Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for best way to cut carbon fiber
Navigating the complexities of sourcing the best way to cut carbon fiber can be a daunting task for international B2B buyers. As industries across Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe increasingly rely on carbon fiber for its lightweight and high-strength properties, the need for effective cutting techniques becomes paramount. This guide serves as a comprehensive resource, addressing various cutting methods, tools, and safety considerations essential for achieving precision and efficiency.
In the following sections, we will explore the most effective cutting techniques, ranging from hand tools to advanced machinery, tailored to different applications—from aerospace to automotive industries. Additionally, we will discuss key factors in supplier vetting, enabling buyers to identify reliable partners that meet their unique needs. Cost considerations, including equipment investment and operational expenses, will also be examined, providing a holistic view of what it takes to successfully integrate carbon fiber cutting into your production processes.
By empowering B2B buyers with actionable insights and practical solutions, this guide aims to facilitate informed purchasing decisions, ensuring that your organization can navigate the global market with confidence and achieve optimal results in carbon fiber cutting. Whether you are based in Brazil, Vietnam, or any other region, understanding these nuances will enhance your operational efficiency and product quality.
Understanding best way to cut carbon fiber Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Hand Saws | Low-cost, requires manual effort, uses metal blades | Prototyping, small-scale projects | Pros: Inexpensive, easy to use. Cons: Labor-intensive, slower cutting speed. |
| Rotary Tools | Versatile, allows for detailed cuts, uses diamond blades | Custom parts, intricate shapes | Pros: High precision, suitable for detailed work. Cons: Generates dust, requires skill to avoid overheating. |
| Angle Grinders | Powerful, fast cutting, suitable for thicker materials | Large-scale manufacturing | Pros: Quick cuts, effective for thick sheets. Cons: High risk of dust inhalation, needs careful handling. |
| Jigsaws | Ideal for curved cuts, compatible with specialized blades | Aerospace, automotive industries | Pros: Flexible cutting options, less dust. Cons: Limited to thinner materials, blade wear can be rapid. |
| Wet Cutting Method | Minimizes dust, utilizes dampening techniques | Precision cutting of rods | Pros: Cleaner cuts, less health risk from dust. Cons: Slower process, suitable only for smaller diameters. |
What Are the Key Characteristics of Hand Saws for Cutting Carbon Fiber?
Hand saws, such as hacksaws and coping saws, are a cost-effective solution for cutting carbon fiber. These tools are readily available and easy to operate, making them suitable for small-scale projects and prototyping. They rely on metal cutting blades with a higher TPI for cleaner cuts. However, the manual nature of hand saws can be labor-intensive and time-consuming, potentially limiting their efficiency for larger operations.
How Do Rotary Tools Enhance Precision in Carbon Fiber Cutting?
Rotary tools, like Dremels, offer versatility and precision for cutting carbon fiber. By using diamond-coated blades, these tools can handle intricate shapes and detailed work, making them ideal for custom parts. While they enable high precision, rotary tools can generate significant amounts of dust, posing health risks. Buyers should consider investing in appropriate safety equipment and ventilation solutions to mitigate these concerns.
What Advantages Do Angle Grinders Provide for Large-Scale Cutting?
Angle grinders are powerful tools designed for rapid cutting, making them suitable for thicker carbon fiber sheets in large-scale manufacturing applications. They can make quick work of straight cuts, but their powerful operation requires careful handling and appropriate safety gear to prevent inhalation of dust. Buyers should weigh the speed and efficiency against the potential hazards involved in using this method.
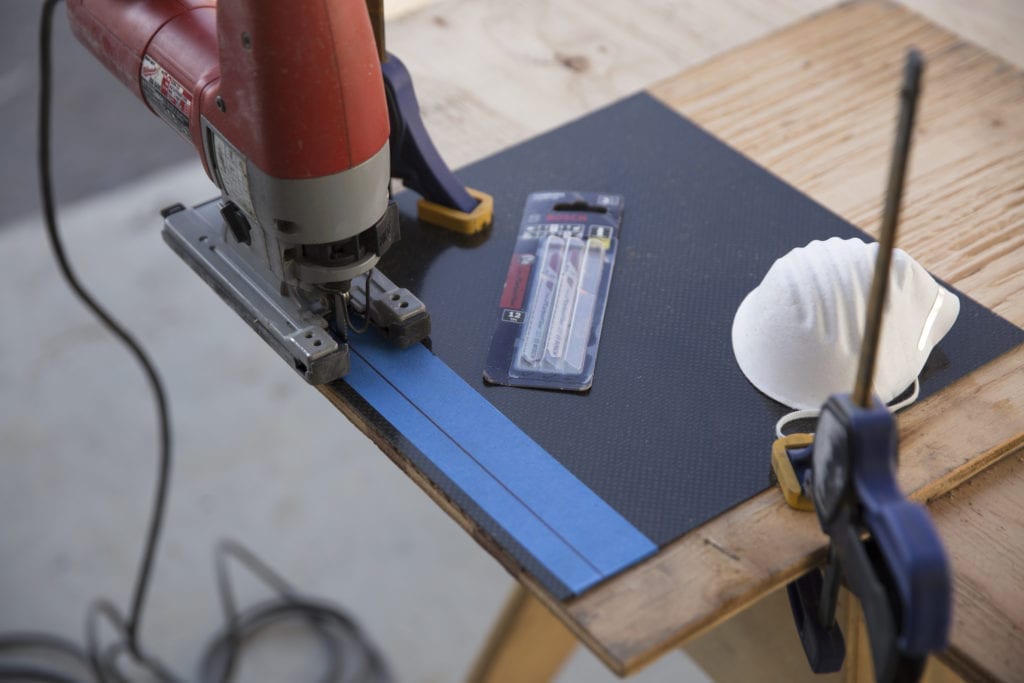
Why Are Jigsaws a Preferred Choice for Curved Cuts in Carbon Fiber?
