Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for best way to cut 1 8 aluminum
In today’s competitive global market, sourcing the best way to cut 1/8 aluminum can pose significant challenges for B2B buyers. Factors such as precision, production volume, and cost-effectiveness play a crucial role in determining the most suitable cutting method for your specific needs. This guide delves into various cutting techniques, including laser cutting, water jet cutting, and CNC machining, providing insights into their respective advantages and limitations. Whether you’re fabricating components for aerospace, automotive, or construction applications, understanding these options is essential for optimizing production processes.
Additionally, the guide addresses key considerations for international buyers, including how to vet suppliers, assess material quality, and navigate logistics across diverse markets in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, including regions like Saudi Arabia and Nigeria. By equipping you with comprehensive knowledge about cutting methods, material properties, and supplier landscapes, this guide empowers you to make informed purchasing decisions that align with your operational goals. Ultimately, our aim is to help you streamline your manufacturing processes while ensuring high-quality outcomes that meet both industry standards and your specific project requirements.
Understanding best way to cut 1 8 aluminum Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Laser Cutting | High precision, minimal thermal distortion | Aerospace, automotive, electronics | Pros: Clean edges, tight tolerances. Cons: Higher cost, requires specialized equipment. |
| Water Jet Cutting | No heat-affected zone, versatile for various materials | Custom fabrication, prototyping | Pros: Excellent for thicker materials, no thermal damage. Cons: Slower than laser cutting, more expensive. |
| CNC Router Cutting | Computer-controlled, suitable for complex shapes | Signage, custom parts manufacturing | Pros: Versatile for different designs, cost-effective for larger runs. Cons: Edges may require finishing, slower than laser/water jet. |
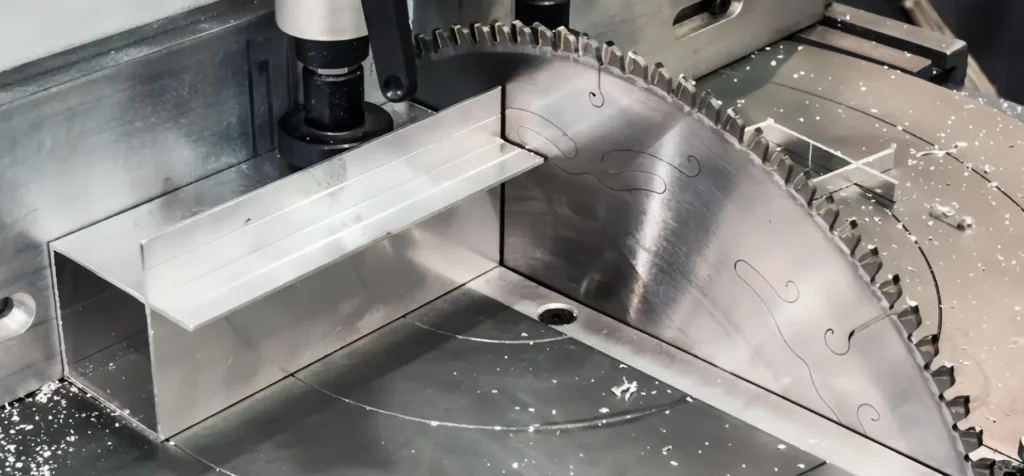
| Band Saw Cutting | Manual or automatic, effective for straight cuts | Metalworking, DIY projects | Pros: Affordable, straightforward operation. Cons: Less precise than other methods, may require deburring. |
| Shearing | Straight-line cuts, minimal distortion | Sheet metal fabrication, HVAC | Pros: Fast, clean cuts with minimal setup. Cons: Limited to specific shapes, not suitable for intricate designs. |
What Are the Key Characteristics of Laser Cutting for 1/8 Aluminum?
Laser cutting is known for its high precision and ability to produce intricate designs without significant thermal distortion. This method is particularly suitable for industries such as aerospace and automotive, where tight tolerances are crucial. B2B buyers should consider the initial investment in laser cutting technology, as it can be higher than other methods. However, the quality of the cut can often justify the cost, especially for high-volume production runs.
How Does Water Jet Cutting Compare for 1/8 Aluminum Applications?
Water jet cutting is unique in that it uses a high-pressure stream of water mixed with abrasive materials to cut through aluminum. This method is advantageous because it does not introduce heat, preventing any thermal damage to the material. It is commonly used in custom fabrication and prototyping, where material integrity is vital. B2B buyers should note that while water jet cutting is effective for thicker materials, it may come at a higher operational cost and slower processing time compared to laser cutting.
What Are the Benefits of CNC Router Cutting for 1/8 Aluminum?
CNC router cutting utilizes computer numerical control to achieve precise cuts, making it ideal for creating complex shapes and designs. This method is widely used in signage and custom parts manufacturing. For B2B buyers, CNC routers can be a cost-effective solution for larger production runs. However, it is important to consider that the edges might require additional finishing work, which can increase the overall production time and cost.
Why Choose Band Saw Cutting for 1/8 Aluminum Projects?
Band saw cutting is a practical choice for manual or automated operations, particularly for straightforward, straight cuts. This method is frequently employed in metalworking and DIY projects due to its affordability and ease of use. B2B buyers should be aware that while band saws are cost-effective, they may not achieve the same level of precision as other cutting methods. Additionally, post-cutting processes like deburring may be necessary to achieve a clean finish.
When Is Shearing the Best Option for Cutting 1/8 Aluminum?
