Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for best small cnc machine
Navigating the global market for the best small CNC machines can present a unique set of challenges for international B2B buyers seeking precision, versatility, and reliability. With diverse applications ranging from woodworking to metal fabrication, identifying the right CNC machine is crucial for achieving operational efficiency and product excellence. This guide is designed to provide comprehensive insights into various types of small CNC machines, their applications, cost considerations, and supplier vetting processes, facilitating informed purchasing decisions across regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe.
B2B buyers specifically in countries like Nigeria and Brazil will find actionable information tailored to their needs. We examine the key metrics and features that define quality CNC machines, including spindle speed, material compatibility, and ease of assembly. Furthermore, we highlight reputable suppliers and manufacturers to assist buyers in navigating their options effectively. This guide not only demystifies the complexities associated with choosing the best CNC machine but also empowers businesses to enhance their production capabilities and stay competitive in a rapidly evolving market.
By leveraging this resource, businesses can streamline their decision-making process, reduce risks associated with poor investments, and ultimately, achieve greater success in their respective industries.
Understanding best small cnc machine Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| CNC Routers | Versatile machines for wood and soft materials; various sizes available | Woodworking, signage, prototyping | Pros: Cost-effective for small businesses, easy to use. Cons: Limited to less dense materials. |
| CNC Milling Machines | Capable of operating on multiple axes; suitable for hard materials | Precision engineering, component production | Pros: High precision, versatile with material types. Cons: May require more operator skill and space. |
| Laser Engravers | Utilizes laser technology for cutting and engraving; high precision | Decoration, small part production, prototyping | Pros: Exceptional detail, fast production. Cons: Limited to specific materials; maintenance can be costly. |
| 3D Printers | Additive manufacturing technology; creates complex geometries | Prototyping, custom components | Pros: Excellent for unique designs, low material waste. Cons: Slower than other CNC machines; material limitations. |
| Mini CNC Lathes | Focuses on cylindrical work; good for small, detailed components | Jewelry making, small part manufacturing | Pros: Compact size, ideal for delicate work. Cons: Limited capacity for larger pieces and materials. |
What Makes CNC Routers Ideal for Small Businesses?
CNC routers are distinguished by their ability to handle a wide variety of materials, particularly softwoods, MDF, and acrylics. They offer customizable sizes that can accommodate various projects, making them an excellent investment for startups and small businesses focused on woodworking, sign-making, and prototyping. When considering a CNC router, B2B buyers should evaluate its ease of use, software compatibility, and potential for expansion in capabilities to meet evolving market requirements.
How Do CNC Milling Machines Enhance Precision Engineering?
CNC milling machines provide a significant advantage in precision engineering applications by moving across multiple axes. This capability makes them suitable for producing complex parts from metals and hard plastics. Ideal for businesses involved in component production or high-precision engineering tasks, buyers should consider factors such as the machine’s rigidity, spindle speed, and tooling compatibility. Investing in a high-quality CNC milling machine can drastically reduce production time while increasing overall precision and repeatability.
Why Choose Laser Engravers for Precision Decoration?
Laser engravers stand out for their ability to cut and engrave with high precision, making them popular in decoration, prototyping, and small part production. They can produce intricate designs quickly and efficiently, allowing businesses to cater to niche markets or personalized productions. When selecting a laser engraver, consider the materials it works with, the power requirements, and potential maintenance needs to ensure it aligns with your production goals.
What Are the Advantages of 3D Printers in Prototyping?
3D printers represent a shift towards additive manufacturing, allowing for unique designs and minimal material waste. They are favored in prototyping environments where complex geometries are essential. For B2B buyers, factors such as print speed, build volume, and material compatibility play crucial roles in selecting the right 3D printer. While they excel in creating custom components, understanding their limitations in speed compared to traditional machining methods is key to integrating them into production workflows effectively.
When Are Mini CNC Lathes a Good Investment for Businesses?
Mini CNC lathes specialize in producing small, cylindrical parts, making them well-suited for sectors like jewelry making, automotive component fabrication, and other precision applications. Their compact size makes them an ideal fit for small businesses with limited space. Buyers should consider the machine’s precision capabilities, tooling options, and software integration when evaluating potential investments. Proper selection can enhance productivity in creating detailed components while minimizing setup time and operational costs.
Key Industrial Applications of best small cnc machine
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of best small cnc machine | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Woodworking | Precision cutting for custom furniture and decor | Enables high-quality craftsmanship and personalization | Material compatibility, warranty options, after-sales support |
| Aerospace | Prototyping of components and parts | Accelerates design iterations, enhances innovation speed | Precision specifications, software compatibility |
| Art & Design | Creating intricate designs in various materials | Fuels creative projects with design flexibility | User-friendly interfaces, versatility of CNC capabilities |
| Automotive | Manufacturing of lightweight parts and components | Reduces production costs and improves operational efficiency | Need for robust material handling and multi-axis capabilities |
| Education & Training | Teaching CNC machining skills with practical applications | Provides hands-on experience and promotes skill development | Support for educational institutions, ease of use, and documentation |
How Are Small CNC Machines Used in Woodworking?
In the woodworking industry, small CNC machines are essential for precision cutting, shaping, and engraving of custom furniture and decorative items. They enable craftsmen to produce intricate details while minimizing material waste. For businesses in regions like South America and Africa, investing in a small CNC machine can significantly enhance product offerings and craftsmanship. Buyers should consider machines that are compatible with various wood types and inquire about after-sales support, which may be crucial for maintaining quality standards.
What Is the Role of Small CNC Machines in Aerospace Prototyping?
