Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for bead blasting vs sandblasting
In the competitive landscape of industrial surface preparation, understanding the differences between bead blasting and sandblasting is crucial for B2B buyers seeking optimal solutions for their specific applications. As businesses in regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe (including markets like Saudi Arabia and Nigeria) navigate the complexities of sourcing effective surface finishing techniques, they face the challenge of selecting the right method that balances efficiency, cost, and safety. This guide provides a comprehensive exploration of bead blasting versus sandblasting, detailing their respective processes, advantages, and ideal applications.
Throughout this guide, we will delve into the various types of abrasive materials used, the contexts in which each method excels, and the critical factors to consider when vetting suppliers. Additionally, we will discuss the cost implications associated with each technique, enabling buyers to make informed decisions that align with their operational goals and budget constraints. By the end of this resource, international B2B buyers will be equipped with the knowledge to confidently navigate the global market for surface preparation technologies, ensuring they choose the most suitable option for their unique needs.
Understanding bead blasting vs sandblasting Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Sandblasting | Uses sharp abrasive materials like sand or aluminum oxide. | Heavy-duty cleaning, rust removal, concrete prep. | Pros: Faster, effective for tough coatings. Cons: Can damage surfaces, creates silica dust. |
| Bead Blasting | Utilizes glass beads for a gentler cleaning process. | Polishing metals, preparing delicate surfaces. | Pros: Produces a smooth finish, less abrasive. Cons: Slower, less effective for heavy coatings. |
| Steel Grit Blasting | Employs steel grit for aggressive surface preparation. | Industrial machinery, heavy equipment maintenance. | Pros: Effective for rough surfaces, cost-effective. Cons: Can leave a rough finish, potential for surface damage. |
| Walnut Shell Blasting | Uses crushed walnut shells for a softer approach. | Cleaning delicate parts, paint stripping. | Pros: Eco-friendly, gentle on surfaces. Cons: Less effective on tough coatings, higher material costs. |
| Ceramic Media Blasting | Involves ceramic beads for a precise finish. | Aerospace, automotive, and electronics industries. | Pros: Highly effective for precision work. Cons: More expensive, requires specialized equipment. |
What Are the Key Characteristics of Sandblasting in B2B Applications?
Sandblasting is characterized by its use of harsh abrasive materials such as sand, aluminum oxide, or steel grit. This method is particularly effective for removing heavy rust, paint, and other stubborn contaminants, making it ideal for industries that require robust surface preparation, such as construction and manufacturing. However, buyers should consider the potential for surface damage and the health risks associated with silica dust exposure, which is heavily regulated in many regions.
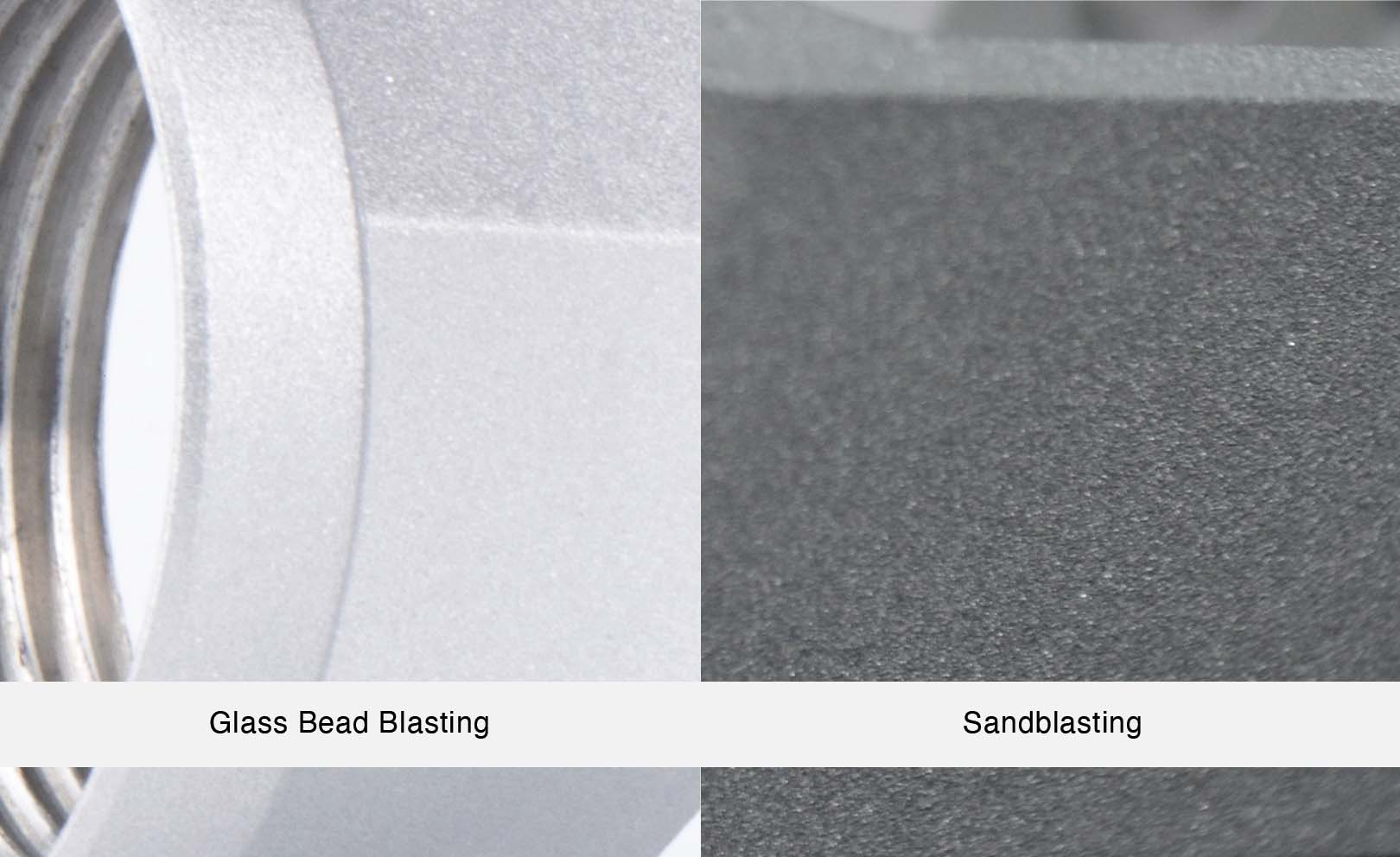
How Does Bead Blasting Differ from Sandblasting for Surface Finishing?