Shearing is a fast and efficient method for producing straight-line cuts with minimal distortion. This technique is commonly used in sheet metal fabrication and HVAC applications. For B2B buyers, the speed and cleanliness of shearing can significantly reduce production time. However, it is important to note that shearing is limited to specific shapes and may not be suitable for intricate designs, which could restrict its applicability in more complex projects.
Key Industrial Applications of best way to cut 1 8 aluminum
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of best way to cut 1 8 aluminum | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Aerospace | Fabrication of structural components for aircraft | Lightweight, high-strength parts enhance fuel efficiency | Suppliers should have certifications (e.g., ISO 9001, AS9100) and experience with aerospace standards. |
| Automotive | Production of custom intercooler end tanks | Improved engine performance through optimized airflow | Look for vendors with capabilities in precision cutting and welding, and compliance with automotive regulations. |
| Construction | Manufacturing of aluminum framing for buildings | Durable and lightweight structures reduce overall costs | Ensure sourcing partners can provide custom sizes and have experience in construction applications. |
| Electronics | Creation of enclosures for electronic devices | Enhanced protection for sensitive components | Suppliers must offer cutting methods that minimize cosmetic damage and ensure precision for electronics fit. |
| Marine | Production of boat components and fittings | Corrosion-resistant parts improve longevity in marine environments | Consider suppliers with expertise in marine-grade materials and cutting techniques that prevent warping. |
In the aerospace industry, the cutting of 1/8 aluminum is crucial for creating lightweight structural components. These parts must meet stringent safety and performance standards, making precision cutting vital. Suppliers in this sector should have relevant certifications, such as AS9100, and demonstrate experience in aerospace manufacturing to ensure compliance with industry regulations.
For the automotive sector, the fabrication of custom intercooler end tanks from 1/8 aluminum enhances engine performance by optimizing airflow. Precision cutting methods like laser or water jet are often preferred to maintain tight tolerances. B2B buyers should prioritize suppliers with advanced cutting capabilities and familiarity with automotive industry standards to ensure high-quality results.
In construction, aluminum framing made from 1/8 aluminum provides a lightweight, durable option for building structures. This material reduces overall construction costs while maintaining structural integrity. Buyers should seek suppliers capable of providing custom sizes and shapes, as well as experience with construction applications to meet specific project needs.
The electronics industry benefits from the precision cutting of 1/8 aluminum for enclosures that protect sensitive components. Minimizing cosmetic damage during the cutting process is essential to ensure the aesthetic quality of the final product. Buyers should focus on sourcing partners that use advanced cutting technologies and have a proven track record in electronics manufacturing.
Finally, in the marine sector, the production of boat components from 1/8 aluminum is vital due to its corrosion-resistant properties. This ensures that parts can withstand harsh marine environments, enhancing the longevity of vessels. Buyers should consider suppliers experienced in marine applications and capable of employing cutting techniques that prevent warping and maintain structural integrity.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘best way to cut 1 8 aluminum’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Navigating High Cutting Costs for Low Production Runs
The Problem: B2B buyers often face the challenge of cutting 1/8 aluminum sheets for low production runs. Traditional cutting methods, such as laser cutting or water jet cutting, can be prohibitively expensive for small quantities, leading to budget constraints that impact overall project viability. This is particularly relevant for companies in regions with limited access to specialized equipment or service providers, where high shipping costs can further exacerbate the financial strain.
The Solution: To address this issue, B2B buyers should consider investing in more versatile, cost-effective tools that can accommodate low-volume production. A portable CNC router or a quality bandsaw designed for metal cutting can be a practical solution. These machines allow for greater flexibility in production volume while maintaining precision. Additionally, companies can explore partnerships with local fabrication shops that offer affordable cutting services for small quantities. Establishing a network of reliable service providers can help mitigate costs, allowing buyers to leverage their capabilities without incurring the overhead of owning expensive equipment.
Scenario 2: Achieving Precision Cuts Without Compromising Quality
The Problem: Precision is paramount when cutting 1/8 aluminum, especially for applications that require tight tolerances, such as components for machinery or custom fabrication. Buyers may struggle to find cutting methods that yield clean, burr-free edges, as rough edges can lead to additional finishing processes, increasing time and costs. This issue is particularly acute for businesses that require aesthetic quality alongside functional precision, such as those in the automotive or aerospace industries.
The Solution: One effective approach is to utilize a CNC plasma cutter or a water jet cutting service, both of which are known for their high precision and minimal heat-affected zones. These cutting methods ensure clean edges and reduce the need for secondary finishing processes. Buyers should also consider specifying the right cutting parameters, such as feed rates and cutting speeds, when working with service providers to optimize for quality. Collaborating with suppliers who understand the nuances of aluminum cutting can lead to better outcomes. Additionally, establishing clear specifications and tolerances in contracts can help ensure that the final product meets the required standards without compromise.
Scenario 3: Managing Equipment Limitations in Diverse Markets
The Problem: For B2B buyers in emerging markets or regions with limited industrial infrastructure, accessing advanced cutting equipment can be a significant barrier. Many companies may rely on outdated machinery or lack the expertise to operate sophisticated tools, leading to inconsistent quality and productivity challenges. This situation can be particularly frustrating for buyers in industries that depend on timely delivery and adherence to stringent quality standards.
