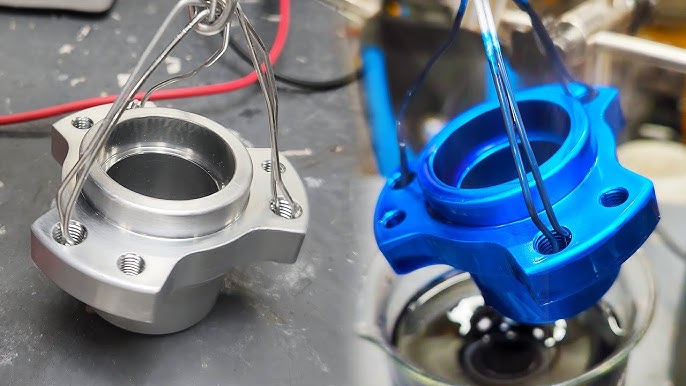
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for anodizing parts
In the competitive landscape of global manufacturing, sourcing high-quality anodized parts can pose significant challenges for international B2B buyers. With the need for enhanced durability, corrosion resistance, and aesthetic appeal, understanding the intricacies of anodizing processes becomes crucial. This guide delves deep into the world of anodizing parts, exploring various types such as Type II and Type III anodization, their applications across industries, and essential factors for supplier vetting.
By addressing critical considerations such as cost implications, production capabilities, and environmental impacts, this resource empowers buyers from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe—specifically Brazil and Nigeria—to make informed purchasing decisions. The anodizing process not only enhances the functionality of aluminum and other metals but also plays a vital role in achieving the desired visual effects for products.
As you navigate the complexities of sourcing anodized components, this guide will provide actionable insights and expert recommendations, ensuring that you partner with reputable suppliers who meet your specific requirements. Equip yourself with the knowledge to confidently procure anodized parts that align with your quality standards and operational needs.
Understanding anodizing parts Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Soft Anodize Type II | Provides a thin, decorative oxide layer; good for coloring | Consumer electronics, architectural parts | Pros: Cost-effective, aesthetic appeal. Cons: Lower wear resistance compared to Type III. |
| Hard Anodize Type III | Thicker, more durable oxide layer; excellent wear resistance | Aerospace, military, automotive components | Pros: Superior durability and corrosion resistance. Cons: Higher cost and potential brittleness. |
| Bright Dip Anodizing | Produces a high-gloss finish; enhances appearance | Decorative applications, luxury goods | Pros: Attractive finish, good for branding. Cons: Less durable than hard anodizing. |
| Media Blasting | Textured finish achieved through abrasive blasting | Industrial parts requiring grip or texture | Pros: Improved surface texture for better adhesion. Cons: Can be less uniform in appearance. |
| Anodizing with PTFE | Incorporates Teflon for enhanced lubricity and wear resistance | High-friction applications, machinery parts | Pros: Reduced friction, excellent wear properties. Cons: More complex process, potentially higher costs. |
What Are the Characteristics of Soft Anodize Type II?
Soft Anodize Type II is characterized by a relatively thin oxide layer that is primarily used for aesthetic purposes. It allows for a variety of colors to be applied, making it ideal for consumer electronics and architectural components where appearance is crucial. When purchasing, buyers should consider the balance between cost and durability, as while it is cost-effective, its wear resistance is lower than other anodizing types.
How Does Hard Anodize Type III Stand Out?
Hard Anodize Type III features a thicker oxide layer that significantly enhances the durability and wear resistance of aluminum parts. This type is commonly used in demanding industries such as aerospace and automotive, where components must withstand harsh environments. Buyers should be aware of the higher costs associated with this anodizing type, but the investment is often justified by the longevity and performance it provides.
What Are the Benefits of Bright Dip Anodizing?
Bright Dip Anodizing is known for its ability to produce a high-gloss finish that enhances the visual appeal of products. This process is often used for decorative applications, including luxury goods and architectural elements. While it offers an attractive finish, buyers should consider that it may not provide the same level of durability as harder anodizing options, making it more suitable for products where aesthetics take precedence over wear resistance.
Why Choose Media Blasting for Anodized Parts?
Media Blasting is a unique anodizing approach that creates a textured finish by using abrasive materials. This technique is especially beneficial for industrial applications requiring improved grip or surface texture. Buyers should evaluate the specific requirements of their applications, as the texture can vary, potentially affecting the uniformity of the anodized surface.
What Are the Advantages of Anodizing with PTFE?
Anodizing with PTFE combines traditional anodizing techniques with Teflon to enhance lubricity and wear resistance. This method is particularly advantageous in high-friction applications, such as machinery parts. While the process may be more complex and costly, the resulting products benefit from reduced friction and increased longevity, making it a worthwhile consideration for industries focused on performance and durability.
Key Industrial Applications of anodizing parts
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of Anodizing Parts | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Aerospace | Aircraft components | Enhanced durability and corrosion resistance | Compliance with industry standards (e.g., AS9100) |
| Automotive | Engine and transmission parts | Improved wear resistance and thermal insulation | Supplier certifications and testing capabilities |
| Electronics | Heat sinks and enclosures | Improved thermal conductivity and aesthetic appeal | Precision machining capabilities and color options |
| Construction | Architectural elements (e.g., window frames) | Long-lasting aesthetics and weather resistance | Customization options for color and finish |
| Medical Devices | Surgical instruments and implants | Biocompatibility and easy sterilization | Regulatory compliance (e.g., ISO 13485) |
How is Anodizing Used in the Aerospace Industry?
