Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for best small cnc mill
Navigating the complexities of sourcing the best small CNC mill can be a daunting task for international B2B buyers, especially in emerging markets such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. With a growing demand for precision machining in various industries, organizations must find reliable suppliers that meet their specific needs while ensuring quality and cost-effectiveness. This guide is designed to empower decision-makers by providing an in-depth analysis of the best small CNC mills available on the market today, focusing on their features, capabilities, and ideal applications.
In this comprehensive resource, we will explore different types of small CNC mills, their diverse applications across sectors, and essential criteria for vetting suppliers. Furthermore, we will address key considerations such as pricing structures, maintenance requirements, and software compatibility. By equipping buyers with actionable insights and expert recommendations, this guide aims to simplify the purchasing process, enabling businesses to make informed decisions that enhance their operational efficiency and competitiveness.
Whether you’re a startup in Brazil looking to develop prototypes or a manufacturing firm in Nigeria seeking to scale production, understanding the nuances of small CNC mills is crucial. Let this guide serve as your roadmap to navigating the global market, helping you identify the best solutions tailored to your unique business challenges.
Understanding best small cnc mill Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
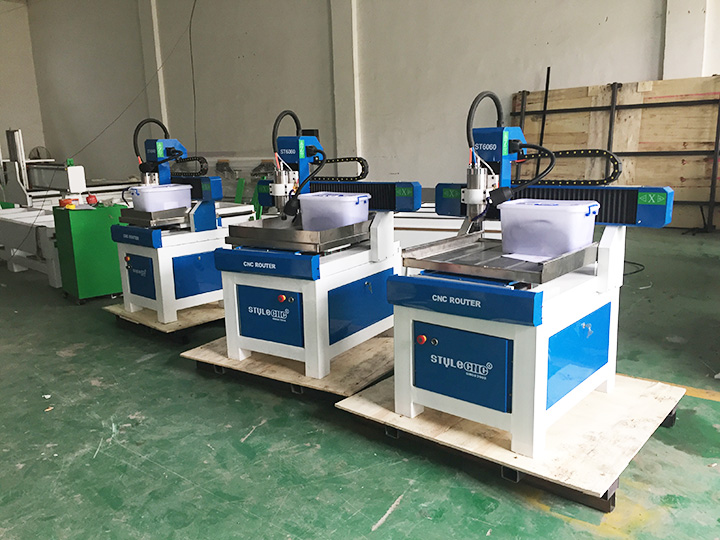
| Desktop CNC Mills | Compact size, user-friendly, suitable for soft materials | Prototyping, small-scale production, education | Pros: Affordable, easy to use; Cons: Limited material options, smaller build volume. |
| 5-Axis CNC Mills | Ability to machine complex geometries, higher precision | Aerospace, automotive, high-tech R&D | Pros: Versatile, high precision; Cons: Higher cost, steeper learning curve. |
| High-Performance CNC Mills | Industrial-grade capabilities in a compact form | Prototyping, small-scale production | Pros: Robust performance, suitable for various materials; Cons: Higher investment required. |
| Multi-Functional CNC Mills | Capable of 3D printing, laser engraving, and milling | Diverse fabrication needs, educational purposes | Pros: Versatile, cost-effective for multi-use; Cons: May require additional attachments, complexity in operation. |
| Entry-Level CNC Mills | Designed for beginners, affordable, basic functionality | Hobbyists, educational institutions | Pros: Low cost, accessible for newcomers; Cons: Limited capabilities, may require upgrades for advanced tasks. |
What are the Characteristics of Desktop CNC Mills?
Desktop CNC mills are compact machines designed for small-scale applications, making them ideal for hobbyists, educational institutions, and small businesses focused on prototyping. They typically handle materials like wood, plastics, and soft metals, offering a user-friendly interface that simplifies the learning curve. When considering a purchase, buyers should evaluate the build volume, spindle speed, and software compatibility to ensure the machine meets their specific needs without overextending their budget.
Why Choose a 5-Axis CNC Mill for Complex Machining?
5-axis CNC mills are distinguished by their ability to machine complex geometries, making them indispensable in industries such as aerospace and automotive. These machines can manipulate parts from multiple angles, enhancing precision and reducing the need for multiple setups. B2B buyers should consider the machine’s capabilities regarding material types, software integration, and cost, as the investment can be significant but often yields higher returns through improved efficiency and quality.
What Makes High-Performance CNC Mills Suitable for Professional Use?
High-performance CNC mills combine industrial-grade capabilities with a compact design, making them suitable for professional workshops and serious hobbyists. They can work with a variety of materials, including steel and aluminum, and are ideal for tasks that require robustness and reliability. Buyers should assess the machine’s specifications against their production needs, as the initial investment can be higher, but the durability and performance often justify the cost over time.
How Do Multi-Functional CNC Mills Enhance Fabrication Capabilities?
Multi-functional CNC mills offer versatility by combining milling, 3D printing, and laser engraving capabilities in one machine. This adaptability is particularly beneficial for small businesses and educational institutions that require a range of fabrication techniques. When purchasing, businesses should consider the machine’s adaptability, available attachments, and the learning curve associated with operating multiple functionalities to maximize their investment.
Why are Entry-Level CNC Mills Ideal for Beginners?
Entry-level CNC mills are specifically designed for newcomers to the CNC machining world. They provide a cost-effective solution for hobbyists and educational institutions, allowing users to learn the basics of CNC milling without significant financial commitment. Buyers should focus on the machine’s ease of use, support resources, and upgrade potential, as these factors can greatly influence the learning experience and future scalability of their operations.
Key Industrial Applications of best small cnc mill
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of best small cnc mill | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Aerospace | Prototyping complex components | Reduces lead time for prototype development and enhances precision | Material compatibility, precision requirements, software integration |
| Automotive | Custom tooling and parts production | Enables rapid production of specialized parts, reducing downtime | Size constraints, material selection, scalability options |
| Electronics | Fabrication of enclosures and PCBs | Increases design flexibility and rapid iteration of prototypes | Software compatibility, precision tolerances, support for multiple materials |
| Education | Teaching CNC machining principles | Provides hands-on experience for students, enhancing skill development | Training resources, ease of use, software accessibility |
| Art and Design | Creating intricate sculptures and installations | Allows for unique designs and customization, enhancing marketability | Material versatility, design software integration, artistic capability |
How is the Best Small CNC Mill Used in Aerospace Applications?
