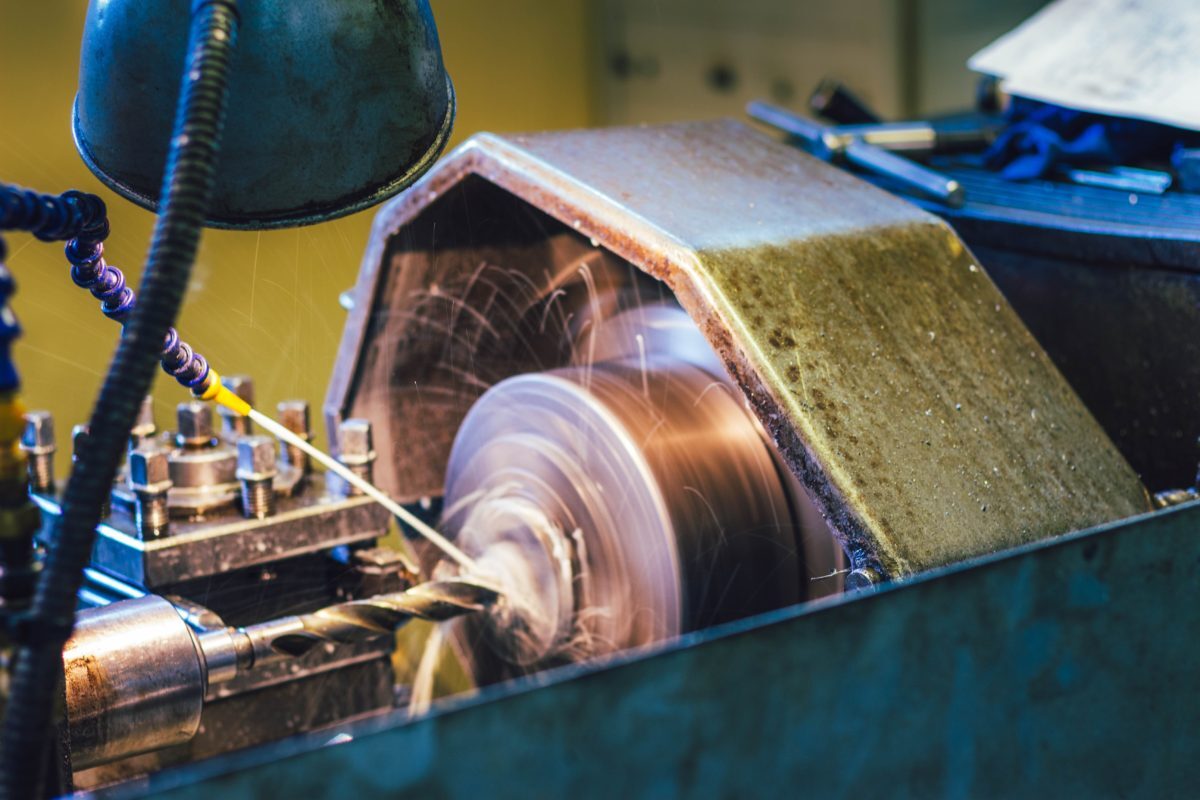
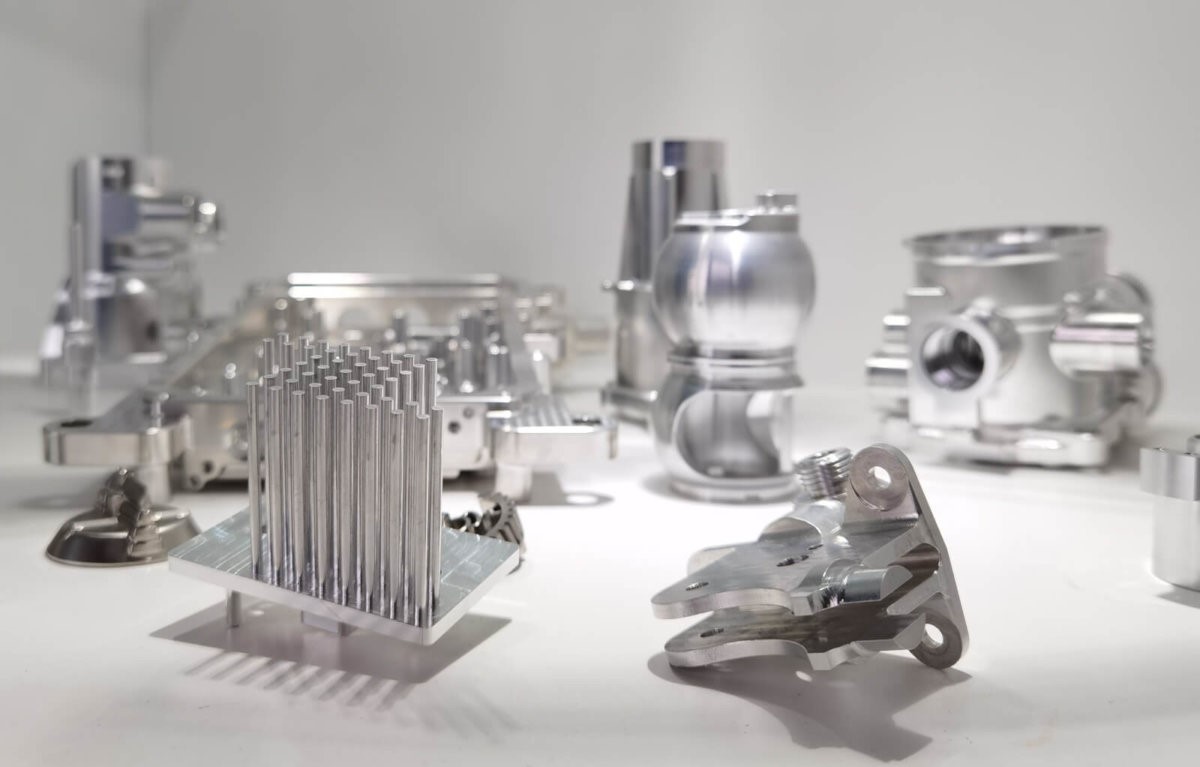
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for best aluminum for machining
Navigating the complexities of sourcing the best aluminum for machining can be a daunting task for international B2B buyers. With various alloys available, each possessing unique properties and applications, making the right choice is crucial for optimizing production efficiency and product quality. This guide serves as a comprehensive resource, exploring the most suitable aluminum alloys for machining, including detailed comparisons of popular grades like 3003 and 6061. We delve into critical factors such as mechanical properties, corrosion resistance, workability, and cost-effectiveness, empowering buyers to make informed decisions tailored to their specific needs.