Aerospace companies leverage small CNC machines for prototyping components that require high precision and surface quality. The ability to quickly iterate designs helps these businesses innovate and respond to market demands. In emerging aerospace sectors in Africa and the Middle East, sourcing CNC machines that meet stringent safety and regulatory standards is vital. Buyers must ensure that machines offer precise specifications and are compatible with advanced design software.
How Can Small CNC Machines Benefit the Art & Design Industry?
The art and design sectors utilize small CNC machines to create intricate designs across various materials, including glass, plastics, and metal. Such flexibility allows artists to experiment with new methods and produce unique, personalized items. For businesses seeking to enter the European market, having a machine that boasts a user-friendly interface and extensive capabilities is critical. Additionally, considering versatility in design options can set them apart from competitors.
Why Are Small CNC Machines Important in Automotive Manufacturing?
In the automotive industry, small CNC machines play a crucial role in manufacturing lightweight parts and components that meet specific design criteria. This capability not only reduces production costs but also enhances operational efficiency by streamlining multiple processes into one. For international buyers in regions such as Brazil and Nigeria, understanding the rigorous material handling and multi-axis operations needs is essential. Investing in machines that offer durability and high precision can lead to significant long-term benefits.
How Do Small CNC Machines Facilitate Education & Training?
Small CNC machines are invaluable in educational settings, providing students with hands-on experience in the machining process. They aid institutions in teaching theory while allowing students to work on practical applications. For educational facilities in regions such as Europe and the Middle East, easy-to-use machines that offer substantial documentation can enhance productivity and learning outcomes. Additionally, support tailored for educational institutions is an essential consideration for effective implementation.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘best small cnc machine’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Limited Versatility in Material Compatibility
The Problem: A B2B enterprise in a growing market often encounters limitations when their small CNC machine cannot handle a diverse range of materials. For instance, a company that manufactures custom signage may discover that their CNC router is only effective with wood, leaving them unable to cater to clients who seek acrylic or metal options. This not only restricts their service offerings but can also hinder profitability, as missing out on lucrative contracts can impact the bottom line.
The Solution: To overcome this challenge, buyers should carefully research and select CNC machines that are explicitly designed to handle multiple material types. Look for models like the Snapmaker 2.0, which integrates various functionalities, including CNC routing, 3D printing, and laser engraving, allowing for versatility across projects. When sourcing machines, inquire about the material compatibility and ensure the machine has adequate spindle speed and cutting power for the intended materials. Additionally, invest in specialized tools or bits that cater to specific materials, ensuring high-quality finishes. User reviews and demos can provide further insights into how well a machine performs with different materials.
Scenario 2: Complexity in Machine Setup and Operation
The Problem: Many businesses struggle with complex CNC machine setups, especially when the workforce lacks technical knowledge. A manufacturer may invest in a high-end CNC machine, only to find that the ongoing setup and operation become a drain on time and resources due to inadequate training and support. This situation often results in increased downtime and frustration among employees, as they grapple with an unfamiliar system that is supposed to streamline operations.
The Solution: To mitigate these issues, buyers should prioritize CNC models that emphasize ease of setup and user-friendly controls. Opt for machines with comprehensive training resources, including video tutorials and detailed manuals. Some brands provide excellent customer service with on-site training options. When purchasing, also consider enlisting the services of a professional installation team to aid in the initial setup. Regular training sessions for team members, as well as a supportive community or forum for troubleshooting, can enhance proficiency and increase machine utilization rates.
Scenario 3: Maintenance and Downtime Challenges
The Problem: A small-scale manufacturer frequently faces unexpected downtime due to maintenance issues in their CNC machine, leading to delayed project timelines and unsatisfied clients. These breakdowns can stem from various factors, including insufficient preventive maintenance and the lack of readily available replacement parts. For companies in competitive markets, even minor delays can severely impact customer relationships and future business opportunities.
The Solution: To address maintenance challenges, businesses should develop a proactive maintenance schedule that includes regular checks and calibrations to extend the life of the CNC machine. Buyers should choose brands known for reliability and access to parts, ideally with global support channels that can provide quick replacement components. Additionally, consider investing in extended warranties or service agreements that cover maintenance costs. Implementing an asset management tool can help track machine usage and predict maintenance needs, minimizing the risk of unexpected breakdowns and ensuring smooth operations. This proactive approach not only enhances productivity but also strengthens customer trust and loyalty.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for best small cnc machine
What Are the Key Properties of Different Materials for Small CNC Machines?
When selecting a small CNC machine, understanding the materials they can process is crucial for optimizing performance and meeting production requirements. Here, we analyze four common materials—wood, aluminum, acrylic, and brass—highlighting their properties, advantages and disadvantages, their suitability for specific end products, and considerations for international B2B buyers.
How Does Wood Perform as a Material in CNC Machining?
Key Properties: Wood is known for its lightweight nature and ease of machining. It typically has good tensile strength, allowing for intricate cuts and shapes. The temperature resistance of wood is moderate, and it is generally not susceptible to corrosion.
Pros & Cons: Wood machining is cost-effective, making it an attractive choice for prototypes and artistic applications. However, it can be less durable than metals, especially in humid conditions, leading to warping. The variances in wood density can complicate milling processes.
Impact on Application: Wood is widely used in creating furniture, crafts, and model making. It is compatible with various design styles, making it a versatile choice for small businesses aiming for customization.
Considerations for International Buyers: Different countries have regulations regarding sustainably sourced wood. Compliance with standards such as FSC (Forest Stewardship Council) certifications can impact sourcing decisions in regions like Africa and South America, where forest policies may vary significantly.
What Are the Benefits of Using Aluminum in CNC Machines?