In the aerospace industry, small CNC mills are essential for prototyping complex components like brackets and housings. These machines facilitate the rapid development of high-precision parts, significantly reducing lead times. Buyers in this sector must consider material compatibility, as aerospace applications often require lightweight yet durable materials. Furthermore, precision requirements are critical due to stringent safety standards, making the choice of CNC mill pivotal for compliance and performance.
What Role Does a Small CNC Mill Play in Automotive Manufacturing?
Small CNC mills are increasingly utilized in automotive manufacturing for custom tooling and the production of specialized parts. They enable manufacturers to create intricate designs that enhance vehicle performance while reducing downtime through rapid prototyping. When sourcing these machines, businesses should focus on size constraints and material selection to ensure the mill can handle the specific types of metals and plastics used in automotive applications. Scalability options are also crucial for adapting to changing production demands.
How Can Electronics Manufacturers Benefit from Small CNC Mills?
In the electronics sector, small CNC mills are employed for the fabrication of enclosures and printed circuit boards (PCBs). These mills enhance design flexibility, allowing manufacturers to quickly iterate on prototypes and tailor designs to specific requirements. For international buyers, especially in emerging markets, it is essential to consider software compatibility and precision tolerances, as these factors directly impact production efficiency and product quality. Additionally, support for multiple materials is vital for diverse electronic applications.
Why Are Small CNC Mills Important for Educational Institutions?
Educational institutions leverage small CNC mills to teach students the fundamentals of CNC machining. These machines provide hands-on experience that enhances skill development and prepares students for careers in manufacturing and design. When sourcing CNC mills for educational purposes, institutions should consider training resources and ease of use to facilitate learning. Moreover, software accessibility is crucial for ensuring that students can engage with the technology effectively.
How Do Artists and Designers Use Small CNC Mills?
Artists and designers utilize small CNC mills to create intricate sculptures and customized installations. These machines offer the ability to produce unique designs that can set their work apart in a competitive market. When sourcing a small CNC mill for artistic applications, buyers should prioritize material versatility and design software integration. The ability to work with various materials allows artists to experiment and innovate, enhancing their creative expression and marketability.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘best small cnc mill’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Difficulty in Selecting the Right CNC Mill for Diverse Applications
The Problem: B2B buyers often struggle to choose the right small CNC mill that can handle a variety of materials and applications. For example, a small manufacturing firm may require a mill that can efficiently process wood, plastics, and soft metals for different product lines. This challenge is compounded by the wide range of options available, each with different specifications, capabilities, and price points. Buyers may feel overwhelmed by technical jargon and uncertain about which features are essential for their specific needs, leading to hesitation in making a purchase.
The Solution: To effectively select the best small CNC mill for diverse applications, buyers should start by clearly defining their project requirements. Create a detailed list of the materials you plan to work with, the expected volume of production, and the types of projects you envision. Once you have this information, research machines that offer versatility in handling multiple materials. For instance, mills like the Bantam Tools Desktop CNC Milling Machine provide a comprehensive ecosystem for prototyping with various materials, while also offering user-friendly software. Additionally, consider reaching out to manufacturers for demos or trial periods, which can provide hands-on experience before making a significant investment. Engaging with online forums or local industry groups can also yield valuable insights from other users regarding their experiences with different models.
Scenario 2: Navigating the Learning Curve of CNC Milling Technology
The Problem: Many B2B buyers face a steep learning curve when transitioning to CNC milling technology, particularly those who are new to the industry. This challenge is especially pronounced for companies in regions like Africa and South America, where access to training resources may be limited. Users may struggle with understanding software interfaces, material/tool combinations, and machine maintenance, leading to frustration and potential production delays. Inadequate training can result in improper machine use, which can damage equipment or produce subpar products.
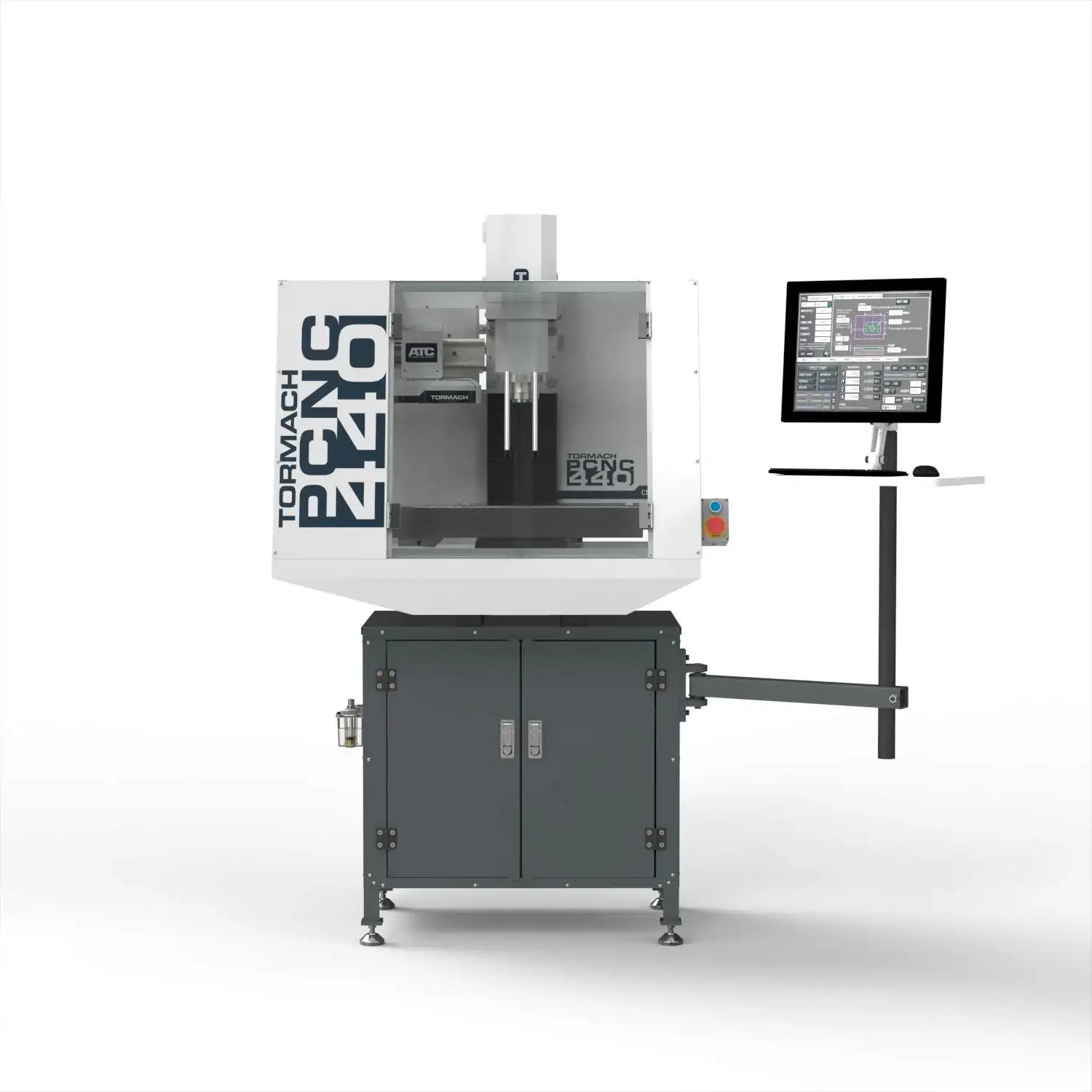
The Solution: To mitigate the learning curve, buyers should invest in comprehensive training programs that are often provided by CNC mill manufacturers. For example, machines such as the Tormach PCNC 440 come with in-house CAM software and online simulations that can be invaluable for new users. Additionally, consider enrolling staff in workshops or online courses focused on CNC operation and programming. Many community colleges and technical schools offer relevant courses that can be tailored to your team’s needs. Moreover, joining user groups or online communities can facilitate knowledge sharing and support among peers facing similar challenges. Establishing a mentorship program within your organization, where experienced operators guide new users, can also foster a culture of continuous learning and improvement.