Jigsaws are particularly effective for making curved and intricate cuts in carbon fiber, especially when using specialized blades designed for the material. They offer flexibility and the ability to attach vacuum systems for dust control. However, jigsaws are generally limited to thinner materials, and blade wear can occur quickly, necessitating frequent replacements. B2B buyers in industries like aerospace and automotive should consider the balance between flexibility and operational costs.
What Makes the Wet Cutting Method Beneficial for Carbon Fiber Rods?
The wet cutting method is a unique approach that minimizes dust generation by using dampening techniques. This method is particularly effective for cutting carbon fiber rods, as it reduces the risk of inhaling harmful dust particles. While it offers cleaner cuts and less health risk, the process is slower and more suited for smaller diameters. B2B buyers focusing on precision and safety in smaller projects may find this method advantageous, despite its slower pace.
Key Industrial Applications of best way to cut carbon fiber
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of best way to cut carbon fiber | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Aerospace | Fabrication of lightweight structural components | Reduces weight, improving fuel efficiency and performance | High precision cutting tools; compliance with safety standards |
| Automotive | Production of composite body panels | Enhances vehicle strength while reducing overall weight | Durable cutting equipment; ability to handle large volumes |
| Sports Equipment | Creation of custom carbon fiber rods and frames | Improves performance and durability of sports gear | Specialized cutting tools for intricate designs; sourcing from reputable suppliers |
| Marine | Manufacturing of boat hulls and components | Increases speed and fuel efficiency, reducing operational costs | Need for water-resistant cutting tools; consideration of local regulations |
| Industrial Manufacturing | Production of custom tooling and fixtures | Increases operational efficiency and reduces production costs | Reliable supply chain for raw materials; adaptability to various cutting methods |
In the aerospace industry, the best way to cut carbon fiber is crucial for fabricating lightweight structural components. These components play a significant role in enhancing fuel efficiency and overall performance of aircraft. Buyers in this sector must prioritize high-precision cutting tools that comply with stringent safety standards, ensuring both quality and safety in their operations.
The automotive sector increasingly relies on carbon fiber for composite body panels, which provide enhanced strength while reducing weight. This combination is vital for improving vehicle performance and fuel efficiency. International buyers should consider sourcing durable cutting equipment capable of handling high volumes, as the automotive industry often requires scalability and consistency in production.
In sports equipment manufacturing, the ability to create custom carbon fiber rods and frames is essential for optimizing performance and durability in high-end sports gear. Buyers in this field need specialized cutting tools that can manage intricate designs while ensuring minimal waste. Partnering with reputable suppliers is crucial to guarantee quality and reliability in the cutting process.
For the marine industry, cutting carbon fiber is integral to producing boat hulls and components that enhance speed and fuel efficiency. This leads to reduced operational costs for boat manufacturers. Buyers must consider the need for water-resistant cutting tools and be aware of local regulations regarding material use and disposal to ensure compliance and sustainability.
Lastly, in industrial manufacturing, the best way to cut carbon fiber is utilized in producing custom tooling and fixtures. This application significantly boosts operational efficiency and can reduce production costs. Buyers should focus on establishing a reliable supply chain for raw materials and ensure that their cutting methods are adaptable to various manufacturing needs, thus enhancing their operational flexibility.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘best way to cut carbon fiber’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Difficulty in Achieving Clean Cuts Without Damage
The Problem:
B2B buyers often struggle with achieving clean cuts on carbon fiber materials, leading to significant waste and compromised product quality. The challenge arises from the inherent properties of carbon fiber, which can splinter, fray, or delaminate when cut improperly. Buyers, particularly in industries such as aerospace, automotive, and sporting goods, face the risk of damaging expensive materials or producing parts that do not meet stringent quality standards. This issue is particularly acute for companies in regions with limited access to specialized cutting tools, forcing them to rely on makeshift solutions that exacerbate the problem.
The Solution:
To achieve clean cuts on carbon fiber, it is essential to invest in specialized cutting tools designed for this material. For instance, using a jigsaw fitted with a carbide blade specifically designed for carbon fiber can drastically improve cut quality. Additionally, employing a backing material like rigid foam or wood during the cutting process helps prevent blow-out and splintering on the underside of the cut. Buyers should also consider using a slow and steady cutting motion to minimize heat generation, which can degrade the epoxy resin binding the fibers. Finally, sourcing equipment from reputable suppliers who provide training on proper cutting techniques can further enhance the quality of cuts, ensuring that the final products meet industry standards.
Scenario 2: Health Hazards Associated with Carbon Fiber Dust
The Problem:
Cutting carbon fiber materials generates fine dust particles that pose serious health risks, including respiratory issues and skin irritation. B2B buyers, especially those in manufacturing sectors, often overlook the importance of safety measures, leading to potential long-term health complications for their workforce. This concern is particularly pressing in regions where safety regulations may be less stringent or enforcement is lax, resulting in a culture that undervalues protective measures.
