacturing sectors.
Key Industrial Applications of black oxide vs black phosphate
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of black oxide vs black phosphate | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Automotive | Black phosphate for engine parts and undercarriages | Enhanced corrosion resistance and durability in harsh environments | Ensure compatibility with local environmental regulations |
| Aerospace | Black oxide for precision instruments and fasteners | Aesthetic appeal with minimal thickness, preserving tolerances | Verify certification standards for aerospace applications |
| Firearms | Black oxide for firearm components | Reduced glare and corrosion protection for tactical use | Source from certified manufacturers with quality assurance |
| Industrial Equipment | Black phosphate for hydraulic systems and machinery components | Improved wear resistance and lubrication properties | Assess the supplier’s experience with heavy-duty applications |
| Decorative Hardware | Black oxide for decorative fittings and tools | Attractive matte finish while maintaining functionality | Focus on suppliers with customization options and quality control |
How is Black Oxide Used in the Aerospace Industry?
In the aerospace sector, black oxide is commonly applied to precision instruments and fasteners. Its sleek, matte finish not only enhances the aesthetic appeal of components but also provides a minimal thickness that preserves tight tolerances essential for aircraft safety. For international buyers, especially from regions like Europe and the Middle East, it’s crucial to source from manufacturers who comply with stringent aerospace certification standards, ensuring reliability and quality in high-stakes environments.
What Role Does Black Phosphate Play in Automotive Applications?
Black phosphate coatings are extensively used in automotive applications, particularly for engine parts and undercarriages. The coating provides superior corrosion resistance, especially when impregnated with oil, making it ideal for components exposed to harsh environmental conditions. For B2B buyers in Africa and South America, it’s vital to consider suppliers who can demonstrate compliance with local environmental regulations, ensuring that the coatings meet both performance and sustainability standards.
Why is Black Oxide Preferred in Firearm Manufacturing?
In the firearms industry, black oxide coatings are favored for their ability to reduce glare and provide a level of corrosion protection critical for tactical applications. The chemical conversion process results in a durable finish that enhances the lifespan of firearm components. International buyers, particularly from regions with stringent gun laws, should prioritize sourcing from certified manufacturers who guarantee quality assurance and compliance with safety standards.
How Does Black Phosphate Enhance Industrial Equipment?
Black phosphate coatings are ideal for hydraulic systems and machinery components within industrial equipment. The coating improves wear resistance and provides excellent lubrication properties, which are essential for the longevity of machinery operating under heavy loads. Buyers from South America and Africa should evaluate suppliers based on their experience with heavy-duty applications and the ability to meet specific performance requirements.
What Are the Benefits of Black Oxide in Decorative Hardware?
In the decorative hardware sector, black oxide is commonly used for fittings and tools due to its attractive matte finish. This aesthetic quality, combined with functional benefits, makes it a popular choice for both commercial and residential applications. B2B buyers should focus on suppliers who offer customization options and maintain rigorous quality control processes to ensure the end products meet both visual and functional expectations.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘black oxide vs black phosphate’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Understanding Corrosion Resistance Needs for Harsh Environments
The Problem: B2B buyers in industries such as automotive and aerospace often face the challenge of selecting the right coating for components that will be exposed to harsh environmental conditions. For instance, a manufacturer in Brazil may require parts that can withstand high humidity and salt exposure. When comparing black oxide and black phosphate coatings, buyers may struggle to understand which option offers superior corrosion resistance for their specific applications, potentially leading to increased costs from premature component failures.
The Solution: To address this issue, buyers should conduct a thorough analysis of their environmental conditions and component requirements before making a decision. Black phosphate coatings are generally more effective in providing corrosion resistance, especially when combined with oil or lubricant, as they create a thick, protective layer that can trap these substances, enhancing durability. It is advisable for buyers to collaborate closely with coating suppliers to ensure that they understand the specific composition of the phosphate coating and its suitability for their applications. Additionally, investing in pre-application testing, such as salt spray tests, can help gauge the performance of the coating under anticipated conditions. This proactive approach not only helps in choosing the right coating but also reduces long-term maintenance costs.
Scenario 2: Balancing Aesthetic Appeal with Functionality
The Problem: In the decorative hardware industry, manufacturers must often balance aesthetic appeal with functional requirements. A company in South Africa producing high-end tools may find that while black oxide coatings provide an attractive matte finish, they may not offer sufficient corrosion resistance without additional treatments. This can lead to customer dissatisfaction and returns due to rusting or wear, ultimately affecting the bottom line.