Scenario 3: Cost Management and Return on Investment (ROI) Concerns
The Problem: B2B buyers often grapple with the financial implications of investing in small CNC mills. Given the varying price ranges of machines, from budget-friendly options to high-end models, companies may find it challenging to justify the initial investment, especially if they are unsure about the potential return on investment (ROI). This concern is particularly relevant for small businesses and startups in emerging markets, where financial resources may be limited. Without a clear understanding of how the machine will enhance productivity or reduce operational costs, decision-makers may hesitate to proceed with a purchase.
The Solution: To effectively manage costs and evaluate ROI, buyers should conduct a thorough cost-benefit analysis before making a purchase. Start by calculating the potential savings and revenue generation that a CNC mill could bring to your operations. For instance, consider how the ability to produce custom parts in-house could reduce outsourcing costs and lead to faster turnaround times for projects. Additionally, look for machines that offer modularity and scalability, allowing you to expand capabilities as your business grows, such as the LongMill Benchtop CNC MK2.5, which is customizable and cost-effective. Another strategy is to explore financing options, such as leasing or financing through manufacturers, which can alleviate upfront costs while allowing you to reap the benefits of enhanced production capabilities. Finally, case studies and testimonials from other businesses that have successfully integrated CNC milling into their operations can provide compelling evidence of potential ROI, helping to ease financial concerns.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for best small cnc mill
When selecting materials for small CNC milling applications, understanding the properties, advantages, and limitations of each material is crucial for optimizing performance and ensuring product quality. Here, we analyze four common materials used in CNC milling: aluminum, plastics, wood, and brass. Each material presents unique characteristics that can significantly impact the application, particularly for international B2B buyers.
What Are the Key Properties of Aluminum in CNC Milling?
Aluminum is a lightweight yet strong material known for its excellent machinability and corrosion resistance. It typically exhibits a temperature rating up to 660°C and can withstand moderate pressure. Its low density makes it ideal for applications requiring reduced weight without sacrificing strength.
Pros: Aluminum is durable, easy to machine, and provides a good surface finish. It is also relatively cost-effective and widely available, making it a popular choice for prototyping and small production runs.
Cons: While aluminum is versatile, it can be prone to scratching and denting. Additionally, certain alloys may have varying machinability, which can complicate manufacturing processes.
Impact on Application: Aluminum is suitable for a variety of applications, including aerospace components, automotive parts, and consumer products. Its compatibility with various media makes it a preferred choice for industries requiring lightweight and durable components.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers in regions like Africa and South America should consider local availability and compliance with international standards such as ASTM and DIN. Understanding the specific aluminum alloy grades is essential to meet project requirements.
How Do Plastics Perform in CNC Milling?
Plastics, such as acrylic, polycarbonate, and nylon, are widely used in CNC milling due to their versatility and ease of machining. They generally have lower temperature ratings, around 100-150°C, and can exhibit varying degrees of chemical resistance.
Pros: Plastics are lightweight, cost-effective, and offer a range of colors and finishes. They are also resistant to corrosion and can be used in applications where metal would be unsuitable.
Cons: Plastics can be less durable than metals and may deform under high temperatures. Additionally, they can be more challenging to achieve fine tolerances compared to metals.
Impact on Application: Plastics are commonly used in consumer goods, medical devices, and automotive interiors. Their compatibility with various media allows for creative applications in design and prototyping.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should be aware of the specific grades of plastics suitable for their applications and ensure compliance with local regulations. Understanding the environmental impact of plastic use is also increasingly important in many regions.
What Are the Benefits of Using Wood in CNC Milling?
Wood is a traditional material in CNC milling, valued for its aesthetic appeal and machinability. It has a wide range of temperature tolerances depending on the type and can exhibit varying levels of moisture resistance.
Pros: Wood is easy to work with, offers a natural finish, and is generally cost-effective. It is also renewable, making it an environmentally friendly option.
Cons: Wood can be prone to warping, splitting, and is less durable than metals. Its mechanical properties can vary significantly based on species, which can affect machining consistency.
