Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for anodizing aluminum process
In today’s competitive landscape, sourcing anodizing aluminum processes presents a unique set of challenges for international B2B buyers. With increasing demand for durable, corrosion-resistant products across various industries—from automotive to construction—understanding the intricacies of anodizing can significantly influence your purchasing decisions. This comprehensive guide aims to demystify the anodizing aluminum process, covering essential aspects such as types of anodizing, applications, and considerations for supplier vetting.
By exploring the different anodizing methods—including sulfuric acid, chromic acid, and hardcoat anodizing—you will gain insights into how these processes can enhance the performance and aesthetic appeal of aluminum products. Additionally, this guide provides valuable information on cost factors, ensuring that you can make budget-conscious decisions without compromising on quality.
Tailored specifically for international B2B buyers from regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe—including key markets like Nigeria and Saudi Arabia—this guide empowers you to navigate the complexities of sourcing anodized aluminum. With a focus on actionable insights and best practices, it equips you with the knowledge needed to make informed, strategic purchasing choices that align with your business objectives. Embrace the potential of anodizing aluminum and unlock new opportunities for your products and projects.
Understanding anodizing aluminum process Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Chromic Acid Anodizing | Thinnest coating (2.5μ), less porous, excellent corrosion resistance | Aerospace, military applications | Pros: Lightweight, good corrosion resistance. Cons: Limited color options, thinner layer. |
| Sulfuric Acid Anodizing | Most common method, thicker coating (5.1 to 30.5μ), easily dyed | Automotive parts, consumer electronics, architectural elements | Pros: Durable, cost-effective, versatile coloring. Cons: Color matching can be inconsistent. |
| Hardcoat Anodizing | Very thick coating (12.7 to 50.8μ), superior hardness | Heavy machinery, military equipment, high-wear components | Pros: Exceptional durability, suitable for harsh conditions. Cons: Darker finish, harder to dye. |
| Decorative Anodizing | Focus on aesthetics, variety of colors, thinner coatings | Consumer products, jewelry, architectural details | Pros: Attractive finishes, customizable colors. Cons: Less durable than other types, may require more maintenance. |
| Electrolytic Coloring | Secondary process for coloring anodized aluminum | Custom consumer products, artistic applications | Pros: Wide range of colors, UV resistant options. Cons: May require additional processing time. |
What are the Key Characteristics of Chromic Acid Anodizing?
Chromic Acid Anodizing produces a very thin oxide layer, making it suitable for applications requiring minimal weight without sacrificing corrosion resistance. This method is particularly favored in aerospace and military industries due to its effectiveness in harsh environments. Buyers should consider that while it offers excellent corrosion protection, the limited color options and thinner coating may not be ideal for all applications.
How Does Sulfuric Acid Anodizing Stand Out?
Sulfuric Acid Anodizing is the most widely used anodizing process, offering a thicker oxide layer that can be easily dyed. This versatility makes it suitable for a wide range of applications, including automotive and consumer electronics. Companies looking for a cost-effective solution that balances durability and aesthetic appeal will find this method advantageous, although color matching can be inconsistent.
What Advantages Does Hardcoat Anodizing Provide?
Hardcoat Anodizing is known for its exceptionally thick oxide layer, which provides superior hardness and wear resistance. This method is ideal for components subjected to high-stress environments, such as military equipment and heavy machinery. While buyers benefit from its durability, they should be aware that the thicker coating can darken the aluminum and may limit dyeing options.
Why Choose Decorative Anodizing for Aesthetic Applications?
Decorative Anodizing focuses on creating visually appealing finishes, available in a wide array of colors. This method is ideal for consumer products and architectural details where appearance is paramount. However, while it offers attractive options, buyers should consider that these finishes may not be as durable as those produced by other anodizing methods, potentially requiring more frequent maintenance.
What is the Role of Electrolytic Coloring in Anodizing?
Electrolytic Coloring is a secondary process applied to anodized aluminum to enhance its aesthetic appeal. This technique allows for a broad spectrum of colors and can provide additional UV resistance. Companies looking to customize their products for artistic applications will find this process valuable, but it may require additional processing time, which could impact production schedules.
Key Industrial Applications of anodizing aluminum process
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of anodizing aluminum process | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Aerospace | Anodized components for aircraft parts | Enhanced corrosion resistance and lightweight design | Compliance with industry standards and certifications |
| Automotive | Anodized exterior and interior parts | Improved durability and aesthetic appeal | Availability of color options and surface finish consistency |
| Construction | Anodized architectural facades and cladding | Long-lasting, low-maintenance exterior finishes | Local climate considerations and compatibility with building codes |
| Electronics | Anodized enclosures for electronic devices | Increased thermal management and wear resistance | Precision in dimensions and adherence to electrical standards |
| Consumer Goods | Anodized cookware and kitchen utensils | Non-reactive, easy-to-clean surfaces | Food safety certifications and color durability |
How is Anodizing Aluminum Applied in the Aerospace Industry?
In the aerospace sector, anodizing aluminum is critical for manufacturing lightweight and corrosion-resistant components, such as aircraft frames and engine parts. The anodized layer protects against harsh environmental conditions, ensuring longevity and safety. International buyers must ensure compliance with stringent aerospace standards and certifications, such as MIL-A-8625, to guarantee quality and performance. Sourcing from suppliers who understand these requirements is essential to mitigate risks and ensure product reliability.
What are the Benefits of Anodizing in the Automotive Industry?
Anodizing aluminum is widely employed in the automotive industry for both exterior and interior components, including trim, wheels, and engine parts. This process enhances durability, providing a protective layer that resists scratches, corrosion, and fading from UV exposure. For buyers in regions like Africa and the Middle East, it’s crucial to consider local environmental conditions that might affect material performance. Additionally, suppliers should offer a variety of color options to meet diverse design preferences while ensuring consistent surface finishes.
How Does Anodizing Enhance Construction Materials?