Bead blasting employs tiny glass beads, which allows for a gentler cleaning process that results in a polished finish. This method is particularly suitable for delicate surfaces like stainless steel or aluminum, where maintaining the integrity of the material is crucial. B2B buyers looking for a refined finish without damaging the substrate will find bead blasting advantageous, although it may be slower and less effective for removing thicker coatings compared to sandblasting.
What Are the Advantages of Steel Grit Blasting in Industrial Settings?
Steel grit blasting is known for its aggressive nature, making it suitable for applications involving heavy machinery and industrial equipment. This method provides a cost-effective solution for preparing rough surfaces but can lead to a rough finish and potential surface damage. Companies in sectors such as mining or heavy manufacturing may favor steel grit blasting for its effectiveness in tough conditions, despite the need for careful handling to avoid damaging components.
In What Scenarios Should Walnut Shell Blasting Be Considered?
Walnut shell blasting is a softer alternative that utilizes crushed walnut shells, making it an eco-friendly option ideal for cleaning delicate parts without causing damage. This method is often employed in industries where preserving the integrity of the material is essential, such as automotive restoration or fine woodworking. While it provides a gentle touch, buyers should weigh its higher material costs and limited effectiveness against tougher coatings.
How Does Ceramic Media Blasting Benefit Precision Industries?
Ceramic media blasting is distinguished by its use of ceramic beads, which provide a high degree of precision for surface finishing. This method is particularly beneficial in industries such as aerospace and electronics, where tight tolerances and smooth finishes are critical. Although ceramic media blasting requires specialized equipment and comes at a higher cost, its effectiveness for precision work makes it a valuable investment for businesses focused on quality and performance.
Key Industrial Applications of bead blasting vs sandblasting
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of bead blasting vs sandblasting | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Aerospace | Surface preparation of aircraft components | Enhances fatigue resistance and extends the lifespan of parts | Quality of abrasives, compliance with aviation standards |
| Automotive | Cleaning and finishing of engine components | Improves performance and reliability of engines | Abrasive material type, cost-effectiveness, and delivery time |
| Oil & Gas | Rust removal and surface preparation for pipelines | Prevents corrosion and ensures safety in operations | Environmental regulations, safety standards, and supplier reliability |
| Construction | Preparation of concrete surfaces for coatings | Ensures better adhesion of coatings, increasing durability | Equipment availability, experience in specific applications |
| Manufacturing | Finishing of metal parts for aesthetic and functional purposes | Enhances product appeal and reduces wear on machinery | Consistency in results, scalability, and technical support |
How is Bead Blasting Used in Aerospace Applications?
In the aerospace industry, bead blasting is crucial for preparing aircraft components. This method effectively removes contaminants without damaging the underlying material, which is essential for ensuring the integrity and performance of high-stress components. International buyers must prioritize suppliers who comply with rigorous aviation standards and provide high-quality glass beads that meet the specific requirements for surface finish and material compatibility.
What Role Does Sandblasting Play in Automotive Manufacturing?
Sandblasting is widely employed in the automotive sector for cleaning and finishing engine components. This aggressive method effectively strips away rust, old paint, and other stubborn coatings, improving the overall performance and reliability of engines. B2B buyers in this field should consider the type of abrasive used, as well as the cost-effectiveness of the process, to ensure they meet production demands without compromising quality.
Why is Bead Blasting Important for Oil & Gas Pipeline Maintenance?
In the oil and gas industry, bead blasting is used to prepare pipelines for coatings and to remove rust. This process is vital for preventing corrosion, which can lead to catastrophic failures and safety hazards. International buyers should focus on suppliers that adhere to environmental regulations and provide materials that are safe and effective for use in harsh conditions.
How Does Sandblasting Benefit Construction Projects?
Sandblasting is commonly utilized in construction to prepare concrete surfaces for coatings. This method ensures that surfaces are clean and free of contaminants, allowing for better adhesion of paints and sealants, which enhances durability. Buyers in this sector should assess the supplier’s equipment capabilities and experience in handling large-scale projects to ensure timely and efficient service.
What Are the Advantages of Bead Blasting in Manufacturing?
In manufacturing, bead blasting is employed to finish metal parts, enhancing both their aesthetic appeal and functional performance. This gentler method allows for precise control over surface texture, reducing wear on machinery. B2B buyers must evaluate suppliers based on their ability to deliver consistent results and provide technical support, which is essential for maintaining production quality and efficiency.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘bead blasting vs sandblasting’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Choosing the Right Process for Surface Preparation
The Problem: Many B2B buyers grapple with selecting the appropriate abrasive blasting technique for their specific application. For instance, a manufacturer in Saudi Arabia may need to clean heavily rusted metal parts but is uncertain whether to use sandblasting for its aggressive cleaning capabilities or bead blasting for a gentler finish. This indecision can lead to suboptimal results, increased costs, or even damage to the materials being processed.
The Solution: To make an informed choice, buyers should conduct a thorough assessment of their surface preparation needs. Start by evaluating the condition of the materials: if they are heavily rusted or coated with thick paint, sandblasting may be the better option due to its aggressive nature. Conversely, if the goal is to achieve a polished finish without damaging the underlying material, bead blasting would be more suitable. It’s crucial to collaborate with experienced suppliers who can provide samples and trial runs, allowing for real-world testing before committing to a large-scale project. Additionally, consider the long-term implications of each process, such as maintenance costs and the need for rework, which can significantly affect overall project budgets.
