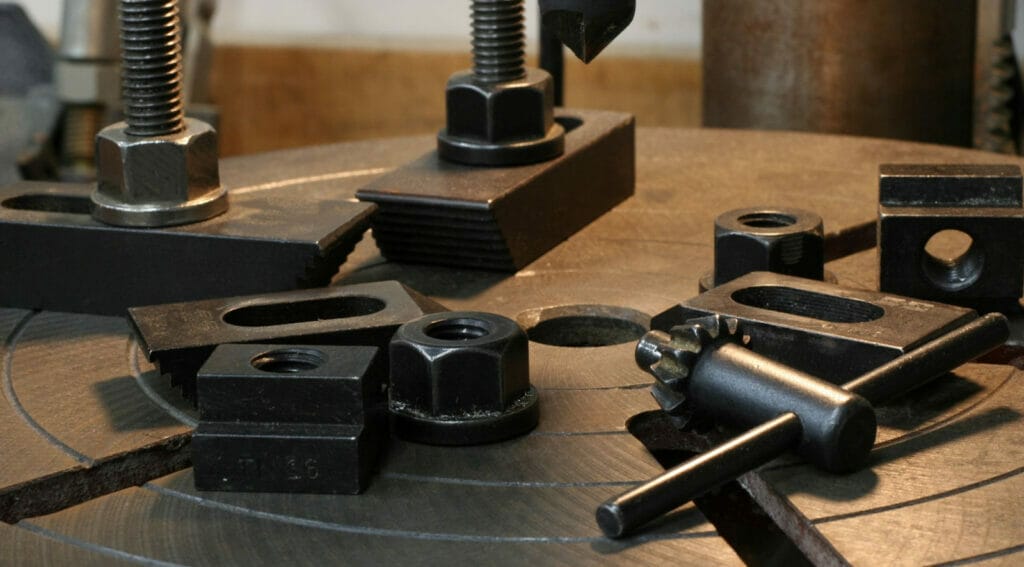
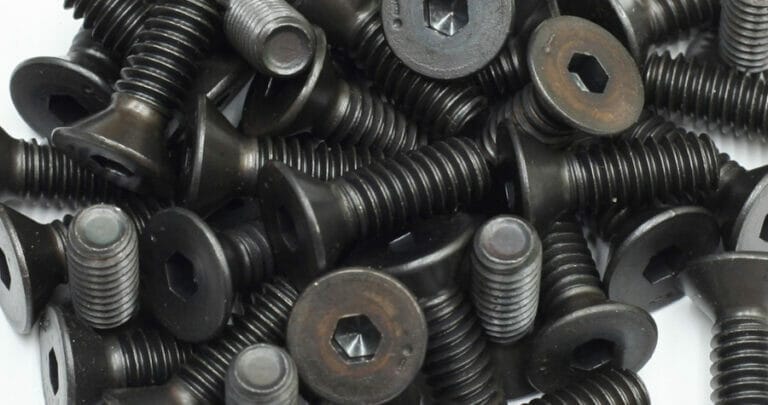
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for black oxide process
In today’s competitive global market, sourcing the right black oxide process for metal finishing can pose significant challenges for international B2B buyers. The intricacies of selecting suitable suppliers, understanding various coating types, and evaluating cost-effectiveness are crucial for businesses aiming to enhance product durability and aesthetics. This guide delves deep into the black oxide process, offering a comprehensive overview of its types, applications across diverse industries, and best practices for supplier vetting.
By highlighting critical insights into the blackening techniques—ranging from hot to cold processes—and their respective benefits, this resource equips buyers from regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe (including key markets like Germany and Brazil) with the knowledge to make informed decisions. Furthermore, we explore the potential cost implications associated with each method and provide actionable strategies for negotiating with suppliers.
Empowered with this information, B2B buyers can confidently navigate the complexities of the black oxide market, ensuring they secure high-quality finishes that meet their precise specifications while optimizing their procurement processes. Whether you are in the automotive, aerospace, or hardware sectors, this guide serves as your essential tool for leveraging the advantages of black oxide coatings effectively.
Understanding black oxide process Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Hot Black Oxide Process | Conducted at high temperatures (141 °C), creates a dense magnetite layer. | Automotive, aerospace, and industrial tools | Pros: Excellent corrosion resistance, suitable for large batches. Cons: Higher operational risks (steam explosions). |
| Mid-Temperature Black Oxide | Operates between 90 °C and 120 °C, fewer toxic emissions. | General manufacturing and hardware | Pros: Safer working environment, reduced fumes. Cons: Slower process compared to hot black oxide. |
| Cold Black Oxide Process | Performed at room temperature, does not convert the surface layer. | Small components and sensitive parts | Pros: Minimal impact on dimensions, suitable for delicate applications. Cons: Limited corrosion resistance without post-treatment. |
| Oil Post-Treatment | Involves applying oil after black oxide to enhance protection. | Firearms, automotive, and consumer goods | Pros: Increases corrosion resistance, customizable oil levels. Cons: May leave an oily residue, affecting aesthetics. |
| Wax/Acrylic Post-Treatment | Utilizes wax or acrylic for a dry finish after black oxide. | Medical devices, electronics, and consumer products | Pros: Provides a non-oily finish, good for aesthetic applications. Cons: May not offer as much corrosion protection as oil treatments. |
What Are the Characteristics and Suitability of Each Black Oxide Process Type?
The Hot Black Oxide Process is characterized by its high-temperature operation, which effectively transforms the metal surface into a robust magnetite layer. This method is particularly suited for large-scale production in industries such as automotive and aerospace, where durability and corrosion resistance are paramount. Buyers should consider the potential risks associated with steam explosions, which necessitate strict safety protocols during operation.
