Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for best way to cut diamond plate
In the dynamic landscape of international manufacturing and construction, sourcing the best way to cut diamond plate presents a significant challenge for B2B buyers. Whether you are operating in Nigeria’s burgeoning construction sector, Saudi Arabia’s expanding industrial landscape, or South America’s diverse markets, understanding the right cutting techniques can influence your project outcomes and cost efficiency. This guide delves into the various methods for cutting diamond plate, including the advantages and limitations of tools such as plasma cutters, circular saws, and shears, ensuring you find the optimal solution for your specific needs.
Beyond just cutting techniques, this comprehensive resource addresses the types of diamond plate available, their applications across different industries, and essential considerations for supplier vetting. With insights into pricing structures and quality benchmarks, this guide empowers international B2B buyers to make informed purchasing decisions. By equipping you with the knowledge to navigate the complexities of sourcing and cutting diamond plate, we aim to enhance your operational efficiency and project success.
Armed with this information, you can confidently engage with suppliers, ensuring that your investment yields the best possible returns in both performance and durability. Join us as we explore the best practices and strategies for effectively cutting diamond plate in today’s global market.
Understanding best way to cut diamond plate Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Angle Grinder with Cut-off Wheel | Versatile tool; effective for straight cuts. | Fabrication, custom projects. | Pros: Cost-effective, portable. Cons: Can produce rough edges; may require cleanup. |
| Plasma Cutter | High precision; suitable for thicker plates. | Industrial applications, large-scale manufacturing. | Pros: Fast cutting; minimal material waste. Cons: Requires skill; can lead to jagged edges if not used carefully. |
| Circular Saw with Metal Blade | Effective for straight cuts; adjustable depth. | Construction, automotive sectors. | Pros: Quick and clean cuts; easy to use. Cons: Noise and safety precautions needed. |
| Shears (Electric or Manual) | Ideal for long, straight cuts; clean edges. | Sheet metal work, HVAC installations. | Pros: Cleaner cuts; less physical strain. Cons: Limited to specific thicknesses; more expensive than manual tools. |
| Tin Snips | Handheld, easy to maneuver; good for small cuts. | DIY projects, custom fittings. | Pros: Affordable; precise for small adjustments. Cons: Labor-intensive for larger sheets; limited cutting capacity. |
What are the Advantages of Using an Angle Grinder with a Cut-off Wheel for Cutting Diamond Plate?
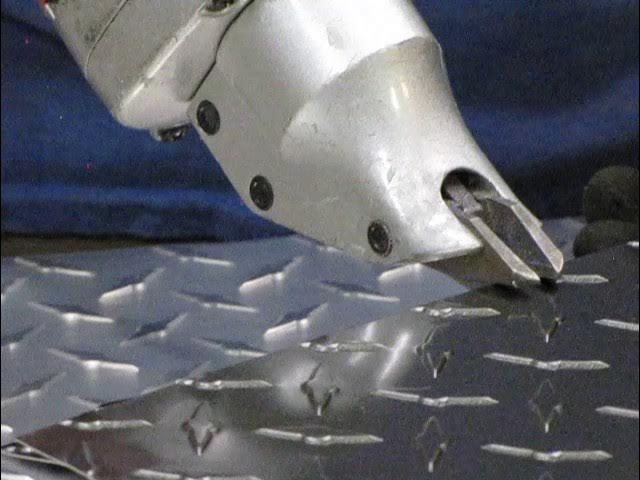
An angle grinder fitted with a cut-off wheel is a popular choice for cutting diamond plate due to its versatility and portability. This tool is particularly useful for straight cuts in various thicknesses of diamond plate. B2B buyers should consider that while angle grinders are cost-effective, they may produce rough edges requiring additional finishing work. This method is ideal for fabrication shops or custom projects where speed and flexibility are essential.
How Does a Plasma Cutter Enhance Efficiency in Diamond Plate Cutting?
Plasma cutters are favored in industrial settings for their precision and ability to handle thicker diamond plates. They provide rapid cutting speeds and minimize material wastage, making them suitable for large-scale manufacturing applications. However, plasma cutting requires skilled operation to avoid jagged edges. B2B buyers should evaluate their workforce’s expertise and the long-term investment in plasma cutting technology to maximize efficiency.
Why is a Circular Saw with a Metal Blade a Good Option for Cutting Diamond Plate?
A circular saw equipped with a metal cutting blade is effective for achieving clean, straight cuts in diamond plate. This tool allows for adjustable cutting depths, making it suitable for various thicknesses. It’s commonly used in construction and automotive sectors. However, buyers should be mindful of the noise generated and implement necessary safety precautions, as this method can be loud and requires protective gear.
When Should B2B Buyers Consider Using Shears for Cutting Diamond Plate?
Shears, whether manual or electric, are ideal for making long, straight cuts in diamond plate while ensuring clean edges. This tool is particularly useful in sheet metal work and HVAC installations. While shears can be more expensive than manual tools like tin snips, they reduce physical strain and provide a more efficient cutting process. Buyers should assess the thickness of the diamond plate they typically handle to determine the best shear option.
How Can Tin Snips Be Utilized Effectively in Cutting Diamond Plate?
Tin snips are a practical choice for B2B buyers engaged in DIY projects or custom fittings, particularly for smaller cuts. They are affordable and easy to maneuver, allowing for precise adjustments. However, tin snips can be labor-intensive for larger sheets, limiting their application in extensive projects. Buyers should consider their specific cutting needs and the frequency of use when deciding to invest in tin snips as part of their tool inventory.
