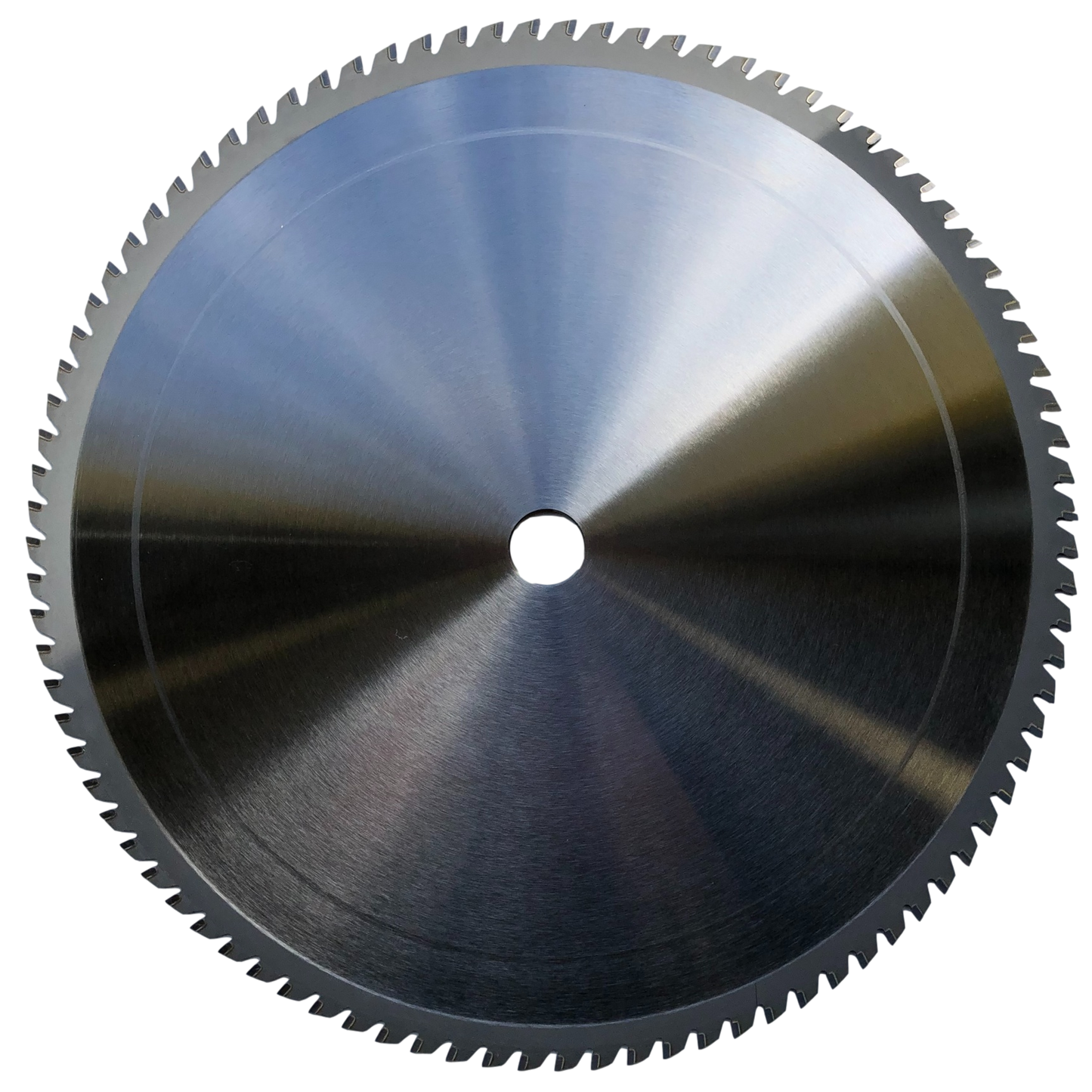
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for best blade to cut stainless steel
The global market for cutting tools presents a unique challenge for B2B buyers, particularly when it comes to sourcing the best blade to cut stainless steel. Stainless steel, known for its durability and corrosion resistance, is widely used across various industries, but selecting the right blade can significantly impact productivity and cost-efficiency. This comprehensive guide addresses the complexities of choosing the optimal cutting tool, covering various blade types, applications, supplier vetting processes, and cost considerations tailored for international buyers from regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, including Brazil and Vietnam.
In navigating this diverse landscape, B2B buyers face the critical task of not only identifying suitable blades but also understanding the specifications that align with their operational needs. The guide delves into essential factors such as material compatibility, blade composition—including high-speed steel and carbide-tipped options—and the advantages of cold saw blades over traditional cutting methods. Furthermore, it emphasizes the importance of supplier reliability and the implications of pricing on long-term procurement strategies. By equipping buyers with in-depth insights and actionable recommendations, this guide empowers businesses to make informed purchasing decisions, ensuring they choose the best blade to cut stainless steel efficiently and effectively, ultimately enhancing their operational capabilities in a competitive marketplace.
Understanding best blade to cut stainless steel Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Cermet Tipped Blades | Made with cermet tips for enhanced durability and precision | Metal fabrication, construction | Pros: Long lifespan, clean cuts; Cons: Higher initial cost. |
| HSS Cold Saw Blades | High-speed steel with cobalt for improved hardness | Heavy-duty cutting in manufacturing | Pros: Resharpenable, efficient; Cons: More brittle, higher breakage risk. |
| Tungsten Carbide Blades | Designed for specific stainless steel grades | Precision cutting in automotive | Pros: Versatile, robust; Cons: Requires specific saws. |
| Band Saw Blades | Operate at lower RPMs to minimize heat generation | General metalworking, fabrication | Pros: Reduced wear, good for thicker materials; Cons: Slower cutting speed. |
| Abrasive Cut-Off Wheels | Ideal for quick cuts on various metals | Maintenance and repair shops | Pros: Cost-effective, easy to use; Cons: Generates heat, less precise. |
What Are Cermet Tipped Blades and Their B2B Applications?