Key Properties: Aluminum boasts a high strength-to-weight ratio, excellent corrosion resistance, and good thermal conductivity. It performs well under pressure, making it suitable for various machining applications.
Pros & Cons: Its durability and lightweight nature make aluminum ideal for a variety of products, including functional components. However, the cost can be on the higher side compared to wood, and machining aluminum requires specialized tools to achieve clean finishes.
Impact on Application: Aluminum is prevalent in manufacturing parts for automotive, aerospace, and electronics due to its strength and lightweight properties. It allows for complex designs without adding excessive weight.
Considerations for International Buyers: Different aluminum grades comply with various standards, such as ASTM and ISO, which buyers in the Middle East and Europe should consider. Import tariffs for raw materials can also affect prices in regions like Nigeria and Brazil.
Why Choose Acrylic as a Material for CNC Projects?
Key Properties: Acrylic is a transparent thermoplastic that exhibits high impact resistance and excellent clarity. It is easy to machine but can melt if exposed to high speeds or temperatures.
Pros & Cons: Acrylic’s aesthetic appeal makes it suitable for signage and display products. However, while it is affordable, it is less durable than metals and can be prone to scratching.
Impact on Application: Acrylic is commonly used in making prototypes, displays, and decorative items. Its versatility allows for intricate designs and shapes that appeal to small businesses focused on innovative products.
Considerations for International Buyers: Stakeholders should be aware of the import and material standards attributed to plastics as per local regulations in South America and Europe. Compliance with REACH regulations in Europe is particularly significant and ensures safety in material usage.
What Role Does Brass Play in CNC Machining?
Key Properties: Brass combines copper and zinc, offering good machinability and a beautiful finish. It has excellent corrosion resistance due to the zinc component and can withstand high temperatures.
Pros & Cons: Brass’s durability and aesthetic quality make it a preferred choice for decorative items and precision components. However, it can be more expensive than other materials and is less ideal for high-stress applications.
Impact on Application: Frequently used for creating fittings, valves, and decorative hardware, brass is ideal for small businesses targeting specialized niches in product design.
Considerations for International Buyers: Brass is often subject to various metallurgical standards (like ASTM and JIS). Import regulations in regions such as the Middle East may necessitate stringent compliance checks for quality assurance.
Summary of Material Selection for Small CNC Machines
| Material | Typical Use Case for best small cnc machine | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Wood | Furniture, crafts, model-making | Cost-effective and easy to customize | Less durable in humid conditions | Low |
| Aluminum | Automotive and aerospace parts | High strength-to-weight ratio | Requires specialized tools for machining | High |
| Acrylic | Prototypes and decorative displays | Aesthetic appeal and versatility | Prone to scratching and less durable | Medium |
| Brass | Decorative hardware and fittings | Excellent durability and finish | Higher cost, less ideal for high-stress applications | High |
This table concisely presents the essential information that B2B buyers need when considering material options for small CNC machining applications, enabling informed decision-making tailored to specific use cases and market conditions.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for best small cnc machine
What Are the Key Manufacturing Processes for Small CNC Machines?
The manufacturing process for small CNC machines involves several critical stages that guarantee precision, durability, and overall performance. Understanding these stages can empower B2B buyers to make informed decisions.
What Are the Main Stages of CNC Machine Manufacturing?
-
Material Preparation
The initial stage involves selecting the appropriate materials, typically high-grade aluminum, steel, or plastics, depending on the targeted use of the CNC machine. The procurement process often demands stringent supplier evaluations to ensure material quality. This is crucial, especially for international buyers, who must verify that sourced materials meet their specific country regulations and standards. -
Forming
The forming stage encompasses machining processes such as milling, turning, or laser cutting. Depending on the machine model, different techniques may be applied:
– CNC Milling: Employs rotary cutters to remove material, allowing for complex shapes and high precision.
– CNC Turning: Utilizes a lathe to create symmetrical parts, essential for components like spindles.
– Laser Cutting: Offers versatility and accuracy for intricate designs, ideal for factories that require low-material wastage. -
Assembly
After forming, components are assembled, which can be an intricate process requiring skilled labor and automated systems. This stage generally includes:
– Aligning parts with key tolerances.
– Installing electrical components such as motors and sensors.
– Integrating software that controls the machine’s operations.
Effective assembly drastically influences machine operational efficiency, impacting productivity for buyers. -
Finishing
In the finishing stage, components undergo treatments such as anodizing, painting, or surface polishing. These processes not only enhance aesthetic appeal but also improve resistance to wear and corrosion. For B2B buyers, a well-finished product can lead to less maintenance and longer machine life, which is a critical factor in ROI calculations.
What Quality Assurance Measures Are Necessary for Made-to-Spec CNC Machines?
Quality assurance is crucial in the CNC machining process. It ensures that products meet international standards and performance expectations, thus fostering buyer confidence.
Which International Standards Should Buyers Look For?
B2B buyers should ensure that their suppliers adhere to various international quality standards, including but not limited to:
-
ISO 9001: This is a widely recognized standard that focuses on quality management systems and is essential for any manufacturer that wants to ensure consistency and quality in their products.
-
CE Marking: Essential for products sold in Europe, this certification indicates that the machine complies with health, safety, and environmental protection standards.
-
API Standards: Valuable particularly for manufacturers involved in the oil and gas industries, ensuring that CNC machinery meets specific operational requirements.
Understanding and verifying compliance with these standards helps mitigate the risks associated with substandard products and supports smoother operational processes across borders.
What Are the Key Quality Control Checkpoints during Manufacturing?