In addition to examining the types of aluminum and their respective applications across industries, this guide offers practical insights on supplier vetting, ensuring that businesses can identify reliable sources in diverse markets, including Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. By understanding the nuances of aluminum grades and their machining characteristics, buyers can enhance their procurement strategies, reduce waste, and ultimately improve their bottom line. This resource is designed to equip you with the knowledge necessary to navigate the global market confidently, ensuring that your projects succeed with the right materials in hand.
Understanding best aluminum for machining Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| 3003 | Good formability, moderate strength, corrosion-resistant | Aerospace, food processing, chemical industries | Pros: Excellent workability; Cons: Limited strength and machinability compared to other alloys. |
| 6061 | High strength, excellent weldability, heat-treatable | Marine, automotive, aerospace applications | Pros: Versatile, good machinability; Cons: Poor formability compared to 3003. |
| 2011 | Free-machining grade, high-speed machining capability | Precision machining, small parts manufacturing | Pros: Exceptional surface finish; Cons: Limited availability in certain forms. |
| 7075 | High strength, low weight, and excellent fatigue resistance | Aerospace structures, military applications | Pros: Superior strength-to-weight ratio; Cons: More expensive and less corrosion-resistant. |
| 5052 | Good corrosion resistance, moderate to high strength | Marine applications, automotive fuel tanks | Pros: Excellent weldability; Cons: Lower machinability compared to other grades. |
What Are the Key Characteristics of 3003 Aluminum Alloy?
The 3003 aluminum alloy is primarily composed of manganese, which enhances its formability and corrosion resistance. It is moderately strengthened through cold working, making it suitable for applications requiring light structural components. B2B buyers should consider 3003 for projects in the aerospace and food processing industries where moderate strength and good workability are essential. However, its limited machinability and lower tensile strength compared to other alloys could pose challenges in high-demand applications.
Why Choose 6061 Aluminum for Versatile Applications?
The 6061 aluminum alloy stands out due to its high strength, excellent weldability, and ability to undergo heat treatment. It is favored in marine and automotive industries due to its favorable strength-to-weight ratio and good machinability. B2B buyers should consider 6061 for structural applications where strength is paramount. However, its poor formability may limit its use in intricate designs, requiring careful consideration during the design phase.
What Makes 2011 Aluminum Ideal for Precision Machining?
2011 aluminum is recognized for its free-machining properties, allowing for high-speed machining and exceptional surface finishes. It is commonly used in the production of small, precision components. B2B buyers should prioritize 2011 when surface finish is critical, such as in the manufacturing of intricate parts. However, the availability of 2011 in certain forms may be limited, necessitating discussions with suppliers to ensure the right material is sourced.
How Does 7075 Aluminum Compare for Structural Integrity?
7075 aluminum is one of the strongest aluminum alloys available, offering excellent fatigue resistance and low weight, making it ideal for aerospace and military applications. B2B buyers looking for materials that can withstand extreme conditions should consider 7075, especially when strength is a critical factor. However, its higher cost and lower corrosion resistance compared to other alloys can be a drawback in less demanding environments.
Why is 5052 Aluminum Preferred for Marine Applications?
5052 aluminum is well-known for its excellent corrosion resistance and moderate to high strength, making it suitable for marine environments and automotive fuel tanks. Its good weldability allows for easy fabrication and assembly. B2B buyers in marine or automotive sectors should consider 5052 for applications where exposure to saltwater or corrosive substances is a concern. However, it may present lower machinability compared to other grades, which should be factored into project planning.
Key Industrial Applications of best aluminum for machining
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of best aluminum for machining | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Aerospace | Aircraft structural components | Lightweight materials enhance fuel efficiency and performance | Compliance with stringent aerospace standards; reliable supply chains |
| Automotive | Engine components and frames | Improved strength-to-weight ratio for better performance | Need for specific alloy grades; global sourcing for consistency |
| Construction | Custom aluminum extrusions for building frameworks | Durability and corrosion resistance ensure longevity | Availability of custom sizes; local vs. international sourcing |
| Electronics | Heat sinks and enclosures | Excellent thermal conductivity enhances equipment efficiency | Precision machining capabilities; sourcing of specific tempers |
| Marine | Boat hulls and fittings | Corrosion resistance in harsh environments increases lifespan | Compliance with marine regulations; sourcing from certified suppliers |
In the aerospace industry, the best aluminum for machining is utilized in manufacturing aircraft structural components such as frames, fuselage, and wing structures. The lightweight nature of aluminum significantly improves fuel efficiency and overall aircraft performance. Buyers in this sector must ensure that their aluminum meets stringent aerospace standards, which often necessitates sourcing from reliable suppliers who can provide certified materials that adhere to international regulations.
In the automotive sector, aluminum alloys are crucial for producing engine components and vehicle frames. These materials offer an excellent strength-to-weight ratio, enhancing vehicle performance while reducing fuel consumption. International buyers must consider specific alloy grades that meet automotive industry standards and ensure a consistent supply chain to avoid production delays, particularly in regions like South America and Europe where automotive manufacturing is prominent.
Construction applications often involve custom aluminum extrusions used in building frameworks, roofing, and cladding. The inherent durability and corrosion resistance of aluminum ensure the longevity of structures, making it a preferred choice for construction projects. Buyers should focus on the availability of custom sizes and shapes, as well as the potential for local sourcing to minimize lead times and shipping costs, especially in developing regions in Africa and the Middle East.