Key Industrial Applications of best way to cut diamond plate
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of best way to cut diamond plate | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Automotive Manufacturing | Custom fabrication of diamond plate components for vehicle frames and interiors | Enhances durability and aesthetic appeal while reducing weight | Ensure precise cutting techniques and tools to maintain tolerances |
| Construction | Use in flooring, wall panels, and protective coverings in commercial buildings | Provides slip resistance and durability, improving safety and longevity | Consider sourcing from local suppliers to reduce transportation costs |
| Aerospace | Cutting diamond plate for aircraft components and maintenance platforms | Reduces weight without sacrificing strength, crucial for performance | Compliance with industry standards and certifications is essential |
| Oil & Gas | Fabrication of diamond plate for offshore platforms and equipment | Increases safety and functionality in harsh environments | Evaluate suppliers based on their ability to meet specific industry regulations |
| Marine | Use in shipbuilding for decks and safety features | Enhances slip resistance and durability in wet environments | Look for suppliers with experience in marine-grade materials |
In the automotive manufacturing sector, diamond plate is often used for custom fabrication of vehicle components, such as frames and interior elements. The best methods for cutting diamond plate, including plasma cutting and circular saw techniques, allow for precise shapes and sizes, enhancing both the durability and aesthetic appeal of the vehicles. Buyers in this sector must ensure that the cutting techniques maintain tight tolerances to meet safety and performance standards.
In construction, diamond plate serves as a popular choice for flooring, wall panels, and protective coverings in commercial buildings. The cutting methods employed must ensure a clean edge to maintain the material’s slip-resistant properties, which are vital for safety. B2B buyers should consider sourcing from local suppliers to minimize transportation costs and ensure timely delivery, particularly in regions with active construction markets.
The aerospace industry utilizes diamond plate for critical components and maintenance platforms due to its lightweight yet robust properties. Cutting this material requires adherence to strict industry standards to ensure safety and performance. Buyers must prioritize sourcing from suppliers who can provide materials that meet these regulatory requirements and ensure the integrity of the final product.
In the oil and gas sector, diamond plate is essential for creating equipment and platforms that withstand harsh environmental conditions. The cutting methods employed must ensure that the material retains its structural integrity while providing functional benefits. Buyers should evaluate suppliers based on their ability to meet specific industry regulations and their experience in working with heavy-duty materials.
Lastly, in the marine industry, diamond plate is commonly used in shipbuilding for decks and safety features. Its slip-resistant properties are crucial for ensuring safety in wet environments. Buyers should look for suppliers experienced in marine-grade materials and capable of providing diamond plate that meets the demanding conditions of maritime applications.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘best way to cut diamond plate’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Difficulty Achieving Clean Cuts in Diamond Plate
The Problem: Many B2B buyers, especially those involved in metal fabrication, face challenges when attempting to achieve clean, precise cuts in diamond plate. Common issues include jagged edges and material blowouts, especially when using plasma cutters or improper blades. These problems can lead to wasted material, increased production costs, and the need for additional finishing work to clean up edges. Such inefficiencies are particularly concerning for businesses operating under tight deadlines and budget constraints.
The Solution: To ensure clean cuts, it is crucial to select the right tools and techniques for cutting diamond plate. For straight cuts, a circular saw equipped with a high-quality metal cutting blade is recommended. This method allows for better control and a smoother finish compared to plasma cutting. Additionally, applying a lubricant such as WD-40 can help reduce friction and prevent material from gumming up the blade. It’s advisable to create a guide using a straight edge clamped down on the plate to maintain accuracy. For intricate cuts, investing in an 18-gauge electric shear can provide cleaner edges and reduce the need for extensive post-cut finishing. Regularly maintaining and replacing blades will also ensure optimal performance and precision.
Scenario 2: Inadequate Tools Leading to Inefficient Operations
The Problem: A significant pain point for international B2B buyers is the lack of appropriate cutting tools for diamond plate, particularly in regions with limited access to advanced machinery. Companies may rely on outdated or inadequate equipment, resulting in slow cutting processes and subpar results. This inefficiency not only affects production timelines but can also compromise the quality of the final product, leading to customer dissatisfaction and potential loss of business.
The Solution: Companies should evaluate their current tool inventory and consider investing in specialized equipment suited for diamond plate cutting. For regions with limited access to advanced machinery, a robust angle grinder with a diamond cutting wheel can serve as a versatile solution for both straight and curved cuts. Training staff on proper cutting techniques and tool maintenance will also enhance efficiency and prolong equipment life. Furthermore, partnering with local suppliers who can provide reliable tools and materials will ensure that businesses have access to the best cutting solutions available, thereby improving operational efficiency and output quality.
Scenario 3: Safety Concerns During the Cutting Process
The Problem: Safety is a paramount concern when cutting diamond plate, particularly in manufacturing environments where multiple workers are present. Buyers may worry about accidents resulting from improper handling of tools or inadequate personal protective equipment (PPE). Injuries not only pose risks to worker safety but can also lead to costly downtime and increased insurance premiums.
The Solution: To mitigate safety risks, companies should implement comprehensive safety protocols during the cutting process. This includes providing all workers with appropriate PPE, such as safety glasses, gloves, and long sleeves to protect against metal shards and sparks. Additionally, investing in cutting tools with safety features, such as guards and automatic shut-off mechanisms, can further enhance worker safety. Conducting regular training sessions on safe cutting practices will empower employees to handle tools properly and recognize potential hazards. By fostering a culture of safety and ensuring all team members are educated on best practices, businesses can minimize accidents and maintain a productive work environment.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for best way to cut diamond plate
What are the Key Materials for Cutting Diamond Plate?
