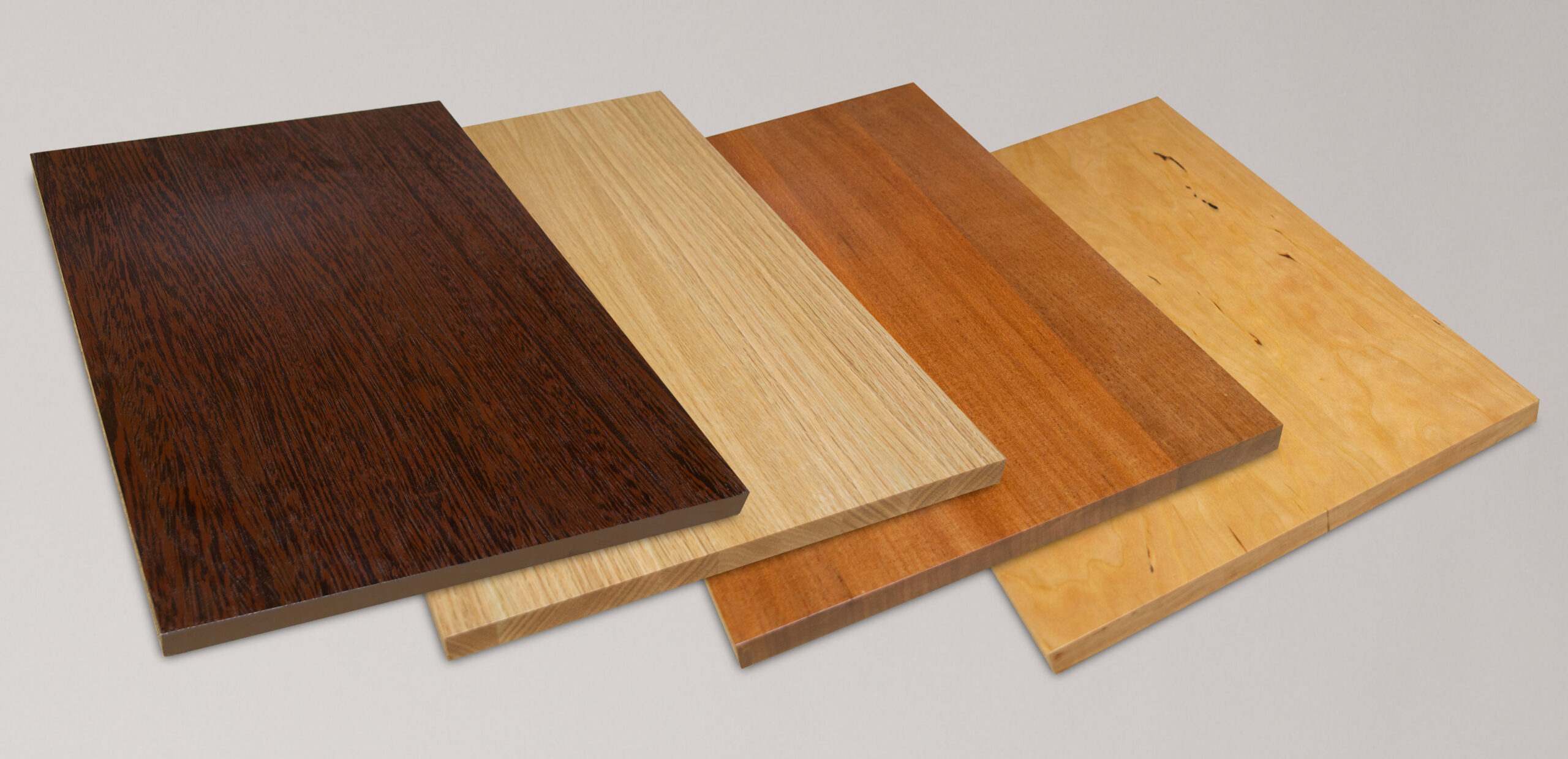
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for best wood for cnc routing
When navigating the global market for the best wood for CNC routing, international buyers often face the challenge of sourcing materials that meet both quality and budgetary constraints. The selection of the right wood is crucial for optimizing CNC machining processes, whether it’s for intricate designs, durable furniture, or high-quality signage. This guide serves as a comprehensive resource, detailing various wood types—including hardwoods like maple and walnut, and softwoods such as cedar and pine—along with their specific applications in CNC routing.
We delve into supplier vetting processes, cost considerations, and regional availability, ensuring that B2B buyers from diverse markets—including Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe (notably Germany and Saudi Arabia)—are equipped with the knowledge needed to make informed purchasing decisions. By understanding the unique properties of each wood type, businesses can enhance their production capabilities, reduce waste, and ultimately deliver superior products to their customers. This guide aims to empower you with actionable insights, enabling you to confidently navigate the complexities of sourcing wood for CNC routing, maximizing both quality and efficiency in your operations.
Understanding best wood for cnc routing Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Birch | Light color, wavy grains, resistant to chips | Furniture, cabinetry, structural components | Pros: Durable, holds screws well; Cons: Can be pricier than softwoods. |
| Maple | Hard, dense, resistant to shocks | Workstations, heavy-duty items | Pros: Excellent durability, smooth finish; Cons: Difficult to work with for intricate designs. |
| Cherry | Reddish-brown, resistant to warping | Furniture, musical instruments | Pros: Attractive finish, versatile; Cons: Higher cost, harder to carve. |
| Oak | Strong, moisture-resistant, pronounced grain | Outdoor furniture, flooring | Pros: Highly durable, suitable for outdoor use; Cons: Heavier and more expensive. |
| Pine | Lightweight, pale color, resistant to shrinking | General furniture, cabinetry | Pros: Cost-effective, easy to work with; Cons: Less durable than hardwoods. |
What Are the Characteristics of Birch Wood for CNC Routing?
Birch is a popular choice for CNC routing due to its light color and wavy grain patterns. It is a hardwood known for its resistance to chips and dents, making it ideal for projects requiring durability, such as furniture and cabinetry. When purchasing birch, buyers should consider its availability and cost, as it can be more expensive than softwoods. Additionally, its ability to hold screws well makes it suitable for structural components, appealing to manufacturers focusing on quality and reliability.