Cermet tipped blades are engineered with a combination of ceramic and metal materials, providing exceptional cutting durability, especially for stainless steel grades up to 316. These blades are ideal for industries like metal fabrication and construction where precision and longevity are critical. Buyers should consider the initial investment against the long-term savings due to their extended lifespan and reduced need for frequent replacements.
How Do HSS Cold Saw Blades Compare for Cutting Stainless Steel?
High-Speed Steel (HSS) cold saw blades, particularly those with cobalt (HSS-E), are favored for their superior hardness and heat resistance. They are particularly effective in heavy-duty manufacturing applications, allowing for efficient cuts while maintaining blade integrity. While they can be resharpened multiple times, the brittleness of HSS-E blades may pose a risk of breakage, making them suitable for businesses with a steady demand for stainless steel cutting.
What Makes Tungsten Carbide Blades a Preferred Choice?
Tungsten carbide blades are specifically designed for cutting certain grades of stainless steel, such as 302 and 304. These blades offer versatility and robustness, making them suitable for precision cutting in automotive and aerospace applications. However, they require specific saws for optimal performance, so buyers should ensure compatibility with existing equipment before investing.
Why Choose Band Saw Blades for Stainless Steel Cutting?
Band saw blades are ideal for cutting stainless steel due to their lower RPM operation, which helps reduce heat generation and prolongs blade life. They are commonly used in general metalworking and fabrication, especially for thicker materials. While they provide a slower cutting speed, their durability and effectiveness in handling various thicknesses make them a solid choice for many B2B applications.
What Are the Advantages of Using Abrasive Cut-Off Wheels?
Abrasive cut-off wheels offer a cost-effective solution for quickly cutting through various metals, including stainless steel. They are widely used in maintenance and repair shops for their ease of use and accessibility. However, they tend to generate more heat, which can affect the quality of the cut and the lifespan of both the wheel and the workpiece. Buyers should weigh these factors against their specific cutting needs and budgets.
Key Industrial Applications of best blade to cut stainless steel
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of best blade to cut stainless steel | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Manufacturing | Precision cutting of stainless steel components for machinery | Enhances production efficiency and product quality | Ensure blades are compatible with existing machinery and materials |
| Construction | Fabrication of stainless steel structures and reinforcements | Provides durability and resistance to corrosion | Consider blade size and type based on project specifications |
| Automotive | Cutting stainless steel for vehicle parts and frames | Improves performance and longevity of automotive components | Source blades that offer high cutting speed and minimal wear |
| Oil & Gas | Cutting stainless steel pipes and fittings for infrastructure | Ensures safety and reliability in harsh environments | Look for blades designed for heavy-duty applications |
| Food Processing | Fabrication of stainless steel equipment for food safety compliance | Maintains hygiene and prevents contamination | Evaluate blades for ease of cleaning and maintenance |
How is the best blade to cut stainless steel utilized in manufacturing?
In the manufacturing sector, the best blades for cutting stainless steel are essential for producing precise components used in machinery. These blades minimize burr formation and provide clean cuts, which are critical for maintaining the integrity of parts that must fit together accurately. Buyers in this sector should prioritize blades that are compatible with their existing equipment and capable of handling various stainless steel grades, especially in regions like Africa and South America where diverse manufacturing practices exist.
What are the applications in construction for stainless steel cutting blades?
In construction, stainless steel is often used for structural elements due to its strength and corrosion resistance. The best blades for cutting stainless steel facilitate the fabrication of beams, columns, and reinforcements. These blades must be robust enough to handle the demands of heavy-duty cutting while providing clean edges to ensure safety and structural integrity. Buyers should consider sourcing blades that meet specific project requirements and local standards, especially in markets like the Middle East, where building codes may vary.
How do automotive industries benefit from stainless steel cutting blades?
The automotive industry relies heavily on stainless steel for parts that require both strength and resistance to corrosion, such as frames and exhaust systems. The best blades for cutting stainless steel enable manufacturers to produce these components efficiently, enhancing the overall performance and lifespan of vehicles. When sourcing blades, automotive manufacturers should focus on those that offer high cutting speeds and durability to withstand the rigorous demands of high-volume production, particularly in Europe where automotive standards are stringent.
What role do stainless steel cutting blades play in the oil and gas sector?
In the oil and gas sector, the best blades for cutting stainless steel are critical for fabricating pipes, fittings, and other components that must endure extreme conditions. These blades ensure precision cuts that contribute to the safety and reliability of infrastructure projects. Buyers in this industry should look for blades designed for heavy-duty applications and capable of cutting through thick materials, particularly in regions like Brazil and Vietnam where oil and gas extraction is a key economic driver.
How is food processing impacted by the use of stainless steel cutting blades?
The food processing industry utilizes stainless steel extensively to comply with hygiene and safety regulations. The best blades for cutting stainless steel are essential for fabricating equipment that meets these standards while ensuring durability and ease of cleaning. Buyers in this sector should evaluate blades based on their ability to maintain hygiene, resist corrosion, and withstand frequent cleaning processes, especially in international markets where food safety regulations may differ significantly.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘best blade to cut stainless steel’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Difficulty in Achieving Clean Cuts Without Excessive Heat
The Problem: B2B buyers often face challenges when cutting stainless steel due to the material’s inherent toughness and heat sensitivity. Traditional cutting methods can generate excessive heat, leading to warping, poor finish quality, and even blade damage. This is especially critical for industries that require precise dimensions and clean edges, such as aerospace or automotive manufacturing. Buyers may find themselves frequently replacing blades or dealing with costly rework, which affects their productivity and operational costs.
The Solution: To achieve clean cuts while minimizing heat generation, buyers should consider investing in high-quality cold saw blades specifically designed for stainless steel. Cold saws operate at lower RPMs and transfer heat generated during cutting to the chips, thus keeping both the blade and the workpiece cool. For optimal performance, buyers should look for blades made from high-speed steel (HSS) or HSS-E, which offer increased hardness and durability. Additionally, using proper cutting fluids can further reduce friction and heat. Buyers should also ensure that their cutting equipment is compatible with these blades to maximize efficiency and minimize downtime.
