Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for best cam software for cnc
In the competitive landscape of CNC machining, sourcing the best CAM software is pivotal for enhancing operational efficiency and driving innovation. As manufacturers across Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe grapple with the complexities of modern production demands, the right CAM software can significantly streamline workflows, reduce costs, and improve product quality. This comprehensive guide aims to equip B2B buyers with critical insights into the leading CAM software solutions available in the global market.
From understanding the unique capabilities of various software types—such as 5-axis machining and high-speed milling—to exploring their specific applications across industries like aerospace, automotive, and medical device manufacturing, this guide covers it all. We delve into essential factors such as supplier vetting, integration capabilities, and cost considerations, ensuring that you have a holistic view of what each software can offer.
By empowering international B2B buyers to make informed decisions, this guide serves as a valuable resource for companies looking to invest in CAM software that aligns with their operational goals. As you navigate the complexities of selecting the ideal software, consider this guide your trusted companion in unlocking the full potential of your CNC machining capabilities.
Understanding best cam software for cnc Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| General Purpose CAM | Versatile toolpath options, user-friendly interfaces | Job shops, educational institutions | Pros: Easy to learn, broad applications. Cons: May lack advanced features for specialized tasks. |
| Cloud-based CAM | Integrated CAD/CAM/PLM, collaborative tools | Digital manufacturing environments | Pros: Enhances collaboration, real-time updates. Cons: Requires stable internet, potential data security concerns. |
| Specialized CAM | Focused on specific industries (e.g., mold, aerospace) | Aerospace, automotive, medical devices | Pros: High precision, tailored features. Cons: Can be expensive, may require specialized training. |
| Integrated CAM | Seamless integration with popular CAD software | High-volume production environments | Pros: Streamlined workflow, reduced errors. Cons: Dependency on CAD software, potential compatibility issues. |
| Automation-focused CAM | Advanced automation features, multi-axis capabilities | High-precision machining sectors | Pros: Increases efficiency, reduces manual input. Cons: Higher initial investment, may need skilled operators. |
What Are the Characteristics of General Purpose CAM Software?
General-purpose CAM software is designed to accommodate a wide range of machining processes, making it suitable for job shops and educational institutions. These solutions typically offer user-friendly interfaces and a variety of toolpath options, allowing both novices and experienced machinists to effectively program CNC machines. When considering a purchase, B2B buyers should evaluate the software’s ease of use, training resources, and adaptability to various machining tasks.
How Does Cloud-based CAM Software Enhance Collaboration?
Cloud-based CAM software integrates CAD, CAM, and Product Lifecycle Management (PLM) tools, facilitating real-time collaboration among team members. This type of software is particularly beneficial for companies transitioning to digital manufacturing environments, as it allows for seamless project management and updates. B2B buyers should assess the software’s security features, internet reliability requirements, and the extent of its integration with existing systems to ensure a smooth implementation.
What Makes Specialized CAM Software Ideal for Certain Industries?
Specialized CAM software targets specific industries such as aerospace, automotive, and medical devices, providing advanced features that cater to their unique manufacturing needs. These solutions often include high-precision toolpath options and capabilities for complex machining operations. Buyers in these sectors should consider the software’s ability to meet regulatory compliance, training requirements for staff, and overall cost-effectiveness when evaluating their options.
Why Choose Integrated CAM Software for High-Volume Production?
Integrated CAM software works seamlessly with popular CAD systems, providing a streamlined workflow that reduces the potential for errors. This is particularly advantageous for high-volume production environments where efficiency and accuracy are paramount. B2B buyers should examine the integration capabilities with their current CAD systems, any additional costs associated with integration, and the software’s ability to scale with their production needs.
What Are the Benefits of Automation-focused CAM Software?
Automation-focused CAM software emphasizes advanced automation features and multi-axis capabilities, making it ideal for high-precision machining sectors. These solutions can significantly enhance operational efficiency by minimizing manual input and optimizing machining processes. When evaluating this type of software, B2B buyers should consider the initial investment costs, the learning curve for operators, and the long-term return on investment through improved productivity.
Key Industrial Applications of best cam software for cnc
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of best cam software for cnc | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Aerospace | Precision part manufacturing for aircraft components | Enhanced accuracy and reduced waste in production | Compatibility with high-precision machining tools |
| Automotive | Toolpath optimization for automotive part production | Increased efficiency and shorter lead times | Support for multi-axis machining capabilities |
| Medical Devices | Custom device fabrication and prototyping | Improved product quality and regulatory compliance | Ability to handle complex geometries and materials |
| Mold and Die Manufacturing | Advanced surface finishing for molds and dies | Superior surface quality and reduced finishing time | Integration with CAD systems for seamless workflow |
| Electronics | PCB and enclosure fabrication | High precision and reduced cycle times | Compatibility with various CNC machines and materials |
How is Best CAM Software Used in the Aerospace Industry?
In the aerospace sector, best CAM software is crucial for the precision manufacturing of aircraft components. These applications typically involve complex geometries that require high accuracy and tight tolerances. By utilizing advanced toolpath optimization features, manufacturers can significantly reduce material waste and production costs while ensuring compliance with stringent industry standards. International buyers, particularly from regions with emerging aerospace industries, must consider software that integrates seamlessly with their existing CNC machinery to enhance operational efficiency.
What Role Does CAM Software Play in Automotive Production?
The automotive industry benefits from CAM software primarily through optimized toolpaths for the production of various components, such as engine parts and chassis elements. The software enables manufacturers to streamline their operations, resulting in increased efficiency and shorter lead times. For businesses in developing markets, selecting CAM software that supports multi-axis machining is essential, as it allows for the production of intricate designs that meet global automotive standards while reducing production cycle times.
