Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for bending machine parts
Navigating the global market for bending machine parts presents a unique set of challenges for international B2B buyers, particularly those from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. With the demand for high-quality bending machines on the rise, sourcing reliable components is critical to ensuring operational efficiency and minimizing downtime. Understanding the intricacies of various bending machine parts, including their functions and applications, is essential for making informed purchasing decisions that can significantly impact productivity and profitability.
This comprehensive guide delves into the diverse types of bending machine parts, from frames and rams to hydraulic systems and control panels. It highlights the importance of selecting the right components tailored to specific operational needs while also addressing the nuances of supplier vetting and the significance of genuine OEM parts. Additionally, it offers insights into cost considerations and maintenance practices to enhance the longevity of your machinery.
By equipping B2B buyers with actionable insights and best practices, this guide empowers them to navigate the complexities of the bending machine parts market with confidence. Whether you’re looking to optimize existing machinery or invest in new equipment, understanding these critical components will help you achieve superior performance and operational excellence in your manufacturing processes.
Understanding bending machine parts Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Frame | Provides structural support; varies in material and design | Heavy-duty metal fabrication | Pros: Durable, supports heavy loads. Cons: May require custom designs for specific needs. |
| Hydraulic System | Uses fluid power to generate bending force; includes pumps | High-volume production environments | Pros: Smooth operation, adaptable to various materials. Cons: Requires regular maintenance to prevent leaks. |
| Control Panel | Digital interface for setting parameters; user-friendly | Precision manufacturing and quality control | Pros: Enhanced control, easy to program. Cons: Potentially complex for untrained operators. |
| Back Gauge | Adjustable stop for accurate material positioning | Mass production, ensuring repeatability | Pros: Increases efficiency and reduces waste. Cons: Misalignment can lead to errors if not calibrated properly. |
| Tooling (Punch & Die) | Customizable tools for specific bends and shapes | Versatile applications across industries | Pros: High precision, tailored to specific jobs. Cons: Tooling can be costly and may require frequent replacement. |
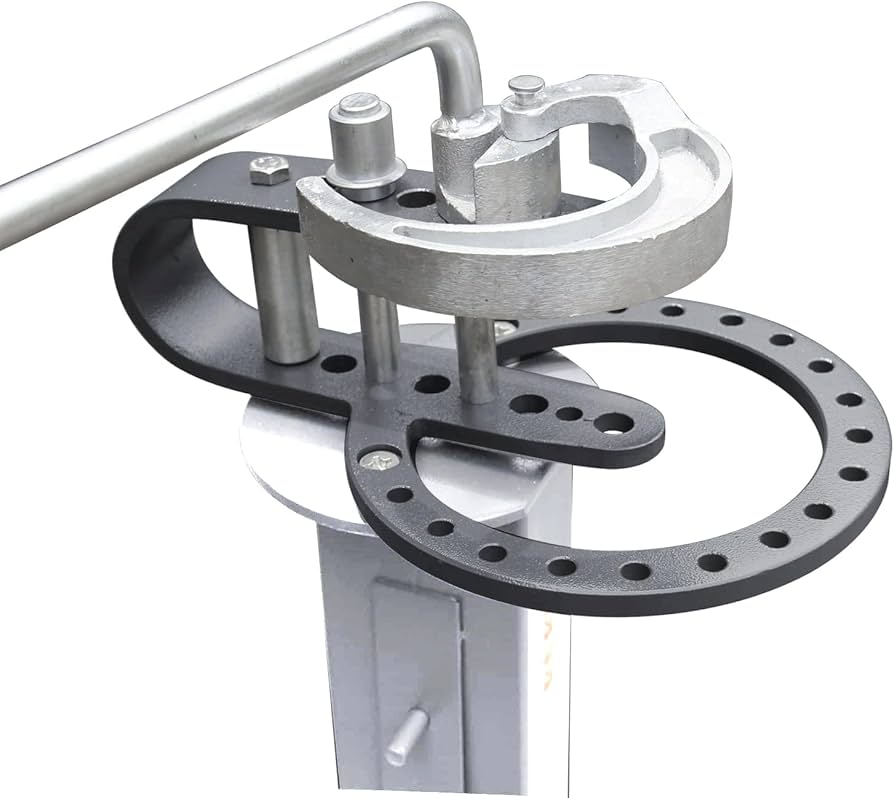
What Are the Key Characteristics of Bending Machine Frames?
The frame of a bending machine is crucial for its structural integrity. Typically made from robust materials like steel, it supports all other components, ensuring stability during operation. B2B buyers should consider the frame’s design and material, as these factors directly affect the machine’s capacity and durability. Custom frames may be necessary for specialized applications, which can lead to increased costs.
How Does the Hydraulic System Enhance Bending Operations?
Hydraulic systems are integral to many bending machines, providing the necessary force to bend materials effectively. These systems allow for smooth and controlled movements, accommodating various material types and thicknesses. For businesses focused on high-volume production, investing in a reliable hydraulic system is essential. However, regular maintenance is required to ensure optimal performance and prevent downtime due to leaks or system failures.
Why Is a Control Panel Important for Bending Machines?
The control panel of a bending machine serves as the operator’s interface for setting parameters such as bend angle and speed. Modern control panels often feature digital displays and programmable settings, enhancing precision in manufacturing. For companies prioritizing quality control and efficiency, investing in advanced control panels can lead to significant productivity gains. However, operators may require training to navigate complex interfaces effectively.
What Role Does the Back Gauge Play in Bending Accuracy?
A back gauge is an adjustable component that ensures accurate positioning of materials before bending. This tool is vital for achieving consistent and repeatable bends, making it indispensable in mass production settings. Buyers should evaluate the back gauge’s adjustability and ease of use, as misalignment can lead to costly errors. Investing in a high-quality back gauge can enhance overall operational efficiency and reduce material waste.