Impact on Application: Wood is ideal for furniture, decorative items, and prototypes where aesthetics are essential. Its compatibility with various finishes allows for diverse applications.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should consider local wood sourcing regulations and certifications, such as FSC or PEFC, to ensure sustainable practices. Knowledge of regional wood species and their properties is also crucial for optimal results.
Why Choose Brass for CNC Milling Projects?
Brass is a copper-zinc alloy known for its excellent machinability and corrosion resistance. It can withstand temperatures up to 300°C and is often used in applications requiring good electrical conductivity.
Pros: Brass offers a superior finish and is highly durable, making it suitable for precision components. Its resistance to corrosion and wear makes it a reliable choice for long-lasting applications.
Cons: Brass can be more expensive than aluminum and plastics. It may also require specific tooling to achieve the desired finish, which can complicate the manufacturing process.
Impact on Application: Brass is commonly used in plumbing fittings, electrical connectors, and decorative hardware. Its compatibility with various media makes it a preferred choice for applications requiring both aesthetic and functional properties.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should be aware of the specific brass alloys and their properties to ensure compliance with international standards. Understanding local sourcing options and pricing fluctuations is also essential for effective budgeting.
Summary Table of Material Selection for CNC Milling
| Material | Typical Use Case for best small cnc mill | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Aluminum | Aerospace components, automotive parts | Lightweight and durable | Prone to scratching | Medium |
| Plastics | Consumer goods, medical devices | Versatile and cost-effective | Less durable than metals | Low |
| Wood | Furniture, decorative items | Aesthetic appeal and renewability | Prone to warping | Low |
| Brass | Plumbing fittings, electrical connectors | Superior finish and durability | Higher cost than aluminum | High |
This strategic material selection guide provides B2B buyers with essential insights into material properties, advantages, and limitations, enabling informed decision-making for CNC milling applications.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for best small cnc mill
What Are the Key Stages in Manufacturing Small CNC Mills?
The manufacturing process of small CNC mills involves several critical stages, each designed to ensure precision and quality. Understanding these stages can help B2B buyers assess the capabilities of potential suppliers.
How Is Material Prepared for CNC Milling?
Material preparation is the foundational step in the manufacturing process. It involves selecting the right raw materials, which can include aluminum, steel, and various plastics. Suppliers should source materials from reputable vendors to ensure quality. The materials are then cut to size, often using saws or laser cutters, before being machined to achieve the desired dimensions. This stage may also involve the use of CAD software to create designs that guide the cutting process.
What Forming Techniques Are Commonly Used?
Forming is the next critical phase where the actual CNC milling occurs. Techniques vary depending on the complexity of the design and the materials used. Typically, small CNC mills utilize subtractive manufacturing, where material is removed from a solid block to create the final product. This process can involve various milling strategies, such as 2-axis, 3-axis, or even 5-axis machining, which allows for more intricate designs and geometries. Advanced CNC mills may also incorporate techniques such as engraving or drilling, expanding their functionality.
How Is Assembly Conducted in CNC Mill Manufacturing?
Once the components are machined, the assembly process begins. This stage is vital for ensuring that all parts fit together correctly and function as intended. In many cases, assembly may involve the integration of electronic components, such as motors and control systems, which necessitates precision in both mechanical and electrical aspects. Suppliers should implement stringent assembly protocols to minimize errors and ensure consistency in the final product.
What Finishing Techniques Enhance the Quality of CNC Mills?
Finishing processes are essential for enhancing both the aesthetic and functional qualities of CNC mills. Common techniques include anodizing, painting, or applying protective coatings to prevent corrosion and wear. Finishing not only improves the appearance but also affects the machine’s performance and longevity. Suppliers should employ quality finishing techniques to meet specific requirements, especially for international buyers who may have unique preferences or standards.
What Quality Assurance Measures Should B2B Buyers Expect?
Quality assurance (QA) is crucial in the manufacturing of small CNC mills, ensuring that the final product meets both industry standards and customer expectations. Various international and industry-specific standards guide these QA processes.
Which International Standards Are Relevant for CNC Mill Manufacturing?
ISO 9001 is a widely recognized international standard for quality management systems. It provides a framework for consistent quality in manufacturing processes, ensuring that suppliers maintain a high level of quality control. Additionally, certifications such as CE mark indicate compliance with European safety and environmental requirements, which can be critical for buyers in Europe and other regions.
What Are the Key QC Checkpoints in CNC Mill Manufacturing?
Quality control (QC) checkpoints are strategically placed throughout the manufacturing process to identify and rectify issues early. The main checkpoints typically include:
- Incoming Quality Control (IQC): This step involves inspecting raw materials upon arrival to ensure they meet specified requirements.
- In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): During the manufacturing process, ongoing checks are performed to monitor machining accuracy and assembly quality.
- Final Quality Control (FQC): Before shipping, the finished CNC mills undergo thorough inspections to verify that they meet all design specifications and quality standards.
These checkpoints help ensure that any defects are caught and addressed before the product reaches the buyer.
What Common Testing Methods Are Used for CNC Mills?
Testing methods for small CNC mills vary but often include dimensional inspections, functional testing, and performance evaluations. Dimensional inspections verify that the machined components adhere to the specified tolerances, while functional testing assesses the machine’s operational capabilities. Performance evaluations may involve running the CNC mill under load to simulate real-world conditions, ensuring that it performs reliably.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control?
Buyers looking to verify a supplier’s quality control measures can employ several strategies. Conducting supplier audits is one of the most effective methods. This involves visiting the manufacturing facility to observe processes and inspect quality control protocols firsthand. Additionally, requesting quality assurance documentation, such as inspection reports and compliance certificates, can provide insights into the supplier’s commitment to quality.
What Are the Nuances of QC and Certifications for International Buyers?
For international buyers, especially those from regions like Africa and South America, understanding the nuances of QC certifications is essential. Different regions may have varying standards and regulations. For instance, while CE marking is crucial in Europe, buyers in Africa may prioritize local certifications that ensure compliance with regional safety standards. It’s important for buyers to communicate their specific requirements and verify that suppliers can meet them.
Conclusion: Why Is Understanding Manufacturing and QC Essential for B2B Buyers?