Every successful manufacturing process embeds quality control checkpoints to ensure that products meet regulatory standards and customer specifications. Common control points include:
-
Incoming Quality Control (IQC):
Inspection of raw materials upon arrival is crucial to prevent defects from entering the production line. For international buyers, ensuring supplier transparency in material sourcing helps assess product legitimacy. -
In-Process Quality Control (IPQC):
During the manufacturing process, regular inspections monitor the dimensional accuracy and performance of components. This continuous assessment helps catch potential errors early, minimizing rework. -
Final Quality Control (FQC):
At the end of the manufacturing process, machines undergo rigorous testing to ensure all specifications are met. This includes functionality tests, user interface checks, and safety assessments. Providing certifications from these assessments is often beneficial for B2B buyers.
What Common Testing Methods Are Utilized in CNC Machine Quality Control?
Several testing methodologies are employed throughout the manufacturing and quality assurance processes to ensure machines meet the desired performance standards:
-
Dimensional Inspection: Utilizes precision tools like calipers and gauges to verify that components adhere to specified tolerances.
-
Functional Testing: Assesses the machine’s operational capability by performing trial runs. This is particularly necessary for CNC equipment that requires complex program execution.
-
Material Testing: Tests such as tensile strength and hardness checks are conducted to confirm that materials used can withstand operational stresses.
How Can B2B Buyers Effectively Verify Supplier Quality Control?
To ensure the integrity of the manufacturing processes employed by suppliers, B2B buyers should engage in thorough supplier evaluations and audits. Strategies include:
-
Supplier Audits: Conducting on-site evaluations can reveal the intricacies of a supplier’s manufacturing process, leading to better quality in products delivered. A physical presence allows buyers to assess facilities, technology, and processes in real-time.
-
Requesting Quality Reports: Buyers should not hesitate to ask for detailed quality control reports, which can include results from FQC testing and material compliance certifications.
-
Utilizing Third-Party Inspection Services: Engaging third-party experts can provide independent verification of compliance with industry standards, alleviating concerns regarding bias in self-reported results from suppliers.
What Are the Quality Assurance Nuances for International Buyers?
B2B buyers from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe must navigate unique challenges related to quality assurance and supplier evaluation. Strategies include:
-
Cultural Understanding: Knowing how local business practices and regulatory frameworks differ can significantly enhance negotiations and ensure that compliance resonates with the supplier’s operational reality.
-
Use of Local Experts: Collaborating with local consultants who understand the regulatory landscape can facilitate smoother transactions and improve quality assurance processes.
-
Exploration of Trade Agreements: Buyers should leverage trade agreements between their countries and suppliers to ensure favorable conditions and compliance standards are met.
By investing time in understanding these manufacturing processes and quality assurance measures, B2B buyers can make informed decisions that enhance operational efficiency and ensure product reliability in their respective markets.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘best small cnc machine’
Introduction
This practical sourcing guide is tailored for B2B buyers seeking the best small CNC machine for various industrial applications. Choosing the right CNC machine is imperative for maximizing efficiency, ensuring precision, and ultimately achieving business success. This checklist will help you navigate the complexities of procurement, from initial requirements to supplier evaluation.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Identifying precise technical specifications for your CNC machine is the first critical step. Consider the size, type of materials you will be working with, and the machining processes required. Make a list of specifications like axis movements (2D, 3D), spindle speeds, and tool compatibility that fit your operational needs to ensure that the machine meets your production goals.
Step 2: Assess Budget Constraints
Understanding your budget is essential for making informed decisions. Consider the total cost of ownership, which includes purchase price, shipping, installation, training, and maintenance. By setting a realistic budget, you can better filter options that deliver value without compromising quality or performance.
Step 3: Evaluate Supplier Capabilities and Certifications
Before committing to a supplier, assess their capabilities as well as any relevant certifications. Look for suppliers with experience in your industry who can demonstrate compliance with international standards such as ISO and CE. Additionally, reviewing their case studies and references from similar businesses can provide insight into their reliability and quality.
Step 4: Analyze Machine Features and Versatility
Investigate the features of each machine to ensure they align with your intended applications. Focus on essential characteristics such as cutting area, material compatibility, and additional capabilities like laser engraving or 3D printing. A versatile machine will enhance your operational flexibility, allowing you to adapt to changing production demands.
Step 5: Request Demonstrations and Trials
Always ask potential suppliers for demonstrations or trials of their machines. Observing the machine in operation can reveal its performance and ease of use. Pay attention to the user interface, setup time, and how easily the machine can be integrated into your existing workflow.
Step 6: Inquire About After-Sales Support and Training
Strong after-sales support can significantly reduce downtime and enhance machine longevity. Confirm what kind of technical assistance is offered, including training sessions, dedicated customer support, and warranty conditions. A robust support system is essential for maintaining operational efficiency and ensuring that your team can effectively utilize the equipment.
Step 7: Negotiate Terms and Finalize Contracts
Once you’ve selected a supplier and product, negotiation is vital. Discuss payment terms, lead times, and any additional guarantees. Clear contractual terms help avoid misunderstandings and establish a strong, collaborative relationship with your supplier moving forward.
This checklist serves as a comprehensive approach to sourcing the best small CNC machine, ensuring that you cover all essential aspects for a successful procurement process.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for best small cnc machine Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components in Sourcing Small CNC Machines?
When it comes to sourcing small CNC machines for B2B operations, understanding the cost structure is pivotal. The primary cost components include materials, labor, manufacturing overhead, tooling, quality control (QC), logistics, and margin.
-
Materials: Depending on the type of CNC machine, material costs can vary significantly. Different components might be constructed from aluminum, steel, or plastics, which impact pricing. Suppliers often negotiate these prices based on material availability and market fluctuations.