How Do Tooling Options Affect Bending Machine Versatility?
Tooling, specifically the punch and die, defines the shapes and angles that can be achieved with a bending machine. Customizable tooling options allow businesses to adapt their machines for various applications, enhancing versatility. While high-precision tooling can lead to superior results, it also represents a significant investment. Buyers should consider the long-term costs associated with tooling, including maintenance and potential replacements, when evaluating their options.
Key Industrial Applications of bending machine parts
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of bending machine parts | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Automotive | Production of vehicle frames and chassis | Enhanced structural integrity and reduced weight | Need for high precision parts and availability of OEM components |
| Construction | Fabrication of steel beams and reinforcements | Improved load-bearing capacity and durability | Sourcing of robust materials and customization options |
| Aerospace | Manufacturing of aircraft components | Compliance with strict safety standards | Requirement for high-quality, lightweight materials |
| HVAC | Creation of ductwork and fittings | Increased energy efficiency and reduced installation time | Focus on compatibility with existing systems and materials |
| Furniture | Production of metal furniture frames and components | Enhanced aesthetic appeal and longevity | Need for diverse design options and finishes |
How Are Bending Machine Parts Utilized in the Automotive Industry?
In the automotive sector, bending machine parts play a pivotal role in the production of vehicle frames and chassis. The precision of components like the ram and die ensures that the bends in metal sheets conform to exact specifications, enhancing the structural integrity while minimizing overall weight. This is crucial for manufacturers aiming to improve fuel efficiency and performance. For international buyers, especially those in regions like Brazil and Saudi Arabia, sourcing high-quality OEM parts is essential to maintain production efficiency and meet safety regulations.
What Role Do Bending Machine Parts Play in Construction?
Bending machine parts are vital in the construction industry for fabricating steel beams and reinforcements. These components facilitate the bending of heavy gauge metals into specific shapes required for structural applications. The benefit is twofold: it improves the load-bearing capacity of structures while ensuring durability against environmental factors. Buyers from Africa and the Middle East should prioritize sourcing robust materials that can withstand local climatic conditions and consider customization options to meet unique project specifications.
How Are Bending Machine Parts Essential in Aerospace Manufacturing?
In aerospace manufacturing, bending machine parts are crucial for producing aircraft components that must meet stringent safety standards. The precision offered by bending machines ensures that components are lightweight yet strong, which is essential for flight safety and performance. International buyers must focus on sourcing high-quality materials that comply with aerospace regulations, as well as ensuring that the bending machines used can handle complex shapes and designs without compromising quality.
How Are Bending Machine Parts Used in HVAC Systems?
In the HVAC industry, bending machine parts are utilized to create ductwork and fittings that ensure efficient airflow and energy conservation. The accurate bending of metal sheets into ducts minimizes air leaks, which can lead to energy loss. Businesses in this sector benefit from sourcing parts that are compatible with existing systems, allowing for seamless integration and installation. Buyers should also consider the availability of various materials to suit different environmental conditions.
What Benefits Do Bending Machine Parts Provide in Furniture Production?
Bending machine parts are increasingly employed in the furniture industry for crafting metal frames and components that enhance both aesthetics and durability. The ability to bend metal into intricate designs allows manufacturers to offer unique products that stand out in the market. For B2B buyers, especially those in Europe, sourcing diverse design options and finishes is crucial to meeting consumer demand and maintaining competitive advantage.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘bending machine parts’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Difficulty Sourcing Genuine Bending Machine Parts
The Problem: Many B2B buyers encounter significant challenges when trying to source genuine OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer) parts for their bending machines. This is particularly true for businesses operating legacy machines that may no longer have readily available parts. The risk here is twofold: using inferior aftermarket parts can lead to machine malfunctions and increased downtime, impacting production efficiency. Additionally, navigating the myriad of suppliers can be daunting, resulting in frustration and uncertainty about the reliability of sourced components.
The Solution: To mitigate these challenges, buyers should establish relationships with reputable suppliers who specialize in OEM parts for bending machines. Conduct thorough research on potential suppliers, focusing on their history, customer reviews, and product quality guarantees. It’s also beneficial to request detailed documentation regarding the parts’ specifications and compatibility with existing machinery. Buyers should consider joining industry-specific forums or networks to connect with other businesses that have faced similar sourcing issues. These platforms can provide insights and recommendations on trusted suppliers, ensuring that you receive genuine parts that enhance the longevity and performance of your bending machines.
Scenario 2: Inconsistent Performance Due to Wear and Tear
The Problem: Over time, bending machine parts such as the ram, punch, and die can experience wear and tear, leading to inconsistent performance. This degradation can result in inaccurate bends, increased scrap rates, and ultimately, financial losses for businesses. For operators in regions with varying material qualities, the challenge is exacerbated, as they may not recognize when to replace or maintain these critical components. As a result, production schedules can be disrupted, and quality control issues may arise.
The Solution: Implementing a proactive maintenance schedule is essential. B2B buyers should invest in training their operators to recognize the signs of wear and understand the maintenance needs of their bending machines. Regular inspections should be scheduled to assess the condition of the ram, punch, and die. Developing a partnership with a service technician or a reliable parts supplier can also streamline the process of identifying when parts need replacement. Keeping a stock of commonly used parts can reduce downtime significantly, allowing for quick replacements when wear is detected. Additionally, investing in high-quality materials and components can enhance the durability of these parts, ensuring consistent performance over a longer period.