In the aerospace sector, anodizing is crucial for manufacturing aircraft components such as landing gear, brackets, and housings. The anodized layer enhances the durability of these parts, providing exceptional corrosion resistance essential for high-altitude and extreme weather conditions. Buyers must ensure that their anodizing suppliers comply with rigorous aerospace standards, such as AS9100, to guarantee the safety and reliability of their components. Additionally, sourcing from certified vendors can mitigate risks related to quality and performance.
What Role Does Anodizing Play in Automotive Applications?
Automotive manufacturers utilize anodizing for engine components, transmission parts, and decorative trims. The anodized surface significantly improves wear resistance, which is vital for parts exposed to high friction and thermal stress. Buyers should consider suppliers that can provide consistent quality and have a proven track record in automotive applications, as well as the ability to meet specific standards like IATF 16949. Additionally, the ability to offer custom finishes can enhance the aesthetic appeal of vehicles.
Why is Anodizing Important for Electronics?
In the electronics industry, anodizing is often applied to heat sinks and enclosures to improve thermal conductivity while providing a sleek, visually appealing finish. The anodized surface not only protects the underlying metal from corrosion but also enhances the part’s ability to dissipate heat effectively. Buyers in this sector should prioritize suppliers who can deliver precision machining capabilities and a variety of color options, as aesthetics and performance are both critical in consumer electronics.
How Does Anodizing Benefit the Construction Industry?
Anodizing is widely used in the construction sector for architectural elements such as window frames, handrails, and facades. This process provides long-lasting aesthetics and superior weather resistance, making it ideal for outdoor applications. Buyers should seek suppliers who can offer customization options to match specific design requirements and ensure the anodized finish adheres to local building codes and standards. The ability to provide samples and prototypes can also be a significant advantage.
What Are the Advantages of Anodizing in Medical Devices?
In the medical field, anodizing is applied to surgical instruments and implants to enhance biocompatibility and facilitate sterilization processes. The anodized surface prevents corrosion and wear, ensuring the longevity and safety of medical devices. Buyers must ensure that their suppliers comply with relevant regulations, such as ISO 13485, to guarantee product quality and safety. Additionally, sourcing from vendors with experience in medical applications can help mitigate risks associated with compliance and performance.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘anodizing parts’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Ensuring Consistent Quality in Anodized Parts
The Problem: B2B buyers often face significant challenges when it comes to the consistency and quality of anodized parts. This issue can arise from variations in the anodizing process, leading to discrepancies in color, thickness, or surface finish. Such inconsistencies not only compromise the aesthetic appeal of products but can also affect their mechanical properties, such as corrosion resistance and durability. For manufacturers in sectors like automotive or aerospace, where precision is critical, subpar anodizing can result in costly reworks or product failures.
The Solution: To ensure consistent quality in anodized parts, buyers should prioritize working with reputable anodizing service providers who adhere to strict quality control measures. Look for suppliers with certifications such as ISO 9001 or AS9100D, which indicate a commitment to quality management systems. Additionally, establish clear specifications for your anodizing needs, including desired thickness, color, and surface finish. Engaging in open communication with the anodizing partner can help ensure they understand your requirements and expectations. Request samples or prototypes before placing large orders to verify that the anodized parts meet your standards.
Scenario 2: Managing Cost and Lead Time in Anodizing Processes
The Problem: B2B buyers often struggle with balancing cost and lead time when sourcing anodized parts. Many suppliers may offer lower prices but could have longer production times, leading to delays in project timelines. Conversely, expedited services may come at a premium, putting pressure on budgets. This dynamic can be particularly challenging for companies that operate on tight schedules and need to deliver their products promptly to maintain competitive advantage.
The Solution: To effectively manage costs and lead times, buyers should engage in thorough market research to identify suppliers that can provide competitive pricing without compromising on quality. Requesting quotes from multiple anodizing service providers can help gauge average costs and lead times in the industry. Establishing long-term relationships with trusted suppliers can also lead to better pricing and priority treatment on orders. Consider utilizing Just-In-Time (JIT) inventory practices to align anodizing schedules with production needs, thereby reducing excess inventory costs and ensuring timely delivery of parts.
Scenario 3: Overcoming Environmental and Regulatory Compliance Challenges
The Problem: Companies that require anodized parts often encounter environmental and regulatory compliance challenges, particularly in regions with strict environmental laws. The anodizing process can produce waste materials and emissions that need to be managed according to local regulations. Failing to comply can result in hefty fines, production delays, and damage to a company’s reputation. This is especially critical for businesses operating in Europe or regions with stringent environmental standards.
The Solution: To navigate environmental compliance effectively, B2B buyers should partner with anodizing service providers who are committed to sustainable practices and can demonstrate compliance with relevant regulations. Look for suppliers that utilize eco-friendly anodizing processes, such as those that minimize chemical waste or utilize closed-loop systems. Conducting audits of potential partners’ facilities can provide insights into their environmental practices. Additionally, buyers should stay informed about local regulations and actively engage with suppliers to ensure that all anodizing processes meet or exceed compliance standards, thus protecting their business from potential liabilities.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for anodizing parts
What Are the Key Properties of Common Materials Used for Anodizing Parts?
When selecting materials for anodizing, several factors must be considered, including mechanical properties, corrosion resistance, and suitability for specific applications. Below is an analysis of four common materials often anodized in B2B settings.
