Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for best free cnc software for beginners
In today’s rapidly evolving manufacturing landscape, sourcing the best free CNC software for beginners poses a significant challenge for international B2B buyers. As businesses seek to optimize their operations while managing costs, the right software can be a game-changer. This guide provides a comprehensive overview of the various types of free CNC software available, including essential CAD, CAM, and CNC control applications. We delve into their specific applications, functionalities, and how they cater to different CNC machines, from desktop routers to industrial milling systems.
Navigating the global market requires more than just an understanding of software features; it demands a keen insight into supplier vetting, compatibility, and potential costs associated with upgrades or additional tools. By equipping B2B buyers, particularly those from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe—including key markets like Brazil and Vietnam—with actionable insights, this guide empowers you to make informed purchasing decisions. You will discover how to leverage free software options that not only meet your immediate needs but also support your long-term business goals. Whether you are just starting out or looking to enhance your existing operations, this guide serves as your roadmap to successfully integrating CNC software into your business strategy.
Understanding best free cnc software for beginners Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| CAD Software | 2D and 3D design capabilities, user-friendly interfaces | Product design, prototyping, custom parts | Pros: Essential for design; many free options. Cons: Steeper learning curve for advanced tools. |
| CAM Software | Converts CAD designs into machine-readable G-code | Manufacturing, CNC machining | Pros: Automates toolpath generation; essential for production. Cons: Limited features in free versions. |
| Integrated CAD/CAM | Combines CAD and CAM functionalities in one tool | Streamlined workflows, small batch production | Pros: Simplifies process; cost-effective. Cons: May lack advanced features of standalone software. |
| Browser-Based Tools | Accessible from any device, often with intuitive UIs | Quick projects, educational purposes | Pros: Easy to use; no installation needed. Cons: May have limitations in functionality and file types. |
| Specialty Software | Focused on specific tasks like engraving or 3D printing | Niche applications, artistic projects | Pros: Tailored features for specific tasks. Cons: May not support broader CNC applications. |
What Are the Key Characteristics of CAD Software for Beginners?
CAD software is essential for any CNC operation as it allows users to create detailed 2D and 3D designs. Popular free options like FreeCAD and Inkscape provide a range of functionalities suitable for beginners. These tools are particularly beneficial for businesses in product design and prototyping, enabling them to visualize and refine their concepts before moving to production. When considering CAD software, businesses should assess the learning curve and the software’s compatibility with CAM tools to ensure a seamless workflow.
How Does CAM Software Facilitate CNC Operations?
CAM software is crucial for converting CAD designs into G-code, which CNC machines use to execute tasks. Free options like Easel and Kiri:Moto enable users to generate toolpaths efficiently, making them ideal for manufacturing and CNC machining applications. For B2B buyers, the choice of CAM software should be based on its ability to handle the specific geometries of their projects and the ease of integration with existing CAD tools. While free versions may have limitations, they often serve as a solid starting point for small businesses.
Why Choose Integrated CAD/CAM Solutions?
Integrated CAD/CAM software combines design and toolpath generation in a single platform, streamlining the workflow. This approach is particularly beneficial for small to medium-sized businesses that require efficiency without incurring high costs. Tools like Fusion 360 offer a comprehensive solution for users looking to manage both design and production processes. Buyers should consider the software’s capabilities in both design and machining, as well as its user-friendliness for teams with varying skill levels.
What Are the Advantages of Browser-Based CNC Software?
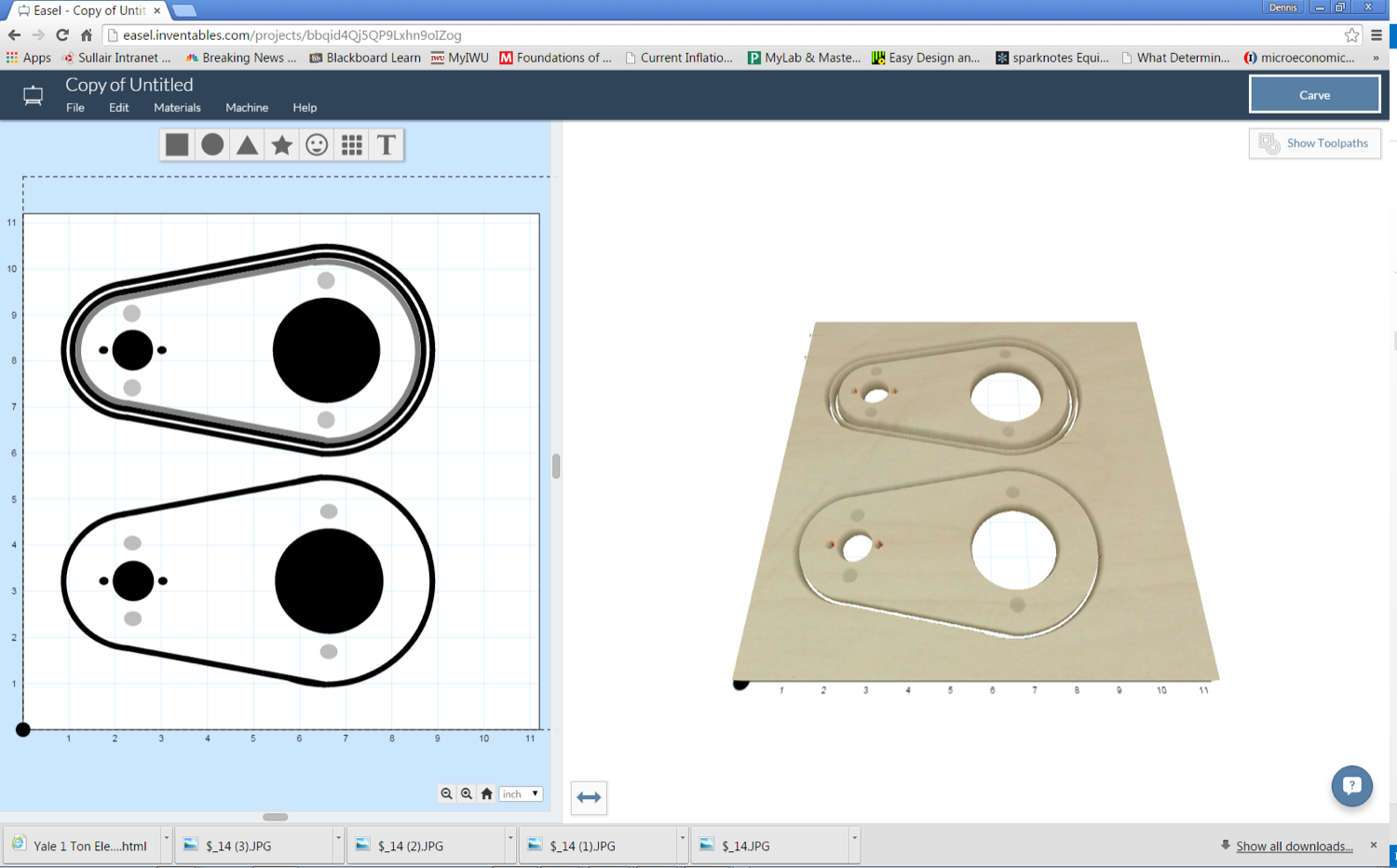
Browser-based CNC software provides accessibility and convenience, allowing users to work on projects from any device without the need for installation. This flexibility is particularly useful for educational institutions or businesses that require quick prototyping. While tools like Easel offer an intuitive interface for beginners, potential buyers should evaluate any limitations in functionality and file compatibility, as these can affect the software’s overall effectiveness in professional settings.
How Does Specialty Software Cater to Niche Applications?