Scenario 3: Complexity in Setting Up and Adjusting Bending Parameters
The Problem: Bending machines often require precise setups and adjustments to achieve the desired bend angles and tolerances. B2B buyers may struggle with the complexity of their machines’ control systems, especially if they are new to operating bending machines or if the machines are equipped with advanced features. Misconfigurations can lead to costly errors, wasted materials, and diminished productivity, creating a sense of frustration among operators and management alike.
The Solution: To tackle this issue, companies should invest in comprehensive training programs for their operators. Training should cover not only the operation of the bending machine but also the specifics of setting bending parameters using the control panel. Additionally, creating a standardized setup procedure can help streamline the process, ensuring that all operators follow the same steps for consistent results. For businesses dealing with diverse materials, developing a reference guide that includes specific settings for different material types and thicknesses can be invaluable. Lastly, leveraging technology such as simulation software can allow operators to visualize and refine setups before actual production, reducing the likelihood of errors and enhancing overall operational efficiency.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for bending machine parts
What Are the Key Materials for Bending Machine Parts?
When selecting materials for bending machine parts, it is essential to consider their properties, advantages, and limitations. This analysis focuses on four common materials: carbon steel, stainless steel, aluminum, and cast iron. Each material has unique characteristics that can significantly impact the performance and longevity of bending machines.
How Does Carbon Steel Perform in Bending Machine Parts?
Carbon steel is widely used in manufacturing bending machine parts due to its excellent strength and durability. It typically has a high tensile strength, making it suitable for high-pressure applications. Additionally, carbon steel can withstand a range of temperatures, which is crucial for machines that operate in varying environments.
Pros: Carbon steel is relatively inexpensive compared to other materials, making it a cost-effective choice for manufacturers. Its machinability allows for easier fabrication of complex parts.
Cons: However, carbon steel is susceptible to corrosion if not properly treated or coated, which can lead to premature failure in humid or wet environments.
Impact on Application: Carbon steel is ideal for parts exposed to mechanical stress but may require protective coatings in regions with high humidity, such as parts of Africa and South America.
Considerations for International Buyers: Compliance with standards such as ASTM A36 is crucial. Buyers should ensure that suppliers can provide the necessary certifications to meet local regulations.
Why Choose Stainless Steel for Bending Machine Parts?
Stainless steel is known for its exceptional corrosion resistance, making it an excellent choice for bending machine parts that may be exposed to moisture or chemicals. It maintains its strength at elevated temperatures, which is beneficial for high-performance applications.
Pros: The durability and aesthetic appeal of stainless steel make it suitable for both functional and visible components of bending machines. Its resistance to rust and staining extends the lifespan of parts.
Cons: The primary drawback is the higher cost compared to carbon steel. Additionally, stainless steel can be more challenging to machine, increasing manufacturing complexity.
Impact on Application: Stainless steel is particularly beneficial in industries such as food processing or pharmaceuticals, where hygiene is paramount.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should look for compliance with standards like ASTM A240 or EN 10088. In regions like the Middle East, where high temperatures and humidity are common, stainless steel is often preferred.
What Are the Benefits of Using Aluminum in Bending Machine Parts?
Aluminum is a lightweight material that offers excellent corrosion resistance and thermal conductivity. It is often used in parts where weight reduction is a priority, such as in portable bending machines.
Pros: The lightweight nature of aluminum allows for easier handling and reduces the overall weight of the machine. It is also resistant to corrosion, making it suitable for various environments.
Cons: However, aluminum has lower tensile strength compared to steel, which may limit its use in high-stress applications. It can also be more expensive than carbon steel.
Impact on Application: Aluminum is ideal for applications requiring portability and ease of use, but it may not be suitable for heavy-duty operations.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should ensure that aluminum parts meet standards such as ASTM B221. In Europe, compliance with EN 573 is also necessary.
Why Is Cast Iron a Consideration for Bending Machine Parts?
Cast iron is known for its excellent wear resistance and ability to absorb vibrations, making it suitable for heavy-duty parts such as machine frames and bases.
Pros: The durability and strength of cast iron make it ideal for applications that require stability and resistance to deformation under load.
Cons: However, cast iron is brittle and can crack under excessive stress. It is also heavier than other materials, which may not be ideal for all applications.
Impact on Application: Cast iron is commonly used in stationary machines where weight and stability are critical, but it may not be suitable for portable equipment.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should ensure compliance with standards like ASTM A48. In regions with strict quality regulations, such as Europe, adherence to EN 1561 is crucial.
Summary Table of Material Selection for Bending Machine Parts
| Material | Typical Use Case for bending machine parts | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Carbon Steel | Structural components, frames | Cost-effective and strong | Susceptible to corrosion | Low |
| Stainless Steel | Parts exposed to moisture or chemicals | Excellent corrosion resistance | Higher cost and machining complexity | High |
| Aluminum | Portable bending machines | Lightweight and corrosion-resistant | Lower tensile strength | Medium |
| Cast Iron | Machine bases and heavy-duty components | Durable and vibration-absorbing | Brittle and heavy | Medium |
This strategic material selection guide provides essential insights for international B2B buyers, aiding in the informed decision-making process regarding bending machine parts.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for bending machine parts
What Are the Main Stages of Manufacturing Bending Machine Parts?
The manufacturing of bending machine parts involves several critical stages, each designed to ensure the final product meets rigorous performance and quality standards. These stages include material preparation, forming, assembly, and finishing. Understanding these processes is vital for B2B buyers looking to source high-quality components for their operations.
How Is Material Prepared for Bending Machine Parts?
The first step in manufacturing bending machine parts is material preparation. This typically involves selecting the appropriate raw materials, such as high-strength steel or aluminum, based on the part’s intended use and performance requirements. The materials are then cut to size using techniques like shearing or laser cutting.