The Mid-Temperature Black Oxide Process operates at a safer range of 90 °C to 120 °C, significantly reducing toxic emissions compared to its hotter counterpart. This process is ideal for general manufacturing and hardware applications. B2B buyers may find this method appealing due to its safer working conditions, although they should be aware that it may not achieve the same rapid results as the hot black oxide process.
For applications requiring minimal dimensional change, the Cold Black Oxide Process is the preferred choice. Conducted at room temperature, this method is suitable for small components and sensitive parts where precision is crucial. However, buyers should note that while this process minimizes dimensional impact, it offers limited corrosion resistance unless followed by a suitable post-treatment.
The Oil Post-Treatment enhances the corrosion resistance of black oxide coatings by applying a protective oil layer. This is particularly advantageous for applications in the firearms and automotive industries, where durability is essential. Buyers should evaluate their specific needs, as the oil can leave a residue that may affect the aesthetic of the final product.
Lastly, the Wax/Acrylic Post-Treatment provides a dry finish, making it suitable for medical devices and electronics where oil residues are undesirable. This method offers a visually appealing finish but may not provide the same level of corrosion protection as oil treatments. Buyers should carefully consider the trade-offs between aesthetics and performance when selecting this option.
Key Industrial Applications of black oxide process
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of black oxide process | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Automotive | Coating of automotive parts like fasteners and gears | Enhanced corrosion resistance and improved aesthetics | Supplier reliability, quality certifications, and lead times |
| Aerospace | Components such as landing gear and engine parts | High durability and reduced weight | Compliance with aerospace standards and testing requirements |
| Medical Devices | Surgical instruments and implants | Biocompatibility and corrosion resistance | Material traceability and adherence to health regulations |
| Firearms & Ammunition | Gun components and accessories | Improved wear resistance and reduced glare | Precision in coating and adherence to safety standards |
| Industrial Hardware | Hand tools and machinery parts | Increased lifespan and reduced maintenance costs | Cost-effectiveness and scalability of production |
How is the black oxide process applied in the automotive sector, and what are the key benefits for B2B buyers?
In the automotive industry, the black oxide process is primarily utilized for coating fasteners, gears, and other components that require enhanced corrosion resistance and a non-reflective surface. This process ensures that parts maintain their integrity under harsh conditions while providing an aesthetically pleasing finish. B2B buyers in this sector must prioritize suppliers that offer reliable quality certifications and quick lead times to keep up with production demands.
What applications does the black oxide process have in the aerospace industry, and what sourcing considerations should buyers keep in mind?
In aerospace, the black oxide process is critical for components like landing gear and engine parts, where weight reduction and durability are paramount. The coating enhances resistance to wear and corrosion, which is essential for maintaining safety and performance standards. Buyers should ensure that suppliers comply with stringent aerospace standards and can provide necessary testing documentation, as the industry demands high levels of quality assurance.
How does the black oxide process benefit medical device manufacturers?
Medical device manufacturers leverage the black oxide process for surgical instruments and implants, where biocompatibility and corrosion resistance are crucial. The coating helps prevent bacterial growth and ensures that instruments remain sterile, which is vital for patient safety. Buyers in this sector should focus on suppliers that can provide material traceability and adhere to strict health regulations to ensure compliance with medical standards.
What advantages does the black oxide process offer in the firearms and ammunition sector?
In the firearms and ammunition industry, the black oxide process is used to coat components such as gun parts and accessories, enhancing wear resistance and providing a non-reflective finish that reduces glare. This is particularly beneficial for tactical applications. Buyers should prioritize precision in coating and compliance with safety standards to ensure that the finished products meet regulatory requirements and perform reliably in the field.
How does the black oxide process enhance industrial hardware applications?
The black oxide process is widely used in industrial hardware for hand tools and machinery parts, where it significantly increases lifespan and reduces maintenance costs. The coating provides a layer of protection against corrosion and wear, making tools more durable. B2B buyers should consider the cost-effectiveness and scalability of production when sourcing these coatings, ensuring that they can meet both quality and volume demands efficiently.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘black oxide process’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Navigating Corrosion Resistance Challenges in Harsh Environments
The Problem: Many B2B buyers, particularly in industries such as automotive and aerospace, struggle with parts that face extreme environmental conditions. These environments can include exposure to moisture, salt, or chemicals, which often lead to corrosion despite the application of a black oxide finish. Buyers may find that while black oxide coatings offer some corrosion resistance, they are not sufficient for parts that require long-lasting protection. This can result in costly replacements and downtime, creating frustration and impacting project timelines.
The Solution: To effectively enhance the corrosion resistance of black oxide-coated parts, it is essential to implement a supplementary post-treatment process. This can involve applying a rust inhibitor or a water-displacing oil after the black oxide coating is applied. These post-treatments fill the micro-pores of the oxide layer, significantly improving corrosion protection without compromising the aesthetic appeal of the black finish. When specifying the black oxide process, buyers should communicate their environmental conditions and performance requirements to their coating supplier. This collaboration will ensure the selected post-treatment method aligns with the specific needs of the application, providing a comprehensive solution to corrosion challenges.
Scenario 2: Ensuring Consistent Quality Across Batches
The Problem: Buyers often face issues with quality inconsistency when procuring black oxide-coated parts in large batches. Variations in coating thickness, color depth, and finish quality can occur due to differences in the coating process or the quality of the raw materials. This inconsistency can lead to rejection of parts, increased scrap rates, and ultimately, customer dissatisfaction. In industries where precision and appearance are critical, such as firearms or consumer electronics, these inconsistencies can be particularly damaging.
The Solution: To mitigate quality inconsistencies, buyers should prioritize sourcing from reputable suppliers who adhere to strict quality control processes and certifications, such as ISO 9001. Before placing large orders, requesting samples for testing is crucial to ensure that the supplier’s black oxide process meets the necessary specifications. Additionally, establishing clear communication regarding the desired outcomes, such as specific color shades and thickness tolerances, will help set expectations. Buyers should also consider implementing regular audits and performance reviews of their suppliers to ensure ongoing adherence to quality standards.