Specialty CNC software focuses on specific tasks such as engraving or 3D printing, making it suitable for businesses with niche applications. While these tools offer tailored features that can enhance productivity in artistic projects, they may lack the versatility of more comprehensive CAD/CAM solutions. B2B buyers should carefully assess their specific needs and the software’s capabilities to ensure it aligns with their operational goals and project requirements.
Key Industrial Applications of best free cnc software for beginners
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of best free cnc software for beginners | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Manufacturing | Prototype Development with CAD/CAM Tools | Accelerates product development cycles and reduces time-to-market. | Compatibility with existing CNC machinery; ease of learning for staff. |
| Art and Design | Custom Signage and Decorative Elements | Enhances brand visibility and customer engagement through unique designs. | Availability of design templates; support for various file formats. |
| Education and Training | Hands-on Learning in CNC Machining | Provides practical skills for students, preparing them for industry jobs. | User-friendliness; access to tutorials and community support. |
| Construction | Fabrication of Components and Fixtures | Improves accuracy in building projects and reduces material waste. | Integration with construction workflows; scalability for larger projects. |
| Furniture Design | Custom Furniture Prototyping | Enables innovation in furniture design, catering to niche markets. | Design flexibility; material compatibility; local support options. |
How is Best Free CNC Software Used in Manufacturing?
In the manufacturing sector, best free CNC software allows businesses to develop prototypes efficiently. By utilizing CAD/CAM tools, companies can create detailed designs and convert them into tool paths for CNC machines. This capability not only shortens the development cycle but also minimizes costs associated with traditional prototyping methods. For international B2B buyers, particularly in emerging markets, the software must integrate seamlessly with existing CNC machinery and be straightforward enough for operators with varying levels of experience.
What Role Does Best Free CNC Software Play in Art and Design?
In the art and design industry, free CNC software is instrumental in creating custom signage and decorative elements. Designers can leverage CAD tools to produce unique artwork or branding materials that stand out in a competitive market. The ability to import various file formats, such as SVG and DXF, is crucial for artists looking to incorporate diverse designs. B2B buyers in this sector should consider the software’s design templates and its compatibility with different CNC machines to ensure smooth operations.
How Does Best Free CNC Software Benefit Education and Training?
Educational institutions utilize best free CNC software to provide hands-on training in CNC machining. By incorporating these tools into their curriculum, schools can equip students with practical skills that are highly sought after in the job market. The software’s user-friendliness and availability of online tutorials significantly enhance the learning experience. For international buyers, especially in regions with developing educational infrastructures, sourcing software that offers robust community support can be a game-changer.
Why is Best Free CNC Software Important in Construction?
In the construction industry, free CNC software is essential for fabricating components and fixtures with high precision. This capability ensures that building projects are executed accurately, leading to reduced material waste and lower costs. Buyers in this sector should prioritize software that can easily integrate into their existing workflows and scale to accommodate larger projects. Additionally, the software should provide reliable support for various construction materials and methods.
How Does Best Free CNC Software Support Furniture Design?
For furniture designers, best free CNC software facilitates the prototyping of custom furniture pieces. This innovation allows designers to explore unique shapes and functionalities, catering to niche markets and enhancing customer satisfaction. The flexibility in design and the software’s ability to work with various materials are critical considerations for B2B buyers. Moreover, access to local support and resources can significantly influence the decision-making process in this competitive industry.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘best free cnc software for beginners’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Navigating Complex User Interfaces in Free CNC Software
The Problem: Many B2B buyers, especially those new to CNC machining, often find themselves overwhelmed by the complexity of free CNC software interfaces. For instance, while software like FreeCAD and Fusion 360 offers powerful features, their steep learning curves can deter beginners. This complexity can lead to frustration, wasted time, and ultimately, a lack of productivity as users struggle to create designs or generate toolpaths effectively. In markets where time is money, such inefficiencies can be detrimental to a business’s bottom line.