The Solution: Buyers should explore alternative cutting methods that do not require heavy machinery but still deliver quality results. Handheld electric shears or specialized metal snips can be effective for smaller jobs and are often more accessible. Additionally, buyers can invest in training programs for their staff to enhance skills in using available equipment more effectively. Establishing relationships with local technical colleges or vocational training centers can provide valuable resources. Moreover, seeking out regional suppliers who offer equipment rental or leasing options can be a viable solution, allowing businesses to access advanced tools without the burden of outright purchase. By leveraging local resources and training, companies can improve their cutting capabilities while navigating equipment limitations.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for best way to cut 1 8 aluminum
When considering the best methods to cut 1/8″ aluminum, it is essential to evaluate the materials and tools that will ensure precision, efficiency, and suitability for various applications. Here, we analyze several common materials and their properties, pros and cons, and implications for international B2B buyers.
What Are the Key Properties of Aluminum for Cutting?
Aluminum, particularly the 6061 and 5052 alloys, is favored for its lightweight, corrosion resistance, and excellent machinability. These alloys are often used in applications requiring good mechanical properties and weldability. The ability to anodize aluminum further enhances its surface finish and durability, making it ideal for various industrial applications.
Which Tools Are Best for Cutting 1/8″ Aluminum?
-
Laser Cutting
– Key Properties: High precision, minimal heat-affected zone.
– Pros: Produces clean edges, suitable for intricate designs, and requires minimal post-processing.
– Cons: Higher operational costs and requires specialized equipment.
– Impact on Application: Ideal for complex shapes and tight tolerances, often used in aerospace and automotive sectors.
– Considerations for International Buyers: Compliance with international standards (e.g., ISO) is crucial, especially in regions like Europe where quality assurance is stringent. -
Water Jet Cutting
– Key Properties: Cold cutting process that does not alter the material properties.
– Pros: Versatile, can cut through various materials, and leaves no heat-affected zone.
– Cons: Slower than laser cutting and may require more maintenance.
– Impact on Application: Suitable for thicker materials and complex shapes, commonly used in manufacturing and construction.
– Considerations for International Buyers: Availability of water jet services may vary; thus, sourcing local suppliers in regions like Africa and South America can be beneficial. -
CNC Router
– Key Properties: Versatile and programmable for various cuts.
– Pros: Cost-effective for low production runs and allows for detailed customization.
– Cons: Edges may require additional finishing, and setup time can be lengthy.
– Impact on Application: Useful for signage and decorative applications where edge finish is less critical.
– Considerations for International Buyers: Ensuring compatibility with local power supplies and software standards is essential, particularly in emerging markets. -
Band Saw
– Key Properties: Good for straight cuts and thicker materials.
– Pros: Relatively inexpensive and easy to operate.
– Cons: Limited to straight cuts and may produce rough edges requiring deburring.
– Impact on Application: Best for bulk cutting and fabrication processes where precision is less critical.
– Considerations for International Buyers: Availability of parts and maintenance services in local markets should be assessed to avoid operational downtimes.
Summary Table of Material Selection for Cutting 1/8″ Aluminum
| Material | Typical Use Case for best way to cut 1/8 aluminum | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Laser Cutting | Aerospace components, intricate designs | High precision, clean edges | Higher operational costs | High |
| Water Jet Cutting | Manufacturing, construction | Versatile, no heat-affected zone | Slower than laser cutting | Medium |
| CNC Router | Signage, decorative applications | Cost-effective for low production runs | Edges may require additional finishing | Medium |
| Band Saw | Bulk cutting, fabrication processes | Inexpensive, easy to operate | Limited to straight cuts, rough edges | Low |
In conclusion, selecting the appropriate cutting method for 1/8″ aluminum involves balancing precision, cost, and application requirements. International B2B buyers should consider local capabilities, compliance with standards, and the specific needs of their projects to make informed decisions.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for best way to cut 1 8 aluminum
What Are the Key Manufacturing Processes for Cutting 1/8″ Aluminum?
When it comes to cutting 1/8″ aluminum, several manufacturing processes are utilized to ensure precision and efficiency. Understanding these processes is crucial for B2B buyers looking to source high-quality aluminum products.
Material Preparation: What Steps Are Involved?
The initial stage of the manufacturing process involves careful material preparation. This includes selecting the appropriate aluminum alloy, with 6061 aluminum being a popular choice due to its excellent machinability and strength. Once the material is selected, it is typically cleaned to remove any contaminants that could affect the cutting process.
During this stage, the aluminum sheets are inspected for defects, ensuring they meet the required specifications. This involves checking for surface imperfections, warping, or other anomalies that could compromise the final product. Proper preparation sets the foundation for a successful cutting operation.
What Cutting Techniques Are Most Effective?
Cutting techniques vary based on the desired finish and production volume. For low production runs with tight tolerances, the following methods are commonly employed:
-
Laser Cutting: This technique is favored for its precision and ability to produce smooth edges without the need for post-processing. High-powered lasers can effectively cut through 1/8″ aluminum sheets, making this a top choice for intricate designs.
-
Water Jet Cutting: Utilizing high-pressure water mixed with abrasives, this method is ideal for thicker materials and provides a clean cut without thermal distortion. It is particularly useful for applications requiring minimal edge finishing.
-
CNC Routing: While CNC routers can handle aluminum cutting, they may not achieve the same edge quality as laser or water jet methods. This technique is more suited for larger sheets and can be cost-effective for medium production runs.
-
Band Saw Cutting: For businesses with smaller operations, a vertical or horizontal band saw can be an economical choice. However, care must be taken to use appropriate blades designed for cutting aluminum to minimize burrs and ensure a clean cut.