When it comes to cutting diamond plate, selecting the right material and method can significantly affect the efficiency, quality, and cost-effectiveness of your operations. Below, we analyze several common materials used in cutting diamond plate, focusing on their properties, advantages, disadvantages, and considerations for international B2B buyers.
1. Aluminum Cutting Blades
Key Properties: Aluminum cutting blades are designed to cut through aluminum and other non-ferrous metals. They typically feature carbide tips that enhance durability and cutting precision.
Pros & Cons: These blades offer a clean cut with minimal burr formation, making them ideal for applications where finish quality is paramount. However, they can be more expensive than standard steel blades, and their lifespan may be shorter when used on thicker diamond plates.
Impact on Application: Aluminum blades are particularly effective for cosmetic diamond plate applications, where aesthetics are important. They are suitable for environments that require non-corrosive materials.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers in regions like Nigeria and Saudi Arabia should ensure compliance with local standards for cutting tools. Familiarity with common blade specifications, such as those outlined by ASTM or DIN, can be beneficial.
2. Plasma Cutters
Key Properties: Plasma cutters utilize high-temperature plasma to melt through metal. They are effective for cutting various materials, including aluminum and steel, with precision.
Pros & Cons: Plasma cutting is fast and can handle thick materials, making it suitable for large-scale operations. However, it can produce rough edges that may require additional finishing, and the initial investment in equipment can be high.
Impact on Application: Plasma cutters are ideal for industrial applications where speed is essential. They are particularly effective for cutting intricate designs or shapes in diamond plate.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should consider the availability of replacement parts and service for plasma cutters in their region. Compliance with safety standards is also crucial, especially in regions with stringent workplace regulations.
3. Circular Saws with Metal Cutting Blades
Key Properties: Circular saws equipped with metal cutting blades can effectively cut through diamond plate. These blades are often designed with carbide tips to enhance longevity.
Pros & Cons: Circular saws provide a good balance of speed and precision, making them suitable for straight cuts. However, they can be noisy and may require additional safety measures, such as hearing protection.
Impact on Application: This method is suitable for both DIY projects and industrial applications, particularly where straight cuts are needed. It is less effective for intricate shapes or curves.
Considerations for International Buyers: Understanding local noise regulations is important when using circular saws in populated areas. Additionally, buyers should ensure that the blades meet international standards for safety and performance.
4. Oxy-Acetylene Torches
Key Properties: Oxy-acetylene torches use a flame produced by burning a mixture of oxygen and acetylene to cut through metal. They are versatile and can be used for various thicknesses of diamond plate.
Pros & Cons: This method is cost-effective and allows for greater control over the cutting process. However, it requires skilled operators to achieve clean cuts, and there is a risk of warping the material due to heat.
Impact on Application: Oxy-acetylene cutting is suitable for heavy-duty applications where precision is less critical. It is often used in repair and maintenance operations.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should be aware of the availability of gas supplies and safety equipment in their region. Compliance with local regulations regarding the use of flammable gases is also essential.
Summary Table of Material Selection for Cutting Diamond Plate
| Material | Typical Use Case for best way to cut diamond plate | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Aluminum Cutting Blades | Cosmetic applications requiring clean cuts | Minimal burr formation | Higher cost and shorter lifespan | Medium |
| Plasma Cutters | Industrial applications needing speed | Fast and efficient for thick materials | Rough edges requiring finishing | High |
| Circular Saws with Metal Blades | DIY projects and straight cuts | Good balance of speed and precision | Noisy and requires safety measures | Medium |
| Oxy-Acetylene Torches | Heavy-duty applications in repair and maintenance | Cost-effective and versatile | Requires skilled operators | Low |
This strategic material selection guide provides essential insights for B2B buyers, enabling informed decisions on the best methods for cutting diamond plate according to their specific needs and regional considerations.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for best way to cut diamond plate
What are the Main Stages in the Manufacturing Process of Diamond Plate?
The manufacturing process for diamond plate involves several key stages that ensure the final product meets quality and performance standards. Understanding these stages is crucial for B2B buyers, as it directly influences the durability and usability of the diamond plate in various applications.
Material Preparation: How is Diamond Plate Material Selected and Processed?
The first stage of manufacturing diamond plate begins with material selection. Typically, diamond plates are made from aluminum, stainless steel, carbon steel, or galvanized steel. The choice of material depends on the intended application and environmental conditions. For instance, aluminum is favored for lightweight and corrosion-resistant applications, while stainless steel is chosen for its strength and durability.
Once the material is selected, it undergoes a series of processes including cutting and surface preparation. Sheets are often cut to size using methods such as shearing, plasma cutting, or laser cutting, which can vary in precision and efficiency. Surface preparation is essential to remove any contaminants and ensure proper adhesion if further processing is required, such as coating or painting.
Forming: What Techniques are Used to Shape Diamond Plate?
After material preparation, the forming stage involves shaping the diamond plate into its desired profile. This can include processes such as stamping, rolling, or bending. The diamond pattern itself is typically formed during the manufacturing process using a die that imprints the design onto the sheet.
For B2B buyers, understanding the forming techniques is vital, as they influence the plate’s structural integrity and aesthetic appeal. For example, stamping can create a more pronounced diamond pattern, while rolling may produce a subtler design. The choice of technique should align with the application requirements, particularly in sectors like automotive or construction, where load-bearing capacity is critical.
Assembly: How is Diamond Plate Integrated into Final Products?