The Solution: Buyers should consider the intended use of their products when choosing a coating. If aesthetic appeal is paramount, black oxide can be a suitable choice, but it’s crucial to apply post-treatment oils or waxes to enhance corrosion resistance. For products that will be exposed to moisture or corrosive environments, opting for black phosphate might be more beneficial due to its superior corrosion resistance and ability to retain lubricants. Furthermore, manufacturers can explore hybrid solutions where a black oxide finish is complemented with a protective layer of oil or a sealant. By clearly communicating these options to customers and educating them about the maintenance requirements, manufacturers can ensure a balance between beauty and durability, leading to higher satisfaction rates.
Scenario 3: Navigating Thickness Constraints in Precision Engineering
The Problem: Precision engineering companies in Europe often deal with tight tolerances in their components. A manufacturer producing intricate parts for medical devices may find that the thickness of coatings can impact the precision of the final product. Black oxide coatings typically add minimal thickness, but buyers may be concerned about the long-term effectiveness of such a thin layer compared to the thicker black phosphate coatings, which can significantly alter dimensions.
The Solution: To overcome this challenge, buyers should evaluate the specific requirements of their precision components and determine the acceptable tolerance levels for their applications. It may be advantageous to use black oxide coatings for parts where dimensional accuracy is critical, while still ensuring adequate protection through post-coating treatments. For applications where a thicker coating is necessary, buyers can request custom black phosphate solutions that are designed to minimize dimensional changes. Engaging with coating specialists can provide insights into advanced application techniques, such as controlled immersion times and optimized chemical compositions, to achieve the desired balance between thickness and protection. This strategic approach ensures that precision requirements are met without compromising on the performance and longevity of the components.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for black oxide vs black phosphate
What Are the Key Properties of Black Oxide and Black Phosphate Coatings?
When evaluating black oxide and black phosphate coatings, it is essential to consider the materials they are typically applied to, as well as their properties and performance characteristics.
1. Steel
Key Properties:
Steel, when treated with black oxide, transforms into magnetite, offering a moderate level of corrosion resistance. Black phosphate, on the other hand, creates a crystalline layer that significantly enhances corrosion resistance, especially when oil-impregnated.
Pros & Cons:
Black oxide provides a sleek finish and minimal thickness, preserving tight tolerances, making it suitable for precision instruments. However, its corrosion resistance is limited without post-treatment oils. Black phosphate, while thicker and potentially affecting tolerances, offers superior wear resistance and acts as a primer for paint adhesion.
Impact on Application:
Black oxide is often used in applications requiring aesthetic appeal, such as decorative hardware and firearms. Black phosphate is more suited for automotive and industrial applications where corrosion resistance and lubricity are critical.
Considerations for International Buyers:
Steel standards vary globally, with ASTM in the U.S. and DIN in Europe being prevalent. Buyers from Africa and South America should ensure compliance with local regulations regarding metal treatments.
2. Stainless Steel
Key Properties:
Stainless steel can benefit from both coatings, but the effectiveness varies. Black oxide enhances the aesthetic and provides some corrosion resistance, while black phosphate significantly improves lubricity and wear resistance.
Pros & Cons:
Black oxide is less effective on stainless steel due to its inherent corrosion resistance, making it less durable in harsh environments. Black phosphate, however, is more effective in improving the surface properties of stainless steel, although it may alter the appearance.
Impact on Application:
Applications include fasteners and components in corrosive environments, where black phosphate is preferred for its ability to trap lubricants.
Considerations for International Buyers:
Buyers should consider the specific grades of stainless steel being used, as different grades may respond differently to these coatings. Compliance with international standards like JIS is crucial for quality assurance.
3. Copper and Copper Alloys
Key Properties:
Copper can be treated with both coatings, but the outcomes differ. Black oxide provides a protective layer that enhances aesthetic appeal, while black phosphate offers a more robust barrier against corrosion.
Pros & Cons:
Black oxide is advantageous for decorative applications due to its uniform appearance. However, it offers limited corrosion protection. Black phosphate, while thicker and potentially impacting tolerances, provides excellent wear resistance and improved durability.
Impact on Application:
Commonly used in electrical components and decorative items, the choice between coatings depends on the application’s exposure to corrosive environments.
Considerations for International Buyers:
The choice of coating should align with local environmental regulations concerning copper treatment, especially in regions with stringent compliance requirements.
Summary Table of Material Selection for Black Oxide vs Black Phosphate
| Material | Typical Use Case for black oxide vs black phosphate | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Steel | Precision instruments, automotive parts | Superior corrosion resistance with phosphate | Limited corrosion protection with black oxide | Medium |
| Stainless Steel | Fasteners, industrial components | Enhanced lubricity with phosphate | Less effective corrosion resistance with oxide | Medium |
| Copper and Alloys | Electrical components, decorative items | Aesthetic appeal with black oxide | Limited durability with black oxide | Medium |
| Zinc Alloys | Fasteners, automotive applications | Good corrosion resistance with phosphate | Dimensional changes due to thicker coatings | Low |
This guide provides an insightful comparison of black oxide and black phosphate coatings, helping international B2B buyers make informed decisions based on material properties, application suitability, and compliance considerations.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for black oxide vs black phosphate
The manufacturing processes for black oxide and black phosphate coatings involve distinct stages, each tailored to enhance the properties of metal components. Understanding these processes, along with quality assurance practices, is crucial for B2B buyers seeking reliable and effective metal finishing solutions.