-
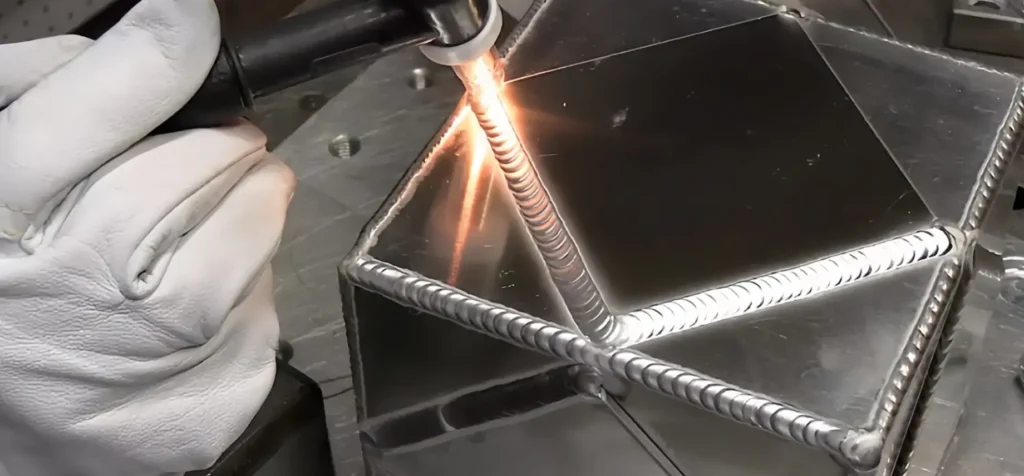
Shearing: This method is often employed for straight cuts, offering a quick and efficient way to cut aluminum sheets. Shearing leaves a clean edge, making it suitable for subsequent welding or assembly.
How is Quality Assurance Implemented in Aluminum Cutting?
Quality assurance is a critical aspect of the manufacturing process, ensuring that products meet international standards and customer specifications.
What International Standards Should Buyers Consider?
B2B buyers should be familiar with relevant international quality standards, such as ISO 9001, which outlines the requirements for a quality management system. Additionally, industry-specific certifications, such as CE marking for European markets or API standards for the oil and gas sector, may be applicable.
What Are the Key Quality Control Checkpoints?
Quality control checkpoints are integral to the manufacturing process and typically include:
-
Incoming Quality Control (IQC): This involves inspecting raw materials upon delivery to ensure they meet specified criteria. Buyers should verify that suppliers conduct thorough IQC checks.
-
In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): Throughout the cutting and finishing processes, regular inspections are conducted to monitor dimensional accuracy and surface quality. This helps identify any deviations from specifications early on.
-
Final Quality Control (FQC): Before products are shipped, a final inspection is conducted to ensure they meet all quality standards. This includes dimensional checks, surface finish evaluations, and functional tests if applicable.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control?
To ensure that suppliers adhere to stringent quality standards, buyers can implement several verification strategies:
-
Supplier Audits: Conducting regular audits of suppliers’ facilities can provide insight into their quality control processes. This includes reviewing their quality management systems and examining their manufacturing practices.
-
Requesting Quality Reports: Suppliers should be able to provide documented evidence of their quality control processes, including inspection reports and compliance certificates. Buyers should request these documents before finalizing any contracts.
-
Third-Party Inspections: Engaging third-party inspection agencies can add an extra layer of assurance. These agencies can perform independent evaluations of the manufacturing processes and product quality, ensuring compliance with relevant standards.
What Are the Quality Control Nuances for International B2B Buyers?
For B2B buyers in regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, understanding the nuances of quality control is essential. Buyers should be aware of local regulations and standards that may differ from international norms.
In regions with less stringent regulations, it is crucial to establish clear quality expectations with suppliers. This may involve setting specific KPIs (Key Performance Indicators) related to defect rates, delivery times, and compliance with industry standards. Additionally, fostering strong communication with suppliers can help address any quality concerns promptly.
Conclusion: Ensuring Quality in Cutting 1/8″ Aluminum
In summary, the manufacturing processes for cutting 1/8″ aluminum involve several key stages, from material preparation to various cutting techniques. Implementing robust quality assurance practices, aligned with international standards, is vital for ensuring product integrity. By understanding these processes and actively verifying supplier quality control measures, B2B buyers can secure high-quality aluminum products that meet their specific needs.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘best way to cut 1 8 aluminum’
In the competitive landscape of metal fabrication, knowing how to effectively cut 1/8″ aluminum can significantly impact production efficiency and cost management. This guide aims to assist B2B buyers in sourcing the best methods and tools for cutting aluminum, tailored to specific needs and production volumes.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Establishing clear technical specifications is crucial for selecting the appropriate cutting method. Consider the intended application of the aluminum parts, required tolerances, and surface finish. For instance, if the parts will be anodized or require laser engraving, smooth edges are essential to minimize post-processing.
Step 2: Assess Production Volume Needs
Identify whether you will need low, medium, or high production runs. For low-volume projects, outsourcing to a local machine shop with capabilities such as laser or water jet cutting might be cost-effective. Conversely, for high-volume production, investing in a CNC router or bandsaw may yield better long-term savings.
Step 3: Evaluate Potential Cutting Methods
Understanding the various cutting methods available can guide you toward the best solution. Common techniques include:
– Laser Cutting: Ideal for intricate designs with tight tolerances, offering clean edges.
– Water Jet Cutting: Suitable for thicker materials and complex shapes, reducing thermal distortion.
– CNC Router: Cost-effective for larger sheets but may require additional finishing work.