How is CAM Software Applied in Medical Device Manufacturing?
In the medical device sector, best CAM software is used for the fabrication and prototyping of custom medical devices. This application requires strict adherence to regulatory compliance, necessitating software that can ensure product quality and traceability. Advanced capabilities in handling complex geometries are vital, as many medical devices require unique designs tailored to specific patient needs. International buyers should prioritize CAM solutions that offer robust support for various materials and machining processes to meet the diverse demands of medical manufacturing.
Why is CAM Software Important for Mold and Die Manufacturing?
For mold and die manufacturers, best CAM software is essential for achieving advanced surface finishing and creating intricate designs. The software aids in optimizing machining processes, which can significantly reduce the time and cost associated with finishing molds. Buyers in this sector, especially from regions with high mold production demands, should look for solutions that integrate well with existing CAD systems, ensuring a smooth workflow from design to production while maintaining high-quality standards.
How Does CAM Software Enhance Electronics Manufacturing?
In electronics manufacturing, best CAM software is applied to fabricate printed circuit boards (PCBs) and enclosures with high precision. The software streamlines the production process, leading to reduced cycle times and increased accuracy. For international B2B buyers in this sector, it is crucial to select CAM solutions that are compatible with various CNC machines and materials, enabling them to adapt to the fast-evolving electronics market while maintaining quality and efficiency.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘best cam software for cnc’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Difficulty Integrating CAM Software with Existing Systems
The Problem: Many B2B buyers face challenges when integrating new CAM software with their existing CAD systems and CNC machinery. This integration often requires significant technical expertise, and a lack of compatibility can lead to workflow disruptions. For manufacturers in regions like Africa and the Middle East, where technical support may be limited, this issue can stall production and increase operational costs.
The Solution: To ensure smooth integration, buyers should conduct thorough compatibility assessments before purchasing CAM software. This involves checking if the CAM solution can seamlessly work with existing CAD systems and CNC machines. Engaging with vendors to request demos can provide insights into integration capabilities. Additionally, opting for software with robust customer support and extensive documentation is crucial. When assessing options, prioritize platforms like Autodesk Fusion, which offers a cloud-based ecosystem that often simplifies integration processes. For buyers in regions with limited local support, leveraging online forums and user communities can provide additional resources and troubleshooting assistance.
Scenario 2: High Learning Curve for New Users
The Problem: A common pain point for companies adopting new CAM software is the steep learning curve associated with advanced features. Novice users, particularly in regions where technical training may be scarce, often struggle to maximize the software’s capabilities, leading to inefficient machining processes and increased downtime.
The Solution: To address this issue, businesses should invest in comprehensive training programs tailored to their workforce. Many CAM software providers, such as Mastercam and Siemens NX, offer training resources, including online tutorials, webinars, and certification programs. Establishing a mentorship system within the organization, where experienced users guide novices, can further enhance learning. Additionally, consider utilizing software with user-friendly interfaces, like Fusion 360, which provides a more intuitive experience for beginners. Encouraging a culture of continuous learning and adaptation to new technologies will not only alleviate the learning curve but also enhance overall operational efficiency.
Scenario 3: Inadequate Technical Support and Documentation
The Problem: B2B buyers often encounter inadequate technical support and documentation for their CAM software, which can hinder troubleshooting and effective usage. This issue is particularly pronounced in less mature markets, such as parts of South America and Africa, where local support resources may be limited or non-existent.
The Solution: To mitigate this challenge, it’s essential to choose CAM software from vendors known for their robust support systems. Prioritize software that offers extensive online resources, such as forums, FAQs, and video tutorials. For instance, platforms like SolidCAM and hyperMILL typically provide comprehensive documentation that can be accessed anytime. Additionally, establishing a relationship with the software provider for dedicated support services can be beneficial. Consider investing in a service package that includes regular updates and direct access to technical experts. Encouraging the formation of user groups within the organization can also foster knowledge sharing and provide a support network for troubleshooting issues collectively. This proactive approach will ensure that your team can effectively utilize the software and maintain productivity levels.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for best cam software for cnc
What Are the Key Materials for CAM Software in CNC Machining?
When selecting the best CAM software for CNC machining, understanding the materials being processed is crucial. Different materials present unique challenges and opportunities that can significantly influence the choice of CAM software. Below, we analyze four common materials used in CNC machining from a B2B perspective, focusing on their properties, advantages, disadvantages, and considerations for international buyers.
How Do Aluminum Properties Affect CAM Software Selection?
Aluminum is a lightweight, corrosion-resistant metal commonly used in various industries, including aerospace and automotive. Its key properties include excellent thermal conductivity and a relatively low melting point, making it easier to machine compared to harder metals.
Pros: Aluminum is durable and cost-effective, allowing for efficient manufacturing processes. Its lightweight nature also makes it suitable for applications where weight reduction is critical.
Cons: While aluminum is easier to machine, it can be prone to deformation under high temperatures, which may require careful management of cutting speeds and feeds.
Impact on Application: Aluminum’s compatibility with various media types makes it a versatile choice for different applications, from structural components to intricate parts.
Considerations for International Buyers: Compliance with international standards such as ASTM and JIS is essential, particularly in regions like Europe and the Middle East, where material specifications are stringent.
What Are the Key Properties of Steel in CNC Machining?
Steel is one of the most widely used materials in manufacturing due to its strength and versatility. It comes in various grades, each with specific properties such as hardness and tensile strength.
Pros: Steel is highly durable and can withstand significant stress, making it suitable for heavy-duty applications. Its availability in various grades allows for tailored solutions based on specific project requirements.