Scenario 2: Frequent Blade Breakage and Reduced Cutting Life
The Problem: In the industrial sector, frequent blade breakage is a significant pain point for B2B buyers who work with stainless steel. The aggressive nature of stainless steel can lead to premature wear and tear on blades, resulting in unexpected downtime and increased replacement costs. This issue is compounded when buyers opt for lower-quality blades that are not engineered to withstand the rigors of cutting tougher materials.
The Solution: To combat blade breakage, buyers should prioritize the selection of blades with cermet tips or carbide-tipped designs. Cermet blades, for instance, offer extended cutting life and are specifically formulated to handle the unique challenges of stainless steel. Moreover, it’s crucial to match the blade type with the specific grade of stainless steel being cut. Buyers should consult with suppliers to understand the optimal blade specifications for their applications. Regular maintenance, including sharpening and proper storage, will also extend the life of the blades. Implementing a proactive inventory management system to track blade performance can further help in making informed purchasing decisions.
Scenario 3: Inconsistent Cutting Performance Leading to Quality Issues
The Problem: B2B buyers often struggle with inconsistent cutting performance, which can lead to quality issues in finished products. Factors such as blade selection, cutting speed, and feed rate can all impact the cutting process. If the blade is not suited for the material or if the settings are incorrect, it can result in ragged edges, burrs, and an overall poor finish. This inconsistency not only affects product quality but can also damage client relationships and harm brand reputation.
The Solution: To ensure consistent cutting performance, buyers should invest in blades that are specifically designed for the type of stainless steel they are working with, taking into account factors such as thickness and alloy grade. It is also vital to establish and adhere to the recommended cutting speeds and feed rates for each type of blade. Buyers can benefit from conducting trial runs to fine-tune their settings based on the specific materials and machinery used. Additionally, implementing quality control measures, such as regular inspections of the cut surfaces and blade condition, can help identify issues before they escalate. Training operators on the nuances of cutting stainless steel can also contribute to more consistent outcomes and improved overall efficiency.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for best blade to cut stainless steel
What Are the Best Materials for Blades to Cut Stainless Steel?
When selecting blades for cutting stainless steel, the choice of material significantly influences performance, durability, and overall cost-effectiveness. Below are analyses of four common materials used in manufacturing blades for this purpose, focusing on their properties, advantages, disadvantages, and considerations for international buyers.
1. High-Speed Steel (HSS)
Key Properties:
High-speed steel blades are known for their ability to withstand high temperatures without losing hardness. They typically feature a chromium content that offers some level of corrosion resistance, making them suitable for cutting stainless steel.
Pros & Cons:
HSS blades are durable and can be resharpened multiple times, extending their lifespan. However, they can be more sensitive to breakage under heavy loads, and their performance may decline when cutting harder grades of stainless steel. The manufacturing process is relatively straightforward, but the initial cost can be moderate.
Impact on Application:
HSS blades are ideal for applications requiring precision cuts in softer stainless steel grades, such as 304 and 316. However, they may struggle with tougher alloys, necessitating careful selection based on the specific stainless steel grade.
International Considerations:
Buyers in regions like Africa and South America should ensure compliance with local standards, such as ASTM or ISO, particularly in industries like construction and manufacturing where safety is paramount.
2. Cermet-Tipped Blades
Key Properties:
Cermet blades combine ceramic and metal properties, resulting in exceptional hardness and wear resistance. This material can handle higher temperatures and provides a longer cutting life compared to traditional HSS.
Pros & Cons:
The primary advantage of cermet-tipped blades is their ability to produce clean cuts with minimal burrs, which is critical in many industrial applications. However, they tend to be more expensive than HSS blades and can be more brittle, increasing the risk of chipping under stress.
Impact on Application:
These blades are particularly effective for cutting thicker sections of stainless steel and are often used in manufacturing environments where precision is crucial.
International Considerations:
Cermet blades may not be as widely available in developing markets, so buyers should consider logistics and sourcing challenges. Compliance with international standards is essential, especially in regulated industries.
3. Tungsten Carbide-Tipped Blades
Key Properties:
Tungsten carbide-tipped blades are known for their exceptional hardness and resistance to wear. They maintain sharpness longer than HSS and are effective in high-speed cutting applications.
Pros & Cons:
These blades offer high durability and can cut through various stainless steel grades efficiently. However, the cost is typically higher than both HSS and cermet blades, and they may require specialized equipment to handle their cutting characteristics.
Impact on Application:
Tungsten carbide-tipped blades are suitable for heavy-duty applications and are often used in industries such as automotive and aerospace, where precision and durability are paramount.
International Considerations:
B2B buyers in Europe and the Middle East should be aware of the stringent regulations regarding materials and safety standards, ensuring that the blades comply with local and international certifications.
4. Bi-Metal Blades
Key Properties:
Bi-metal blades consist of a high-speed steel edge welded to a flexible steel body, providing both durability and flexibility. This design allows them to withstand the rigors of cutting stainless steel while maintaining a sharp edge.
Pros & Cons:
The flexibility of bi-metal blades reduces the risk of breakage, making them suitable for a variety of cutting applications. However, they may not last as long as tungsten carbide-tipped blades and can be less effective on thicker materials.
Impact on Application:
These blades are versatile and can be used for both straight and curved cuts in stainless steel, making them a popular choice in fabrication shops.
International Considerations:
When sourcing bi-metal blades, buyers should verify compliance with relevant standards in their region, particularly in industries that prioritize safety and quality.
Summary Table
| Material | Typical Use Case for best blade to cut stainless steel | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| High-Speed Steel (HSS) | Precision cuts in softer stainless steel grades | Resharpenable and durable | Sensitive to breakage under heavy loads | Medium |
| Cermet-Tipped Blades | Cutting thicker sections of stainless steel | Clean cuts with minimal burrs | Higher cost and more brittle | High |
| Tungsten Carbide-Tipped | Heavy-duty applications in automotive and aerospace | Exceptional hardness and durability | Requires specialized equipment | High |
| Bi-Metal Blades | Versatile cutting in fabrication shops | Flexible and resistant to breakage | Shorter lifespan compared to carbide blades | Medium |
This guide provides valuable insights for B2B buyers looking to make informed decisions on the best blades for cutting stainless steel, ensuring they choose the right material for their specific applications and market conditions.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for best blade to cut stainless steel
What Are the Main Stages in the Manufacturing Process of Stainless Steel Cutting Blades?