Once the materials are cut, they undergo processes such as deburring and cleaning to remove any sharp edges or contaminants that could affect the integrity of the parts. Proper material preparation is crucial, as it directly impacts the quality of the final product and the efficiency of subsequent manufacturing processes.
What Forming Techniques Are Used in Bending Machine Parts Manufacturing?
The forming stage is where the prepared materials are shaped into their final forms. Various techniques can be employed, including:
- Hydraulic Pressing: Utilizes hydraulic force to bend or shape materials. This method is prevalent in the production of complex shapes and is highly effective for thick materials.
- CNC Machining: Computer Numerical Control (CNC) machining allows for precise shaping of parts, enabling manufacturers to create intricate designs with high accuracy.
- Stamping: A process that uses dies to cut and form materials into desired shapes. Stamping is efficient for high-volume production and can yield consistent results.
Each technique has its advantages and is selected based on the part specifications, production volume, and required tolerances.
How Does Assembly Contribute to the Quality of Bending Machine Parts?
Once the individual components have been formed, they are assembled into complete parts. This stage may involve welding, bolting, or riveting, depending on the design and structural requirements of the part.
Quality control measures during assembly are crucial, as improper assembly can lead to defects that affect performance and safety. Skilled technicians often oversee this stage to ensure that all components fit together correctly and meet the specified tolerances.
What Finishing Processes Are Necessary for Bending Machine Parts?
The finishing stage enhances the durability and aesthetic appeal of the parts. Common finishing processes include:
- Surface Treatment: Methods such as powder coating, anodizing, or galvanizing protect parts from corrosion and wear.
- Machining: Additional machining may be necessary to achieve the desired surface finish or dimensional accuracy.
- Quality Inspections: After finishing, parts undergo rigorous inspection to ensure they meet all design specifications and quality standards.
Finishing processes not only improve the appearance of the parts but also extend their lifespan, making them more reliable in operational environments.
What Are the Key Quality Assurance Standards for Bending Machine Parts?
Quality assurance (QA) is critical in the manufacturing of bending machine parts, ensuring that products meet both international standards and customer expectations. Several standards apply, including:
- ISO 9001: This international standard outlines the criteria for a quality management system. It emphasizes a process approach to ensure consistent quality in products and services.
- CE Marking: Particularly relevant for European markets, CE marking indicates that products meet EU safety, health, and environmental protection standards.
- API Standards: For parts intended for use in the oil and gas industry, compliance with American Petroleum Institute (API) standards is essential.
What Are the Key Quality Control Checkpoints During Manufacturing?
Quality control in the manufacturing process typically involves several checkpoints, including:
- Incoming Quality Control (IQC): This step involves inspecting raw materials upon arrival to ensure they meet specified standards before production begins.
- In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): Throughout the manufacturing process, quality checks are conducted to identify any defects or deviations from specifications early on.
- Final Quality Control (FQC): Once assembly and finishing are complete, a final inspection is performed to ensure that the parts meet all quality standards and specifications before shipment.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify the Quality Control Processes of Suppliers?
For international B2B buyers, verifying a supplier’s quality control processes is essential to ensure they receive high-quality products. Here are some strategies:
- Conduct Audits: Regular audits of suppliers can help assess their manufacturing processes and quality control measures. This can be done through on-site visits or third-party assessments.
- Request Quality Reports: Suppliers should be able to provide documentation related to their quality management system, including compliance with ISO 9001 and other relevant standards.
- Third-Party Inspections: Engaging independent inspection agencies to evaluate the quality of parts before shipment can provide an added layer of assurance, particularly for high-value components.
What Nuances Should International Buyers Consider in Quality Assurance?
International buyers must navigate various regulatory landscapes when sourcing bending machine parts. This includes understanding specific quality certifications required in their regions, such as CE marking in Europe or compliance with local safety standards in Africa and South America.
Additionally, cultural differences in business practices may affect quality assurance processes. Building strong relationships with suppliers and clear communication about quality expectations can mitigate misunderstandings and ensure that parts meet the required specifications.
By understanding the manufacturing processes and quality assurance measures involved in producing bending machine parts, B2B buyers can make informed decisions that enhance their operational efficiency and product reliability.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘bending machine parts’
In the competitive landscape of metal fabrication, sourcing high-quality bending machine parts is crucial for ensuring operational efficiency and product quality. This guide provides a practical checklist for B2B buyers seeking to procure these essential components, ensuring that you make informed decisions that align with your business needs.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Before initiating the sourcing process, clearly outline your technical requirements. This includes understanding the specific parts needed, such as the ram, die, and hydraulic systems, as well as their compatibility with existing machinery. Properly defining these specifications will guide your search and help avoid costly mistakes.
- Consider material types: Different materials may require different tooling.
- Identify machine compatibility: Ensure parts are suitable for your specific bending machine model.
Step 2: Research Reliable Suppliers
Conduct thorough research to identify suppliers with a solid reputation in the industry. Look for established companies that specialize in bending machine parts and have a history of serving clients in your region. Reliable suppliers will have positive reviews and testimonials from previous customers.
- Check for industry certifications: Certifications can indicate a supplier’s commitment to quality.
- Evaluate their product range: A diverse product offering can simplify your sourcing process.
Step 3: Evaluate Potential Suppliers
Before committing to a supplier, it’s crucial to vet them thoroughly. Request company profiles, case studies, and references from buyers in a similar industry or region. This step ensures that the supplier has experience meeting the needs of businesses like yours.
- Assess their customer service: Quick and effective communication is essential for resolving issues.
- Review their technical support: Suppliers should offer assistance for installation and maintenance.
