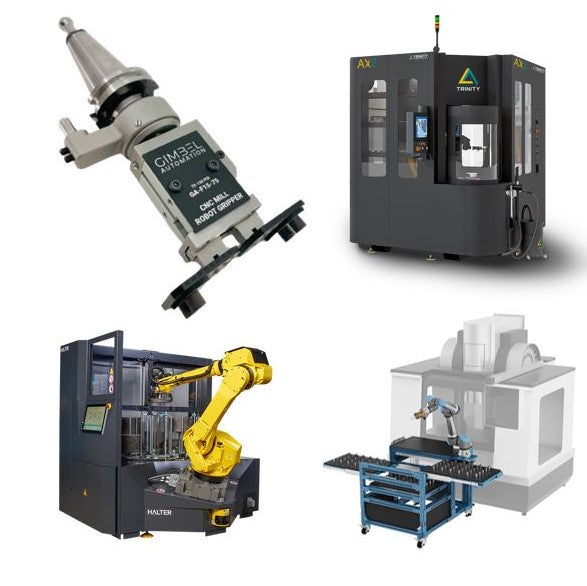
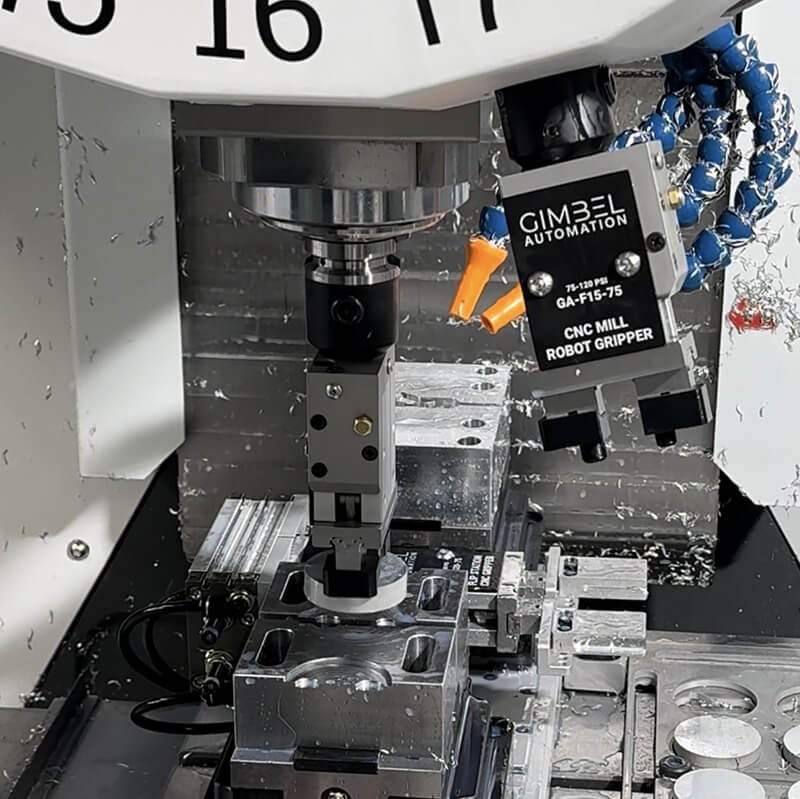
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for automated cnc machine
In today’s competitive landscape, sourcing automated CNC machines can be a daunting task for international B2B buyers. The complexity of the global market, combined with the need for efficiency and precision in manufacturing, presents a significant challenge for companies looking to enhance their production capabilities. This guide aims to demystify the process by providing a comprehensive overview of automated CNC machines, including various types, applications, and the latest technological advancements.
From vertical and horizontal mills to multi-axis solutions, understanding the diverse options available is crucial for making informed purchasing decisions. Additionally, we delve into the importance of supplier vetting, ensuring that buyers can identify reliable partners who meet their specific operational needs. Cost considerations are also addressed, equipping you with the necessary insights to navigate budget constraints while still achieving optimal production efficiency.
This guide is particularly beneficial for international B2B buyers from regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, including countries like Vietnam and Nigeria. By arming you with essential knowledge about sourcing, technology trends, and supplier selection, this resource empowers you to make strategic investments in automated CNC machines that will drive your business forward in an increasingly automated world.
Understanding automated cnc machine Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Vertical Machining Centers (VMC) | High-speed spindle, vertical orientation, and a variety of tool options | Aerospace, automotive parts, and mold making | Pros: Precision machining, versatile. Cons: Space-consuming, may require skilled operators. |
| Horizontal Machining Centers (HMC) | Horizontal spindle orientation, multi-axis capabilities, and automatic pallet changers | High-volume production, complex geometries | Pros: Efficient for large batches, improved chip removal. Cons: Higher initial investment. |
| 5-Axis CNC Machines | Ability to machine complex shapes with simultaneous movement on five axes | Aerospace, medical device manufacturing | Pros: High precision, reduces setup time. Cons: More complex programming and maintenance. |
| CNC Lathes | Rotating workpiece with stationary cutting tools, often includes live tooling | Shaft and cylindrical part manufacturing | Pros: Efficient for round parts, quick setup. Cons: Limited to rotational parts. |
| Robotic Automation Systems | Integration of robots for loading/unloading, high flexibility in production | Assembly lines, high-volume repetitive tasks | Pros: Increased efficiency, reduced labor costs. Cons: Initial setup complexity, requires integration expertise. |
What Are Vertical Machining Centers and Their B2B Relevance?
Vertical Machining Centers (VMC) are characterized by their vertically oriented spindle, which allows for precise machining of components. They are particularly suitable for industries such as aerospace and automotive, where intricate parts are common. When considering a VMC, B2B buyers should evaluate their production volume and the complexity of the parts to be machined, as these machines require skilled operators and adequate floor space.