Anodized aluminum is increasingly popular in construction, particularly for architectural facades and cladding systems. The anodized finish not only offers aesthetic appeal but also contributes to the building’s durability and maintenance ease. Buyers from Europe and South America should pay attention to local climate conditions, as these can influence the choice of anodizing thickness and color. Ensuring compatibility with local building codes and standards is vital for successful project execution.
In What Ways Does Anodizing Benefit Electronics?
In the electronics industry, anodizing aluminum enclosures helps improve thermal management and wear resistance, which are crucial for device longevity and performance. The anodized surface also provides an excellent base for additional coatings or finishes. International B2B buyers need to consider precision in dimensions and adherence to electrical safety standards when sourcing anodized components. Choosing a supplier with expertise in electronics manufacturing can significantly reduce potential quality issues.
Why is Anodizing Important for Consumer Goods?
Anodizing aluminum is a common practice in producing cookware and kitchen utensils, as it creates non-reactive surfaces that are easy to clean and maintain. This process enhances the durability of the products, making them suitable for everyday use. Buyers, particularly in regions like Africa and South America, should prioritize suppliers that adhere to food safety certifications to ensure compliance with health regulations. Additionally, the availability of durable color options can enhance product appeal in competitive markets.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘anodizing aluminum process’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Difficulty in Achieving Desired Aesthetic Finishes
The Problem: One common challenge B2B buyers face is the inconsistency in achieving specific aesthetic finishes when anodizing aluminum components. Many manufacturers struggle with color matching, resulting in variations that don’t meet the brand standards or client expectations. This inconsistency can lead to wasted materials, increased production costs, and potential delays in project timelines.
The Solution: To mitigate this issue, it is crucial to establish clear specifications for the anodizing process from the outset. Buyers should collaborate closely with anodizing service providers to understand the limitations and capabilities of different anodizing methods, such as sulfuric acid versus hardcoat anodizing. Request samples of previous work to assess color consistency and finish quality. Additionally, consider utilizing electrolytic coloring techniques for more reliable color outcomes, as these methods bond the dye to the oxide layer more effectively. By ensuring thorough communication and specifying tolerances for color and finish, buyers can significantly reduce discrepancies and enhance satisfaction with the final product.
Scenario 2: Managing Environmental Compliance and Sustainability Concerns
The Problem: In today’s global market, environmental compliance is a significant concern for B2B buyers, particularly those in regions with strict regulations. The anodizing process can produce waste that may be harmful if not managed correctly. Companies face the dilemma of balancing production efficiency with sustainability, often leading to anxiety over compliance and potential penalties.
The Solution: To address these environmental concerns, B2B buyers should prioritize partnering with anodizing facilities that adhere to industry standards and environmental regulations. It is advisable to request documentation of the anodizing facility’s waste management practices and environmental certifications. Investing in anodizing processes that utilize eco-friendly electrolytes and recycling systems can further minimize environmental impact. Engaging in a collaborative relationship with the anodizing partner can also facilitate regular audits and assessments of compliance measures, ensuring that both parties maintain a commitment to sustainability. By adopting these practices, buyers can confidently meet regulatory requirements while promoting a sustainable image in the marketplace.
Scenario 3: Cost Overruns Due to Inefficient Anodizing Processes
The Problem: Cost management is a critical concern for B2B buyers, and inefficiencies in the anodizing process can lead to unexpected expenses. Factors such as poor material preparation, extended processing times, and inadequate equipment can result in higher costs per unit and reduced profitability. Buyers often feel the pressure of needing to deliver quality products while adhering to tight budgets.
The Solution: To combat cost overruns, buyers should conduct a thorough evaluation of their anodizing partners’ processes before committing to contracts. Analyzing the entire anodizing workflow—from cleaning and preparation to final sealing—can reveal potential inefficiencies. Investing in suppliers that utilize advanced technologies and automation can optimize the anodizing process, reducing turnaround times and minimizing labor costs. Furthermore, establishing clear timelines and quality standards in the contract can help keep projects on track and within budget. Regular communication and feedback loops with the anodizing provider can also enhance collaboration and ensure that both parties are aligned on cost-efficiency goals, ultimately leading to improved financial outcomes.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for anodizing aluminum process
What Are the Key Materials Used in the Anodizing Aluminum Process?
In the anodizing aluminum process, the selection of materials is crucial for achieving optimal performance and durability of the finished product. Here, we analyze four common materials used in anodizing aluminum, focusing on their properties, advantages, disadvantages, and considerations for international B2B buyers.
1. Sulfuric Acid
Key Properties:
Sulfuric acid is the most widely used electrolyte in the anodizing process. It allows for a coating thickness ranging from 5.1 to 30.5 micrometers. Its ability to create a porous oxide layer enhances adhesion for subsequent coloring and sealing processes.
Pros & Cons:
The primary advantage of sulfuric acid anodizing is its cost-effectiveness and the production of a durable, hard coating. However, the color matching can be inconsistent due to process variability, which may not meet specific aesthetic requirements.
Impact on Application:
Sulfuric acid anodizing is particularly suitable for outdoor applications, such as automotive parts and architectural components, due to its excellent corrosion resistance.
Considerations for International Buyers:
Buyers from regions like Africa and the Middle East should be aware of local regulations regarding chemical handling and disposal. Compliance with international standards such as ASTM and MIL-A-8625 is essential for quality assurance.
2. Chromic Acid
Key Properties:
Chromic acid anodizing produces a thinner oxide layer (approximately 2.5 micrometers) but offers exceptional corrosion resistance. This method is particularly effective for aerospace applications.
Pros & Cons:
While chromic acid anodizing provides excellent corrosion protection, its thinner layer limits its suitability for high-wear applications. Additionally, the process is generally more expensive than sulfuric acid anodizing.
Impact on Application:
This method is ideal for components exposed to harsh environments, such as aircraft parts, where weight and corrosion resistance are critical.