Scenario 3: Addressing Environmental and Safety Concerns
The Problem: As global regulations around environmental safety become stricter, B2B buyers are increasingly concerned about the environmental impact of the black oxide coating process. Traditional methods can produce hazardous waste and fumes that pose risks to both workers and the environment. Buyers in regions like Europe and North America are particularly sensitive to these issues, as non-compliance can lead to legal repercussions and damage to brand reputation.
The Solution: To address these environmental and safety concerns, buyers should explore suppliers that utilize eco-friendly black oxide processes. For instance, the mid-temperature and cold black oxide processes generate fewer toxic fumes compared to traditional hot black oxide methods. Buyers should inquire about the chemicals used in the black oxide solution and ensure that suppliers comply with local environmental regulations. Additionally, investing in suppliers that have implemented waste management and recycling programs can significantly reduce the environmental footprint of the coating process. By prioritizing sustainability, buyers not only protect their workforce and the environment but also enhance their corporate social responsibility profile.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for black oxide process
What Materials Are Commonly Used in the Black Oxide Process?
The black oxide process is versatile and can be applied to various materials, each with unique properties and implications for B2B buyers. Understanding these materials is crucial for selecting the right one for specific applications, especially in international markets.
1. Ferrous Metals (Steel and Iron)
Key Properties: Ferrous metals, primarily steel and iron, exhibit excellent strength and are highly adaptable to various manufacturing processes. Their temperature and pressure ratings can vary widely based on the alloy composition, but they generally offer good corrosion resistance when treated with black oxide.
Pros & Cons: The primary advantage of using ferrous metals is their durability and cost-effectiveness. However, they can be susceptible to rust if not properly treated, and the black oxide coating provides only mild corrosion resistance unless supplemented with post-treatments. Manufacturing complexity is moderate, as these materials are widely available and easy to process.
Impact on Application: Ferrous metals are commonly used in automotive, aerospace, and industrial applications. Their compatibility with various media makes them suitable for environments where strength and wear resistance are critical.
Considerations for International Buyers: Compliance with standards such as ASTM A967 or DIN 50938 is essential. Buyers from regions like Europe and the Middle East may prefer specific grades of steel that meet local regulations.
2. Stainless Steel
Key Properties: Stainless steel is known for its superior corrosion resistance and aesthetic appeal. The black oxide process can enhance its surface properties without significantly altering its dimensional tolerances.
Pros & Cons: The primary advantage of stainless steel is its resistance to rust and staining, making it ideal for applications in harsh environments. However, it can be more expensive than ferrous metals, and the black oxide coating may not adhere as well without proper surface preparation. The manufacturing complexity is higher due to the need for specialized processes.
Impact on Application: Stainless steel is widely used in food processing, medical equipment, and architectural applications. Its compatibility with various media, including corrosive substances, makes it a preferred choice in these sectors.
Considerations for International Buyers: Compliance with standards such as ASTM A240 or EN 10088 is crucial. Buyers should also consider the specific grades of stainless steel that are favored in their local markets, such as 304 or 316.
3. Copper
Key Properties: Copper offers excellent electrical conductivity and corrosion resistance. The black oxide process can enhance its aesthetic appeal while providing a degree of protection against tarnishing.
Pros & Cons: The key advantage of copper is its conductivity, making it ideal for electrical applications. However, it can be more expensive than ferrous metals and may require additional treatments to enhance corrosion resistance. The manufacturing complexity is moderate, but care must be taken to avoid oxidation during processing.
Impact on Application: Copper is commonly used in electrical components and plumbing applications. Its compatibility with various media makes it suitable for environments where conductivity is essential.
Considerations for International Buyers: Compliance with standards such as ASTM B152 or EN 1977 is important. Buyers should also be aware of local preferences for copper grades, especially in regions with specific electrical or plumbing standards.
4. Aluminum
Key Properties: Aluminum is lightweight and offers excellent corrosion resistance. The black oxide process can improve its surface hardness and wear resistance.
Pros & Cons: The main advantage of aluminum is its lightweight nature, which is beneficial in applications where weight reduction is critical. However, it can be more costly than ferrous metals, and the black oxide process may not provide the same level of durability as with steel. Manufacturing complexity can be higher due to the need for specialized techniques.
Impact on Application: Aluminum is widely used in aerospace, automotive, and consumer products. Its compatibility with various media makes it suitable for applications requiring lightweight materials.
Considerations for International Buyers: Compliance with standards such as ASTM B449 or ISO 10074 is essential. Buyers should also consider local preferences for aluminum grades, especially in industries like aerospace.
Summary Table
| Material | Typical Use Case for black oxide process | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ferrous Metals | Automotive and industrial parts | Cost-effective and durable | Mild corrosion resistance | Low |
| Stainless Steel | Medical and food processing equipment | Superior corrosion resistance | Higher cost and manufacturing complexity | High |
| Copper | Electrical components and plumbing | Excellent conductivity | Higher cost and oxidation sensitivity | Medium |
| Aluminum | Aerospace and consumer products | Lightweight and corrosion resistant | Higher cost and lower durability | Medium |
This guide provides a strategic overview of material selection for the black oxide process, helping B2B buyers make informed decisions tailored to their specific applications and regional considerations.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for black oxide process
What Are the Main Stages of the Black Oxide Manufacturing Process?
The black oxide process is a chemical conversion coating technique widely utilized in various industries to enhance the corrosion resistance and aesthetic appeal of metal components. The manufacturing process generally consists of several key stages: material preparation, forming, assembly, and finishing.
Material Preparation: How Is the Metal Prepared for Black Oxide Coating?