How Do Horizontal Machining Centers Enhance Production Efficiency?
Horizontal Machining Centers (HMC) utilize a horizontal spindle and often come equipped with automatic pallet changers, making them ideal for high-volume production environments. They excel in machining complex geometries and are widely used in sectors like automotive and heavy machinery. Buyers should consider the initial investment against the potential for increased throughput and reduced cycle times, particularly in batch production scenarios.
Why Choose 5-Axis CNC Machines for Complex Machining Needs?
5-Axis CNC Machines enable simultaneous movement along five different axes, allowing for the creation of highly complex shapes in a single setup. This capability is crucial in industries like aerospace and medical device manufacturing, where precision is paramount. B2B buyers must assess their product requirements and programming capabilities, as these machines can be more challenging to operate and maintain compared to traditional CNC machines.
What Are the Advantages of CNC Lathes in Manufacturing?
CNC Lathes are designed for rotating workpieces, making them ideal for manufacturing cylindrical and shaft-like parts. They often include live tooling, which allows for additional operations without changing setups. This type of machine is particularly beneficial for manufacturers focused on producing high volumes of round parts. Buyers should evaluate their specific part requirements and consider the efficiency of setup times when investing in CNC lathes.
How Do Robotic Automation Systems Transform Manufacturing Processes?
Robotic Automation Systems integrate robotic arms into CNC machining processes for loading and unloading parts, significantly enhancing production efficiency. They are especially useful in assembly lines and environments requiring high-volume repetitive tasks. For B2B buyers, the initial complexity and cost of integrating these systems can be offset by the reduction in labor costs and the ability to maintain consistent quality in production.
Key Industrial Applications of automated cnc machine
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of automated cnc machine | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Aerospace | Precision component manufacturing | High accuracy and repeatability, reducing material waste | Compliance with strict industry standards and certifications |
| Automotive | Production of complex engine parts | Increased throughput and reduced labor costs | Availability of specialized tooling and fixtures |
| Medical Devices | Fabrication of surgical instruments and implants | Enhanced precision and reliability in critical applications | Need for biocompatible materials and regulatory compliance |
| Electronics | PCB manufacturing and assembly | Improved speed and efficiency in high-volume production | Capability to handle small, intricate components |
| Energy (Oil & Gas) | Machining of valves and fittings for pipelines | Greater durability and performance under high pressure | Consideration for materials that withstand harsh environments |
How Are Automated CNC Machines Used in the Aerospace Industry?
Automated CNC machines are integral to the aerospace sector, where precision is paramount. These machines are used to manufacture components such as turbine blades and fuselage parts, ensuring high accuracy and repeatability. This automation minimizes material waste and enhances production efficiency, which is critical in a highly competitive market. International buyers should consider sourcing machines that comply with strict aerospace standards, ensuring they can meet regulatory requirements in their respective regions.
What Role Do Automated CNC Machines Play in Automotive Production?
In the automotive industry, automated CNC machines are employed to produce complex engine components and chassis parts. These machines facilitate high-volume production with reduced labor costs, enabling manufacturers to meet increasing demand while maintaining quality. Buyers should focus on sourcing machines that can accommodate specialized tooling and fixtures, which are essential for producing diverse automotive parts efficiently.
How Are Automated CNC Machines Transforming Medical Device Manufacturing?
The medical device industry relies on automated CNC machines to fabricate surgical instruments and implants with high precision. These machines ensure reliability in critical applications, where any deviation can lead to severe consequences. Buyers in this sector must prioritize sourcing equipment that can work with biocompatible materials and adhere to stringent regulatory compliance standards, ensuring product safety and efficacy.
In What Ways Do Automated CNC Machines Enhance Electronics Manufacturing?
In the electronics sector, automated CNC machines are used for manufacturing printed circuit boards (PCBs) and assembling electronic components. These machines improve speed and efficiency, particularly in high-volume production environments, allowing manufacturers to keep pace with rapid technological advancements. When sourcing CNC machines, international buyers should ensure that the equipment can handle small, intricate components, which are increasingly common in modern electronics.
How Are Automated CNC Machines Beneficial in the Energy Sector?
Automated CNC machines are vital in the energy sector, particularly for machining valves and fittings used in oil and gas pipelines. These machines offer enhanced durability and performance under high pressure, which is essential for maintaining safety and efficiency in energy production. Buyers should consider sourcing machines that can work with materials capable of withstanding harsh environmental conditions, ensuring longevity and reliability in their applications.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘automated cnc machine’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Difficulty in Finding Skilled Operators for Automated CNC Machines
The Problem: In regions such as Africa and South America, businesses often struggle to find qualified operators for automated CNC machines. The shortage of skilled labor can lead to production delays, increased training costs, and a bottleneck in operational efficiency. Companies may invest heavily in automation technology, only to find that they lack the human resources necessary to leverage its full potential. This situation can be particularly frustrating for companies aiming to scale operations or improve productivity in a competitive market.
The Solution: To address this challenge, businesses should consider investing in comprehensive training programs for their current workforce. Partnering with local technical schools or universities can help develop a pipeline of skilled labor tailored to specific operational needs. Additionally, investing in user-friendly automation technology that includes intuitive interfaces and simplified programming can significantly reduce the learning curve for new operators. For instance, machines with built-in training modes or simulation software can enable employees to practice without the risk of damaging expensive equipment. Furthermore, implementing mentorship programs where experienced operators guide newcomers can foster a culture of continuous learning and skill development within the organization.