Considerations for International Buyers:
Buyers in Europe may face stricter regulations regarding the use of chromic acid due to environmental concerns. Understanding compliance with REACH regulations is vital for manufacturers in this region.
3. Hardcoat Anodizing
Key Properties:
Hardcoat anodizing utilizes sulfuric acid but operates under higher voltage and lower temperatures, resulting in a thicker oxide layer (12.7 to 50.8 micrometers). This method enhances wear resistance, making it suitable for demanding applications.
Pros & Cons:
The key advantage of hardcoat anodizing is its ability to produce a surface harder than tool steel. However, the process can be more complex and time-consuming, leading to higher manufacturing costs.
Impact on Application:
This anodizing type is ideal for products that experience high abrasion, such as military equipment and industrial machinery components.
Considerations for International Buyers:
Manufacturers from South America should consider the availability of equipment and expertise for hardcoat anodizing, as it may not be as widely practiced in some regions.
4. Electrolytic Coloring
Key Properties:
Electrolytic coloring is a secondary process that can be applied to anodized aluminum, allowing for a wide range of color finishes. This technique uses metal salts to bond colors to the oxide layer.
Pros & Cons:
The primary advantage is the aesthetic appeal and customization it offers. However, achieving precise color matching can be challenging, and the process may add time and cost to production.
Impact on Application:
Electrolytic coloring is often used in consumer products, architectural elements, and decorative items, where appearance is as crucial as functionality.
Considerations for International Buyers:
Buyers in regions with strong branding requirements, such as Europe, may prioritize this process for its ability to enhance product differentiation.
Summary Table of Materials for Anodizing Aluminum Process
| Material | Typical Use Case for anodizing aluminum process | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sulfuric Acid | Automotive parts, architectural components | Cost-effective, durable coating | Inconsistent color matching | Medium |
| Chromic Acid | Aerospace applications | Excellent corrosion resistance | Thinner layer limits wear resistance | High |
| Hardcoat Anodizing | Military equipment, industrial machinery | Surface harder than tool steel | More complex and time-consuming | High |
| Electrolytic Coloring | Consumer products, decorative items | Aesthetic appeal and customization | Difficult color matching, added production time | Medium |
This strategic material selection guide provides valuable insights for B2B buyers navigating the anodizing aluminum process, ensuring informed decision-making for diverse applications across various international markets.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for anodizing aluminum process
What Are the Main Stages in the Manufacturing Process of Anodizing Aluminum?
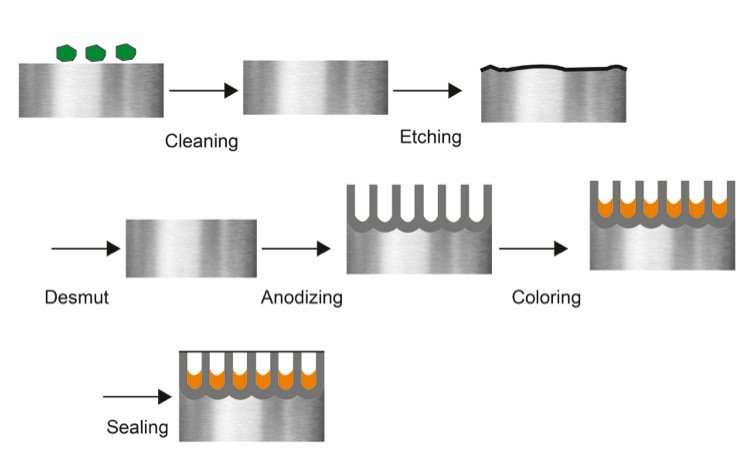
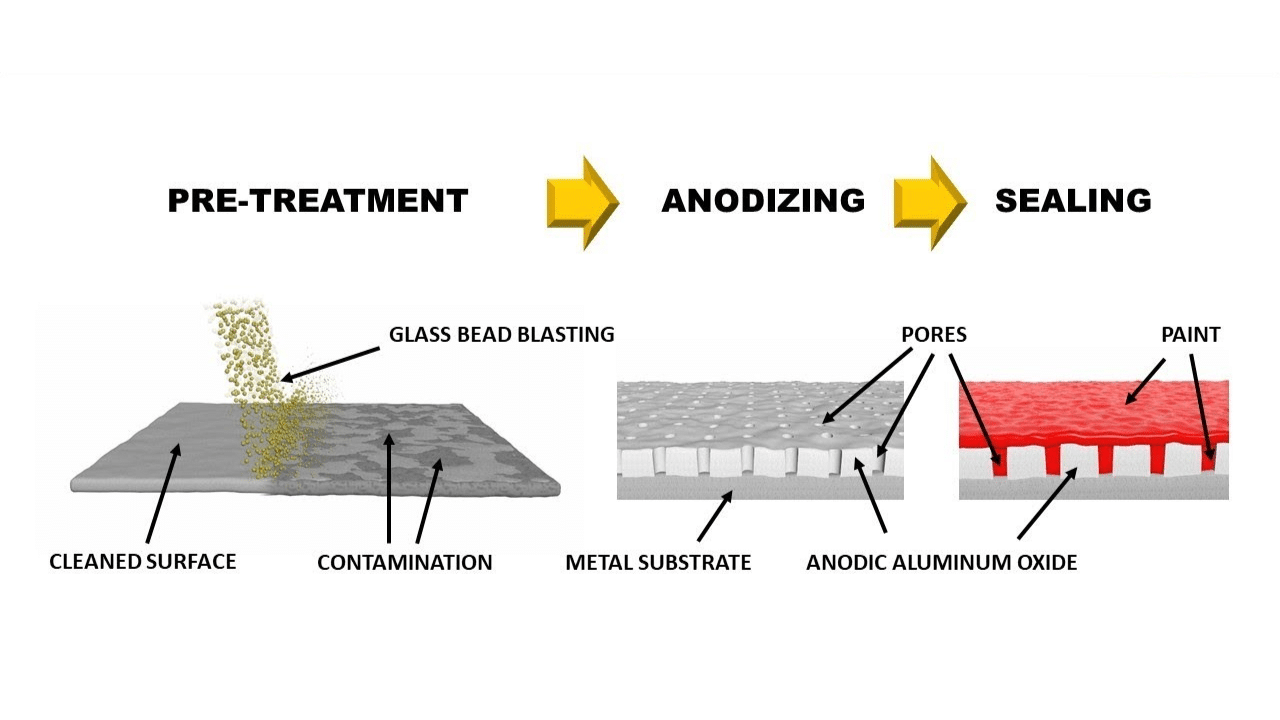
The anodizing aluminum process encompasses several critical stages that ensure high-quality results. Understanding these stages helps B2B buyers evaluate suppliers effectively.