Step 4: Research and Select Suppliers
Thoroughly vet suppliers who specialize in aluminum cutting services. Look for companies that have experience with 1/8″ aluminum and can provide case studies or references from similar projects. Consider geographic location as well; local suppliers may reduce shipping costs and lead times.
Step 5: Verify Equipment Capabilities
Before finalizing a supplier, confirm their equipment capabilities. Ensure that they possess advanced machinery, such as a Kern laser or industrial water jet, and understand the materials they work with. Request samples of previous work to assess quality and precision.
Step 6: Request Quotes and Compare Costs
Gather quotes from multiple suppliers to understand the market rates for your project. When comparing quotes, consider not only the price but also the services included, such as finishing options and lead times. This comprehensive analysis will help you make an informed decision.
Step 7: Establish Communication and After-Service Support
Strong communication with your chosen supplier is vital for project success. Discuss timelines, potential challenges, and support options for after-service care. A responsive supplier can provide invaluable assistance, especially if adjustments or re-cuts are needed.
By following this checklist, B2B buyers can confidently navigate the complexities of sourcing the best methods for cutting 1/8″ aluminum, ensuring that their production processes are efficient and cost-effective.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for best way to cut 1 8 aluminum Sourcing
When sourcing cutting solutions for 1/8″ aluminum, understanding the comprehensive cost structure is crucial for B2B buyers, especially in international markets such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. This section delves into the key components influencing costs and pricing, as well as strategic buyer tips for optimizing procurement.
What Are the Key Cost Components for Cutting 1/8″ Aluminum?
-
Materials: The price of 1/8″ aluminum sheets varies based on alloy type, with 6061 aluminum being a popular choice due to its excellent machinability and strength. Buyers should evaluate the market prices for aluminum sheets regularly, as fluctuations can significantly impact overall costs.
-
Labor: Labor costs encompass the expenses associated with the skilled workforce needed to operate cutting machines, such as CNC routers, water jets, or lasers. In regions with lower labor costs, such as parts of Africa or South America, outsourcing cutting tasks may lead to significant savings.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes costs related to facility maintenance, utilities, and equipment depreciation. Buyers should inquire about these overhead costs when assessing suppliers, as they can vary greatly between regions and affect the final price.
-
Tooling: The cost of tools used for cutting aluminum, such as blades for band saws or router bits, must also be factored in. Investing in high-quality tools may incur higher initial costs but can enhance efficiency and reduce waste in the long run.
-
Quality Control (QC): Ensuring precision in cutting 1/8″ aluminum is critical, especially for applications requiring tight tolerances. QC processes may add to the overall cost, but they are essential for maintaining product integrity and minimizing returns or rework.
-
Logistics: Shipping costs can vary significantly based on the distance, mode of transport, and the volume of materials being sourced. International buyers should consider Incoterms that best suit their logistics needs, as they dictate responsibilities for shipping and insurance.
-
Margin: Suppliers will include a margin on top of their costs to ensure profitability. Understanding typical margins in the industry can aid buyers in negotiating better deals.
How Do Price Influencers Affect Sourcing Decisions?
-
Volume and Minimum Order Quantity (MOQ): Larger order volumes typically result in lower per-unit costs. Buyers should assess their needs and consider bulk purchasing to achieve cost savings.
-
Specifications and Customization: Custom cutting services that accommodate specific designs or tolerances may come at a premium. Buyers should weigh the benefits of customization against the additional costs.
-
Material Quality and Certifications: Suppliers offering certified materials may charge more, but these certifications can assure buyers of the quality and reliability of the aluminum.
-
Supplier Factors: The reputation and reliability of the supplier can influence pricing. Established suppliers may charge higher prices, but they often provide better service and quality assurance.
-
Incoterms: Understanding Incoterms is crucial for international buyers. Terms like FOB (Free on Board) or CIF (Cost, Insurance, and Freight) can significantly affect total landed costs.
What Are the Best Buyer Tips for Cost-Efficiency?
-
Negotiate Effectively: Build relationships with suppliers to negotiate better terms. Understanding the supplier’s cost structure can provide leverage in discussions.
-
Consider Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Evaluate not just the purchase price but also the long-term costs associated with maintenance, quality control, and potential wastage.
-
Leverage Local Suppliers: In regions like Africa and South America, local suppliers may offer more competitive pricing due to lower shipping costs and tariffs.
-
Stay Informed on Market Trends: Regularly monitor aluminum prices and market conditions to make informed purchasing decisions.
Disclaimer on Indicative Prices
Prices for cutting 1/8″ aluminum can vary widely based on the factors discussed above. Buyers should conduct thorough market research and obtain multiple quotes to ensure competitive pricing tailored to their specific needs.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing best way to cut 1 8 aluminum With Other Solutions
Introduction
In the realm of manufacturing and fabrication, selecting the right method to cut 1/8″ aluminum is crucial for achieving quality results while optimizing costs and resources. With various cutting technologies available, businesses must evaluate the best solution that aligns with their production needs, budget constraints, and desired outcomes. This analysis compares the conventional cutting methods against alternative solutions, providing B2B buyers with valuable insights to make informed decisions.