What Are the Main Stages in the Manufacturing Process for Black Oxide and Black Phosphate Coatings?
Material Preparation
Before any coating can take place, thorough material preparation is essential. For both black oxide and black phosphate coatings, the metal surfaces must be cleaned to remove oils, grease, and contaminants. This is typically achieved through degreasing methods such as solvent cleaning or alkaline cleaning. In some cases, pickling may be employed to eliminate oxides or scale, enhancing the reactivity of the surface for the subsequent coating processes.
Forming and Coating Application
Black Oxide Coating Process:
- Chemical Treatment: The black oxide process involves immersing the cleaned metal in an alkaline solution, often containing selenium, at elevated temperatures. This chemical conversion transforms the metal surface into magnetite (Fe₃O₄), resulting in a sleek black finish.
- Post-Treatment: After coating, a light oil or wax may be applied to enhance corrosion resistance and provide a protective layer.
Black Phosphate Coating Process:
- Phosphating Bath Preparation: The black phosphate coating begins with the preparation of a phosphating bath containing phosphoric acid and metal phosphates, primarily manganese phosphate.
- Immersion and Reaction: The cleaned and possibly activated metal component is submerged in the phosphating bath, where a chemical reaction forms an insoluble crystalline layer on the surface. This process typically occurs at controlled temperatures between 140°F and 190°F (60°C and 88°C).
- Post-Treatment Procedures: Similar to black oxide, rinsing and neutralization are critical to remove residual chemicals. Drying follows to prevent flash rusting.
Assembly and Finishing
Once the coating is applied, components may undergo additional assembly or finishing processes depending on the final product requirements. This can include machining, additional surface treatments, or integration into larger assemblies. The finishing processes should consider maintaining the integrity of the coating to ensure optimal performance.
How Is Quality Assurance Implemented in Black Oxide and Black Phosphate Coating Processes?
Quality assurance in the manufacturing of black oxide and black phosphate coatings involves adherence to international standards and specific industry regulations.
What International Standards Should B2B Buyers Be Aware Of?
Both black oxide and black phosphate coatings should comply with relevant international standards such as ISO 9001, which outlines requirements for quality management systems. Additionally, industry-specific certifications may apply, including:
- CE Marking: Indicates compliance with European safety standards.
- API Standards: Relevant for coatings used in the oil and gas industry.
- ASTM Standards: These provide specifications for the performance and testing of coatings.
What Are the Key Quality Control Checkpoints?
Quality control checkpoints are essential for ensuring that the coatings meet specified performance criteria. Common checkpoints include:
- Incoming Quality Control (IQC): Inspection of raw materials before they enter the production process.
- In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): Continuous monitoring during the coating application to ensure consistent results.
- Final Quality Control (FQC): A thorough examination of the finished product, including visual inspections and performance testing.
Which Testing Methods Are Commonly Used for Quality Assurance?
To validate the quality of black oxide and black phosphate coatings, several testing methods are employed:
- Thickness Measurement: Techniques such as magnetic gauges or eddy current meters are used to assess coating thickness.
- Adhesion Testing: Scratch tests or tape tests evaluate the adhesion of the coating to the substrate.
- Corrosion Resistance Testing: Salt spray tests measure the effectiveness of the coatings in protecting against corrosion.
- Visual Inspection: A critical assessment of the coating’s appearance and uniformity.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control?
For international buyers, verifying a supplier’s quality control measures is crucial. Here are effective strategies:
- Supplier Audits: Conducting on-site audits can provide insights into the supplier’s manufacturing processes and quality assurance practices.
- Quality Reports: Requesting documentation of quality control processes, testing results, and certifications can help assess reliability.
- Third-Party Inspections: Engaging independent inspection agencies can offer an unbiased evaluation of the supplier’s capabilities and compliance with standards.
What Are the Quality Control Considerations for International B2B Buyers?
When sourcing black oxide and black phosphate coatings from suppliers in regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, buyers should consider the following:
- Regulatory Compliance: Ensure that suppliers meet local and international regulations relevant to their industry.
- Cultural and Logistical Factors: Understand the regional practices that may affect quality control and manufacturing processes.
- Communication: Establish clear communication channels to discuss quality expectations and resolve any issues promptly.