1. Material Preparation
The first step in anodizing aluminum is material preparation, which is crucial for achieving a uniform anodized layer. This involves cleaning the aluminum parts to remove any contaminants, oils, or residues that could affect the anodizing process. Common cleaning methods include alkaline cleaning and acidic pickling, which help in stripping the existing oxide layer and preparing the surface for anodizing.
2. Forming
After cleaning, the aluminum components may undergo forming processes, such as machining or extrusion, depending on the desired shape and specifications. This stage is essential as it ensures that the parts meet the required dimensions and tolerances before anodizing. Proper forming techniques contribute to the structural integrity of the final product.
3. Anodizing
The anodizing itself is an electrochemical process where the cleaned aluminum is immersed in an electrolyte solution, typically sulfuric or chromic acid. An electrical current is then passed through the solution, converting the surface of the aluminum into a thick anodized oxide layer. The thickness and properties of this layer can be controlled by adjusting parameters such as voltage, temperature, and immersion time. This stage is pivotal, as it not only enhances corrosion resistance but also allows for secondary processes like dyeing.
4. Finishing
Post-anodizing, the components undergo finishing processes, which may include sealing, dyeing, or additional surface treatments. Sealing is crucial as it closes the pores of the anodized layer, enhancing durability and corrosion resistance. Various sealing methods, such as hot water sealing or cold sealing, can be employed based on the application requirements. If coloring is desired, the anodized parts can be dyed using electrolytic or dip coloring techniques, providing a range of aesthetic options for manufacturers.
What Quality Control Measures Are Essential in the Anodizing Process?
Quality assurance is paramount in the anodizing aluminum process to ensure that the final products meet international standards and customer expectations. Effective quality control measures include various checkpoints and testing methods.
International Standards and Certifications
B2B buyers should look for suppliers that adhere to recognized international standards, such as ISO 9001, which focuses on quality management systems. Additionally, industry-specific certifications like MIL-A-8625 for military applications or CE marking for European products can provide assurance regarding compliance with safety and quality requirements.
Key Quality Control Checkpoints
-
Incoming Quality Control (IQC): Before any anodizing begins, raw materials must be inspected to ensure they meet specified quality standards. This includes checking for defects in the aluminum and verifying material certificates.
-
In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): During the anodizing process, various parameters such as voltage, temperature, and immersion time must be continuously monitored. This ensures that the anodized layer develops correctly and adheres to the specified thickness.
-
Final Quality Control (FQC): After anodizing and finishing, the parts undergo final inspections. This includes visual inspections for surface defects, measurement of anodized layer thickness, and testing for corrosion resistance. Common testing methods include salt spray tests and adhesion tests to evaluate the durability of the anodized layer.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control Practices?
For international B2B buyers, particularly from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, verifying supplier quality control practices is vital. Here are actionable strategies to ensure compliance and reliability.
Conducting Supplier Audits
Regular audits of potential suppliers can provide insights into their quality management systems and manufacturing processes. Buyers should assess the supplier’s adherence to international standards and their capability to maintain consistent quality throughout production. An audit can also reveal whether the supplier has adequate equipment and trained personnel for quality assurance.
Requesting Quality Control Reports
B2B buyers should not hesitate to request quality control documentation, including inspection reports and certificates of conformity. These documents should detail the testing methods used and the results achieved. A reputable supplier will have no qualms about providing this information to demonstrate their commitment to quality.
Engaging Third-Party Inspectors
Utilizing third-party inspection services can further validate a supplier’s quality assurance practices. These independent organizations can conduct inspections at various stages of the production process, ensuring compliance with the specified standards. This added layer of verification can give buyers greater confidence in their supplier’s capabilities.
What Are the Quality Control and Certification Nuances for International B2B Buyers?
Navigating the complexities of quality control and certification can be challenging for B2B buyers operating across different regions. Understanding local regulations and industry standards is essential.
Regional Certification Requirements
Different regions may have specific certification requirements that impact product acceptance. For example, CE marking is mandatory for products sold within the European Union, while UL certification may be necessary for products entering North American markets. Understanding these nuances helps buyers avoid regulatory pitfalls.
Cultural and Communication Considerations
Cultural differences can influence communication styles and business practices. B2B buyers should establish clear lines of communication with suppliers, ensuring that quality expectations are understood. Regular updates and feedback can foster a collaborative relationship, ultimately enhancing product quality.
Leveraging Local Expertise
Collaborating with local experts or consultants can provide valuable insights into the specific quality control requirements and standards relevant to particular markets. This approach is especially beneficial for buyers new to a region, as it helps navigate the complexities of local regulations and certification processes.
In conclusion, understanding the manufacturing processes and quality assurance measures for anodizing aluminum is crucial for B2B buyers. By focusing on material preparation, forming, anodizing, and finishing stages, along with robust quality control practices, buyers can ensure they partner with reliable suppliers who meet their standards and expectations.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘anodizing aluminum process’
To assist international B2B buyers in sourcing the anodizing aluminum process effectively, this guide provides a structured checklist designed to streamline the procurement process. This checklist emphasizes critical considerations to ensure that you partner with a supplier who meets your technical and business requirements.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Before engaging with suppliers, clearly outline the technical specifications required for your anodized aluminum products. This includes determining the desired thickness of the anodized layer, the type of anodizing (e.g., sulfuric, chromic, or hardcoat), and any specific color finishes you may need. Having well-defined specifications helps suppliers provide accurate quotes and ensures that the final product meets your quality standards.