In the electronics industry, aluminum is commonly used for heat sinks and enclosures due to its excellent thermal conductivity. This property enhances the efficiency of electronic devices by dissipating heat effectively. Buyers need to prioritize precision machining capabilities to meet the exact specifications required for electronic components, and they should consider sourcing from suppliers who can offer specific tempers for optimal performance.
The marine industry benefits from aluminum’s corrosion resistance, making it ideal for boat hulls and fittings. This characteristic extends the lifespan of marine equipment exposed to harsh environmental conditions. Buyers in this sector must ensure compliance with marine regulations and consider sourcing aluminum from certified suppliers to guarantee quality and reliability, particularly for international projects in regions with significant maritime activity.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘best aluminum for machining’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Difficulty in Selecting the Right Aluminum Alloy for Specific Applications
The Problem:
B2B buyers often face the challenge of selecting the appropriate aluminum alloy for their machining needs. With various options like 3003 and 6061 available, it can be overwhelming to determine which alloy is best suited for specific applications. For instance, a buyer in the aerospace industry may require a lightweight yet strong material that can withstand harsh environmental conditions, while another in the automotive sector may prioritize formability over strength. This decision-making complexity can lead to project delays and increased costs if the wrong alloy is chosen.
The Solution:
To navigate this challenge, buyers should conduct a thorough assessment of their project requirements. Start by listing the mechanical properties needed, such as tensile strength, yield strength, and corrosion resistance. For example, if the application demands superior strength and heat resistance, aluminum 6061-T6 is recommended due to its excellent mechanical properties and machinability. Conversely, for applications that require good formability, 3003 may be more suitable. Furthermore, collaborating with suppliers who have extensive knowledge of aluminum alloys can provide valuable insights. Request samples to test how different alloys perform under specific machining processes, allowing for informed decision-making that aligns with your project goals.
Scenario 2: Challenges in Machining Aluminum Alloys Leading to Increased Production Costs
The Problem:
Machining aluminum can present unique challenges, particularly when dealing with certain alloys that are not designed for easy machinability. For example, some buyers might find that while 3003 is widely used, it may not perform as well in machining applications compared to harder alloys like 6061 or 2011. This can result in longer machining times, increased tool wear, and ultimately higher production costs, particularly for manufacturers under pressure to maintain tight profit margins.
The Solution:
To address machining difficulties, buyers should prioritize selecting aluminum alloys that have been optimized for machinability. Alloys such as 2011 are often considered “free machining” and can lead to better surface finishes and reduced tool wear. Additionally, it is crucial to employ appropriate machining techniques, such as using the right cutting speeds, feeds, and tooling specifically designed for aluminum. Investing in high-quality cutting tools with coatings designed for aluminum can also improve efficiency and reduce costs. Establishing a relationship with a reliable supplier who can provide guidance on the best practices for machining specific alloys can further enhance productivity.
Scenario 3: Issues with Supply Chain and Availability of Aluminum Alloys
The Problem:
B2B buyers often encounter supply chain disruptions that affect the availability of specific aluminum alloys. This issue is particularly pronounced for international buyers sourcing materials from different regions, where logistical challenges can lead to delays in production timelines. For instance, a buyer in Europe might struggle to find specific grades like 6061 or 2011 due to regional shortages or import restrictions, resulting in halted operations and the inability to meet client demands.
The Solution:
To mitigate supply chain issues, buyers should diversify their sourcing strategies. Establishing relationships with multiple suppliers across different regions can provide backup options when one source becomes unavailable. Furthermore, exploring local suppliers or manufacturers who can provide custom aluminum extrusions tailored to specific needs can significantly reduce lead times. It is also advisable to maintain an inventory of critical alloys to cushion against supply disruptions. Regularly communicating with suppliers about potential shortages or delays can help buyers plan ahead and adjust their production schedules accordingly. By taking proactive steps to secure a stable supply of aluminum, businesses can maintain their operational efficiency and meet customer expectations consistently.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for best aluminum for machining
When selecting aluminum for machining, it’s vital to understand the characteristics and applications of various alloys. This guide focuses on four commonly used aluminum alloys: 3003, 6061, 7075, and 2011. Each alloy presents unique properties and advantages that can significantly impact machining processes and end-product performance.
What Are the Key Properties of Aluminum Alloy 3003?
Aluminum alloy 3003 is primarily composed of manganese, which enhances its corrosion resistance and workability. This alloy is known for its moderate strength and excellent formability, making it suitable for applications such as storage containers and truck roofs. However, it is not heat-treatable, which limits its strength enhancement capabilities.
Pros: Its good weldability and formability make it ideal for light structural applications. Additionally, its resistance to corrosion is beneficial in environments exposed to moisture.
Cons: While it offers decent machinability, it is less machinable than harder alloys, which can lead to challenges in achieving precise tolerances. Its lower yield strength makes it unsuitable for heavy-duty applications.
How Does Aluminum Alloy 6061 Compare for Machining Applications?
Aluminum alloy 6061 is one of the most versatile aluminum alloys, containing silicon and magnesium as its primary alloying elements. This alloy is known for its excellent strength-to-weight ratio and good corrosion resistance, making it a popular choice in the aerospace and automotive industries.
Pros: It is heat-treatable, which allows for different tempers to be produced, enhancing its machinability and weldability. Its high strength makes it suitable for structural applications, and it performs well in extreme environments.
Cons: While 6061 offers good machinability, certain tempers like T6 can be challenging to form. It may require specialized tooling to achieve optimal results during machining.
What Makes Aluminum Alloy 7075 a Preferred Choice for High-Strength Applications?
7075 aluminum alloy is recognized for its high strength and is often used in aerospace applications. It contains zinc as the primary alloying element, which contributes to its exceptional strength properties.
Pros: The high strength-to-weight ratio makes it ideal for applications requiring durability without adding excessive weight. It is also heat-treatable, which enhances its mechanical properties.
Cons: 7075 is more expensive than other aluminum alloys and can be challenging to machine due to its toughness. It may require advanced machining techniques and tools to achieve the desired finish.
Why Is Aluminum Alloy 2011 Considered a Free-Machining Alloy?