Before black oxide coating can begin, the metal components must undergo thorough preparation to ensure optimal adhesion and performance of the coating. This involves:
-
Cleaning: Parts are cleaned using alkaline detergents to eliminate contaminants such as oils, dirt, and rust. This step is critical as any residual contaminants can compromise the quality of the finish.
-
Rinsing: Following cleaning, the components are rinsed in water to remove any detergent residues.
-
Acid Pickling: In some cases, an acid pickling step may be employed to remove any remaining oxide films. This step is optional and depends on the condition of the metal surface.
-
Final Rinsing: A final rinse is conducted to ensure all residues from the cleaning and pickling processes are completely removed.
Forming: What Techniques Are Used in the Black Oxide Process?
Once the components are prepared, they are subjected to the black oxide coating process. This can be accomplished through three primary methods:
-
Hot Black Oxide Process: Conducted at elevated temperatures (around 141°C or 286°F), this method allows for rapid conversion of the surface to magnetite (Fe3O4). It is the most common technique due to its efficiency in handling large batches.
-
Mid-Temperature Black Oxide Process: Operating between 90°C and 120°C (194°F – 248°F), this method is safer than the hot process as it produces fewer toxic fumes. It is suitable for applications that require lower temperature processing.
-
Cold Black Oxide Process: This method occurs at room temperature (20°C to 30°C or 68°F – 86°F) and does not convert the surface to an oxide. It is less common but can be used for specific applications where heat-sensitive materials are involved.
The choice of method will depend on the specific requirements of the application, including the desired finish and the materials being treated.
What Quality Control Measures Are Implemented in the Black Oxide Process?
Quality assurance is vital in the black oxide process to ensure that the coatings meet international standards and customer specifications. Key quality control (QC) practices include:
Which International Standards Apply to Black Oxide Coating?
Several international standards govern the quality of black oxide coatings. Among the most relevant are:
-
ISO 9001: This standard outlines the requirements for a quality management system. Suppliers must demonstrate their ability to provide consistent products that meet customer and regulatory requirements.
-
CE Marking: Particularly relevant for products sold within the European Economic Area, CE marking indicates that a product complies with safety and environmental protection standards.
-
API Standards: For components used in the oil and gas industry, compliance with American Petroleum Institute (API) standards is crucial.
What Are the Key QC Checkpoints in the Black Oxide Process?
Quality control checkpoints are established throughout the manufacturing process to ensure that any defects are identified and addressed promptly. The main checkpoints include:
-
Incoming Quality Control (IQC): This initial step involves inspecting raw materials and components before they enter the production line. Suppliers must verify the quality and specifications of materials received.
-
In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): During the manufacturing process, periodic checks are performed to monitor critical parameters, such as temperature and chemical concentrations, ensuring that they remain within specified limits.
-
Final Quality Control (FQC): After the black oxide coating is applied, a final inspection is conducted to assess the coating’s appearance, adhesion, and corrosion resistance. This may involve visual inspections and various testing methods.
What Testing Methods Are Commonly Used for Black Oxide Coatings?
Various testing methods are employed to evaluate the quality of black oxide coatings, including:
-
Adhesion Testing: This is conducted to ensure that the coating adheres properly to the substrate. Common methods include the cross-hatch test and tape test.
-
Corrosion Resistance Testing: Salt spray tests (ASTM B117) are frequently used to evaluate the coating’s ability to withstand corrosion in harsh environments.
-
Thickness Measurement: The thickness of the black oxide coating is measured using non-destructive testing methods, such as eddy current or magnetic induction techniques.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control?
For international B2B buyers, particularly those in regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, verifying the quality control processes of suppliers is essential. Buyers can take the following steps:
-
Conduct Audits: Regular audits of suppliers’ facilities can provide insights into their quality management systems and adherence to industry standards.
-
Request Quality Reports: Suppliers should be able to provide detailed quality reports, including data from IQC, IPQC, and FQC stages, as well as results from testing methods.
-
Engage Third-Party Inspectors: Utilizing third-party inspection services can add an additional layer of assurance, ensuring that the products meet the required specifications and standards.
-
Review Certifications: Buyers should verify that suppliers hold relevant certifications, such as ISO 9001 or API, which signify adherence to recognized quality standards.
What Are the Specific Quality Control Nuances for International Buyers?
B2B buyers from different regions may encounter unique challenges related to quality control. Understanding local regulations, cultural differences in business practices, and logistics complexities is vital. For example:
-
Compliance with Local Regulations: Buyers must ensure that suppliers comply with both international standards and local regulations in their respective markets.
-
Cultural Considerations: Understanding the business culture of suppliers can facilitate better communication and collaboration, leading to improved quality outcomes.
-
Logistical Challenges: Transporting coated parts internationally can introduce risks. Buyers should work with suppliers to establish robust shipping and handling procedures to mitigate these risks.
In conclusion, the black oxide process offers significant benefits for various industries. By understanding the manufacturing processes and implementing rigorous quality control measures, B2B buyers can ensure that they receive high-quality products that meet their specific needs.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘black oxide process’
Introduction
Navigating the procurement of black oxide coating processes requires careful consideration and strategic planning. This step-by-step checklist aims to guide international B2B buyers through the essential actions necessary to identify, evaluate, and select the right suppliers for black oxide services. By following these steps, you can ensure a successful sourcing experience that meets your technical and business needs.
1. Define Your Technical Specifications
Before reaching out to suppliers, clearly outline your technical requirements for the black oxide process. Consider the materials you need coated (e.g., ferrous metals, stainless steel) and any specific performance characteristics, such as corrosion resistance or aesthetic requirements.
- Identify the type of black oxide process required (hot, mid-temperature, or cold).
- Specify the dimensions and tolerances of the parts to be coated.