In some cases, diamond plate may be part of a larger assembly, especially in industries such as automotive and machinery. During the assembly stage, diamond plates can be welded, bolted, or riveted to other components. It is essential to ensure that the joining methods used do not compromise the integrity of the diamond plate.
Quality assurance in this phase often includes verifying joint strength through testing methods such as tensile testing or shear testing. B2B buyers should inquire about the assembly techniques employed by suppliers, as these can affect the overall performance of the finished product.
Finishing: What Final Touches are Applied to Diamond Plate?
The finishing stage involves applying protective coatings or surface treatments to enhance durability and resistance to wear and corrosion. Common methods include anodizing for aluminum plates, galvanizing for steel plates, and powder coating for aesthetic appeal. This stage is crucial, particularly for applications exposed to harsh environments, such as outdoor installations or industrial settings.
Buyers should consider the type of finishing that aligns with their specific needs. For instance, powder coating may be ideal for aesthetic applications, while anodizing provides additional protection against corrosion.
What Quality Assurance Measures are Essential for Cutting Diamond Plate?
Quality assurance (QA) is a critical aspect of the diamond plate manufacturing process. It ensures that the products meet international standards and customer expectations. Understanding these QA measures can help B2B buyers make informed decisions when selecting suppliers.
Which International Standards Should Buyers Look For?
B2B buyers should be aware of various international standards that govern the manufacturing of diamond plate. ISO 9001, which focuses on quality management systems, is a fundamental certification that suppliers should possess. Additionally, industry-specific certifications such as CE marking (for European markets) and API (for oil and gas sectors) can also indicate adherence to quality standards.
These certifications ensure that the manufacturing processes are regularly audited and that products meet safety and performance criteria. Buyers should request proof of these certifications during the supplier selection process.
What are the Key Quality Control Checkpoints in the Manufacturing Process?
Quality control (QC) checkpoints are integral to ensuring that diamond plates meet specified standards at various stages of production. Common checkpoints include:
- Incoming Quality Control (IQC): Inspects raw materials upon receipt to ensure they meet specifications.
- In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): Monitors production processes to catch defects early, ensuring that any non-conformance is addressed immediately.
- Final Quality Control (FQC): Conducts a thorough inspection of the finished product, including dimensional checks, surface quality assessments, and performance testing.
Implementing these checkpoints helps maintain high-quality standards and reduces the risk of defects in the final product.
How Can Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control Processes?
To ensure that suppliers maintain robust QC processes, B2B buyers can take several steps:
- Conduct Audits: Regular audits of suppliers can provide insights into their manufacturing processes and quality control measures.
- Request QC Reports: Suppliers should be able to provide detailed QC reports that outline testing results and compliance with industry standards.
- Third-Party Inspections: Engaging third-party inspection services can offer an unbiased assessment of a supplier’s quality control processes and product quality.
These measures are especially important for international buyers from regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, where varying quality standards may exist.
What are the Common Testing Methods for Ensuring Diamond Plate Quality?
Testing methods play a crucial role in verifying the quality of diamond plates. Common methods include:
- Tensile Testing: Measures the strength of the material and its ability to withstand pulling forces.
- Shear Testing: Evaluates the material’s ability to resist sliding forces.
- Impact Testing: Assesses how well the material can absorb energy during sudden impacts.
- Corrosion Resistance Testing: Determines the material’s durability in corrosive environments, particularly important for plates used in outdoor or marine applications.
By understanding these testing methods, B2B buyers can better evaluate the quality of diamond plates and ensure they meet the necessary performance criteria for their applications.
Conclusion: How Can B2B Buyers Make Informed Decisions?
In summary, understanding the manufacturing processes and quality assurance measures involved in cutting diamond plates is essential for B2B buyers. By focusing on material selection, forming techniques, assembly methods, and finishing processes, buyers can ensure they procure high-quality products that meet their specific needs. Moreover, verifying suppliers’ adherence to international quality standards and engaging in thorough QC practices can further enhance product reliability and performance.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘best way to cut diamond plate’
To successfully cut diamond plate, it’s essential to follow a structured approach. This guide provides a step-by-step checklist tailored for B2B buyers seeking efficient methods and reliable suppliers. By adhering to these steps, you can ensure quality cuts while minimizing waste and maximizing safety.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Before sourcing equipment or services, clearly outline your technical requirements. This includes specifying the type of diamond plate (aluminum, steel, etc.), thickness, and intended application. Having precise specifications will help you communicate effectively with suppliers and ensure they meet your needs.
Step 2: Research Cutting Methods
Understand the various cutting techniques available for diamond plate. Popular methods include:
– Plasma Cutting: Suitable for thick plates but may require practice for clean edges.
– Circular Saw with Metal Blade: Offers precision for straight cuts and is widely accessible.
– Tin Snips for Short Cuts: Ideal for smaller projects where intricate cuts are needed.
Selecting the right method is crucial for achieving the desired finish and efficiency.
Step 3: Evaluate Potential Suppliers
Before committing, it’s crucial to vet suppliers thoroughly. Request company profiles, case studies, and references from buyers in a similar industry or region. Investigate their experience with diamond plate cutting to ensure they have the necessary expertise and equipment.
Step 4: Verify Equipment and Tool Quality
Assess the quality of cutting tools and machines offered by suppliers. Look for equipment that is:
– Designed for Durability: Ensure tools can withstand the demands of cutting diamond plate.
– Compatible with Your Material: Confirm that the equipment can handle the specific type and thickness of diamond plate you require.