How Does Maple Compare as a Wood Choice for CNC Projects?
Maple is one of the hardest woods available, characterized by its density and resistance to electrical shocks. This makes it an excellent option for CNC routing projects that require durability, such as workstations and heavy-duty items. Buyers should be aware that while maple provides a smooth finish and does not require fillers, it can be challenging to work with due to its hardness. Therefore, investing in the right tools and machinery is crucial for achieving optimal results.
Why Is Cherry Wood a Versatile Option for CNC Routing?
Cherry wood is known for its stunning reddish-brown tones and resistance to warping, making it a versatile choice for various applications, including furniture and musical instruments. Its natural beauty and smooth finish enhance the aesthetic appeal of finished products. However, buyers should note that cherry can be more expensive and challenging to carve compared to other woods. Understanding the balance between cost and quality is essential for B2B buyers looking to enhance their product offerings.
What Makes Oak Ideal for Outdoor CNC Projects?
Oak is a heavy hardwood recognized for its strength and moisture resistance, making it particularly suitable for outdoor applications such as garden furniture and flooring. Its pronounced grain patterns add visual interest to any project. While oak is highly durable, buyers should consider its weight and cost, which can be higher than other wood types. When sourcing oak, it is important for buyers to assess their specific needs, including environmental conditions, to ensure longevity and performance.
What Are the Advantages of Using Pine for CNC Routing?
Pine is a lightweight softwood that offers a cost-effective solution for various CNC routing applications, including general furniture and cabinetry. Its pale color and ease of workability make it a favorite among beginners and experienced machinists alike. However, pine’s lower durability compared to hardwoods may be a concern for buyers focusing on long-term use. Evaluating the trade-offs between cost and durability is vital for B2B buyers aiming to optimize their production processes while managing budgets effectively.
Key Industrial Applications of best wood for cnc routing
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of best wood for cnc routing | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Furniture Manufacturing | Custom furniture components (tables, chairs) | High-quality, durable products that enhance aesthetics | Availability of specific wood types and local sourcing |
| Musical Instrument Making | Crafting instruments (guitars, pianos) | Superior acoustic properties and craftsmanship | Need for specific wood species with acoustic qualities |
| Construction and Carpentry | Structural elements (beams, panels) | Strength and stability for long-lasting structures | Compliance with local building regulations and standards |
| Signage and Branding | CNC routed signage and displays | Eye-catching designs that attract customers | Sourcing weather-resistant wood for outdoor applications |
| Arts and Crafts | Intricate carvings and sculptures | Unique, high-value products that appeal to collectors | Quality of wood grain and finish for aesthetic appeal |
How is Best Wood for CNC Routing Used in Furniture Manufacturing?
In the furniture manufacturing sector, CNC routing is leveraged to create custom components such as tables and chairs. The precision of CNC machines allows manufacturers to design intricate patterns and shapes while maintaining the structural integrity of the wood. For international buyers, especially in regions like Europe and the Middle East, sourcing locally available hardwoods such as oak or walnut can reduce costs while ensuring quality. The challenge lies in selecting woods that balance aesthetics with durability, as furniture must withstand daily use.
What Role Does Best Wood for CNC Routing Play in Musical Instrument Making?
Musical instrument makers utilize CNC routing to craft components like guitar bodies and piano cases, where the choice of wood significantly impacts sound quality. Hardwoods like maple and mahogany are favored for their acoustic properties and durability. For B2B buyers in South America and Africa, understanding the specific acoustic characteristics of various woods is crucial for sourcing the right materials. The challenge is often the consistency in wood quality, as any variations can affect the final instrument’s sound.
How is Best Wood for CNC Routing Applied in Construction and Carpentry?
In construction, CNC routing is employed to produce structural elements such as beams and panels. Hardwoods provide the necessary strength and stability for load-bearing applications. International buyers from regions like Germany and Saudi Arabia must consider local building codes and sourcing practices to ensure compliance. The main concern is acquiring wood that meets specific strength requirements while also being cost-effective, particularly in bulk purchasing scenarios.
What is the Importance of Best Wood for CNC Routing in Signage and Branding?
CNC routed signage is crucial for branding, allowing companies to create visually appealing displays that attract customers. Woods like cedar and cypress are often chosen for their weather-resistant properties, making them ideal for outdoor signage. For businesses operating in diverse climates, such as those in Africa and the Middle East, sourcing durable wood is essential. The challenge lies in finding suppliers who can provide consistent quality while meeting specific design requirements.
How is Best Wood for CNC Routing Utilized in Arts and Crafts?
In the arts and crafts sector, CNC routing is used to create intricate carvings and sculptures, where the choice of wood can enhance the visual appeal. Woods with a fine grain, such as cherry or beech, are preferred for their aesthetic qualities. B2B buyers must focus on the quality of the wood grain and finish to ensure that the final product meets artistic standards. The primary challenge is sourcing high-quality wood consistently, which can vary significantly based on regional availability and supplier reliability.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘best wood for cnc routing’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Navigating the Cost-Effectiveness of Wood Choices
The Problem: Many B2B buyers face significant challenges when selecting the right wood for CNC routing, especially regarding cost. For businesses operating in regions like Africa or South America, local wood availability may vary greatly, leading to inflated prices for certain types of hardwood or softwood. This cost concern can stifle project budgets, particularly for small to medium enterprises that rely on precise material specifications to maintain profitability. Additionally, buyers may struggle with the trade-off between quality and expense, finding it difficult to justify higher costs for premium woods without clear benefits.
The Solution: To mitigate cost concerns, buyers should prioritize sourcing wood locally whenever possible. By identifying reliable local suppliers or partnering with timber merchants who specialize in regional woods, businesses can access more affordable materials that meet their CNC routing needs without compromising quality. Moreover, buyers can conduct thorough market research to understand the price variations between different wood types, enabling informed decisions. For projects requiring a balance of quality and budget, consider starting with more economical options like plywood or MDF for prototype work and transitioning to higher-quality hardwoods for final products. This phased approach allows for cost savings while ensuring that the final output meets the desired specifications.
