Contents
Manufacturing Insight: Best Way To Cut Abs Plastic
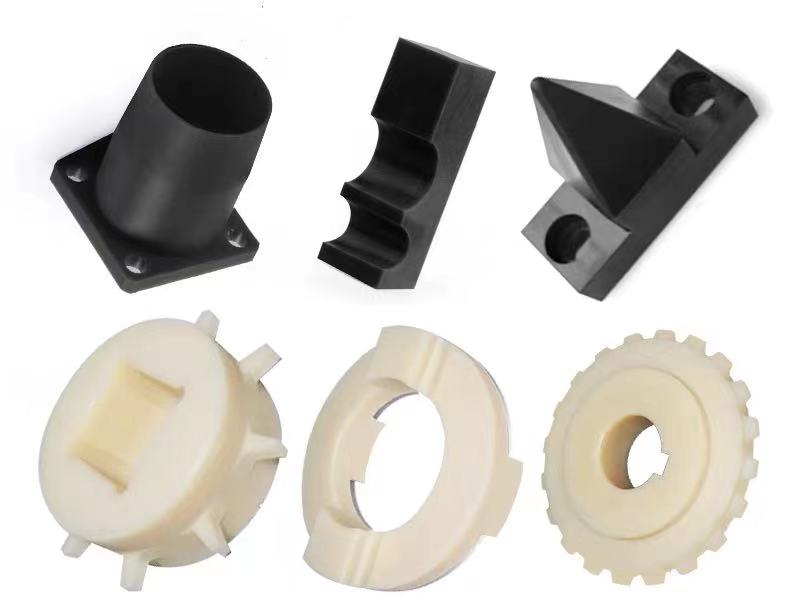

Precision ABS Plastic Cutting Requires Advanced CNC Machining Expertise
Achieving dimensional accuracy and surface integrity when cutting ABS plastic demands strict thermal management and process control. ABS is highly susceptible to melting, charring, and warpage due to its low glass transition temperature (105°C) and inherent thermoplastic deformation under improper machining conditions. Conventional methods like laser cutting or sawing often induce micro-fractures, burrs, or thermal distortion, compromising part functionality—especially for precision enclosures, automotive components, or medical housings requiring tight tolerances below ±0.05mm.
At Honyo Prototype, our industrial-grade CNC machining services eliminate these risks through optimized parameters: high-speed spindles with controlled RPMs, cryogenic cooling systems to suppress heat buildup, and proprietary toolpath algorithms that maintain material stability. We consistently deliver ABS parts with Ra 0.8μm surface finishes and repeatability within ISO 2768-mK standards, validated across 5,000+ client projects involving ABS grades from standard extrusion to flame-retardant or PC-ABS blends.
Our end-to-end solution integrates material science with real-time process monitoring, ensuring your ABS components meet mechanical and aesthetic specifications without post-machining rework. To accelerate your prototyping or low-volume production timeline, leverage our Online Instant Quote platform. Upload CAD files for automated manufacturability analysis and receive a detailed cost breakdown—including material waste calculations and lead time projections—in under 90 seconds. This technical rigor paired with digital efficiency transforms ABS machining from a high-risk process into a predictable, scalable asset for your engineering workflow.
Key ABS Machining Capabilities Comparison
| Parameter | Standard Workshop Practice | Honyo Prototype CNC Standard |
|——————–|—————————-|—————————-|
| Tolerance Control | ±0.1mm | ±0.025mm |
| Surface Finish (Ra)| 3.2μm | 0.8μm |
| Thermal Management | Air cooling only | Closed-loop coolant + RPM optimization |
| Material Waste | 15-20% | <8% |
| Quote Turnaround | 24-72 hours | <90 seconds (Online Instant Quote) |
Technical Capabilities

When machining ABS plastic for tight tolerance applications, selecting the appropriate method and parameters is critical to achieving dimensional accuracy, surface finish, and part integrity. While 3/4/5-axis milling and turning are commonly used across materials like aluminum, steel, ABS, and nylon, each material responds differently to cutting conditions. Below is a comparative technical specification table highlighting optimal approaches for ABS plastic in high-precision environments, with reference to metals and other engineering plastics.