-
Labor: The cost of skilled labor for assembly and quality inspections can vary globally. In regions with lower labor costs, such as parts of Africa and South America, machine assembly can be cheaper, affecting the overall price. Conversely, labor-intensive customization can lead to increased costs.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes utilities, rent, equipment maintenance, and indirect labor costs. Efficient factories with lower overheads can offer better pricing, making it essential for buyers to consider the manufacturing locations of potential suppliers.
-
Tooling: Including specialized cutting tools and fixtures, tooling costs can add a significant amount to the initial investment. Custom tooling for niche CNC applications often dictates higher prices, which may be justified through enhanced machine performance.
-
Quality Control (QC): Investing in QC processes ensures that machines meet required specifications and standards. QC costs can vary widely based on the required certifications, impacting the total initial price. Buyers should seek suppliers with strong QC processes to minimize future operational risks.
-
Logistics: Shipping costs are an essential aspect of the total cost, especially for international purchases. Freight costs can significantly affect pricing due to distance, shipping methods, and import/export duties.
-
Margin: The profit margin that suppliers factor into the pricing is often influenced by production volume. Lower volumes may result in higher margins to cover fixed costs, while larger orders typically enjoy more favorable pricing.
What Influences the Pricing of Small CNC Machines?
Several factors can affect the pricing of small CNC machines, particularly relevant for international B2B buyers:
-
Volume/MOQ: Minimum order quantities dictate pricing; larger orders usually lower per-unit costs. Buyers should consider leveraging bulk orders to negotiate better terms.
-
Specifications and Customization: Customized solutions tailored to specific industry needs often involve higher upfront costs. Balancing essential custom features with budget constraints is key.
-
Material and Quality Certifications: Machines built with higher quality materials or those that meet international certification standards often command premium prices. Understanding the trade-offs between cost and quality is crucial.
-
Supplier Factors: The reputation and reliability of the supplier greatly influence pricing. Established suppliers with proven track records may charge more but can offer peace of mind regarding quality and service.
-
Incoterms: Terms of shipment affect costs considerably. Understanding the nuances of international trade agreements can lead to cost reductions and more favorable shipping arrangements.
How Can Buyers Achieve Cost-Efficiency When Sourcing CNC Machines?
-
Negotiate Actively: Leverage competitive supplier quotes and be prepared to discuss terms regarding delivery times and volume discounts. Explore alternatives such as flexible payment options, which can enhance budget performance.
-
Consider Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Beyond the purchase price, consider operational costs like maintenance, energy consumption, and potential downtime. An inexpensive machine may incur higher TCO because of lower reliability.
-
Pricing Nuances for International Buyers: Understand the challenges of currency fluctuations and tariffs, especially for buyers in Africa and South America. Establishing contracts in stable currencies or including price adjustment clauses can mitigate risks.
Conclusion
Successfully sourcing small CNC machines involves a thorough understanding of both cost structures and pricing influencers. By focusing on these elements and leveraging effective negotiation tactics, international B2B buyers can enhance their operational efficiency while optimizing procurement costs. Keep in mind that indicative prices will vary based on numerous factors, and it’s advisable to conduct thorough market research and supplier evaluations before making significant investments.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing best small cnc machine With Other Solutions
Understanding Alternative Solutions to the Best Small CNC Machine
In the growing landscape of manufacturing and design, small CNC machines play a pivotal role by offering precision, flexibility, and efficiency. However, depending on specific business needs, various alternatives can achieve similar objectives. This section compares small CNC machines with laser engravers and traditional manual machining methods to provide international B2B buyers with actionable insights for better decision-making.
Comparison Table
| Comparison Aspect | Best Small CNC Machine | Laser Engraver | Manual Machining |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | High precision in cutting and milling across various materials. | Excellent for engraving and cutting softer materials. | Variable precision; performance largely depends on skill level. |
| Cost | Moderate ($200 – $3,000), depending on capabilities. | Generally lower ($150 – $1,500), suitable for decorative work. | Can vary widely; significant upfront investment in tools and training. |
| Ease of Implementation | Easy setup; user-friendly software available. | Typically straightforward with plug-and-play capability. | High learning curve; requires manual skill development and experience. |
| Maintenance | Moderate; regular software updates and occasional mechanical servicing needed. | Low; minimal maintenance required for laser tubes and optics. | High; frequent maintenance needed for tools, plus potential for wear and tear. |
| Best Use Case | Versatile for small batch production, prototyping, and crafts. | Ideal for custom designs, signage, and delicate work on various materials. | For projects requiring bespoke craftsmanship or where CNC technology is not suitable. |
Detailed Breakdown of Alternatives
Laser Engraver
Laser engravers are an appealing alternative for businesses focused on design elements, such as signage and intricate detailing. These devices excel at engraving and cutting softer materials like wood, acrylic, and leather. Pros include affordability, lower maintenance demands, and user-friendly operation. However, laser engravers lack the versatility in handling metals and larger workpieces compared to CNC machines, which can limit their application for more complex projects.
Manual Machining
Despite being less common in contemporary manufacturing settings, traditional manual machining remains a valid alternative, especially in highly skilled hands. This method allows for customized and bespoke components with intricate details. The primary advantage of manual machining lies in the ability to handle a broad range of materials and techniques reflective of the artisan’s skill. However, the disadvantages are notable: it requires significant upfront investment in tools, extensive training, and is time-consuming, with performance being highly reliant on the operator’s expertise. Given the evolving market demands, few businesses choose solely manual methods in favor of the speed and precision offered by CNC technology.