Step 2: Research Potential Suppliers
Conduct thorough research to identify suppliers with a proven track record in anodizing aluminum. Look for companies with experience in your specific industry, as this can significantly impact the quality and suitability of the anodized products. Evaluate their online presence, customer reviews, and case studies to gauge their credibility and expertise.
Step 3: Evaluate Supplier Certifications
Verify that your potential suppliers possess relevant certifications, such as ISO 9001 for quality management or compliance with military specifications like MIL-A-8625. Certifications indicate a commitment to quality and adherence to industry standards, which is crucial for maintaining the integrity of your products. Additionally, ask for documentation that showcases their anodizing processes and quality control measures.
Step 4: Request Samples for Testing
Before making a final decision, request samples of anodized aluminum products from shortlisted suppliers. This step is essential to assess the quality, finish, and performance of their anodizing process firsthand. Evaluate the samples against your technical specifications and consider conducting tests for durability, corrosion resistance, and color consistency.
Step 5: Inquire About Lead Times and Production Capacity
Discuss lead times and the production capacity of your potential suppliers. Understanding their ability to meet your timelines is critical, especially if you have specific project deadlines. Ensure that they can accommodate your order volume without compromising quality, as this will impact your supply chain efficiency.
Step 6: Evaluate Pricing Structures and Terms
Carefully analyze the pricing structures offered by different suppliers. Look beyond just the base price; consider factors such as minimum order quantities, payment terms, and any potential additional costs for custom specifications. Ensure that the pricing aligns with your budget while still delivering the quality required for your applications.
Step 7: Establish Communication and Support Channels
Finally, ensure that the supplier provides clear communication channels and support throughout the procurement process. A responsive supplier can address any concerns, provide updates on production status, and assist with any technical questions that may arise. Building a strong communication framework fosters a collaborative relationship and enhances overall satisfaction.
By following this checklist, international B2B buyers can streamline their sourcing process for anodizing aluminum, ensuring that they select a supplier that meets their technical and business needs effectively.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for anodizing aluminum process Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components in the Anodizing Aluminum Process?
Understanding the cost structure for the anodizing aluminum process is crucial for international B2B buyers. The main cost components include materials, labor, manufacturing overhead, tooling, quality control (QC), logistics, and margins.
-
Materials: The primary materials involved are aluminum substrates and the electrolytic solutions used in anodizing, typically sulfuric or chromic acid. The quality and source of these materials can significantly impact costs. For instance, sourcing high-purity aluminum may be more expensive but could yield better anodized finishes.
-
Labor: Skilled labor is necessary for operating anodizing equipment and ensuring quality throughout the process. Labor costs vary by region, with countries in Africa or South America potentially offering lower wages compared to Europe or the Middle East. However, the availability of skilled labor should also be considered.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This encompasses utilities, maintenance, and depreciation of anodizing equipment. Higher energy costs, especially in regions with unstable power supplies, can lead to increased overhead expenses.
-
Tooling: Initial setup costs for anodizing lines can be significant. Buyers should consider the cost of specialized tooling for different anodizing methods (e.g., hardcoat anodizing requires more sophisticated equipment).
-
Quality Control (QC): Rigorous QC measures are essential to ensure that anodized finishes meet industry standards, such as MIL-A-8625. The costs associated with testing and inspection should be factored into the overall pricing.
-
Logistics: Transportation costs for raw materials and finished products can vary widely based on geographic location and the selected Incoterms. Buyers in remote areas may face higher shipping costs.
-
Margin: Suppliers typically include a profit margin in their pricing. Understanding the average margin in the anodizing industry can help buyers gauge whether the quoted prices are competitive.
How Do Price Influencers Impact Anodizing Aluminum Costs?
Several factors influence pricing in the anodizing aluminum market, particularly for international B2B buyers.
-
Volume/MOQ: Larger order volumes often lead to better pricing. Suppliers may offer discounts for bulk purchases, which can substantially reduce the cost per unit.
-
Specifications/Customization: Unique specifications or custom finishes can increase costs. Custom colors or special treatments may require additional processing, impacting the overall price.
-
Materials: The choice of aluminum alloy and the quality of anodizing chemicals can alter costs. Higher-quality materials typically yield better performance but come at a premium.
-
Quality/Certifications: Suppliers with certifications or superior quality standards may charge more. Buyers should weigh the benefits of these certifications against potential cost increases.
-
Supplier Factors: Supplier reputation, reliability, and location can affect pricing. Established suppliers may command higher prices due to their experience and quality assurance processes.
-
Incoterms: The chosen Incoterm affects the total landed cost. Buyers should understand which costs are included in the quoted price and what additional expenses they may incur.
What Are the Best Negotiation and Cost-Efficiency Tips for International Buyers?
To maximize cost-efficiency in sourcing anodized aluminum, buyers should consider the following tips:
-
Negotiate Terms: Engage in discussions about pricing, especially for larger orders. Suppliers may be willing to offer discounts or more favorable payment terms for high-volume purchases.
-
Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Evaluate the long-term costs associated with anodized products, including maintenance and potential replacements. A lower initial price may not always equate to cost savings over time.
-
Understand Pricing Nuances: International buyers should be aware of currency fluctuations and how they may impact pricing. Locking in exchange rates or using forward contracts can mitigate risks.
-
Research Suppliers: Conduct thorough research on potential suppliers, focusing on their production capabilities, lead times, and past performance. This information can inform negotiation strategies and help ensure quality.