Scenario 2: Ensuring the Right Wood Type for Specific CNC Projects
The Problem: A common pain point for B2B buyers is the confusion surrounding the selection of appropriate wood types for specific CNC projects. With a plethora of options available, many businesses struggle to understand which wood will yield the best results for their intended applications, such as furniture making, signage, or intricate carvings. This uncertainty can lead to wasted materials, time, and labor, ultimately impacting project timelines and financial outcomes.
The Solution: To address this challenge, buyers should invest time in understanding the properties of various wood types and how they align with their specific CNC routing needs. Developing a comprehensive material guide that includes information on hardness, workability, and finish quality can serve as a valuable resource for decision-making. Additionally, collaborating with experienced CNC machinists or wood specialists can provide insights into best practices for selecting wood based on project requirements. For example, using maple for durable furniture or basswood for detailed engravings can enhance the quality of the final product. Moreover, conducting small test runs with different wood types can help determine the most suitable options before committing to larger quantities.
Scenario 3: Overcoming Challenges with Wood Stability and Quality
The Problem: Another significant issue faced by B2B buyers is the inconsistency in wood quality and stability, which can lead to warping, splitting, or other defects during the CNC routing process. This problem is particularly acute in regions with varying climates, where humidity and temperature fluctuations can affect wood properties. Such inconsistencies can result in additional costs for rework and waste, as well as jeopardize client satisfaction and project delivery timelines.
The Solution: To combat wood stability issues, buyers should prioritize sourcing kiln-dried lumber that has been treated to reduce moisture content and improve dimensional stability. This proactive approach minimizes the risk of warping and other defects during machining. Furthermore, it’s beneficial to establish relationships with suppliers who provide a quality assurance guarantee on their wood products. Implementing a stringent inspection process upon receipt of materials can also help identify any defects before the CNC routing process begins. For businesses working in challenging climates, investing in climate-controlled storage for wood can protect inventory from environmental fluctuations, ensuring that only the highest quality materials are used for projects.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for best wood for cnc routing
What are the Best Wood Types for CNC Routing?
When selecting wood for CNC routing, it is essential to consider the specific properties and characteristics of various materials. This analysis focuses on four common wood types: Birch, Maple, Cedar, and MDF, evaluating their suitability from a B2B perspective, particularly for international buyers in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe.
How Does Birch Perform in CNC Routing Applications?
Birch is a popular choice for CNC routing due to its fine grain and durability. It is resistant to chipping and dents, making it ideal for intricate designs and structural components. Birch exhibits good screw-holding capabilities, enhancing its use in furniture and cabinetry.
Pros: Birch is relatively affordable, easy to machine, and provides a smooth finish. Its resistance to wear makes it suitable for high-traffic applications.
Cons: While Birch is strong, it can be susceptible to moisture, which may affect its longevity in humid environments.
Impact on Application: Birch is compatible with various finishes and adhesives, allowing for versatility in product design.
Considerations for International Buyers: Birch is widely available in Europe and North America, but sourcing may vary in Africa and South America. Compliance with local standards (e.g., ASTM) is crucial for ensuring product quality.
What Makes Maple a Preferred Choice for CNC Routing?
Maple is renowned for its hardness and durability, making it suitable for applications requiring strength, such as heavy-duty furniture and work surfaces. Its fine, consistent grain allows for detailed carving and machining.
Pros: Maple is resistant to wear and impacts, making it ideal for high-use items. It also does not require fillers after machining, which can save on finishing costs.
Cons: The density of Maple can make it more challenging to work with, requiring specialized tools. Additionally, its cost is higher compared to softer woods.
Impact on Application: Maple’s density provides excellent stability, making it suitable for items exposed to temperature fluctuations.
Considerations for International Buyers: Maple is commonly used in Europe and North America, but sourcing may be limited in other regions. Buyers should ensure compliance with local regulations regarding wood sourcing and treatment.
Why Choose Cedar for CNC Routing Projects?
Cedar is favored for its natural resistance to decay and pleasant aroma. Its softwood characteristics allow for easy machining, making it suitable for both indoor and outdoor applications.
Pros: Cedar is lightweight and easy to work with, making it ideal for detailed projects. Its weather-resistant properties make it suitable for outdoor furniture and structures.
Cons: Cedar’s softness can lead to dents and scratches, making it less suitable for high-wear applications.
Impact on Application: Cedar is particularly effective for outdoor signs and furniture due to its resistance to moisture and insects.
Considerations for International Buyers: Cedar is often sourced locally in regions with cedar forests, but buyers should verify the sustainability of their sources. Compliance with environmental regulations is essential, particularly in Europe.
How Does MDF Compare for CNC Routing?
MDF (Medium Density Fiberboard) is an engineered wood product made from wood fibers, wax, and resin. It is widely used in CNC routing due to its uniform density and smooth surface.
Pros: MDF is cost-effective and easy to machine, allowing for intricate designs without the risk of splintering. Its smooth surface is ideal for painting and veneering.
Cons: MDF is less durable than solid wood and can be susceptible to moisture damage, which may limit its use in certain applications.
Impact on Application: MDF is commonly used for prototypes and decorative items, where cost and ease of machining are prioritized over durability.
Considerations for International Buyers: MDF is readily available globally, but buyers should ensure compliance with health and safety standards regarding formaldehyde emissions, particularly in Europe.
Summary Table of Best Wood Types for CNC Routing
| Material | Typical Use Case for best wood for cnc routing | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Birch | Furniture, cabinetry, intricate designs | Durable, resistant to chipping | Susceptible to moisture | Medium |
| Maple | Heavy-duty furniture, work surfaces | High durability, smooth finish | Requires specialized tools | High |
| Cedar | Outdoor furniture, signs | Weather-resistant, easy to machine | Soft, prone to dents | Medium |
| MDF | Prototypes, decorative items | Cost-effective, easy to machine | Less durable, moisture-sensitive | Low |
This guide provides a comprehensive overview of wood types suitable for CNC routing, enabling B2B buyers to make informed decisions based on their specific needs and regional considerations.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for best wood for cnc routing
What Are the Main Stages of Manufacturing Best Wood for CNC Routing?