Cons: Steel can be more challenging to machine than softer metals, requiring specialized tools and CAM software capabilities for effective processing.
Impact on Application: Steel is commonly used in automotive parts, machinery, and structural components, where strength and durability are paramount.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should consider the common steel grades used in their region and ensure compliance with local standards to avoid issues during manufacturing.
How Does Plastic Material Influence CAM Software Choices?
Plastics are increasingly popular in CNC machining due to their lightweight and versatile nature. Common types include ABS, PVC, and polycarbonate, each with distinct properties.
Pros: Plastics are generally less expensive to machine and can be molded into complex shapes, making them ideal for prototyping and low-volume production.
Cons: Plastics can have lower durability compared to metals and may not perform well under high temperatures or stress, limiting their applications.
Impact on Application: Plastics are widely used in consumer goods, automotive interiors, and medical devices, where weight and design flexibility are crucial.
Considerations for International Buyers: Understanding the specific plastic grades and their compliance with international standards is vital, especially in industries like healthcare, where material safety is critical.
What Are the Considerations for Machining Wood?
Wood is a traditional material used in CNC machining, particularly in furniture and cabinetry. Its properties vary widely based on species, with key factors including density, grain structure, and moisture content.
Pros: Wood is easy to machine and can be finished to a high aesthetic quality. It is also renewable, making it an environmentally friendly choice.
Cons: Wood can warp or split during machining, requiring careful handling and specific CAM software features to optimize cutting paths.
Impact on Application: Wood is primarily used in furniture, cabinetry, and decorative items, where appearance and craftsmanship are essential.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should be aware of regional preferences for wood species and ensure compliance with sustainability certifications, which are increasingly important in markets like Europe.
Summary Table of Material Selection for CAM Software
| Material | Typical Use Case for best cam software for cnc | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Aluminum | Aerospace components, automotive parts | Lightweight and corrosion-resistant | Prone to deformation under heat | Medium |
| Steel | Heavy-duty machinery, structural components | Highly durable and strong | More challenging to machine | Medium to High |
| Plastic | Consumer goods, automotive interiors | Cost-effective and versatile | Lower durability under stress | Low |
| Wood | Furniture, cabinetry | Easy to machine and aesthetically pleasing | Can warp or split during machining | Low to Medium |
By understanding the properties and implications of these materials, B2B buyers can make informed decisions when selecting CAM software that aligns with their manufacturing needs and regional compliance standards.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for best cam software for cnc
What are the Typical Manufacturing Processes for CAM Software in CNC Machining?
When selecting the best CAM software for CNC machining, understanding the manufacturing processes it supports is crucial for optimizing production efficiency. Here, we outline the main stages involved in the manufacturing process and highlight key techniques that align with modern CNC operations.
What Are the Main Stages of Manufacturing with CAM Software?
-
Material Preparation:
The first stage involves selecting and preparing the raw materials necessary for machining. This includes activities such as cutting materials into manageable sizes, treating them to enhance properties, and inspecting for quality. For CAM software, the material type influences toolpath generation, feed rates, and machining strategies. The software should allow for material input, which can optimize the machining process by adjusting parameters accordingly. -
Forming:
Forming is where the material undergoes physical transformation. This can involve various techniques such as milling, turning, drilling, and laser cutting, which CAM software must adequately support. Advanced CAM solutions provide comprehensive toolpath strategies that account for the geometry of the part, ensuring efficient machining with minimal waste. -
Assembly:
In some manufacturing environments, parts are not just machined but also assembled. CAM software can facilitate this process by generating assembly instructions and coordinating the machining of components that fit together. This is particularly important in complex projects where precision and timing are critical. -
Finishing:
The finishing stage is crucial for ensuring that parts meet required specifications and surface quality. Techniques such as grinding, polishing, and coating can be part of this phase. Effective CAM software can simulate these processes, allowing manufacturers to visualize the end product and make necessary adjustments before actual machining.
How Does Quality Assurance Fit into the Manufacturing Process?
Quality assurance (QA) is an integral part of the manufacturing process, ensuring that all outputs meet specified standards and customer expectations. For B2B buyers, understanding the QA protocols associated with their CAM software is essential for maintaining operational integrity.
What Are the Relevant International Standards for Quality Assurance?
-
ISO 9001:
This is a globally recognized standard for quality management systems (QMS). It ensures that organizations consistently meet customer and regulatory requirements. B2B buyers should look for suppliers with ISO 9001 certification as it signifies a commitment to quality. -
Industry-Specific Certifications:
Depending on the sector, additional certifications may be relevant. For instance, the CE mark is crucial for products sold in Europe, while API certification is essential for the oil and gas industry. Buyers should verify that their suppliers comply with relevant industry standards to mitigate risks.
What Are the Key Quality Control Checkpoints in Manufacturing?
Quality control (QC) involves systematic inspections and testing at various stages of the manufacturing process. Key checkpoints include:
-
Incoming Quality Control (IQC):
This is the first line of defense against defects. IQC involves inspecting raw materials upon arrival to ensure they meet specified standards before they enter the production process. -
In-Process Quality Control (IPQC):
During manufacturing, ongoing inspections are conducted to monitor process stability and product quality. This can involve using statistical process control (SPC) techniques to identify trends and variances. -
Final Quality Control (FQC):
After production, FQC ensures that the final products conform to design specifications. This often involves functional testing and visual inspections before items are shipped to customers.
What Common Testing Methods Are Used in Quality Assurance?
B2B buyers should be aware of various testing methods that ensure the quality of machined parts:
- Dimensional Inspection: Utilizing tools such as calipers and CMM (Coordinate Measuring Machines) to verify that parts meet specified dimensions.