In conclusion, the manufacturing processes and quality assurance measures for black oxide and black phosphate coatings are critical for ensuring the performance and reliability of coated components. By understanding these processes and implementing robust quality control measures, B2B buyers can make informed decisions when selecting suppliers for their metal finishing needs.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘black oxide vs black phosphate’
Introduction
This guide serves as a practical checklist for B2B buyers seeking to procure black oxide and black phosphate coatings. Understanding the differences between these two coating processes, along with their respective advantages and applications, is essential for making informed sourcing decisions. By following this checklist, buyers can ensure they select the right coating solution for their specific needs while also identifying reliable suppliers.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Start by clearly outlining your project requirements, including the type of metal substrate, desired appearance, and specific performance characteristics. This will help you determine whether black oxide or black phosphate is more suitable for your application.
– Consider factors such as: corrosion resistance, thickness, and the environment in which the coated components will be used.
Step 2: Identify Your Application Needs
Different applications may call for distinct coating properties. Analyze the specific operational conditions your components will face, such as exposure to moisture, chemicals, or mechanical wear.
– Key considerations include:
– Corrosion resistance: Black phosphate typically offers superior protection, especially when oil-impregnated.
– Lubrication needs: If friction reduction is critical, black phosphate may be preferable due to its ability to trap lubricants.
Step 3: Evaluate Supplier Capabilities
Before committing to a supplier, assess their capabilities and experience in providing the coating you require. Request information about their production processes, equipment, and quality control measures.
– Important aspects to review:
– Certifications: Ensure the supplier meets industry standards relevant to your application.
– Past performance: Ask for case studies or testimonials from clients in similar industries.
Step 4: Request Sample Coatings
Before placing a bulk order, request sample coatings to evaluate their performance and compatibility with your materials. This step is crucial to ensure the coating meets your specifications and expectations.
– Examine factors such as:
– Adhesion: Conduct tests to verify the bond between the coating and substrate.
– Appearance: Assess the finish to ensure it aligns with your aesthetic requirements.
Step 5: Compare Pricing and Lead Times
Collect quotes from multiple suppliers and compare pricing structures, taking into account factors such as order size, coating thickness, and additional services like packaging or delivery.
– Look for:
– Total cost of ownership: Consider not just the initial price but also potential costs related to maintenance and longevity of the coatings.
– Lead times: Ensure the supplier can meet your project deadlines without compromising quality.
Step 6: Verify Post-Treatment Options
Inquire about any post-treatment options available, such as oiling or waxing for black oxide coatings, which can enhance their corrosion resistance. Understanding these options can help you optimize the performance of the coatings.
– Consider the following:
– Durability: Assess how post-treatment affects the longevity and performance of the coating.
– Maintenance requirements: Determine if additional care or reapplication is necessary over time.
Step 7: Establish a Quality Control Process
After selecting a supplier, implement a quality control process to monitor the performance of the coatings in your applications. Regular inspections and feedback loops can help ensure consistent quality and performance.
– Focus on:
– Periodic testing: Schedule regular evaluations of the coatings under actual operating conditions.
– Supplier feedback: Maintain open communication with your supplier regarding any issues or improvements needed.
By following these steps, B2B buyers can make informed decisions when sourcing black oxide and black phosphate coatings, ensuring they select the right solutions for their specific industrial applications.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for black oxide vs black phosphate Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components for Black Oxide and Black Phosphate Coatings?
When evaluating the cost structure for black oxide and black phosphate coatings, several critical components must be considered:
-
Materials: The primary materials for black oxide include alkaline solutions containing iron and sometimes selenium, while black phosphate typically uses manganese phosphate and phosphoric acid. Material costs can vary significantly based on quality and availability, particularly for international buyers in regions like Africa and South America.
-
Labor: Labor costs are influenced by the complexity of the coating process. Black oxide typically requires less labor due to its simpler application method, whereas black phosphate may involve more extensive surface preparation and post-treatment processes, leading to higher labor costs.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes expenses such as utilities, equipment maintenance, and facility costs. Given the differences in processing, overhead may be slightly higher for black phosphate due to longer treatment times and additional equipment for handling the chemical processes.
-
Tooling: While both coatings may require specialized tooling for application, black phosphate may necessitate more robust equipment due to its thicker coating requirements.
-
Quality Control (QC): QC measures are essential for both coatings to ensure adherence to specifications. The cost of testing and inspections can vary based on the complexity of the coating and the industry standards required.
-
Logistics: Transportation and shipping costs can be substantial, especially for international shipments. The choice of Incoterms can significantly impact these costs, with CIF (Cost, Insurance, and Freight) generally being more expensive than FOB (Free on Board).
-
Margin: Supplier margins can differ based on market demand and competition. Established suppliers may have higher margins due to brand reputation and reliability.
How Do Pricing Influencers Affect Black Oxide and Black Phosphate Coating Costs?
Several key factors influence the pricing of black oxide and black phosphate coatings:
-
Volume and Minimum Order Quantity (MOQ): Larger orders typically result in lower per-unit costs due to economies of scale. Buyers should negotiate MOQs that align with their production needs to optimize pricing.