The Solution:
Implementing a comprehensive safety protocol is critical for mitigating health hazards associated with carbon fiber dust. Companies should invest in high-quality personal protective equipment (PPE) for their workers, including respirators, gloves, and protective suits. Additionally, establishing well-ventilated workspaces with proper dust extraction systems, such as downdraft tables or shop vacuums, can significantly reduce airborne particles during cutting. Training sessions focused on the hazards of carbon fiber and the importance of safety protocols can foster a culture of health and safety. By prioritizing worker safety, businesses not only comply with regulations but also enhance productivity by reducing downtime due to health-related issues.
Scenario 3: Cost Implications of Improper Cutting Techniques
The Problem:
B2B buyers frequently face financial strain due to the high costs associated with improper cutting techniques, which can lead to material wastage and the need for additional labor to rectify mistakes. This issue is especially pronounced in competitive markets where margins are tight, and any inefficiencies can lead to significant losses. Companies in developing markets may also struggle with limited access to quality tools, forcing them to rely on subpar methods that exacerbate these financial challenges.
The Solution:
To mitigate the cost implications of improper cutting techniques, businesses should conduct a thorough assessment of their current cutting processes and invest in training for their employees. Utilizing advanced cutting tools, such as laser cutters or water jets, can provide precision and reduce waste significantly. Additionally, establishing clear cutting protocols and investing in high-quality materials and blades tailored for carbon fiber can further enhance efficiency. Companies should also consider collaborating with suppliers who offer consultation and support, allowing them to optimize their cutting processes. By adopting a strategic approach to cutting carbon fiber, businesses can improve their bottom line while ensuring the quality and integrity of their products.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for best way to cut carbon fiber
When selecting the best methods to cut carbon fiber, it is essential to consider the tools and materials involved in the process. Here, we analyze four common materials used for cutting carbon fiber, focusing on their properties, advantages, disadvantages, and implications for international B2B buyers.
What are the Key Properties of Hand Saws for Cutting Carbon Fiber?
Hand saws, such as hacksaws and coping saws, are popular choices for cutting carbon fiber sheets. These tools typically feature high-tooth-per-inch (TPI) blades, which allow for finer cuts. The key properties of hand saws include their simplicity, low cost, and ease of use. They are particularly effective for straight cuts and can be employed in various settings, from workshops to field applications.
Pros: Hand saws are affordable and require minimal maintenance. They are also versatile, making them suitable for both straight cuts and intricate shapes when paired with the right blade.
Cons: The main limitation is the time and effort required for larger projects, as hand saws can be labor-intensive. Additionally, the blades may dull quickly when cutting through dense materials like carbon fiber.
How Do Rotary Tools Enhance the Cutting of Carbon Fiber?
Rotary tools, such as Dremels, are advantageous for their precision and ability to handle detailed work. They can utilize various attachments, including diamond-coated cutting wheels, which are more durable than standard metal cutting wheels. This versatility allows for both cutting and finishing tasks.
Pros: Rotary tools are excellent for intricate designs and can cut through carbon fiber without generating excessive heat, which can damage the epoxy matrix.
Cons: They can produce a significant amount of dust, necessitating proper ventilation and dust collection systems. Additionally, the initial investment in quality rotary tools can be higher than hand saws.
What Advantages Do Jigsaws Offer for Cutting Carbon Fiber?
Jigsaws are particularly effective for cutting curves and tight corners in carbon fiber sheets. They can accommodate specialized blades designed for composite materials, which significantly extend their cutting life compared to standard metal blades.
Pros: Jigsaws provide a high degree of control and are capable of making precise cuts. They can also be fitted with dust extraction systems, minimizing airborne particles during operation.
Cons: The cost of jigsaws and specialized blades can be higher than other manual options. Moreover, if not used correctly, they can lead to fraying or splintering at the cut edges.
What Role Do Angle Grinders Play in Cutting Carbon Fiber?
Angle grinders are powerful tools that can quickly cut through carbon fiber, particularly in thicker materials. They are often used in industrial settings where speed is essential.
Pros: Angle grinders are highly efficient and can handle heavy-duty cutting tasks. Their ability to use various abrasive wheels makes them versatile for different applications.
Cons: They require a higher level of skill to operate safely, and without proper protective gear, they can pose significant health risks due to dust and debris. The cost of angle grinders and their accessories can also be substantial.
Summary for International B2B Buyers
When considering these tools, international B2B buyers should be aware of local regulations and standards, such as ASTM, DIN, or JIS, that may affect tool selection and usage. Additionally, preferences for specific tools may vary by region, influenced by factors such as availability, cost, and local practices.
| Material | Typical Use Case for best way to cut carbon fiber | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hand Saws | Cutting sheets for prototypes and small projects | Low cost and easy to use | Labor-intensive and blades dull quickly | Low |
| Rotary Tools | Detailed cutting and finishing | Precision and versatility in design | Produces dust and higher initial investment | Med |
| Jigsaws | Curved cuts and intricate designs | High control and can minimize dust | Higher cost and potential for fraying edges | Med |
| Angle Grinders | Heavy-duty cutting in industrial applications | Fast and efficient for thick materials | Requires skill and poses health risks if misused | High |
This table provides a quick reference for B2B buyers looking to select the most suitable cutting method for carbon fiber, taking into account performance, cost, and operational considerations.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for best way to cut carbon fiber
What Are the Main Stages in the Manufacturing Process of Cutting Carbon Fiber?
The manufacturing process for cutting carbon fiber involves several critical stages, each designed to ensure that the final product meets the stringent requirements of quality and performance. Understanding these stages can help B2B buyers make informed decisions when sourcing carbon fiber components.
Material Preparation: How Is Carbon Fiber Prepared for Cutting?
Before cutting, carbon fiber materials must be adequately prepared. This involves selecting the appropriate type of carbon fiber sheet or rod based on the application requirements. Buyers should consider factors such as thickness, weave pattern, and resin type, which can influence the cutting process.