Scenario 2: High Maintenance Costs and Downtime of Automated CNC Machines
The Problem: Many companies face the challenge of high maintenance costs associated with their automated CNC machines. Frequent breakdowns can lead to significant downtime, affecting production schedules and ultimately harming profitability. In regions with limited access to spare parts or expert technicians, the situation becomes even more critical. Organizations may find themselves in a cycle of reactive maintenance rather than proactive care, leading to escalating costs and operational inefficiencies.
The Solution: To mitigate these issues, companies should adopt a preventive maintenance strategy tailored to their specific automated CNC machines. This includes regular inspections, timely replacement of wear parts, and utilizing monitoring systems that provide real-time data on machine performance. Investing in quality spare parts and establishing relationships with reliable suppliers can ensure that necessary components are readily available, minimizing downtime. Additionally, many manufacturers offer remote diagnostic tools that can help identify potential issues before they lead to significant failures. Training maintenance staff on these tools can empower them to perform diagnostics and repairs swiftly, further reducing the risk of prolonged disruptions.
Scenario 3: Integration Challenges with Existing Manufacturing Systems
The Problem: As businesses expand their operations and incorporate automated CNC machines, they often encounter difficulties in integrating these new systems with their existing manufacturing processes. This can lead to inefficiencies, data silos, and a lack of synchronization between different production stages. For companies in Europe and the Middle East, where technology adoption is crucial for maintaining competitive advantage, the inability to seamlessly connect new machines with legacy systems can significantly hinder productivity.
The Solution: To successfully integrate automated CNC machines into existing workflows, companies should conduct a thorough analysis of their current systems and identify compatibility issues early on. Working with manufacturers who provide comprehensive integration support can ease this transition. Consider adopting modular automation solutions that allow for gradual upgrades to existing systems rather than a complete overhaul. Additionally, investing in industry-standard communication protocols, such as OPC UA or MQTT, can facilitate smoother data exchange between machines and existing software systems. Employing a phased implementation approach, where new machines are tested in parallel with existing operations, can also reduce risks and ensure that integration is successful without disrupting ongoing production.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for automated cnc machine
When selecting materials for automated CNC machines, it is essential to consider their properties, advantages, and limitations. This analysis focuses on four common materials: aluminum, steel, titanium, and plastics. Each material offers unique characteristics that can significantly impact the performance and suitability of CNC machined components.
What Are the Key Properties of Aluminum in CNC Machining?
Aluminum is renowned for its lightweight and excellent corrosion resistance. It typically withstands temperatures up to 200°C and has a low density, making it an ideal choice for applications requiring reduced weight without sacrificing strength. Its thermal conductivity is also high, enabling efficient heat dissipation during machining processes.
Pros and Cons:
Aluminum is easy to machine, which reduces manufacturing complexity and costs. However, it can be less durable than other metals, particularly in high-stress applications. The cost of aluminum is generally moderate, making it accessible for various projects.
Impact on Application:
Aluminum is compatible with various media, including water and oils, making it suitable for diverse environments. However, its lower strength compared to steel may limit its use in heavy-duty applications.
Considerations for International Buyers:
B2B buyers from regions like Africa and South America should ensure compliance with international standards such as ASTM B221 for aluminum extrusions. Understanding local market conditions and sourcing options is crucial for cost-effective procurement.
How Does Steel Compare as a Material for CNC Machines?
Steel, particularly carbon steel, is favored for its high strength and durability. It can withstand extreme temperatures and pressures, making it suitable for heavy-duty applications. Steel’s corrosion resistance can be enhanced through various treatments, such as galvanization.
Pros and Cons:
Steel is highly durable and offers excellent wear resistance. However, it is heavier than aluminum, which may not be ideal for all applications. The manufacturing complexity can be higher due to the need for specialized tooling and machining techniques, resulting in a higher relative cost.
Impact on Application:
Steel is compatible with a wide range of media, including corrosive substances, when treated appropriately. Its strength makes it suitable for components subjected to high stress and fatigue.
Considerations for International Buyers:
International buyers should be aware of compliance with standards such as ASTM A36 for structural steel. Additionally, understanding local steel grades and sourcing practices is essential for effective supply chain management.
What Are the Benefits of Using Titanium in CNC Machining?
Titanium is known for its exceptional strength-to-weight ratio and outstanding corrosion resistance, particularly in harsh environments. It can withstand temperatures up to 600°C, making it suitable for high-performance applications.
Pros and Cons:
The key advantage of titanium is its strength and lightweight nature, which is ideal for aerospace and medical applications. However, it is more challenging to machine than aluminum or steel, leading to higher manufacturing costs and complexity.
Impact on Application:
Titanium’s compatibility with aggressive media, such as saltwater and acids, makes it a preferred choice for marine and chemical processing applications.
Considerations for International Buyers:
B2B buyers must consider compliance with standards like ASTM B348 for titanium. The higher cost of titanium can be a barrier, so understanding local market dynamics is crucial for effective budgeting.
How Do Plastics Fit into CNC Machining Applications?
Plastics, such as polycarbonate and nylon, are increasingly used in CNC machining due to their lightweight and versatility. They can withstand moderate temperatures and are resistant to many chemicals.
Pros and Cons:
Plastics are easy to machine and cost-effective, making them suitable for low-stress applications. However, they lack the strength and durability of metals, which may limit their use in high-performance environments.
Impact on Application:
Plastics are compatible with various media, including water and oils, but may not perform well under high temperatures or mechanical stress.
Considerations for International Buyers:
Buyers should ensure compliance with relevant standards such as ASTM D638 for plastic materials. Understanding the specific properties of different plastics is essential for selecting the right material for the application.