2. Research and Identify Potential Suppliers
Conduct thorough market research to compile a list of potential suppliers that specialize in black oxide processes. Look for companies with a proven track record and relevant industry experience.
- Utilize online directories, industry forums, and trade shows to find reputable suppliers.
- Check their website for certifications, client testimonials, and case studies.
3. Evaluate Potential Suppliers
Before committing to a supplier, it’s crucial to perform a comprehensive evaluation. Request detailed information about their capabilities, equipment, and past projects to gauge their expertise.
- Inquire about their production capacity and lead times.
- Ask for references from clients in similar industries or regions to validate their reliability.
4. Verify Supplier Certifications and Standards
Ensure that the suppliers comply with industry standards and certifications relevant to the black oxide process. This guarantees that the coatings meet quality and safety requirements.
- Look for ISO certifications, particularly ISO 9001:2015, which reflects a commitment to quality management.
- Confirm compliance with environmental regulations, especially if your operations are in regions with strict guidelines.
5. Request Samples and Conduct Testing
Before finalizing your supplier, request samples of their black oxide coatings. Conduct thorough testing to verify that the coatings meet your specifications and performance criteria.
- Evaluate the samples for appearance, thickness, and corrosion resistance.
- Perform durability tests to ensure the coating can withstand operational conditions.
6. Negotiate Terms and Conditions
Once you’ve selected a supplier, negotiate the terms of the contract. This includes pricing, payment terms, delivery schedules, and warranty provisions.
- Ensure clarity on the scope of work and any post-treatment options for enhanced corrosion resistance.
- Discuss penalties for delays or quality issues to protect your interests.
7. Establish a Communication Plan
Effective communication is critical throughout the sourcing process. Establish a clear communication plan with your chosen supplier to facilitate smooth collaboration.
- Set regular check-ins to discuss progress, address issues, and provide feedback.
- Ensure that there is a designated point of contact for both parties to streamline communication.
By following this checklist, you can confidently navigate the sourcing process for black oxide coating services, ensuring that you partner with a supplier who meets your technical and business requirements.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for black oxide process Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components of the Black Oxide Process?
When evaluating the costs associated with the black oxide process, several key components come into play. These include:
-
Materials: The primary materials involved are the oxidizing chemicals, including sodium hydroxide, nitrates, and nitrites. The quality and sourcing of these chemicals can significantly impact costs, especially for international buyers who may face tariffs or varying shipping costs.
-
Labor: Skilled labor is essential for managing the black oxide coating process, which involves chemical handling and quality checks. Labor costs can vary widely based on regional wage standards, with higher wages in Europe and lower in regions like Africa and South America.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This encompasses the costs related to facility maintenance, utilities, and equipment depreciation. Overhead can be a substantial part of the total cost, particularly for companies operating in high-cost areas or those with advanced equipment.
-
Tooling: Although the black oxide process does not require extensive tooling, initial setup costs for specialized baths and cleaning equipment can be significant. The investment in quality tooling can improve efficiency and reduce long-term operational costs.
-
Quality Control (QC): Ensuring the finished product meets specifications is critical. QC processes, including testing for coating thickness and adherence, require both time and resources, contributing to the overall cost.
-
Logistics: Shipping costs, particularly for international transactions, can fluctuate based on distance, shipping method, and local regulations. Incoterms also play a vital role in determining who bears the costs and risks during transportation.
-
Margin: Suppliers typically add a profit margin on top of their costs, which can vary based on market demand, competition, and perceived value of the coating quality. This margin can be a significant factor in the final pricing.
What Influences the Pricing of Black Oxide Coating Services?
Several factors can influence the pricing structure of black oxide coating services:
-
Volume/MOQ: Pricing often decreases with higher order volumes. Suppliers may offer discounts for bulk orders, making it advantageous for buyers to consolidate their needs.
-
Specifications and Customization: Customized solutions, such as specific shades or additional post-treatments, can raise costs. Buyers should clearly define their requirements to avoid unexpected charges.
-
Material Quality and Certifications: High-quality materials or those with specific certifications (like ISO or ASTM) tend to be more expensive. Buyers should assess whether the additional costs align with their operational needs.
-
Supplier Factors: The reputation, location, and operational capabilities of the supplier can impact pricing. Established suppliers may charge more due to their experience and reliability, while emerging suppliers might offer competitive rates to gain market share.
-
Incoterms: Understanding the chosen Incoterms is essential for calculating total costs. Different terms dictate shipping responsibilities and costs, which can significantly affect overall pricing.
How Can Buyers Negotiate Better Pricing for Black Oxide Coatings?
International B2B buyers, particularly from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, can implement several strategies for cost-effective procurement:
-
Conduct Market Research: Understanding prevailing market rates and supplier capabilities can empower buyers during negotiations. A thorough analysis of competitor pricing and service offerings is invaluable.
-
Leverage Volume Discounts: Buyers should consider consolidating orders or collaborating with other companies to achieve higher volumes, thereby accessing better pricing tiers.
-
Focus on Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Evaluating TCO rather than just upfront costs can lead to better long-term decisions. This includes considering factors like durability, maintenance, and potential rework costs associated with inferior coatings.
-
Be Aware of Pricing Nuances: Different regions may have varying pricing structures due to local economic conditions, labor costs, and material availability. Buyers should adjust their expectations accordingly and be prepared to negotiate based on these factors.