Step 4: Verify Quality Assurance Processes
Quality assurance is critical when sourcing bending machine parts. Inquire about the supplier’s quality control measures to ensure that the components meet industry standards. This includes checking for the use of genuine OEM parts and adherence to international quality standards.
- Request documentation: Look for certificates of authenticity and compliance.
- Inspect sample parts if possible: Evaluating physical samples can provide insights into the quality of the parts.
Step 5: Understand Lead Times and Delivery Options
Clarify the lead times associated with your order and the available delivery options. Timely delivery is crucial to avoid production delays, so ensure that the supplier can meet your scheduling requirements.
- Discuss shipping methods: Depending on your location, shipping options may vary significantly.
- Consider local suppliers for faster delivery: Proximity can reduce lead times and shipping costs.
Step 6: Evaluate Pricing and Payment Terms
Price is a significant factor in any procurement process. Compare quotes from different suppliers but be cautious of prices that seem too low, as they may indicate inferior quality. Additionally, review payment terms to ensure they align with your financial policies.
- Inquire about bulk discounts: If you plan to order in larger quantities, negotiate for better pricing.
- Understand payment options: Flexible payment terms can ease cash flow management.
Step 7: Finalize Contracts and Agreements
Once you’ve selected a supplier, ensure that all agreements are documented in a formal contract. This contract should outline the terms of the sale, including warranties, return policies, and support services.
- Include service-level agreements (SLAs): SLAs can ensure accountability for delivery and quality.
- Review legal implications: Make sure you understand the terms to avoid any potential disputes.
By following this checklist, B2B buyers can effectively navigate the complexities of sourcing bending machine parts, ensuring that they select the right components and suppliers to meet their operational needs.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for bending machine parts Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components in Bending Machine Parts Sourcing?
When sourcing bending machine parts, it is crucial to understand the various cost components that contribute to the final pricing. These include:
-
Materials: The cost of raw materials such as steel, aluminum, and other metals significantly impacts pricing. Higher-grade materials that offer better durability and performance typically come at a premium.
-
Labor: Labor costs encompass the wages of skilled workers involved in the manufacturing process, which can vary widely based on geographic location. For instance, labor costs in Europe may be higher compared to those in South America or Africa.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes expenses related to factory operations, such as utilities, maintenance, and depreciation of machinery. Efficient operations can help mitigate these costs.
-
Tooling: The design and manufacturing of specialized tooling, such as punches and dies, can be costly, especially if custom tooling is required for specific applications.
-
Quality Control (QC): Ensuring that parts meet industry standards and specifications incurs additional costs. Investing in rigorous QC processes can lead to long-term savings by reducing defects and rework.
-
Logistics: Transportation costs for shipping parts from the manufacturer to the buyer are essential to consider, particularly in international trade where tariffs and customs may apply.
-
Margin: Suppliers will add a markup to cover their costs and profit margins. This can vary based on the supplier’s market positioning and competition.
How Do Price Influencers Affect Bending Machine Parts Costs?
Several factors can influence the pricing of bending machine parts, including:
-
Volume and Minimum Order Quantity (MOQ): Ordering larger quantities often leads to bulk pricing discounts. Buyers should negotiate favorable terms based on their projected needs.
-
Specifications and Customization: Customized parts designed for specific applications typically come at a higher cost. It is essential to balance the need for customization against budget constraints.
-
Material Quality and Certifications: Parts that require special certifications or come from reputable manufacturers may command higher prices due to the assurance of quality and compliance with industry standards.
-
Supplier Factors: The reputation, reliability, and location of the supplier can significantly affect pricing. Established suppliers may charge more for their proven track record.
-
Incoterms: Understanding the chosen Incoterms (International Commercial Terms) is vital, as they define responsibilities for shipping costs, insurance, and risk management. This can ultimately affect the total landed cost.
What Are the Best Negotiation Strategies for B2B Buyers?
Buyers should employ effective negotiation strategies to ensure cost-efficiency:
-
Understand Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Evaluate not just the purchase price but the total cost over the part’s lifecycle, including maintenance, potential downtime, and replacement costs.
-
Leverage Volume Discounts: If your business can commit to larger orders, use this leverage to negotiate better terms.
-
Build Relationships with Suppliers: Establishing strong partnerships can lead to better pricing, priority service, and favorable credit terms.
-
Research Market Rates: Conduct thorough market research to understand typical pricing and identify competitive offers. This knowledge empowers buyers during negotiations.
-
Consider Local Suppliers: Sourcing from local suppliers can reduce logistics costs and lead times, making it a cost-effective option, especially for urgent needs.
What Should International Buyers Consider in Pricing Nuances?
For international buyers, especially those in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, there are specific nuances to consider:
-
Currency Fluctuations: Be aware of exchange rates, as they can significantly affect the final price of imported parts.
-
Import Tariffs and Duties: Research applicable tariffs and import duties that may increase the overall cost of sourcing parts from abroad.
-
Cultural Differences in Negotiation: Understand the cultural context of the supplier’s country, as negotiation styles and business practices can differ widely.
-
Regulatory Compliance: Ensure that parts comply with local regulations and standards to avoid additional costs related to non-compliance.
Disclaimer on Pricing
Prices for bending machine parts can vary significantly based on the factors outlined above. This analysis serves as a general guide and should not be considered definitive. Buyers are encouraged to conduct their due diligence and obtain quotes from multiple suppliers to ensure competitive pricing.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing bending machine parts With Other Solutions
Introduction: Understanding Alternatives in Bending Solutions
In the metal fabrication industry, selecting the right equipment and components is crucial for optimizing production efficiency and quality. While bending machine parts are integral to traditional bending processes, there are alternative solutions available that can achieve similar objectives. This analysis compares bending machine parts with two viable alternatives: CNC laser cutting systems and hydraulic press brakes. By evaluating the performance, cost, ease of implementation, maintenance, and best use cases of each solution, B2B buyers can make informed decisions that align with their specific operational needs.