Aluminum Alloys: The Most Common Choice for Anodizing
Aluminum alloys, particularly 6061 and 7075, are the most frequently anodized materials due to their excellent mechanical properties and lightweight nature. They exhibit good corrosion resistance and can withstand moderate temperatures, making them suitable for various applications, from automotive to aerospace.
Pros: Aluminum alloys are highly durable, lightweight, and have excellent machinability. They can be anodized to achieve a range of aesthetic finishes, which is appealing for consumer-facing products.
Cons: The cost of high-grade aluminum alloys can be significant, and they may require complex manufacturing processes. Additionally, they can be susceptible to thermal stress cracking under extreme conditions.
Impact on Application: Aluminum alloys are compatible with a wide range of media, making them versatile for different environments. However, their performance can be affected by the anodizing process, particularly in terms of color retention and surface hardness.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers from regions like Africa and South America should ensure compliance with local standards (e.g., ASTM or ISO) to avoid issues in procurement and manufacturing.
Titanium: A Premium Material for Specialized Applications
Titanium is another material that can be anodized, often used in high-performance applications such as medical devices and aerospace components. It offers superior strength-to-weight ratios and excellent corrosion resistance.
Pros: Titanium is incredibly durable and biocompatible, making it ideal for medical applications. The anodizing process can also enhance its aesthetic appeal, providing vibrant colors.
Cons: The cost of titanium is significantly higher than aluminum, and its machining can be complex and time-consuming. This can lead to higher overall production costs.
Impact on Application: Titanium parts are suitable for harsh environments, including marine and chemical applications, due to their exceptional corrosion resistance. However, the anodized layer can be more brittle than that of aluminum.
Considerations for International Buyers: Compliance with medical and aerospace standards (e.g., ASTM F136 for titanium used in medical implants) is crucial for buyers in these sectors, especially in Europe and the Middle East.
Magnesium Alloys: Lightweight Yet Challenging
Magnesium alloys are known for their low density and high strength, making them attractive for applications where weight savings are critical, such as in automotive and aerospace industries.
Pros: Magnesium alloys offer excellent machinability and can be anodized to improve corrosion resistance and surface finish.
Cons: They are more prone to corrosion compared to aluminum and titanium, which can limit their applications. Additionally, the anodizing process can be more complex due to the material’s reactivity.
Impact on Application: While magnesium alloys can be used in various environments, their susceptibility to corrosion may limit their use in applications exposed to moisture or chemicals.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should be aware of the specific anodizing techniques required for magnesium and ensure they are compliant with local and international standards to avoid quality issues.
Zinc: Cost-Effective but Limited
Zinc is less commonly anodized but can be used in specific applications, particularly in galvanizing processes. It offers decent corrosion resistance and is often used as a sacrificial anode.
Pros: Zinc is cost-effective and provides good protection against corrosion, making it suitable for budget-sensitive projects.
Cons: Its mechanical properties are inferior to those of aluminum and titanium, and the anodizing process may not significantly enhance its performance.
Impact on Application: Zinc is primarily used in environments where corrosion resistance is essential, but its limited mechanical properties may restrict its use in demanding applications.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers must ensure that zinc products meet relevant standards (e.g., ASTM B633 for electroplated zinc) to ensure quality and compliance.
Summary Table of Material Selection for Anodizing Parts
| Material | Typical Use Case for anodizing parts | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Aluminum Alloys | Automotive, Aerospace | Lightweight and durable | Susceptible to thermal cracking | Medium |
| Titanium | Medical devices, Aerospace | Superior strength and biocompatibility | High cost and complex machining | High |
| Magnesium Alloys | Automotive, Aerospace | Excellent machinability | Prone to corrosion | Medium |
| Zinc | Galvanizing, budget applications | Cost-effective | Limited mechanical properties | Low |
This strategic material selection guide provides a comprehensive overview for international B2B buyers, ensuring informed decisions that align with their specific application needs and compliance requirements.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for anodizing parts
What Are the Main Stages in the Manufacturing Process of Anodizing Parts?
The manufacturing process for anodizing parts involves several critical stages that ensure quality and performance. Understanding these stages helps B2B buyers make informed decisions when sourcing anodized components.
Material Preparation: What Steps Are Involved?
Material preparation is the foundational step in anodizing. It begins with selecting the appropriate aluminum alloy, as certain alloys yield better anodized finishes. Once the material is chosen, the following steps are taken:
-
Cleaning: Parts are thoroughly cleaned to remove oils, dirt, and oxidation. This is typically achieved through ultrasonic cleaning or chemical degreasing.
-
Surface Conditioning: After cleaning, the aluminum surface may be mechanically or chemically treated to enhance the anodizing process. This may involve etching or sanding to create a uniform surface.
-
Rinsing: Rinsing is essential to eliminate any residues from cleaning agents, ensuring that no contaminants affect the anodizing process.
How Are Parts Formed and Assembled Before Anodizing?
Once the material is prepared, the forming and assembly stage comes into play. This stage focuses on shaping the aluminum parts to meet design specifications. Key techniques include:
-
CNC Machining: This is a prevalent method for creating precise shapes and features in aluminum parts, ensuring that the dimensions align with engineering drawings.
-
Stamping and Extrusion: These processes are used for high-volume production, allowing for the efficient creation of complex shapes.