Scenario 2: Managing Safety and Environmental Compliance
The Problem: In regions like Nigeria and the Middle East, stringent safety regulations regarding airborne contaminants and worker health pose significant challenges for companies utilizing abrasive blasting methods. Sandblasting, in particular, generates silica dust, which can lead to serious health issues and requires adherence to strict environmental regulations. Buyers may be hesitant to proceed with sandblasting due to these potential liabilities.
The Solution: Buyers can mitigate these concerns by opting for bead blasting, which produces no silica dust and is generally considered a safer alternative. When choosing between processes, it’s essential to engage with suppliers who prioritize safety and compliance. Request documentation demonstrating adherence to local and international regulations, as well as training programs for workers involved in abrasive blasting operations. Implementing proper ventilation systems and personal protective equipment (PPE) will further enhance workplace safety. For buyers committed to sustainability, focusing on suppliers that utilize eco-friendly media for blasting can also help align their operations with environmental goals.
Scenario 3: Balancing Cost-Effectiveness with Quality
The Problem: Cost pressures are a constant concern for B2B buyers in competitive markets, particularly in regions like South America and Europe. Buyers may find themselves weighing the cost differences between sandblasting and bead blasting, unsure which method provides the best value for their specific applications. A common dilemma is whether the lower initial costs of sandblasting justify its potential for higher long-term maintenance and rework expenses.
The Solution: To effectively balance cost and quality, buyers should focus on the total cost of ownership rather than just initial expenses. Conduct a cost-benefit analysis that includes the initial setup costs, labor expenses, and the potential for rework or damage to components. While sandblasting may appear cheaper upfront, the risk of surface damage and the need for additional finishing steps can inflate overall costs. In contrast, bead blasting may have higher initial costs but can offer a more refined finish with less risk of damage, resulting in lower maintenance costs over time. Engaging with suppliers to obtain detailed quotes that break down all associated costs can provide greater transparency and aid in making a well-informed decision.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for bead blasting vs sandblasting
What Are the Key Properties of Common Materials Used in Bead Blasting and Sandblasting?
When selecting materials for bead blasting or sandblasting, understanding the properties of the substrates involved is crucial. Here, we analyze four common materials: steel, aluminum, concrete, and glass, focusing on their performance characteristics, advantages, disadvantages, and specific considerations for international B2B buyers.
Steel: The Durable Workhorse
Key Properties: Steel is known for its high tensile strength and durability. It can withstand high temperatures and pressures, making it suitable for heavy-duty applications. Its corrosion resistance can be enhanced with coatings, but untreated steel is susceptible to rust.
Pros & Cons: Steel’s durability makes it ideal for applications requiring robust surface preparation. However, sandblasting can be overly aggressive, potentially leading to pitting or surface damage. Bead blasting, while gentler, may not be as effective for heavy rust removal.
Impact on Application: Steel surfaces benefit from both methods but require careful consideration of the abrasive media used. Sandblasting is effective for removing heavy coatings, while bead blasting is better for achieving a polished finish.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers from regions like Saudi Arabia and Nigeria should be aware of local regulations regarding dust emissions from sandblasting, as silica dust poses health risks. Compliance with standards like ASTM or DIN for surface preparation is essential.
Aluminum: The Lightweight Champion
Key Properties: Aluminum is lightweight, corrosion-resistant, and has good thermal conductivity. It is often used in applications where weight savings are critical, such as in aerospace and automotive industries.
Pros & Cons: Bead blasting is preferred for aluminum as it provides a smooth finish without damaging the surface. Sandblasting can be too aggressive, leading to surface roughness and potential structural weaknesses.
Impact on Application: Bead blasting effectively removes oxidation and prepares aluminum for painting or anodizing. Sandblasting may be less suitable due to the risk of surface damage.
Considerations for International Buyers: In Europe, adherence to environmental regulations regarding the use of aluminum in manufacturing is critical. Buyers should also consider the availability of specific bead blasting media that comply with local standards.
Concrete: The Construction Standard
Key Properties: Concrete is a strong, durable material commonly used in construction. It is resistant to compression but can be susceptible to surface wear and degradation over time.
Pros & Cons: Sandblasting is effective for removing surface contaminants and preparing concrete for coatings. However, it can lead to micro-cracking if not used carefully. Bead blasting offers a gentler approach, reducing the risk of damage.
Impact on Application: For concrete surfaces, sandblasting is often the go-to method for heavy-duty cleaning, while bead blasting is better for finishing touches.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers in regions with stringent construction standards should ensure compliance with local building codes and environmental regulations when selecting blasting methods.
Glass: The Fragile Finisher
Key Properties: Glass is brittle and requires careful handling. It is commonly used in decorative applications and requires a delicate approach to surface finishing.
Pros & Cons: Bead blasting is the preferred method for glass as it provides a smooth finish without causing breakage. Sandblasting, however, can easily damage glass surfaces.
Impact on Application: Bead blasting allows for intricate designs and finishes on glass, making it suitable for artistic applications. Sandblasting is generally avoided due to the risk of shattering.
Considerations for International Buyers: For buyers in the Middle East and Africa, understanding local market preferences for glass products is essential. Compliance with safety standards for handling and processing glass is also critical.
Summary Table of Material Selection for Bead Blasting vs Sandblasting
| Material | Typical Use Case for bead blasting vs sandblasting | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Steel | Heavy industrial applications requiring surface preparation | High durability and strength | Risk of pitting with sandblasting | Medium |
| Aluminum | Aerospace and automotive components needing weight reduction | Smooth finish with bead blasting | Sandblasting can weaken surface | Medium |
| Concrete | Construction surfaces needing cleaning and preparation | Effective for heavy-duty cleaning | Risk of micro-cracking with sandblasting | Low |
| Glass | Decorative items and artistic applications | Delicate finishing without damage | Sandblasting can shatter glass | High |
This guide provides a strategic overview for B2B buyers to make informed decisions on material selection for bead blasting and sandblasting, ensuring compliance with international standards and regulations.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for bead blasting vs sandblasting
What Are the Key Manufacturing Processes for Bead Blasting and Sandblasting?
Understanding the manufacturing processes for bead blasting and sandblasting is essential for B2B buyers looking to select the right surface preparation technique for their specific applications. Both processes share similarities but differ significantly in execution, materials used, and end results.