Comparison Table
| Comparison Aspect | Bending Machine Parts | CNC Laser Cutting Systems | Hydraulic Press Brakes |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | High precision and repeatability; suitable for various materials and thicknesses. | Exceptional accuracy; ideal for intricate designs and thin materials. | Strong force application; effective for thick materials and heavy-duty tasks. |
| Cost | Moderate initial investment; ongoing costs for maintenance and spare parts. | Higher upfront costs; lower operational costs due to minimal material waste. | Varies widely; can be cost-effective for large-scale production but may require significant investment. |
| Ease of Implementation | Requires skilled operators for setup and adjustments; straightforward installation. | Complex setup and programming; requires specialized training. | Relatively simple to set up but requires operator training for optimal performance. |
| Maintenance | Regular maintenance needed for optimal performance; parts may require replacement. | Low maintenance due to fewer moving parts; however, optics and software updates are essential. | Moderate maintenance; hydraulic systems may require regular checks for leaks and pressure. |
| Best Use Case | Ideal for high-volume production of consistent bends in various materials. | Best suited for detailed and intricate cuts in thin materials or complex shapes. | Optimal for heavy-duty applications requiring significant force for bending thick materials. |
Detailed Breakdown of Alternatives
CNC Laser Cutting Systems
CNC laser cutting systems utilize high-powered lasers to cut through materials with incredible precision. The primary advantage of this technology is its ability to create intricate designs and complex shapes without the need for physical tooling changes. This minimizes waste and allows for faster production times. However, the initial investment is considerably higher than that of traditional bending machines, and programming the CNC system requires specialized skills. Additionally, laser cutting is most effective on thinner materials, making it less suitable for heavy-duty applications.
Hydraulic Press Brakes
Hydraulic press brakes are another alternative that utilizes hydraulic force to bend materials. They excel in applications requiring significant bending power, particularly for thick metal sheets. The advantages of hydraulic press brakes include their versatility in handling various materials and thicknesses and their ability to produce consistent bends. However, they can be expensive, particularly for high-capacity models. Moreover, while their setup is straightforward, operators must be trained to maximize their efficiency and safety.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Solution for Your Needs
When deciding between bending machine parts and alternative solutions, it is essential for B2B buyers to consider their specific production requirements, budget constraints, and operational capabilities. Bending machines provide a reliable option for high-volume production with consistent results, while CNC laser cutting systems offer precision for intricate designs, albeit at a higher cost. Hydraulic press brakes serve as a robust alternative for heavy-duty applications but may involve significant initial investment. Ultimately, the choice will depend on the unique needs of the business, production goals, and the materials being processed. By carefully evaluating these aspects, buyers can select the most suitable bending solution that aligns with their operational strategy and growth objectives.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for bending machine parts
What Are the Critical Technical Properties of Bending Machine Parts?
Understanding the technical specifications of bending machine parts is vital for B2B buyers seeking quality and efficiency in their metal fabrication processes. Here are some essential properties to consider:
-
Material Grade
Material grade indicates the type of material used in manufacturing bending machine components. Common materials include high-carbon steel for durability and resistance to wear, and aluminum for lightweight applications. Choosing the right material ensures longevity and optimal performance, which can significantly impact production efficiency and costs. -
Tolerance
Tolerance refers to the allowable deviation from specified dimensions in parts. Tight tolerances are crucial for maintaining the accuracy of bends and ensuring that products meet design specifications. For B2B buyers, understanding tolerance levels can prevent costly errors and reworks, enhancing the overall quality of the manufactured goods. -
Load Capacity
Load capacity defines the maximum weight a bending machine part can support during operation. This specification is essential for ensuring that the machine can handle specific materials and thicknesses without compromising performance or safety. Proper load capacity assessment helps buyers choose machines suitable for their operational needs, minimizing downtime and enhancing productivity. -
Surface Finish
The surface finish of bending machine parts affects both aesthetic and functional aspects. A smoother finish can reduce friction during operation, leading to less wear and tear over time. For buyers, selecting parts with the appropriate surface finish can translate into lower maintenance costs and improved product quality. -
Hydraulic Pressure Rating
For hydraulic bending machines, the hydraulic pressure rating indicates the maximum pressure the system can handle. This specification is critical for ensuring safe and efficient operation, particularly when bending thicker materials. Buyers should verify this rating to ensure compatibility with their production requirements, avoiding equipment failure and operational delays.
What Are Common Trade Terms in the Bending Machine Industry?
Familiarity with industry terminology is essential for effective communication and negotiation in the B2B marketplace. Here are several key terms that buyers should know:
-
OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
OEM refers to companies that produce parts or equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer. In the context of bending machines, sourcing OEM parts ensures compatibility and quality, which is vital for maintaining machine performance. Buyers often prefer OEM parts to avoid issues associated with aftermarket alternatives. -
MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ is the smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell. Understanding MOQ is crucial for buyers, especially when planning inventory and budgeting. It can impact purchasing decisions, particularly for small businesses or those needing specialized components in limited quantities. -
RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a document used by buyers to solicit price quotes from suppliers for specific products or services. Issuing an RFQ allows buyers to compare prices, quality, and terms from different manufacturers, facilitating informed decision-making. This process is essential for maximizing value and ensuring competitive pricing in procurement. -
Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
Incoterms are internationally recognized terms that define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in international transactions. Understanding these terms is vital for B2B buyers as they dictate shipping responsibilities, risk transfer, and cost allocation. Familiarity with Incoterms helps avoid misunderstandings and disputes in cross-border trade. -
Lead Time
Lead time refers to the amount of time it takes from placing an order to receiving the goods. This metric is critical for planning production schedules and ensuring timely delivery. Buyers should inquire about lead times when negotiating contracts, as it can significantly affect project timelines and operational efficiency.