The manufacturing process for cutting blades designed specifically for stainless steel involves several critical stages, each ensuring that the final product meets high performance and durability standards.
Material Preparation
The first stage involves selecting and preparing high-quality materials. Typically, manufacturers use high-speed steel (HSS), carbide, or cermet materials, each chosen for its specific cutting properties. The raw materials undergo rigorous inspection to ensure they meet predefined specifications for hardness and composition. Material preparation may also include heat treatment processes that enhance the material’s toughness and resistance to wear.
Forming Techniques
The next step is forming the blade. This is usually achieved through processes such as forging, stamping, or laser cutting. Forging is favored for its ability to create a denser, stronger blade, while stamping is more cost-effective for mass production. Laser cutting offers precision, ensuring that the blade dimensions are exact and that the cutting edges are sharp. This stage may also involve the creation of specialized tooth designs, which are critical for efficient cutting through tough stainless steel grades.
Assembly of Components
In this stage, various components of the blade, such as the teeth and the core, are assembled. For example, cermet-tipped blades will have cermet tips brazed onto the steel body. The assembly process must ensure that all parts are securely joined, as any weakness can lead to catastrophic failure during use. Manufacturers may employ advanced technologies, such as automated robotic systems, to ensure precision and consistency in assembly.
Finishing Processes
The finishing stage is crucial for enhancing the blade’s performance and longevity. This may include grinding the edges to achieve a sharp, precise cut, surface treatments to reduce friction, and coating to prevent rust. Some manufacturers also apply anti-vibration technologies to reduce noise and improve cutting stability. Each blade undergoes a final inspection to verify that it meets the required specifications.
What Quality Assurance Standards Are Relevant for Stainless Steel Cutting Blades?
Quality assurance is vital in the manufacturing of stainless steel cutting blades to ensure they perform effectively and safely. Various international and industry-specific standards guide the quality assurance process.
ISO 9001 and Other International Standards
ISO 9001 is a widely recognized standard for quality management systems. Compliance with ISO 9001 indicates that a manufacturer has established processes to consistently meet customer and regulatory requirements. This certification involves regular audits and continuous improvement practices.
Other relevant standards may include CE marking, which indicates conformity with health, safety, and environmental protection standards for products sold within the European Economic Area. For specific industries, such as oil and gas, certifications from the American Petroleum Institute (API) may also be required.
Quality Control Checkpoints: What Should B2B Buyers Look For?
Quality control (QC) checkpoints are essential to ensure that each blade meets the required standards throughout the manufacturing process. Key checkpoints include:
-
Incoming Quality Control (IQC): This involves inspecting raw materials before they enter the production process. Buyers should verify that suppliers have stringent IQC procedures to ensure only high-quality materials are used.
-
In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): During manufacturing, quality checks should be performed at various stages to catch any deviations early. This may include dimensional checks, material hardness tests, and visual inspections.
-
Final Quality Control (FQC): After the manufacturing process, blades undergo final inspections to ensure they meet all specifications. This stage may include testing for cutting efficiency, durability, and dimensional accuracy.
What Common Testing Methods Are Used to Ensure Blade Quality?
Manufacturers employ various testing methods to assess the quality and performance of stainless steel cutting blades. Common testing methods include:
-
Hardness Testing: This is conducted to ensure that the blade material meets hardness specifications, which is crucial for cutting performance. Methods such as Rockwell or Vickers hardness tests are commonly used.
-
Cutting Tests: Actual cutting tests may be performed on samples to evaluate the blade’s performance under real-world conditions. This includes measuring the quality of the cut and the blade’s lifespan during use.
-
Vibration Testing: For blades designed with anti-vibration technology, manufacturers may conduct vibration tests to ensure that the design effectively reduces vibrations during operation.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control?
B2B buyers can take several steps to verify the quality control measures of potential suppliers, ensuring that they are investing in high-quality products.
Audits and Reports
Conducting supplier audits is a proactive approach to assess the quality management systems in place. Buyers can request audit reports that detail compliance with relevant standards, such as ISO 9001. This provides insight into the supplier’s processes and commitment to quality.
Third-Party Inspections
Engaging third-party inspection services can offer an unbiased evaluation of the manufacturing processes and final products. These services can verify that the blades meet specified standards and provide certification that can be crucial for international transactions.
What Are the Quality Control Nuances for International B2B Buyers?
For international buyers, particularly from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, understanding the nuances of quality control is essential.
Regulatory Compliance
Different countries have varying regulations regarding product safety and quality. Buyers must ensure that suppliers comply with local regulations in their markets, which may require additional certifications beyond ISO or CE.
Cultural and Communication Considerations
Cultural differences can impact business practices, including quality expectations. It’s crucial for buyers to establish clear communication channels and expectations with suppliers to avoid misunderstandings.
Logistics and Supply Chain Factors
Lastly, international shipping introduces additional variables that can affect product quality. Buyers should work with suppliers who have robust logistics and supply chain management practices to ensure that products arrive in optimal condition.
In conclusion, a comprehensive understanding of the manufacturing processes and quality assurance practices for stainless steel cutting blades is vital for B2B buyers. By focusing on these aspects, buyers can make informed decisions and establish successful partnerships with suppliers.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘best blade to cut stainless steel’
Introduction
This guide serves as a practical checklist for B2B buyers looking to procure the best blades for cutting stainless steel. The right blade not only enhances cutting efficiency but also reduces operational costs and downtime. By following these steps, you can ensure that you choose a blade that meets your specific needs while also sourcing from reliable suppliers.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Before searching for suppliers, it’s essential to define the technical specifications of the blades you need. Consider factors such as the type of stainless steel you will be cutting (e.g., grades 304, 316), the thickness of the material, and the cutting method (e.g., cold saw, band saw).