Making the Right Choice for Your Business Needs
Selecting the best solution for your business requires a thorough understanding of your specific requirements and goals. Businesses needing high-volume production or precise, repeatable outcomes may find that investing in a small CNC machine is the most advantageous choice. Conversely, companies focusing on custom decor, signage, or low-volume production may find laser engravers better suited, providing cost savings with less complexity. Lastly, manual machining could still hold merit for specialized craftsmanship, especially where high levels of detail are paramount. Conducting a careful analysis of each alternative’s strengths and weaknesses against your operational context will guide you to the most fitting solution.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for best small cnc machine
What Key Technical Properties Should You Consider for the Best Small CNC Machines?
Understanding the essential technical properties of CNC machines is crucial for B2B buyers, particularly when selecting equipment that aligns with operational needs and budget constraints. Here are critical specifications commonly assessed:
1. Material Compatibility
The range of materials a CNC machine can process—such as wood, plastics, aluminum, and brass—determines its functionality across diverse applications. For businesses that need versatility, machines with a broader material compatibility allow them to expand their services without investing in multiple machines.
2. Spindle Speed
Spindle speed, measured in revolutions per minute (RPM), indicates how fast the cutting tool rotates. Higher spindle speeds can enhance efficiency, particularly in cutting softer materials, while lower speeds are often better suited for hard materials. Buyers should consider the spindle speed in conjunction with the types of projects they anticipate to undertake.
3. Working Area
The working area denotes the maximum dimensions of the material a CNC machine can handle. A larger working area enables businesses to undertake bigger projects or multiple smaller projects simultaneously, which is essential for scaling operations and catering to diverse customer needs.
4. Precision and Tolerance
Precision is critical in ensuring that every component is produced to exact specifications. Tolerance refers to the permissible limit of variation in a physical dimension. High precision and low tolerance rates indicate superior machining capability, which directly correlates with product quality—a vital factor when bidding for high-stakes contracts.
5. Ease of Use and Software Compatibility
User-friendly interfaces and software that is compatible with popular CAD/CAM programs make machines more accessible to operators, especially those new to CNC technology. This specification is especially advantageous for companies investing in training and onboarding, allowing quicker adoption of the technology.
6. Build Quality and Stability
The construction of the CNC machine influences its longevity and reliability. A stable machine minimizes vibrations during operations, leading to higher quality output. Considering build quality is important for avoiding frequent repairs and maintaining productivity levels.
What Are Common Trade Terms Used in the CNC Machine Industry?
Navigating the landscape of CNC machine procurement requires familiarity with specific industry terminology. Here are key terms that B2B buyers should know:
1. OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
OEM refers to a company that produces parts or equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer. For buyers, sourcing from trusted OEMs ensures quality and compatibility with existing systems, heightening confidence in the investment.
2. MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ indicates the smallest number of units that a supplier is willing to sell. Buyers must be aware of MOQs when planning purchases, as they can affect inventory management, cash flow, and profitability, especially for smaller businesses or those just starting.
3. RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a document used to solicit price quotes from suppliers. Engaging in the RFQ process allows buyers to compare offers comprehensively, create negotiation leverage, and optimize purchasing decisions based on detailed cost analysis.
4. Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
Incoterms are a set of predefined international trade rules published by the International Chamber of Commerce (ICC). They clarify the responsibilities of sellers and buyers in shipping logistics, which is crucial for international buyers to understand regarding delivery timelines and cost management.
5. CAM (Computer-Aided Manufacturing)
CAM software helps automate manufacturing processes based on CAD designs. Buyers should consider the compatibility of the CNC machine with popular CAM software for streamlined production processes and improved design accuracy.
By understanding these technical properties and trade terms, B2B buyers can make informed decisions regarding their investments in CNC machinery, enhancing operational capabilities and aligning equipment with strategic business goals.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the best small cnc machine Sector
What Are the Global Drivers Influencing the Best Small CNC Machine Market?
The global small CNC machine market is witnessing significant momentum, driven by several factors, including the digitization of manufacturing processes and the increasing demand for customized solutions. As industries aim to enhance productivity, precision, and efficiency, small CNC machines have emerged as invaluable tools. Countries in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, particularly Nigeria and Brazil, are experiencing a surge in small-scale manufacturing enterprises. These markets benefit from low labor costs, increased accessibility to advanced technology, and an emphasis on local production to meet rising consumer demand.
Emerging B2B tech trends are shaping the procurement landscape. Key technologies such as IoT integration, AI-driven automation, and cloud-based software are enhancing the capabilities of small CNC machines, making them more versatile and user-friendly. This trend is particularly advantageous for small businesses looking to optimize operations without extensive upfront investment. Additionally, many manufacturers are increasingly offering machine-as-a-service (MaaS) models, allowing businesses to access technology without high capital expenditures, which is particularly appealing to startups in developing regions.
How Are Sustainability and Ethical Sourcing Impacting the Small CNC Machine Sector?
Sustainable practices and ethical sourcing are becoming critical considerations for international B2B buyers of small CNC machines. The environmental impact of manufacturing is under scrutiny, prompting businesses to seek CNC solutions that minimize waste and energy consumption. Many suppliers are adopting sustainable practices by utilizing eco-friendly materials and processes, thereby reducing their carbon footprint. This shift is not merely a compliance measure; it is a business imperative, as buyers increasingly prefer vendors who can demonstrate environmental responsibility.
Certifications related to sustainability, such as ISO 14001 or the use of recycled materials, play a crucial role in the sourcing decisions of B2B buyers. Suppliers that emphasize “green” certified components can position themselves more effectively in the market, appealing to buyers who prioritize ethical supply chains. As small CNC machines become integral in various industries, the demand for ethically sourced materials and components will continue to rise, reinforcing the importance of sustainability in manufacturing processes.