Quality tools will not only improve cutting precision but also enhance safety during the cutting process.
Step 5: Request Sample Cuts
Before finalizing your supplier, ask for sample cuts to evaluate their capabilities. This allows you to:
– Assess Edge Quality: Check for smoothness and any signs of burrs or jagged edges.
– Evaluate Turnaround Time: Ensure they can meet your project deadlines.
Sample cuts will provide insight into the supplier’s workmanship and reliability.
Step 6: Ensure Compliance with Safety Standards
Verify that your suppliers adhere to safety regulations relevant to your region. This is particularly important when dealing with cutting processes that can produce hazardous materials. Ensure they provide:
– Safety Certifications: Look for compliance with international safety standards.
– Protective Equipment Recommendations: Confirm that they advocate for the use of safety gear during cutting.
Step 7: Establish a Post-Cutting Support Plan
Finally, ensure your supplier offers post-cutting support, including:
– Edge Finishing Services: Ask if they provide services to clean or finish edges after cutting.
– Technical Support: Verify that they have a team available for assistance if issues arise during the cutting process.
This support can enhance your overall experience and ensure the longevity of your diamond plate applications.
By following this checklist, B2B buyers can effectively navigate the process of cutting diamond plate, ensuring quality outcomes while fostering strong supplier relationships.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for best way to cut diamond plate Sourcing
When considering the cost structure and pricing for cutting diamond plate, several components and influencers come into play that B2B buyers must analyze thoroughly. Understanding these elements can help in making informed purchasing decisions, particularly in international markets like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe.
What Are the Key Cost Components in Cutting Diamond Plate?
-
Materials: The cost of diamond plate varies significantly based on the type of metal used—aluminum, stainless steel, or carbon steel. Each material has different price points, which are influenced by global market fluctuations. Thicker plates typically cost more, so determining the required thickness based on your application is crucial for budgeting.
-
Labor: Labor costs will depend on the complexity of the cutting process and the skill level required. Skilled labor, especially for precision cutting methods like CNC plasma cutting, will incur higher wages. In regions with lower labor costs, such as parts of Africa and South America, buyers might find more cost-effective options.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes costs related to facilities, utilities, and administrative expenses. Overhead can vary by region and supplier, affecting the overall pricing structure. Buyers should consider these factors when evaluating quotes from different suppliers.
-
Tooling: The type of cutting tools used—whether saws, plasma cutters, or shears—will influence the initial investment and ongoing maintenance costs. Higher quality tools often lead to better precision and reduced waste, which can offset costs over time.
-
Quality Control (QC): Implementing stringent quality control measures can add to the costs but is essential for ensuring that the finished product meets specifications. Buyers should inquire about the QC processes of potential suppliers, especially when sourcing from different regions.
-
Logistics: Shipping and handling costs can significantly impact total expenses, especially for international transactions. Factors such as distance, shipping method, and the weight of the materials will affect logistics costs. Understanding Incoterms is essential for clarifying who bears these costs.
-
Margin: Suppliers will typically add a profit margin to their costs, which can vary widely. Buyers should benchmark against industry standards to ensure they are getting a fair deal.
How Do Price Influencers Impact the Cost of Cutting Diamond Plate?
-
Volume/MOQ: Purchasing in bulk can lead to substantial discounts. Many suppliers offer tiered pricing based on the minimum order quantity (MOQ), so it’s advantageous for buyers to consolidate orders when possible.
-
Specifications and Customization: Custom cuts or specific material requirements can increase costs. Clearly defining specifications upfront can help avoid unexpected expenses later.
-
Supplier Factors: The reputation and reliability of suppliers can influence pricing. Established suppliers may charge more but offer better quality assurance and customer service.
-
Certifications and Quality: Suppliers offering certified materials, such as ISO or ASTM standards, may charge a premium. However, these certifications can provide assurance of quality, especially for critical applications.
What Are the Best Buyer Tips for Cost-Efficiency?
-
Negotiation: Engage suppliers in discussions about pricing, especially if you have a long-term relationship or plan for repeat orders. Many suppliers are willing to negotiate terms to secure a deal.
-
Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Consider not just the upfront cost but the total cost over the product’s lifecycle, including maintenance, potential waste, and rework costs. A cheaper initial price may lead to higher costs down the line if quality is compromised.
-
Pricing Nuances for International Buyers: Understand regional market conditions and how they affect pricing. Be aware of currency fluctuations, tariffs, and trade agreements that could impact overall costs when sourcing from different countries.
Disclaimer for Indicative Prices
Pricing for cutting diamond plate can fluctuate based on market conditions, material availability, and supplier pricing strategies. It’s recommended to obtain multiple quotes and conduct a thorough analysis of costs and benefits before making purchasing decisions.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing best way to cut diamond plate With Other Solutions
Exploring Alternative Methods for Cutting Diamond Plate
When it comes to cutting diamond plate, various methods can yield different results depending on the specific requirements of a project. Understanding the strengths and weaknesses of each method allows B2B buyers to make informed decisions tailored to their operational needs. Below, we compare the best way to cut diamond plate against other viable alternatives.
| Comparison Aspect | Best Way To Cut Diamond Plate | Alternative 1: Plasma Cutting | Alternative 2: Circular Saw with Metal Blade |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | High precision and clean cuts | Good for quick cuts, but can be jagged | Offers clean cuts but less precision in curves |
| Cost | Moderate initial investment | Higher initial cost for equipment | Lower equipment cost, but blades wear out quickly |
| Ease of Implementation | Requires specific tools and setup | Needs skill and practice to master | Simple setup, easy to use for most operators |
| Maintenance | Regular tool maintenance needed | Plasma equipment requires upkeep | Blades need frequent replacement |
| Best Use Case | Ideal for large, intricate projects | Suitable for thick materials and large sections | Best for straight cuts and smaller projects |
What Are the Pros and Cons of Plasma Cutting for Diamond Plate?