The Solution: To mitigate this issue, buyers should prioritize software with intuitive interfaces and robust community support. Options like Easel or Kiri:Moto offer user-friendly platforms that combine CAD and CAM functionalities, allowing beginners to transition smoothly from design to machining. Additionally, investing time in community forums and tutorial resources can enhance understanding and usability. For example, manufacturers can organize training sessions for their teams, leveraging online tutorials or local workshops to help users familiarize themselves with the software. This proactive approach not only improves team competence but also maximizes the software’s potential, leading to better project outcomes.
Scenario 2: Limited Functionality of Free Software Packages
The Problem: Many free CNC software options come with significant limitations, such as restricted features or export capabilities. For instance, while a software might allow basic 2D design, it may not support advanced 3D modeling or exporting to various file formats. This can be particularly problematic for businesses that require versatility in their projects, as they may end up needing to invest in additional paid software to meet their full range of design and machining needs.
The Solution: B2B buyers should carefully assess their specific requirements before selecting free CNC software. It’s crucial to identify software that offers a balance between free features and the potential for upgrades. For instance, Fusion 360 provides a robust free version for hobbyists, which could be suitable for small businesses looking to explore CNC machining without immediate costs. Buyers should also consider software with modular features that allow for incremental upgrades as their needs evolve. Engaging with vendors to understand potential future costs and capabilities can help businesses make informed decisions that align with their long-term operational goals.
Scenario 3: Integration Challenges with Existing CNC Machines
The Problem: A common challenge faced by B2B buyers is the integration of free CNC software with existing machines. Some software may only be compatible with specific hardware, leading to wasted time and resources if the chosen software cannot effectively communicate with the CNC equipment. This compatibility issue can create bottlenecks in production, especially in environments where multiple machines are used, and software needs to work seamlessly across them.
The Solution: Buyers should conduct thorough compatibility checks before selecting any CNC software. It is essential to verify whether the software supports the specific CNC machine types and their control systems, such as GRBL or Mach3. Many software options, like Easel, provide comprehensive compatibility guides and user reviews that can inform these decisions. Additionally, reaching out to software developers or community forums can provide insights into integration experiences from other users. Establishing a test phase where the software is trialed on a limited basis with existing machines can help confirm compatibility before committing to a full rollout, ensuring a smoother implementation process.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for best free cnc software for beginners
What are the Key Properties of Common Materials Used with Free CNC Software?
When selecting free CNC software for beginners, understanding the materials that will be processed is crucial. Different materials have unique properties that affect machining performance, software compatibility, and end-product quality. Below, we analyze four common materials and their implications for B2B buyers, particularly in regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe.
How Do Wood Materials Impact CNC Machining?
Wood is one of the most popular materials used in CNC machining, particularly for beginners. It is relatively easy to work with, making it an ideal choice for those just starting. Key properties include a low density, which allows for easier cutting and shaping, and a natural resistance to corrosion.
Pros & Cons: Wood is durable and cost-effective, but its complexity arises from variations in grain and moisture content, which can affect machining precision. Additionally, certain hardwoods can be more challenging to machine than softwoods.
Impact on Application: Software like Easel and Carbide Create is particularly well-suited for wood, as they can handle 2D and 2.5D designs effectively.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should consider local wood species availability and compliance with environmental regulations regarding deforestation. Standards such as the FSC (Forest Stewardship Council) certification may be relevant.
What Are the Benefits of Using Plastics in CNC Projects?
Plastics, including acrylic and polycarbonate, are increasingly used in CNC applications due to their versatility and ease of machining. Key properties include lightweight characteristics and excellent corrosion resistance, making them suitable for various applications.
Pros & Cons: Plastics are generally less expensive than metals and can be machined into complex shapes. However, they may not withstand high temperatures or mechanical stresses as well as metals, limiting their use in certain applications.
Impact on Application: Free CAD/CAM software can effectively handle plastic designs, especially when using tools like Fusion 360 or Kiri:Moto.
Considerations for International Buyers: Compliance with local regulations regarding plastic waste and recycling is essential. Standards like ISO 11469 may be applicable, particularly in Europe.
How Does Metal Machining Differ from Other Materials?
Metals such as aluminum and brass are often used in CNC machining for their strength and durability. Key properties include high tensile strength and excellent thermal conductivity, which are essential for applications requiring robustness.
Pros & Cons: While metals provide superior durability, they can be more expensive and complex to machine compared to wood or plastics. The initial investment in CNC equipment and software may also be higher.
Impact on Application: Software like Fusion 360 can manage complex metal designs, but users must ensure their CNC machines are capable of handling the required speeds and feeds for metal.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should be aware of compliance with international standards like ASTM or DIN for metal quality. Import tariffs and local manufacturing capabilities may also impact cost.
What Role Do Composites Play in CNC Machining?
Composites, such as fiberglass and carbon fiber, are becoming increasingly popular due to their lightweight and high-strength properties. Key properties include excellent fatigue resistance and low thermal expansion.
Pros & Cons: Composites can be more expensive than traditional materials but offer superior performance in specific applications. They may require specialized tooling and software for effective machining.
Impact on Application: Advanced software like Fusion 360 can effectively handle composite designs, but users must be cautious about tool wear and machining parameters.
Considerations for International Buyers: Compliance with industry standards for composite materials, such as ASTM D3039, is critical. Additionally, buyers should consider the availability of local suppliers for composite materials.
Summary Table of Material Selection for CNC Software
| Material | Typical Use Case for best free cnc software for beginners | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Wood | Furniture, signs, and decorative items | Easy to machine and cost-effective | Variability in grain and moisture | Low |
| Plastics | Prototyping, signage, and lightweight components | Versatile and corrosion-resistant | Limited high-temperature use | Medium |
| Metals | Structural components, tools, and machinery | High strength and durability | Higher machining complexity | High |
| Composites | Aerospace, automotive parts, and specialized applications | Lightweight and high strength | Expensive and requires special tooling | High |
This analysis provides a comprehensive overview of materials relevant to CNC machining, enabling B2B buyers to make informed decisions based on their specific needs and regional considerations.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for best free cnc software for beginners
What Are the Main Stages of Manufacturing Processes for CNC Software?