- Material Testing: Techniques such as tensile testing and hardness testing assess the physical properties of materials to ensure they meet performance requirements.
- Functional Testing: Assessing whether the final product performs as intended under real-world conditions.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control?
For international buyers, ensuring the quality of suppliers is paramount. Here are some strategies to verify supplier QC:
-
Audits:
Conducting regular audits of suppliers can provide insights into their quality management practices. This may include reviewing their QMS and observing their production processes. -
Quality Reports:
Requesting detailed quality reports can help buyers understand the supplier’s performance over time, including defect rates and corrective actions taken. -
Third-Party Inspections:
Engaging third-party inspection services can add an extra layer of assurance. These independent entities can perform inspections and testing on behalf of the buyer to verify compliance with quality standards.
What Are the QC and Certification Nuances for International Buyers?
B2B buyers from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe may face unique challenges concerning QC and certifications. Factors to consider include:
- Regulatory Differences: Different regions may have varying regulatory requirements that impact product certification. Buyers should familiarize themselves with local regulations to avoid compliance issues.
- Cultural Considerations: Understanding cultural attitudes towards quality and production can aid in establishing effective communication with suppliers.
- Logistical Challenges: International shipping and transportation can affect product quality. Buyers should ensure that suppliers are equipped to handle logistics efficiently and maintain product integrity throughout the supply chain.
By comprehensively understanding manufacturing processes and quality assurance measures, B2B buyers can make informed decisions when selecting CAM software for CNC machining. This knowledge empowers them to choose solutions that not only meet their operational needs but also align with quality standards essential for international markets.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘best cam software for cnc’
Choosing the best CAM software for CNC operations is a pivotal decision for any manufacturing business. This guide provides a practical checklist to help international B2B buyers navigate the selection process effectively, ensuring that you choose software that aligns with your operational needs and growth ambitions.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Start by outlining the specific requirements of your CNC operations. Consider factors such as the types of materials you will be machining, the complexity of the designs, and the level of automation required. Clearly defined specifications will help narrow down your software options to those that best suit your operational capabilities.
Step 2: Assess Compatibility with Existing Systems
Ensure that the CAM software integrates seamlessly with your current CAD systems and CNC machines. Compatibility is crucial for streamlining workflows and minimizing the learning curve for your team. Check if the software supports common file formats used in your industry, such as DXF, IGES, or STEP.
Step 3: Evaluate User-Friendliness and Learning Curve
Select software that is intuitive and user-friendly, particularly if your team includes novice users. A steep learning curve can hinder productivity and increase training costs. Look for options that offer comprehensive tutorials, support resources, and community forums for assistance.
Step 4: Consider Scalability and Future-Proofing
Choose a CAM software solution that can grow with your business. As your operations expand, you may need additional features or capabilities. Assess whether the software provider offers regular updates and enhancements, as well as the ability to add modules or functionalities as needed.
Step 5: Verify Supplier Reputation and Support Services
Research potential suppliers to verify their credibility in the market. Look for established companies with a track record of delivering reliable software solutions. Additionally, evaluate their customer support services, including availability, response times, and the quality of technical assistance provided.
Step 6: Request Demonstrations and Trials
Before making a final decision, request demonstrations or trial versions of the software. This will allow you to assess its functionality in real-world scenarios and determine whether it meets your expectations. Pay attention to how well the software handles the specific tasks relevant to your operations.
Step 7: Compare Pricing and Total Cost of Ownership
Finally, evaluate the pricing structure of each software option. Consider not only the upfront costs but also the long-term expenses, including maintenance, upgrades, and training. A lower initial price might come with hidden costs that could affect your budget in the long run.
Following this checklist will equip you with the insights needed to make an informed decision when procuring CAM software for your CNC operations, ultimately enhancing your manufacturing efficiency and competitiveness in the global market.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for best cam software for cnc Sourcing
When sourcing the best CAM software for CNC applications, understanding the comprehensive cost structure and pricing nuances is essential for international B2B buyers. This analysis provides insights into the various cost components, price influencers, and valuable tips for negotiating and optimizing your purchasing strategy.
What Are the Key Cost Components of CAM Software?
-
Materials and Licensing Fees: The primary costs associated with CAM software are licensing fees, which can vary significantly based on the software’s capabilities and the number of users. Subscription models are increasingly common, with monthly or annual fees that may also include updates and support.
-
Labor Costs for Implementation and Training: Implementing new CAM software often requires training for existing staff, which can incur additional labor costs. Organizations should consider the time spent on training and the potential productivity loss during this transition.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This encompasses costs related to maintaining IT infrastructure, including servers and network systems needed to support the software. For cloud-based solutions, ongoing internet costs and potential data storage fees are relevant.
-
Tooling and Hardware Integration: Some CAM software may necessitate specific hardware or tooling upgrades to optimize performance. This could mean additional investment in CNC machinery or peripherals, which can significantly influence the total cost.
-
Quality Control (QC) and Assurance: The effectiveness of CAM software can be evaluated through QC measures that may require further investment in testing and validation. This ensures that the software meets the required specifications and quality standards for production.
-
Logistics and Support Services: If your CAM software requires technical support, installation services, or regular maintenance, these costs must be factored into the total investment. Some vendors may charge additional fees for on-site support or extended service agreements.
-
Profit Margin: Finally, the supplier’s margin will impact the price. Established brands may have higher margins due to their reputation and reliability, while newer entrants might offer lower prices to gain market share.
What Influences Pricing for CAM Software?