-
Specifications and Customization: Customization requests can lead to increased costs. Buyers should clearly communicate their requirements to avoid unexpected expenses.
-
Material Quality and Certifications: Higher quality materials and relevant certifications (e.g., ISO, ASTM) may increase initial costs but can lead to lower Total Cost of Ownership (TCO) due to enhanced durability and performance.
-
Supplier Factors: The supplier’s location, reputation, and production capabilities can significantly affect pricing. Buyers should conduct due diligence to select reliable suppliers who offer competitive pricing without compromising quality.
-
Incoterms: The choice of shipping terms can influence the overall cost structure. Understanding the implications of each Incoterm can help buyers manage logistics costs more effectively.
What Buyer Tips Can Help Optimize Costs for Black Oxide and Black Phosphate Coatings?
To enhance cost-efficiency in sourcing black oxide and black phosphate coatings, buyers should consider the following strategies:
-
Negotiation: Leverage volume purchasing and long-term contracts to negotiate better pricing. Establishing strong relationships with suppliers can also yield favorable terms.
-
Understanding Total Cost of Ownership: Assess the long-term implications of coating choices, including maintenance, durability, and replacement costs. Investing in higher-quality coatings may result in lower overall expenses.
-
Pricing Nuances for International Buyers: Buyers from regions like Africa, South America, and the Middle East should be aware of currency fluctuations, tariffs, and import duties that can impact pricing. It’s advisable to factor these elements into the total cost calculation.
-
Market Research: Regularly monitor market trends and competitor pricing to stay informed about potential cost fluctuations and opportunities for negotiation.
In conclusion, understanding the comprehensive cost structure and pricing dynamics of black oxide and black phosphate coatings is essential for international B2B buyers. By considering these factors and employing strategic sourcing practices, companies can optimize their procurement processes and enhance their overall profitability.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing black oxide vs black phosphate With Other Solutions
In the competitive landscape of metal finishing, B2B buyers often seek the most effective coating solutions for their specific applications. While black oxide and black phosphate coatings are popular choices, it’s essential to consider alternative methods that might better align with certain operational needs or product specifications. This analysis compares these two coatings against alternative solutions, focusing on performance, cost, implementation ease, maintenance, and ideal use cases.
| Comparison Aspect | Black Oxide Vs Black Phosphate | Alternative 1: Zinc Coating | Alternative 2: Anodizing |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | Moderate corrosion resistance; improves with oil. | High corrosion resistance; sacrificial protection. | Excellent corrosion and wear resistance; electrical insulation. |
| Cost | Generally low cost for small parts. | Moderate cost; varies with thickness. | Higher cost due to extensive processing. |
| Ease of Implementation | Relatively straightforward; quick application. | Requires surface preparation; longer application time. | Complex process; requires specialized equipment. |
| Maintenance | Needs reapplication of oil for prolonged protection. | Minimal maintenance; self-healing properties. | Low maintenance; resistant to degradation. |
| Best Use Case | Decorative tools, firearms, precision instruments. | Automotive parts, outdoor structures, marine applications. | Aerospace components, electronics, architectural finishes. |
What are the Advantages and Disadvantages of Zinc Coating?
Zinc coating, often referred to as galvanization, is a widely used method for enhancing corrosion resistance in steel. The process involves applying a layer of zinc, which acts as a sacrificial barrier against corrosion. One of its significant advantages is that it provides robust protection even in harsh environments, making it ideal for outdoor applications. However, the initial cost can be moderate, and the coating process may require more extensive surface preparation than black oxide or black phosphate.
What are the Key Features of Anodizing as an Alternative?
Anodizing is an electrochemical process primarily applied to aluminum and its alloys, which enhances corrosion resistance and surface hardness. The process creates a thick oxide layer that can also provide electrical insulation. Anodizing offers excellent durability and is particularly beneficial for applications in aerospace and electronics. However, it is typically more expensive than both black oxide and black phosphate, and the complexity of the process may deter some manufacturers.
How Do Black Oxide and Black Phosphate Compare to Alternatives?
When comparing black oxide and black phosphate to alternatives like zinc coating and anodizing, it becomes clear that each solution has its strengths and limitations. Black oxide is suitable for applications where aesthetic appeal and minimal thickness are priorities, while black phosphate excels in lubrication and paint adhesion. On the other hand, zinc coating and anodizing provide superior corrosion protection and durability, albeit at a higher cost and complexity.
Conclusion: How to Choose the Right Coating Solution?