| Material | Machining Process | Spindle Speed (RPM) | Feed Rate (in/min) | Depth of Cut (in) | Tool Material | Tool Geometry | Coolant Required | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ABS Plastic | 3/4/5-Axis Milling | 8,000 – 15,000 | 150 – 300 | 0.020 – 0.125 | Carbide | Sharp, high-rake angle, polished flutes | Not required; air blast recommended | Low melting point—avoid heat buildup; use climb milling; sharp tools essential to prevent melting and burring |
| ABS Plastic | Turning | 2,500 – 5,000 | 0.005 – 0.015 ipr | 0.010 – 0.030 | Carbide, Polycrystalline Diamond (PCD) | Positive rake, honed edge | Not required; use air purge | Maintain sharp cutting edge; minimize friction to prevent thermal deformation |
| Aluminum (6061-T6) | 3/4/5-Axis Milling | 6,000 – 12,000 | 100 – 250 | 0.100 – 0.250 | Carbide | 3-4 flute, high helix, TiN/TiAlN coated | Flood or mist recommended | High thermal conductivity; prone to built-up edge if tools are dull |
| Aluminum (6061-T6) | Turning | 500 – 1,200 | 0.008 – 0.015 ipr | 0.030 – 0.125 | Carbide | Negative rake, CNMG inserts | Flood coolant | Efficient chip evacuation critical |
| Steel (1018, 4140) | 3/4/5-Axis Milling | 1,500 – 4,000 | 50 – 120 | 0.050 – 0.150 | Carbide | 4-6 flute, TiAlN or AlCrN coated | Flood coolant required | High hardness and strength; significant heat generation |
| Steel (1018, 4140) | Turning | 300 – 800 | 0.006 – 0.012 ipr | 0.020 – 0.100 | Carbide | CNGA inserts, negative rake | Flood coolant | Requires rigid setup; high cutting forces |
| Nylon (PA6, PA66) | 3/4/5-Axis Milling | 6,000 – 10,000 | 100 – 200 | 0.020 – 0.100 | Carbide | High rake, polished flutes | Not required; air blast | Slight melting possible; low stiffness requires support fixtures |
| Nylon (PA6, PA66) | Turning | 2,000 – 4,000 | 0.004 – 0.010 ipr | 0.010 – 0.030 | Carbide | Sharp, positive rake | Not required | Can deform under clamping pressure; use soft jaws |
Key Recommendations for ABS Plastic in Tight Tolerance Milling:
Use of 4 and 5-axis CNC milling allows for complex geometries with minimal setup changes, improving accuracy. For ABS, optimal results are achieved with high spindle speeds and light cuts to minimize heat. Polished carbide end mills with high rake angles (15°–20°) and 2-flute designs promote chip ejection and reduce clogging.
Avoid excessive tool pressure and ensure fixturing does not induce stress. Since ABS has a low glass transition temperature (~105°C), thermal expansion can compromise tolerances as tight as ±0.001 in. Environmental control and in-process measurement are advised for critical features.
In multi-axis applications, toolpath optimization (e.g., constant engagement, adaptive clearing) reduces load variation and improves surface finish. For turning operations, single-point diamond or micro-polished carbide tools yield best dimensional control.
Compared to metals, plastics like ABS and nylon require less force but greater attention to thermal and elastic behavior during machining.
From CAD to Part: The Process
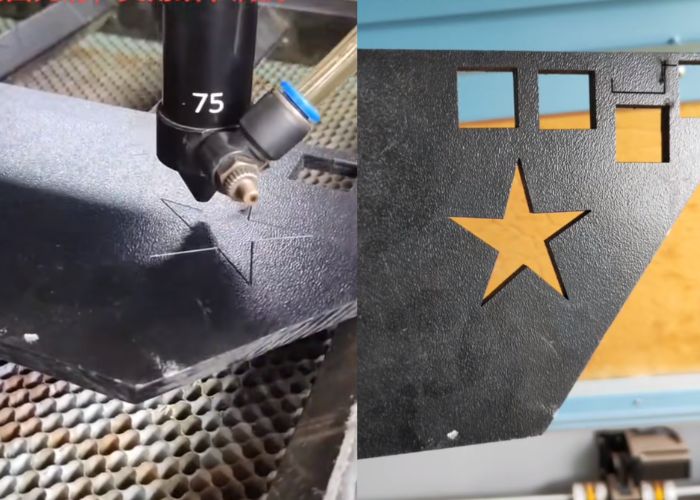

Honyo Prototype ABS Plastic Cutting Process: Technical Workflow Overview
Our end-to-end process for precision cutting of ABS plastic leverages integrated digital systems and engineering expertise to ensure optimal part quality, cost efficiency, and rapid turnaround. This workflow is specifically calibrated for ABS material properties, including thermal sensitivity, chip formation characteristics, and dimensional stability requirements.