How Is Material Prepared for Bead Blasting and Sandblasting?
The preparation phase is critical in both bead blasting and sandblasting. This stage involves cleaning and inspecting the surfaces to be treated. For bead blasting, surfaces are typically cleaned of contaminants such as oil, grease, or dirt to ensure optimal adhesion and results. In contrast, sandblasting may involve a more extensive initial cleaning due to its aggressive nature, particularly when dealing with heavily rusted or coated surfaces.
What Are the Forming Techniques Used in Bead Blasting and Sandblasting?
Once materials are prepared, they undergo forming processes. In bead blasting, materials are usually subjected to a low-pressure blast of glass beads, which gently abrade the surface without causing significant material removal. This technique is ideal for achieving a smooth finish on metals such as aluminum or stainless steel. Conversely, sandblasting employs high-pressure jets of abrasive materials like silica sand or aluminum oxide, making it suitable for removing thick layers of paint, rust, or other stubborn contaminants. The choice of technique will significantly affect the final surface quality and integrity.
How Does the Assembly Stage Differ Between Bead Blasting and Sandblasting?
In many cases, the assembly stage may not be directly impacted by the blasting method itself, but the choice between bead blasting and sandblasting can influence subsequent assembly processes. For instance, components that have undergone bead blasting may have a smoother finish, making them easier to assemble and fit together without additional machining. In contrast, parts that have been sandblasted may require additional finishing processes to achieve the desired tolerances and surface quality.
What Finishing Techniques Are Commonly Used After Bead Blasting and Sandblasting?
The finishing stage is where the differences between bead blasting and sandblasting become more pronounced. Bead blasting results in a polished surface that is often ready for coating or painting with minimal additional work. This is particularly beneficial for aesthetic applications or components that require a specific finish. Sandblasting, while effective at preparing surfaces, often leaves a rougher texture that may necessitate additional grinding or polishing to achieve a satisfactory finish before further processing.
What Quality Assurance Measures Are Critical in Bead Blasting and Sandblasting?
Quality assurance (QA) is paramount in ensuring that the blasting processes meet the required standards and specifications. For B2B buyers, understanding the QA measures in place can help mitigate risks associated with defective products.
Which International Standards Should B2B Buyers Consider for Blasting Processes?
International standards such as ISO 9001 play a significant role in the quality assurance of bead blasting and sandblasting processes. These standards provide a framework for consistent quality management systems, ensuring that suppliers maintain high-quality practices. Industry-specific certifications, such as CE marking for European markets or API standards for oil and gas applications, are also essential for verifying compliance with regional regulations.
What Are the Key Quality Control Checkpoints in Bead Blasting and Sandblasting?
Quality control checkpoints are integral to both bead blasting and sandblasting processes. Typically, these checkpoints include:
- Incoming Quality Control (IQC): This involves inspecting raw materials and abrasive media to ensure they meet specified standards before production begins.
- In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): During the blasting process, operators should conduct regular checks to monitor parameters such as pressure, abrasive flow rate, and surface cleanliness. This ensures that any deviations from the set standards are identified and corrected promptly.
- Final Quality Control (FQC): After the blasting process, a thorough inspection is performed to assess the surface finish and ensure it meets the required specifications. This may involve visual inspections, surface roughness measurements, and adherence to industry standards.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control Practices?
B2B buyers should take proactive steps to verify the quality control practices of potential suppliers. This can be achieved through:
- Audits: Conducting on-site audits of suppliers can provide insight into their operational practices, quality management systems, and adherence to international standards.
- Quality Reports: Requesting detailed quality reports, including testing results and compliance certifications, can help buyers assess the reliability of the supplier’s processes.
- Third-Party Inspections: Engaging third-party inspection agencies to evaluate the supplier’s processes and outputs can provide an unbiased assessment of quality and adherence to standards.
What Are the Nuances of Quality Control for International B2B Buyers?
For international B2B buyers, particularly in regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, understanding the nuances of quality control is vital. Different regions may have varying standards and regulations that impact the quality assurance processes. For instance, buyers in the European Union must ensure compliance with CE regulations, while those in the Middle East may need to adhere to specific local standards.
Additionally, cultural differences in business practices can affect how quality assurance is perceived and implemented. Buyers should foster open communication with suppliers to ensure mutual understanding of quality expectations and standards, which can help bridge any gaps that may arise due to regional differences.
In conclusion, selecting between bead blasting and sandblasting requires a comprehensive understanding of the manufacturing processes and quality assurance measures in place. By considering the nuances of each method and the associated quality standards, B2B buyers can make informed decisions that align with their specific application needs and regulatory requirements.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘bead blasting vs sandblasting’
When considering the procurement of bead blasting or sandblasting services, it’s essential to have a structured approach to ensure you make informed decisions. This guide provides a checklist to help international B2B buyers navigate the complexities of selecting the right blasting method and supplier for their specific needs.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Establishing clear technical specifications is vital for determining whether bead blasting or sandblasting is appropriate for your application. Consider the materials you need to treat, the desired finish, and the level of surface preparation required. For instance, if you require a polished finish on delicate components, bead blasting may be preferable.
Step 2: Assess the Application Requirements
Evaluate the specific applications for which you need blasting services. Different industries may have unique requirements, such as aerospace or automotive, where surface integrity is critical. Identify whether you need to remove heavy coatings, rust, or achieve a smooth finish, as this will influence your choice between the two methods.
Step 3: Research and Shortlist Potential Suppliers
Conduct thorough research to identify suppliers who specialize in either bead blasting or sandblasting. Look for companies with a strong reputation in your industry and gather a list of potential candidates. Pay attention to their experience, the range of services offered, and their geographical reach, particularly in regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe.
Step 4: Verify Supplier Certifications and Compliance
Ensure that the suppliers you are considering have the necessary certifications and comply with local and international safety regulations. This is particularly important for sandblasting, which can produce harmful silica dust. Look for certifications like ISO or environmental compliance that demonstrate a commitment to safety and quality standards.