The manufacturing processes behind CNC software involve several stages that ensure the final product meets the needs of users, particularly beginners in the CNC field. Understanding these stages can help B2B buyers assess the reliability and usability of the software.
How Is Material Prepared for CNC Software Development?
Material preparation in the context of CNC software refers to the foundational coding and design aspects that create the software’s functionality. This includes:
- Requirement Analysis: Gathering specifications from potential users to understand their needs, particularly focusing on ease of use for beginners.
- Software Architecture Design: Structuring the software to accommodate various CNC machines and processes, including CAD and CAM functionalities.
- Prototyping: Developing initial versions of the software to test functionality and user interface, ensuring that it is intuitive for beginners.
This preparatory work is critical as it sets the stage for all subsequent development and directly impacts user experience.
What Techniques Are Used in the Forming Stage of CNC Software Development?
The forming stage involves the actual coding and development of the software. Key techniques include:
- Agile Development: Many software developers adopt Agile methodologies to iteratively develop and refine the software. This approach allows for regular feedback from users, particularly helpful for beginner-focused software.
- Modular Programming: Dividing the software into modules, such as CAD, CAM, and machine control, enhances maintainability and allows for easier updates. This is crucial for beginners who may require frequent updates to improve usability.
- User-Centered Design: Emphasizing user experience (UX) and user interface (UI) design principles ensures that beginners can navigate the software without extensive training.
By utilizing these techniques, developers can create software that is not only functional but also accessible to users with limited experience.
How Is Assembly Conducted in CNC Software Development?
Assembly in this context refers to the integration of various components of the software. This includes:
- Integration Testing: After developing each module, rigorous testing is conducted to ensure that all components work seamlessly together. This step is crucial for preventing issues that could confuse beginner users.
- User Acceptance Testing (UAT): Involving actual users to test the software in real-world scenarios helps identify any usability issues before the final release. Feedback from beginners is particularly valuable here to ensure the software meets their needs.
This assembly stage is vital for delivering a cohesive product that functions well across different CNC machines and applications.
What Finishing Processes Are Applied to CNC Software?
Finishing processes involve final adjustments and quality checks before the software is released to the public. Key activities include:
- Performance Optimization: Ensuring the software runs smoothly on various hardware setups, particularly for entry-level CNC machines, which are common in markets like Africa and South America.
- Documentation and Tutorials: Providing comprehensive user manuals, tutorials, and support resources is essential for helping beginners understand how to use the software effectively.
- Feedback Loop: Establishing a system for users to report bugs and request features post-launch helps maintain the software’s relevance and usability.
These finishing touches are critical for ensuring a positive user experience and fostering long-term customer satisfaction.
How Is Quality Assurance Implemented in CNC Software Development?
Quality assurance (QA) is a critical component of CNC software development, ensuring that the product is reliable and meets international standards.
What International Standards Are Relevant for CNC Software Quality Assurance?
International standards such as ISO 9001 play a vital role in establishing a framework for quality management systems (QMS). Key aspects include:
- Documentation: Maintaining comprehensive documentation throughout the development process helps ensure traceability and accountability.
- Continuous Improvement: Emphasizing a culture of continuous improvement allows developers to adapt to changing user needs and technological advancements.
- Customer Feedback Mechanisms: Implementing structured feedback mechanisms helps developers understand user experiences and areas for improvement.
For B2B buyers, verifying adherence to these standards can provide confidence in the software’s reliability.
What Are the Key Quality Control Checkpoints in CNC Software Development?
Quality control (QC) checkpoints are crucial for maintaining software integrity. Common checkpoints include:
- Incoming Quality Control (IQC): Assessing the quality of raw materials, such as coding libraries and frameworks, used in the software.
- In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): Monitoring the development process through regular code reviews and testing to catch issues early.
- Final Quality Control (FQC): Conducting thorough testing before release, including functional testing, performance testing, and user acceptance testing.
These checkpoints are essential for ensuring that the software is robust and user-friendly, particularly for beginners.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control?
B2B buyers can employ several strategies to verify a supplier’s quality control processes:
- Audits: Conducting regular audits of the supplier’s development processes can help ensure compliance with quality standards.
- Quality Assurance Reports: Requesting detailed QA reports that outline testing methods, results, and any corrective actions taken can provide insights into the supplier’s commitment to quality.
- Third-Party Inspections: Engaging third-party organizations to assess the software can offer an unbiased evaluation of its quality and reliability.
These measures are particularly important for international buyers from regions like Africa and South America, where software quality may vary significantly.
What QC and Certification Nuances Should International B2B Buyers Consider?
When purchasing CNC software from international suppliers, B2B buyers should be aware of specific QC and certification nuances:
- Regional Compliance: Ensure that the software complies with local regulations and standards, which can vary significantly across regions.
- Localization: Consider whether the software supports local languages and currencies, enhancing usability for beginners in different markets.
- Support and Training: Evaluate the availability of training resources and customer support, which are crucial for beginners who may require additional assistance.
By understanding these nuances, international B2B buyers can make informed decisions and ensure they select the best CNC software for their needs.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘best free cnc software for beginners’
Introduction
Navigating the world of CNC software can be daunting, especially for beginners. This guide provides a structured checklist for B2B buyers seeking the best free CNC software options. By following these steps, you can ensure that your choice aligns with your operational needs and maximizes your investment in CNC technology.
Step 1: Identify Your Specific CNC Requirements
Before diving into software options, clarify what you need. Consider the type of CNC machine you have, the materials you’ll be working with, and the complexity of the designs you intend to create.