After forming, parts may undergo assembly, where various components are joined together. This could involve welding, riveting, or using adhesives, depending on the design requirements.
What Finishing Techniques Are Used in Anodizing?
Finishing is the final stage in the manufacturing process. Anodizing involves immersing the aluminum parts in an electrolytic solution, typically sulfuric acid, where an oxide layer is formed. This step can vary based on the desired finish:
-
Type II Anodizing: This is used for cosmetic finishes and provides moderate corrosion resistance.
-
Type III Hard Anodizing: This method creates a thicker, more durable layer suitable for high-wear applications.
-
Color Anodizing: Dyes can be added during the anodizing process to achieve vibrant colors, which are then sealed to ensure permanence.
Following anodizing, parts are sealed to enhance corrosion resistance. This sealing process can involve hot water, steam, or chemical sealing methods.
What Quality Control Measures Are Essential for Anodizing Parts?
Quality assurance is a critical aspect of the anodizing process, ensuring that the final products meet international standards and customer expectations.
Which International Standards Apply to Anodizing Processes?
B2B buyers should be aware of relevant international standards that govern the anodizing process. Key standards include:
-
ISO 9001: This standard focuses on quality management systems, ensuring that manufacturers consistently meet customer and regulatory requirements.
-
ISO 13485: Particularly relevant for medical device manufacturers, this standard ensures that anodized parts used in medical applications meet stringent quality and safety requirements.
-
IATF 16949: This is crucial for automotive parts, ensuring that anodized components meet the industry’s specific quality standards.
What Are the Critical Checkpoints in Quality Control?
Quality control checkpoints are integral to maintaining the integrity of anodized parts. Common checkpoints include:
-
Incoming Quality Control (IQC): This involves inspecting raw materials and components upon arrival to ensure they meet specifications.
-
In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): During the manufacturing process, random checks are conducted to monitor the anodizing parameters, such as temperature and pH levels.
-
Final Quality Control (FQC): After anodizing, parts undergo rigorous testing for thickness, adhesion, and corrosion resistance. This may include visual inspections and measurements using tools like micrometers and calipers.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control?
To ensure that suppliers adhere to quality standards, B2B buyers should consider several verification methods:
What Auditing Practices Should Buyers Implement?
Auditing suppliers is a proactive approach to quality assurance. Buyers can conduct:
-
On-Site Audits: Visiting the supplier’s facility to evaluate their processes, equipment, and adherence to quality standards.
-
Documentation Review: Requesting and reviewing quality manuals, process documentation, and compliance certificates.
How Can Reports and Third-Party Inspections Enhance Quality Assurance?
-
Quality Reports: Suppliers should provide regular quality reports detailing their quality control measures, inspection results, and any deviations from standards.
-
Third-Party Inspections: Engaging independent inspection agencies can provide an unbiased assessment of the supplier’s quality practices. This is particularly valuable for international transactions where buyers may not have direct oversight.
What Are the Quality Control Nuances for International B2B Buyers?
B2B buyers from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe face unique challenges when sourcing anodized parts internationally.
How Do Regulatory and Compliance Differences Impact Quality Control?
Buyers should be aware of the differing regulations and compliance requirements in various countries. It’s essential to ensure that suppliers understand and comply with local and international standards, as non-compliance can lead to costly delays and reputational damage.
What Should Buyers Know About Logistics and Quality Assurance?
Finally, logistics plays a significant role in quality assurance. Buyers must consider:
-
Transport Conditions: Ensuring that anodized parts are transported in conditions that prevent damage or contamination.
-
Customs Regulations: Understanding customs regulations in both the exporting and importing countries to avoid delays that could impact product quality.
By comprehensively understanding the manufacturing processes and quality assurance measures in anodizing, B2B buyers can make informed decisions and select reliable suppliers that meet their specific needs.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘anodizing parts’
Introduction
Navigating the procurement of anodized parts requires a strategic approach to ensure quality and compliance with industry standards. This guide provides a step-by-step checklist tailored for B2B buyers, enabling you to make informed decisions while sourcing anodized components. By following these steps, you can streamline your procurement process, reduce risks, and enhance the overall quality of your products.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Clearly outline the technical requirements for your anodized parts. This includes material type, dimensions, and desired anodizing finish (e.g., Type II or Type III). Defining these specifications upfront is crucial as it helps suppliers understand your needs and ensures that the final products meet your expectations.
- Material Considerations: Specify the aluminum alloy or other materials you require.
- Finish Requirements: Determine whether you need soft anodize for aesthetics or hard anodize for wear resistance.
Step 2: Research Potential Suppliers
Conduct thorough research to identify suppliers with a strong reputation in anodizing. Look for companies that specialize in your required anodizing type and have experience serving similar industries. This step is vital to ensure you partner with a reliable provider who can deliver quality parts.
- Industry Experience: Prioritize suppliers with a proven track record in your specific industry.
- Customer Reviews: Seek out testimonials or case studies to gauge customer satisfaction.
Step 3: Evaluate Supplier Certifications
Verify that potential suppliers hold relevant certifications, such as ISO 9001 or IATF 16949. These certifications indicate adherence to quality management systems and industry standards, which is essential for ensuring consistent product quality.
- Document Verification: Request copies of certifications and check their validity.
- Compliance with Regulations: Ensure suppliers comply with local and international environmental and safety regulations.
Step 4: Request Samples and Prototypes
Before placing a bulk order, request samples or prototypes of anodized parts. This allows you to assess the quality, finish, and adherence to your specifications firsthand. Sampling is a critical step to mitigate risks associated with large orders.