What Is the Evolution of CNC Technology and Its Relevance to Today’s B2B Landscape?
CNC technology has evolved significantly since its inception in the mid-20th century. Initially, these machines were limited to large industrial settings, but technological advancements have democratized access, allowing small businesses to harness their benefits. The emergence of more compact, user-friendly CNC machines has further facilitated adoption among smaller enterprises and hobbyists. Today, small CNC machines feature enhanced functionalities such as multidimensional cutting, engraving, and even laser processing, making them applicable across various sectors, from woodworking to metal machining.
This evolution has transformed how small businesses operate, enabling them to compete and innovate on scales previously unattainable. With the increasing integration of smart technologies, the CNC landscape is set for further transformation, which will expand opportunities and efficiencies for international B2B buyers seeking versatility and precision in their manufacturing processes. As small CNC machines become indispensable in modern production, understanding their history helps illustrate their current importance in facilitating global trade and meeting diverse manufacturing needs.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of best small cnc machine
-
How do I choose the right small CNC machine for my business needs?
Selecting the right small CNC machine involves assessing your specific requirements, including the materials you plan to work with, the project size, and the intended applications. Start by determining the machine’s compatibility with various materials (wood, metal, plastic) and its precision capabilities. Consider factors like the size of the work area, ease of use, and potential for upgrades. Research and compare different models, looking for user reviews and industry certifications to ensure quality and value for your investment. -
What types of small CNC machines are available for different applications?
Small CNC machines come in various types, including routers, milling machines, engraving machines, and lathes. CNC routers are ideal for woodworking and intricate designs. Milling machines offer versatility for cutting and drilling through diverse materials. Engraving machines specialize in finer details, suitable for signage and artisanal work. Determine your application’s specific demands to identify the best type among these options to maximize your operational efficiency. -
What are the common payment terms when sourcing CNC machines internationally?
Payment terms in international trade can vary widely among suppliers. Common practices include advance payment, letters of credit, or a mix of upfront and 30-60 day payment terms post-delivery. It’s crucial to discuss these terms upfront and consider using a verified payment method, especially for large transactions. Additionally, factor in currency fluctuations and potential additional costs related to tariffs or import fees to avoid unexpected expenses. -
What is the minimum order quantity (MOQ) for CNC machines, and how does it affect pricing?
Minimum order quantities (MOQs) for CNC machines can vary significantly by supplier, often ranging from one unit to multiple units. Sourcing in bulk might yield discounts, but it requires a careful assessment of your current business capability and storage constraints. Understanding the MOQ helps you negotiate better pricing and ensures a stable supply chain if you plan to scale production. Always clarify MOQ conditions and associated pricing with your supplier early in the procurement process. -
How can I ensure the quality of CNC machines before purchasing?
To ensure quality before purchasing a CNC machine, conduct thorough research on potential suppliers. Request certifications such as ISO or CE for machine compliance with international standards. Seek out product demonstrations, samples, or customer test reports to validate performance and durability. Additionally, ask for warranties or service agreements, which can indicate the supplier’s confidence in their products and their commitment to after-sales support. -
What should I consider regarding transportation and logistics when importing CNC machines?
Transportation and logistics are critical when importing CNC machines. Consider the machine’s dimensions and weight, which will influence shipping costs and methods. Evaluate the reliability of transport carriers and the shipping routes available to your destination. It’s also essential to familiarize yourself with import regulations in your country, including customs duties and documentation requirements. Engaging a freight forwarder can streamline the process, ensuring compliance and efficient delivery. -
Are there customization options available for small CNC machines?
Many suppliers offer customization options for small CNC machines to meet specific business needs. Customizations can include specialized tooling, software choices, or additional features such as laser engraving capabilities. Be prepared to discuss your project requirements with the supplier and clarify the implications on lead times and costs. Custom solutions can enhance operational productivity, but ensure that any specifications align with your existing workflows and equipment. -
What kind of after-sales support is typically available for CNC machine purchases?
After-sales support is critical when investing in a CNC machine. Most reputable suppliers offer warranties, repair services, and technical support to ensure ongoing functionality. This may include training for your staff, access to spare parts, and responsiveness to operational issues. Clarify the scope of after-sales support before completing your purchase to establish clear expectations for maintenance and assistance during the machine’s lifecycle.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.
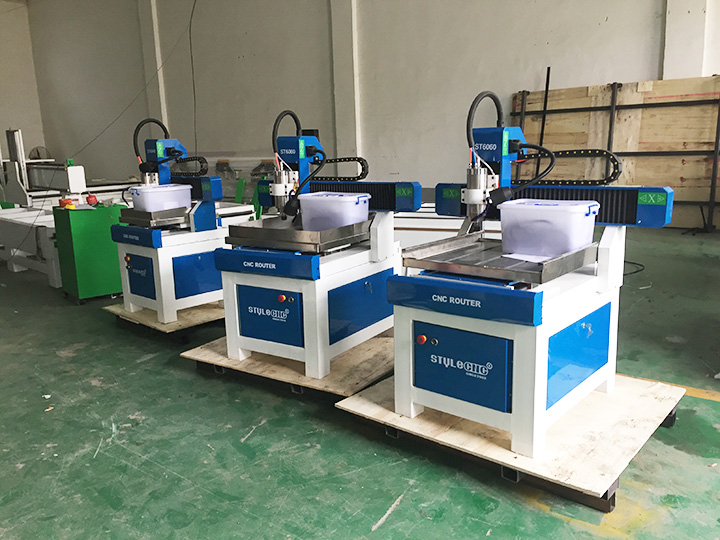
Top 8 Best Small Cnc Machine Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. Sainsmart – Genmitsu 3018 PROver
Domain: cncsourced.com
Registered: 2020 (5 years)
Introduction: [{‘Product’: ‘Sainsmart Genmitsu 3018 PROver’, ‘Price’: ‘$345’, ‘Working Area’: ‘300 x 180 x 45 mm’, ‘Precision’: ‘Around 0.003″‘, ‘Material Compatibility’: ‘Wood, MDF, acrylic, polycarbonate, PCB’, ‘Pros’: [‘Easy to set up’, ‘Affordable’, ‘Variety of materials’, ‘Optional laser engraver upgrade’], ‘Cons’: [‘Less sturdy than pricier models’]}, {‘Product’: ‘MakerMade M2’, ‘Price’: ‘$1,199’, ‘Workin…
2. Shapeoko – Beginner Friendly CNC Machine
Domain: reddit.com
Registered: 2005 (20 years)
Introduction: Shapeoko 4 recommended as a suitable CNC machine for beginners. Considerations for starting a CNC business include potential limitations of desktop machines such as speed, power, and maintenance needs. Suggestion to utilize resources like r/hobbycnc for further learning.