Step 5: Request and Evaluate Quotes
Once you have a shortlist of suppliers, request detailed quotes that outline the costs associated with both bead blasting and sandblasting services. Compare the quotes not only on price but also on the services included, such as surface preparation techniques and any additional finishing options. Ensure that the quotes reflect your technical specifications and application requirements.
Step 6: Conduct On-site Visits or Virtual Tours
If possible, arrange on-site visits to the suppliers’ facilities or request virtual tours. This allows you to assess their capabilities, cleanliness, and adherence to safety protocols. Observing their equipment and processes can provide valuable insights into their operational standards and help you gauge their expertise.
Step 7: Gather References and Testimonials
Before making a final decision, ask suppliers for references or testimonials from previous clients, especially those in similar industries. This can give you a better understanding of their reliability, quality of work, and customer service. Engaging with past clients can also provide insights into any challenges you may face and how the supplier addressed them.
By following this checklist, B2B buyers can make informed decisions when sourcing bead blasting or sandblasting services, ensuring that they choose the right method and supplier to meet their specific needs.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for bead blasting vs sandblasting Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components for Bead Blasting and Sandblasting?
Understanding the cost structure of bead blasting and sandblasting is essential for international B2B buyers looking to make informed sourcing decisions. Each process involves various cost components, including materials, labor, manufacturing overhead, tooling, quality control (QC), logistics, and profit margins.
Materials: The primary difference in materials used significantly affects pricing. Sandblasting typically employs cheaper abrasives like silica sand or aluminum oxide, making it a more cost-effective option for heavy-duty applications. In contrast, bead blasting utilizes glass beads, which are generally more expensive but provide a gentler finish. This difference can influence the overall cost, especially for large volume orders.
Labor: Labor costs can vary based on the complexity and duration of the blasting process. Sandblasting often requires more aggressive techniques and thus may necessitate skilled labor for effective execution, potentially increasing labor costs. Bead blasting, while gentler, may still require trained personnel to achieve the desired finish, impacting labor expenses differently.
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes the costs associated with equipment maintenance, facility expenses, and utilities. Sandblasting setups might incur higher overhead due to the need for more robust equipment to handle the aggressive materials used. Conversely, bead blasting equipment may have lower maintenance costs, reflecting in a more favorable overhead structure.
Tooling: The tooling costs can also differ. Sandblasting might require more frequent replacement of nozzles and other components due to wear from harsh abrasives. Bead blasting equipment, while possibly having higher initial costs, may require less frequent replacements, influencing long-term cost considerations.
Quality Control (QC): Ensuring the quality of the blasting process is critical, particularly when dealing with precision applications. The costs associated with QC can vary depending on the chosen method. Bead blasting usually requires rigorous quality checks to ensure the surface finish meets industry standards, which could add to the overall costs.
Logistics: Transportation and handling of materials also play a significant role. The weight and fragility of the abrasive materials used in bead blasting may increase shipping costs compared to the more durable materials used in sandblasting. Additionally, international buyers must consider customs duties and regulations, especially in regions like Africa and the Middle East.
Margin: Finally, suppliers will incorporate their profit margins into the pricing structure. Understanding the market dynamics and competitive landscape can help buyers gauge reasonable margins for their specific sourcing needs.
How Do Price Influencers Impact Bead Blasting and Sandblasting Costs?
Several factors influence the pricing of bead blasting and sandblasting, including volume, specifications, material quality, and supplier reliability.
Volume/MOQ: Suppliers often offer tiered pricing based on the quantity ordered. Higher volumes typically lead to lower per-unit costs. Buyers should assess their needs to take advantage of bulk pricing opportunities, especially in regions with high demand.
Specifications and Customization: Custom requirements may lead to increased costs. Buyers should clearly outline their specifications to avoid unexpected expenses. Unique project needs can necessitate additional tooling or processes, impacting the overall price.
Materials: The type and quality of abrasives used significantly affect pricing. Buyers should evaluate the trade-offs between cost and quality, particularly when long-term performance and surface finish are critical.
Quality and Certifications: Suppliers with industry certifications or higher quality standards may charge a premium. However, this investment can lead to better long-term results and reduced maintenance costs.
Supplier Factors: Reliability and experience of the supplier can also influence pricing. Established suppliers may offer better service and quality assurance, which can justify higher costs.
Incoterms: Understanding the terms of shipping and delivery is crucial for international transactions. Incoterms dictate responsibilities and costs associated with transporting goods, which can affect the total landed cost.
What Are the Best Buyer Tips for Cost-Efficiency in Bead Blasting and Sandblasting?
For international buyers, especially from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, it is essential to navigate the nuances of sourcing effectively. Here are some tips for achieving cost-efficiency:
-
Negotiate Terms: Don’t hesitate to negotiate prices, especially for large orders. Building a relationship with suppliers can lead to better pricing and terms over time.
-
Consider Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Evaluate the TCO rather than just the initial price. This includes maintenance, operational costs, and potential downtime. A slightly higher upfront cost may result in lower long-term expenses.
-
Research Local Suppliers: Engaging with local suppliers can reduce logistics costs and improve lead times. Understanding local market conditions can also lead to better pricing strategies.
-
Stay Informed on Pricing Trends: Regularly monitor market trends for abrasives and blasting services to anticipate price fluctuations.
-
Be Clear on Requirements: Clearly define project specifications and requirements to avoid scope creep and associated costs.
Disclaimer: The prices for bead blasting and sandblasting services can vary widely based on the factors mentioned above. Buyers should conduct thorough market research and obtain multiple quotes to ensure they are getting competitive pricing.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing bead blasting vs sandblasting With Other Solutions
Exploring Alternatives to Bead Blasting and Sandblasting
When selecting surface preparation methods, it is essential to consider alternatives that may offer unique benefits or efficiencies. Bead blasting and sandblasting are both established techniques, but other solutions may provide better performance, cost-effectiveness, or specific application advantages. This section compares bead blasting and sandblasting against two viable alternatives: dry ice blasting and chemical stripping.