In conclusion, navigating the complexities of the anodizing aluminum process requires a comprehensive understanding of cost structures, pricing influencers, and effective negotiation strategies. By considering these factors, international B2B buyers can make informed decisions that align with their operational needs and budget constraints.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing anodizing aluminum process With Other Solutions
Exploring Alternatives to the Anodizing Aluminum Process
In the quest for enhanced durability and aesthetic appeal in aluminum products, the anodizing aluminum process is a popular choice among manufacturers. However, it is essential for B2B buyers to consider alternative surface treatment methods that may better suit specific project requirements. This section provides a comparative analysis of anodizing aluminum against other viable solutions, including powder coating and plating, to help businesses make informed decisions.
| Comparison Aspect | Anodizing Aluminum Process | Powder Coating | Plating |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | Excellent corrosion resistance; hard, durable finish; porous for dyeing | Good corrosion resistance; thick, uniform finish; less durable than anodizing | Varies widely; can provide a very smooth finish; good for decorative purposes |
| Cost | Moderate; cost-effective for large batches | Generally lower; bulk application can reduce costs | Can be high; dependent on metal type and thickness |
| Ease of Implementation | Requires specialized equipment and knowledge | Relatively easy; less equipment needed | Complex; requires precise control and skilled labor |
| Maintenance | Low; resistant to wear and easy to clean | Moderate; may chip or scratch over time | Varies; can corrode or wear off without proper care |
| Best Use Case | High-performance applications; outdoor and industrial uses | Consumer products; furniture; applications needing color | Decorative items; electronic components requiring conductivity |
What Are the Advantages and Disadvantages of Powder Coating?
Powder coating is a popular alternative that involves applying a dry powder to the surface of aluminum, which is then cured under heat. This method offers a durable finish that is resistant to scratches and corrosion, making it suitable for a variety of applications, including consumer goods and outdoor furniture.
Pros: Powder coating is generally more cost-effective than anodizing, especially for large production runs. It also provides a thicker finish that can cover surface imperfections better than anodizing. Additionally, the process is environmentally friendly, as it produces minimal waste.
Cons: However, powder coating does not offer the same level of corrosion resistance as anodizing, particularly in harsh environments. The finish can also chip more easily and may require more maintenance over time to retain its appearance.
How Does Plating Compare to Anodizing?
Plating, which involves depositing a layer of metal onto the aluminum surface, can enhance aesthetic appeal and provide additional protection. Various types of plating, such as nickel or chrome plating, can be applied to achieve different finishes and properties.
Pros: Plating can offer a highly attractive finish that is smooth and reflective, making it ideal for decorative items and electronic components. It can also provide good conductivity and is often used in electronics.
Cons: The main drawbacks of plating are its variable performance and higher cost. Depending on the thickness and type of metal used, the durability and resistance to wear can differ significantly. Additionally, plating can corrode over time if not properly maintained, requiring more frequent upkeep than anodized surfaces.
How Can B2B Buyers Choose the Right Solution?
When selecting a surface treatment method, B2B buyers should evaluate their specific needs, including the intended application, environmental conditions, and aesthetic requirements. Anodizing is ideal for high-performance, outdoor applications due to its superior corrosion resistance and durability. In contrast, powder coating may be more suitable for less demanding environments where cost-effectiveness and color variety are priorities. Plating can be the best choice for decorative or electronic components that require a smooth finish and conductivity.
By carefully considering these factors, businesses can choose the most appropriate surface treatment solution that aligns with their operational goals and customer expectations.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for anodizing aluminum process
What Are the Key Technical Properties of the Anodizing Aluminum Process?
In the anodizing aluminum process, understanding the critical technical properties is essential for B2B buyers to ensure they select the right materials for their applications. Here are some of the most important specifications:
-
Material Grade
Aluminum alloys are categorized into various grades, such as 6061, 6063, and 7075, each with distinct mechanical properties and corrosion resistance. Selecting the appropriate grade is crucial as it influences the anodizing quality and the final product’s performance. For instance, 6061 is often preferred for structural applications due to its excellent strength-to-weight ratio. -
Coating Thickness
The thickness of the anodized layer can vary significantly, typically ranging from 5.1 to 50.8 microns, depending on the anodizing process used. This specification is vital because it directly affects the durability, corrosion resistance, and aesthetic appeal of the aluminum. Buyers should consider their end-use requirements when determining the necessary coating thickness. -
Tolerances
Tolerances refer to the permissible limits of variation in dimensions and coating thickness. Tight tolerances are critical in industries like aerospace and automotive, where precision is paramount. Buyers should communicate their tolerance requirements clearly to ensure compatibility with manufacturing processes and final applications. -
Hardness
The anodized layer’s hardness can vary based on the anodizing method. Hardcoat anodizing, for example, produces a layer that can be harder than tool steel, making it suitable for high-wear applications. Understanding hardness specifications helps buyers select the right anodizing process based on their product’s intended use. -
Color Consistency
While anodizing allows for dyeing, achieving consistent color across batches can be challenging due to process variability. Buyers should be aware of this and may need to specify color requirements in detail, particularly for products where aesthetics are a key consideration. -
Environmental Resistance
Anodized aluminum exhibits superior resistance to environmental factors, including UV radiation, moisture, and temperature fluctuations. This property is particularly important for outdoor applications, ensuring longevity and maintaining appearance over time.
What Are Common Trade Terms Related to Anodizing Aluminum?