Summary of Material Selection for Automated CNC Machines
| Material | Typical Use Case for automated cnc machine | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Aluminum | Aerospace components, automotive parts | Lightweight and corrosion-resistant | Less durable under high stress | Medium |
| Steel | Structural components, heavy machinery | High strength and durability | Heavier and more complex to machine | High |
| Titanium | Aerospace, medical implants | Exceptional strength-to-weight ratio | Difficult to machine, high cost | High |
| Plastics | Prototyping, low-stress applications | Easy to machine and cost-effective | Lower strength and durability | Low |
This guide provides a comprehensive overview of material selection for automated CNC machines, helping international B2B buyers make informed decisions based on their specific needs and regional considerations.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for automated cnc machine
What Are the Main Stages of Manufacturing for Automated CNC Machines?
Manufacturing automated CNC machines involves a series of well-defined stages that ensure precision, efficiency, and quality. Understanding these stages can help B2B buyers make informed decisions about their suppliers and the machines they invest in.
How is Material Prepared for CNC Machining?
The first stage in the manufacturing process is material preparation. High-quality raw materials, often metal alloys or plastics, are sourced based on the specifications of the CNC machine being manufactured. This stage involves:
- Material Selection: Choosing the appropriate material is crucial. Factors like tensile strength, machinability, and corrosion resistance are considered.
- Cutting and Shaping: The raw materials are cut to size using saws or shears. This initial shaping is vital for optimizing the subsequent machining processes.
- Surface Treatment: Depending on the material, surface treatments such as coating or polishing may be applied to enhance durability and performance.
What Techniques Are Used in Forming CNC Machines?
The forming stage is where the bulk of machining occurs, utilizing advanced techniques to achieve the desired specifications. Key techniques include:
- CNC Milling: This process involves removing material from a workpiece using rotating cutters. CNC milling is essential for creating complex shapes and features with high precision.
- Turning: In this process, the workpiece rotates while a stationary cutting tool removes material. This is typically used for cylindrical components.
- Additive Manufacturing: Increasingly, some manufacturers are incorporating 3D printing techniques to create complex geometries that traditional methods cannot achieve.
How Are Automated CNC Machines Assembled?
Once the components are machined, assembly begins. This stage requires meticulous attention to detail to ensure that all parts fit together correctly. Key steps include:
- Component Inspection: Each part undergoes inspection to verify dimensions and tolerances before assembly.
- Assembly Techniques: Depending on the design, components may be assembled using mechanical fasteners, welding, or adhesive bonding.
- Integration of Automation Systems: For automated CNC machines, integrating robotic systems and control interfaces is crucial. This involves programming and testing to ensure seamless operation.
What Finishing Processes Are Commonly Used for CNC Machines?
Finishing processes enhance the machine’s appearance and functionality. Common finishing techniques include:
- Deburring: This removes sharp edges and imperfections from machined components, improving safety and performance.
- Coating: Applying protective coatings can prevent corrosion and wear, extending the machine’s lifespan.
- Final Inspection: After finishing, a comprehensive inspection ensures that the machine meets all specifications and quality standards.
What Quality Control Measures Are Essential for CNC Machine Manufacturing?
Quality assurance (QA) is vital in CNC machine manufacturing to ensure reliability and performance. A structured QA process typically includes several checkpoints and standards.
What International Standards Should B2B Buyers Be Aware Of?
For B2B buyers, understanding international quality standards is crucial. Relevant standards include:
- ISO 9001: This standard outlines the criteria for a quality management system, emphasizing customer satisfaction and continuous improvement.
- CE Marking: This certification indicates compliance with European safety and environmental requirements, making it essential for machines sold in the European market.
- API Standards: For industries like oil and gas, compliance with American Petroleum Institute standards is critical for ensuring safety and reliability.
What Are the Key Quality Control Checkpoints During Production?
Quality control checkpoints help maintain manufacturing standards throughout the production process. Common checkpoints include:
- Incoming Quality Control (IQC): This involves inspecting raw materials and components upon receipt to ensure they meet specified criteria.
- In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): During manufacturing, regular checks are performed to monitor the machining process, ensuring that tolerances are maintained.
- Final Quality Control (FQC): Before shipment, the finished product undergoes a thorough inspection to confirm it meets all specifications and quality standards.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control?
Ensuring that suppliers adhere to stringent quality control measures is essential for B2B buyers. Here are effective strategies to verify supplier QC:
What Are the Best Practices for Conducting Supplier Audits?
Conducting audits is a proactive way to assess a supplier’s quality processes. Key practices include:
- Scheduled Audits: Regular audits help ensure that suppliers consistently meet quality standards. These audits should cover processes, documentation, and compliance with international standards.
- Checklist-Based Evaluation: Use checklists to evaluate specific criteria, including material sourcing, manufacturing processes, and quality control measures.
How Can Buyers Utilize Quality Reports and Third-Party Inspections?
Quality reports provide insights into a supplier’s performance. Buyers should:
- Request Quality Reports: Ask for documentation that details the quality control processes and results, including any certifications.
- Engage Third-Party Inspectors: Utilizing third-party inspection services can provide an unbiased assessment of the supplier’s quality control practices, ensuring transparency and reliability.
What Are the Nuances of Quality Control for International B2B Buyers?
For international B2B buyers, understanding the nuances of quality control is crucial, particularly when sourcing from diverse regions such as Africa, South America, and the Middle East. Key considerations include:
- Cultural Differences: Different regions may have varying approaches to quality assurance. Understanding these differences can help buyers navigate supplier relationships more effectively.
- Regulatory Compliance: Buyers must ensure that suppliers comply with local regulations and international standards, which may vary significantly by region.
- Language Barriers: Clear communication is essential for effective quality control. Buyers should consider language proficiency when selecting suppliers to avoid misunderstandings.