Aluminum alloy 2011 is specifically designed for excellent machinability, making it a popular choice for precision machining applications. Its high lead content allows for better chip formation and surface finish.
Pros: The exceptional machinability of 2011 means faster production rates and reduced tooling wear, leading to cost savings in manufacturing. It is ideal for complex shapes and intricate designs.
Cons: The presence of lead in 2011 raises environmental and health concerns, leading to restrictions in some regions. Additionally, its corrosion resistance is lower than that of other alloys, limiting its use in certain applications.
What Should International B2B Buyers Consider When Selecting Aluminum Alloys?
International buyers, particularly from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, should be aware of compliance with local standards such as ASTM, DIN, or JIS. Understanding the specific requirements for strength, corrosion resistance, and fabrication methods is crucial. Additionally, factors such as availability, lead times, and cost fluctuations can impact procurement decisions.
| Material | Typical Use Case for best aluminum for machining | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 3003 | Storage containers, truck roofs | Excellent corrosion resistance | Limited strength and machinability | Medium |
| 6061 | Aerospace components, automotive parts | High strength and versatility | Challenging to form in some tempers | Medium |
| 7075 | Aircraft structures, high-stress applications | Exceptional strength-to-weight ratio | Expensive and difficult to machine | High |
| 2011 | Precision machined parts | Superior machinability | Lower corrosion resistance and environmental concerns | Medium |
This table summarizes the key aspects of each aluminum alloy, providing a clear reference for B2B buyers to make informed decisions based on their specific machining needs.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for best aluminum for machining
What Are the Main Stages of Manufacturing Aluminum for Machining?
The manufacturing process of aluminum suitable for machining involves several critical stages that ensure the final product meets industry standards and client specifications. Understanding these stages is essential for B2B buyers looking to ensure quality and consistency in their aluminum supply.
Material Preparation: Sourcing and Initial Processing
The first step in the manufacturing process is sourcing high-quality aluminum ingots or scrap. Suppliers often focus on specific alloys like 6061 or 3003, which are favored for their machinability and mechanical properties. Once sourced, the material undergoes initial processing, which includes melting and refining to eliminate impurities. This step is crucial as it directly affects the alloy’s performance characteristics.
After melting, the aluminum is cast into specific shapes, such as billets or slabs, which can be further processed. The casting method can influence the microstructure of the aluminum, and techniques such as direct chill (DC) casting are commonly used to improve grain structure, enhancing the material’s machinability.
Forming: Shaping and Extruding Aluminum
Once the aluminum is prepared, the next stage involves forming the material into desired shapes. This can be achieved through several methods, including extrusion, rolling, and forging. Extrusion is particularly popular for creating complex shapes and profiles, as it allows for precise dimensions and surface finishes.
In the extrusion process, heated aluminum is forced through a die to create long shapes with uniform cross-sections. This technique is essential for producing components used in various applications, from automotive parts to structural elements in construction. The choice of forming technique will depend on the final application and the desired mechanical properties of the aluminum.
Assembly: Joining and Fabrication Techniques
After forming, the next phase is assembly, where various components are joined to create finished products. Techniques such as welding, riveting, and adhesive bonding are commonly employed. For example, aluminum alloys like 6061 are often welded due to their excellent weldability, while 3003 may be used in applications requiring good corrosion resistance.
Careful consideration of the joining method is vital, as it can impact the structural integrity and performance of the final product. For B2B buyers, understanding the specific requirements of their application can help in selecting the appropriate assembly techniques.
Finishing: Surface Treatment and Quality Control
The final manufacturing stage involves finishing processes, which enhance the material’s aesthetic and functional properties. Common finishing techniques include anodizing, painting, and polishing. Anodizing not only improves corrosion resistance but also allows for a range of color options, making it a popular choice for decorative applications.
Quality control during the finishing stage is critical. Suppliers must adhere to international standards to ensure consistency and reliability in their products.
How Is Quality Assurance Implemented in Aluminum Manufacturing?
Quality assurance is an integral part of the aluminum manufacturing process, ensuring that the products meet specified standards and customer expectations. This is particularly important for B2B buyers who rely on the consistency and reliability of their suppliers.
What Are the Relevant International Standards for Aluminum Quality?
For B2B buyers, understanding the relevant international standards is crucial. ISO 9001 is a widely recognized standard that outlines criteria for a quality management system. Compliance with ISO 9001 ensures that suppliers maintain a consistent quality of products and services.
In addition to ISO standards, industry-specific certifications like CE (Conformité Européenne) for European markets and API (American Petroleum Institute) standards for specific applications are also essential. These certifications assure buyers that the materials meet rigorous quality and safety requirements.
What Are the Key Quality Control Checkpoints?
Quality control checkpoints are established throughout the manufacturing process to monitor and verify product quality. These checkpoints typically include:
- Incoming Quality Control (IQC): Verification of raw materials before they enter the production process. This ensures that only materials meeting specified standards are used.
- In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): Continuous monitoring during the manufacturing stages to identify any deviations from standards in real-time.
- Final Quality Control (FQC): Comprehensive inspection and testing of finished products before they are shipped to clients. This includes dimensional checks, surface finish evaluations, and mechanical property assessments.
What Common Testing Methods Are Used for Aluminum Quality Assurance?
Various testing methods are employed to assess the quality of aluminum products. Common methods include:
- Tensile Testing: Measures the strength and ductility of the material.
- Hardness Testing: Evaluates the hardness of the aluminum, which can indicate its machinability.
- Non-Destructive Testing (NDT): Techniques such as ultrasonic testing and dye penetrant inspection assess internal and surface defects without damaging the material.
B2B buyers should inquire about the specific testing methods employed by suppliers and request test reports to ensure compliance with their quality standards.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control?
For international B2B buyers, particularly those in regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, verifying supplier quality control is essential to avoid potential issues in the supply chain.
What Steps Can Buyers Take to Verify Quality Control?
-
Supplier Audits: Conducting regular audits of suppliers can provide insight into their quality management practices and adherence to international standards.
-
Requesting Quality Reports: Buyers should request detailed quality reports, including results from IQC, IPQC, and FQC stages. These documents should outline the testing methods used and any corrective actions taken for non-conformance.