For B2B buyers evaluating coating options, the decision should be guided by specific application requirements, budget constraints, and environmental conditions. If aesthetics and minimal thickness are critical, black oxide might be the best choice. For enhanced corrosion resistance and lubrication needs, black phosphate is advantageous. However, for outdoor applications or those requiring robust protection, zinc coating or anodizing could prove more effective despite higher costs. Ultimately, understanding the unique attributes of each option will empower buyers to make informed decisions that align with their operational goals.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for black oxide vs black phosphate
Understanding the technical properties and trade terminology associated with black oxide and black phosphate coatings is essential for B2B buyers, particularly those involved in manufacturing, automotive, and precision instrument industries. This knowledge aids in making informed decisions regarding material selection, processing, and procurement.
What Are the Key Technical Properties of Black Oxide and Black Phosphate Coatings?
-
Corrosion Resistance
– Definition: The ability of a coating to protect metal substrates from corrosion.
– Importance: Black oxide coatings provide moderate corrosion resistance, which can be enhanced with oil treatments. In contrast, black phosphate coatings offer superior corrosion resistance, especially when impregnated with oil, making them ideal for environments exposed to moisture and corrosive agents. -
Coating Thickness
– Definition: The measurable depth of the coating applied to a substrate.
– Importance: Black oxide coatings typically range from 0.5 to 1.5 microns, preserving tight tolerances in precision applications. Black phosphate coatings, however, can be significantly thicker, ranging from 5 to 25 microns, which may affect dimensional tolerances and fitment in assemblies. -
Material Compatibility
– Definition: The suitability of a coating for various metals.
– Importance: Black oxide coatings can be applied to steel, stainless steel, copper, and zinc, while black phosphate coatings are primarily used on steel. Understanding material compatibility ensures that the selected coating will bond effectively and perform as expected in the intended application. -
Lubricity
– Definition: The ability of a coating to reduce friction between surfaces.
– Importance: Black phosphate coatings excel in lubricity due to their microporous structure, which can trap oils and reduce wear in moving parts. This property is crucial for components in engines and machinery, where friction reduction is vital for performance and longevity. -
Aesthetic Appeal
– Definition: The visual characteristics of the coating, including color and finish.
– Importance: Black oxide provides a uniform matte black finish, which is aesthetically pleasing for decorative applications. Black phosphate coatings, while effective for functional purposes, typically have a less uniform gray or dark crystalline appearance, which may not be suitable for all applications. -
Adhesion Properties
– Definition: The ability of a coating to adhere to the substrate.
– Importance: The adhesion properties of black phosphate coatings make them an excellent primer for subsequent paint applications, enhancing the durability and longevity of painted surfaces. In contrast, black oxide coatings can require additional treatments to improve adhesion.
What Are Common Trade Terms Relevant to Black Oxide and Black Phosphate Coatings?
-
OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
– Definition: A company that produces parts or equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer.
– Significance: Understanding OEM relationships is crucial for B2B buyers looking to procure parts that meet specific manufacturing standards and compatibility requirements. -
MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
– Definition: The smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell.
– Significance: Knowing the MOQ is vital for budget-conscious buyers, as it affects initial procurement costs and inventory management strategies. -
RFQ (Request for Quotation)
– Definition: A document sent to suppliers requesting pricing and terms for specific products or services.
– Significance: An RFQ helps buyers compare offers from multiple suppliers, ensuring they receive competitive pricing and terms before making purchasing decisions. -
Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
– Definition: A set of international rules that define the responsibilities of sellers and buyers in the shipping of goods.
– Significance: Familiarity with Incoterms is essential for international transactions, as they clarify who bears the risk and costs during shipping, thus minimizing misunderstandings between trading partners. -
Lead Time
– Definition: The time taken from placing an order to receiving the goods.
– Significance: Understanding lead times is critical for supply chain management, especially when coordinating production schedules and inventory levels. -
Surface Preparation
– Definition: The process of cleaning and treating a substrate before applying a coating.
– Significance: Effective surface preparation is crucial for ensuring optimal adhesion and performance of coatings, impacting the longevity and effectiveness of the final product.
By familiarizing themselves with these technical properties and trade terms, B2B buyers can make more informed decisions when selecting between black oxide and black phosphate coatings, ensuring they meet the specific needs of their applications.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the black oxide vs black phosphate Sector
What Are the Key Market Trends Influencing Black Oxide and Black Phosphate Coatings?
The market for black oxide and black phosphate coatings is currently shaped by several global drivers, including the increasing demand for corrosion-resistant coatings in various industries such as automotive, aerospace, and manufacturing. B2B buyers from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe are particularly focused on sourcing materials that enhance product durability while maintaining cost-effectiveness. As industries evolve, the trend towards lightweight materials and advanced coatings is gaining traction, leading to innovations in both black oxide and black phosphate technologies.
Emerging technologies, such as nanotechnology and advanced chemical formulations, are enhancing the properties of these coatings, allowing for superior performance in extreme conditions. Buyers are increasingly looking for suppliers that can provide tailored solutions to meet specific application requirements, emphasizing the importance of strategic partnerships in the sourcing process. Furthermore, the rise of digital platforms for procurement is streamlining the sourcing process, enabling buyers to compare options and make informed decisions swiftly.