Once the correct material is chosen, it must be thoroughly cleaned to remove any contaminants that could affect the cutting quality. This may involve using solvents or specialized cleaning agents. Proper storage conditions are also essential to maintain the integrity of the material before cutting.
Forming: What Techniques Are Used to Cut Carbon Fiber?
The actual cutting of carbon fiber can be performed using various techniques, each suited for different applications and desired outcomes.
-
Hand Tools: For smaller-scale operations or prototypes, hand tools such as hacksaws and coping saws can be effective. They allow for precision and control, although they may not be suitable for high-volume production due to slower cutting speeds.
-
Rotary Tools: Tools like Dremel or other rotary cutting instruments are often used for intricate cuts. However, care must be taken to avoid overheating the material, which can degrade the resin and release harmful dust.
-
Jigsaws and Angle Grinders: For larger components, jigsaws equipped with specialized blades for carbon fiber offer both speed and precision. Angle grinders can also be used but require more caution due to the potential for generating excessive heat.
-
CNC Machines: For large-scale production, CNC (Computer Numerical Control) machines are the preferred choice. They provide high precision and repeatability, essential for meeting tight tolerances in manufacturing.
Assembly: How Are Carbon Fiber Parts Assembled?
Once the cutting is complete, the next stage is assembly. This may involve bonding, fastening, or layering carbon fiber components. The choice of adhesive is crucial, as it must be compatible with the resin used in the carbon fiber.
Additionally, precise alignment during assembly is vital to ensure structural integrity. Some manufacturers may employ automated systems for assembly, which can enhance consistency and reduce labor costs.
Finishing: What Are the Final Steps in the Carbon Fiber Cutting Process?
The final stage involves finishing processes, including sanding and edge sealing. Sanding is crucial to remove any rough edges left from cutting and to prepare the surface for painting or coating if required. Edge sealing is also important to prevent delamination and enhance the durability of the component.
What Quality Assurance Measures Should B2B Buyers Expect?
Quality assurance (QA) is a critical component of the manufacturing process, ensuring that the final product meets international and industry-specific standards. For B2B buyers, understanding these measures can help verify supplier credibility and product reliability.
Which International Standards Apply to Carbon Fiber Manufacturing?
ISO 9001 is the most recognized international standard for quality management systems. It sets the framework for ensuring consistent quality and customer satisfaction. Compliance with ISO 9001 indicates that the manufacturer has implemented effective processes and controls throughout the production cycle.
In addition to ISO standards, industry-specific certifications such as CE (Conformité Européenne) and API (American Petroleum Institute) may apply depending on the end-use of the carbon fiber products. These certifications ensure that the products meet safety and performance criteria relevant to their respective industries.
What Are the Key Quality Control Checkpoints?
Quality control (QC) checkpoints are essential to maintaining product integrity throughout the manufacturing process. Common QC checkpoints include:
-
Incoming Quality Control (IQC): This step involves inspecting raw materials upon arrival to ensure they meet specified standards. This can include visual inspections, dimensional checks, and material testing.
-
In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): During manufacturing, regular inspections and tests are conducted to monitor the production process. This may involve checking the cutting precision, adhesive application, and assembly alignment.
-
Final Quality Control (FQC): Once production is complete, final inspections are performed to ensure that the finished products meet all specifications. This can include functional testing, dimensional verification, and surface quality checks.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control?
B2B buyers can take several steps to verify the quality control processes of potential suppliers:
-
Audits: Conducting on-site audits can provide firsthand insight into the supplier’s manufacturing processes and quality control measures. This can help assess their compliance with international standards.
-
Quality Reports: Requesting documentation of previous quality control reports can help buyers understand the supplier’s track record in maintaining quality.
-
Third-Party Inspections: Engaging third-party inspection services can offer an unbiased assessment of the supplier’s quality control measures and product quality.
What Are the Quality Control Considerations for International B2B Buyers?
For international buyers, especially from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, additional QC considerations may apply.
-
Regulatory Compliance: Different regions may have unique regulations governing the use of carbon fiber products. Understanding these regulations is crucial for ensuring compliance and avoiding potential legal issues.
-
Cultural and Language Barriers: These barriers can impact communication regarding quality expectations. Clear documentation and agreements can mitigate misunderstandings.
-
Supply Chain Reliability: International buyers should assess the reliability of suppliers in terms of delivery times and quality consistency. This is particularly important when dealing with custom or high-volume orders.
By understanding the manufacturing processes and quality assurance measures involved in cutting carbon fiber, B2B buyers can make informed decisions that align with their operational needs and quality expectations. This knowledge not only enhances supplier relationships but also contributes to the overall success of projects involving carbon fiber components.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘best way to cut carbon fiber’
In the pursuit of effective carbon fiber cutting, this guide provides a structured approach to sourcing the best methods and equipment. By following these steps, B2B buyers can ensure they make informed decisions that align with their operational needs and safety standards.
Step 1: Assess Your Cutting Requirements
Understanding your specific cutting requirements is vital. Consider the type of carbon fiber materials you will be working with, whether sheets, rods, or complex shapes. Each application may require different cutting techniques, so evaluating the dimensions, thickness, and the intricacy of the cuts needed will guide your choice of tools and methods.
Step 2: Identify Suitable Cutting Methods
Explore the various methods available for cutting carbon fiber. Common techniques include hand saws, rotary tools, angle grinders, and jigsaws, each offering unique advantages. For instance, hand saws are cost-effective and provide precise cuts, while rotary tools are excellent for intricate shapes. Match the method to your operational capacity and the desired outcome.