The manufacturing process for wood suitable for CNC routing involves several critical stages, ensuring that the final product meets the quality and performance expectations of B2B buyers. Understanding these stages helps buyers make informed decisions when sourcing wood from suppliers.
1. Material Preparation: How Is Wood Processed Before CNC Routing?
The first stage in the manufacturing process is material preparation. This involves selecting the right type of wood based on the project requirements, such as hardwood for durability or softwood for ease of machining. After selection, logs are debarked and cut into manageable sizes.
Key Techniques:
– Drying: Wood must be dried to a specific moisture content to prevent warping and ensure stability during machining. This is often achieved through kiln drying, which is crucial for maintaining the integrity of the wood.
– Milling: The wood is then milled to achieve uniform thickness and width, which is essential for precise CNC routing. This process also includes planing to create a smooth surface.
2. Forming: What Techniques Are Used in CNC Routing?
Once the material is prepared, the next stage is forming, which involves the actual CNC routing process. Here, the wood is shaped into the desired forms using CNC machines programmed with design files.
Key Techniques:
– CNC Machining: CNC routers use computerized controls to guide cutting tools. This allows for high precision and repeatability, essential for intricate designs. Various tools and bits can be utilized depending on the wood type and the intricacies of the design.
– 3D Carving: For more complex designs, 3D carving techniques may be employed, which require specific wood types that can withstand varied cutting depths and angles without tearing.
3. Assembly: How Are CNC Routed Parts Joined Together?
In projects requiring multiple components, the assembly stage comes into play. This stage involves joining the CNC-routed pieces together to create the final product.
Key Techniques:
– Joinery: Techniques such as doweling, mortise and tenon, or using adhesives are common in wood assembly. The choice of joinery method depends on the intended use and structural requirements of the final product.
– Finishing Touches: Before assembly, parts may be sanded or treated to ensure a smooth surface and prepare them for finishing.
4. Finishing: What Are the Final Steps in Wood Preparation?
The finishing stage is crucial for enhancing the aesthetic and functional properties of the wood. This includes applying stains, paints, or protective coatings.
Key Techniques:
– Sanding: Multiple grades of sandpaper are used to achieve a smooth finish, which is essential for both appearance and touch.
– Coating: Various finishes such as varnishes, oils, or lacquers are applied to protect the wood from moisture, UV light, and wear. This not only enhances durability but also adds to the visual appeal of the product.
What Quality Assurance Measures Should B2B Buyers Expect?
Quality assurance (QA) is vital in the wood manufacturing process, ensuring that the final products meet international standards and customer expectations. For B2B buyers, understanding the QA measures in place can significantly influence sourcing decisions.
Relevant International Standards for Wood Manufacturing
Buyers should look for suppliers that adhere to recognized international standards, as this demonstrates a commitment to quality and safety. Key standards include:
- ISO 9001: This standard outlines criteria for a quality management system, focusing on meeting customer and regulatory requirements while improving satisfaction.
- CE Marking: In Europe, CE marking indicates conformity with health, safety, and environmental protection standards for products sold within the European Economic Area.
- FSC Certification: The Forest Stewardship Council (FSC) certification ensures that wood products come from responsibly managed forests, promoting sustainable practices.
What Are the Key QC Checkpoints in Wood Manufacturing?
Quality control checkpoints are integral to maintaining product integrity throughout the manufacturing process. Common QC checkpoints include:
- Incoming Quality Control (IQC): This involves inspecting raw materials upon arrival to ensure they meet specified standards. This is the first line of defense against subpar materials.
- In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): During manufacturing, ongoing inspections are conducted to monitor adherence to quality standards and specifications. This can include checking dimensions, moisture content, and machining accuracy.
- Final Quality Control (FQC): Before shipment, the final product undergoes a thorough inspection to ensure it meets all quality standards and customer specifications.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control?
For international B2B buyers, verifying the quality control processes of suppliers is essential for ensuring product reliability. Here are several methods to consider:
- Supplier Audits: Conducting on-site audits can provide insights into the supplier’s manufacturing processes, quality control measures, and adherence to international standards. This direct observation can help identify any potential issues before placing large orders.
- Quality Reports: Requesting quality assurance reports, including test results and compliance certifications, can help buyers assess a supplier’s reliability and quality commitment.
- Third-Party Inspections: Engaging third-party inspection services can provide an unbiased assessment of the supplier’s quality control practices. These services can conduct random checks and provide detailed reports on findings.
What Are the QC and Certification Nuances for International B2B Buyers?
International buyers, especially those from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, should be aware of specific nuances in quality control and certification processes:
- Regulatory Compliance: Different regions have varying regulations regarding wood sourcing and manufacturing. Buyers should familiarize themselves with local regulations and ensure that suppliers comply with them.
- Cultural and Economic Factors: Understanding the local business culture and economic conditions can influence supplier relationships and negotiations. Building strong partnerships with suppliers can facilitate smoother transactions and better quality assurance outcomes.
- Traceability: For buyers in Europe, especially, traceability of wood products is critical due to stringent regulations. Ensuring that suppliers can provide a clear chain of custody for their wood products is essential for compliance and sustainability claims.
By understanding these manufacturing processes and quality assurance measures, B2B buyers can make informed decisions when sourcing wood for CNC routing, ensuring they receive high-quality products that meet their specific needs.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘best wood for cnc routing’
Introduction
Sourcing the best wood for CNC routing is critical for achieving high-quality results in your projects. This guide provides a step-by-step checklist to help B2B buyers effectively navigate the procurement process, ensuring that they select the right wood type based on their specific needs and project requirements.
Step 1: Define Your Project Requirements
Understanding the specific needs of your project is the first step in sourcing wood. Consider the type of product you aim to create, the level of detail required, and the durability needed for the final piece.
– Key Considerations:
– Type of CNC routing (e.g., 3D carving vs. engraving).
– Expected usage (indoor furniture vs. outdoor structures).
Step 2: Research Available Wood Types
Different woods have distinct properties that make them suitable for various CNC applications. Familiarize yourself with the characteristics of hardwoods and softwoods to determine which aligns best with your project.