-
Third-Party Inspections: Engaging third-party inspection services can provide an unbiased evaluation of a supplier’s quality control processes and product quality.
-
Certifications and Compliance: Buyers should verify that suppliers hold relevant certifications and comply with international quality standards. This can often be confirmed through documentation or direct communication with the supplier.
What Are the QC and Certification Nuances for International Buyers?
For international B2B buyers, understanding the nuances of quality control and certification is vital. Different regions may have varying standards and regulations that affect the procurement process. For instance, European buyers might require CE certification, while buyers in the Middle East may prioritize compliance with local standards.
Additionally, language barriers and differences in regulatory environments can pose challenges. Establishing clear communication channels with suppliers and seeking assistance from local representatives can help navigate these complexities effectively.
In conclusion, understanding the manufacturing processes and quality assurance protocols for aluminum suitable for machining is essential for B2B buyers. By focusing on material preparation, forming techniques, assembly methods, and rigorous quality control measures, businesses can ensure they procure high-quality aluminum that meets their specific needs.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘best aluminum for machining’
Introduction
This sourcing guide is designed to assist B2B buyers in identifying and procuring the best aluminum for machining. Selecting the right aluminum alloy is critical for ensuring optimal performance and cost-effectiveness in manufacturing processes. By following this step-by-step checklist, you can make informed decisions that align with your specific project requirements.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Establishing clear technical specifications is the foundation of your sourcing process. Determine the mechanical properties required for your application, including tensile strength, yield strength, and corrosion resistance.
– Consider factors such as:
– The specific machining processes you will employ (e.g., milling, turning).
– The environmental conditions the aluminum will face (e.g., exposure to moisture or chemicals).
Step 2: Identify Suitable Aluminum Alloys
Research the various aluminum alloys that meet your specifications. Common alloys for machining include 3003 and 6061, each with unique properties that cater to different applications.
– Key considerations:
– 3003: Known for excellent workability and corrosion resistance, suitable for general-purpose applications.
– 6061: Offers greater strength and is highly versatile, ideal for structural applications and high-stress environments.
Step 3: Evaluate Potential Suppliers
Before making a commitment, thoroughly evaluate potential suppliers. Request detailed company profiles, case studies, and references from previous clients in similar industries.
– Look for:
– Certifications that validate quality standards (e.g., ISO 9001).
– Reviews or testimonials that reflect reliability and customer service.
Step 4: Request Material Samples
Always request material samples before finalizing your order. Testing samples allows you to assess the alloy’s machinability and performance in your specific application.
– Focus on:
– Machining tests to evaluate the ease of processing.
– Surface finish and integrity after machining to ensure it meets your quality standards.
Step 5: Verify Compliance with Industry Standards
Ensure that the aluminum you are sourcing complies with relevant industry standards and regulations. This is especially important if your application involves safety-critical components.
– Check for:
– Material certifications that demonstrate compliance with international standards (e.g., ASTM, EN).
– Documentation that confirms the absence of harmful substances (e.g., RoHS compliance).
Step 6: Negotiate Pricing and Terms
Once you have selected a supplier, engage in negotiations to secure favorable pricing and terms. Understand the total cost of ownership, including shipping and handling fees.
– Consider:
– Volume discounts for bulk purchases.
– Payment terms and delivery timelines that suit your operational requirements.
Step 7: Establish a Quality Assurance Process
Implement a quality assurance process to monitor the performance of the aluminum throughout its lifecycle. This includes inspecting incoming materials and conducting regular evaluations during the machining process.
– Important aspects:
– Develop a checklist for quality inspections based on your specifications.
– Collaborate with your supplier for continuous feedback to ensure ongoing quality improvement.
By adhering to this comprehensive checklist, you can effectively navigate the complexities of sourcing the best aluminum for machining, ensuring that you meet your operational goals while maintaining high standards of quality and performance.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for best aluminum for machining Sourcing
Understanding the cost structure and pricing nuances in sourcing aluminum for machining is essential for B2B buyers, especially when operating across diverse international markets. This analysis will explore the key components of costs, price influencers, and strategic buyer tips to optimize sourcing decisions.
What are the Key Cost Components in Sourcing Aluminum for Machining?
-
Materials: The base cost of aluminum varies significantly depending on the alloy type, such as 6061 or 3003, and market fluctuations. High-grade alloys typically command higher prices due to their enhanced properties, such as strength and corrosion resistance. For instance, 6061 is often preferred for structural applications, leading to increased demand and cost.
-
Labor: Labor costs encompass the workforce required for machining processes, which can vary based on geographic location. Countries with higher labor costs, like Germany, may influence the overall price of machined parts. In contrast, regions with lower labor costs may offer more competitive pricing.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes expenses associated with operating machinery, facility maintenance, and utilities. Efficient production processes can reduce overhead costs, which is crucial for competitive pricing.
-
Tooling: The cost of tooling is significant in the machining process. Custom tooling can be expensive but necessary for precision work, particularly for unique designs or specifications. Standardized tooling can help reduce costs.
-
Quality Control (QC): Ensuring product quality through rigorous testing and inspections adds to the overall cost. Certifications (e.g., ISO) may be required for international buyers, particularly in industries like aerospace and automotive, impacting the final pricing.
-
Logistics: Shipping and handling costs vary widely based on the origin, destination, and Incoterms. Understanding these costs is vital for accurate budgeting. For international buyers, factors such as tariffs and import duties can significantly affect total expenses.
-
Margin: Suppliers typically apply a margin to cover their risks and ensure profitability. This margin can vary based on market conditions, competition, and the supplier’s position in the supply chain.
How Do Price Influencers Impact Sourcing Decisions?
-
Volume and Minimum Order Quantity (MOQ): Larger orders often qualify for bulk pricing discounts. Understanding a supplier’s MOQ can help buyers negotiate better rates, particularly in regions where economies of scale can be leveraged.
-
Specifications and Customization: Custom specifications can lead to higher costs due to additional machining processes. Buyers should weigh the need for customization against standard options to optimize costs.