- Key Considerations:
- Material Composition: Different stainless steel grades require specific blade materials for optimal performance.
- Blade Size and Type: Determine the appropriate diameter and tooth configuration for your equipment.
Step 2: Research Blade Types Suitable for Stainless Steel
Understanding the various blade types available is crucial in making an informed decision. Common options include high-speed steel (HSS) blades, carbide-tipped blades, and cermet-tipped blades. Each has its pros and cons depending on the application.
- Specifics to Note:
- HSS vs. HSS-E: HSS-E blades contain cobalt, offering enhanced hardness and heat resistance, making them suitable for harder stainless steel grades.
- Cermet-Tipped Blades: These blades provide longer life and cleaner cuts, ideal for production environments.
Step 3: Evaluate Potential Suppliers
Before committing to a purchase, vet potential suppliers thoroughly. Request detailed company profiles, product specifications, and case studies demonstrating their experience with stainless steel cutting solutions.
- What to Look For:
- Industry Experience: Suppliers with a strong track record in your specific industry can offer better insights into suitable products.
- Customer References: Seek testimonials from other businesses that have sourced similar blades.
Step 4: Verify Quality Certifications
Quality assurance is paramount when sourcing cutting blades. Ensure that the suppliers hold relevant industry certifications, such as ISO or equivalent standards, which indicate their adherence to quality manufacturing processes.
- Importance of Certifications:
- Consistency in Quality: Certified manufacturers are more likely to deliver products that meet your specifications consistently.
- Regulatory Compliance: This is particularly important if you are exporting products to regions with stringent quality regulations.
Step 5: Request Samples and Test Performance
Once you have shortlisted suppliers, request samples of the blades for testing. This step allows you to evaluate the performance of the blades in real-world conditions, ensuring they meet your requirements.
- Testing Criteria:
- Cutting Speed and Precision: Measure how well the blade performs on your specific stainless steel grades.
- Durability: Assess how many cuts the blade can make before requiring resharpening or replacement.
Step 6: Compare Pricing and Terms
After testing, compare the pricing and terms offered by the suppliers. Look beyond the initial cost; consider factors like minimum order quantities, shipping costs, and warranty terms.
- Cost Considerations:
- Total Cost of Ownership: Factor in the lifespan of the blade and potential savings from reduced downtime and maintenance.
- Payment Terms: Favorable payment terms can improve cash flow and reduce upfront costs.
Step 7: Establish a Long-term Relationship
Once you select a supplier, aim to establish a long-term relationship. This can lead to better pricing, priority service, and access to new product offerings as they become available.
- Benefits of Long-term Relationships:
- Consistent Supply: Ensures you have reliable access to high-quality blades as your business grows.
- Collaboration Opportunities: Suppliers may provide insights or innovations that can enhance your cutting operations.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for best blade to cut stainless steel Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components for Sourcing Stainless Steel Cutting Blades?
When sourcing blades for cutting stainless steel, several cost components play a critical role in determining the overall price. Key elements include:
-
Materials: The type of steel used in the blade, such as High-Speed Steel (HSS) or tungsten carbide, significantly impacts costs. Cermet-tipped blades, known for durability and performance, command higher prices due to their premium material composition.
-
Labor: Skilled labor is essential for manufacturing high-quality blades. Labor costs can vary by region, impacting overall pricing structures. Manufacturers in countries with higher labor costs may pass these expenses on to buyers.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes costs associated with machinery, facility maintenance, and utilities. Advanced manufacturing processes, such as precision laser cutting or heat treatment, contribute to higher overhead costs.
-
Tooling: The initial investment in tooling for blade production can be substantial. Custom tooling for specific blade designs may lead to increased costs, especially for low-volume orders.
-
Quality Control (QC): Rigorous QC processes ensure that blades meet industry standards, particularly for demanding applications. Enhanced QC measures can add to production costs but are essential for maintaining product quality.
-
Logistics: Shipping costs, especially for international transactions, can significantly affect the final price. Factors such as distance, shipping method, and customs duties play a role in logistics expenses.
-
Margin: Suppliers typically include a profit margin in their pricing. This margin can vary based on the supplier’s market position and the competitiveness of their offerings.
How Do Price Influencers Impact the Cost of Stainless Steel Cutting Blades?
Several factors influence the pricing of stainless steel cutting blades, particularly for B2B buyers:
-
Volume/MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity): Purchasing in bulk often yields discounts, reducing the per-unit cost. Suppliers may offer tiered pricing based on order volume, encouraging larger purchases.
-
Specifications and Customization: Custom designs or specific blade specifications can lead to higher costs. Buyers should weigh the necessity of customization against potential savings from standard products.
-
Material Quality and Certifications: Blades certified to meet international standards (such as ISO or ANSI) may cost more but offer assurance of quality and performance. Investing in certified blades can reduce the total cost of ownership over time.
-
Supplier Factors: Supplier reputation, reliability, and customer service can impact pricing. Established suppliers may command higher prices due to their track record of quality and service.
-
Incoterms: Understanding Incoterms is crucial for international buyers as they define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers regarding shipping, insurance, and tariffs. This knowledge can help avoid unexpected costs.
What Are Effective Buyer Tips for Negotiating Prices on Stainless Steel Cutting Blades?
International B2B buyers should consider several strategies to negotiate better pricing on stainless steel cutting blades:
-
Research and Benchmarking: Conduct market research to understand average prices and quality standards. Benchmarking against competitors can provide leverage in negotiations.
-
Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Evaluate not just the purchase price but also factors like durability, maintenance, and potential downtime. A higher upfront cost might be justified by lower long-term expenses.
-
Leverage Relationships: Building long-term relationships with suppliers can lead to better pricing and terms. Loyal customers often receive preferential treatment in pricing negotiations.
-
Explore Payment Terms: Flexible payment terms can ease cash flow and may encourage suppliers to offer discounts. Discussing payment options upfront can lead to mutually beneficial agreements.
-
Consider Local Suppliers: Sourcing from local suppliers can reduce logistics costs and lead times. Additionally, local partnerships may offer better service and support.