Step 3: Evaluate Safety Protocols
Prioritize safety by implementing the appropriate protocols. Carbon fiber dust can be hazardous, leading to respiratory issues and skin irritation. Invest in personal protective equipment (PPE) such as respirators, gloves, and safety goggles. Additionally, ensure proper ventilation and consider using a downdraft table or shop vac to mitigate dust during cutting operations.
Step 4: Research and Select Quality Tools
Selecting high-quality cutting tools is essential for achieving clean cuts and minimizing wear. Look for tools specifically designed for carbon fiber, such as carbide-tipped jigsaw blades or diamond-coated cutting wheels for rotary tools. Quality tools not only enhance performance but also reduce the frequency of replacements, leading to long-term cost savings.
Step 5: Engage with Experienced Suppliers
Establish relationships with reputable suppliers who specialize in carbon fiber cutting tools and equipment. Investigate their product range, customer service, and technical support. Request testimonials or case studies from other businesses in your sector to gauge their reliability and expertise. A knowledgeable supplier can offer insights into the best practices for your specific cutting needs.
Step 6: Test Cutting Techniques
Before committing to a large order, conduct tests with various cutting techniques and tools. This hands-on approach allows you to assess the effectiveness of different methods in your operational context. Pay attention to cut quality, dust generation, and the overall ease of use. Document your findings to inform future procurement decisions.
Step 7: Plan for Maintenance and Upgrades
Consider the long-term maintenance and potential upgrades of your cutting equipment. Regular maintenance extends the lifespan of your tools and ensures consistent performance. Stay informed about advancements in cutting technology that could enhance efficiency or safety in your operations, and plan for periodic upgrades as needed.
By following this practical sourcing checklist, B2B buyers can confidently navigate the complexities of cutting carbon fiber, ensuring both safety and efficiency in their operations.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for best way to cut carbon fiber Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components for Cutting Carbon Fiber?
When analyzing the costs associated with cutting carbon fiber, it’s essential to break down the various components that contribute to the overall cost structure. Key cost components include:
-
Materials: The primary expense is the carbon fiber itself, which varies significantly based on quality and source. Additional materials like cutting blades, PPE, and backing materials also contribute to the costs.
-
Labor: Skilled labor is often required to operate cutting machinery and ensure precision in cuts. Labor costs can vary widely depending on regional wage standards and the complexity of the cutting task.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes costs related to facility maintenance, utilities, and equipment depreciation. A higher volume of cutting may lead to reduced per-unit overhead costs.
-
Tooling: The initial investment in specialized cutting tools can be significant. Tools such as jigsaws, angle grinders, and rotary tools come with varying price points, impacting the overall cost structure.
-
Quality Control (QC): Ensuring the integrity of cut parts often requires additional QC processes, which can add to labor and material costs. Testing for defects or dimensional accuracy is crucial, particularly for industries demanding high precision.
-
Logistics: Transportation of materials and finished products can introduce additional costs, particularly for international buyers. Import duties, shipping fees, and local distribution expenses should be considered.
-
Margin: Suppliers will typically include a margin based on their operational costs and market conditions. Understanding the supplier’s pricing strategy can help buyers negotiate better.
How Do Price Influencers Affect Carbon Fiber Cutting Costs?
Several factors can influence the pricing of carbon fiber cutting services, particularly for international buyers:
-
Volume and Minimum Order Quantity (MOQ): Larger orders often lead to reduced prices per unit. Buyers should inquire about volume discounts and the MOQ to optimize costs.
-
Specifications and Customization: Custom cuts or specialized dimensions can increase costs. Standardized parts generally offer better pricing due to streamlined production processes.
-
Material Quality and Certifications: Higher-quality carbon fiber with certifications (like ISO) typically commands higher prices. Buyers should weigh the benefits of quality against their project requirements.
-
Supplier Factors: The reliability and reputation of suppliers can significantly impact pricing. Established suppliers may charge a premium for their services, but this can be offset by reduced risks and higher quality.
-
Incoterms: Understanding the shipping terms and responsibilities defined by Incoterms can influence overall costs. Buyers should clarify whether prices include shipping, insurance, and duties to avoid unexpected expenses.
What Are the Best Buyer Tips for Cost Efficiency in Carbon Fiber Cutting?
To maximize cost efficiency, B2B buyers should consider the following strategies:
-
Negotiation: Engage suppliers in negotiations to explore pricing flexibility, especially for larger orders. Building long-term relationships can also yield better terms over time.
-
Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Evaluate not just the upfront costs but the entire lifecycle costs associated with the cutting process. This includes maintenance, disposal, and potential rework costs.
-
Pricing Nuances for International Buyers: For buyers from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, understanding local market conditions and supplier capabilities is crucial. Currency fluctuations, import tariffs, and local competition can all impact final pricing.
-
Research and Comparison: Conduct thorough research to compare prices from various suppliers. Online platforms can facilitate price comparisons and provide insights into supplier performance and customer reviews.