By comprehensively understanding the manufacturing processes and quality assurance measures associated with automated CNC machines, B2B buyers can make informed decisions that enhance their operational efficiency and product quality.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘automated cnc machine’
This guide serves as a practical checklist for international B2B buyers seeking to procure automated CNC machines. With the growing demand for efficiency and precision in manufacturing, understanding the key steps in sourcing these machines can significantly impact operational success.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Understanding your specific needs is crucial before engaging with suppliers. Consider factors such as the types of materials you will be machining, the complexity of the parts, and the required precision levels. Additionally, define the size and capacity of the CNC machine necessary for your production volume. This clarity will help you communicate effectively with potential suppliers.
Step 2: Research Market Trends and Innovations
Stay informed about the latest advancements in CNC technology and automation systems. Look into trends such as Industry 4.0 integration, robotic automation, and flexible manufacturing systems. By understanding current market innovations, you can make informed decisions and identify machines that offer competitive advantages in productivity and efficiency.
Step 3: Evaluate Potential Suppliers
Before committing to a supplier, conduct thorough due diligence. Request comprehensive company profiles, including their history, technical expertise, and customer testimonials. Investigate their experience in your specific industry and seek references from similar businesses to gauge reliability and performance.
Step 4: Assess Compliance and Certifications
Verify that potential suppliers comply with international quality standards and possess relevant certifications, such as ISO 9001 or CE marking. These certifications indicate that the supplier adheres to recognized quality management practices. This step is crucial for ensuring that the machines you purchase meet safety and performance standards.
Step 5: Request Detailed Quotations and Comparisons
Once you have narrowed down potential suppliers, request detailed quotations that include pricing, delivery timelines, warranty terms, and post-sale support. Compare these quotations not only on cost but also on the value-added services offered, such as training and maintenance support. This comprehensive evaluation will help you make a more informed decision.
Step 6: Visit Manufacturing Facilities (if possible)
Whenever feasible, arrange to visit the supplier’s manufacturing facilities. This firsthand experience allows you to assess the production processes, quality control measures, and overall operational capabilities. Engaging directly with the supplier can also facilitate better communication and relationship building.
Step 7: Plan for Installation and Training
Consider the logistics of machine installation and the training required for your team. Discuss the supplier’s support for installation, calibration, and staff training to ensure a smooth transition. Proper training is essential for maximizing the capabilities of your new CNC machine, reducing downtime, and enhancing productivity from the outset.
By following these steps, B2B buyers can navigate the complexities of sourcing automated CNC machines effectively, ensuring they invest in technology that meets their operational needs and contributes to their competitive edge.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for automated cnc machine Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components in Automated CNC Machine Sourcing?
When sourcing automated CNC machines, understanding the cost structure is crucial for effective budgeting and negotiation. The primary cost components include:
-
Materials: High-quality materials significantly influence the machine’s durability and performance. Common materials include steel, aluminum, and specialized alloys that can enhance machining capabilities.
-
Labor: Skilled labor is essential for both the manufacturing process and ongoing maintenance of CNC machines. Labor costs can vary significantly based on geographic location and skill level.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This encompasses costs related to facilities, utilities, and administrative expenses associated with the production of CNC machines. Overhead can vary based on the manufacturer’s operational efficiency.
-
Tooling: Tooling costs include the necessary cutting tools, fixtures, and additional equipment that enable the CNC machine to perform various tasks. These costs can be substantial, particularly for machines designed for specialized applications.
-
Quality Control (QC): Ensuring the machines meet specified quality standards involves additional costs. This includes testing, inspection, and compliance with relevant certifications, which can vary by region and industry.
-
Logistics: Shipping and handling costs can add to the overall expenditure, especially for international buyers. Factors such as distance, shipping methods, and customs duties play a significant role in logistics costs.
-
Margin: Manufacturers typically include a margin in their pricing to cover risks and ensure profitability. This margin can fluctuate based on market conditions, demand, and competition.
How Do Price Influencers Affect Automated CNC Machine Costs?
Several factors can influence the pricing of automated CNC machines:
-
Volume/MOQ: Manufacturers often provide discounts for bulk orders or minimum order quantities (MOQs). Understanding the pricing structure related to order size can lead to significant savings.
-
Specifications and Customization: Customized machines tailored to specific operational needs can incur higher costs. Buyers should weigh the benefits of customization against the additional expense.
-
Materials: The choice of materials directly impacts the price. For instance, premium materials may enhance machine performance but also increase costs.
-
Quality and Certifications: Machines that meet higher quality standards or possess industry certifications may command higher prices. Buyers should assess whether the additional investment aligns with their operational requirements.
-
Supplier Factors: The reputation, reliability, and support offered by suppliers can also influence pricing. Engaging with established suppliers may provide better value through added services like training and maintenance.
-
Incoterms: The terms of shipping and delivery can significantly affect the final cost. Understanding Incoterms will help buyers anticipate additional costs such as insurance and customs duties.
What Tips Can Help Buyers Optimize Costs in CNC Machine Procurement?
For international B2B buyers, particularly from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, several strategies can enhance cost efficiency:
-
Negotiation: Always negotiate pricing and terms. Suppliers may have room for flexibility, especially for larger orders or long-term partnerships.
-
Focus on Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Evaluate not just the upfront cost but the TCO, which includes maintenance, operational efficiency, and potential downtime costs. A lower initial price may lead to higher long-term expenses.
-
Understand Pricing Nuances for International Buyers: Be aware of currency fluctuations, import tariffs, and local taxes that may affect the overall price when sourcing machines from international suppliers.
-
Research and Compare Suppliers: Take the time to compare multiple suppliers. Different manufacturers may offer various pricing structures, warranty terms, and support options that can impact overall value.