Disclaimer Regarding Pricing
Prices for black oxide coating services can vary widely based on numerous factors, including but not limited to location, supplier capabilities, and market demand. The figures discussed herein are indicative and should be verified through direct communication with suppliers to ensure accuracy and relevance to specific sourcing needs.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing black oxide process With Other Solutions
Exploring Alternatives to the Black Oxide Process in Metal Coating
In the quest for optimal metal finishing solutions, the black oxide process stands out for its unique benefits, particularly in enhancing corrosion resistance and aesthetics. However, it’s essential to consider alternative methods that may better align with specific project requirements or industry standards. This analysis compares the black oxide process with two viable alternatives: powder coating and electroplating.
| Comparison Aspect | Black Oxide Process | Powder Coating | Electroplating |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | Provides moderate corrosion resistance, aesthetic appeal, and minimal thickness increase. | Excellent durability and corrosion resistance; can provide a thicker layer. | High corrosion resistance and customizability in finish thickness and color. |
| Cost | Generally low to moderate cost; economical for large batches. | Moderate to high cost; initial setup can be expensive. | High cost due to materials and complex setup; economical for high-volume production. |
| Ease of Implementation | Straightforward chemical process; requires specific equipment and safety measures. | Requires specialized equipment and skill for application; curing process needed. | Complex setup; requires precise control over current and bath chemistry. |
| Maintenance | Low maintenance; occasional reapplication may be needed for high-wear applications. | Low maintenance; surface can be easily cleaned. | Requires regular maintenance of the electroplating bath and equipment. |
| Best Use Case | Ideal for automotive parts, fasteners, and tools where aesthetics and mild protection are needed. | Best for consumer products, appliances, and industrial parts needing a tough finish. | Suitable for electronic components, decorative items, and applications needing high precision. |
Detailed Breakdown of Alternatives
Powder Coating
Powder coating is a widely used finishing process that involves applying a dry powder to a metal surface, which is then cured under heat. This method offers excellent durability and abrasion resistance, making it suitable for high-wear applications. Its ability to provide a thicker layer than black oxide contributes to superior corrosion resistance. However, the initial setup costs can be high, and the process requires specialized equipment and trained personnel. Additionally, the curing time can delay production schedules.
Electroplating
Electroplating involves depositing a layer of metal onto a substrate using an electrical current. This method is highly customizable, allowing for various thicknesses and finishes, including color options. Electroplating excels in providing superior corrosion resistance and is commonly used in applications such as electronics and decorative finishes. However, the process is complex and requires meticulous control over the plating bath and parameters, leading to higher operational costs. Regular maintenance of the equipment is also necessary to ensure consistent quality.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Metal Coating Solution
When selecting a metal coating solution, B2B buyers must assess their specific needs against the advantages and limitations of each method. The black oxide process is ideal for applications requiring a balance of aesthetics and moderate protection, particularly in industries like automotive and aerospace. In contrast, powder coating and electroplating offer enhanced durability and customization, making them suitable for more demanding environments. Ultimately, understanding the operational requirements, cost implications, and desired performance characteristics will guide buyers in making an informed decision tailored to their unique applications.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for black oxide process
What Are the Key Technical Properties of the Black Oxide Process?
Understanding the critical specifications of the black oxide process is essential for B2B buyers to ensure product quality and compliance with industry standards. Here are several key properties:
-
Material Grade
– The material grade determines the compatibility of the metal substrate with the black oxide process. Common materials include ferrous metals (e.g., carbon steel) and some non-ferrous metals (e.g., aluminum, copper). Selecting the appropriate material grade is vital, as it influences the effectiveness and durability of the black oxide coating. -
Coating Thickness
– The typical thickness of a black oxide coating ranges from 1 to 2 micrometers. This minimal thickness is crucial for maintaining the dimensional integrity of components, especially in industries like automotive and aerospace where tight tolerances are required. A thinner coating minimizes the risk of interference with assembly processes. -
Corrosion Resistance
– While black oxide coatings enhance corrosion resistance, their effectiveness can vary based on the application and environmental conditions. B2B buyers should consider post-treatment options, such as oil or wax coatings, to further improve corrosion protection, particularly in harsh environments. -
Surface Finish
– The black oxide process results in a smooth, non-reflective surface finish that is aesthetically pleasing. This property is particularly important for components that are visible in end products, such as automotive parts and tools, as it enhances the overall look while also reducing glare. -
Wear Resistance
– The black oxide finish provides a level of abrasion resistance, making it suitable for components subject to wear. This property is critical in applications where parts interact with each other, as it helps extend the lifespan of the components and reduces maintenance costs. -
Environmental Compliance
– It is essential for manufacturers to adhere to environmental regulations, especially in regions like Europe where compliance is strictly enforced. The black oxide process must utilize environmentally friendly chemicals and processes to meet these standards, making it necessary for buyers to verify compliance with local laws.
What Are Common Trade Terms Associated with the Black Oxide Process?
Familiarity with industry jargon can significantly enhance communication between buyers and suppliers. Here are several common terms related to the black oxide process:
-
OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
– An OEM refers to a company that produces parts or equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer. Understanding OEM specifications is crucial for ensuring compatibility and quality in the black oxide process, as these parts often undergo rigorous testing and quality control. -
MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
– MOQ is the minimum number of units a supplier is willing to produce for an order. Knowing the MOQ helps buyers manage inventory costs and ensures that production schedules align with demand, particularly for custom black oxide finishes. -
RFQ (Request for Quotation)
– An RFQ is a document sent to suppliers to solicit price quotes for specific products or services. For black oxide coatings, an RFQ should detail the material, coating specifications, and quantity required to ensure accurate pricing and lead times. -
Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
– Incoterms are standardized trade terms that define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in international transactions. Familiarity with Incoterms is vital for B2B buyers involved in cross-border procurement of black oxide coated parts, as they outline shipping, insurance, and risk management. -
Lead Time
– Lead time refers to the amount of time from placing an order to receiving the finished product. In the context of the black oxide process, understanding lead times is essential for project planning and ensuring timely delivery of components. -
Post-Treatment
– Post-treatment refers to additional processes applied after the black oxide coating to enhance properties such as corrosion resistance and appearance. This term is crucial for buyers to understand the full scope of treatment options available and their implications for performance and durability.