Conclusion
Understanding the cost components and pricing dynamics of carbon fiber cutting is essential for international B2B buyers. By focusing on key influencers and employing strategic negotiation and purchasing strategies, buyers can achieve better pricing and ensure their cutting processes align with their operational goals. It’s advisable to continuously monitor market trends and supplier capabilities to adapt to changing conditions and optimize costs.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing best way to cut carbon fiber With Other Solutions
Exploring Alternatives for Cutting Carbon Fiber: A Comprehensive Comparison
When it comes to cutting carbon fiber, selecting the right method is crucial for achieving optimal results. Various techniques exist, each with its unique advantages and drawbacks. This analysis compares the best methods for cutting carbon fiber with alternative solutions, focusing on their performance, cost, ease of implementation, maintenance, and best use cases.
| Comparison Aspect | Best Way To Cut Carbon Fiber | Alternative 1: Laser Cutting | Alternative 2: Waterjet Cutting |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | High precision and clean cuts | Exceptional accuracy and speed | Good precision with minimal waste |
| Cost | Low initial investment | Higher capital and operating costs | Moderate to high costs, depending on setup |
| Ease of Implementation | Requires basic tools | Requires specialized machinery | Requires specialized machinery |
| Maintenance | Low maintenance | High maintenance for equipment | Moderate maintenance required |
| Best Use Case | DIY projects and small batches | Large-scale production and intricate designs | Thick materials and complex shapes |
What Are the Pros and Cons of Using Laser Cutting for Carbon Fiber?
Laser cutting is a highly precise method that utilizes focused light beams to cut through materials. Its performance is exceptional, allowing for intricate designs and clean edges. However, the initial investment in laser cutting equipment can be substantial, making it less appealing for smaller operations. Additionally, the machinery requires skilled operators and regular maintenance, which can increase overall operational costs. Laser cutting is best suited for large-scale production where precision and speed are critical.
How Does Waterjet Cutting Compare for Carbon Fiber Applications?
Waterjet cutting employs a high-pressure stream of water, often mixed with abrasive materials, to slice through various materials, including carbon fiber. This method is advantageous due to its ability to handle thick materials and produce minimal waste. The precision is good, but the setup can be costly, and operation requires specialized equipment and trained personnel. Waterjet cutting is ideal for complex shapes and larger batches, making it suitable for industrial applications.
Conclusion: How Should B2B Buyers Choose the Right Carbon Fiber Cutting Solution?
B2B buyers must assess their specific needs when selecting a cutting method for carbon fiber. For smaller operations or DIY projects, traditional hand tools or rotary tools may suffice, offering low costs and ease of implementation. Conversely, businesses focused on high-volume production or intricate designs should consider investing in laser or waterjet cutting technologies, despite their higher costs and maintenance requirements. Ultimately, the decision should be guided by the scale of production, desired precision, and available budget, ensuring that the chosen method aligns with the operational goals of the business.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for best way to cut carbon fiber
What Are the Key Technical Properties to Consider When Cutting Carbon Fiber?
When engaging in the cutting of carbon fiber, understanding its technical properties is essential for ensuring quality and precision in production. Here are several critical specifications that B2B buyers should be aware of:
-
Material Grade
Carbon fiber is available in various grades, which determine its strength, stiffness, and weight. Higher-grade materials typically provide better performance but come at a higher cost. For instance, aerospace-grade carbon fiber is often used in high-performance applications, while lower grades might suffice for consumer goods. Understanding the grade helps buyers select the appropriate material for their specific applications, ensuring durability and functionality. -
Thickness
The thickness of carbon fiber sheets or rods significantly impacts the cutting method and tools required. Thicker materials may require more robust cutting equipment, while thinner materials might be more susceptible to splintering. Buyers need to match the cutting technique to the material thickness to achieve clean cuts without damaging the fibers. -
Tolerance
Tolerance refers to the allowable variation in dimensions of the cut parts. Tight tolerances are crucial for applications requiring high precision, such as aerospace or automotive components. Understanding the required tolerances helps buyers specify the appropriate cutting methods and equipment that can consistently meet these standards. -
Fiber Orientation
The orientation of the carbon fibers within the material affects its strength and cutting behavior. Cutting against the fiber direction can lead to fraying and a rough finish. Buyers should consider fiber orientation when designing parts to ensure that the cutting process aligns with the material’s structural integrity. -
Epoxy Resin Type
The type of epoxy resin used to bond the carbon fibers influences the cutting process and the potential release of harmful dust. Some resins may become toxic when heated during cutting. Buyers should inquire about the resin type to ensure safe cutting practices and appropriate protective measures. -
Surface Finish
The desired surface finish of the cut edges can dictate the choice of cutting tools and methods. A smooth finish may require additional sanding or polishing, while a rough cut might be acceptable for some applications. By understanding the required surface finish, buyers can select the right cutting techniques to minimize post-processing time.
What Common Trade Terms Should B2B Buyers Know in the Carbon Fiber Cutting Industry?
Familiarity with industry terminology is vital for effective communication and negotiation in B2B transactions. Here are several key terms that buyers should understand:
-
OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
This term refers to companies that produce parts or equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer. In carbon fiber cutting, OEMs often require precise specifications for components, making it crucial for buyers to understand their needs and quality standards. -
MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ is the smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell. Understanding MOQs helps buyers assess their purchasing strategies and budget constraints, especially when sourcing specialized carbon fiber materials or cutting tools. -
RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a document used to solicit price quotes from suppliers. It typically includes detailed specifications, quantities, and delivery requirements. Utilizing RFQs effectively can help buyers secure competitive pricing and ensure that suppliers understand their exact needs. -
Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
Incoterms are a set of predefined commercial terms published by the International Chamber of Commerce that clarify the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in international trade. Familiarity with these terms helps buyers understand shipping responsibilities, insurance, and costs associated with transporting carbon fiber materials. -
Lead Time
Lead time refers to the time taken from placing an order to receiving the goods. Understanding lead times is crucial for buyers to plan their production schedules effectively and ensure timely delivery of carbon fiber components. -
CFR (Cost and Freight)
CFR is an Incoterm indicating that the seller is responsible for the cost of transporting goods to a specified port, while the buyer assumes responsibility once the goods are loaded onto the vessel. Knowing CFR helps buyers evaluate total costs and logistics when importing carbon fiber materials.