Comparison Table
| Comparison Aspect | Best Way To Cut 1/8 Aluminum | Alternative 1: Laser Cutting | Alternative 2: Water Jet Cutting |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | High precision, smooth edges | Exceptional precision, minimal heat-affected zone | Good precision, no heat distortion |
| Cost | Moderate initial investment | Higher initial costs; variable per cut | High operational costs; depends on material thickness |
| Ease of Implementation | Requires skilled operation | Requires skilled operator; setup time needed | Requires specialized equipment; slower setup |
| Maintenance | Moderate; regular tool maintenance | High; requires regular calibration | High; complex machinery maintenance |
| Best Use Case | Prototyping and small runs | High-volume production, intricate designs | Thick materials or complex shapes |
Detailed Breakdown of Alternatives
Laser Cutting
Laser cutting is a popular method for cutting aluminum due to its high precision and ability to create intricate designs with minimal material wastage. This method utilizes focused laser beams, which can cut through various thicknesses of aluminum, including 1/8″. The primary advantage of laser cutting is its speed and accuracy, making it ideal for high-volume production runs. However, the initial investment in laser cutting equipment can be substantial, and operational costs may vary based on the complexity of the designs. Additionally, it requires skilled operators to manage the equipment effectively.
Water Jet Cutting
Water jet cutting employs a high-pressure jet of water, often mixed with abrasives, to cut through materials like aluminum. This method is beneficial for applications where heat distortion must be avoided, as it does not introduce heat to the material being cut. Water jet cutting is versatile and can handle thicker materials, making it suitable for complex shapes and detailed designs. However, the operational costs can be high, particularly for thicker aluminum, and the setup time may delay production. It also requires specialized maintenance, further adding to operational overhead.
Conclusion
Choosing the right method for cutting 1/8″ aluminum hinges on a company’s specific needs, including production volume, budget, and desired precision. While traditional methods such as bandsaw cutting may suffice for low-volume or DIY projects, advanced techniques like laser and water jet cutting offer superior precision and efficiency for larger-scale operations. B2B buyers should carefully assess their production requirements and consider the long-term costs and benefits of each alternative to ensure they select the most appropriate cutting solution for their aluminum fabrication projects.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for best way to cut 1 8 aluminum
What Are the Key Technical Properties to Consider When Cutting 1/8″ Aluminum?
When cutting 1/8″ aluminum, understanding specific technical properties is crucial for ensuring quality and efficiency in production. Here are some essential specifications that B2B buyers should prioritize:
-
Material Grade: The most common aluminum grades for cutting are 6061 and 5052. Grade 6061 is ideal for structural applications due to its strength and weldability, while 5052 offers excellent corrosion resistance. Selecting the right grade affects the cutting method and final product durability.
-
Thickness Tolerance: Tolerance refers to the allowable deviation in thickness from the nominal measurement. For 1/8″ aluminum, maintaining tight tolerances (±0.005″) is critical for applications requiring precise fits, such as automotive parts or custom fabrication. Understanding tolerance requirements helps in choosing the appropriate cutting method.
-
Surface Finish Requirements: The surface finish of cut aluminum affects its aesthetic and functional properties. A smooth finish is often needed for anodizing or painting processes. Different cutting methods produce varying finishes, with laser cutting yielding cleaner edges compared to bandsaw cuts, which may require additional deburring.
-
Heat Affected Zone (HAZ): The heat generated during cutting can alter the material properties in the adjacent areas, known as the heat affected zone. Minimizing HAZ is essential to maintain the integrity and strength of the aluminum. Techniques such as waterjet cutting minimize thermal impact, making them suitable for sensitive applications.
-
Production Volume: The expected production volume influences the choice of cutting method. For low-volume runs, manual methods or CNC routers may suffice, while high-volume production typically necessitates automated solutions like laser cutting or waterjet technology for efficiency and consistency.
-
Lead Time: Understanding lead time is crucial for planning and inventory management. Different cutting methods have varying turnaround times. For instance, laser cutting can quickly produce complex shapes but may require longer setup times compared to simpler methods like shearing.
What Are the Common Trade Terms Used in Aluminum Cutting?
Familiarity with industry terminology is vital for effective communication and negotiation in B2B transactions. Here are several key terms relevant to the cutting of 1/8″ aluminum:
-
OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer): This term refers to companies that produce parts or equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer. Understanding OEM relationships is essential for sourcing quality aluminum components that meet specific standards.
-
MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity): MOQ defines the smallest number of units a supplier is willing to sell. Knowing the MOQ helps buyers assess whether they can meet production needs without incurring excess costs or inventory.
-
RFQ (Request for Quotation): An RFQ is a document sent to suppliers to request pricing, specifications, and terms for the desired products. Utilizing RFQs can help buyers compare options and secure competitive pricing for aluminum cutting services.
-
Incoterms (International Commercial Terms): These are a set of predefined international trade terms that clarify the responsibilities of buyers and sellers regarding shipping, insurance, and tariffs. Understanding Incoterms is crucial for international transactions, ensuring clarity in logistics and cost management.
-
Deburring: This is the process of removing sharp edges or burrs from cut aluminum. It is a critical step to ensure safety and improve the finish of the final product. Knowing about deburring techniques can help in selecting the right cutting method that minimizes post-processing.
-
CNC (Computer Numerical Control): CNC refers to automated cutting machines that use computer programming to control movement. CNC routers and mills are commonly used for precision cutting of aluminum, offering high repeatability and complexity in designs.
By comprehensively understanding these technical properties and trade terms, B2B buyers can make informed decisions about cutting 1/8″ aluminum, ensuring they select the right methods and suppliers to meet their production needs.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the best way to cut 1 8 aluminum Sector
What Are the Global Drivers Influencing the Market for Cutting 1/8 Aluminum?
The market for cutting 1/8 aluminum is shaped by several global drivers, notably the increasing demand for lightweight materials across various industries such as automotive, aerospace, and construction. This trend is particularly pronounced in developing regions like Africa and South America, where infrastructure projects are booming. The proliferation of advanced cutting technologies, including CNC machining, laser cutting, and water jet cutting, is enabling businesses to meet the stringent quality standards required for high-precision applications.