Comparison Table
| Comparison Aspect | Bead Blasting Vs Sandblasting | Dry Ice Blasting | Chemical Stripping |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | Effective for light to moderate coatings; less aggressive than sandblasting | Excellent for removing contaminants without damage; non-abrasive | Highly effective for heavy coatings; may require multiple applications |
| Cost | Moderate; lower than sandblasting due to less abrasive material used | Higher initial cost due to equipment and media | Variable; depends on chemicals used and application scale |
| Ease of Implementation | Moderate; requires skilled operators | Requires specialized equipment and training | Generally easy; can often be applied by unskilled labor |
| Maintenance | Moderate; equipment requires regular checks | High; equipment must be maintained to avoid breakdowns | Low; once applied, requires minimal upkeep |
| Best Use Case | Ideal for polishing and cleaning delicate surfaces | Best for sensitive components or environments needing non-abrasive methods | Suitable for heavy-duty industrial applications with thick coatings |
Detailed Breakdown of Alternatives
What Are the Advantages of Dry Ice Blasting?
Dry ice blasting utilizes solid carbon dioxide pellets as the abrasive medium. This method is non-abrasive, which makes it highly suitable for cleaning delicate surfaces without causing damage. The process is environmentally friendly, as it produces no secondary waste. However, the initial investment for dry ice blasting equipment can be high, and it requires specialized training for operators to ensure effective use. Additionally, it may not be as effective for removing heavy rust or multiple layers of paint as sandblasting.
How Does Chemical Stripping Compare?
Chemical stripping involves applying solvents or chemical agents to dissolve coatings. This method is particularly advantageous for heavy-duty applications where thick layers of paint or rust are present. It is relatively easy to implement, requiring minimal specialized equipment. However, it can pose safety risks due to the use of volatile chemicals, necessitating stringent safety measures and potentially leading to environmental concerns. Moreover, the effectiveness of chemical stripping can vary based on the type of coating and may require multiple applications for complete removal.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Surface Preparation Method
When deciding between bead blasting, sandblasting, and alternative methods, B2B buyers should evaluate their specific needs, including the type of surface, the desired finish, and budget constraints. Bead blasting and sandblasting provide reliable performance for various applications, while dry ice blasting and chemical stripping offer unique benefits that may be better suited for particular tasks. By understanding the strengths and limitations of each method, buyers can make informed decisions that align with their operational requirements and long-term goals.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for bead blasting vs sandblasting
What Are the Key Technical Properties of Bead Blasting and Sandblasting?
When comparing bead blasting and sandblasting, several critical technical properties define each process and their suitability for various applications. Understanding these specifications is essential for B2B buyers to make informed decisions.
-
Material Grade
– Bead blasting typically utilizes soda-lime glass beads, while sandblasting may employ materials like aluminum oxide or silicon carbide. The choice of material affects the process’s aggressiveness and surface finish. For instance, glass beads provide a smoother finish, making them ideal for delicate surfaces, while harder materials in sandblasting are better for heavy-duty cleaning tasks. This specification is vital for industries requiring precise surface finishes, such as aerospace or automotive. -
Abrasive Size
– The size of the abrasive particles influences the effectiveness and outcome of both blasting processes. Bead blasting generally uses larger glass beads (typically 0.1 to 0.5 mm), which yield a gentler impact, suitable for polishing. In contrast, sandblasting employs finer abrasive materials for more aggressive material removal. Understanding abrasive size helps buyers select the appropriate process for their specific cleaning or finishing needs. -
Air Pressure
– Bead blasting operates at lower air pressures compared to sandblasting. This lower pressure results in a gentler application, reducing the risk of surface damage. For industries where preserving the integrity of the material is crucial, such as in the manufacturing of precision parts, this property becomes significant. Buyers should assess the required air pressure for their specific applications to prevent unintended damage during surface preparation. -
Surface Roughness
– The outcome of each blasting process is often evaluated by the surface roughness it achieves. Sandblasting typically results in a rougher finish, making it suitable for applications requiring strong adhesive bonds for coatings. Conversely, bead blasting offers a smoother surface, which is advantageous for aesthetic applications or where a polished look is desired. Understanding surface roughness is essential for buyers in industries like construction, automotive, and consumer goods. -
Cleaning Effectiveness
– The effectiveness of each process varies based on the type of contaminants being removed. Sandblasting excels at removing heavy rust and thick coatings, making it the preferred choice for heavy-duty applications. On the other hand, bead blasting is effective for cleaning and polishing surfaces without removing significant material. Buyers must consider the type of surface and contaminants involved in their projects to choose the most effective blasting method.
What Are Common Trade Terms Related to Bead Blasting and Sandblasting?
Familiarity with industry terminology is crucial for B2B buyers when navigating procurement and supplier communications.
-
OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
– This term refers to companies that produce parts or equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer. In the context of blasting, OEMs often require specific surface finishes to meet quality standards. Understanding OEM specifications helps buyers ensure compatibility and quality in their supply chain. -
MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
– MOQ refers to the smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell. For buyers in the blasting industry, knowing the MOQ can help manage inventory costs and ensure that they meet production requirements without overcommitting resources. -
RFQ (Request for Quotation)
– An RFQ is a document sent to suppliers requesting pricing information for specific products or services. When considering bead blasting or sandblasting services, an RFQ helps buyers gather competitive quotes, ensuring they receive the best value for their investments. -
Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
– These are a set of predefined international trade terms that clarify the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in the shipping process. Understanding Incoterms is essential for B2B buyers involved in international procurement, as they dictate how costs and risks are shared during shipping. -
Surface Preparation
– This term encompasses all the processes involved in preparing a surface for further treatment, such as painting or coating. In the context of bead blasting and sandblasting, effective surface preparation is critical for achieving optimal adhesion and finish quality, making it a key consideration for buyers.
By understanding these technical properties and trade terms, B2B buyers can make informed decisions that align with their specific needs in the bead blasting and sandblasting markets.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the bead blasting vs sandblasting Sector
What Are the Key Market Dynamics in Bead Blasting and Sandblasting?