By understanding these technical properties and trade terms, B2B buyers can make informed decisions when sourcing and cutting carbon fiber, ultimately leading to improved product quality and operational efficiency.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the best way to cut carbon fiber Sector
What Are the Current Market Dynamics and Key Trends in Cutting Carbon Fiber?
The carbon fiber market is experiencing significant growth, driven by its increasing applications across various industries, including aerospace, automotive, and sporting goods. This demand is largely propelled by the material’s unique properties, such as high strength-to-weight ratio and corrosion resistance. International B2B buyers, particularly in regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, are witnessing a shift towards advanced cutting technologies. Emerging trends include the adoption of automated cutting systems, which enhance precision and reduce waste, alongside the growing popularity of CNC machines for complex shapes and patterns.
Moreover, the sourcing landscape is evolving with a focus on localized supply chains. B2B buyers are increasingly seeking suppliers who can offer shorter lead times and better service, particularly in regions like Brazil and Vietnam where the manufacturing infrastructure is rapidly developing. Additionally, the integration of digital technologies, such as AI and IoT, is transforming traditional processes, enabling real-time monitoring and improved efficiency in cutting operations. As buyers navigate these dynamics, they must stay informed about advancements in cutting tools, safety standards, and best practices to optimize their operations.
How Important Is Sustainability and Ethical Sourcing in the Carbon Fiber Cutting Sector?
Sustainability has become a crucial consideration for B2B buyers in the carbon fiber sector. The environmental impact of carbon fiber production and disposal has led to increased scrutiny from consumers and regulators alike. Businesses are now expected to demonstrate a commitment to sustainable practices, from sourcing raw materials to the cutting and manufacturing processes. Ethical supply chains that prioritize environmentally friendly practices not only enhance brand reputation but also align with the growing consumer demand for sustainable products.
Buyers should look for suppliers that offer ‘green’ certifications and materials, such as recyclable carbon fiber composites or those produced with reduced emissions. The use of water-based adhesives and low-VOC (volatile organic compounds) resins is also gaining traction. By prioritizing sustainability in their sourcing strategies, B2B buyers can mitigate risks related to compliance and market acceptance while contributing to a more sustainable industry.
What Is the Evolution and History of Carbon Fiber Cutting Techniques?
The cutting of carbon fiber has evolved significantly over the past few decades. Initially, rudimentary methods such as hand saws and manual cutting tools were prevalent. However, as the demand for precision and efficiency increased, manufacturers began adopting more advanced techniques. The introduction of rotary tools, jigsaws, and angle grinders marked a turning point, allowing for more intricate designs and faster production times.
With the advent of CNC (Computer Numerical Control) technology, the cutting process has become even more refined. These automated systems enable precise cuts and complex geometries that were previously unattainable. Today’s market offers a range of cutting tools, from diamond-coated blades to specialized jigsaw blades designed specifically for carbon fiber, reflecting the industry’s commitment to innovation and quality. As B2B buyers navigate this landscape, understanding the evolution of cutting techniques can inform their purchasing decisions and operational strategies.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of best way to cut carbon fiber
-
How do I ensure a clean cut when working with carbon fiber?
To achieve a clean cut in carbon fiber, proper preparation and technique are essential. Use a high-quality cutting tool suitable for carbon fiber, such as a jigsaw with a specialized blade or a rotary tool with a diamond-coated wheel. Ensure you use a backing material to prevent splintering and apply masking tape over the cut line for better accuracy. Always prioritize safety by wearing protective gear to minimize exposure to carbon dust. -
What is the best tool for cutting carbon fiber sheets?
The best tool for cutting carbon fiber sheets depends on the thickness and complexity of the cut. For straight cuts, a jigsaw with a carbide blade or a hacksaw with a fine-toothed blade works well. For intricate shapes, a rotary tool with a diamond blade is recommended. Always ensure the chosen tool is appropriate for the task to avoid damaging the material and to achieve precise cuts. -
How should I handle and store carbon fiber materials?
Carbon fiber materials should be handled with care to avoid damage. Store them in a cool, dry place away from direct sunlight to prevent degradation of the epoxy resin. Use protective covers or bags to prevent dust accumulation and physical damage. When handling, wear gloves to avoid skin irritation from carbon dust and ensure proper ventilation in your workspace to manage airborne particles. -
What are the safety considerations when cutting carbon fiber?
Safety is paramount when cutting carbon fiber due to the release of fine dust that can irritate the skin and respiratory system. Always wear protective gloves, a dust mask or respirator, safety goggles, and long-sleeved clothing. Use tools with dust collection systems, such as a downdraft table or a shop vacuum, to minimize airborne particles. Ensure your workspace is well-ventilated to further reduce health risks. -
What is the minimum order quantity (MOQ) for carbon fiber cutting tools?
The MOQ for carbon fiber cutting tools can vary significantly by supplier and region. Typically, it ranges from a few units to several dozen, depending on the manufacturer’s capabilities and market demand. When sourcing tools, inquire about bulk purchasing options to negotiate better pricing and to ensure you have the necessary equipment for your projects. -
How can I vet suppliers for carbon fiber cutting tools?