-
Plan for Future Needs: Consider scalability and adaptability when selecting CNC machines. Investing in machines that can grow with your business can save costs in the long run.
Disclaimer
Prices mentioned in this analysis are indicative and may vary based on the specific machine configurations, supplier negotiations, and market conditions. Always consult directly with suppliers for the most accurate and up-to-date pricing information.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing automated cnc machine With Other Solutions
Exploring Alternatives to Automated CNC Machines
In the landscape of modern manufacturing, businesses often seek solutions that optimize production efficiency and quality. While automated CNC machines have established themselves as a popular choice for precision machining, several alternatives exist that can also meet operational needs. Understanding these alternatives allows B2B buyers to make informed decisions that align with their specific requirements and budget constraints.
| Comparison Aspect | Automated CNC Machine | Robotic Workcells | Manual CNC Machining |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | High precision, repeatable results; can operate continuously. | High throughput with flexible programming for various tasks. | Variable precision; dependent on operator skill and fatigue. |
| Cost | Higher initial investment but lower operating costs over time. | Moderate initial setup cost; can be costly if highly customized. | Low initial investment; higher long-term labor costs. |
| Ease of Implementation | Requires significant training and integration time. | Moderate complexity; requires training for programming and maintenance. | Simple to set up, but relies heavily on skilled labor. |
| Maintenance | Regular maintenance needed; often requires specialized technicians. | Requires ongoing maintenance for robots and software updates. | Minimal maintenance; mostly operator-dependent. |
| Best Use Case | Ideal for high-volume, repetitive machining tasks. | Best for diverse production needs where flexibility is key. | Suitable for low-volume, custom jobs or prototyping. |
What Are the Advantages and Disadvantages of Robotic Workcells?
Robotic workcells represent a strong alternative to automated CNC machines, particularly in environments requiring versatility. These systems can handle a range of tasks from loading and unloading to assembly and inspection. The primary advantage of robotic workcells is their ability to adapt to different manufacturing processes without significant reconfiguration. However, they often come with moderate setup costs and require skilled operators for programming and maintenance, which can lead to increased operational complexity.
How Does Manual CNC Machining Compare?
Manual CNC machining is a traditional method that remains relevant for certain applications. Its primary advantage lies in its lower initial investment and simplicity of setup. This method allows for high levels of customization and is ideal for low-volume production or prototyping where precision is less critical. However, it is heavily reliant on skilled labor, which can introduce variability in product quality and lead to higher long-term costs due to labor expenses.
Conclusion: How to Choose the Right Solution for Your Manufacturing Needs
When evaluating the best manufacturing solution, B2B buyers should consider their specific operational goals, budgetary constraints, and the skill level of available workforce. Automated CNC machines are highly effective for high-volume, precision tasks but come with a higher upfront cost and complexity. Robotic workcells offer flexibility and efficiency for varied tasks, while manual CNC machining remains a viable option for low-volume, custom projects. By carefully analyzing these alternatives, businesses can select a solution that not only meets their immediate needs but also positions them for future growth and adaptability in an evolving manufacturing landscape.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for automated cnc machine
What Are the Key Technical Properties of Automated CNC Machines?
When considering the procurement of automated CNC machines, understanding their technical properties is crucial for ensuring that the selected equipment meets production needs. Here are several essential specifications that B2B buyers should prioritize:
-
Material Grade
The material grade of a CNC machine significantly affects its durability and performance. Common materials include cast iron, steel, and aluminum, each offering different strength and weight characteristics. A higher-grade material typically translates to better machine stability, reduced vibrations, and improved precision, which are vital for high-quality production. -
Tolerance Levels
Tolerance refers to the permissible limit of variation in a physical dimension. In CNC machining, tighter tolerances (e.g., ±0.001 inches) indicate higher precision. For industries like aerospace or medical devices, where exact specifications are critical, understanding tolerance levels is essential. Machines capable of maintaining tight tolerances reduce rework and waste, ultimately improving profitability. -
Axis Configuration
The number of axes in a CNC machine defines its ability to perform complex tasks. Standard configurations include 3-axis, 4-axis, and 5-axis systems. A 5-axis machine, for example, can machine parts from multiple angles without repositioning, enhancing productivity and precision. For businesses aiming for advanced manufacturing capabilities, investing in multi-axis machines can offer a competitive edge. -
Spindle Speed
Spindle speed, measured in revolutions per minute (RPM), is a critical factor influencing machining efficiency and surface finish. Higher spindle speeds allow for faster material removal rates, which can significantly reduce cycle times. However, buyers must also consider the material being machined, as different materials require specific spindle speeds for optimal results. -
Power Consumption
Power consumption is an important operational consideration, especially for businesses looking to minimize costs. Automated CNC machines vary in energy efficiency, and understanding the kilowatt requirements can help buyers assess long-term operating expenses. Selecting energy-efficient machines can lead to substantial savings over time, aligning with sustainability goals. -
Automation Features
Automation capabilities, such as robotic loading/unloading and pallet changers, enhance productivity by reducing manual intervention. Machines equipped with advanced automation features can operate continuously, improving throughput and allowing for lights-out manufacturing. For companies in competitive markets, investing in automation is essential for maximizing efficiency and minimizing labor costs.
What Are Common Trade Terms Related to Automated CNC Machines?