The bead blasting and sandblasting sectors are experiencing transformative growth driven by a combination of technological advancements and evolving industrial demands. Globally, the increasing emphasis on surface preparation in manufacturing, construction, and automotive industries is propelling the demand for these abrasive blasting techniques. Key markets in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe are particularly active, influenced by rapid urbanization and infrastructure development. For instance, countries like Nigeria and Saudi Arabia are investing heavily in construction, leading to a surge in demand for effective surface finishing solutions.
Emerging trends highlight the shift towards more sophisticated blasting technologies, such as automated and robotic systems, which enhance efficiency and precision. These innovations not only reduce labor costs but also minimize material waste, appealing to cost-sensitive international buyers. Additionally, the rise of Industry 4.0 practices is prompting businesses to seek integrated solutions that streamline operations and improve supply chain visibility. Buyers should consider suppliers that leverage data analytics to optimize their processes, thereby ensuring timely delivery and reducing downtime.
How Do Sustainability and Ethical Sourcing Impact Bead Blasting and Sandblasting?
Sustainability has become a pivotal concern in the bead blasting and sandblasting sectors, particularly as global regulations tighten around environmental impact. Sandblasting, which generates silica dust, poses health risks and has led to increased scrutiny and regulatory measures. In contrast, bead blasting is seen as a safer alternative, producing no silica dust and utilizing lead-free materials. B2B buyers are increasingly prioritizing suppliers who adhere to stringent environmental standards and can demonstrate compliance with local and international regulations.
Ethical sourcing is also gaining traction, with businesses striving to establish supply chains that reflect their commitment to sustainability. This includes sourcing abrasive materials that are recycled or manufactured with minimal environmental impact. Certifications such as ISO 14001, which focus on effective environmental management systems, are becoming essential for suppliers looking to differentiate themselves in a competitive marketplace. Buyers in regions like Europe and the Middle East are particularly inclined towards partnerships with suppliers that can provide evidence of sustainable practices and materials.
What Is the Historical Context of Bead Blasting and Sandblasting?
The origins of blasting techniques can be traced back to the late 19th century when sandblasting was first introduced as a method for surface cleaning and preparation. Initially used in construction and shipbuilding, it became a standard process for removing paint and rust from metal surfaces. Over time, the industry recognized the limitations of sandblasting, particularly its abrasive nature and health hazards associated with silica dust. This led to the development of bead blasting in the mid-20th century, which offered a gentler, more refined approach to surface finishing. Today, both methods continue to evolve, adapting to the changing needs of various industries and the increasing demand for sustainable practices.
Conclusion
For international B2B buyers, understanding the dynamics of bead blasting and sandblasting is crucial for making informed sourcing decisions. By focusing on market trends, sustainability, and the historical context of these techniques, buyers can identify reliable suppliers that align with their operational goals and ethical standards. As the landscape continues to evolve, staying abreast of these factors will ensure that businesses remain competitive and compliant in their respective markets.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of bead blasting vs sandblasting
-
1. How do I choose between bead blasting and sandblasting for my project?
Choosing between bead blasting and sandblasting largely depends on the specific requirements of your project. If you’re dealing with delicate surfaces or need a polished finish, bead blasting is the ideal choice as it uses gentler materials and lower pressure. Conversely, if you need to remove heavy rust, paint, or surface irregularities from tougher materials, sandblasting is more effective due to its aggressive nature. Always consider the material being treated and the desired finish to make the best decision. -
2. What are the safety considerations when using sandblasting and bead blasting?
Safety is paramount in both processes. Sandblasting can produce harmful silica dust, posing serious health risks if inhaled, leading to strict regulations in many regions. On the other hand, bead blasting is generally safer as it does not produce silica dust and uses lead-free materials. It’s essential to ensure that workers are equipped with appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE) and that safety measures are in place, especially in areas with stringent health regulations. -
3. What is the typical cost difference between bead blasting and sandblasting?
Generally, sandblasting tends to be more cost-effective than bead blasting due to the lower cost of abrasive materials like sand or aluminum oxide. However, the overall cost will depend on various factors such as the size of the project, equipment used, and the specific application. When budgeting, consider not just the material costs but also the potential need for additional surface finishing, which might be required after sandblasting. -
4. How can I ensure the quality of bead blasting or sandblasting services from suppliers?
To ensure quality, start by vetting suppliers through their certifications and industry experience. Request samples of previous work or customer testimonials to gauge their capabilities. Additionally, inquire about their quality assurance processes, including how they monitor the effectiveness of their blasting techniques and any post-treatment inspections they conduct. An ISO certification can also be a good indicator of a supplier’s commitment to quality. -
5. What are the logistics involved in sourcing blasting services internationally?
When sourcing blasting services internationally, consider the logistics of shipping parts to and from the service provider. Factor in lead times for transportation, customs clearance, and any potential tariffs or duties. It’s advisable to establish clear communication with your supplier about timelines and costs. Additionally, ensure that the supplier is familiar with the shipping regulations and standards in your region to avoid any compliance issues. -
6. Can bead blasting and sandblasting be customized for specific applications?
Yes, both bead blasting and sandblasting can be customized to meet specific application needs. Suppliers can adjust the type of abrasive material, pressure settings, and duration of the blasting process to achieve desired results. When discussing your project with potential suppliers, clearly outline your requirements and any specific challenges you face. A reputable supplier will be able to offer tailored solutions to meet your needs. -
7. What are the minimum order quantities (MOQs) for blasting services?
Minimum order quantities for blasting services can vary significantly based on the supplier and the nature of the work. Some suppliers may have low MOQs for small projects, while others may require larger quantities to justify setup costs. It’s important to clarify these details upfront to ensure that your project fits within the supplier’s capabilities and to avoid unexpected costs. -
8. What payment terms should I expect when engaging with international suppliers for blasting services?
Payment terms can vary widely among international suppliers. Common practices include upfront deposits, milestone payments, or payment upon completion. It’s essential to negotiate terms that protect both parties, especially considering currency exchange rates and potential international transaction fees. Always ensure that you have a clear agreement in writing to avoid misunderstandings and establish trust with your supplier.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.