Conclusion
Sourcing the best blades for cutting stainless steel involves a comprehensive understanding of cost structures, pricing influencers, and effective negotiation strategies. By analyzing these factors, international B2B buyers can make informed decisions, ensuring they achieve optimal value in their procurement processes. Always remember that prices can vary significantly based on the factors discussed, and it is wise to seek multiple quotes to ensure competitive pricing.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing best blade to cut stainless steel With Other Solutions
Understanding Alternatives for Cutting Stainless Steel
When it comes to cutting stainless steel, selecting the right tool is crucial for achieving optimal results. While specialized blades designed for stainless steel are highly effective, there are alternative methods and technologies available that may suit different operational needs. This analysis will compare the best blade for cutting stainless steel against two viable alternatives: cold saws and plasma cutting.
Comparison Table
| Comparison Aspect | Best Blade To Cut Stainless Steel | Cold Saw | Plasma Cutting |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | High precision, clean cuts | Excellent durability, resharpenable | Versatile, fast cutting |
| Cost | Moderate (e.g., $48.75 – $171.75) | Higher initial investment | High operational costs (gas/electricity) |
| Ease of Implementation | User-friendly, requires basic setup | Requires specialized machinery | Requires skilled operators |
| Maintenance | Regular sharpening needed | Resharpenable, less frequent replacement | Maintenance on equipment and consumables |
| Best Use Case | Small to medium projects | High-volume production | Large scale, complex shapes |
In-Depth Analysis of Alternatives
What are Cold Saws and How Do They Compare?
Cold saws utilize high-speed steel blades that cut stainless steel while minimizing heat generation. This method is particularly effective for high-volume production due to its durability and ability to resharpen blades up to 15 times. While cold saws can have a higher initial investment compared to traditional blades, their longevity and precision make them a cost-effective solution for businesses that regularly work with stainless steel. However, the need for specialized machinery can limit flexibility, especially for smaller operations.
How Does Plasma Cutting Work and What Are Its Advantages?
Plasma cutting employs a high-velocity jet of ionized gas to cut through stainless steel. This method is known for its versatility, as it can be used on various thicknesses and shapes of metal, making it ideal for complex projects. Plasma cutting is faster than traditional methods, which can significantly increase productivity. However, the operational costs associated with gas and electricity can be high, and it requires skilled operators to ensure precision and safety. This may pose a challenge for companies looking to minimize labor costs.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Solution for Your Needs
When selecting a method for cutting stainless steel, B2B buyers must consider various factors such as performance, cost, and operational requirements. The best blade for cutting stainless steel offers a balance of precision and affordability, making it suitable for small to medium projects. In contrast, cold saws provide durability and efficiency for high-volume needs, while plasma cutting excels in versatility for complex shapes. Ultimately, the right choice will depend on the specific demands of the project, available budget, and the operational capabilities of the business.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for best blade to cut stainless steel
What Are the Key Technical Properties for Selecting the Best Blade to Cut Stainless Steel?
When choosing a blade for cutting stainless steel, understanding the essential technical properties is crucial for ensuring optimal performance and longevity. Here are several critical specifications to consider:
-
Material Composition
The blade’s material significantly influences its cutting efficiency and durability. Common materials include High-Speed Steel (HSS), HSS-E (with cobalt), and carbide-tipped options. HSS blades are suitable for general cutting, while HSS-E offers superior hardness and heat resistance, making it ideal for tougher stainless steel grades. Carbide-tipped blades provide longevity but are sensitive to heat and require lower cutting speeds. -
Tooth Configuration
The tooth design of a blade directly impacts its cutting ability and finish quality. Common configurations include Alternate Top Bevel (ATB) and Triple Chip Grind (TCG). ATB blades are preferred for cleaner cuts in thin materials, whereas TCG blades are better suited for thicker stainless steel, as they reduce chip build-up and heat. -
Kerf Width
The kerf width refers to the thickness of the cut made by the blade. A thinner kerf generally results in less material wastage and faster cutting speeds. However, a thicker kerf may be necessary for added stability in tougher cutting applications. Selecting the right kerf width is critical for balancing speed and precision. -
RPM Rating
The revolutions per minute (RPM) rating indicates the maximum speed at which a blade can operate safely. Stainless steel requires lower RPMs to prevent overheating and blade damage. Understanding the RPM requirements ensures compatibility with your cutting machinery and helps prevent operational hazards. -
Bore Size
The bore size is the diameter of the hole in the center of the blade, which must match the spindle of the saw for secure mounting. Ensuring the correct bore size is vital for safe operation and effective cutting performance.
What Are Common Trade Terms Used in the Stainless Steel Cutting Industry?
Familiarity with industry jargon is essential for smooth transactions and communication. Here are several key terms that B2B buyers should understand:
-
OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
This term refers to companies that produce parts or equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer. In the context of saw blades, OEM products often ensure compatibility and quality assurance, making them a reliable choice for industrial applications. -
MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ indicates the smallest number of units a supplier is willing to sell. Understanding MOQ is essential for budgeting and inventory planning, especially for businesses looking to maintain a steady supply of blades for production. -
RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a document sent to suppliers requesting pricing and terms for specific products. It is a critical step in the procurement process, enabling buyers to compare offers and negotiate better deals based on their cutting needs. -
Incoterms
International Commercial Terms (Incoterms) define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in international transactions. Understanding these terms helps businesses navigate shipping logistics, costs, and risks associated with importing saw blades and other materials. -
TPI (Teeth Per Inch)
TPI refers to the number of teeth on a blade per inch of cutting length. Higher TPI is suitable for finer cuts, while lower TPI is ideal for faster, rougher cuts. This measurement is crucial for selecting the right blade for specific cutting applications. -
Heat Treatment
This refers to the process of altering the physical and sometimes chemical properties of a blade by heating and cooling. Heat treatment enhances hardness and wear resistance, which is essential for cutting through tough materials like stainless steel.
By understanding these properties and terms, B2B buyers can make informed decisions when sourcing the best blades for cutting stainless steel, ultimately leading to improved operational efficiency and reduced costs.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the best blade to cut stainless steel Sector
What Are the Current Market Dynamics and Trends in the Best Blade to Cut Stainless Steel?