-
Volume and Minimum Order Quantities (MOQ): Larger purchases or multi-user licenses often result in discounts. Understanding the vendor’s pricing tiers based on volume can lead to significant savings.
-
Specifications and Customization Needs: Custom features or specific industry requirements (e.g., aerospace or automotive) can increase costs. Buyers should clearly define their needs to avoid unnecessary expenses.
-
Quality Certifications and Standards: Software that meets international standards or has specific certifications may come at a premium. However, these certifications can provide assurance of quality and compliance, which may justify the higher price.
-
Supplier Factors and Reputation: Established suppliers with a strong track record may charge more due to their reliability and customer support. It’s essential to weigh the benefits of reputation against potential cost savings from lesser-known providers.
-
Incoterms and International Trade Considerations: Understanding Incoterms is crucial for international buyers. They dictate the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in shipping, which can affect overall costs. For instance, CIF (Cost, Insurance, and Freight) terms might lead to higher initial costs but offer more security against loss or damage.
What Are the Best Buyer Tips for Cost-Efficiency?
-
Negotiate Pricing and Terms: Don’t hesitate to negotiate with vendors. Many are open to offering discounts for long-term commitments or multiple licenses.
-
Calculate Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Beyond the initial purchase price, consider ongoing costs such as maintenance, updates, and potential training. A lower upfront cost might lead to higher TCO over time.
-
Consider Cloud vs. On-Premise Solutions: While cloud-based solutions may have lower initial costs, they come with ongoing subscription fees. Evaluate your organization’s needs and growth plans to determine the most cost-effective solution.
-
Research and Compare Multiple Suppliers: Don’t settle for the first quote. Comparing options can reveal significant price variations and help identify the best fit for your business needs.
-
Stay Informed About Market Trends: The CAM software landscape is dynamic, with frequent updates and new entrants. Staying informed can help you recognize when to invest in new technology or negotiate better terms with current suppliers.
Conclusion
Understanding the cost structure and pricing dynamics of CAM software for CNC applications is crucial for B2B buyers, especially in diverse regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. By considering all cost components and leveraging negotiation tactics, businesses can optimize their software investments and ensure they select a solution that meets both their operational needs and budget constraints.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing best cam software for cnc With Other Solutions
In the competitive landscape of CNC machining, the choice of software plays a pivotal role in determining operational efficiency and product quality. While various CAM software solutions offer robust features tailored for specific manufacturing needs, alternative methods and technologies can also achieve similar objectives. This section compares leading CAM software against alternative solutions to help B2B buyers make informed decisions.
| Comparison Aspect | Best Cam Software For CNC | Alternative 1: Manual Programming | Alternative 2: Open-Source CAM Software |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | High precision, multi-axis capabilities | Variable, heavily dependent on programmer skill | Good for basic tasks, limited advanced features |
| Cost | Subscription-based, can be high | Low (labor cost only) | Free, but may require customization |
| Ease of Implementation | User-friendly, requires training | Steep learning curve, requires expertise | Moderate; community support available |
| Maintenance | Regular updates, support included | Minimal, but reliant on user knowledge | Varies, community-driven updates |
| Best Use Case | Complex manufacturing, high-volume production | Simple, repetitive tasks | Prototyping, educational purposes |
What Are the Pros and Cons of Manual Programming as an Alternative to CAM Software?
Manual programming involves writing the G-code directly for CNC machines. This approach can be highly beneficial for simple machining tasks where precision is not as critical. One of the primary advantages is cost-effectiveness, as it requires only the labor of skilled programmers. However, the steep learning curve presents a significant barrier; inexperienced operators may struggle with the complexities of manual coding. Furthermore, the performance can be inconsistent, heavily relying on the programmer’s skill set. In environments where production volume and speed are crucial, manual programming can quickly become a bottleneck.
How Does Open-Source CAM Software Compare?
Open-source CAM software provides a flexible and cost-effective alternative to commercial solutions. It is free to use, making it appealing for startups and educational institutions. These platforms often foster a collaborative environment where users can customize features to better suit their needs. However, the performance may not match that of leading commercial CAM software, particularly for advanced machining tasks. Additionally, the level of support can be inconsistent since it largely depends on community contributions. While it can serve well for prototyping and educational purposes, companies focused on high-volume production may find it lacking in capability and reliability.
Conclusion: How Can B2B Buyers Choose the Right Solution for Their CNC Needs?
Selecting the appropriate CAM software or alternative solution hinges on several factors, including the complexity of manufacturing tasks, budget constraints, and the skill level of the workforce. For organizations engaged in high-precision and complex machining, investing in leading CAM software is often justified due to its advanced features and support. Conversely, businesses that handle simpler tasks may benefit from manual programming or open-source options, especially if they are budget-conscious or looking to foster in-house programming expertise. Ultimately, the decision should align with the specific operational requirements and long-term strategic goals of the organization.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for best cam software for cnc
What Are the Key Technical Properties to Consider When Selecting CAM Software for CNC?
When evaluating the best CAM software for CNC applications, understanding specific technical properties is crucial for making informed purchasing decisions. Below are key specifications that directly impact operational efficiency and product quality in a B2B context:
1. Material Compatibility
Material compatibility refers to the range of materials the CAM software can effectively process, including metals, plastics, and composites. Different materials require specific cutting speeds, feeds, and tool types, making this property vital for manufacturers. A software that can handle a diverse array of materials allows businesses to expand their service offerings and meet varied client demands.
2. Tolerance Levels
Tolerance levels indicate the precision with which the CAM software can produce parts. In industries such as aerospace or medical devices, where minute specifications are critical, choosing software that can maintain tight tolerances is essential. A higher tolerance capability minimizes rework and waste, directly affecting the bottom line by reducing production costs and enhancing product quality.