-
Material Quality and Certifications: Higher quality materials and specific certifications can increase costs but may be necessary for certain applications. Buyers should assess whether the benefits justify the additional expense.
-
Supplier Factors: The reliability, reputation, and location of suppliers can influence pricing. Established suppliers may offer better quality assurance but at a premium.
-
Incoterms: Understanding delivery terms (e.g., FOB, CIF) is crucial for managing logistics costs and responsibilities. These terms dictate who bears the risk and costs at various stages of shipping.
What Buyer Tips Can Enhance Cost Efficiency in Sourcing?
-
Negotiation Strategies: Establishing long-term relationships with suppliers can facilitate better negotiation outcomes. Transparency about your sourcing needs and future volume can lead to favorable terms.
-
Evaluating Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Beyond the initial purchase price, consider long-term factors such as maintenance, durability, and the potential for rework. A lower upfront cost may lead to higher TCO if the material requires more frequent replacement or repair.
-
Pricing Nuances for International Buyers: Buyers from regions like Africa, South America, and the Middle East should account for currency fluctuations, geopolitical risks, and local economic conditions when evaluating prices. Engaging local distributors can also provide insights into market-specific pricing strategies.
-
Understanding Indicative Prices: Always seek quotes from multiple suppliers to understand market pricing. Keep in mind that prices can fluctuate based on global aluminum market trends, so it’s wise to stay informed about industry developments.
By comprehensively analyzing these cost components and influencers, B2B buyers can make informed decisions that align with their operational needs and budgetary constraints.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing best aluminum for machining With Other Solutions
When evaluating the best aluminum for machining, it’s essential to consider various alternatives that can meet similar requirements in different applications. This analysis aims to provide B2B buyers with insights into how aluminum compares to other materials and solutions, facilitating informed decision-making for their specific needs.
Comparison of Best Aluminum for Machining Against Alternatives
| Comparison Aspect | Best Aluminum For Machining | Alternative 1: Steel Alloys | Alternative 2: Plastic Composites |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | Excellent strength-to-weight ratio; good machinability | High tensile strength; durable under heavy loads | Lightweight; good impact resistance; limited temperature tolerance |
| Cost | Moderate; varies by alloy and treatment | Generally lower cost than aluminum but varies by grade | Lower cost; generally less expensive than metals |
| Ease of Implementation | Requires specific machining tools and techniques | Widely available; familiar to most machinists | Easier to mold and shape; less tooling required |
| Maintenance | Low; resistant to corrosion and wear | Moderate; prone to rust without treatment | Low; can degrade under UV exposure and high temperatures |
| Best Use Case | Aerospace, automotive, and structural applications | Heavy machinery, construction, and automotive frames | Non-structural applications, consumer products, and prototypes |
Detailed Breakdown of Alternatives
Alternative 1: Steel Alloys
Steel alloys, particularly those like carbon steel and stainless steel, offer significant strength and durability, making them ideal for applications that require heavy load-bearing capabilities. The tensile strength of steel is generally higher than that of aluminum, allowing it to be used effectively in structural applications. However, steel is heavier, which can be a disadvantage in industries where weight is a critical factor. Additionally, while machining steel is familiar to most machinists, it often requires more robust tooling and can lead to increased wear and tear on equipment.
Alternative 2: Plastic Composites
Plastic composites, such as reinforced polymers, present an interesting alternative to aluminum. They are lightweight, resistant to corrosion, and can be molded into complex shapes, making them suitable for applications where form and weight are critical. However, their performance under extreme conditions, such as high temperatures or heavy loads, is often limited compared to aluminum or steel. While the initial cost of plastic composites may be lower, their long-term durability and performance in demanding environments can raise questions about overall value.
Conclusion: How to Choose the Right Solution for Your Needs
When selecting the best solution for machining, B2B buyers must evaluate their specific project requirements, including performance expectations, budget constraints, and the environmental conditions the material will face. Aluminum remains a top choice for its excellent balance of strength, weight, and machinability, particularly in aerospace and automotive applications. However, steel alloys may be more appropriate for heavy-duty applications, while plastic composites can offer cost-effective solutions for lightweight and non-structural needs. By understanding the strengths and limitations of each option, buyers can make informed decisions that align with their operational goals and project specifications.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for best aluminum for machining
What Are the Critical Technical Properties of Aluminum for Machining?
When selecting aluminum for machining, understanding the technical properties is vital to ensure the material meets application requirements. Here are key specifications that B2B buyers should consider:
1. Material Grade
Aluminum alloys are categorized into series based on their primary alloying elements. For machining, the most common grades are 3003 and 6061. The 3003 alloy is known for its excellent formability and moderate strength, making it suitable for applications requiring good workability. In contrast, 6061 offers superior strength and is heat-treatable, which enhances its machinability and suitability for structural applications. Knowing the right grade can significantly impact the performance and longevity of the final product.
2. Yield Strength
Yield strength refers to the maximum stress that a material can withstand before it deforms. In machining, higher yield strength allows for more robust applications and reduces the likelihood of deformation during the manufacturing process. For instance, 6061 aluminum has a yield strength of approximately 276 MPa, making it ideal for parts subjected to significant loads, while 3003 has a lower yield strength of about 186 MPa, suitable for lighter applications.
3. Machinability Rating
Machinability is a critical factor affecting production efficiency and cost. It indicates how easily a material can be machined to the desired shape and finish. Aluminum alloys like 6061 generally have a good machinability rating, while 3003 offers acceptable machinability but may present challenges due to its lower strength. Understanding machinability ratings helps buyers select the right alloy for their production processes, impacting tool wear and surface finish.
4. Tolerance
Tolerance defines the permissible limit of variation in a physical dimension. In machining, tight tolerances are essential for ensuring parts fit and function as intended. Buyers must specify tolerances based on the application’s requirements. For example, aerospace components often require tighter tolerances than automotive parts. Clear tolerance specifications help manufacturers produce components that meet rigorous industry standards.
5. Corrosion Resistance
Aluminum’s natural oxide layer provides excellent corrosion resistance, which is crucial for applications exposed to harsh environments. Grades such as 6061 are particularly well-suited for marine applications due to their enhanced corrosion resistance. Buyers should consider the operating environment of the final product to ensure that the selected aluminum alloy will perform reliably over time.