– Examples:
– Hardwoods like maple and cherry are ideal for intricate designs due to their density and durability.
– Softwoods such as pine and fir are often more affordable and easier to work with for larger, less detailed projects.
Step 3: Evaluate Local Availability
Cost-effectiveness often hinges on local availability. Sourcing wood that is readily available in your region can significantly reduce transportation costs and lead times.
– Action Items:
– Check local suppliers or timber merchants.
– Assess the sustainability of sourcing from local forests.
Step 4: Assess Quality and Specifications
Once you have a shortlist of wood types, evaluate their quality based on grade and moisture content. High-quality wood will not only enhance the aesthetics of your final product but also improve machining performance.
– Quality Indicators:
– Look for certifications (e.g., FSC certified) that indicate sustainable sourcing.
– Inspect for defects such as knots or warping.
Step 5: Verify Supplier Credentials
Before making a purchase, it is essential to verify the credibility of your suppliers. Research their reputation in the industry and request documentation that demonstrates their reliability.
– Documentation to Request:
– Supplier certifications and quality control processes.
– References from other B2B clients in similar industries.
Step 6: Request Samples
Prior to placing a bulk order, request samples of the wood you intend to purchase. This allows you to evaluate the material’s workability, finish, and compatibility with your CNC machinery.
– Benefits of Sampling:
– Test for machining efficiency and finish quality.
– Ensure the wood meets your aesthetic and functional requirements.
Step 7: Negotiate Terms and Pricing
Once you are satisfied with the wood quality and supplier reliability, engage in negotiations regarding pricing and terms. Establishing clear agreements will help prevent misunderstandings and ensure a smooth procurement process.
– Negotiation Points:
– Discuss bulk pricing discounts and payment terms.
– Confirm delivery timelines and return policies in case of defects.
By following this checklist, B2B buyers can make informed decisions when sourcing wood for CNC routing, ultimately enhancing the quality and efficiency of their production processes.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for best wood for cnc routing Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components in Sourcing Wood for CNC Routing?
When sourcing wood for CNC routing, it’s essential to consider several cost components that contribute to the overall expense. These include materials, labor, manufacturing overhead, tooling, quality control (QC), logistics, and supplier margins.
-
Materials: The choice of wood significantly impacts the cost. Hardwoods like maple and walnut typically command higher prices due to their density and durability, while softwoods such as pine or cedar are generally more affordable. Local availability also plays a crucial role; sourcing wood that is native to your region can lead to considerable savings.
-
Labor: The complexity of the machining process influences labor costs. More intricate designs require skilled labor, which can increase overall expenses. Conversely, simpler projects may allow for the use of less expensive labor, reducing costs.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This encompasses all indirect costs associated with production, such as utilities, rent, and equipment depreciation. Understanding these costs can help buyers negotiate better terms with suppliers.
-
Tooling: The need for specialized tools and machinery to work with specific wood types can add to the upfront investment. For instance, harder woods may require more robust tooling, leading to higher costs.
-
Quality Control (QC): Ensuring the wood meets specific standards involves QC processes that can incur additional costs. Certifications for sustainability or quality assurance can also affect pricing.
-
Logistics: Shipping costs vary depending on the distance from the supplier, especially for international transactions. Understanding Incoterms and logistics can help buyers manage these costs effectively.
-
Margin: Suppliers typically add a margin to their costs, which can vary based on market demand, competition, and the supplier’s business strategy.
How Do Price Influencers Affect the Cost of Wood for CNC Routing?
Several factors influence pricing in the wood market. These include volume or minimum order quantities (MOQ), specifications and customization requests, material quality and certifications, supplier reliability, and Incoterms.
-
Volume/MOQ: Larger orders often result in lower per-unit costs. Negotiating MOQ can be beneficial for buyers looking to reduce their overall expenditure.
-
Specifications/Customization: Custom cuts or specific wood grain requirements can increase costs due to the additional labor and tooling involved. Buyers should clearly communicate their needs to avoid unexpected expenses.
-
Materials: The type of wood selected—hardwood versus softwood—directly affects pricing. High-quality, certified materials will come at a premium but may yield better results in the long term.
-
Quality/Certifications: Wood that is certified sustainable or meets specific industry standards can cost more. However, these certifications can be crucial for companies focused on environmental responsibility.
-
Supplier Factors: Establishing long-term relationships with suppliers can lead to better pricing and more favorable terms. Consider the supplier’s reputation and reliability in delivering quality products on time.
-
Incoterms: Understanding shipping terms is vital. For instance, “FOB” (Free on Board) may require the buyer to manage shipping logistics, while “CIF” (Cost, Insurance, and Freight) includes shipping in the price, affecting overall costs.
What Buyer Tips Can Help Optimize Costs When Sourcing Wood for CNC Routing?
For international B2B buyers, especially those in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, optimizing costs when sourcing wood for CNC routing involves strategic negotiation and an understanding of the Total Cost of Ownership (TCO).
-
Negotiation: Always negotiate pricing, especially for bulk orders. Suppliers may be willing to offer discounts or better terms to secure large contracts.
-
Cost-Efficiency: Conduct a thorough analysis of the entire supply chain, from sourcing to delivery. This includes evaluating local suppliers to minimize transportation costs.
-
Total Cost of Ownership: Consider not just the purchase price but also the longevity and durability of the wood. Investing in higher-quality materials can reduce maintenance and replacement costs over time.
-
Pricing Nuances for International Buyers: Be aware of currency fluctuations and tariffs that may affect pricing. Establishing contracts in stable currencies can mitigate these risks.
Disclaimer
Prices for wood can vary significantly based on market conditions, regional availability, and supplier relationships. The information provided here is for indicative purposes only and may not reflect current market prices. Always consult multiple suppliers and conduct due diligence to obtain accurate and up-to-date pricing.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing best wood for cnc routing With Other Solutions
Introduction: Understanding Alternative Solutions for CNC Routing
When selecting the best wood for CNC routing, it’s essential to consider alternatives that may serve similar purposes. Various materials and methods can achieve comparable results, each with unique strengths and weaknesses. In this analysis, we will compare the best wood options for CNC routing against two viable alternatives: engineered wood products and composite materials. This comparison will help B2B buyers make informed decisions based on their specific project requirements.