By grasping these technical properties and industry terms, B2B buyers can make informed decisions when sourcing products that utilize the black oxide process, ensuring alignment with their operational requirements and quality standards.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the black oxide process Sector
What Are the Key Market Trends Influencing the Black Oxide Process Sector?
The black oxide process sector is witnessing a dynamic shift influenced by several global drivers. The increasing demand for corrosion-resistant coatings across diverse industries, including automotive, aerospace, and industrial manufacturing, is a primary catalyst for market growth. As international B2B buyers from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe seek suppliers, they are particularly interested in high-quality black oxide coatings that can enhance the durability and aesthetics of their products.
Emerging technologies, such as automated coating systems and enhanced chemical formulations, are reshaping sourcing trends. Buyers are increasingly leaning towards suppliers that utilize advanced processing techniques, such as the hot black oxide method, which offers faster turnaround times and improved efficiency for large batch production. Additionally, the mid-temperature and cold black oxide processes are gaining traction due to their lower environmental impact and reduced risk of toxic emissions.
Furthermore, the rise of digital procurement platforms is transforming how B2B buyers source black oxide services. These platforms provide comprehensive access to suppliers’ capabilities, certifications, and customer reviews, enabling buyers to make informed decisions quickly. As sustainability becomes a priority, buyers are also looking for suppliers who demonstrate compliance with environmental standards, thereby enhancing their competitiveness in the global market.
How Can B2B Buyers Ensure Sustainability and Ethical Sourcing in the Black Oxide Process?
Sustainability is becoming an increasingly critical consideration for B2B buyers in the black oxide process sector. The environmental impact of traditional manufacturing processes, including chemical waste and energy consumption, has prompted a shift towards greener practices. Buyers are encouraged to seek suppliers who have implemented environmentally friendly methods, such as using water-based or biodegradable chemicals in the black oxide coating process.
Ethical sourcing is equally important. Buyers must evaluate their suppliers’ supply chain practices to ensure they are aligned with sustainable and ethical standards. This includes verifying that raw materials are sourced responsibly and that the manufacturing processes adhere to regulations that protect workers and the environment.
Additionally, certifications such as ISO 14001 (Environmental Management) and other ‘green’ certifications can serve as reliable indicators of a supplier’s commitment to sustainability. Buyers should prioritize partnerships with suppliers who possess these certifications, as they often reflect a rigorous approach to minimizing environmental impact while maximizing product quality.
How Has the Black Oxide Process Evolved Over Time?
The black oxide process has undergone significant evolution since its inception. Initially developed for military applications, the process has expanded into various industries due to its unique properties. The transition from manual to automated processes has enhanced efficiency and consistency, allowing for the mass production of coated parts without sacrificing quality.
The introduction of new chemical formulations has also improved the effectiveness of black oxide coatings, providing better corrosion resistance and aesthetic appeal. Today, the black oxide process is recognized not only for its functional benefits but also for its versatility across numerous applications, including automotive components, industrial machinery, and consumer goods. This evolution reflects the sector’s responsiveness to changing market demands and technological advancements, further solidifying its relevance in the global manufacturing landscape.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of black oxide process
-
How do I select the right black oxide coating supplier for my needs?
Choosing the right black oxide coating supplier involves evaluating their experience, capabilities, and certifications. Look for suppliers with a proven track record in your specific industry, whether it’s automotive, aerospace, or industrial applications. Request samples to assess the quality of their work, and inquire about their production processes, including the types of black oxide methods they employ (hot, mid-temperature, or cold). Additionally, consider their ability to accommodate your lead times and logistics requirements, especially for international shipping. -
What is the best black oxide coating process for my metal components?
The best black oxide coating process depends on the material and application of your components. For ferrous metals, the hot black oxide process is widely preferred due to its effectiveness and durability. If you’re working with non-ferrous metals like aluminum or copper, ensure the supplier can adapt their processes accordingly. Also, consider the environmental conditions your parts will face; this may influence your choice between hot, mid-temperature, or cold black oxide processes based on their corrosion resistance capabilities. -
What are the common applications of black oxide coatings in various industries?
Black oxide coatings are used across multiple industries, including automotive, aerospace, military, and consumer goods. They enhance corrosion resistance, reduce glare, and provide an aesthetically pleasing finish. Common applications include fasteners, tools, and various mechanical components where wear resistance and a non-reflective surface are critical. Understanding the specific needs of your industry will help in selecting the appropriate coating process and ensuring compliance with relevant standards. -
What are the minimum order quantities (MOQ) for black oxide coatings?
Minimum order quantities for black oxide coatings can vary significantly between suppliers. Some may have MOQs as low as 100 units for standard applications, while others might require larger quantities, especially for custom orders. It’s essential to discuss your requirements upfront and understand how MOQs can affect pricing and lead times. Additionally, consider the potential for batch processing to optimize costs if you need a larger volume of components. -
How can I ensure quality assurance in the black oxide coating process?
To ensure quality assurance, ask suppliers about their quality control processes and certifications, such as ISO standards. Request detailed documentation of their coating procedures, including pre-treatment, application, and post-treatment processes. It’s also beneficial to establish a clear communication channel for feedback and inspections throughout the production process. Consider arranging for third-party inspections if your project has stringent quality requirements or if you’re dealing with high-value components. -
What payment terms are typically offered for international orders of black oxide coatings?
Payment terms for international orders of black oxide coatings can vary widely. Many suppliers may offer net 30 or net 60 payment terms, while others might require a deposit upfront, especially for custom orders. It’s advisable to negotiate terms that align with your cash flow needs and to clarify the payment methods accepted (e.g., wire transfers, letters of credit). Be mindful of currency fluctuations and potential international transaction fees that could affect your overall costs. -
What logistics considerations should I keep in mind when sourcing black oxide coatings internationally?