What Are Common Trade Terms in Aluminum Machining?
Familiarity with industry terminology can streamline the procurement process. Here are essential trade terms relevant to B2B buyers:
1. OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
OEM refers to companies that produce parts or equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer. Understanding OEM relationships is crucial for buyers who need components that fit into larger systems or products.
2. MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ indicates the smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell. This term is important for buyers to understand, as it affects inventory management and cost efficiency. Higher MOQs may lead to increased upfront costs, while lower MOQs can facilitate more flexible purchasing.
3. RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a document used to invite suppliers to bid on specific products or services. It outlines the buyer’s requirements, including specifications, quantities, and delivery timelines. Submitting an RFQ helps buyers obtain competitive pricing and ensures that all suppliers are evaluated on the same criteria.
4. Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
Incoterms are predefined commercial terms published by the International Chamber of Commerce (ICC) that clarify the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in international trade. Familiarity with Incoterms helps buyers understand shipping costs, risk management, and delivery obligations, ensuring smooth transactions across borders.
5. T6 Temper
T6 temper refers to a specific heat treatment process that enhances the strength and machinability of aluminum alloys. Understanding the implications of different tempers, such as T6, helps buyers select materials that will perform optimally in their intended applications.
By grasping these critical properties and trade terms, B2B buyers can make informed decisions, ensuring that their machining projects proceed smoothly and effectively.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the best aluminum for machining Sector
What Are the Current Trends Driving the Best Aluminum for Machining Market?
The global aluminum machining market is witnessing significant growth, driven by several key factors. First, the lightweight and corrosion-resistant properties of aluminum make it an essential material across industries, including aerospace, automotive, and construction. In regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, the demand for high-performance aluminum alloys—particularly 6061 and 3003—has surged due to their versatility and strength.
Emerging technologies are reshaping sourcing strategies, with advancements in automation and AI enhancing the efficiency of aluminum machining processes. For international B2B buyers, this means access to improved precision and reduced lead times. Additionally, digital platforms and marketplaces are facilitating easier sourcing of aluminum products, allowing buyers to compare prices and specifications from multiple suppliers globally.
Another noteworthy trend is the customization of aluminum products. Businesses are increasingly seeking tailored solutions, such as custom extrusions, to meet specific project requirements. This demand for customization is further fueled by the growing trend of modular construction and lightweight design in various applications. As companies prioritize agility and responsiveness in their supply chains, sourcing from manufacturers that offer flexibility and rapid turnaround times will be crucial.
How Are Sustainability and Ethical Sourcing Influencing the Aluminum Machining Sector?
Sustainability has become a cornerstone of modern business practices, significantly influencing sourcing decisions in the aluminum machining sector. The environmental impact of aluminum production and machining processes has raised concerns among international buyers. As a result, companies are increasingly looking for suppliers who adhere to sustainable practices, including energy-efficient manufacturing and reduced carbon footprints.
Ethical sourcing is another critical consideration. Buyers are keen on ensuring that their aluminum products are sourced from suppliers who respect labor rights and promote fair trade. Certifications such as ISO 14001 for environmental management and the Aluminium Stewardship Initiative (ASI) certification for responsible sourcing are becoming essential benchmarks for buyers seeking to align their procurement strategies with sustainability goals.
Moreover, the use of recycled aluminum is gaining traction, as it significantly reduces energy consumption and emissions compared to primary aluminum production. Buyers are encouraged to seek materials with a high recycled content, as this not only contributes to sustainability but also enhances the overall performance and cost-effectiveness of the final products.
How Has the Aluminum for Machining Market Evolved Over Time?
The evolution of aluminum as a preferred material for machining can be traced back to its unique combination of properties, including lightweight strength, corrosion resistance, and excellent machinability. Initially, aluminum was primarily used in the aerospace industry due to its favorable strength-to-weight ratio. Over time, its applications have expanded into various sectors such as automotive, construction, and consumer goods.
The introduction of different aluminum alloys has further diversified its use in machining. For instance, the development of heat-treated alloys like 6061-T6 has significantly improved machinability, making aluminum suitable for more demanding applications. Additionally, innovations in machining technologies have allowed for more precise and efficient processing of aluminum, catering to the increasing complexity of modern designs.
As international markets continue to evolve, the demand for high-quality aluminum alloys that meet specific industry requirements is expected to grow. This evolution presents opportunities for B2B buyers to leverage advanced materials and technologies, ensuring they remain competitive in their respective markets.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of best aluminum for machining
-
How do I solve challenges in sourcing aluminum for machining?
When sourcing aluminum for machining, consider establishing relationships with multiple suppliers to ensure competitive pricing and reliability. Conduct thorough research to assess their certifications and industry reputation. It’s also beneficial to request samples of the specific aluminum alloy you need to evaluate its machinability and quality. Lastly, leveraging trade shows and industry networks can help you connect with reputable suppliers who understand your unique requirements. -
What is the best aluminum alloy for precision machining?
6061 aluminum alloy is often regarded as the best choice for precision machining due to its excellent strength-to-weight ratio and good machinability. Its heat-treated variants, particularly 6061-T6, provide superior mechanical properties, making it suitable for a wide range of applications, including aerospace and automotive components. However, if formability is a priority, 3003 aluminum alloy, known for its good workability, may be more suitable for less demanding applications. -
What are the minimum order quantities (MOQs) for aluminum suppliers?
Minimum order quantities can vary significantly among suppliers, typically ranging from 100 kg to several tons. It is essential to inquire about MOQs when negotiating with potential suppliers, as some may offer flexibility for new customers or smaller projects. Understanding these terms helps you manage inventory costs and ensures you can meet project demands without overcommitting resources. -
How can I verify the quality of aluminum before purchasing?
To ensure the quality of aluminum, request mill test reports (MTRs) or certificates of compliance that detail the alloy composition and mechanical properties. Additionally, consider third-party testing or certifications from recognized standards such as ISO or ASTM. Engaging in a supplier audit or visiting their manufacturing facilities can also provide insights into their quality control processes and overall production capabilities. -
What payment terms are common when sourcing aluminum?