Comparison Table
| Comparison Aspect | Best Wood For CNC Routing | Engineered Wood Products | Composite Materials |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | Excellent durability and finish quality; suitable for detailed work | Good structural integrity; consistent performance | High strength-to-weight ratio; versatile in applications |
| Cost | Varies significantly by type; generally higher for hardwoods | Generally lower cost; produced in large quantities | Varies, but often more expensive than wood; requires specialized processing |
| Ease of Implementation | Requires skilled craftsmanship; variable cutting speeds based on wood type | Easier to machine; uniform density simplifies CNC operations | Requires specific tooling; may need additional processing |
| Maintenance | Low maintenance if properly finished; wood can warp if not treated | Generally low; resistant to warping and splitting | Low, but can degrade if exposed to moisture without proper sealing |
| Best Use Case | Ideal for furniture, cabinetry, and intricate designs | Suitable for structural applications and furniture | Excellent for exterior applications and high-stress environments |
Detailed Breakdown of Alternatives
Engineered Wood Products
Engineered wood products, such as plywood and MDF, are manufactured from wood fibers glued together under heat and pressure. These products offer excellent stability and are less prone to warping than solid wood. They can be more cost-effective, making them attractive for large-scale projects. However, their performance in terms of finish quality may not match that of solid hardwood, especially for high-end applications.
Composite Materials
Composite materials, including fiberglass and polymer-based solutions, provide a unique alternative to traditional wood. They exhibit a high strength-to-weight ratio and are versatile across various applications, particularly in environments exposed to moisture and temperature fluctuations. Although they may come at a higher initial cost and require specialized processing, composites often outperform wood in durability and resistance to environmental stressors. Their downside is the need for precise tooling and the potential for additional processing steps.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Solution for Your Needs
For B2B buyers, the decision between the best wood for CNC routing and alternative materials depends on specific project requirements, budget constraints, and desired performance characteristics. If the goal is to create aesthetically pleasing furniture or intricate designs, solid hardwood may be the best choice. However, for projects requiring cost efficiency and stability, engineered wood products could be more suitable. Alternatively, composite materials might be the best fit for applications in harsh environments. Evaluating these factors will help buyers select the most appropriate solution tailored to their operational needs.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for best wood for cnc routing
What Are the Key Technical Properties of Wood for CNC Routing?
When selecting wood for CNC routing, understanding specific technical properties is crucial for ensuring optimal machining outcomes. Here are some essential specifications that B2B buyers should consider:
1. Material Grade
Material grade defines the quality and characteristics of the wood. It is essential for determining the wood’s durability, appearance, and workability. Higher-grade materials typically exhibit fewer defects, making them suitable for high-end applications. In CNC routing, using higher-grade wood can reduce machine wear and improve the quality of the finished product.
2. Density
Wood density affects its strength, weight, and resistance to wear and tear. Denser woods, such as maple and oak, provide greater durability and are ideal for projects requiring structural integrity. Conversely, lighter woods like pine are easier to handle and machine but may not be suitable for heavy-duty applications. Understanding density helps buyers choose the right material based on project requirements.
3. Moisture Content
Moisture content is a critical factor affecting the machining process and the final product’s stability. Wood with high moisture content may warp or crack during CNC routing. Ideally, wood should have a moisture content of around 6-8% for optimal machining. Buyers must ensure that the wood is adequately dried to prevent issues that could lead to costly rework.
4. Grain Pattern
The grain pattern influences the aesthetics and machinability of the wood. Consistent grain patterns are easier to work with and produce better finishes. Irregular grain can lead to tear-out during routing, affecting the quality of the final product. Understanding grain patterns allows buyers to choose wood that meets both functional and aesthetic requirements.
5. Finish Capability
The ability of wood to accept finishes is essential for projects that require aesthetic appeal. Some woods, like cherry and walnut, take stains and finishes well, enhancing their visual qualities. Others may require additional preparation to achieve a similar effect. Buyers should consider how the chosen wood will respond to finishing processes to ensure project success.
What Common Trade Terminology Should B2B Buyers Know?
Familiarity with industry jargon can significantly enhance communication and decision-making in the purchasing process. Here are some common terms relevant to wood sourcing and CNC routing:
1. OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
An OEM refers to a company that produces parts or equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer. In the context of wood products, understanding OEM relationships can help buyers identify reliable suppliers who meet specific quality and design standards.
2. MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ indicates the smallest amount of product a supplier is willing to sell. This term is crucial for B2B buyers looking to manage inventory costs effectively. Knowing the MOQ helps in budgeting and ensuring that orders align with production needs without incurring unnecessary expenses.
3. RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a document sent to suppliers requesting a quote for specific products or services. For wood procurement, an RFQ can include details like type, grade, and quantity of wood required. This process helps buyers compare prices and terms across multiple suppliers, ensuring competitive sourcing.
4. Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
Incoterms are a set of rules that define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in international transactions. Understanding these terms is vital for B2B buyers engaging in cross-border wood sourcing, as they clarify who bears the cost and risk during transportation.
5. Lead Time
Lead time refers to the amount of time it takes from placing an order until the product is delivered. In CNC routing, knowing the lead time for wood supplies is essential for project planning and scheduling. Buyers should factor in lead times to avoid delays in production.
By grasping these technical properties and trade terms, B2B buyers can make informed decisions when selecting the best wood for CNC routing, leading to successful project outcomes and enhanced business operations.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the best wood for cnc routing Sector
What are the Current Market Dynamics and Key Trends in the Best Wood for CNC Routing?
The global wood market for CNC routing is shaped by several key dynamics that international B2B buyers must navigate. As countries in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe continue to industrialize, there is a growing demand for high-quality wood products that meet diverse applications ranging from furniture to intricate carvings. One of the primary drivers of this demand is the increasing popularity of DIY projects and small-scale manufacturing, which is particularly evident in emerging markets.