- Quality Assessment: Evaluate the samples for durability, appearance, and dimensional accuracy.
- Adjustments: Use this opportunity to provide feedback and make any necessary adjustments before full-scale production.
Step 5: Negotiate Terms and Conditions
Engage in discussions to clarify pricing, lead times, and payment terms with your chosen supplier. Effective negotiation can lead to favorable terms that benefit both parties and foster a long-term relationship.
- Volume Discounts: Inquire about pricing structures for bulk orders.
- Delivery Schedules: Confirm lead times and any penalties for delays to ensure timely delivery.
Step 6: Confirm Quality Control Processes
Ensure that your supplier has robust quality control measures in place. Inquire about their testing methods for anodized parts, including corrosion resistance and adhesion tests. This step is essential to guarantee that the parts meet your quality standards.
- Inspection Protocols: Ask about their inspection and testing procedures.
- Non-Conformance Handling: Understand their process for addressing any defects or issues that may arise.
Step 7: Establish a Communication Plan
Set up a clear communication plan for ongoing interactions with your supplier. Regular updates on order status, changes in specifications, or potential issues will help maintain transparency and foster a collaborative relationship.
- Point of Contact: Designate a primary contact for streamlined communication.
- Regular Updates: Schedule periodic check-ins to discuss any developments or concerns.
By following this checklist, B2B buyers can ensure a more efficient and effective sourcing process for anodized parts, ultimately leading to better quality products and stronger supplier relationships.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for anodizing parts Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components in Anodizing Parts Sourcing?
When sourcing anodized parts, understanding the cost structure is critical. The primary cost components include materials, labor, manufacturing overhead, tooling, quality control (QC), logistics, and supplier margins.
-
Materials: The most significant cost often comes from the raw materials, primarily aluminum and the chemicals used in the anodizing process (e.g., sulfuric acid, dyes). The choice of aluminum alloy can affect the price, as certain alloys may offer better mechanical properties or corrosion resistance but come at a premium.
-
Labor: Labor costs depend on the complexity of the anodizing process and the skill level required. Specialized labor may be needed for certain types of anodizing (e.g., hard anodizing), which can increase costs.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This encompasses facility costs, utilities, maintenance of anodizing equipment, and other indirect costs. Efficient operations can mitigate these expenses, making it essential to evaluate potential suppliers’ operational efficiencies.
-
Tooling: Custom tooling or fixtures may be necessary for certain anodized parts, particularly for complex designs. These initial investments can significantly impact the overall price, especially for low-volume orders.
-
Quality Control: Ensuring high-quality anodized parts often requires rigorous QC processes. Costs associated with testing, inspection, and certifications (such as ISO 9001) should be factored into the pricing structure.
-
Logistics: Shipping costs can vary significantly based on the distance, volume, and weight of the anodized parts. International shipping may involve additional customs duties and handling fees, impacting the total cost.
-
Supplier Margin: Each supplier will add a margin to their costs, influenced by their market position and service offerings. It’s essential to compare quotes from multiple suppliers to ensure competitive pricing.
What Influences Pricing for Anodized Parts?
Several factors can influence the pricing of anodized parts, including:
-
Volume and Minimum Order Quantity (MOQ): Higher order volumes often lead to reduced per-unit costs due to economies of scale. Conversely, smaller orders may incur higher prices due to the fixed costs associated with production setups.
-
Specifications and Customization: Unique specifications or extensive customization can increase costs. Buyers should balance the need for specific attributes against potential price hikes.
-
Materials Quality and Certifications: The quality of the aluminum and the anodizing process can significantly impact pricing. Certifications (e.g., aerospace or automotive standards) may also raise costs but are crucial for certain industries.
-
Supplier Factors: Reliability, reputation, and location of the supplier can affect costs. Suppliers with advanced technology or certifications might charge more but offer better quality and faster turnaround times.
-
Incoterms: The agreed Incoterms (International Commercial Terms) can influence logistics costs. Buyers should clarify these terms to avoid unexpected charges related to shipping and delivery.
How Can Buyers Optimize Costs in Anodizing Parts Sourcing?
-
Negotiation: Engage suppliers in discussions regarding pricing and payment terms. Establishing a long-term relationship can often lead to better pricing and terms.
-
Cost-Efficiency Analysis: Conduct a thorough Total Cost of Ownership (TCO) analysis, which considers not only the purchase price but also lifecycle costs, maintenance, and potential downtime.
-
Pricing Nuances for International Buyers: For buyers in regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, understanding local market conditions and currency fluctuations can help in negotiating better prices. It’s advisable to be aware of additional costs such as tariffs and taxes that may apply when importing anodized parts.
-
Request for Quotation (RFQ): Always send RFQs to multiple suppliers to compare offers comprehensively. This not only provides a better understanding of market rates but also strengthens your negotiation position.