In terms of market dynamics, fluctuations in raw material prices and global supply chain disruptions are compelling B2B buyers to adopt a more proactive sourcing strategy. This includes diversifying their supplier base and considering local suppliers to mitigate risks associated with international logistics. The heightened focus on quality assurance and compliance with international standards is also influencing sourcing decisions, as buyers prioritize suppliers with proven track records and certifications.
How Are Sustainability and Ethical Sourcing Shaping the Black Oxide and Black Phosphate Market?
Sustainability is becoming a pivotal factor for B2B buyers in the black oxide and black phosphate sectors. The environmental impact of coating processes, particularly concerning waste generation and chemical usage, is under scrutiny. As a result, many companies are transitioning towards eco-friendly alternatives and seeking suppliers that adhere to sustainable practices. This shift not only aligns with regulatory requirements but also enhances brand reputation among environmentally conscious consumers.
Ethical sourcing practices are increasingly important, particularly in regions where supply chains may be less transparent. Buyers are now prioritizing suppliers who can demonstrate a commitment to ethical labor practices, fair trade, and responsible sourcing of raw materials. Certifications such as ISO 14001 (Environmental Management) and ISO 45001 (Occupational Health and Safety) are becoming essential criteria in the supplier selection process.
Moreover, the adoption of green materials and processes in the production of black oxide and black phosphate coatings is gaining momentum. This includes using non-toxic chemicals and reducing energy consumption during manufacturing. B2B buyers who prioritize these factors can not only reduce their environmental footprint but also gain a competitive edge in markets that increasingly value sustainability.
What Is the Historical Context of Black Oxide and Black Phosphate Coatings?
The evolution of black oxide and black phosphate coatings dates back to the early 20th century when industrial applications began to recognize the necessity of protecting metal surfaces from corrosion. Black oxide coatings were first developed as a means to improve aesthetic appeal and corrosion resistance in firearms and precision instruments. Over time, advancements in chemical formulations and application methods led to the widespread adoption of black oxide in various sectors, including automotive and aerospace.
On the other hand, black phosphate coatings emerged as an effective solution for enhancing corrosion resistance and wear properties in steel components. The chemical processes involved in phosphate coating have evolved significantly, with modern techniques allowing for greater control over the coating’s thickness and properties. As both technologies have matured, they have adapted to meet the evolving demands of industries focused on performance, durability, and sustainability.
In summary, understanding the historical context of these coatings provides B2B buyers with valuable insights into their development and application, helping them make informed sourcing decisions in an increasingly competitive marketplace.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of black oxide vs black phosphate
-
How do I choose between black oxide and black phosphate for my project?
Choosing between black oxide and black phosphate depends on your specific application needs. Black oxide offers a sleek matte finish and minimal thickness, making it suitable for decorative items and precision instruments. However, its corrosion resistance is limited without additional oil treatments. Conversely, black phosphate provides superior corrosion protection and wear resistance, ideal for automotive and industrial applications, albeit with a thicker coating that may affect tolerances. Assess your project requirements, including environmental conditions and aesthetic preferences, to make an informed decision. -
What industries commonly use black oxide and black phosphate coatings?
Black oxide coatings are frequently utilized in industries such as firearms, automotive, and precision instruments where aesthetic appeal and minimal dimensional change are crucial. In contrast, black phosphate coatings are prevalent in the automotive sector, manufacturing of engine parts, and hydraulic systems, where enhanced corrosion resistance and lubrication are vital. Understanding the industry applications can help you determine which coating aligns with your product requirements. -
What are the typical lead times for sourcing black oxide and black phosphate coatings?
Lead times can vary significantly based on supplier capabilities and order volume. Generally, standard orders for black oxide coatings can be processed within 1-3 weeks, while black phosphate coatings may take 2-4 weeks due to the additional steps involved in the phosphating process. For international buyers, it’s essential to communicate clearly with suppliers about your timelines and consider potential delays in logistics or customs clearance. -
What factors should I consider when vetting suppliers for black oxide and black phosphate coatings?
When vetting suppliers, focus on their industry experience, certifications (such as ISO 9001), and customer reviews. Request samples to evaluate coating quality and durability. Additionally, inquire about their production capacity, turnaround times, and flexibility in meeting your customization needs. It’s also crucial to assess their logistics capabilities, especially for international shipping, to ensure timely delivery. -
Can I customize the thickness and finish of black oxide and black phosphate coatings?
Yes, both black oxide and black phosphate coatings can be customized to meet specific project requirements. Black oxide coatings typically range from 0.5 to 1.5 microns in thickness, while black phosphate coatings can vary from 5 to 25 microns, depending on the application. Discuss your desired specifications with the supplier, as they may offer tailored solutions to achieve the required finish and performance characteristics. -
What are the minimum order quantities (MOQs) for black oxide and black phosphate coatings?