– Machine Compatibility: Ensure that the software is compatible with your CNC machine’s specifications.
– Design Complexity: Determine if you need basic 2D designs or more advanced 3D modeling capabilities.
Step 2: Research Available Free Software Options
Once you know your requirements, research the free CNC software available. Look for platforms that offer comprehensive features without hidden costs.
– User Reviews: Check online forums and review sites to gauge user experiences with the software.
– Feature Comparison: Create a comparison chart of features such as CAD/CAM capabilities, ease of use, and support for different file formats.
Step 3: Evaluate User-Friendliness
The ease of use is critical, especially for beginners. Software that is intuitive and user-friendly can significantly reduce the learning curve.
– Interface Design: Look for software with a clean, organized interface that simplifies the design process.
– Tutorial Availability: Ensure that there are ample tutorials or resources available to help you get started quickly.
Step 4: Check for Community Support
A strong user community can be invaluable, especially for beginners. Community forums can provide troubleshooting tips and creative ideas.
– Active Forums: Look for software that has active online communities or support forums.
– Documentation: Ensure there is comprehensive documentation or a knowledge base to assist users.
Step 5: Test the Software
Take advantage of the free nature of these software options by testing them out before making a final decision.
– Trial Runs: Download and use multiple software packages to see which one aligns best with your workflow.
– Sample Projects: Attempt to create sample projects to assess the software’s performance and functionality.
Step 6: Assess Integration Capabilities
Evaluate how well the software integrates with other tools you may be using. This is crucial for streamlining your processes.
– File Export/Import: Check if the software allows for easy import/export of various file formats like STL, DXF, or G-code.
– Compatibility with Other Tools: Consider if the software can work seamlessly with other design or manufacturing tools you have.
Step 7: Gather Feedback from Your Team
Before finalizing your choice, gather feedback from your team members who will be using the software. Their insights can help in making a more informed decision.
– Team Preferences: Understand which features are most important to them and how they prefer to work.
– Trial Collaboratively: If possible, conduct a collaborative trial where team members can test the software together and provide feedback.
By following this practical checklist, you can make a well-informed decision when selecting the best free CNC software for your needs, ensuring that your investment supports your operational goals effectively.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for best free cnc software for beginners Sourcing
Analyzing the cost structure and pricing dynamics of free CNC software is essential for international B2B buyers, particularly in regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. Understanding how these software solutions are sourced can help businesses maximize their investment and operational efficiency.
What Are the Key Cost Components in Sourcing Free CNC Software?
While free CNC software does not have an upfront purchase cost, there are several hidden cost components that businesses should consider:
-
Materials: In this context, materials refer to the hardware and systems that support the software’s functionality. For instance, CNC machines require compatible operating systems, which may involve costs for hardware upgrades or maintenance.
-
Labor: Skilled labor is crucial for effectively utilizing CNC software. Training costs for employees to learn the software can be significant, especially for more complex programs like Fusion 360. Factor in the time required for training and the potential productivity loss during the learning phase.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes costs associated with running CNC operations, such as electricity, software updates, and IT support. Although the software itself is free, the ongoing operational costs can accumulate.
-
Tooling: Depending on the complexity of designs, additional investments may be necessary for tooling that works with the software. This can include specialized bits or attachments for the CNC machine.
-
Quality Control (QC): Ensuring that the outputs from the CNC machine meet quality standards may require additional software or processes, leading to increased costs.
-
Logistics: For companies operating across borders, logistics costs related to software integration, support, and updates can impact the overall cost structure.
-
Margin: While free software might appear cost-effective, businesses should consider the potential margins lost if the software does not meet production needs efficiently.
How Do Price Influencers Affect Sourcing Decisions for CNC Software?
Several factors can influence the effective cost of free CNC software:
-
Volume/MOQ: While software is free, the overall investment may vary based on the number of licenses or installations required. Bulk usage can lead to economies of scale in training and support.
-
Specifications/Customization: Many free software options have limitations in functionality. Companies may need to invest in additional tools or paid versions to meet specific requirements, which can significantly affect total costs.
-
Quality and Certifications: Software that comes with certifications or is backed by reputable suppliers may offer better support and reliability, which justifies a potential investment in paid solutions.
-
Supplier Factors: The reputation and reliability of the software provider can influence long-term costs. Established suppliers often provide better support and updates, reducing future operational risks.
-
Incoterms: For international buyers, understanding the terms of service and support agreements is crucial. Different suppliers may offer varying levels of support based on geographic locations, impacting the total cost of ownership.
What Are the Best Buyer Tips for Cost-Efficient CNC Software Sourcing?
For B2B buyers in emerging markets or regions with diverse economic challenges, strategic sourcing of CNC software can lead to significant cost savings:
-
Negotiate for Better Terms: Even with free software, suppliers may offer premium support or additional features for a fee. Negotiating these terms can help achieve a better overall value.
-
Focus on Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Analyze not just the initial costs but also the long-term implications of using free software, including training, maintenance, and potential upgrades.
-
Evaluate Pricing Nuances for International Markets: Be aware of regional variations in software support and functionality. Certain software may perform better in specific locales, so consider local user experiences and reviews.
-
Explore Community and Open Source Options: Many free CNC software solutions have active communities. Engaging with these communities can provide insights into maximizing software usage and troubleshooting common issues without incurring additional costs.
In conclusion, while free CNC software can be an attractive option for many businesses, understanding the comprehensive cost structure and influencing factors is essential for informed sourcing decisions. By considering these aspects, B2B buyers can enhance their operational efficiency and minimize unexpected expenses.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing best free cnc software for beginners With Other Solutions
Introduction: Exploring Alternatives in CNC Software
In the rapidly evolving landscape of CNC machining, selecting the right software is crucial for enhancing productivity and efficiency. While there are excellent free CNC software options available for beginners, it’s essential to consider alternative solutions that may better fit specific operational needs or budget constraints. This analysis compares the best free CNC software for beginners with other viable alternatives, focusing on performance, cost, ease of implementation, maintenance, and best use cases.