Conclusion and Disclaimer
The indicative pricing for anodizing parts can vary widely based on the factors discussed. It is crucial for buyers to conduct diligent research and engage in thorough negotiations to secure the best possible pricing for their specific needs. Always consult multiple suppliers and consider all cost components to achieve optimal value in anodized parts sourcing.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing anodizing parts With Other Solutions
In the dynamic landscape of metal finishing, businesses often seek alternatives to anodizing parts to meet specific performance, aesthetic, and budgetary requirements. Understanding the various solutions available can empower B2B buyers to make informed decisions that align with their operational needs and product specifications.
| Comparison Aspect | Anodizing Parts | Powder Coating | Electroplating |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | Excellent corrosion resistance, enhanced durability, and aesthetic appeal with a hard oxide layer. | Good UV resistance, available in various colors, and durable finish. | Provides a smooth, shiny finish; excellent for conductivity and corrosion protection. |
| Cost | Moderate initial cost; potential high setup costs for large operations. | Generally lower cost than anodizing; however, it may vary based on color and finish complexity. | Higher initial costs due to equipment and material requirements; ongoing costs for maintenance. |
| Ease of Implementation | Requires specialized equipment and expertise; more complex for DIY applications. | Easier to implement with less stringent environmental controls; suitable for larger batches. | Complex process requiring precise control over the plating environment; not DIY-friendly. |
| Maintenance | Low maintenance; resistant to dirt and grime. | Moderate maintenance; may require touch-ups and can fade over time. | Higher maintenance; potential for wear and corrosion over time. |
| Best Use Case | Ideal for aerospace, automotive, and decorative applications needing durability. | Suitable for consumer goods, furniture, and outdoor equipment with aesthetic needs. | Best for electronic components, automotive parts requiring conductivity, and decorative metal items. |
What are the Pros and Cons of Powder Coating as an Alternative to Anodizing?
Powder coating is a popular alternative that applies a dry powder to metal surfaces, which is then cured under heat to form a durable finish. One of the primary advantages of powder coating is its cost-effectiveness compared to anodizing, especially for larger projects. It offers a broad color palette and can achieve a variety of textures, making it appealing for decorative applications. However, powder coating may not provide the same level of corrosion resistance as anodizing, and its longevity can be affected by UV exposure and environmental factors, necessitating more frequent maintenance.
How Does Electroplating Compare to Anodizing?
Electroplating involves depositing a layer of metal onto a substrate through an electrochemical process. This method excels in providing a shiny finish and can enhance conductivity, making it ideal for electronic components. Additionally, electroplating can improve corrosion resistance but may not be as durable as anodizing in demanding environments. The initial costs of electroplating can be significant due to the need for specialized equipment and materials. Moreover, the process requires careful control to avoid defects, which can complicate implementation.
How Can B2B Buyers Choose the Right Solution for Their Needs?
When selecting the appropriate finishing solution, B2B buyers should evaluate the specific requirements of their applications, including performance criteria, aesthetic goals, and budget constraints. Anodizing is an excellent choice for applications demanding high durability and corrosion resistance, particularly in aerospace or automotive sectors. Conversely, if cost and aesthetic variety are paramount, powder coating may be the better option. For electronic applications requiring conductivity, electroplating stands out. Ultimately, understanding the unique advantages and limitations of each method will guide buyers in making a decision that best aligns with their operational objectives and customer expectations.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for anodizing parts
What Are the Key Technical Properties of Anodizing Parts in B2B Transactions?
When considering anodized aluminum parts for various applications, understanding critical technical properties is essential. These properties not only influence the performance and durability of the parts but also impact the overall cost and suitability for specific projects.
1. Material Grade
Material grade refers to the specific composition and quality of the aluminum alloy used. Different grades, such as 6061 or 7075, offer varying levels of strength, corrosion resistance, and machinability. For B2B buyers, selecting the appropriate material grade is crucial as it directly affects the performance characteristics of the anodized parts, ensuring they meet industry standards and application requirements.
2. Anodizing Type
There are several anodizing types, including Type II (soft anodize) and Type III (hard anodize). Type II is typically used for decorative purposes and provides moderate corrosion resistance, while Type III offers superior durability and wear resistance, making it ideal for high-stress applications. Understanding the differences allows buyers to choose the right anodizing type based on their specific needs, whether aesthetic or functional.
3. Thickness of Anodized Layer
The thickness of the anodized layer is measured in microns and is critical for performance. A thicker layer generally provides better wear and corrosion resistance, while a thinner layer may be suitable for cosmetic applications. This specification is vital for B2B buyers to ensure the longevity and functionality of the parts in their intended environment.
4. Tolerance
Tolerance refers to the permissible variation in dimensions for anodized parts. Tight tolerances are essential for precision applications, where even minor deviations can lead to performance issues. Establishing clear tolerance requirements helps prevent costly rework or failures, making it a critical consideration for buyers in industries such as aerospace and automotive.
5. Surface Finish
The surface finish of anodized parts affects both aesthetics and functionality. Common finishes include matte, gloss, and textured. The choice of finish can influence adhesion for paints or coatings and the overall appearance of the product. B2B buyers should specify their desired surface finish to ensure the final product aligns with their branding and functional requirements.
What Common Trade Terms Should B2B Buyers Understand in Anodizing?
Navigating the terminology associated with anodizing can enhance communication and streamline procurement processes for B2B buyers.
1. OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
OEM refers to a company that produces parts or equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer. Understanding this term is crucial for buyers seeking anodized parts that meet specific performance standards set by established brands.
2. MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ is the smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell. For anodizing services, knowing the MOQ helps buyers plan their purchases and budget effectively, especially when dealing with specialized or custom anodized parts.
3. RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a document sent to suppliers to solicit price quotes for specific products or services. When seeking anodized parts, submitting an RFQ allows buyers to compare prices and terms from multiple vendors, ensuring they secure the best deal.
4. Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
Incoterms are a series of pre-defined commercial terms published by the International Chamber of Commerce (ICC) that clarify the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in international transactions. Familiarity with Incoterms helps B2B buyers understand shipping costs, risks, and insurance responsibilities related to anodized parts.
5. Lead Time
Lead time refers to the time taken from placing an order to receiving the finished product. For anodizing services, knowing the lead time is essential for project planning and ensuring timely delivery of parts to meet production schedules.
Understanding these technical properties and trade terms empowers B2B buyers to make informed decisions when sourcing anodized parts, ultimately enhancing operational efficiency and product quality.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the anodizing parts Sector
What Are the Current Market Dynamics and Key Trends in Anodizing Parts?
The anodizing parts market is witnessing significant growth, driven by the rising demand for lightweight, durable materials across various industries such as aerospace, automotive, and consumer goods. The global push for enhanced product performance is leading manufacturers to adopt anodizing processes that improve corrosion resistance and aesthetic appeal. Notably, the adoption of advanced technologies such as automation and Industry 4.0 is transforming sourcing strategies, allowing for more efficient production and quality control. This trend is particularly relevant for international B2B buyers from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, who are increasingly looking for reliable suppliers that can meet their specific requirements.
Emerging trends include a shift towards customization, with buyers seeking tailored anodizing solutions that cater to unique specifications and applications. The rise of digital platforms for procurement is also notable, as these platforms facilitate easier access to suppliers and enhance transparency in pricing and service offerings. Furthermore, the growing emphasis on quick turnaround times and just-in-time delivery is reshaping the supply chain dynamics, compelling suppliers to optimize their processes and logistics capabilities. As a result, international buyers must stay informed about these shifts to effectively navigate the anodizing parts market.
How Is Sustainability Influencing Sourcing Decisions for Anodizing Parts?
Sustainability is becoming a pivotal factor in the sourcing of anodizing parts, with increasing scrutiny on environmental impacts and ethical supply chains. Anodizing processes are inherently more eco-friendly compared to traditional metal finishing methods, as they produce minimal waste and do not release harmful volatile compounds. Buyers are, therefore, encouraged to partner with suppliers who prioritize sustainable practices, such as using biodegradable chemicals and implementing waste-reduction strategies.
The importance of ethical sourcing is underscored by the rising demand for certifications that validate a supplier’s commitment to environmentally responsible practices. Green certifications, such as ISO 14001, can serve as a benchmark for buyers to assess potential partners. Additionally, the use of recycled aluminum in anodizing processes not only supports sustainability efforts but also appeals to cost-conscious buyers looking to optimize their material sourcing. By focusing on suppliers who align with these sustainability goals, international B2B buyers can enhance their corporate social responsibility (CSR) profiles while securing high-quality anodized parts.
What Is the Historical Context of Anodizing in the B2B Sector?
The anodizing process has evolved significantly since its inception in the early 20th century. Initially developed for the aerospace industry to enhance aluminum’s corrosion resistance, anodizing has expanded to various sectors, including automotive and electronics. Over the decades, advancements in technology and processes have improved the quality and efficiency of anodizing, allowing for greater customization and color options.
Historically, anodizing was limited by the technology available, which constrained its applications. However, the introduction of more sophisticated electrolytic processes and the ability to manipulate the anodic layer have made anodizing a preferred choice for many manufacturers. This evolution is crucial for B2B buyers today, as understanding the historical context can provide insights into the reliability and performance of anodized parts, influencing their sourcing decisions and partnerships in the global market.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of anodizing parts
-
How do I solve issues with anodized parts that show signs of corrosion?
Corrosion on anodized parts can occur if the anodizing layer is compromised or if there is exposure to harsh environments. To address this, first ensure that the anodizing was done correctly and meets the required specifications. If corrosion is detected, you may need to strip the anodized layer and re-anodize the part. Regular maintenance, including cleaning with non-abrasive materials, can help prevent future issues. If sourcing from suppliers, inquire about their quality assurance processes and ensure they use proper sealing techniques post-anodization to enhance corrosion resistance. -
What is the best anodizing process for enhancing durability in extreme conditions?
For applications requiring high durability, Type III hard anodizing is recommended. This process creates a thicker anodic layer that significantly improves wear and corrosion resistance, making it suitable for parts exposed to extreme conditions, such as aerospace or automotive components. When selecting a supplier, ensure they have experience with hard anodizing and can provide certifications that guarantee the process meets industry standards. -
How can I customize the color of anodized parts for my project?
Customizing the color of anodized parts is achievable through the dyeing process during anodization. Suppliers typically offer a range of colors; however, the vibrancy can vary based on the anodizing type and thickness. When ordering, communicate your specific color requirements and request samples to ensure the final product meets your expectations. It’s essential to work with a supplier experienced in color anodizing to achieve consistent and high-quality results. -
What are the minimum order quantities (MOQs) for anodized parts?
Minimum order quantities can vary significantly among suppliers, often depending on the complexity and size of the parts. Some manufacturers may have MOQs as low as 50 units for standard parts, while custom designs could require higher volumes. When sourcing, discuss your needs upfront to understand the supplier’s capacity and flexibility. If your order falls below their MOQ, consider negotiating a trial batch or exploring alternative suppliers who may accommodate smaller orders. -
What payment terms are typically offered by anodizing suppliers?