Plasma cutting is a popular alternative for those who require quick and efficient cuts. Its performance is commendable, particularly for thicker diamond plates, as it can cut through materials rapidly. However, the initial investment for plasma cutting equipment can be substantial. Moreover, while plasma cutters are adept at straight cuts, they may produce jagged edges if not operated skillfully. This method may require significant practice to achieve precision, making it less accessible for those without prior experience. Overall, plasma cutting is best suited for large-scale operations where time efficiency is critical.
How Does Using a Circular Saw with a Metal Blade Compare?
A circular saw fitted with a metal-cutting blade is another effective alternative for cutting diamond plate. This method is relatively low-cost and straightforward, allowing operators to make straight cuts with relative ease. It excels in smaller projects where quick, clean cuts are needed without extensive setup. However, the circular saw may not be the best choice for intricate designs or curves, as it lacks the precision of other methods. Additionally, the blades tend to wear out quickly, requiring regular replacements, which can add to long-term costs. This approach is ideal for smaller operations or projects that do not require complex cuts.
Conclusion: Which Cutting Method is Right for Your Business Needs?
Choosing the right method for cutting diamond plate depends on various factors, including project scale, budget, and the desired precision of cuts. For B2B buyers, the best way to cut diamond plate often involves investing in equipment that offers a balance of performance and cost-effectiveness. If speed and the ability to handle thick materials are paramount, plasma cutting may be the preferred choice. Conversely, for straightforward, smaller-scale projects, a circular saw could suffice. Ultimately, the decision should align with the specific operational needs and capabilities of the business, ensuring optimal results for diamond plate cutting.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for best way to cut diamond plate
What Are the Key Technical Properties of Diamond Plate for Cutting?
When cutting diamond plate, understanding its technical properties is essential for ensuring quality outcomes in your projects. Here are some critical specifications to consider:
-
Material Grade: Diamond plate can be made from various materials, including aluminum, stainless steel, and carbon steel. Each material has distinct properties affecting its machinability, weight, and resistance to corrosion. For instance, aluminum diamond plate is lightweight and resistant to rust, making it ideal for automotive applications, while stainless steel provides superior durability and is preferred in environments where hygiene is critical.
-
Thickness: The thickness of diamond plate, often measured in gauge, directly impacts the cutting process. Common thicknesses range from 1/8 inch to 1/4 inch. Thicker plates may require more robust cutting tools and techniques, while thinner plates can be handled with lighter equipment. Knowing the thickness helps in selecting the appropriate cutting tools and ensuring a clean cut.
-
Tolerances: Tolerance refers to the allowable deviation from a specified dimension. In B2B applications, tight tolerances are critical for ensuring parts fit together correctly, especially in precision engineering. Understanding the tolerance levels required for your project will help in selecting the right cutting method and tools.
-
Finish Type: The finish of diamond plate affects both aesthetics and functionality. Common finishes include mill finish, polished, and anodized. Each finish has implications for cutting techniques; for example, a polished finish may require more careful handling to avoid scratching during the cutting process.
-
Weight: The weight of diamond plate varies by material and thickness, impacting handling and transport logistics. For international buyers, understanding weight is crucial for calculating shipping costs and ensuring compliance with local regulations.
What Are Common Trade Terms in the Diamond Plate Industry?
Familiarizing yourself with industry jargon can enhance communication and negotiations with suppliers. Here are some essential terms:
-
OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer): This term refers to companies that produce parts or equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer. Understanding OEM relationships can help buyers identify reliable suppliers for diamond plate products that meet specific industry standards.
-
MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity): MOQ specifies the smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell. Knowing the MOQ is vital for budgeting and planning inventory, especially for international buyers who may face higher shipping costs for small orders.
-
RFQ (Request for Quotation): An RFQ is a formal process in which a buyer requests price quotes from suppliers. It is essential for comparing costs and ensuring you receive competitive pricing for diamond plate materials and services.
-
Incoterms: These are international commercial terms that define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in shipping goods. Familiarity with Incoterms such as FOB (Free on Board) and CIF (Cost, Insurance, and Freight) is crucial for understanding shipping arrangements and liability, particularly in cross-border transactions.
-
CNC (Computer Numerical Control): CNC refers to automated cutting machines that can produce precise cuts in diamond plate. For businesses looking for high-volume production with consistent quality, understanding CNC capabilities can inform equipment investments and operational efficiencies.
By grasping these technical properties and trade terms, B2B buyers can make informed decisions when sourcing diamond plate, ensuring they select the right materials and methods for their specific applications.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the best way to cut diamond plate Sector
What Are the Current Market Dynamics and Key Trends in Cutting Diamond Plate?
The global diamond plate market is experiencing significant growth driven by various factors, including rising industrial activities, demand for durable materials, and advancements in cutting technologies. Notably, B2B buyers from regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe are increasingly seeking efficient and cost-effective solutions for cutting diamond plates. The preference for aluminum and stainless steel diamond plates is on the rise due to their lightweight and corrosion-resistant properties, making them ideal for applications in construction, automotive, and decorative projects.