When sourcing black oxide coatings internationally, consider shipping costs, customs regulations, and potential import duties that can impact your overall budget. Ensure your supplier has experience with international shipping and can provide necessary documentation to facilitate customs clearance. Additionally, discuss the lead times for production and shipping, as well as any potential delays that could arise due to logistical challenges. Establishing a reliable logistics partner can help streamline the process. -
Can I customize the black oxide coating process for specific requirements?
Yes, many suppliers offer customization options for the black oxide coating process to meet specific requirements. You can discuss your needs regarding thickness, finish, and additional post-treatment processes that enhance corrosion resistance or aesthetic appeal. Customization may also include adjusting the process for different metals or specific environmental conditions. Make sure to communicate your expectations clearly and consider conducting trials to ensure the customized solution meets your needs effectively.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.
Top 8 Black Oxide Process Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. Fractory – Black Oxide Coating
Domain: fractory.com
Registered: 2000 (25 years)
Introduction: Black Oxide Coating is a chemical conversion coating primarily for ferrous metals, but also adapted for stainless steel, copper, aluminium, and zinc. It converts the surface layer of a metal into an oxide, providing a black, non-reflective finish that enhances corrosion resistance and appearance. The layer thickness is between one and two micrometres. The coating process is used in automotive, aer…
2. Cleveland Black Oxide – Chemical Conversion Coating
Domain: clevelandblackoxide.com
Registered: 1999 (26 years)
Introduction: Black Oxide is a chemical conversion coating process that forms a black iron oxide (magnetite, Fe3O4) on the surface of ferrous metals. It involves a chemical reaction between the iron on the metal surface and oxidizing salts in the black oxide solution, which includes penetrates, catalysts, activators, and proprietary additives. Black oxide offers mild corrosion resistance, which can be enhanced …
3. Birchwood Technologies – DIY Black Oxide Coating Products
Domain: birchwoodtechnologies.com
Registered: 2012 (13 years)
Introduction: DIY Black Oxide Coating and Finishing products include: New Tru Temp 2nd Gen Black Oxide, New Tru Temp Stainless Black Oxide, Black Oxide Zinc Phosphate, Traditional Patinas, Steel Patinas, Decorative Finishes, Brush-On and Finishing Gels, Metal Cleaners and Preps, New Rust Converter PRO, Rust Preventives, and Finishing Equipment. The black oxide finishes provide corrosion resistance, dimension un…
4. Wayken – Black Oxide Coating
Domain: waykenrm.com
Registered: 2013 (12 years)
Introduction: Black Oxide Coating is a type of conversion coating that provides a black/matte finish to metal surfaces. It involves a chemical process where machined metal parts are dipped into an alkaline solution, converting the iron on the surface into magnetite (Fe3O4). The process includes five steps: Cleaning, Rinsing, Descaling/Pickling, Black Oxide Finish, and After-Finish. The black oxide finish can be…
5. SWD Inc – Black Oxide Coating Solutions
Domain: swdinc.com
Registered: 1996 (29 years)
Introduction: Black oxide is a conversion coating formed by a chemical reaction when parts are immersed in an alkaline aqueous salt solution at approximately 285 degrees F. It produces a magnetite (Fe3 O4) on the surface of ferrous alloy parts. Non-ferrous metals can also be oxidized under suitable conditions. The process involves five basic steps: clean, rinse, black oxide, rinse, and supplementary coating (af…
6. Hubs – Black Oxide Coating
Domain: hubs.com
Registered: 1998 (27 years)
Introduction: Black oxide coating is a conversion coating applied to ferrous metals to improve corrosion resistance, reduce light reflection, and enhance appearance. It is typically applied to metals such as iron, steel, stainless steel, zinc, and copper, creating a smooth, black surface finish that enhances corrosion and wear resistance. Common applications include fasteners, hardware, tools, automotive and ae…
7. Pro Tool Reviews – Black Oxide Coated Accessories
Domain: protoolreviews.com
Registered: 2008 (17 years)
Introduction: Black oxide coatings are commonly found on drill bits, folding knives, and other cutting accessories. They are created through a chemical conversion process rather than electroplating, allowing application to various materials including steel, stainless steel, aluminum, cast iron, copper, brass, bronze, and zinc. The benefits of black oxide coatings include protection against oxidation, retention …
8. Jiga – Black Oxide Coating
Domain: jiga.io
Registered: 2020 (5 years)
Introduction: Black oxide coating, also known as blackening, is a hot chemical conversion coating applied to ferrous metals and stainless steels. It transforms the metal surface into magnetite (Fe₃O₄) or similar dark oxide compounds, creating a dense, durable, and visually uniform finish. The process involves several steps: cleaning and degreasing, pickling (acid etch), immersion in a black oxide bath (heated a…
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for black oxide process
As the demand for durable and aesthetically pleasing metal finishes continues to rise globally, the black oxide process stands out as a key solution for B2B buyers. Its ability to enhance corrosion resistance while maintaining tight tolerances makes it particularly valuable in industries such as automotive, aerospace, and hardware manufacturing. By leveraging strategic sourcing, international buyers can ensure they partner with suppliers who provide high-quality black oxide coatings that meet their specific needs, thereby optimizing their supply chains and reducing operational risks.
The versatility of black oxide processing, which accommodates various metals including ferrous and non-ferrous materials, presents an opportunity for companies across diverse sectors. Additionally, the advancements in post-treatment techniques significantly enhance the protective qualities of black oxide finishes, ensuring longevity and performance.
Looking ahead, businesses in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe should actively explore partnerships with reputable suppliers to capitalize on the benefits of black oxide coatings. By prioritizing strategic sourcing, companies can not only improve their product offerings but also position themselves favorably in an increasingly competitive market. Engage with experts today to discover how the black oxide process can elevate your manufacturing capabilities.