Top 10 Bead Blasting Vs Sandblasting Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. Enviro-Tech Coatings – Coating and Metal Finishing Services
Domain: enviro-tech-coatings.com
Registered: 2012 (13 years)
Introduction: Enviro-Tech Coatings offers a wide range of coating, painting, and metal finishing services for various industries. Their services include: 1. Painting OEM parts 2. Metal finishing 3. Metal cleaning using glass beads, walnut shells, and ceramic media 4. Painting for steel and pipe fabricators 5. Fusion bonded epoxy for underground piping Additionally, they provide full surface reconditioning servi…
2. Glass Bead Blasting vs Sandblasting – Key Differences
Domain: reddit.com
Registered: 2005 (20 years)
Introduction: The discussion revolves around the differences between glass bead blasting and sandblasting for anodised aluminium. Key points include: 1. Glass bead blasting provides a smoother finish that hides machining marks and is easier to clean, while sandblasting results in a rougher, sandpaper-like texture that is difficult to clean. 2. The finish from glass bead blasting is closer to matte but shinier t…
3. RIE Coatings – Sandblasting & Bead Blasting Services
Domain: riecoatings.com
Registered: 1998 (27 years)
Introduction: RIE Coatings offers sandblasting and bead blasting services for surface preparation on aluminum and steel. Sandblasting is an aggressive technique used for heavy-duty applications like rust removal, while bead blasting is for precision cleaning and finishing. Sandblasting specifications include SS-PC-SP-SXX 9906020 and MIL-A-21380. Sandblasting uses aluminum oxide as an abrasive, which is durable …
4. Orchid – Sandblasting and Bead Blasting Solutions
Domain: orchid.ganoksin.com
Registered: 1996 (29 years)
Introduction: Sandblasting uses clean, sharp sand or other media like garnet, silicon carbide, aluminum oxide, propelled by high pressure air to abrade surfaces, removing more metal and leaving a dull matte finish. Bead blasting uses tiny round glass beads, which are lighter, softer, and rounder, resulting in less material removal and a matte to sparkling finish depending on bead size and air pressure. Sandblas…
5. Eziil – Bead Blasting Solutions
Domain: eziil.com
Registered: 2015 (10 years)
Introduction: Bead blasting is a surface finishing technique using small, spherical media (typically glass beads) to clean, deburr, and finish metal parts. Key media types include: 1. Glass Bead Blasting Media – Produces a smooth, satin-like finish while preserving surface details. 2. Ceramic Beads – More aggressive, suitable for faster cutting and removal of substantial contaminants. 3. Plastic Blasting Media …
6. Starblast – Matte Finish Blasting Media
Domain: 1911forum.com
Registered: 2000 (25 years)
Introduction: Sand blasting produces a very rough texture and gray color, while bead blasting results in a smooth texture and silver color. Aluminum oxide is preferred for stripping finishes and achieving a gray color. Dupont’s “Starblast” is recommended for a matte yet smooth finish. Bead blasting with fine media yields a uniform and smooth finish, preserving markings on the pistol. The grit size of blasting m…
7. Practical Machinist – Abrasive Materials for Stainless Steel Finishing
Domain: practicalmachinist.com
Registered: 2000 (25 years)
Introduction: 1. Aluminum Oxide Abrasive Material: Used for achieving a factory-like finish on stainless steel. 2. Glass Beads: Recommended for matching most factory matte stainless finishes. 3. Grit Sizes: 60 grit to 120 grit for glass beads; 70-80 grit for aluminum oxide. 4. Steel Wool: Extra fine steel wool used after blasting to reduce sharpness and minimize fingerprints. 5. WD40: Used in conjunction with s…
8. Precista – PRS-18
Domain: watchuseek.com
Registered: 2000 (25 years)
Introduction: The discussion revolves around the differences between sand blasted and bead blasted finishes. Bead blasting produces a more polished finish compared to sand blasting, which yields a coarser texture. The Precista PRS-18 is mentioned as having a ‘heavy’ bead blasted finish. Sand blasting is typically used for surface abrasion and cleaning, while bead blasting is used to clean or harden surfaces wit…
9. Abitl – Abrasive Blasting Solutions
Domain: abitl.com
Registered: 2000 (25 years)
Introduction: Abrasive blasting, also known as sandblasting, media blasting, or grit blasting, is a method of surface cleaning and preparation that modifies surfaces using various types of abrasives. Key types include: 1. Sand Blasting – Uses dry silica abrasive particles; effective for rust removal but poses health risks. 2. Wet Blasting – Injects water to control airborne dust; suitable for surfaces needing l…
10. ProBlast MN – Glass Bead Blasting Solutions
Domain: problastmn.com
Registered: 2008 (17 years)
Introduction: Glass Bead Blasting:
– Suitable for steel, stone, wood, fiberglass, aluminum, and concrete.
– Aggressive media with less than 2% embedment and no dust.
– Made from recycled bottles, cost-effective, and reusable.
– Silica-free and inert, environmentally friendly.
– Mohs Hardness: 6.
Garnet Sand Blasting:
– Made from crushed Almandite or Andradite deposits, available in various sizes.
– Can have …
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for bead blasting vs sandblasting
In the competitive landscape of surface finishing, understanding the distinctions between bead blasting and sandblasting is crucial for international B2B buyers. Bead blasting offers a gentler approach, ideal for applications requiring precision and minimal surface damage, making it suitable for industries where aesthetics and surface integrity are paramount. Conversely, sandblasting excels in aggressive cleaning and surface preparation, particularly for heavy-duty tasks that demand rapid results.
Strategic sourcing of these services can significantly impact operational efficiency and product quality. By aligning with suppliers who specialize in the appropriate blasting techniques, companies can optimize costs while ensuring compliance with safety regulations. Given the regulatory scrutiny surrounding sandblasting due to silica dust concerns, investing in bead blasting may also offer a safer and more sustainable option.
As you navigate your sourcing decisions, consider the specific needs of your operations. Engage with trusted suppliers in your region—be it in Africa, South America, the Middle East, or Europe—who can provide tailored solutions that align with your business objectives. The future of surface finishing is bright for those who choose wisely. Make informed choices today to enhance your competitive edge in the global market.