Emerging technologies such as CNC plasma cutting and advanced shearing techniques are revolutionizing the cutting process. These methods offer precision, speed, and reduced material wastage, appealing to businesses aiming for operational efficiency. Additionally, the integration of automation in manufacturing processes is facilitating a shift toward more streamlined supply chains, which is crucial for international buyers looking to optimize their procurement strategies.
Moreover, the demand for customized solutions is increasing. B2B buyers are looking for suppliers that can provide tailored products and cutting services to meet specific project requirements. The ability to offer flexible, just-in-time delivery is becoming a competitive advantage, particularly for businesses in fast-paced industries.
How Is Sustainability Influencing the Cutting Diamond Plate Market?
Sustainability is becoming a pivotal concern for B2B buyers in the diamond plate sector. The environmental impact of manufacturing processes, including energy consumption and waste generation, is under scrutiny. Buyers are increasingly prioritizing suppliers who demonstrate a commitment to sustainable practices, such as minimizing waste and reducing carbon footprints. This trend is particularly significant in regions like Europe, where regulatory frameworks are stringent regarding environmental standards.
Ethical sourcing is also gaining traction. Companies are seeking to ensure that their supply chains are transparent and responsible, particularly when sourcing raw materials. Certifications like ISO 14001 for environmental management and other ‘green’ certifications are becoming essential criteria for selecting suppliers. These certifications not only enhance brand reputation but also align with the values of increasingly eco-conscious consumers.
Furthermore, the use of recyclable materials in diamond plate production is an emerging trend that resonates well with sustainability goals. B2B buyers are encouraged to inquire about the recyclability of the diamond plates they source, as well as the sustainability practices of their suppliers. Adopting such materials can significantly contribute to a company’s overall sustainability strategy, making it an attractive option for businesses looking to enhance their corporate social responsibility profiles.
What Is the Historical Context of Cutting Diamond Plate in B2B?
The cutting of diamond plate has evolved significantly over the decades, transitioning from manual methods to highly automated and precise technologies. Historically, diamond plates were primarily cut using basic hand tools and rudimentary techniques, which often resulted in imprecise cuts and material wastage. As industrial demands grew, so did the need for more efficient and reliable cutting methods.
The introduction of power tools, such as circular saws and plasma cutters, marked a turning point in the industry. These tools not only improved cutting accuracy but also reduced labor costs and time. In recent years, advancements in CNC technology have further transformed the landscape, allowing for intricate designs and high-volume production with minimal waste.
Today, the cutting of diamond plate is not just about functionality; it also involves considerations of aesthetics, sustainability, and efficiency. B2B buyers are now more informed and demand innovative solutions that align with modern industry standards. The evolution of cutting techniques reflects a broader trend toward enhanced performance, sustainability, and customization in the manufacturing sector, ensuring that suppliers who adapt to these changes remain competitive in the market.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of best way to cut diamond plate
-
How do I cut diamond plate without damaging it?
To cut diamond plate effectively without causing damage, utilize tools designed for metal cutting. A circular saw equipped with a metal cutting blade or an angle grinder with a cutoff wheel are both excellent choices. For precise straight cuts, use a straight edge as a guide. Always ensure you wear appropriate safety gear, including gloves and eye protection, to safeguard against sharp edges and flying debris. Additionally, consider scoring the metal before breaking it to achieve a cleaner cut. -
What is the best tool for cutting diamond plate?
The best tool for cutting diamond plate depends on the thickness and type of material. For thinner sheets, tin snips are effective for intricate cuts. For straight cuts in thicker materials, a circular saw with a metal cutting blade or a plasma cutter is recommended for speed and precision. Electric shears can also provide a clean edge for longer cuts. Always test your chosen method on a scrap piece to ensure the quality of your cuts before proceeding with your project. -
What thickness of diamond plate can I cut with standard tools?
Standard tools like circular saws and angle grinders can typically handle diamond plate up to 1/4 inch thick. For thicker materials, specialized equipment such as CNC plasma cutters or industrial shears may be necessary to achieve clean, accurate cuts without excessive wear on the tools. When selecting diamond plate, consider the thickness in relation to your cutting capabilities and project requirements. -
What should I look for in a supplier for diamond plate?
When sourcing diamond plate, prioritize suppliers who offer high-quality materials with clear specifications regarding thickness, material type, and surface treatment. Verify the supplier’s reputation through customer reviews and industry certifications. Additionally, inquire about their capabilities for customization, such as cutting to specific dimensions, and their adherence to quality assurance processes. Establishing a relationship with a reliable supplier can facilitate smoother transactions and better support for your projects. -
What are the minimum order quantities (MOQ) for diamond plate?
Minimum order quantities can vary significantly among suppliers and depend on factors such as material type and market demand. Some suppliers may allow orders as low as a single sheet, while others may require bulk orders of several tons to ensure cost efficiency. Always confirm MOQ details before placing an order, as this can impact your budgeting and project timelines. -
How can I ensure quality assurance when sourcing diamond plate?
To ensure quality assurance when sourcing diamond plate, request material certifications and test reports from your supplier. These documents should detail the metal’s composition, strength, and any relevant compliance with international standards. Establishing a quality control process, including inspecting samples before full orders, can also mitigate risks associated with material defects. Regular communication with your supplier can help maintain quality throughout the production and shipping processes. -
What payment terms should I negotiate with diamond plate suppliers?
When negotiating payment terms with diamond plate suppliers, consider options such as upfront deposits, net payment terms, or letter of credit arrangements. Aim for terms that provide you with sufficient time to inspect the materials upon receipt before final payment. Discussing payment methods that offer buyer protection can also safeguard your investment, especially in international transactions where risk factors may be higher. -
What logistics considerations should I keep in mind when ordering diamond plate internationally?