Current sourcing trends highlight a shift towards locally sourced materials, which not only reduces costs but also supports local economies. Buyers are increasingly seeking hardwoods such as maple and oak due to their durability and aesthetic appeal, but there’s also a significant interest in softwoods like pine and cedar for their workability and cost-effectiveness. Additionally, the rise of e-commerce platforms is making it easier for B2B buyers to access suppliers and compare products on a global scale, further influencing purchasing decisions.
Emerging technologies in CNC machinery are also impacting sourcing strategies. Advanced CNC routing machines are capable of handling a wider variety of wood types with precision, leading buyers to explore new materials that may have previously been deemed unsuitable. As these technologies evolve, they will likely drive innovation in product offerings, creating opportunities for suppliers to differentiate themselves in the market.
How is Sustainability and Ethical Sourcing Impacting the Best Wood for CNC Routing?
In today’s market, sustainability and ethical sourcing are paramount considerations for B2B buyers in the wood sector. The environmental impact of logging and deforestation has led to increased scrutiny of supply chains, prompting businesses to adopt more responsible sourcing practices. Buyers are urged to look for wood products that are certified by recognized environmental standards, such as the Forest Stewardship Council (FSC) and the Programme for the Endorsement of Forest Certification (PEFC). These certifications ensure that the wood is sourced from responsibly managed forests, promoting biodiversity and reducing carbon footprints.
Moreover, the demand for “green” materials is not just a trend but a crucial factor in maintaining a competitive edge. Companies that prioritize sustainability are increasingly favored by consumers, making it essential for B2B buyers to align their sourcing strategies with these values. Additionally, using reclaimed or recycled wood is gaining traction, offering a unique appeal to environmentally conscious consumers while also providing a cost-effective alternative for manufacturers.
Investing in sustainable wood sourcing not only enhances a company’s brand reputation but can also lead to long-term cost savings. By establishing strong relationships with ethical suppliers, businesses can secure a consistent quality of wood while minimizing risks associated with supply chain disruptions and regulatory compliance.
How Has the Best Wood for CNC Routing Evolved Over Time?
The evolution of wood selection for CNC routing reflects broader changes in technology and market demands. Historically, woodworkers relied on locally available materials, but as CNC technology advanced, so did the range of woods that could be effectively machined. This shift allowed for the introduction of diverse species, each with unique properties that cater to specific applications.
In the past, softwoods were primarily used for basic construction and furniture making, while hardwoods dominated the market for premium products. However, the increasing capabilities of CNC machines have enabled the effective use of both hardwoods and softwoods in intricate designs, leading to a more balanced market.
Today, the focus on aesthetics, durability, and sustainability has transformed the wood sourcing landscape. As B2B buyers become more discerning, they are not just looking for the cheapest option but rather the best combination of quality, cost, and environmental responsibility. This evolution continues to shape the industry, driving innovation and fostering a greater appreciation for the diverse qualities that different wood types can offer in CNC routing applications.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of best wood for cnc routing
-
How do I choose the right wood for CNC routing projects?
Choosing the right wood for CNC routing involves considering several factors such as project requirements, wood properties, and budget constraints. For projects requiring durability and aesthetic appeal, hardwoods like maple, cherry, or walnut are excellent choices due to their strength and finish. Conversely, if cost is a primary concern or you are a beginner, softwoods such as pine or MDF are easier to work with and more affordable. Assess the intended use of the final product and the intricacy of the design to make an informed decision. -
What is the best wood for CNC sign making?
Cypress is often regarded as the best wood for CNC sign making due to its soft density, which makes it easy to carve and engrave. Its natural weather resistance is an added advantage for outdoor signage. Other suitable options include cedar for its pleasant aroma and durability, and basswood for its lightweight nature and ability to achieve intricate details. Selecting a wood type that aligns with your design complexity and environmental conditions will enhance the longevity and visual appeal of your signs. -
What are the minimum order quantities (MOQ) for wood suppliers?
Minimum order quantities (MOQ) can vary significantly among suppliers, particularly depending on the type of wood and the supplier’s location. Many suppliers set MOQs ranging from a few hundred to several thousand board feet. It’s essential to communicate your needs directly with potential suppliers, especially if you’re looking to source locally in regions like Africa or South America, where supply chains may differ. Negotiating MOQs can also be possible if you express interest in establishing a long-term relationship. -
How can I ensure quality when sourcing wood for CNC routing?
To ensure quality when sourcing wood for CNC routing, consider visiting suppliers to inspect the materials firsthand. Request samples to evaluate grain consistency, strength, and finish. It’s also beneficial to inquire about the supplier’s sourcing practices, certifications, and any quality assurance protocols they have in place. Establishing a clear communication channel for discussing your specific requirements will help mitigate risks associated with material quality. -
What payment terms should I expect when sourcing wood internationally?
Payment terms can vary widely depending on the supplier and the nature of the transaction. Common arrangements include upfront payments, deposits with balance upon delivery, or payment upon receipt. For international transactions, you may encounter options such as Letter of Credit (LC) for added security. It’s crucial to discuss and agree on payment terms before finalizing any agreements to avoid potential disputes and ensure a smooth procurement process. -
How do I vet suppliers for sourcing wood for CNC projects?
Vetting suppliers involves researching their reputation, quality standards, and customer feedback. Start by checking online reviews, industry certifications, and references from other businesses. Engaging in direct communication with potential suppliers can also reveal their responsiveness and willingness to accommodate your needs. Additionally, attending trade shows or industry events can provide opportunities to meet suppliers in person and assess their offerings more closely. -
What are the logistics considerations for importing wood for CNC routing?
When importing wood for CNC routing, consider factors such as shipping costs, customs regulations, and delivery timelines. Ensure that the supplier provides necessary documentation, including bills of lading and certificates of origin, to facilitate customs clearance. Additionally, work with logistics partners experienced in handling timber products to streamline the shipping process. Understanding the import regulations in your region, particularly in places like Europe or the Middle East, is essential to avoid delays. -
Can I customize wood dimensions and finishes when ordering for CNC routing?