Furthermore, the rise of Industry 4.0 is impacting sourcing trends, as companies increasingly seek automation and integrated systems that enhance efficiency. International buyers are now more inclined to partner with suppliers who can provide not just materials but also cutting services, enabling them to streamline their operations and reduce lead times. This shift towards integrated solutions is particularly relevant in regions like the Middle East, where large-scale projects necessitate rapid and precise fabrication methods.
How Are Sustainability and Ethical Sourcing Impacting the Cutting of 1/8 Aluminum?
Sustainability has become a critical consideration for B2B buyers in the aluminum sector. The environmental impact of aluminum production and processing is significant, making it essential for companies to prioritize ethical sourcing practices. Buyers are increasingly looking for suppliers who demonstrate compliance with environmental regulations and who can provide certifications that indicate sustainable practices, such as recycled aluminum content or energy-efficient manufacturing processes.
Incorporating green certifications into procurement strategies not only minimizes environmental footprints but also enhances brand reputation. As international buyers from regions like Europe and North America demand more transparency in supply chains, the emphasis on ethical sourcing is expected to grow. This trend aligns with global efforts to reduce carbon emissions and promote sustainable industrial practices, making it imperative for suppliers to adapt accordingly.
What Is the Evolution of Cutting Technologies for 1/8 Aluminum?
The evolution of cutting technologies for 1/8 aluminum has been marked by significant advancements over the past few decades. Initially dominated by traditional methods like sawing and shearing, the industry has witnessed a transformative shift towards more sophisticated techniques such as laser and water jet cutting. These modern methods not only enhance precision but also reduce waste, making them more appealing to environmentally-conscious buyers.
As industries continue to innovate, the demand for cutting solutions that can accommodate complex designs and high tolerances has surged. The introduction of CNC machines has further revolutionized the sector, allowing for automated, high-speed cutting that meets the rigorous demands of today’s manufacturing landscape. This evolution reflects a broader trend towards digitalization and automation in manufacturing, which is set to redefine the way aluminum is processed in the future.
What Are the Best Practices for Cutting 1/8 Aluminum in a B2B Context?
For B2B buyers seeking the best practices for cutting 1/8 aluminum, several key considerations should be prioritized. First, understanding the specific requirements of your project—such as tolerances, volume, and finish—will guide the selection of the appropriate cutting method. For low production runs, options like CNC routers or laser cutting services may be most effective, as they provide high accuracy with minimal post-processing.
Additionally, collaborating with local suppliers who possess the latest cutting technology can significantly enhance efficiency. Establishing strong partnerships with vendors that offer integrated services—from material sourcing to cutting and finishing—can streamline operations and reduce costs. Lastly, maintaining a focus on sustainability by choosing suppliers committed to ethical practices will not only align with global standards but also resonate positively with environmentally-conscious consumers.
By navigating these dynamics, international B2B buyers can position themselves advantageously in the competitive landscape of the aluminum sector.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of best way to cut 1 8 aluminum
-
How do I choose the right cutting method for 1/8 aluminum?
Selecting the appropriate cutting method for 1/8 aluminum depends on your production volume, desired edge quality, and available budget. For low-volume production with high precision, laser cutting is ideal due to its clean edges and minimal waste. Water jet cutting is another excellent option, particularly for intricate designs. If you have access to a CNC router, it can be used, although it may require additional deburring. For simpler tasks, a bandsaw or shearing may suffice, especially if aesthetics are less critical. -
What are the advantages of laser cutting for aluminum?
Laser cutting offers several benefits for aluminum fabrication. It provides high precision, allowing for intricate designs and tight tolerances, which is essential for components requiring anodization or engraving. The process minimizes material waste and produces clean edges, reducing the need for further finishing. Additionally, laser cutting can handle various thicknesses, making it versatile for different projects. However, it may require a higher initial investment compared to traditional methods. -
What is the best tool for cutting 1/8 aluminum sheet metal?
The best tool for cutting 1/8 aluminum sheet metal depends on your specific needs. For high-volume production, a CNC laser cutter or water jet is recommended for their precision and efficiency. For smaller projects, a vertical bandsaw equipped with a blade specifically designed for metal cutting can be effective. Alternatively, shearing machines can produce smooth edges with minimal distortion. Each method has its pros and cons, so consider your budget and required output quality when making a choice. -
How can I ensure the quality of my aluminum cuts?
To ensure the quality of your aluminum cuts, it’s crucial to choose the right cutting method and tool. Regular maintenance of cutting equipment is essential to maintain precision. Implementing a quality control process, including inspections of cut edges and dimensions, can help identify issues early. Additionally, consider using high-quality aluminum sheets, as variations in material quality can affect the cutting outcome. Working with experienced suppliers who understand your specifications can also enhance the overall quality. -
What are the typical minimum order quantities (MOQs) for cutting services?
Minimum order quantities (MOQs) for cutting services can vary widely based on the supplier and the complexity of the project. Generally, MOQs can range from a few pieces for small custom jobs to hundreds or thousands for standardized parts. It’s advisable to communicate your specific requirements to potential suppliers to understand their MOQs. Many manufacturers offer flexibility for initial orders, especially for new clients, so don’t hesitate to negotiate terms that suit your business needs. -
What payment terms should I expect when sourcing aluminum cutting services internationally?