An in-depth understanding of the manufacturing processes and quality assurance measures associated with small CNC mills equips B2B buyers to make informed purchasing decisions. By focusing on the key stages of manufacturing and the relevant quality control standards, buyers can ensure they select suppliers who not only deliver high-quality products but also align with their operational and regulatory needs. This insight is particularly valuable for international buyers navigating the complexities of global supply chains.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘best small cnc mill’
Introduction
In the competitive landscape of manufacturing and prototyping, selecting the right small CNC mill is crucial for enhancing productivity and ensuring precision. This practical sourcing guide aims to equip B2B buyers with a clear checklist to navigate the procurement process effectively, ensuring that they make informed decisions tailored to their specific needs.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Establishing clear technical specifications is the foundation of your procurement process. Consider factors such as build volume, spindle speed, and material compatibility. This step ensures that the CNC mill you select meets your operational requirements, whether for prototyping, custom fabrication, or small-scale production.
- Build Volume: Determine the maximum dimensions of the parts you intend to produce.
- Spindle Speed: Assess the speed range needed for the materials you will work with.
Step 2: Assess Your Budget Constraints
Understanding your budget is vital for narrowing down your options. CNC mills come in a wide range of prices, and knowing your financial limits will help you focus on machines that offer the best value without compromising quality.
- Initial Cost vs. Long-term Investment: Consider not only the purchase price but also ongoing costs such as maintenance, software licenses, and tooling.
Step 3: Evaluate Potential Suppliers
Before committing to a purchase, thoroughly vet potential suppliers. This step is crucial to ensure reliability and quality. Request company profiles, case studies, and references from buyers in similar industries or regions.
- Supplier Reputation: Look for reviews and testimonials to gauge customer satisfaction and product reliability.
- After-Sales Support: Ensure the supplier offers robust support, including training and troubleshooting.
Step 4: Verify Compliance with Industry Standards
Ensure that the CNC mills you are considering comply with relevant industry standards and certifications. This verification is important for quality assurance and can affect your operation’s credibility.
- Certifications: Look for ISO or other relevant certifications that indicate adherence to quality management standards.
- Safety Standards: Confirm that the machines meet safety regulations pertinent to your industry.
Step 5: Request Demonstrations or Samples
Whenever possible, request a demonstration or sample parts produced by the CNC mill. This step allows you to evaluate the machine’s capabilities firsthand and assess the quality of the final product.
- Hands-On Experience: Observing the machine in action can help you determine if it meets your expectations for precision and efficiency.
- Material Testing: If feasible, conduct tests with your materials to ensure compatibility and performance.
Step 6: Understand Software and Compatibility
The software used to operate the CNC mill is just as important as the hardware itself. Investigate the compatibility of the machine’s software with your existing systems and the learning curve associated with it.
- Included Software: Check if the software is included in the purchase price or if it incurs additional costs.
- Ease of Use: Consider user-friendliness, especially if multiple team members will operate the machine.
Step 7: Negotiate Terms and Conditions
Finally, before finalizing the purchase, negotiate terms and conditions with the supplier. This step is essential for securing the best deal and ensuring clarity on warranties, delivery timelines, and return policies.
- Warranties and Guarantees: Understand the warranty terms and what they cover.
- Delivery and Installation: Confirm delivery timelines and whether installation support is provided.
By following this checklist, B2B buyers can confidently navigate the procurement of a small CNC mill, aligning their choices with operational needs and strategic goals.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for best small cnc mill Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components in Sourcing Small CNC Mills?
When sourcing small CNC mills, understanding the cost structure is critical for B2B buyers. The main cost components include materials, labor, manufacturing overhead, tooling, quality control (QC), logistics, and profit margin.
-
Materials: The type of materials used in the construction of CNC mills can significantly impact costs. High-quality metals and composite materials provide durability but may increase the overall price. For instance, mills designed for soft metals typically use less expensive materials compared to those capable of handling harder alloys.
-
Labor: Labor costs can vary widely depending on the supplier’s location. For buyers in Africa or South America, local labor rates may be lower, potentially reducing the final price. However, skilled labor is essential for precision manufacturing, influencing costs based on the expertise required.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes utilities, rent, and administrative expenses incurred during production. Suppliers with high overhead costs may pass these expenses onto buyers, affecting pricing. It’s advisable to evaluate suppliers not only on their product offerings but also on their operational efficiency.
-
Tooling: The initial investment in tooling can be substantial, especially for CNC mills that require specific components for various materials. Custom tooling may be needed for specialized applications, which can further increase costs.
-
Quality Control (QC): Rigorous QC processes ensure that the machines meet performance standards, but they also add to production costs. Buyers should consider suppliers with established QC practices, as this may reduce long-term maintenance costs.
-
Logistics: Shipping and handling costs can vary based on the destination and supplier location. For international buyers, understanding Incoterms can help clarify who is responsible for shipping costs and insurance, which can affect the total price.
-
Margin: Finally, the supplier’s profit margin will influence the final price. Understanding the market rates and expected margins for different CNC mills can help buyers negotiate better terms.
What Influences the Pricing of Small CNC Mills?
Several factors can influence the pricing of small CNC mills, including volume and minimum order quantity (MOQ), specifications and customization, material quality, certification requirements, and supplier characteristics.
-
Volume/MOQ: Purchasing in larger quantities often leads to reduced per-unit costs. Buyers should negotiate MOQ terms that align with their operational needs to optimize costs.
-
Specifications and Customization: Customizing a CNC mill to meet specific operational needs can increase costs. Buyers should weigh the benefits of customization against the potential for higher expenses.
-
Material Quality/Certifications: Mills built with certified materials can command higher prices. Buyers in regulated industries should prioritize suppliers who provide necessary certifications, ensuring compliance with industry standards.
-
Supplier Factors: The reputation and reliability of the supplier play a crucial role in pricing. Established suppliers may charge a premium but often deliver better quality and service, which can be a worthwhile investment.
-
Incoterms: Understanding the implications of different Incoterms can help buyers manage logistics costs effectively. For example, choosing FOB (Free on Board) can allow buyers to control shipping costs, while DDP (Delivered Duty Paid) might simplify the purchasing process but could lead to higher upfront costs.
What Tips Can Help Buyers Negotiate Better Prices for CNC Mills?