Familiarity with industry-specific terminology is essential for effective communication and negotiation in B2B transactions. Here are some key terms related to the anodizing aluminum process:
-
OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
An OEM is a company that produces parts or equipment that may be marketed by another company. In the context of anodizing, OEMs often seek anodized aluminum components for their products, making it crucial for suppliers to understand the specifications required by their OEM partners. -
MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ refers to the smallest quantity of products that a supplier is willing to sell. This term is significant in anodizing as it can affect pricing and inventory management. Buyers should be aware of MOQs to negotiate terms that align with their production needs. -
RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a document issued by a buyer to solicit price bids from suppliers for specific products or services. In anodizing, submitting an RFQ with detailed specifications helps ensure that suppliers provide accurate quotes, facilitating better decision-making. -
Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
Incoterms are a series of predefined commercial terms published by the International Chamber of Commerce, outlining the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in international transactions. Understanding these terms is critical for B2B buyers involved in cross-border procurement of anodized aluminum products. -
Lead Time
Lead time refers to the time it takes from placing an order until the product is delivered. This term is especially relevant in the anodizing industry, where processing times can vary based on the complexity of the project and current workload. -
Surface Finish
Surface finish refers to the texture and appearance of the anodized layer. This property is vital for applications where aesthetics are important, such as architectural components or consumer products. Buyers should specify their surface finish requirements to achieve the desired outcome.
By understanding these technical properties and trade terms, B2B buyers can make informed decisions that align with their project specifications and operational needs, ultimately leading to successful procurement of anodized aluminum products.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the anodizing aluminum process Sector
What Are the Key Market Trends in the Anodizing Aluminum Process Sector?
The anodizing aluminum process market is experiencing robust growth, driven by several global factors. The demand for lightweight, durable materials in industries such as automotive, aerospace, and construction is propelling the adoption of anodized aluminum. In regions like Africa and South America, infrastructure development is a key driver, as countries strive to modernize their urban environments. In the Middle East, high temperatures and humidity levels necessitate corrosion-resistant materials, making anodized aluminum an ideal choice for outdoor applications.
Emerging technologies are also shaping sourcing trends in this sector. Automation and advanced electrochemical processes are enhancing efficiency and reducing production costs, making it easier for international buyers to access high-quality anodized products. Digital platforms for procurement are gaining traction, allowing buyers to compare suppliers globally, ensuring competitive pricing and quality assurance. Additionally, the rise of Industry 4.0 is leading to smarter manufacturing processes, which can provide real-time data on product quality and supply chain management.
How Is Sustainability Shaping Sourcing Decisions in the Anodizing Aluminum Sector?
Sustainability is becoming a critical factor for B2B buyers in the anodizing aluminum sector. The environmental impact of traditional manufacturing processes is under scrutiny, prompting companies to seek suppliers who prioritize eco-friendly practices. Anodizing is inherently a more sustainable option compared to other finishing techniques, as it uses less harmful chemicals and generates minimal waste.
Ethical sourcing is increasingly important as companies strive to align their operations with global sustainability goals. Buyers are encouraged to partner with suppliers that have green certifications, such as ISO 14001, which demonstrates a commitment to environmental management. Additionally, sourcing from suppliers who use recycled aluminum contributes to a circular economy, reducing the carbon footprint associated with raw material extraction. This focus on sustainability not only enhances brand reputation but also meets the growing consumer demand for environmentally responsible products.
What Is the Historical Context of Anodizing Aluminum Processes?
The anodizing aluminum process has evolved significantly since its inception in the early 20th century. Originally developed for military applications, the technique was quickly adopted across various industries due to its ability to enhance aluminum’s corrosion resistance and aesthetic appeal. By the 1960s, anodizing had become a standard practice in architectural applications, with anodized aluminum being used for everything from skyscraper facades to consumer electronics.
As technological advancements continued, the process became more refined, allowing for greater customization in terms of color and finish. Today, with the integration of advanced electrochemical techniques and a heightened focus on sustainability, anodizing aluminum has solidified its position as a preferred method for treating aluminum surfaces, catering to a diverse range of applications from industrial machinery to high-end consumer goods. This historical context underscores the importance of anodizing as a versatile and essential process in modern manufacturing.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of anodizing aluminum process
-
How do I choose the right anodizing process for my aluminum products?
Choosing the right anodizing process depends on your specific requirements, such as desired thickness, color, and application environment. Sulfuric acid anodizing is the most common due to its durability and ability to accept dyes, making it suitable for a wide range of applications. If you need a thicker, harder coating for high-wear parts, consider hardcoat anodizing. For applications where corrosion resistance is critical but aesthetics are less important, chromic acid anodizing may be appropriate. Always consult with your anodizing supplier to determine the best process based on your product specifications and end-use. -
What are the typical lead times for anodizing aluminum orders?
Lead times for anodizing aluminum can vary based on factors such as order volume, complexity, and the specific anodizing process chosen. Generally, standard lead times range from 1 to 4 weeks. For urgent projects or larger quantities, it’s advisable to communicate your timeline requirements upfront. Establishing a good relationship with your supplier can also lead to expedited processing for future orders, so consider discussing your long-term needs to optimize lead times. -
What minimum order quantities (MOQs) are common in anodizing aluminum?
Minimum order quantities for anodizing services can vary by supplier and the complexity of the project. Some suppliers may have MOQs as low as 50 pieces for standard items, while custom or complex parts may require higher volumes, often starting at 100 or more. It’s essential to discuss your needs with potential suppliers to negotiate MOQs that align with your production capabilities and budget. Always factor in the cost of setup and processing when evaluating MOQs. -
How do I ensure quality control during the anodizing process?
Quality control in anodizing involves multiple stages, including pre-treatment cleaning, anodizing parameters, and post-treatment inspection. Request detailed process documentation from your supplier, including compliance with relevant industry standards such as MIL-A-8625. Conduct on-site audits if possible, or request samples for testing. Establishing clear quality expectations and regular communication with your supplier will help ensure that the final product meets your specifications and performance requirements. -
What payment terms are typically offered for anodizing aluminum services?
Payment terms for anodizing services can vary significantly based on the supplier’s policies and your business relationship. Common arrangements include net 30 or net 60 days after delivery, but many suppliers may require a deposit upfront, especially for larger orders. It’s advisable to negotiate terms that work for both parties, considering factors like order size, frequency of business, and your creditworthiness. Always ensure that payment terms are clearly outlined in the contract to avoid any misunderstandings. -
What are the environmental considerations associated with anodizing aluminum?