3. SYIL – X7 Small CNC Mill
Domain: us.syil.com
Registered: 2001 (24 years)
Introduction: {‘model’: ‘SYIL X7’, ‘type’: ‘Small CNC Mill’, ‘dimensions’: {‘axis_travels’: ‘400×300×380 mm’, ‘table_size’: ‘27.56″×11.81″ (700×300 mm)’, ‘floor_size’: ‘70.87 × 62.99 × 88.58″ (1800×1600×2250 mm)’, ‘weight’: ‘2200 kg’}, ‘capacity’: {‘max_table_load’: ‘330 lb (150 kg)’, ‘max_tool_diameter’: ‘2.4″ (63 mm)’, ‘max_tool_length’: ‘7.8″ (200 mm)’, ‘max_tool_weight’: ‘6.6 lb (3 kg)’}, ‘travel’: {‘x_trav…
4. Omio – X8; Shapeoko – 3 & 5 Pro
Domain: chiefdelphi.com
Registered: 1998 (27 years)
Introduction: Omio X8 – popular choice for CNC under $5000; capable of machining aluminum and polycarbonate; users praise its ease of use and reliability. Shapeoko 3 – used for polycarbonate and aluminum; noted for being user-friendly and improving speed in newer versions. Shapeoko 5 Pro – 4′ x 4′ bed, newer model with improved features, recommended for various materials. MillRight Power Route Plus XL – large f…
5. Avid – 4×8 CNC Router
Domain: woodweb.com
Registered: 1995 (30 years)
Introduction: CNC routers recommended for a small custom furniture shop; needs: cutting sheet goods and solid wood parts (up to 2″ thick); limited to single-phase power and limited space; size preference: 4×8; mentioned brands: Avid, CAMaster, DB CNC, Shop Sabre; suggestions for rigid machines due to solid wood machining; emphasis on investing in quality to avoid future upgrades.
6. Carbide 3D – Shapeoko Series Overview
Domain: community.carbide3d.com
Registered: 2013 (12 years)
Introduction: The discussion focuses on CNC machines, particularly the Shapeoko series. The key product details mentioned include: 1. Models: Shapeoko 4, Shapeoko 4 Pro, Shapeoko 5 Pro, Nomad 3. 2. Size and Working Area: SO4 Standard (16″x16″), SO5 Pro (4’x4′), Nomad 3 (8″x8″x3″). 3. Features: The Shapeoko Pro offers faster cutting and a lit work area, while the Nomad is suitable for small precision projects li…
7. STYLECNC – STG6090
Domain: stylecnc.com
Registered: 2015 (10 years)
Introduction: { “Brand”: “STYLECNC”, “Model”: “STG6090”, “Table Size”: “2′ x 3′ (24″ x 36″, 600mm x 900mm)”, “Price Range”: “$2,580 – $3,200”, “Stock Availability”: “360 Units in Stock Available for Sale Every Month”, “Warranty”: “One-Year Limited Warranty for Entire Machine (Extended Warranties Available for Major Parts)”, “Money Back Guarantee”: “30-Day Money Back Guarantee for Your Purchase”, “Technical Supp…
8. CNC Mill – Affordable Steel Cutting Solutions
Domain: practicalmachinist.com
Registered: 2000 (25 years)
Introduction: CNC mill under $10k, capable of cutting steel, with x-axis reach of 10″-20″ and z-axis reach of 7″-15″. Suitable for creating smaller engine and car parts made of aluminum or steel. Potential models mentioned include Tormach 440/770, CNC Express, CNC Baron Mill, PRO4824, Fadal Model 904-1, Haas 1997 VF1, and Mazak VQC15.
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for best small cnc machine
In conclusion, navigating the landscape of small CNC machines requires a strategic sourcing approach to ensure alignment with business goals and market demands. Buyers should prioritize machines that combine versatility, robustness, and ease of use, such as the Sainsmart Genmitsu 3018 PROver for entry-level applications or the MakerMade M2 for larger furniture projects. By leveraging insights into machine specifications, material compatibility, and reliability, businesses can enhance productivity while minimizing costs.
For international based B2B buyers in regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, this is an opportune moment to invest in advanced CNC technology. As market competitiveness increases, adopting efficient machining solutions can lead to improved product offerings and customer satisfaction. Importantly, staying informed about technological trends and supplier capabilities will empower businesses to make informed decisions.
Take action today by assessing your specific operational needs and exploring the best small CNC machines that align with your strategy. Investing in quality machinery now will pave the way for future growth and innovation, positioning your organization for success in the manufacturing landscape.