Payment terms in the aluminum supply chain can vary based on the supplier’s policies and your business relationship. Common terms include net 30, net 60, or upfront deposits for larger orders. For international transactions, consider using letters of credit or escrow services to mitigate risks. Clear communication about payment expectations is crucial to maintaining a smooth transaction process. -
How do I navigate international shipping for aluminum products?
When shipping aluminum internationally, consider logistics factors like customs regulations, tariffs, and shipping costs. Partnering with a freight forwarder experienced in handling metal shipments can streamline this process. Ensure that all necessary documentation, such as bills of lading and import/export permits, is in order to prevent delays. Additionally, choose a reliable shipping method that balances cost and delivery time based on your urgency. -
What customization options are available for aluminum products?
Many suppliers offer customization options, including cutting, shaping, and finishing aluminum products to meet specific project requirements. Be sure to discuss your needs regarding dimensions, tolerances, and surface finishes with potential suppliers. Customization can also extend to alloy selection and treatment processes, ensuring that the final product aligns with your engineering specifications and performance standards. -
How do I find reliable aluminum suppliers in international markets?
Finding reliable aluminum suppliers in international markets requires thorough research and vetting. Start by utilizing online B2B marketplaces and industry directories to identify potential suppliers. Look for reviews, ratings, and case studies that demonstrate their reliability. Engaging in trade shows or industry associations can also provide insights and connections. Lastly, consider initiating small trial orders to evaluate their service, quality, and responsiveness before committing to larger purchases.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.
Top 7 Best Aluminum For Machining Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. Reddit – Aluminum Grades for Machine Parts
Domain: reddit.com
Registered: 2005 (20 years)
Introduction: Preferred grades of aluminum for machine parts include 6061-T6, 6082, and 7075. 6061-T6 is noted for being strong, readily available, inexpensive, and easy to machine. 6082 is also mentioned as a suitable option. 7075 is much stronger than 6061 but is significantly more expensive. Cast tooling plates like MIC-6 are available but can be costly. The discussion emphasizes the importance of rigidity a…
2. Howard Precision – Aluminum Alloy Solutions
Domain: howardprecision.com
Registered: 1998 (27 years)
Introduction: Aluminum Alloy Series 1xxx: 99% pure aluminum, highly ductile, excellent corrosion resistance, used in electrical and chemical industries. Common products: aluminum bus bars, heat sinks.
Aluminum Alloy Series 2xxx: Copper as primary alloying element, excellent machinability, high strength, poor corrosion resistance. Popular choice in aerospace, specifically 2024-T351 plate.
Aluminum Alloy Seri…
3. Precision Machining – Aluminum Parts Solutions
Domain: practicalmachinist.com
Registered: 2000 (25 years)
Introduction: Project requires turning and slotting small aluminum parts (6mm diameter, 32mm long). Key operations include drilling a 4mm hole, turning the OD to 6mm, slotting with an endmill, chamfering slots, and parting off. Main criteria: surface finish and minimal burs. Suggested aluminum alloys: 2011-T3, 6061, 7075 (T6 temper preferred for better machinability). Considerations for material: bar stock vs t…
4. Hobby Machinist – 6061-T6 Aluminum Alloy
Domain: hobby-machinist.com
Registered: 2010 (15 years)
Introduction: 6061-T6 is recommended as a good all-purpose aluminum alloy, known for its strength, bendability in the annealed state, weldability, and good anodizing properties. However, it is not suitable for casting. For casting, machining, and welding, a different alloy may be needed, but specific recommendations were not provided in the discussion.
5. Rapid Axis – Aluminum Grades for CNC Machining
Domain: rapidaxis.com
Registered: 2018 (7 years)
Introduction: Aluminum Grades Ideal for CNC Machining: 1. 6061 Aluminum Alloy: – Characteristics: Excellent strength-to-weight ratio, good corrosion resistance, weldability. – Benefits: Ease of machining, suitable for various applications. – Downsides: Not as strong as some alloys, susceptible to stress cracking. – Applications: Automotive parts, marine components, construction hardware, electronic enclosures. …
6. Pentaprecision – Aluminium Alloys
Domain: pentaprecision.co.uk
Registered: 2006 (19 years)
Introduction: Aluminium Alloys: 6082, 7075/L95, 5083, 2014A, 6061. Key Attributes: 6082 – Medium strength, excellent corrosion resistance, good weldability, good machinability, low cost. 7075 – Exceptional strength, less corrosion resistance, average machinability. 5083 – Medium strength, high resistance to seawater and chemicals, fair machinability. 2014A – High strength, very good machinability, poor corrosio…
7. First Mold – Aluminum CNC Machining
Domain: firstmold.com
Registered: 2016 (9 years)
Introduction: Aluminum CNC Machining involves the use of various aluminum alloys, each with distinct characteristics and applications. Key alloys include: 1. 6061 Aluminum: Known for its versatility, strength, corrosion resistance, and machinability. Commonly used in structural components across marine, automotive, and aerospace industries. 2. 7075 Aluminum: One of the strongest aluminum alloys, primarily used …
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for best aluminum for machining
In navigating the complexities of aluminum sourcing for machining, understanding the distinct properties of various alloys is paramount. Alloys such as 3003 and 6061 each serve unique applications, with 3003 excelling in formability and corrosion resistance, while 6061 offers superior strength and versatility for structural needs. By aligning your material choices with project specifications, you can enhance production efficiency and product performance.
Strategic sourcing is not just about selecting materials; it involves fostering relationships with reliable suppliers who can provide high-quality aluminum that meets international standards. This is particularly crucial for businesses in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, where access to premium materials can significantly impact competitive advantage.
As industries evolve and demand for lightweight, durable materials grows, staying informed about advancements in aluminum alloys will be essential. Embrace innovation by exploring customized solutions that cater to your specific machining needs. By making informed sourcing decisions today, you can position your business for success in the dynamic global market. Engage with trusted suppliers and consider the long-term benefits of sourcing the best aluminum for your machining projects.