Understanding trade terminology is equally important for B2B buyers engaging in procurement. Here are several commonly used terms in the CNC machine industry:
-
OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
An OEM refers to a company that produces parts or equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer. In the CNC context, an OEM might produce the machine itself or specific components such as tool holders or spindle motors. Engaging with reputable OEMs ensures quality and compatibility with existing systems. -
MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ specifies the smallest quantity of products a supplier is willing to sell. For CNC machines and related parts, understanding MOQ is crucial for budget planning and inventory management. Buyers should negotiate MOQs that align with their production schedules to avoid excess inventory costs. -
RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a formal request sent to suppliers to obtain price quotes for specific products or services. In the CNC industry, RFQs help buyers evaluate multiple suppliers based on pricing, delivery times, and service options. Properly crafted RFQs can lead to better pricing and terms. -
Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
Incoterms define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in international transactions, particularly regarding shipping and delivery. Familiarity with Incoterms like FOB (Free on Board) or CIF (Cost, Insurance, and Freight) is vital for understanding liability and costs involved in transporting CNC machines. -
FMS (Flexible Manufacturing System)
An FMS is an integrated system that utilizes CNC machines along with automated material handling and storage systems. FMS enhances production flexibility, allowing manufacturers to adapt quickly to changing demands. Understanding FMS can help buyers explore advanced automation options for their operations. -
CNC Controller
The CNC controller is the brain of the machine, interpreting the programmed instructions and controlling the machine’s movements. Different controllers offer varying functionalities, such as ease of programming, user interface, and integration capabilities. Selecting a machine with a user-friendly CNC controller can reduce training time and increase operational efficiency.
By familiarizing themselves with these technical properties and trade terms, B2B buyers can make informed decisions that optimize their manufacturing processes and enhance their competitive position in the market.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the automated cnc machine Sector
What Are the Current Market Dynamics and Key Trends in the Automated CNC Machine Sector?
The global automated CNC machine market is being propelled by several key drivers, including the increasing demand for precision manufacturing and the need for higher operational efficiency. As industries across Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe strive to modernize their manufacturing processes, the adoption of automation technologies has become imperative. Notably, the rise of Industry 4.0, characterized by smart factories and interconnected devices, is reshaping how companies approach production. B2B buyers are increasingly looking for solutions that offer not only high precision but also flexibility and scalability to adapt to changing market demands.
Emerging technologies such as AI-driven analytics and IoT-enabled machines are enhancing decision-making processes and improving machine utilization rates. For instance, predictive maintenance powered by AI can significantly reduce downtime and improve overall productivity. Additionally, the trend towards modular automation systems allows manufacturers to customize their setups, thereby optimizing their workflows and reducing lead times. This adaptability is particularly appealing to international B2B buyers in regions like Nigeria and Vietnam, where rapid industrialization is occurring.
Moreover, the competitive landscape is witnessing an influx of innovative players offering diverse solutions, from integrated automation systems to standalone robots. This variety provides buyers with the opportunity to select machines that best fit their specific operational needs, ultimately driving down costs and enhancing productivity. As a result, understanding these market dynamics is crucial for B2B buyers seeking to invest in automated CNC machines.
How Is Sustainability Influencing Sourcing Decisions for Automated CNC Machines?
The importance of sustainability and ethical sourcing in the CNC machine sector cannot be overstated. As global awareness of environmental issues grows, B2B buyers are increasingly prioritizing suppliers that demonstrate a commitment to sustainable practices. This includes the use of eco-friendly materials, energy-efficient machines, and waste reduction strategies throughout the manufacturing process.
Ethical supply chains are becoming a key consideration, particularly for international buyers who are scrutinizing the practices of their suppliers. Certifications such as ISO 14001 for environmental management and adherence to international labor standards are now essential criteria in the supplier selection process. By opting for manufacturers that prioritize sustainability, companies can mitigate their environmental impact while enhancing their brand reputation in the marketplace.
Furthermore, there is a rising trend towards the use of ‘green’ materials in the production of CNC machines. Innovations in manufacturing processes, such as utilizing recycled materials or non-toxic substances, are gaining traction. Buyers are advised to seek out suppliers who not only provide high-quality machinery but also demonstrate a commitment to reducing their carbon footprint. This shift towards sustainable sourcing not only aligns with global environmental goals but can also lead to cost savings and improved operational efficiency.
What Is the Historical Context of Automated CNC Machines Relevant to Today’s B2B Landscape?
The evolution of automated CNC machines dates back to the mid-20th century when the introduction of numerical control (NC) systems revolutionized the manufacturing landscape. Initially, these machines operated on pre-programmed instructions, but advancements in technology led to the development of computer numerical control (CNC), allowing for greater precision and flexibility.
In the 1980s and 1990s, the integration of CAD/CAM software further enhanced the capabilities of CNC machines, enabling complex designs to be manufactured with ease. As industries began to realize the cost-saving potential of automation, the demand for CNC machines surged, leading to innovations in machine design and functionality.
Today, the focus has shifted towards automation that not only increases production efficiency but also integrates seamlessly with other smart technologies. This historical context is vital for B2B buyers as it highlights the continuous evolution of CNC machinery and the importance of investing in technology that will remain relevant in an increasingly automated future. Understanding these trends can provide valuable insights for making informed purchasing decisions that align with long-term business strategies.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of automated cnc machine
-
How do I choose the right automated CNC machine for my business needs?
Choosing the right automated CNC machine involves assessing your specific production requirements, including the types of materials you will work with, the complexity of the parts, and the desired output volume. Consider factors such as machine capabilities (e.g., milling, turning, 5-axis machining), integration with existing systems, and automation features like pallet changers or robotic arms. Additionally, consult with suppliers to understand their offerings and ask for demonstrations or case studies relevant to your industry. -
What factors should I consider when vetting suppliers of automated CNC machines?
When vetting suppliers, focus on their industry reputation, experience, and customer reviews. Check for certifications and compliance with international standards, which can indicate quality assurance. Evaluate their support services, including training, maintenance, and spare parts availability. Additionally, consider their ability to customize machines according to your needs and their responsiveness to inquiries, which reflects their customer service quality. -
What is the typical minimum order quantity (MOQ) for automated CNC machines?