To effectively vet suppliers for carbon fiber cutting tools, consider their industry reputation, product quality, and customer reviews. Request product samples to assess quality firsthand and verify their certifications and compliance with international standards. Engage in direct communication to evaluate their responsiveness and support, and inquire about their logistics capabilities to ensure timely delivery. -
What payment terms should I expect when purchasing carbon fiber products internationally?
Payment terms for international purchases of carbon fiber products typically include options like letter of credit, wire transfer, or payment upon delivery. Expect to negotiate terms based on your relationship with the supplier and the order size. It’s advisable to establish clear terms upfront to avoid any misunderstandings and to protect your investment. -
How do I manage logistics when importing carbon fiber materials?
Managing logistics for importing carbon fiber materials involves selecting reliable freight forwarders with experience in handling composite materials. Understand the customs regulations in your country and ensure all documentation is accurate and complete. Consider using incoterms to define responsibilities for shipping, insurance, and duties. Regular communication with your supplier and logistics provider is crucial to ensure timely delivery and compliance with international shipping standards.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.
Top 6 Best Way To Cut Carbon Fiber Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. Reddit – Carbon Frame Cutting Methods
Domain: reddit.com
Registered: 2005 (20 years)
Introduction: Carbon frames are typically cut on a CNC milling machine. Alternative methods include using a bandsaw or Dremel, but these can create harmful carbon fiber dust. Wire cutters are not suitable as they will damage the edges. It’s advised to use protective gear due to the carcinogenic nature of carbon fiber dust. For DIY enthusiasts, pre-cut frames or professional cutting services like cncdrones or se…
2. Dragonplate – Carbon Fiber Cutting Tools
Domain: dragonplate.com
Registered: 2003 (22 years)
Introduction: Dragonplate’s Carbon Fiber products are easy to cut with the right tools. Recommended tools include: bandsaw, scrollsaw, jigsaw, table saw with fine-tooth carbide blade, CNC router with carbide bit, Dremel tool, hacksaw with fine-grit blade, coping saw, angle grinder, and jigsaw with tungsten carbide blade. For CNC cutting, use a 1/8″ Burr Style Solid Carbide Downcut Bit. Spindle speed and cutting…
3. RC Groups – Carbon Fiber Cutting Tools
Domain: rcgroups.com
Registered: 2001 (24 years)
Introduction: 1/16″ thick carbon fiber plate; recommended cutting tools include solid carbide end mills with Ti coating, Dremel carbide grit bits, and diamond-studded cutting tools; safety precautions include wearing a dust mask, eye protection, and using a vacuum to manage dust; cutting methods suggested include using a Sherline mill, scroll saw, or wet tile saw with diamond blades; emphasis on avoiding overhe…
4. Flite Test – Carbon Fiber Rods
Domain: flitetest.com
Registered: 2010 (15 years)
Introduction: Carbon fiber rods up to about 4mm in diameter; cutting method involves using a sharp razor blade and a wet paper towel to minimize dust; recommended sanding with 300-grit paper for a smooth finish.
5. Oyiiy – Carbon Fiber Sheets 100% 3K Laminate
Domain: rocketryforum.com
Registered: 2001 (24 years)
Introduction: Carbon Fiber Sheets: 1. 0.5mm 200x300mm 100% Carbon Fiber Sheet Laminate Plate Panel 3K Twill Matte Finish Black – $14.99 2. Oyiiy 600X500X0.5MM, 1.0MM, 1.5MM, 2.0MM, 2.5MM, 3.0MM, 3.5MM, 4.0MM, 4.5MM, 5.0MM, 6.0MM, 7.0MM, 8.0MM, 10.0MM Carbon Fiber Sheets 100% 3K Carbon Fiber Laminate Plate Twill Weave Panel Sheet – $52.98 3. HHIP 4002-0018 R8 SHANK FLY CUTTER WITH 2-1/2″ HEAD, 5/16″ Tool Bit – $…
6. Easy Composites – Essential Tools & Equipment
Domain: easycomposites.co.uk
Registered: 2009 (16 years)
Introduction: Tools & Equipment: 1. SET-8C Perma-Grit Set of 8 Hand Tools in a Wallet Coarse – £74.99 each 2. SB280 Perma-Grit Sanding Block Large – £25.83 each 3. RD3 19mm + 32mm Cutting Discs with Arbor – £17.49 each 4. PP-SGL Safety Glasses – £4.75 each 5. JSB1 Perma-Grit Bosch/Makita Jigsaw Blade – £4.38 each 6. PP-P2 P2 Valved Moulded Disposable Respirator – £2.95 each 7. PP-SGG Safety Goggles – £3.75 each…
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for best way to cut carbon fiber
The effective cutting of carbon fiber requires a combination of the right tools, safety precautions, and techniques tailored to specific applications. International B2B buyers should consider investing in both manual and powered cutting tools, such as hacksaws, jigsaws, and angle grinders, ensuring they select blades designed specifically for carbon fiber to achieve optimal results. Additionally, prioritizing safety with proper personal protective equipment (PPE) is critical to mitigate health risks associated with carbon fiber dust.
Strategic sourcing plays a pivotal role in this process. By establishing relationships with reliable suppliers who provide high-quality cutting tools and materials, businesses can enhance their operational efficiency and reduce costs in the long term. Furthermore, focusing on local suppliers can help buyers in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe minimize logistics challenges while supporting regional economies.
As the demand for carbon fiber continues to rise across various industries, now is the time for B2B buyers to refine their cutting practices and establish robust sourcing strategies. By doing so, they can position themselves for success in a competitive market while contributing to sustainable manufacturing practices. Engage with trusted suppliers today to explore the latest innovations in carbon fiber cutting solutions.