Yes, many suppliers offer customization options for wood dimensions and finishes to meet specific project requirements. When discussing your order, clearly communicate your desired specifications, including thickness, width, length, and any particular finishes or treatments. Customization may affect pricing and lead times, so it’s important to clarify these aspects upfront. Establishing a strong relationship with your supplier can also lead to more flexible customization options over time.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.
Top 10 Best Wood For Cnc Routing Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. Midlands CNC – Best Woods for CNC Machining
Domain: midlandscnc.co.uk
Registered: 2017 (8 years)
Introduction: Best Woods for CNC Machining:
1. **Beginner Level:**
– MDF boards
– Plywood
– Particleboards
– Maple (cheaper hardwood)
– Cedar (affordable softwood)
– Spruce (affordable softwood)
2. **CNC Routing:**
– **Hardwoods:**
– Birch: Light in color, resistant to chips and dents.
– Maple: Dense, durable, and resistant to electrical shocks.
– Ash: Heavy, suitable for f…
2. Wood Species – CNC Creations
Domain: reddit.com
Registered: 2005 (20 years)
Introduction: Common wood species mentioned for CNC creations include: poplar, pine, Russian birch plywood, walnut, cedar, red oak, soft maple, alder, mesquite, hemlock, larch, and Baltic birch plywood. Users noted preferences for hardwoods over softwoods for better quality and ease of machining. Specific uses include signs, small goods, and inlaid cutting boards.
3. Components By Design – Best Wood Types for CNC Projects
Domain: componentsbydesign.com
Registered: 2010 (15 years)
Introduction: Best Type of Wood for CNC Projects: 1. Hardwood: – Ash: Light-colored, heavy hardwood with lots of rings. – Beech: Strong, stiff, shock-resistant hardwood with small pores. – Birch: Light-colored, stiff hardwood with a wavy grain. – Cherry: Light reddish-brown, strong, and resistant to warping. – Mahogany: Beautiful reddish-brown, ideal for engraving. – Maple: Long-lasting hardwood with even grain…
4. Carbide3D – Plywood and Hardwood Recommendations
Domain: community.carbide3d.com
Registered: 2013 (12 years)
Introduction: 1. Birch Plywood: Used by initial poster, decent results but not the best choice for v-carving.
2. Baltic Birch: Good quality plywood but hard to find; not ideal for v-carving.
3. Hardwoods: Maple, Walnut, and Poplar recommended for their flat smooth grain; good for carving but may require paint for contrast.
4. MDF: Can carve well if painted; unpainted results are less visually appealing.
5. …
5. Onefinity CNC – Recommended Wood Types for 3D Carving
Domain: forum.onefinitycnc.com
Registered: 2020 (5 years)
Introduction: Recommended wood types for 3D bias relief carving include cherry, mesquite, hickory, maple, mahogany, walnut, and poplar. Cherry is favored for its crisp lines, while maple is noted for its fine detail and light color. Mesquite and eucalyptus are preferred in desert regions, with ironwood being one of the hardest options. Bamboo is also mentioned as a strong alternative. Avoid oak due to its grain…
6. Inventables – Recommended Wood Types for Carving
Domain: discuss.inventables.com
Registered: 2001 (24 years)
Introduction: 1. Wood Types Recommended for Carving:
– Ash: Good finish, but requires significant finishing work.
– Beech: Solid hardwood, better for detailed carvings, but can burn at high RPMs.
– Poplar: Easy to cut, higher feed rate, but can tear out or chip.
– Cherry: Medium wood, holds details well.
– Soft Maple: Good for detailed carvings, looks great when finished.
– Alder: …
7. Easel – Walnut Carving Wood
Domain: forum.easel.com
Registered: 1997 (28 years)
Introduction: This company, Easel – Walnut Carving Wood, is a notable entity in the market. For specific product details, it is recommended to visit their website directly.
8. Probotix – CNC Wood Blanks
Domain: probotix.com
Registered: 2006 (19 years)
Introduction: CNC Wood Blanks are high-quality, precision-cut wood materials designed for CNC machining. They are available in various types of wood, including hardwoods and softwoods, and come in different sizes and thicknesses to suit various projects. Ideal for woodworking, crafting, and prototyping, these blanks ensure smooth finishes and consistent results. They are suitable for both professional and hobby…
9. RouterForums – Best Wood Types for CNC Routing
Domain: routerforums.com
Registered: 2004 (21 years)
Introduction: Best wood types for CNC routing: walnut, cherry, maple. Avoid hickory due to its stringy nature. Important factors: wood must be well dried for optimal results, avoid freshly cut wood from sawmills. Construction grade lumber is not recommended due to poor cutting quality and potential for tear-outs. Exotic woods like wenge and cocobolo can provide good finishes but may require sharp tooling and ca…
10. STYLECNC – Automatic CNC Routers
Domain: stylecnc.com
Registered: 2015 (10 years)
Introduction: Automatic CNC Routers for Woodworking – STYLECNC offers a variety of CNC wood routers suitable for both beginners and professionals. Key features include:
– Available in 3, 4, or 5 axes for 2D, 2.5D, and 3D cutting, milling, carving, drilling, and grooving.
– Popular woodworking applications include cabinet making, sign making, furniture making, and home decorations.
– Common table sizes: 2ft x…
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for best wood for cnc routing
In summary, strategic sourcing for CNC routing materials hinges on understanding the unique properties and applications of various wood types. Hardwoods like maple, oak, and cherry offer durability and aesthetic appeal, ideal for high-end projects, while softwoods such as pine and cedar provide cost-effective options for less demanding applications. By aligning your sourcing strategy with local availability and market trends, you can optimize both cost and quality in your CNC routing endeavors.
For international B2B buyers from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, the emphasis should be on establishing relationships with reliable suppliers who can provide quality wood that meets your specific machining needs. Consider the long-term benefits of investing in sustainable sourcing practices, which not only enhance product quality but also contribute to environmental responsibility.
Looking ahead, as CNC technology continues to evolve, the demand for specialized wood types will only grow. Embrace this opportunity to refine your sourcing strategy, ensuring that you remain competitive in a dynamic market. Engage with local suppliers and global networks to discover innovative wood solutions that can elevate your CNC projects to new heights.