When negotiating prices for CNC mills, several strategies can enhance cost-efficiency and ensure a favorable Total Cost of Ownership (TCO).
-
Leverage Total Cost of Ownership: Buyers should consider not only the initial purchase price but also maintenance, operational costs, and potential downtime. A slightly higher upfront cost may yield savings in the long run through better reliability and lower maintenance.
-
Understand Pricing Nuances for International Buyers: Buyers in regions like Africa or South America should be aware of currency fluctuations, import duties, and tariffs that could affect the total cost. Engaging with local suppliers or those with experience in exporting to these regions can help mitigate risks.
-
Negotiate Payment Terms: Flexible payment options can ease cash flow constraints. Discussing terms such as partial payments or extended payment periods may provide financial flexibility without compromising the purchase.
-
Seek Multiple Quotes: Obtaining quotes from multiple suppliers can provide leverage in negotiations. It allows buyers to compare pricing structures and identify the best overall value.
-
Explore After-Sales Support: Inquire about after-sales services, including training, maintenance, and support. A supplier offering robust support may justify a higher price due to the long-term benefits provided.
By understanding these cost components, pricing influencers, and negotiation strategies, B2B buyers can make informed decisions when sourcing small CNC mills, ensuring they achieve both quality and value in their purchases.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing best small cnc mill With Other Solutions
Understanding the Alternatives to the Best Small CNC Mill
When evaluating the best small CNC mill for your operations, it’s essential to consider alternative solutions that may also meet your manufacturing needs. These alternatives can provide similar capabilities in terms of precision and functionality, but they may differ in cost, ease of use, and maintenance requirements. Below, we compare the best small CNC mill with two viable alternatives: traditional manual milling machines and 3D printing technologies.
| Comparison Aspect | Best Small CNC Mill | Traditional Manual Milling Machine | 3D Printing Technology |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | High precision and speed | Moderate precision, slower speeds | Varies; can achieve complex geometries |
| Cost | $1,700 – $5,495 | $2,000 – $10,000+ | $300 – $5,000+ |
| Ease of Implementation | User-friendly software | Requires skilled operator | Requires software knowledge |
| Maintenance | Moderate (software updates) | High (mechanical maintenance) | Low (occasional calibration) |
| Best Use Case | Prototyping, small-scale production | Custom parts, heavy materials | Rapid prototyping, complex shapes |
What Are the Advantages and Disadvantages of Traditional Manual Milling Machines?
Traditional manual milling machines offer a hands-on approach to machining, where skilled operators control the cutting process. One significant advantage is their ability to handle larger workpieces and materials that may be too robust for smaller CNC mills. However, they require a higher level of expertise, which can lead to variability in performance and quality. Additionally, maintenance can be intensive due to the mechanical components involved, making them less suitable for small businesses or startups with limited resources.
How Does 3D Printing Technology Compare to Small CNC Mills?
3D printing technology has gained popularity for its ability to create complex geometries and intricate designs quickly. It often has lower upfront costs compared to CNC mills, making it accessible for small businesses and startups. However, the materials used in 3D printing can limit the final product’s strength and durability compared to machined parts. Furthermore, the learning curve associated with 3D printing software can be steep, and the technology may not be suitable for all manufacturing applications, particularly those requiring high precision or specific material properties.
Conclusion: Which Manufacturing Solution Is Right for You?
Choosing the right manufacturing solution depends on various factors, including your specific production needs, budget constraints, and the materials you intend to work with. If your focus is on high precision and small-scale production, the best small CNC mill may be the ideal choice. However, if your projects involve larger components or require a more hands-on approach, traditional manual milling machines might be more appropriate. Alternatively, for rapid prototyping and complex design requirements, exploring 3D printing technologies could yield significant benefits. Ultimately, understanding the strengths and weaknesses of each option will empower you to make an informed decision that aligns with your operational goals.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for best small cnc mill
What Are the Key Technical Properties of a Small CNC Mill?
When selecting the best small CNC mill for your business, understanding the technical specifications is crucial for making informed decisions. Here are several key properties to consider:
1. Build Volume
The build volume refers to the maximum size of the material that can be machined. It is typically expressed in three dimensions (length, width, and height). A larger build volume allows for the machining of bigger parts or multiple smaller parts in one operation, which can significantly enhance productivity. For B2B buyers, this is vital as it determines the range of projects the mill can handle.
2. Spindle Speed
Spindle speed, measured in RPM (revolutions per minute), indicates how fast the cutting tool rotates. Higher spindle speeds allow for faster material removal and smoother finishes, particularly on harder materials. For businesses focusing on high-precision parts, understanding spindle speed helps in selecting a CNC mill that meets their production speed and quality requirements.
3. Material Compatibility
Different CNC mills are designed to handle various materials such as wood, plastics, aluminum, and even harder metals. Knowing the material capabilities of a machine is essential for B2B buyers, as it directly influences the types of projects that can be executed. Selecting a mill with the right material compatibility ensures versatility and efficiency in production.
4. Tolerance
Tolerance refers to the allowable variation in a manufactured part’s dimensions. It is a critical specification that impacts the precision and fit of components in assembly processes. For B2B operations, ensuring that a CNC mill can achieve the required tolerances is essential for maintaining quality standards and minimizing rework costs.
5. Number of Axes
The number of axes on a CNC mill determines its machining capabilities. Most small CNC mills operate on three axes (X, Y, and Z), but some advanced models offer four or five axes, allowing for more complex geometries and greater precision. Businesses that require intricate designs or multi-sided machining should prioritize mills with higher axes capabilities.
What Are Common Trade Terms Related to Small CNC Mills?
Understanding industry jargon is essential for effective communication and negotiation. Here are some common terms that B2B buyers should be familiar with:
1. OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
An OEM is a company that produces parts or equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer. In the context of CNC mills, understanding whether a machine is an OEM product can impact quality assurance and warranty considerations.
2. MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ refers to the smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell. This term is significant for B2B buyers as it affects purchasing decisions and inventory management. Knowing the MOQ helps businesses plan their budgets and ensure they meet supplier requirements.
3. RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a document that a buyer sends to suppliers asking for pricing and terms for specific goods or services. For buyers of CNC mills, issuing an RFQ can streamline the procurement process and ensure they receive competitive offers tailored to their needs.
4. Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
Incoterms are a set of international rules that define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in shipping agreements. Familiarity with these terms helps B2B buyers understand shipping costs, risks, and responsibilities, which is crucial when sourcing equipment from global suppliers.
5. CAM (Computer-Aided Manufacturing)
CAM refers to software that facilitates the manufacturing process by controlling machine tools through computer systems. Understanding CAM is important for B2B buyers as it directly impacts the programming and operational efficiency of CNC mills.
Conclusion
Navigating the landscape of small CNC mills requires a solid grasp of both technical specifications and industry terminology. By understanding these critical properties and terms, B2B buyers can make informed decisions that align with their operational needs and strategic goals.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the best small cnc mill Sector
What Are the Current Market Dynamics and Key Trends in the Small CNC Mill Sector?
The global small CNC mill market is being driven by increasing demand for precision manufacturing across various industries, such as aerospace, automotive, and consumer electronics. Key trends include the growing adoption of automation and digital technologies, which enhance operational efficiency and reduce lead times. As manufacturers seek to optimize production processes, the integration of CNC milling machines into small-scale operations is becoming more prevalent, enabling businesses to produce high-quality prototypes and finished products in-house.
Emerging technologies, such as cloud-based software solutions and advanced CAD/CAM systems, are reshaping how CNC milling machines are utilized. For international B2B buyers, particularly from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, the ability to customize and adapt these machines to local materials and manufacturing processes is crucial. Additionally, the rise of e-commerce platforms facilitates easier access to a broader range of CNC milling options, fostering competition and innovation within the market. Buyers should be aware of the importance of vendor reliability, technical support, and the availability of spare parts when sourcing equipment.
How Do Sustainability and Ethical Sourcing Impact the Small CNC Mill Market?
Sustainability and ethical sourcing are becoming integral considerations in the B2B landscape, particularly in the small CNC mill sector. The environmental impact of manufacturing processes is under increasing scrutiny, leading buyers to seek machines that are not only efficient but also eco-friendly. This includes CNC mills that utilize energy-efficient motors and generate less waste during production.
Moreover, the importance of ethical supply chains cannot be overstated. Buyers are increasingly demanding transparency from manufacturers regarding their sourcing practices and labor conditions. Certifications such as ISO 14001 for environmental management and Fair Trade certifications for materials can provide assurance that suppliers are adhering to sustainable practices. For B2B buyers, prioritizing suppliers who align with these values not only supports ethical practices but also enhances brand reputation and consumer trust.
What Is the Evolution of the Small CNC Mill Market?
The small CNC mill market has evolved significantly over the last few decades. Initially designed for industrial applications, CNC milling technology has transitioned into more compact and affordable formats suitable for small businesses and hobbyists. The introduction of desktop CNC mills has democratized access to precision machining, enabling startups and entrepreneurs to prototype and produce components without the need for large-scale manufacturing facilities.
As technology has advanced, the capabilities of small CNC mills have expanded, now offering features such as 5-axis machining and compatibility with various materials, including metals and plastics. This evolution reflects the changing needs of manufacturers and the increasing complexity of design requirements in various industries. For international B2B buyers, understanding this evolution is essential for making informed decisions about equipment that meets current and future manufacturing demands.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of best small cnc mill
-
How do I choose the right small CNC mill for my business needs?
Choosing the right small CNC mill involves assessing your specific requirements such as the materials you will be working with, the complexity of the designs, and your production volume. Consider factors like the machine’s build volume, spindle speed, number of axes, and software compatibility. Additionally, evaluate the level of user support and training available from the supplier. Conducting a cost-benefit analysis based on your production goals will also help ensure you select a machine that meets both your operational and financial needs. -
What are the key specifications to look for in a small CNC mill?
Key specifications to consider include build volume, spindle speed, and the number of axes. The build volume determines the size of parts you can create, while spindle speed affects the machining efficiency and material compatibility. A 3-axis mill is suitable for most applications, but a 5-axis machine offers greater versatility for complex geometries. Additionally, assess the machine’s material handling capabilities, software integration, and ease of use, especially if your team lacks extensive CNC experience. -
What is the average price range for small CNC mills suitable for B2B applications?
The average price range for small CNC mills typically varies from $1,400 to over $6,000, depending on features and capabilities. Entry-level models, like the LongMill Benchtop CNC MK2.5, start around $1,459, while more advanced machines, such as the Tormach 440, can go up to $6,990. Be sure to factor in additional costs such as tooling, software, and maintenance when budgeting for your CNC mill purchase, as these can significantly impact the total investment. -
How can I vet suppliers of small CNC mills for international procurement?
Vetting suppliers involves conducting thorough research to assess their reputation, product quality, and customer service. Check online reviews, request references, and evaluate their experience in international trade. Additionally, ensure that they comply with relevant industry standards and certifications. Engaging in direct communication and asking for product demonstrations can also provide insights into their operational capabilities. Lastly, consider suppliers that offer warranties and after-sales support, which are crucial for long-term partnerships. -
What are the typical payment terms for purchasing a small CNC mill internationally?
Payment terms can vary significantly by supplier and region, but common arrangements include a deposit upfront (usually 30-50%) with the balance due before shipping or upon delivery. Some suppliers may offer financing options or payment through letters of credit, especially for larger transactions. It’s essential to negotiate terms that align with your cash flow and budget constraints while ensuring that they are secure and enforceable in international trade. -
What customization options are available for small CNC mills?
Many suppliers offer customization options to tailor CNC mills to specific business needs. This can include modifications to the machine’s size, spindle type, or software configurations. Some manufacturers provide additional tooling or attachments for specialized tasks, such as laser engraving or 3D printing. Discussing your requirements with potential suppliers can lead to personalized solutions that enhance the machine’s functionality and efficiency for your specific applications. -
What quality assurance measures should I expect when purchasing a small CNC mill?
Reputable suppliers should have established quality assurance (QA) processes in place. This typically includes pre-shipment inspections to verify machine specifications, performance testing, and adherence to international standards. Suppliers may also offer warranties that cover defects in materials or workmanship. It’s advisable to request documentation of their QA procedures and any certifications that demonstrate their commitment to product quality. -
How do I handle logistics when importing small CNC mills into my country?