The MOQ for automated CNC machines can vary significantly based on the manufacturer and the complexity of the machine. Some suppliers may offer a single unit for specialized machines, while others might set higher MOQs for standard models due to production efficiencies. It’s essential to discuss your requirements with potential suppliers to understand their policies and negotiate terms that suit your operational needs. -
What payment terms should I expect when purchasing automated CNC machines internationally?
Payment terms for international purchases typically include options such as advance payment, letter of credit, or staggered payments based on milestones (e.g., deposit upon order, balance before shipment). Be sure to clarify these terms with your supplier, as they can vary widely. Additionally, consider currency fluctuations and transaction fees, and explore payment protection options to mitigate risks associated with international trade. -
How can I ensure quality assurance (QA) for my CNC machines?
To ensure quality assurance, request documentation of the supplier’s QA processes, including certifications like ISO 9001. Ask for detailed specifications, test results, and inspection reports for the machines. It’s also beneficial to arrange for factory visits or virtual inspections to observe the manufacturing process. Establish a clear agreement on warranty terms and post-sale support, which can safeguard your investment. -
What are the logistics considerations for importing automated CNC machines?
Logistics for importing CNC machines involve several key considerations, including shipping methods (air vs. sea), customs clearance procedures, and duties/tariffs applicable in your country. Collaborate with freight forwarders experienced in machinery transport to ensure compliance with regulations. Additionally, plan for installation and setup at your facility, accounting for any special requirements like foundation work or electrical connections. -
Can I customize an automated CNC machine to fit my specific manufacturing processes?
Yes, many manufacturers offer customization options for automated CNC machines to accommodate specific manufacturing processes. Customizations can include software adaptations, tooling changes, and integration with existing systems. Discuss your requirements with suppliers early in the process to understand the feasibility of your requests and any associated costs or lead times. -
What are the advantages of integrating automation with CNC machining?
Integrating automation with CNC machining enhances productivity by reducing manual labor, increasing precision, and minimizing downtime. Automated systems, such as robotic arms and pallet changers, enable continuous operation, allowing for higher output and improved efficiency. This integration also supports better resource management, as it can lead to reduced waste and more consistent product quality, ultimately driving profitability for manufacturers.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.
Top 5 Automated Cnc Machine Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. Robotiq – Machine Tending Solution
Domain: blog.robotiq.com
Registered: 2006 (19 years)
Introduction: Robotiq Machine Tending Solution; integrates with CNC machines using the same buttons, lights, and switches as human operators; includes hardware and software elements for automation; Robotiq Machine Tending Configurator for application kit configuration; Machine Tending Wizard for software setup; suitable for various CNC machines including lathes, milling machines, routers, plasma cutters, laser …
2. Fastems – CNC Automation Solutions
Domain: fastems.com
Registered: 1996 (29 years)
Introduction: Fastems offers CNC automation solutions that reduce human intervention in manufacturing processes using machine tools. Key features include: 1. **Automation Systems**: Includes Milling Machine Automation, Turning Machine Automation, and other metalworking processes. 2. **CNC Supportive Processes**: Automates operations such as deburring, finishing, measuring, and marking. 3. **Production Planning …
3. DMG MORI – Automation Solutions for CNC Machines
Domain: us.dmgmori.com
Registered: 2013 (12 years)
Introduction: Automation of CNC Machines by DMG MORI focuses on enhancing economical production through automated processes. Key benefits include: 1. Easy to use – user-friendly interfaces and single-source supplier for machines and automation. 2. Proven technology – compatibility and process integration with existing systems. 3. Night shifts – machines can operate unmanned during off-hours. 4. Increased compet…
4. Halter CNC Automation – Robotic Loading Solutions
Domain: haltercncautomation.com
Registered: 2013 (12 years)
Introduction: Halter CNC Automation offers a range of robotic loading solutions for CNC machines, including: 1. Basic Pro 12 – Loading robot for turning and milling; workpiece diameter: 0.39″ – 5.31″; max load capacity: 26.45 lbs. 2. Universal Compact 12 – Covers workpieces up to 10.63″; max load capacity: 55.11 lbs / 77.16 lbs; max total weight on rotating table: 1653 lbs. 3. Universal Premium 25/35 – Workpiec…
5. Mazak – Advanced Manufacturing Solutions
Domain: mazak.com
Registered: 1998 (27 years)
Introduction: 5-Axis Machining Centers, Additive Manufacturing (AM), Automation, CNC Turning Centers, Friction Stir Welding (FSW), Horizontal Machining Centers, Multi-Tasking Machines, Swiss-Style Production Turning Machines, Vertical Machining Centers.
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for automated cnc machine
As the global manufacturing landscape evolves, strategic sourcing of automated CNC machines emerges as a pivotal factor in enhancing operational efficiency and competitiveness. By investing in advanced automation technologies, businesses can mitigate labor shortages, streamline production processes, and significantly reduce operational costs. Key takeaways include the importance of selecting reliable suppliers who offer integrated automation solutions, as well as the necessity of evaluating the total cost of ownership to maximize ROI.
For B2B buyers in regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, understanding the nuances of automation—ranging from robotics to flexible manufacturing systems—can unlock new avenues for growth. Emphasizing collaboration with suppliers who provide tailored solutions will not only address unique regional challenges but also support sustainable practices.
Looking ahead, the integration of cutting-edge CNC automation technologies will be essential for companies aiming to thrive in an increasingly competitive market. Now is the time to engage with industry leaders, explore innovative solutions, and position your business for success in the future of manufacturing. Embrace the potential of automation and start your journey towards enhanced productivity and profitability today.