Payment terms for international sourcing of aluminum cutting services typically include options like advance payment, partial payment upon order confirmation, and the balance upon delivery. Common methods include wire transfers, letters of credit, or online payment platforms. It’s essential to discuss and agree on payment terms upfront to avoid misunderstandings. Ensure that you consider currency fluctuations and potential transaction fees, especially when dealing with suppliers from different countries. -
How can I vet suppliers for aluminum cutting services?
Vetting suppliers for aluminum cutting services involves several key steps. Begin by researching potential suppliers’ reputations through online reviews and industry forums. Request samples of their work to assess quality and precision. Inquire about their certifications, such as ISO standards, which can indicate their commitment to quality. Additionally, visiting their facility or requesting a virtual tour can provide insights into their operational capabilities and quality control processes. -
What logistics considerations should I keep in mind for international shipments?
When planning international shipments of aluminum cutting services, consider factors such as shipping methods, customs regulations, and lead times. Choose a reliable logistics provider experienced in handling metal products to ensure safe transport. Understand the import/export regulations in your country and the supplier’s country, including tariffs and duties. It’s also wise to factor in potential delays due to customs clearance, so plan your project timelines accordingly to avoid disruptions.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.
Top 7 Best Way To Cut 1 8 Aluminum Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. Welding Web – Aluminum Sheet Cutting Tools
Domain: weldingweb.com
Registered: 2003 (22 years)
Introduction: 1/8″ aluminum sheet metal; recommended cutting methods include: vertical metal bandsaw, table saw, plasma cutter, circular saw with carbide blade, jigsaw, and shearing. Specific products mentioned: Harbor Freight bandsaw, Skil circular saw with 24T carbide blade, and Morse (Metal Devil) blade for aluminum. Additional tips include using beeswax to prevent galling, sandwiching material between plywo…
2. TugNuts – 1/4 Aluminum Plate 12 x 24
Domain: tugnuts.com
Registered: 2007 (18 years)
Introduction: 1/4″ aluminum plate, dimensions: 12″ x 24″, intended to be cut into two 6″ x 24″ pieces.
3. Make It From Metal – Band Saw & Circular Saw
Domain: makeitfrommetal.com
Registered: 2018 (7 years)
Introduction: 1. Band Saw: Ideal for cutting thick aluminum plates (0.5″ or thicker). Recommended blade speed: 250 feet per minute. Ideal TPI for thick aluminum: 10-14. Use coolant or light oil like WD-40 to prevent clogging.
2. Circular Saw: Fast and provides clean cuts. Use carbide teeth blades designed for non-ferrous metals. Recommended to use lubricant (WD-40 or wax sticks) to prevent blade plugging. Can …
4. Garage Journal – Smooth Aluminum Sheet
Domain: garagejournal.com
Registered: 2006 (19 years)
Introduction: 1/8″ thick smooth aluminum sheet, dimensions 30″ x 48″, intended to be cut into 4 pieces of 15″ x 24″ each. The surface is smooth and somewhat polished, matching existing aluminum structures. The cutting tool considered is a 7-1/4″ circular saw with a Diablo blade for aluminum, with concerns about marring the surface during cutting. Alternative methods discussed include using tape for protection a…
5. Carbide 3D – Aluminium Plates & Cutting Tools
Domain: community.carbide3d.com
Registered: 2013 (12 years)
Introduction: Aluminium stock, 500x500mm plates, 12″ x 24″ sheet and plate 6061, 1/8″ and 1/4″ thick pieces, maximum thickness 10mm, normal thickness 5mm, Milwaukee cordless jigsaw with coarse blade (10 TPI), Diablo blade for aluminum, Evolution Rage metal cutting blades, portable handheld bandsaw, drop-type bandsaw, standard bandsaw, metal-cutting bandsaw.
6. Scrollsawer – Aluminum Cutting Techniques
Domain: forum.scrollsawer.com
Registered: 2000 (25 years)
Introduction: Cutting 1/8″ thick soft alloy aluminum requires careful handling and specific techniques. Recommendations include: 1. Use a slow speed on the saw to manage heat buildup. 2. Support the material well to prevent bending. 3. Lubricate the blade with kerosene to prevent rust and reduce friction. 4. Use fine-toothed blades (e.g., 2/0, 3, or 5) for better cutting performance. 5. Consider sandwiching the…
7. Sawzall – Effective Cutting Tool
Domain: chiefdelphi.com
Registered: 1998 (27 years)
Introduction: This company, Sawzall – Effective Cutting Tool, is a notable entity in the market. For specific product details, it is recommended to visit their website directly.
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for best way to cut 1 8 aluminum
The effective cutting of 1/8″ aluminum hinges on understanding the nuances of various techniques and tools available. As highlighted throughout this guide, options such as laser cutting, water jet cutting, and CNC machining are particularly advantageous for achieving precise tolerances and smooth finishes. For businesses looking to maintain quality while controlling costs, partnering with local providers who offer these specialized services can be a strategic advantage.
Moreover, investing in the right equipment, whether it be a bandsaw, table saw, or shearing machine, can significantly impact production efficiency, especially for low to medium volume runs. The importance of selecting the appropriate method cannot be overstated, as it not only affects the quality of the end product but also influences subsequent processes such as anodizing and welding.
As international B2B buyers from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe navigate their sourcing strategies, they should prioritize collaboration with suppliers who understand local market demands and can offer tailored solutions. By leveraging these insights, businesses can streamline their operations, reduce lead times, and enhance product quality. Embrace these strategic sourcing opportunities to stay competitive in the global market and drive growth in your aluminum fabrication projects.