Handling logistics for importing CNC mills involves coordinating shipping, customs clearance, and delivery. Work with a freight forwarder experienced in machinery imports to manage these aspects efficiently. Ensure all shipping documentation, including invoices and certificates of origin, is accurate and complete to avoid delays. Familiarize yourself with your country’s import regulations and tariffs for machinery to estimate costs and ensure compliance, which can streamline the entire process and minimize disruptions.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.
Top 8 Best Small Cnc Mill Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. Shapeoko Pro – Versatile CNC for Hobbyists
Domain: reddit.com
Registered: 2005 (20 years)
Introduction: 1. Shapeoko Pro – Off-the-shelf experience for wood, plastic, and foam; suitable for hobbyists. 2. CNC4Newbie – More DIY-oriented, offers more machine for the buck; not ideal for metal cutting. 3. Tormach 440 – Cheapest gateway machine for metalworking; small but a good starting point before moving to larger commercial machines. 4. DIY conversion of a bench mill or manual mill (e.g., Bridgeport) t…
2. Carbide 3D – Nomad 3
Domain: in3dtec.com
Registered: 2017 (8 years)
Introduction: [{‘name’: ‘Nomad 3 by Carbide 3D’, ‘build_volume’: ‘8’’ x 8’’ x 3’’’, ‘spindle_speed’: ‘9,000 – 24,000 RPM’, ‘materials’: ‘Wood, plastics, soft metals’, ‘software’: ‘Carbide Create and Carbide Motion’, ‘price’: ‘Approximately $2,800’, ‘ideal_for’: ‘Hobbyists and makers, small businesses, educational institutions’}, {‘name’: ‘Shapeoko 4 by Carbide 3D’, ‘build_volume’: ’33’’ x 33’’ x 4’’’, ‘spindle_…
3. SYIL – X7 Small CNC Mill
Domain: us.syil.com
Registered: 2001 (24 years)
Introduction: {“model”:”SYIL X7″,”type”:”Small CNC Mill”,”axis_travels”:{“X”:”400 mm”,”Y”:”300 mm”,”Z”:”380 mm”},”automatic_tool_changer”:{“type”:”12-pocket umbrella”,”max_tool_diameter”:”63 mm”,”max_tool_length”:”200 mm”,”max_tool_weight”:”3 kg”,”tool_to_tool_time”:”1.5 s”},”spindle”:{“type”:”BT30″,”max_speed”:”12,000 rpm”,”motor_output”:{“rate”:”7.5 kW”,”max”:”11 kW”}},”feed”:{“cutting_feed”:”10,000 mm/min”,”…
4. Rusnok – Benchtop CNC Mill for Hobbyists
Domain: practicalmachinist.com
Registered: 2000 (25 years)
Introduction: – Type: Benchtop CNC Mill
– Intended Use: Hobbyist workshop
– Key Tasks: Milling 1515 8020 pieces, specifically anchor fasteners
– Required Tooling: 2-flute 13/16″ endmill
– Budget: $10,000
– Desired Features: 2-axis CNC capability, ability to machine mild steel
– Recommendations: Rusnok mill, Burke No 4, Diamond mills, Dyna Mectronics 2800, Prototrak CNC knee mill, CNC Max Tabletop CNC Milling Ma…
5. Little Machine Shop – CNC Machines
6. STYLECNC – 2025 Best Small Desktop CNC Milling Machine
Domain: stylecnc.com
Registered: 2015 (10 years)
Introduction: {“Product Name”: “2025 Best Small Desktop CNC Milling Machine”, “Brand”: “STYLECNC”, “Model”: “ST6060E”, “Price”: {“Standard Edition”: “$3,000”, “Pro Edition”: “$4,000”}, “Stock Availability”: “360 Units in Stock Available for Sale Every Month”, “Certification”: “CE certification”, “Warranty”: “One-Year Limited Warranty for Entire Machine (Extended Warranties Available for Major Parts)”, “Money Ba…
7. Sainsmart – Genmitsu 3018 PROver
Domain: cncsourced.com
Registered: 2020 (5 years)
Introduction: [{‘name’: ‘Sainsmart Genmitsu 3018 PROver’, ‘price’: ‘$345’, ‘working_area’: ‘300 x 180 x 45 mm’, ‘precision’: ‘Around 0.003″‘, ‘material_compatibility’: ‘Wood, MDF, acrylic, polycarbonate, and PCB’, ‘pros’: [‘Easy to set up’, ‘Very affordable’, ‘Works with a variety of materials’, ‘Optional laser engraver upgrade option’], ‘cons’: [‘More expensive brands are sturdier’, ‘Simplicity may limit capab…
8. Haas Automation – Desktop CNC Machines
Domain: haascnc.com
Registered: 1996 (29 years)
Introduction: Best Desktop CNC Machines from Haas Automation include the Desktop Mill and Desktop Lathe. These machines are designed for small-scale production and prototyping, offering precision and reliability. The Desktop Mill is ideal for machining small parts, while the Desktop Lathe is suited for turning operations. Both machines feature user-friendly controls and are compatible with Haas tooling and acce…
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for best small cnc mill
What Are the Key Insights for International B2B Buyers of Small CNC Mills?
In the evolving landscape of manufacturing, small CNC mills have emerged as indispensable tools for precision fabrication and prototyping. Their compact size and versatility cater to a broad spectrum of applications, from hobbyist projects to professional production runs. For B2B buyers, understanding the unique features and capabilities of these machines is essential for making informed purchasing decisions that align with operational needs and budget constraints.
Strategic sourcing is crucial in this context, enabling businesses to identify the right suppliers, negotiate favorable terms, and ensure a seamless integration of these machines into their workflows. Buyers should prioritize not only the technical specifications—such as build volume, spindle speed, and material compatibility—but also consider the support services offered by manufacturers, including software integration and training.
As the global market continues to expand, particularly in regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, the demand for efficient and precise manufacturing solutions will only grow. Now is the time for international buyers to leverage these insights and invest in small CNC mills that can enhance productivity and drive innovation. Engage with suppliers, explore options, and position your business at the forefront of the manufacturing revolution.