By grasping these technical properties and trade terms, B2B buyers can make more informed decisions when sourcing bending machine parts, ultimately enhancing their operational efficiency and product quality.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the bending machine parts Sector
What Are the Current Market Dynamics and Key Trends in the Bending Machine Parts Sector?
The bending machine parts market is experiencing significant growth driven by increasing demand for precision manufacturing across various industries such as automotive, aerospace, and construction. The global shift towards automation and Industry 4.0 technologies is reshaping sourcing strategies for international B2B buyers. Notably, advancements in CNC technology and the integration of IoT in bending machines are enhancing operational efficiency and product quality. As manufacturers increasingly seek to optimize their production processes, the demand for high-quality, durable bending machine parts continues to rise.
Emerging trends indicate a growing preference for customized and modular machine components, allowing manufacturers to tailor solutions to specific production needs. This flexibility not only enhances productivity but also minimizes downtime—a critical factor for businesses operating in competitive markets like Africa and South America, where rapid turnaround times are essential. Additionally, suppliers are increasingly focusing on providing comprehensive service packages that include maintenance, support, and access to spare parts, which can significantly enhance the longevity of machines and reduce operational costs.
International buyers are also becoming more discerning, emphasizing the importance of sourcing from reputable suppliers who can provide genuine OEM parts. This trend is particularly pronounced in regions such as the Middle East and Europe, where regulatory compliance and adherence to quality standards are paramount. Understanding these market dynamics is crucial for B2B buyers as they navigate the complexities of sourcing bending machine parts to ensure operational excellence and competitive advantage.
How Can Sustainability and Ethical Sourcing Impact B2B in the Bending Machine Parts Sector?
Sustainability is increasingly becoming a core consideration for B2B buyers in the bending machine parts sector. The environmental impact of manufacturing processes, including carbon emissions and resource depletion, is prompting businesses to seek suppliers who prioritize sustainable practices. This shift is not only beneficial for the environment but also aligns with the growing consumer demand for corporate responsibility.
Ethical sourcing practices, including transparency in the supply chain, are gaining importance. Buyers are looking for suppliers who can demonstrate responsible sourcing of raw materials and adherence to labor standards. Certifications such as ISO 14001 for environmental management and ISO 45001 for occupational health and safety can serve as indicators of a supplier’s commitment to sustainability and ethical practices.
Moreover, the use of ‘green’ materials in the production of bending machine parts is becoming more prevalent. Suppliers who offer eco-friendly alternatives, such as recycled metals or sustainably sourced materials, can provide a competitive edge. For B2B buyers in regions like Europe, where regulatory frameworks are increasingly stringent regarding environmental impact, prioritizing sustainability in sourcing decisions is not just a trend but a strategic necessity.
What Is the Historical Context of Bending Machine Parts Development?
The evolution of bending machine parts can be traced back to the industrial revolution when manual bending processes were predominant. As industries expanded and the demand for precision increased, the introduction of hydraulic and CNC technologies revolutionized the bending process. This shift allowed for greater accuracy, repeatability, and efficiency in metal fabrication.
Over the years, manufacturers have continuously refined bending machine designs and components, leading to the development of specialized parts that enhance performance and durability. The focus has shifted from merely functional components to high-performance parts that integrate advanced technology, such as sensors and automation controls. This evolution not only reflects technological advancements but also the growing emphasis on reducing waste and improving productivity in manufacturing processes.
Understanding this historical context is vital for B2B buyers, as it highlights the importance of selecting parts that not only meet current operational needs but are also compatible with future technological advancements. As the industry continues to evolve, staying informed about these changes will enable buyers to make strategic sourcing decisions that align with their long-term goals.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of bending machine parts
-
How do I ensure the quality of bending machine parts before purchasing?
To ensure quality, request certifications and quality assurance documentation from suppliers. Look for OEM parts, as these typically adhere to strict manufacturing standards. Conducting a supplier audit or visiting the facility can provide insights into their manufacturing processes. Additionally, consider sourcing parts from well-established brands known for their reliability in the industry. Lastly, check for customer reviews and testimonials to gauge the supplier’s reputation. -
What is the best way to choose the right bending machine parts for my needs?
The best approach is to analyze your specific bending requirements, including material type, thickness, and desired bend angles. Consult with the machine manufacturer or a specialist who can recommend suitable parts based on your operational needs. Ensure the parts are compatible with your existing machinery to prevent issues. Additionally, consider the availability of replacement parts and support services from the supplier to maintain machine efficiency in the long run. -
How can I verify the credibility of a bending machine parts supplier?
Start by checking the supplier’s business licenses and certifications, which demonstrate their compliance with industry standards. Look for reviews and ratings from other businesses in your region or industry. Establish communication with their customer service to assess responsiveness and professionalism. Engaging in discussions about their production processes and warranty policies can also provide insights into their credibility. If possible, seek references from previous clients to gain further assurance. -
What are the typical minimum order quantities (MOQs) for bending machine parts?
Minimum order quantities can vary significantly based on the supplier and type of parts. Some suppliers may have MOQs as low as one unit for standard components, while custom or specialized parts might require larger orders, often ranging from 10 to 100 units. It’s advisable to discuss your requirements upfront with the supplier to understand their policies. If you’re ordering in bulk, negotiating better pricing or terms may be possible. -
What payment terms should I expect when sourcing bending machine parts internationally?