Anodizing is generally considered an environmentally friendly process because it uses non-toxic chemicals and produces minimal waste. However, it’s crucial to verify that your chosen supplier adheres to local environmental regulations and employs sustainable practices. Ask about their waste management procedures and any certifications they hold regarding environmental compliance. This diligence not only helps in minimizing ecological impact but also enhances your brand’s reputation among eco-conscious consumers. -
How do I vet potential anodizing suppliers for international orders?
Vetting anodizing suppliers involves assessing their experience, certifications, and production capabilities. Start by reviewing their portfolio and client testimonials to gauge reliability and quality. Request certifications such as ISO 9001 or specific anodizing standards relevant to your industry. It’s also beneficial to conduct on-site visits or virtual tours to understand their processes better. Establishing clear communication and asking for samples can further ensure that the supplier can meet your specifications and delivery timelines. -
What should I consider regarding logistics when sourcing anodized aluminum?
When sourcing anodized aluminum, logistics play a crucial role in timely delivery and cost management. Consider factors such as shipping methods, customs regulations, and potential tariffs, especially for international shipments. Work with suppliers who have experience in international logistics to avoid delays. Discuss packaging requirements to protect the anodized finish during transport. Establishing a robust logistics plan, including clear communication with your supplier, can help streamline the entire process and ensure your products arrive in optimal condition.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.
Top 7 Anodizing Aluminum Process Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. Bonnell Aluminum – Anodizing Solutions
Domain: bonnellaluminum.com
Registered: 2007 (18 years)
Introduction: Bonnell Aluminum specializes in anodizing processes that enhance aluminum’s natural oxide film, resulting in a durable aluminum oxide coating with hardness comparable to ruby or sapphire. The anodizing process involves several critical steps: pre-treatment with alkaline detergents, rinsing, chemical milling (etching), desmutting, anodizing in a sulfuric acid electrolyte, coloring with organic or i…
2. Hubs – Anodizing Services
Domain: hubs.com
Registered: 1998 (27 years)
Introduction: Anodizing is an electrochemical process used to finish parts made from aluminum and other metals, providing additional sturdiness and an attractive finish. It involves coating a metal part with an oxide surface layer, ensuring resistance to corrosion and wear. Common substrates include aluminum, magnesium, and titanium. The main types of anodizing are Type I (Chromic Acid Anodize), Type II (Sulfur…
3. Wayken RM – Anodized Aluminum Solutions
Domain: waykenrm.com
Registered: 2013 (12 years)
Introduction: Anodized aluminum is treated with an electrolytic process to create a durable and corrosion-resistant oxide layer on the surface. This process enhances the visual qualities of aluminum and allows for color changes. The anodizing process is suitable for conductive materials, primarily aluminum, and can also be applied to non-ferrous metals like titanium and magnesium. Key steps in anodizing include…
4. Valence Surface Tech – Anodized Aluminum Solutions
Domain: valencesurfacetech.com
Registered: 2014 (11 years)
Introduction: Anodized aluminum is aluminum that has undergone an anodizing process to create a durable and protective oxide layer on its surface. The anodizing process involves immersing aluminum in an electrolyte bath and applying an electrical current, resulting in enhanced corrosion resistance, increased hardness, and improved aesthetic appeal. The main types of anodized aluminum include: Type I (chromic ac…
5. Sybridge – Anodizing Solutions
Domain: sybridge.com
Registered: 2003 (22 years)
Introduction: Anodizing is a process that thickens the natural oxide layer on a metal part’s surface, primarily used for aluminum and titanium, as well as other non-ferrous metals. There are three types of anodizing according to MIL-A-8625: Type I (chromic acid, thin oxide layer), Type II (sulfuric acid, thicker oxide layer suitable for coloration), and Type III (hard anodizing, even thicker oxide layer). Benef…
6. Gabrian – Anodized Aluminum Solutions
Domain: gabrian.com
Registered: 2000 (25 years)
Introduction: Anodized aluminum is a finish that adds corrosion protection and color to aluminum products. It involves a process that thickens the naturally occurring oxide layer on aluminum, enhancing its properties. Key benefits include improved wear resistance, increased corrosion resistance, enhanced dye adhesion, better heat dissipation, and unchanged strength of the aluminum. Anodized aluminum has a porou…
7. Neway Precision – Anodized Aluminum Parts
Domain: newayprecision.com
Registered: 2017 (8 years)
Introduction: Anodized Aluminum Parts: Anodizing Process and Benefits Overview: Aluminum is lightweight, corrosion-resistant, and versatile. Anodizing enhances its properties through an electrochemical process that creates a protective oxide layer. Types of Anodizing: 1. Type I: Sulfuric Acid Anodizing – Cost-effective, easy to handle, colorless, transparent oxide film, high hardness, good wear resistance, but …
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for anodizing aluminum process
In the evolving landscape of aluminum processing, strategic sourcing of anodized aluminum presents significant advantages for international buyers. The anodizing process enhances aluminum’s natural properties, providing a durable, corrosion-resistant finish that meets diverse industry needs, from automotive to aerospace and architecture. By understanding the three primary anodizing methods—chromic acid, sulfuric acid, and hardcoat anodizing—buyers can make informed decisions tailored to their specific applications and cost considerations.
Investing in anodized aluminum not only improves product longevity but also elevates aesthetic appeal, making it a preferred choice across various sectors. Furthermore, with sustainability becoming a priority, anodizing stands out as an environmentally friendly process, offering minimal harmful effects on the environment.
Looking ahead, companies in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe should leverage the benefits of anodized aluminum to enhance their competitive edge. Engaging with reliable suppliers and exploring innovative anodizing solutions can unlock new opportunities for growth and differentiation in the market. Take the next step in your sourcing strategy by collaborating with experienced anodizing partners to maximize the value of your products.