Comparison Table
| Comparison Aspect | Best Free CNC Software for Beginners | Alternative 1: Fusion 360 | Alternative 2: Easel |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | Good for basic 2D/3D design | High performance for complex jobs | Adequate for simple 2D/2.5D jobs |
| Cost | Free | Free for hobbyists, subscription for advanced features | Free |
| Ease of Implementation | Moderate learning curve | Steep learning curve | User-friendly, intuitive interface |
| Maintenance | Low (open-source updates) | Moderate (regular updates) | Low (cloud-based, auto-updates) |
| Best Use Case | Hobbyists, basic projects | Professional, complex designs | Beginners, educational purposes |
Detailed Breakdown of Alternatives
Alternative 1: Fusion 360
Fusion 360 is a powerful CAD/CAM software widely recognized for its extensive capabilities, including 3D modeling and simulation. While it is free for hobbyists, its complexity can be overwhelming for beginners. However, its robust feature set makes it ideal for professionals looking to execute intricate designs and multi-axis machining. The steep learning curve may require additional training resources, making it less suitable for those seeking quick implementation. Regular updates ensure that users benefit from the latest advancements, but the need for consistent internet access for cloud-based features might be a drawback for some.
Alternative 2: Easel
Easel, developed by Inventables, is a browser-based CAD/CAM tool that is particularly appealing to beginners due to its straightforward interface and ease of use. It provides essential functionalities for 2D and 2.5D projects, making it an excellent choice for educational environments or hobbyists focused on simpler tasks. The integrated design and toolpath generation streamline the workflow, allowing users to quickly create and execute projects. However, its limitations in 3D capabilities may hinder users who need more advanced machining options, making it less versatile compared to other software like Fusion 360.
Conclusion: How to Choose the Right CNC Software Solution
When evaluating CNC software solutions, B2B buyers should consider their specific operational requirements, budget constraints, and the complexity of the projects they intend to undertake. While the best free CNC software for beginners offers a solid foundation for basic tasks, alternatives like Fusion 360 and Easel provide distinct advantages that may align better with specific needs. Buyers should weigh the pros and cons of each option, keeping in mind factors such as performance, ease of use, and maintenance, to select a solution that optimally supports their CNC machining objectives.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for best free cnc software for beginners
What Are the Key Technical Properties to Consider When Choosing Free CNC Software?
When evaluating free CNC software, several technical properties are critical for ensuring optimal performance and compatibility with your operations. Understanding these specifications helps B2B buyers make informed decisions that align with their manufacturing needs.
-
File Format Compatibility
Different CNC software supports various file formats for importing and exporting designs. Common formats include STL, DXF, and SVG. Compatibility with these formats is crucial because it determines how easily designs can be transferred between CAD and CAM software. A lack of support for common formats can lead to inefficiencies and potential errors in the machining process. -
Operating System Support
The operating system on which the CNC software runs can affect its usability. Many free options are available for Windows, Mac, and Linux. It’s essential to ensure that the software you choose is compatible with your existing hardware. This consideration prevents the additional costs associated with upgrading systems or purchasing new machines. -
User Interface and Learning Curve
A user-friendly interface is vital for beginners. The complexity of the software can significantly impact the learning curve. Software like Easel offers a straightforward design process, making it accessible for new users. Conversely, more complex software, such as FreeCAD, may require additional training, which can result in increased downtime and productivity loss. -
G-code Generation Capability
The ability to generate G-code is a fundamental feature of CNC software. G-code is the language that CNC machines understand, dictating their movements. Software that efficiently converts designs into G-code is essential for seamless machining operations. Look for software that allows for customization of the G-code settings to optimize machine performance. -
Limitations of Free Versions
Many free CNC software options come with limitations, such as restricted features or usage time. Understanding these constraints is important for planning your production schedule and ensuring that the software meets your long-term needs. Evaluate whether the free version can handle your projects or if an upgrade to a paid version may be necessary.
What Are Common Trade Terms in CNC Software Procurement?
Familiarity with industry jargon is essential for effective communication and negotiation in the B2B landscape. Here are some common terms you might encounter:
-
OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
An OEM refers to a company that produces parts or equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer. In CNC machining, understanding OEM relationships can help in sourcing compatible software and hardware solutions. -
MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ indicates the smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell. In the context of CNC software, understanding MOQ can assist buyers in negotiating software licenses or additional features, particularly when dealing with vendors that offer tiered pricing. -
RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a document issued by a buyer to solicit price bids from suppliers. In the context of CNC software, an RFQ can be used to inquire about pricing for software licenses, support services, or additional modules that may be required for specific projects. -
Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
Incoterms are a series of pre-defined commercial terms published by the International Chamber of Commerce (ICC) relating to international commercial law. While primarily used in shipping and logistics, understanding Incoterms can be beneficial when dealing with software purchases that involve cross-border transactions. -
CAM (Computer-Aided Manufacturing)
CAM software is used to create the machine instructions (G-code) necessary for CNC machines to execute designs. Familiarity with CAM is essential for understanding how design translates into manufacturing, ensuring that your software choice adequately supports your production needs.
By grasping these technical properties and trade terms, B2B buyers can navigate the landscape of free CNC software more effectively, ensuring that they select solutions that align with their operational goals and budget constraints.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the best free cnc software for beginners Sector
What Are the Current Market Dynamics and Key Trends in the Best Free CNC Software for Beginners Sector?