Payment terms can vary widely among suppliers, but common practices include advance payment, letters of credit, and net payment terms (e.g., net 30 or net 60 days). For international transactions, consider using escrow services to ensure both parties fulfill their obligations. Always clarify payment methods, currency preferences, and any additional fees such as shipping or customs duties. Establishing a clear contract outlining payment terms can help prevent disputes later. -
How can I customize bending machine parts to fit my specifications?
Most reputable suppliers offer customization options for bending machine parts. Start by discussing your specific requirements with the supplier, including dimensions, materials, and design features. Providing detailed specifications or drawings can facilitate the customization process. Keep in mind that customized parts may have longer lead times and potentially higher costs. Ensure that the supplier has the capability and experience to deliver quality custom components. -
What logistics considerations should I keep in mind when importing bending machine parts?
When importing parts, consider shipping methods, lead times, and customs regulations for your country. Choose a reliable logistics partner familiar with international shipping to avoid delays. Ensure that all paperwork, including invoices and customs declarations, is accurate and complete to prevent issues at customs. Additionally, factor in shipping costs and insurance to protect your investment during transit. -
What should I do if I encounter issues with bending machine parts after purchase?
Immediately contact the supplier to report any issues, such as defects or compatibility problems. Most reputable suppliers will have a return policy or warranty in place. Document the problem with photos and detailed descriptions to aid in the claims process. If the issue is due to manufacturing defects, you may be eligible for a replacement or refund. Establishing a good relationship with your supplier can also facilitate smoother resolutions for future transactions.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.
Top 6 Bending Machine Parts Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. Harsle – Bending Machine Components
Domain: harsle.com
Registered: 2014 (11 years)
Introduction: 1. Frame: Provides structural support for the bending machine. 2. Bed: Flat surface for placing material, often with V-shaped grooves for tooling. 3. Ram: Moving part that applies force to bend material, can move vertically or horizontally. 4. Punch: Upper tool that contacts the material to apply bending force, attached to the ram. 5. Die: Lower tool that supports the material during bending, fixe…
2. Ridgid – Bending Tools
Domain: store.ridgid.com
Registered: 1995 (30 years)
Introduction: Bending Tools include 300 Series Plumbing Benders, 400 Series Instrument Benders, 600 Series HD Benders, Model 456 Tri-Bender, Ratchet Bender, and Spring-Type Tube Benders.
3. Pines – Bending Machine Spare Parts
Domain: pines-eng.com
Registered: 2014 (11 years)
Introduction: Bending Machine Spare Parts, OEM spare parts for all Pines Benders, support for legacy machines, service technicians available for evaluations, detailed historical records for technical details, global support for minimizing downtime.
4. Ercolina – Replacement Parts and Tooling
Domain: shop.ercolina-usa.com
Registered: 2000 (25 years)
Introduction: Replacement Parts for Ercolina Tube and Pipe Benders include: Rotary Draw Tooling for all Ercolina models, Individual Pipe, Tube, and Square Tube Center Formers and Counterbend Dies, Rotary Draw Tooling Kits for Pipe, Tube, and Square, Angle Roll Tooling Sets (CE35, CE40, CE50, CE60, CE70, CE100) for Pipe and Tube sizes, Mandrel Tooling for 030 MegaBender, TM76, Erco 65, and Erco 76, Flexible Stee…
5. Baileigh – 12 Universal Bend Plate UBP-1200-325
Domain: jmcautomotiveequipment.com
Registered: 2010 (15 years)
Introduction: [{‘name’: ‘Baileigh 12″ Universal Bend Plate UBP-1200-325’, ‘description’: ‘The 12″ Universal Die Plate for RDB-325 allows the fabricator to bend solid bar or rounds to into very tight radii. The UPB-1200 universal bend plate is made from solid steel for long life.’, ‘price’: ‘$1,805.99’, ‘original_price’: ‘$2,167.00’}, {‘name’: ‘Huth PUNCH-250 H5300-250 Punch’, ‘description’: ‘Punch for H5300-250…
6. Shannon Machines – Heating Wire
Domain: shannonmachines.com
Registered: 2012 (13 years)
Introduction: Spare-parts for Shannon plastic sheet bending and polishing machines include:
1. **Heating Wire**:
– **0.9 mm**: Cut to machine length, 10 cm longer for easy replacement. Suitable for: ABM-D, HR, HRK, HRM, HRT, X-WIRE.
– **1.6 mm**: Cut to machine length, 10 cm longer for easy replacement. Suitable for: ABM-D, HR, HRM, HRP, HRP-D, HRP-S, HRT, HRT-D.
– **Roll Heating Wire**: Available in …
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for bending machine parts
In the ever-evolving landscape of metal fabrication, understanding the critical components of bending machines is paramount for optimizing operational efficiency and reducing downtime. The strategic sourcing of bending machine parts—ranging from frames and hydraulic systems to specialized tooling—ensures that businesses can maintain high productivity levels while minimizing operational risks. By prioritizing genuine OEM parts, buyers can benefit from improved reliability, enhanced safety, and better overall performance of their machinery.
For international B2B buyers in regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, the ability to source high-quality bending machine parts is not just a matter of convenience; it’s a strategic imperative. Building strong relationships with reputable suppliers facilitates timely access to essential components, which in turn supports sustained business growth and innovation.
As we look to the future, the focus should remain on leveraging technology and supplier partnerships to streamline sourcing processes. By investing in robust supply chains and embracing advancements in machinery, businesses can position themselves to thrive in a competitive global market. Now is the time to take proactive steps in sourcing bending machine parts that align with your operational goals—ensuring your business is well-equipped to meet the demands of tomorrow.