Minimum order quantities (MOQs) can differ based on the supplier and the specific coating process. Typically, MOQs for black oxide coatings may start at 100 to 500 units, while black phosphate coatings could require higher quantities due to the more complex production process. It’s advisable to clarify MOQs with potential suppliers to ensure they align with your project scale and budget. -
What payment terms should I expect when sourcing coatings internationally?
Payment terms can vary widely among suppliers. Common arrangements include upfront payments, deposits, or payment upon delivery. For international transactions, consider using secure payment methods such as letters of credit or escrow services to mitigate risk. Always negotiate terms that suit your financial capabilities while ensuring the supplier’s reliability and commitment to fulfilling the order. -
How do I ensure quality assurance for coatings received from international suppliers?
To ensure quality assurance, request detailed documentation on the coating process, including material safety data sheets (MSDS) and quality control protocols. Consider conducting a pre-shipment inspection to verify that the coatings meet your specifications. Establishing clear communication with your supplier regarding quality expectations and potential penalties for non-compliance can also help safeguard against receiving subpar products.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.
Top 6 Black Oxide Vs Black Phosphate Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. First Mold – Black Oxide Coating
Domain: firstmold.com
Registered: 2016 (9 years)
Introduction: Black Oxide Coating: A conversion coating process that enhances corrosion resistance and aesthetic appeal for ferrous materials like iron and steel. The process converts the surfaces of iron products to magnetite, resulting in a dark black surface while maintaining the mechanical properties and dimensions of the materials. The multi-stage process includes cleaning, coating application, rinsing, an…
2. Reddit – Zinc-Plating & Black Phosphate
Domain: reddit.com
Registered: 2005 (20 years)
Introduction: Zinc-Plating: Very good corrosion resistance; Black Phosphate: Good corrosion resistance.
3. Anoplate – Conversion Coatings
Domain: anoplate.com
Registered: 1996 (29 years)
Introduction: Conversion Coatings include Black Oxide, Phosphate, and Chromate. Black Oxide is a protective surface formed through a chemical reaction with iron, offering corrosion resistance, a matte black appearance, and is cost-competitive. Applications include model railroad tracks, firearm components, and precision bearings. Specifications include AMS 2485, MIL C 13924, and MIL DTL 13924. Phosphate coating…
4. Caswell Plating – Black Oxide Finish
Domain: forum.caswellplating.com
Registered: 1997 (28 years)
Introduction: Black Oxide: An oxidation process that forms a thin layer on iron or carbon steel, resulting in a dark grey or black finish. It is less durable and provides a less even finish compared to Parkerizing and hot caustic blueing. It is easier to apply but less effective in corrosion resistance due to its inability to penetrate the steel deeply.
Parkerizing: A phosphating process that creates a thicke…
5. Practical Machinist – Manganese Phosphate Coating
Domain: practicalmachinist.com
Registered: 2000 (25 years)
Introduction: Manganese phosphate coating is a conversion process used primarily for military guns and hunting firearms, often referred to as parkerizing. The process involves cleaning and degreasing parts, abrasive blasting for better adhesion, and submerging in a hot solution (around 180°F) for approximately 10 minutes. The solution reacts with the metal, creating a dull gray to black finish. It is noted that…
6. Astro – Nano Sockets
Domain: garagejournal.com
Registered: 2006 (19 years)
Introduction: Nano sockets with manganese phosphate coating; brands mentioned include Astro and Sunex; Astro sockets are preferred for their coating quality; Capri Tools sockets are also recommended; black oxide finish is disliked for being hard to clean; phosphate coating is noted for better durability and corrosion resistance.
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for black oxide vs black phosphate
How Can Strategic Sourcing Enhance Your Decision on Black Oxide vs. Black Phosphate?
In the competitive landscape of international manufacturing, understanding the nuances between black oxide and black phosphate coatings is vital for optimizing product performance and longevity. Black oxide offers aesthetic appeal and minimal thickness, making it suitable for applications requiring tight tolerances. However, its corrosion resistance is limited without post-treatment. Conversely, black phosphate provides superior corrosion protection and wear resistance, ideal for components exposed to harsh environments, although it introduces greater thickness that may affect tolerances.
For B2B buyers in regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, strategic sourcing becomes essential. By evaluating suppliers based on their expertise in these coatings, buyers can ensure they select the right finishing process that aligns with their specific operational needs and cost considerations.
Looking ahead, the demand for high-performance coatings will continue to rise as industries prioritize durability and efficiency. Engage with suppliers who can provide tailored solutions and insights, ensuring your sourcing strategy positions your business for success in an evolving marketplace. Act now to leverage these insights, enhancing your procurement decisions and fostering long-term partnerships.