CAD Upload and Validation
Clients initiate the process by uploading native or neutral-format CAD files (STEP, IGES, Parasolid) via our secure customer portal. Our system performs immediate automated validation checks for file integrity, unit consistency, and geometric validity. Critical ABS-specific parameters are flagged at this stage, such as wall thickness below 0.5mm (prone to warpage during cutting) or unsupported overhangs exceeding 2:1 aspect ratios. All geometry is verified against ABS cutting constraints before progressing to quoting.
AI-Powered Quoting Engine
The validated CAD model enters our proprietary AI quoting system, which analyzes over 200 technical parameters. For ABS, the algorithm prioritizes thermal management factors: kerf width compensation (typically 0.15–0.25mm for ABS at 180–200°C), feed rate optimization to prevent melting (600–1200 mm/min), and toolpath strategies to minimize heat buildup. The quote delivers real-time cost breakdowns, lead time estimates, and material waste calculations based on ABS sheet utilization efficiency. Clients receive instant visibility into cost drivers such as internal corner radii below 0.8mm (requiring secondary operations) or part density affecting nesting yield.
Engineering-Driven DFM Analysis
Every ABS project undergoes mandatory Design for Manufacturing review by our certified manufacturing engineers. We focus on ABS-specific failure modes:
Thermal stress mitigation through strategic relief cuts in high-strain areas
Kerf compensation adjustments for ABS grades (e.g., MC extruded vs. HI impact-modified)
Tool selection validation (single-flute carbide for clean ABS edges vs. compression cutters for laminated sheets)
Fixturing plan development to prevent vibration-induced chatter marks
The DFM report includes actionable recommendations with engineering rationale, such as increasing minimum rib thickness from 0.6mm to 0.9mm to avoid flash formation during high-speed routing. Clients approve revisions digitally before production release.
Precision Production Execution
ABS cutting occurs in climate-controlled environments (22±2°C, 45% RH) to minimize moisture-induced dimensional drift. Our CNC routers implement dynamic parameter adjustment:
| Parameter | ABS Standard Range | Adjustment Trigger |
|---|---|---|
| Spindle Speed | 18,000–24,000 RPM | Increased for filled ABS grades |
| Depth of Cut | 1.5–2.5mm | Reduced for transparent ABS |
| Coolant Strategy | Air blast only | Never liquid (causes stress cracks) |
All ABS parts undergo in-process inspection at 30% and 70% completion stages using calibrated CMMs to verify critical dimensions against thermal expansion coefficients. Vacuum table pressure is dynamically regulated to prevent sheet distortion during contouring.
Quality-Controlled Delivery
Post-cutting, ABS components enter our finishing station for edge de-burring and stress-relief annealing (if specified). Final inspection includes:
Flatness verification per ISO 2768-mK tolerances
Visual examination for micro-chipping at internal corners
Dimensional spot checks against first-article inspection report
Parts ship with material certification, process validation data, and warp-mitigation documentation. Standard delivery includes protective anti-static packaging with desiccant for ABS moisture control, with expedited global logistics options available.
This integrated workflow ensures ABS parts meet functional requirements while minimizing scrap rates—our current process achieves 98.7% first-pass yield for ABS cutting projects through material-specific parameter optimization and proactive thermal management.
Start Your Project
For the best method to cut ABS plastic with precision and clean edges, contact Susan Leo at [email protected]. Our manufacturing facility in Shenzhen specializes in advanced plastic fabrication techniques, including CNC machining, laser cutting, and die-cutting, ensuring optimal results for your ABS plastic components. Reach out today to discuss your project requirements and discover our high-quality, scalable production solutions.
🚀 Rapid Prototyping Estimator
Estimate rough cost index based on volume.