The global market for CNC software, particularly free options catering to beginners, is witnessing significant growth driven by several factors. Firstly, the increasing accessibility of CNC machines has democratized manufacturing, allowing small businesses and startups across regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe to engage in CNC machining without the burden of high software costs. Emerging technologies such as cloud computing and artificial intelligence are also enhancing the functionality of free CNC software, allowing for more intuitive user interfaces and automated design capabilities.
Moreover, the rise of online communities and resources has fostered a collaborative environment where users can share knowledge, designs, and troubleshooting tips, further supporting the adoption of free CNC software. Key players like Carbide 3D and Inventables are continually updating their offerings, ensuring that their tools remain relevant and user-friendly. Another notable trend is the increasing integration of 3D modeling capabilities within free software, reflecting the demand for more complex designs and applications in industries ranging from prototyping to arts and crafts.
For international B2B buyers, especially in developing regions, sourcing strategies now prioritize software that offers comprehensive training and support to ensure a smoother transition into CNC operations. As these markets grow, the demand for adaptable and user-friendly software solutions will likely continue to rise, positioning free CNC software as an essential resource for budding manufacturers.
How Does Sustainability and Ethical Sourcing Impact the Best Free CNC Software for Beginners?
Sustainability is becoming a paramount consideration in the sourcing of CNC software, even in the realm of free options. While the software itself may not directly impact the environment, the broader implications of its use—such as energy consumption and material waste in manufacturing—are critical. Companies are increasingly expected to adopt sustainable practices, including utilizing software that promotes efficient material usage and minimizes waste.
Ethical sourcing plays a crucial role in this context, as businesses seek software solutions from companies that demonstrate a commitment to social responsibility. This includes transparency in their operations and the promotion of fair labor practices within their supply chains. Furthermore, certifications such as ISO 14001 (Environmental Management) can serve as indicators of a software provider’s dedication to sustainability.
For B2B buyers, particularly those in regions sensitive to environmental issues, selecting free CNC software from companies that prioritize sustainability can enhance their brand reputation and align with consumer preferences for eco-friendly products. As the market evolves, the emphasis on green certifications and sustainable practices will likely influence purchasing decisions, making it imperative for software providers to adapt accordingly.
What Is the Evolution of CNC Software and Its Relevance to B2B Buyers?
The evolution of CNC software has been marked by significant technological advancements and a shift towards accessibility. Initially, CNC programming was reserved for industrial applications with costly software solutions that required specialized knowledge. However, with the advent of open-source platforms and the rise of 3D printing, the landscape has changed dramatically.
Free CAD and CAM software options have emerged, allowing beginners to create designs and control CNC machines without the steep financial investment that was once a barrier to entry. This democratization of technology has facilitated innovation and creativity among small businesses and entrepreneurs in diverse markets.
Today, the focus is on user-friendliness and comprehensive support, catering to a global audience that includes not only seasoned machinists but also hobbyists and educational institutions. As these tools continue to evolve, their relevance to B2B buyers lies in their ability to streamline operations, reduce costs, and foster creativity, thereby empowering a new generation of manufacturers across the globe.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of best free cnc software for beginners
-
How do I choose the right free CNC software for my business needs?
Choosing the right free CNC software requires evaluating your specific applications and skill level. Start by identifying whether you need CAD, CAM, or CNC control software. Consider user-friendliness, as some software like Easel is designed for beginners, while others like FreeCAD may have a steeper learning curve. Additionally, assess the compatibility with your CNC machine and the types of materials you will work with. Testing multiple options can help you determine which software aligns best with your workflow. -
What is the best free CAD software for beginners in CNC machining?
For beginners, Inkscape and Easel are excellent choices for CAD software. Inkscape is particularly strong for 2D designs, allowing for SVG and DXF exports, while Easel combines CAD and CAM functionalities in a user-friendly interface. If you’re looking for 3D capabilities, FreeCAD offers comprehensive features, although it requires more time to learn. Evaluate the complexity of your projects to choose the software that best meets your design needs. -
Are there free CAM software options suitable for 3D CNC machining?
Yes, there are several free CAM software options for 3D CNC machining. Fusion 360 offers a free tier for hobbyists, providing robust 3D CAD/CAM tools. Kiri:Moto is another browser-based option that excels in generating toolpaths from 3D models and images. These options allow for complex machining without upfront costs, making them ideal for businesses just starting in CNC operations. -
What should I consider when vetting CNC software suppliers?
When vetting CNC software suppliers, consider their reputation, user reviews, and support offerings. Look for suppliers that provide comprehensive documentation, tutorials, and customer support channels. Assess the community around the software; a strong user community can be invaluable for troubleshooting and learning. Additionally, check for software updates and maintenance policies to ensure longevity and reliability. -
How do payment terms work for international software purchases?
Payment terms for international software purchases can vary significantly. Common methods include credit cards, bank transfers, or online payment platforms like PayPal. Ensure you clarify the payment terms upfront, including any potential transaction fees or currency conversion costs. Some suppliers may offer discounts for upfront payments or bulk purchases, so inquire about any available options that may reduce costs. -
What are the logistics involved in accessing free CNC software globally?
Accessing free CNC software globally is generally straightforward, as most options are available for download online. However, consider internet bandwidth and speed, especially in regions with limited connectivity. Ensure that the software is compatible with your operating system and hardware specifications. Be aware of any regional restrictions or licensing agreements that may affect software usage in specific countries. -
What quality assurance measures should I implement when using free CNC software?
Implementing quality assurance measures involves regular testing and validation of the software’s output. Create a checklist to verify that the generated G-code aligns with your design specifications before running it on your CNC machine. Additionally, maintain a feedback loop where operators can report issues, and regularly update the software to benefit from bug fixes and improvements. Document all procedures to ensure consistency and traceability. -
Can I customize free CNC software to better suit my business needs?