3. Toolpath Generation
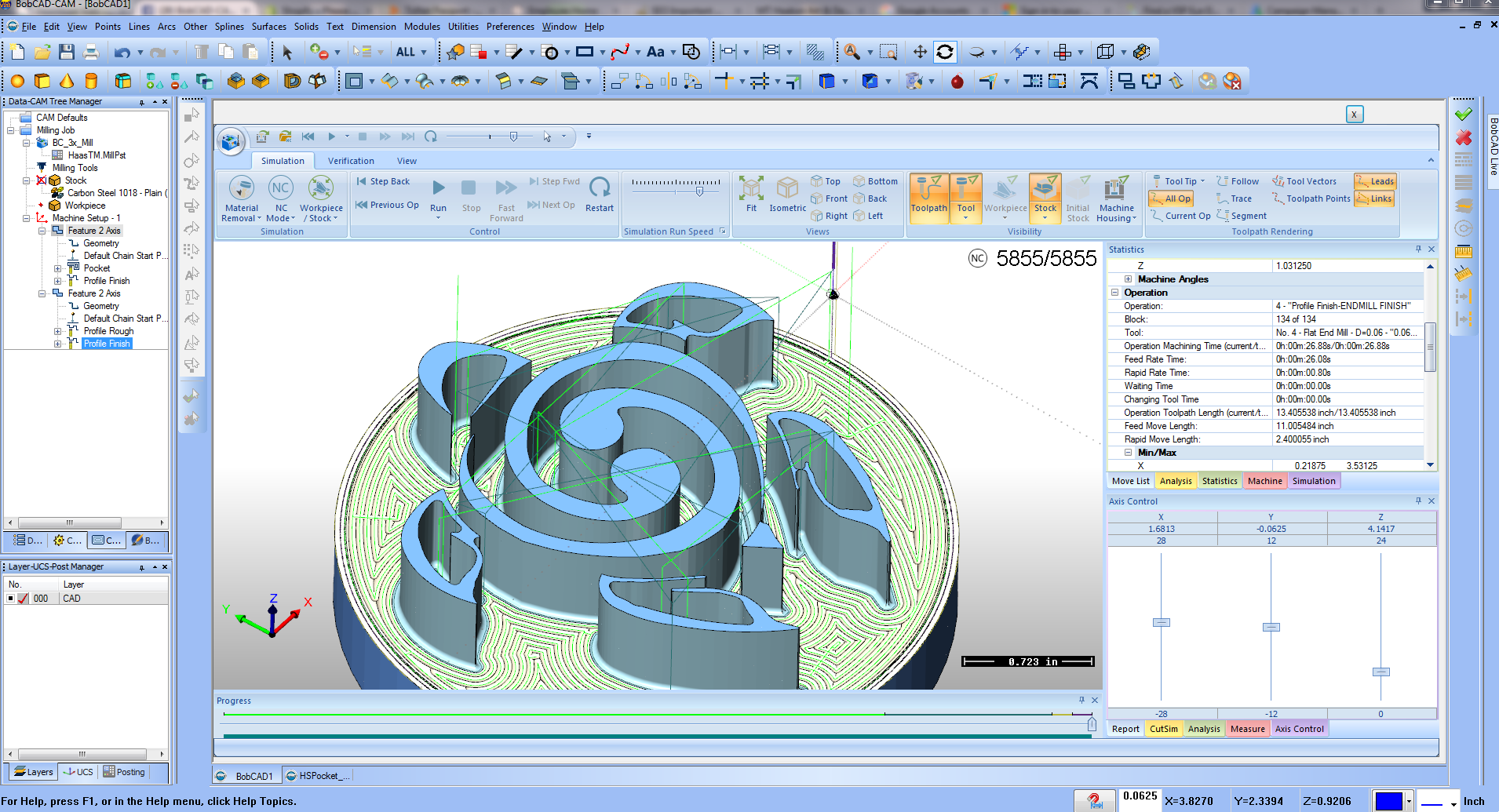
Toolpath generation is the process by which the CAM software calculates the optimal path for the cutting tool based on the CAD model. Efficient toolpath generation reduces machining time and enhances surface finish quality. Software that offers advanced toolpath strategies, such as adaptive machining or multi-axis capabilities, can significantly improve productivity and operational efficiency.
4. Post-Processing Options
Post-processing refers to the conversion of toolpath data into G-code, which CNC machines understand. Different machines require specific G-code formats; hence, a CAM software with flexible post-processing options is crucial. This ensures compatibility with various CNC machines, reducing downtime and enabling smoother production transitions.
5. Simulation and Verification Tools
Simulation tools allow users to visualize the machining process before actual production, helping identify potential issues like collisions or tool wear. Verification tools check the generated G-code for errors that could lead to machine crashes or defects. Effective simulation and verification capabilities enhance safety and reduce costly mistakes in production, making them essential for B2B manufacturers.
What Are Common Trade Terms in the CAM Software Industry?
Understanding industry jargon can facilitate smoother negotiations and partnerships when selecting CAM software. Here are several key terms that B2B buyers should be familiar with:
1. OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
OEM refers to companies that produce parts or equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer. In the context of CAM software, it often pertains to software developed for specific CNC machines. Choosing software from reputable OEMs ensures compatibility and support, which can be critical for businesses with specialized machinery.
2. MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ signifies the minimum quantity of units a supplier is willing to sell. This term is particularly relevant when purchasing licenses for CAM software or associated hardware. Understanding MOQ can help businesses budget effectively and avoid overcommitment when scaling operations.
3. RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a document issued when a company wants to obtain pricing for specific products or services. For CAM software purchases, issuing an RFQ can help gather multiple quotes, enabling better price comparisons and negotiation leverage.
4. Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
Incoterms are standardized international trade terms that define the responsibilities of sellers and buyers regarding the delivery of goods. Familiarity with these terms is essential for B2B buyers, especially when dealing with international suppliers, as they outline who pays for shipping, insurance, and tariffs.
5. Version Control
Version control refers to the management of changes to software applications. In a fast-evolving field like CAM, understanding version control is vital for ensuring that your software remains up-to-date with the latest features and security updates. This impacts operational efficiency and the software’s adaptability to changing manufacturing needs.
By grasping these technical properties and trade terms, B2B buyers can make more informed decisions, ensuring they select the best CAM software tailored to their unique operational requirements.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the best cam software for cnc Sector
What Are the Current Market Dynamics Influencing the Best CAM Software for CNC?
The global landscape of Computer-Aided Manufacturing (CAM) software is rapidly transforming, driven by technological advancements and evolving industry needs. One of the key drivers is the increasing complexity of manufacturing operations, necessitating sophisticated software solutions that can handle multi-axis machining and automate processes. This is particularly relevant for international B2B buyers in regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, where manufacturers are striving to enhance productivity and precision to remain competitive.
Emerging trends in the B2B tech space include the adoption of cloud-based CAM solutions, which facilitate real-time collaboration and data sharing across global teams. For instance, software like Autodesk Fusion is gaining traction for its integrated platform that combines CAD, CAM, and Product Lifecycle Management (PLM), appealing to modern manufacturers seeking streamlined workflows. Moreover, the rise of Industry 4.0 emphasizes the need for software that can integrate with IoT devices, enabling predictive maintenance and smarter resource management.
International buyers should also note the increasing importance of training and support when selecting CAM software. As experienced machinists retire, there is a growing demand for user-friendly solutions that can be easily adopted by a younger, tech-savvy workforce. Software providers that offer robust educational resources and customer support will likely have a competitive edge in these emerging markets.
How Is Sustainability Shaping the Sourcing of CAM Software for CNC?
Sustainability and ethical sourcing are becoming paramount in the decision-making processes of B2B buyers in the CAM software sector. As manufacturers globally face pressure to reduce their environmental impact, the demand for CAM solutions that promote efficient resource usage and waste reduction is on the rise. For instance, software that optimizes tool paths can significantly decrease material waste, thereby contributing to a more sustainable manufacturing process.
Moreover, many software companies are now focusing on ethical supply chains and environmental certifications. B2B buyers are increasingly looking for CAM software vendors that demonstrate a commitment to sustainability through certifications such as ISO 14001 or initiatives that promote the use of recycled materials. The adoption of ‘green’ technologies in CAM solutions can also enhance a company’s brand reputation and appeal to environmentally conscious clients.
As international markets evolve, integrating sustainability into sourcing strategies will not only help companies comply with regulatory requirements but also align with the values of a growing segment of consumers who prioritize environmental responsibility. Therefore, B2B buyers should prioritize software solutions that not only improve operational efficiency but also contribute to a sustainable future.
What Is the Evolution of CAM Software and Its Impact on B2B Buying Decisions?
The evolution of CAM software has been marked by significant technological advancements since its inception. Originally designed for basic toolpath generation, early CAM systems lacked the sophistication required for complex machining operations. Over the decades, software solutions have evolved to include features such as multi-axis machining, advanced simulation capabilities, and integration with CAD systems, significantly enhancing their functionality.
The introduction of cloud-based CAM software has further revolutionized the market, allowing for greater flexibility and collaboration across borders. This shift has enabled manufacturers in diverse regions, including Africa and South America, to access advanced technologies without the need for substantial upfront investments in hardware.
Today’s B2B buyers are increasingly discerning, valuing not only the technical capabilities of CAM software but also the vendor’s ability to provide support, training, and updates. As the market continues to evolve, understanding the historical context of CAM software development will equip buyers with insights into which solutions are best suited for their specific needs and future growth. By recognizing these trends, international buyers can make informed decisions that align with their operational goals and market demands.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of best cam software for cnc
-
How do I select the right CAM software for my CNC operations?
Selecting the right CAM software involves assessing your specific machining needs, such as the complexity of parts, production volume, and the types of materials you work with. Consider the software’s compatibility with your existing CAD systems, user interface, and the level of technical support available. Additionally, evaluate features like multi-axis machining, automation capabilities, and ease of integration into your workflow. Engaging with vendor demos and trials can provide insight into usability and functionality, enabling you to make an informed decision. -
What is the best CAM software for small to medium-sized CNC shops?
For small to medium-sized CNC shops, Autodesk Fusion 360 is often recommended due to its user-friendly interface and powerful features, including integrated CAD/CAM capabilities. Mastercam also stands out for its extensive toolpath options and strong educational resources. Both options offer scalability and support for diverse machining operations, making them suitable for shops looking to grow without overwhelming complexity. -
How can I ensure the CAM software I choose is customizable for my specific needs?
When evaluating CAM software, inquire about customization options during discussions with vendors. Many providers offer modular software that allows you to add or remove features based on your operational requirements. Additionally, check if the software supports scripting or API integrations, enabling you to tailor workflows. Engaging with existing users through forums or testimonials can provide insights into the software’s flexibility and adaptability in real-world applications. -
What are the common payment terms for purchasing CAM software internationally?