Payment terms can differ widely based on the supplier’s policies and the nature of the transaction. Common terms include payment upon order, partial upfront payments, or net 30 to net 60 days after delivery. For international transactions, consider the risks involved, including currency fluctuations and import duties. Always clarify payment terms before finalizing your order and ensure that they align with your financial capabilities and cash flow management practices. -
How do I vet suppliers for anodizing services internationally?
To vet international anodizing suppliers, start by checking their certifications, such as ISO 9001 or industry-specific standards relevant to your sector. Request references from previous clients and evaluate their production capabilities and lead times. Additionally, consider visiting the facility, if feasible, to assess quality control processes firsthand. Online reviews and industry forums can also provide valuable insights into a supplier’s reputation and reliability. -
What logistics considerations should I keep in mind when importing anodized parts?
When importing anodized parts, consider shipping methods, lead times, and customs regulations specific to your country. Ensure that the supplier can provide the necessary documentation, such as certificates of compliance and origin, to facilitate smooth customs clearance. Additionally, factor in shipping costs, insurance, and potential delays in transit. Collaborating with a logistics provider experienced in international trade can help streamline the process and mitigate risks. -
What quality assurance practices should I expect from an anodizing supplier?
A reputable anodizing supplier should have robust quality assurance practices in place, including in-process inspections and final product testing. They should conduct tests for thickness, adhesion, and corrosion resistance to ensure that the anodized parts meet specifications. Inquire about their quality control protocols, including any certifications they hold and the frequency of audits. A commitment to quality assurance not only ensures the durability of the parts but also reduces the risk of costly rework or replacements.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.
Top 6 Anodizing Parts Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. Caswell Plating – Anodizing Systems
Domain: caswellplating.com
Registered: 1997 (28 years)
Introduction: This company, Caswell Plating – Anodizing Systems, is a notable entity in the market. For specific product details, it is recommended to visit their website directly.
2. TFG USA – Custom Fasteners & Metal Solutions
Domain: tfgusa.com
Registered: 2008 (17 years)
Introduction: QMS 9001:2015 Certified; Capabilities: Cold Heading, Custom Fasteners, Laser Cutting, Metal Injection Molding, Pipe and Tubing, Castings (Aluminum Die Casting, Centrifugal Casting, Die Casting, Investment Casting, Lost Foam Casting, Permanent Mold Casting, Rapid Prototype Casting, Sand Casting), Extrusion (Aluminum, Brass, Steel), Fabrication (Aluminum, Metal, Steel), Metal Stamping, Roll Forming,…
3. Anodize Solutions – Anodizing Services
Domain: anodizesolutions.com
Registered: 2014 (11 years)
Introduction: Soft Anodize Type II: For cosmetic color; Hard Anodize Type III: For high wear applications; Bright Dip: For a high gloss finish; Media Blasting: For a textured finish; Masking/Plugging: Protect areas from being anodized.
4. SendCutSend – Anodizing Service
Domain: sendcutsend.com
Registered: 2015 (10 years)
Introduction: Anodizing is a finishing service offered by SendCutSend for sheet metal parts. Key details include:
– No minimum quantity required for anodizing.
– Pricing starts at $0.50 per part for bulk orders.
– Anodizing adds 7-10 business days to processing time.
– Recommended to separate anodized parts into their own order for faster processing.
– Materials available for anodizing:
– 5052 Aluminum:…
5. Five Flute – Anodized Aluminum Parts
Domain: fiveflute.com
Registered: 2019 (6 years)
Introduction: Anodized aluminum parts are created through an electrochemical process that converts the metal surface into a durable, corrosion-resistant anodic oxide finish. Key properties include corrosion resistance, increased surface hardness, decorative color options, improved paint or adhesive adherence, electrical insulation, and prevention of galling. The anodizing process involves cleaning, pre-treatmen…
6. Arrma Forum – Anodizing Aluminum Essentials
Domain: arrmaforum.com
Registered: 2015 (10 years)
Introduction: Materials needed for anodizing aluminum at home include: sulfuric acid, distilled water, several tanks (containers), a cathode (aluminum wire or titanium), degreaser, lye, acid neutralizer, a power source, and dye (for coloring). Optional items include an agitator for the acid bath, Scotch-Brite pads for cleaning, ping pong balls (to prevent acid mist), a cheap tea kettle for heating dye, a fish t…
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for anodizing parts
What Are the Key Benefits of Strategic Sourcing in Anodizing Parts?
In conclusion, strategic sourcing of anodized parts presents significant advantages for international B2B buyers, especially in regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. By leveraging anodizing’s durability, corrosion resistance, and aesthetic appeal, companies can enhance the performance and longevity of their products while also minimizing maintenance costs. The eco-friendly nature of anodizing further aligns with the growing demand for sustainable manufacturing practices.
Establishing reliable partnerships with trusted anodizing suppliers ensures that businesses can obtain high-quality products tailored to their specific requirements. Buyers should prioritize suppliers who offer a range of anodizing options, including Type II and Type III coatings, to meet diverse application needs. Additionally, understanding the potential limitations, such as thermal stress cracking and color range constraints, will empower buyers to make informed decisions.
As the demand for anodized aluminum parts continues to rise, businesses are encouraged to adopt strategic sourcing practices that not only enhance product quality but also foster innovation. By proactively engaging with suppliers and exploring new anodizing technologies, companies can position themselves for success in an increasingly competitive global market. Now is the time to invest in quality anodized solutions that will elevate your product offerings and drive business growth.