Customization options for free CNC software vary widely. Some programs, like FreeCAD, allow users to modify the source code, enabling tailored functionalities. Others may offer plugins or add-ons to enhance features. Before committing to a particular software, explore its customization capabilities and community resources. Engaging with user forums can provide insights into successful customizations implemented by other businesses.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.
Top 9 Best Free Cnc Software For Beginners Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. Carbide 3D – Free CNC Software Solutions
Domain: carbide3d.com
Registered: 2013 (12 years)
Introduction: Free CNC Software options include CAD, CAM, and CNC control software. Key free CAD software includes: 1. FreeCAD – A free 3D CAD parametric program, outputs STL, STEP, SVG, or DXF, runs on Mac, Windows, and Linux. 2. Solvespace – Free 3D CAD program, better for mechanical parts, exports STL or STEP files, runs on Mac, Windows, and Linux. 3. Inkscape – Free for 2D designs, exports SVG and DXF files…
2. Easel – Free Software for CNC Tasks
Domain: reddit.com
Registered: 2005 (20 years)
Introduction: 1. Easel: Free software with a paid plan option. Suitable for basic CNC tasks. 2. Carbide Create: Free version available, but requires a pro subscription for G-code output. Older version (V6) allows saving G-code. 3. Autodesk Fusion 360: Free for hobbyists, combines CAD and CAM, steeper learning curve. 4. Openbuilds Control: Free G-code sender software. 5. Universal Gcode Sender: Another free G-co…
3. Minimillr – Browser-based CAD/CAM Tools
Domain: minimillr.com
Registered: 2021 (4 years)
Introduction: 1. Easel: Browser-based CAD/CAM tool, 2D/2.5D only, limited free version, supports SVG import/export, auto-tabs, custom feeds/speeds, GRBL compatible.
2. Kiri:Moto: Browser-based CAM tool, supports 3D STL files, image to heightmap feature, suitable for 3D relief work.
3. Fusion 360: Free for hobby users, complex with a steep learning curve, offers 2D/3D CAD tools, 2.5/3 axis milling, limited file …
4. CNC Cookbook – Best Free CAM Software
Domain: cnccookbook.com
Registered: 2007 (18 years)
Introduction: Best Free CAM Software + CAD & CNC [2024 Update] includes recommended software for beginners: CAM Software, CNC Control Software, CAD Software, Feeds and Speeds Calculator, and CNC Simulator. Key products mentioned are Fusion 360, Carbide Create, GRBL, G-Wizard Feeds and Speeds Calculator, and G-Wizard Editor and Simulator. G-Wizard Calculator offers a free trial with many features remaining free …
5. Kiri:Moto – Browser-Based CNC & 3D Printing Software
Domain: forum.makerforums.info
Registered: 2019 (6 years)
Introduction: 1. Kiri:Moto: Browser-based, open source, supports CNC mills, routers, laser cutters, and 3D printers. Handles complex shapes well. 2. FreeCAD: Offers substantial CAM capabilities, learning curve is improving, includes a Path module for generating g-code. 3. Camotics: Visualizes g-code before running on CNC machines. 4. JSCut: Simple, 2.5D software with limited features, supports SVG input. 5. Ble…
6. Easel – All-in-One CNC Software Solution
Domain: easel.com
Registered: 1997 (28 years)
Introduction: Easel is an all-in-one CNC software solution designed for design and CNC machining. Key features include: 1. Design tools for creating stunning and functional designs tailored for artisans and professionals. 2. Carving capabilities for achieving perfect cuts on various projects. 3. Workflow optimization to reduce waste and maximize profitability. 4. 3D carving with STL file imports. 5. A design li…
7. Vectric – Key CNC Design Software
Domain: vectric.com
Registered: 2005 (20 years)
Introduction: Vectric offers powerful and easy-to-use design software for CNC machining, including the following products: 1. Cut2D: A vector drawing and editing software package with powerful 2D machining strategies for CNC routing, milling, or engraving. 2. VCarve: Built on the same interface as Cut2D, it adds 2.5D toolpath functionality including v-carving, chamfer, fluting, prism, and moulding toolpaths, al…
8. Inventables – Easel® CNC Software
Domain: inventables.com
Registered: 2001 (24 years)
Introduction: Easel® is an all-in-one CNC software solution designed for ease of use, allowing users to start carving in minutes. It offers a 30-day free trial and is optimized for X-Carve and X-Carve Pro machines. Easel Pro supports over 30 types of CNC routers and includes features like 3D carving, STL file import, and a fast learning curve with no prior experience required. Subscription plans include PRO MON…
9. Langmuir Systems – Design Software Essentials
Domain: forum.langmuirsystems.com
Registered: 2017 (8 years)
Introduction: 1. **Inkscape**: A design software used to create and convert drawings into .svg files. Highly recommended for beginners, especially for artistic projects. 2. **Fusion 360**: A powerful CAD software that can process DXF and SVG files to create g-code. It is free for hobbyists but may be overwhelming for simple projects. 3. **FireControl**: Software required for operating CNC machines, specifically…
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for best free cnc software for beginners
In the rapidly evolving landscape of CNC machining, the availability of free software offers a significant advantage for beginners and small businesses alike. By strategically sourcing the best free CNC software, international buyers can reduce their initial investment while gaining access to powerful tools that facilitate design, toolpath generation, and machine operation. Notable options like FreeCAD, Easel, and Fusion 360 provide diverse functionalities that cater to both 2D and 3D machining needs, ensuring that users can find a solution that fits their specific requirements.
As B2B buyers from regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe explore these software solutions, it is essential to consider not only the features but also the community support and resources available for learning. Engaging with user communities and online tutorials can significantly enhance the learning curve and operational efficiency.
Looking ahead, the landscape of CNC software will continue to expand, offering even more sophisticated tools. By remaining proactive in exploring these free resources, businesses can position themselves for growth and innovation in CNC machining. Take the next step—evaluate these software options and empower your operations today.