Payment terms for international software purchases can vary widely based on the vendor and the specific agreement. Typically, buyers may encounter options such as upfront payment, installment plans, or leasing agreements. It’s important to clarify currency exchange rates and any potential transaction fees beforehand. Ensure that you understand the implications of payment terms on software licensing, updates, and support services to avoid future complications. -
How do I verify the reliability of a CAM software vendor?
Verifying a CAM software vendor involves researching their market reputation, customer reviews, and case studies. Look for industry certifications or awards that demonstrate their credibility. Engaging with current customers through forums or social media can provide first-hand insights into their experience with the software and customer support. Additionally, request a demo or trial period to assess the software’s performance and the vendor’s responsiveness to inquiries. -
What is the typical lead time for obtaining CAM software and support in Africa and South America?
Lead times for obtaining CAM software can vary based on the vendor’s location and the complexity of the installation. Typically, you can expect a timeframe ranging from a few weeks to several months, especially if customization or training is required. Vendors with a local presence in Africa or South America may offer faster support and implementation. Always confirm timelines and support availability before finalizing your purchase to ensure timely integration into your operations. -
Are there minimum order quantities (MOQ) for CAM software licenses?
Most CAM software vendors do not impose strict minimum order quantities (MOQ) for licenses, as software is typically sold on a per-user or per-machine basis. However, bulk licensing discounts may be available for larger organizations or educational institutions. When negotiating, inquire about volume pricing or subscription models that can lower overall costs. Understanding your future growth plans can also help you decide whether to purchase additional licenses upfront or scale gradually. -
What quality assurance practices should I follow when implementing CAM software?
Implementing quality assurance (QA) practices during the CAM software integration process is crucial for ensuring optimal performance. Start with a thorough testing phase, including simulations of machining processes to identify any discrepancies. Regularly review machining outputs against design specifications to validate accuracy and efficiency. Additionally, maintain open communication with your vendor for ongoing support and updates, and consider training sessions for your team to ensure everyone is proficient in using the software effectively.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.
Top 5 Best Cam Software For Cnc Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. Practical Machinist – Key Software Tools
Domain: practicalmachinist.com
Registered: 2000 (25 years)
Introduction: 1. LazyCam: Used for generating G-code for Mach3 milling, but has limitations in the number of layers and support documentation. More suited for engraving than full 3D machining. 2. Fusion 360: Recommended for hobbyists, allows input of material type, and is considered user-friendly. 3. NX: Mentioned as the best CAM software by users with extensive experience, particularly for complex parts and 5-…
2. Carbide 3D – Free CNC Software Options
Domain: carbide3d.com
Registered: 2013 (12 years)
Introduction: Free CNC Software options available for various CNC machines including Shapeoko and Nomad. Key software includes: 1. FreeCAD – Free 3D CAD parametric program, outputs STL, STEP, SVG, DXF, runs on Mac, Windows, Linux. 2. Solvespace – Free 3D CAD program, better for mechanical parts, exports STL, STEP, runs on Mac, Windows, Linux. 3. Inkscape – Free 2D design software, exports SVG, DXF, runs on Mac,…
3. Vectric – VCarve Software
Domain: vectric.com
Registered: 2005 (20 years)
Introduction: VCarve is a powerful and intuitive software solution for creating and cutting parts on a CNC router. It offers 2.5D decorative carving strategies and the ability to import 3D models. The software is available in two editions: ‘Desktop’ for small CNC machines (24″ x 24″ bed size) and ‘Pro’ for larger machines with unlimited job and toolpath size. Key features include:
– 2D Import & Editing: Import …
4. CAMWorks – Integrated CNC Programming Software
Domain: camworks.com
Registered: 2001 (24 years)
Introduction: CAMWorks is a fully integrated CNC programming software designed for the manufacturing industry, offering solutions for various machining processes including 2.5 Axis Milling, 3 Axis Milling, Multi-Axis Milling, Mill-Turn, Turning, Wire EDM, and High-Speed Machining. Key features include:
– Seamless integration with SOLIDWORKS and Solid Edge, ensuring complete associativity between CAD and CAM da…
5. CNC Machines – Various Models and Software
Domain: ncwoodworker.net
Registered: 2005 (20 years)
Introduction: 1. Shapeoko 2 CNC Router – 12″x12″ – Software: Inventables Easel
2. Rockler Shark Pro Plus CNC Machine – Software: V Carve Pro (older version)
3. Laguna Swift CNC – 4×8 – Software: Aspire, Creo
4. Custom Home Built CNC – 3′ x 4′ – Software: Vectric Aspire, Rhinoceros 7
5. ShopBot PRT96 – 96″ x 48″ x 6″ – Software: ArtCam PartWizard, TurboCad
6. Shapeoko Pro – Software: Carbide Create Pro, Carbide …
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for best cam software for cnc
In navigating the complexities of modern manufacturing, the selection of the right CAM software is crucial for optimizing CNC operations. Key takeaways from our exploration emphasize the importance of aligning software capabilities with specific business needs, whether that be general machining, advanced multi-axis operations, or integration with existing CAD systems. For international B2B buyers, particularly in regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, understanding the unique strengths of leading CAM solutions—such as Mastercam, Autodesk Fusion, and Siemens NX CAM—can significantly enhance operational efficiency and product quality.
Strategic sourcing of CAM software not only facilitates improved workflow and productivity but also empowers businesses to stay competitive in a rapidly evolving market. As you consider your options, look for solutions that offer robust support, user-friendly interfaces, and scalability to accommodate future growth.
As the manufacturing landscape continues to transform, now is the time to invest in the right tools that will drive your business forward. Engage with vendors, request demos, and evaluate how these solutions can meet your evolving needs. Your strategic sourcing decision today will shape the future of your manufacturing capabilities tomorrow.