The global market for cutting blades, particularly those designed for stainless steel, is witnessing significant growth due to various factors. With the rise in construction, manufacturing, and automotive industries, the demand for high-quality cutting tools has surged. Key trends include the adoption of advanced materials such as cermet and high-speed steel (HSS-E) in blade manufacturing, which enhance durability and cutting efficiency. As international buyers, particularly from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, evaluate their sourcing strategies, it is essential to consider not only the performance of the blades but also their compatibility with local machinery and conditions.
Technological advancements are reshaping the landscape, with innovations in blade design and production processes leading to better precision and reduced waste. For instance, blades that feature anti-vibration slots and specialized coatings are becoming increasingly popular, as they minimize heat generation and extend tool life. Additionally, the trend towards automation in manufacturing processes is influencing the type of blades required, as companies seek to streamline operations and improve productivity. International buyers should stay informed about these advancements to ensure they are sourcing the most efficient tools available.
Moreover, regional dynamics play a crucial role. In emerging markets like Brazil and Vietnam, the increasing focus on infrastructure development drives demand for reliable cutting tools. Buyers must navigate local regulations and import duties, which can affect pricing and availability. By understanding these market dynamics and sourcing trends, businesses can make informed decisions that align with their operational needs and growth objectives.
How Important Are Sustainability and Ethical Sourcing in the Best Blade to Cut Stainless Steel?
Sustainability is increasingly becoming a critical factor in B2B sourcing decisions, especially in the cutting tools industry. The production of blades, particularly those made from high-speed steel and cermet materials, involves processes that can have significant environmental impacts. International buyers are now prioritizing suppliers that demonstrate a commitment to sustainable practices, such as using recycled materials and minimizing waste during production.
Ethical sourcing is equally important. Companies are under pressure to ensure their supply chains are transparent and that materials are sourced responsibly. This includes verifying that suppliers adhere to environmental regulations and labor standards. In the context of cutting blades, certifications such as ISO 14001 for environmental management and ISO 9001 for quality management can serve as indicators of a supplier’s commitment to sustainability and ethical practices.
Buyers should also consider the lifecycle of the blades they purchase. Opting for products that can be resharpened multiple times, like high-quality cold saw blades, not only reduces waste but also offers cost savings over time. As the global market shifts towards more sustainable practices, aligning sourcing strategies with these values will not only fulfill regulatory requirements but also enhance brand reputation and customer loyalty.
How Has the Best Blade to Cut Stainless Steel Evolved Over Time?
The evolution of blades designed for cutting stainless steel reflects significant advancements in materials science and manufacturing technology. Initially, standard carbon steel blades were the norm; however, they quickly proved inadequate for the demands of stainless steel, which is known for its toughness and resistance to wear.
The introduction of high-speed steel (HSS) blades marked a turning point, offering improved hardness and heat resistance. This was further enhanced with the development of HSS-E blades, which incorporate cobalt to improve performance in cutting harder materials. Today, the most advanced blades utilize cermet tips, which combine ceramic and metal to provide exceptional durability and cutting efficiency, particularly in high-volume industrial applications.
As industries continue to evolve, so too will the cutting tools used, with ongoing research and development focused on enhancing performance while minimizing environmental impact. Understanding this historical context helps B2B buyers appreciate the significance of selecting the right blade for their specific applications, ensuring they leverage the best technology available to meet their operational demands.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of best blade to cut stainless steel
-
How do I choose the right blade for cutting stainless steel?
Choosing the right blade for cutting stainless steel involves considering several factors, including the type of stainless steel, the thickness of the material, and the cutting method. For instance, cold saw blades are ideal for precision cuts in thicker materials, while cermet-tipped blades excel in reducing burrs and sparking. Assess your specific requirements, such as the desired finish quality and production volume, and consult with suppliers for recommendations tailored to your needs. -
What is the best blade material for cutting stainless steel?
The best blade materials for cutting stainless steel typically include High-Speed Steel (HSS) and carbide-tipped blades. HSS blades, particularly those with cobalt (HSS-E), offer high hardness and durability, making them suitable for tougher grades of stainless steel. Carbide-tipped blades provide excellent cutting life and are ideal for high-volume applications. Evaluate your cutting conditions to determine which material will yield the best results for your operations. -
What factors should I consider when sourcing saw blades internationally?
When sourcing saw blades internationally, consider the supplier’s reputation, product quality, and compliance with international standards. Evaluate their experience in the industry and check for certifications that ensure reliability. Additionally, assess logistics capabilities, including shipping times, customs handling, and after-sales support. Establish clear communication regarding your specifications to avoid misunderstandings and ensure that the products meet your expectations. -
What are the minimum order quantities (MOQ) for stainless steel cutting blades?
Minimum order quantities (MOQ) for stainless steel cutting blades can vary significantly among suppliers. Some manufacturers may offer MOQs as low as 10 units, while others might require orders of 100 or more. It’s essential to discuss your needs with potential suppliers and negotiate MOQs that align with your production requirements. Additionally, inquire about bulk discounts, which could lead to cost savings on larger orders. -
How can I ensure the quality of the blades I purchase?
To ensure the quality of the blades you purchase, request product samples before placing a large order. Evaluate the blades based on their cutting performance, durability, and finish quality. Additionally, ask suppliers for quality assurance documentation, including material certifications and testing reports. Establish a clear return policy in case the products do not meet your specifications, and consider third-party inspections for added assurance. -
What payment terms are commonly offered by suppliers of cutting blades?
Payment terms offered by suppliers of cutting blades can vary widely. Common options include payment in advance, net 30 or net 60 days after delivery, and letters of credit for larger transactions. When negotiating payment terms, consider your cash flow and the supplier’s reputation. It’s advisable to establish terms that protect your interests while ensuring a smooth transaction process. -
What logistics considerations should I keep in mind when importing saw blades?