When ordering diamond plate internationally, consider factors such as shipping costs, delivery times, and import regulations specific to your country. Work closely with your supplier to understand their shipping capabilities and any potential customs duties or tariffs that may apply. Ensure that the logistics provider you choose has experience in handling heavy metal shipments and can provide tracking information throughout the shipping process for better transparency.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.
Top 10 Best Way To Cut Diamond Plate Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. Reddit – 1/8 Steel Diamond Plate
Domain: reddit.com
Registered: 2005 (20 years)
Introduction: 1/8″ thick steel diamond plate; recommended cutting tool: 12″ DW8200; suitable for do-it-yourself homeowners.
2. Pirate4x4 – 1/8 Diamond Plate Sheet
3. Chief Delphi – Cutting Tools Guide
Domain: chiefdelphi.com
Registered: 1998 (27 years)
Introduction: This company, Chief Delphi – Cutting Tools Guide, is a notable entity in the market. For specific product details, it is recommended to visit their website directly.
4. Hobart Welders – Diamond Plate Cutting Guide
Domain: weldtalk.hobartwelders.com
Registered: 1999 (26 years)
Introduction: 1/4 inch diamond plate; cutting methods: oxy/acetylene (O/A) setup, angle grinder with cutoff wheel, skill saw; recommended tools: 4 inch angle grinder, oxy/acetylene torch with appropriate cutting tip; safety precautions: use cutoff guard, wear glasses and shield, secure tanks during transport.
5. Make It From Metal – Band Saw & Circular Saw
Domain: makeitfrommetal.com
Registered: 2018 (7 years)
Introduction: 1. Band Saw: Ideal for cutting thick aluminum plates (0.5″ or thicker). Recommended blade speed: 250 feet per minute. Ideal TPI: 10-14. Use coolant or light oil like WD-40 to prevent clogging.
2. Circular Saw: Fast and provides clean cuts. Safety precautions: clamp the plate, use full-face mask, gloves. Recommended blade: carbide teeth designed for non-ferrous metals. Use lubricant (WD-40 or wax …
6. Mountain Buzz – Strap Slot Cutting Guide
Domain: mountainbuzz.com
Registered: 1998 (27 years)
Introduction: Cutting strap slots in diamond plate side boards; recommended tools include router with carbide bit, jig saw, Dremel with cut-off wheel, or circular saw; initial hole drilling suggested for precision; emphasis on deburring and smoothing edges after cutting; goal is to create a simple 1-inch strap slot.
7. MTBR – Diamond Plate Cutting Tools
Domain: mtbr.com
Registered: 1996 (29 years)
Introduction: Tools suggested for cutting diamond plate include: 6-inch angle grinder with abrasive cutting disks, band saw, jigsaw, plasma cutter, and Dremel tool. For aluminum diamond plate, proper metal cutting saw blades are recommended, and using oil (like chain lube) while cutting is advised to prevent blade damage. A vice is also suggested for stability while cutting.
8. Phillips – CNC Laser Cutting Machines
Domain: phillipscorp.com
Registered: 1996 (29 years)
Introduction: Phillips offers high-quality CNC Laser Cutting Machines including EFC CNC Laser Cutting Machine, TFC CNC Laser Cutting Machine, and BFC CNC Laser Cutting Machine. These machines are designed for precision cutting of aluminium sheets and plates, suitable for various applications in industries such as aerospace, construction, and metalworking. Tools for cutting aluminium include Metal Shears for she…
9. Metals Depot – Aluminum Diamond Plate
Domain: metalsdepot.com
Registered: 1999 (26 years)
Introduction: Aluminum Diamond Plate – Highly Polished – 3003-H22: Highly reflective, economical, good forming, drilling, and welding ability, raised diamond lug pattern for slip resistance. FTQ option available for added grip. Aluminum Diamond Plate – Mill Finish – 6061-T6: Strength, skid resistance, and durability, used in industrial applications, easy to weld and drill, limited formability, dull mill finish….
10. NC Woodworker – Aluminum Diamond Plate Cutting Tools
Domain: ncwoodworker.net
Registered: 2005 (20 years)
Introduction: To cut Aluminum Diamond Plate (Tread Plate), various tools and blades can be used: 1. **Circular Saw**: Requires a carbide-tipped blade designed for non-ferrous metals. More teeth (40 or more for a 10″ blade) are preferable to avoid clogging. 2. **Jig Saw**: A variable speed jig saw with a fine metal blade is effective for smaller cuts. 3. **Hacksaw**: A hacksaw with a fine tooth blade can be used…
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for best way to cut diamond plate
In conclusion, selecting the best method for cutting diamond plate is crucial for optimizing operational efficiency and achieving high-quality results in your projects. The insights gathered underscore the importance of using appropriate tools—such as plasma cutters, angle grinders, and tin snips—tailored to the specific thickness and material of the diamond plate. For international B2B buyers, especially in regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, understanding local sourcing options can significantly enhance cost-effectiveness and ensure timely delivery.
Strategic sourcing not only helps in acquiring the right equipment but also enables buyers to establish strong relationships with suppliers who can provide ongoing support and expertise. As the demand for diamond plate applications continues to grow across various industries, now is the ideal time to explore innovative cutting solutions that can elevate your projects.
We encourage you to engage with reliable suppliers and stay abreast of advancements in cutting technology. By doing so, you will be well-positioned to leverage the best practices in diamond plate cutting, ensuring your business remains competitive and responsive to market demands.