When importing saw blades, consider logistics aspects such as shipping methods, delivery times, and customs regulations. Choose a reliable freight forwarder who can navigate import duties and taxes specific to your country. Additionally, ensure that the supplier provides appropriate packaging to prevent damage during transit. Establish clear communication regarding delivery timelines to manage expectations and maintain production schedules. -
Can I customize the blades to meet specific requirements?
Many suppliers offer customization options for saw blades to meet specific requirements, such as size, tooth configuration, or material composition. Discuss your unique cutting needs with potential suppliers to explore available customization options. Customization may involve additional costs and longer lead times, so be sure to factor these into your planning. It’s also advisable to request prototypes to test performance before finalizing larger orders.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.
Top 8 Best Blade To Cut Stainless Steel Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. Evolution – 7 Stainless Steel Cutting Blade
Domain: store.evolutionpowertools.com
Registered: 2000 (25 years)
Introduction: {“products”: [{“name”: “Evolution 180BLADESSN”,”size”: “7 in.”,”teeth”: “48T”,”arbor”: “20mm”,”price”: “$48.00″,”application”: “Designed specifically to cut 302, 303 & 304 grades of Stainless Steel only.”,”compatible_with”: “Evolution EVOSAW180HD, RAGE-B, RAGE4, Jancy MCSL07”},{“name”: “Evolution 185BLADESSN”,”size”: “7-1/4 in.”,”teeth”: “48T”,”arbor”: “20mm”,”price”: “$48.00″,”application”: “Desi…
2. OSHLUN – 7-1/4 Cermet Tipped Saw Blade
Domain: sliversmill.com
Registered: 2002 (23 years)
Introduction: {“products”:[{“name”:”OSHLUN 7-1/4″x36 Tooth Cermet Tipped Saw Blade”,”size”:”7-1/4″”,”bore”:”5/8″”,”teeth”:”36 ATB”,”kerf”:”0.055″”,”description”:”Cermet tipped saw blade designed for cutting stainless steel up to 316. Suitable for portable saws.”,”price”:”$48.75″,”model”:”SBFS-072536″,”shipping”:”Qualifies for FREE SHIPPING in the US on orders over $49″},{“name”:”OSHLUN 14″x66 Tooth Cermet Tippe…
3. Sawblade – HSS-E Cold Saw Blades
Domain: sawblade.com.au
Introduction: HSS Cold Saw Blade (High Speed Steel), HSS-E Cold Saw Blade; HSS-E blade contains 5-8% cobalt for higher hardness, tempering resistance, and heat hardness; HSS-E is preferred for stainless steel or harder steels; HSS-E has higher breakage sensitivity; Cold saw blades can be resharpened up to 15 times; Cold saw blades transfer heat to the chip, keeping the blade and work cold.
4. Facebook – Versatile Cutting Solutions
Domain: facebook.com
Registered: 1997 (28 years)
Introduction: This company, Facebook – Versatile Cutting Solutions, is a notable entity in the market. For specific product details, it is recommended to visit their website directly.
5. Evolution – 10 Stainless Steel TCT Blade
Domain: lumberjocks.com
Registered: 2005 (20 years)
Introduction: Evolution 10BLADESSN | 10 in. | 66T | 1 in. Arbor | Stainless Steel TCT Blade designed to cut stainless steel grades 302, 303 & 304.
6. Diablo – Steel Demon Carbide-Tipped Saw Blade
Domain: garagejournal.com
Registered: 2006 (19 years)
Introduction: 1. Fine tooth carbide tipped blades recommended for cutting mild stainless steel. 2. Diablo 6 in. 8-TPI Steel Demon Carbide-Tipped Thick Metal Cutting Reciprocating Saw Blade mentioned as effective. 3. Carbide tipped blades are noted for cutting tough materials like cast iron and stainless steel. 4. Importance of using cutting oil (like WD40) to extend blade life. 5. Recommendations for slower spe…
7. Cold Saw Shop – Steel Cutting Saw Blades
Domain: coldsawshop.com
Registered: 2018 (7 years)
Introduction: Steel Cutting Saw Blades | Stainless Steel Cutting Blades, Cold Saw Blades (HSS), M2 DMo5 Cold Saw Blades, M35 Co5 Cobalt Cold Saw Blades, M2 & M35 TiN Coated Cold Saw Blades, M35 TiAlN Coated Cold Saw Blades, Non-Ferrous Saw Blades, HSS for Aluminum, HSS for Copper Tubes, Carbide Tipped for Aluminum, Carbide & Cermet Blades for CNC Saws, Carbide Blades for Dry Cut Saws, Friction Saw Blades, Sharp…
8. Evolution – Rage 2 Chopsaw
Domain: practicalmachinist.com
Registered: 2000 (25 years)
Introduction: Evolution Rage 2 chopsaw; special saw blade for stainless steel; price: $120; suitable for cutting Multipurpose Type 304 Stainless Steel 90 Degree Angle, 1/4″ Thick, 4″ X 6″ Leg Lgs., 1′ Long; recommended tooth configuration for stainless: 10 degree rake with modified atb/flat; Tenryu stainless blade recommended, approx. $250 for 14″ blade.
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for best blade to cut stainless steel
In the competitive landscape of stainless steel cutting, selecting the right blade is crucial for enhancing operational efficiency and reducing costs. As outlined, blades with cermet tips, such as those from Oshlun, offer durability and precision, making them ideal for various stainless steel grades, including 316. Furthermore, high-speed steel (HSS) blades, particularly HSS-E variants, provide exceptional performance for tougher stainless steel applications, although they may require more careful handling due to breakage sensitivity.
Strategic sourcing plays a vital role in ensuring that businesses not only procure high-quality cutting tools but also foster relationships with reliable suppliers. This approach can lead to better pricing, improved product availability, and access to innovative technologies that enhance productivity.
Looking ahead, international B2B buyers from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe should prioritize suppliers who demonstrate a commitment to quality and sustainability. By investing in superior cutting tools, businesses can significantly enhance their operational capabilities and remain competitive in an evolving market. Embrace the opportunity to refine your sourcing strategy today and unlock the potential for increased efficiency and profitability in your stainless steel cutting operations.