Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for anodized vs alodine
In the ever-evolving landscape of aluminum finishing, international B2B buyers face the critical challenge of selecting between anodized and Alodine (chem film) coatings. Understanding the nuances of these two processes is essential for sourcing reliable, corrosion-resistant aluminum components that meet specific application requirements. This guide delves into the intricacies of anodizing and Alodine, exploring their respective benefits, cost implications, and suitability for various industries, from aerospace to automotive.
Throughout this comprehensive resource, we will cover the types of anodizing and Alodine finishes available, the key applications where each excels, and practical tips for vetting suppliers to ensure quality and compliance with international standards. Additionally, we will provide insights into cost considerations, helping you make informed purchasing decisions tailored to your market, whether in Africa, South America, the Middle East, or Europe.
By equipping yourself with this essential knowledge, you can navigate the global market with confidence, ensuring that your procurement process aligns with the unique needs of your business. This guide is designed to empower you, the B2B buyer, to make strategic choices that enhance your product offerings and drive success in a competitive marketplace.
Understanding anodized vs alodine Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Type I Anodizing | Thin, non-porous layer; provides minimal corrosion resistance | Aerospace, automotive, electronics | Pros: Excellent surface for painting; Cons: Limited corrosion protection. |
| Type II Anodizing | Thicker, porous layer; enhances corrosion resistance | Military, marine, industrial equipment | Pros: High durability; Cons: Higher cost and longer processing time. |
| Type III Anodizing | Hard anodizing; significantly increases surface hardness | Aerospace, defense, tooling | Pros: Exceptional wear resistance; Cons: Limited color options. |
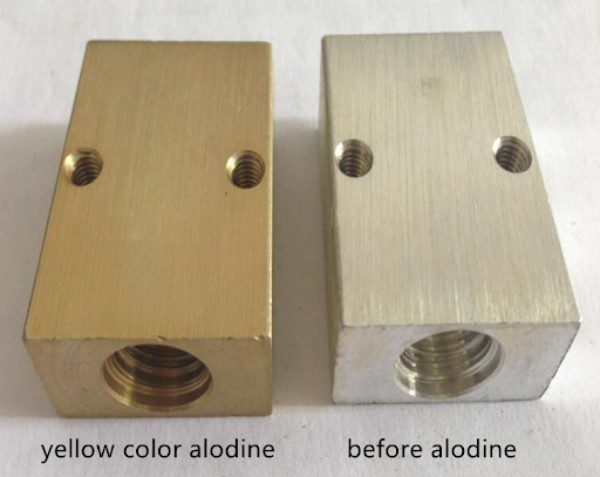
| Alodine Type I | Hexavalent chromium-based; thicker coating for corrosion protection | Aerospace, military, electrical | Pros: Excellent corrosion resistance; Cons: Environmental concerns with hexavalent chromium. |
| Alodine Type II | Non-hexavalent chromium; lighter coating for conductivity | Electrical components, heat exchangers | Pros: Retains electrical conductivity; Cons: Less corrosion resistance than Type I. |
What are the Key Features of Different Types of Anodizing?
Type I Anodizing is characterized by a thin, non-porous layer that provides minimal corrosion resistance. It is often used in industries like aerospace and automotive, where aesthetic finishes are important. While it offers an excellent surface for painting, its limited corrosion protection may not suit all applications, especially in harsh environments.
Type II Anodizing involves a thicker, porous layer that significantly enhances corrosion resistance, making it ideal for military and marine applications. This type is known for its durability and is suitable for parts that require additional protection. However, the higher costs and longer processing times can be a consideration for budget-conscious buyers.
Type III Anodizing, or hard anodizing, creates a surface that is significantly harder than standard anodizing. This makes it suitable for demanding applications in aerospace and defense industries where wear resistance is critical. While it offers exceptional durability, the limited color options may restrict aesthetic choices.
How Does Alodine Compare to Anodizing?
Alodine Type I coatings utilize hexavalent chromium and provide a thicker layer for corrosion protection. This type is commonly used in aerospace and military applications. While it offers excellent corrosion resistance, environmental regulations regarding hexavalent chromium can pose challenges for manufacturers aiming to comply with sustainability standards.
Alodine Type II coatings, on the other hand, are non-hexavalent and provide a lighter coating that retains electrical conductivity. This makes them particularly suitable for electrical components and heat exchangers. While they offer the advantage of conductivity, they may not provide the same level of corrosion resistance as Type I coatings, which is a key consideration for buyers in corrosive environments.
In summary, the choice between anodizing and Alodine coatings depends on specific application needs, including environmental conditions, conductivity requirements, and budget constraints. Understanding these variations will help B2B buyers make informed decisions tailored to their operational demands.
Key Industrial Applications of anodized vs alodine
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of anodized vs alodine | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Aerospace | Anodized aluminum components for aircraft parts | Enhanced corrosion resistance and weight reduction | Compliance with aerospace industry standards and certifications |
| Automotive | Alodine-treated parts for electrical components | Retention of electrical conductivity and corrosion protection | Cost-effectiveness and speed of application |
| Military & Defense | Anodized coatings on tactical equipment | Improved durability and resistance to harsh environments | Proven track record in military applications and reliability |
| Marine | Alodine finish on components exposed to saltwater | Long-lasting protection against corrosion in harsh conditions | Resistance to saltwater corrosion and regulatory compliance |
| Electronics | Anodized heat sinks for thermal management | Improved heat dissipation and performance reliability | Compatibility with existing systems and thermal conductivity requirements |
How is Anodized Aluminum Used in Aerospace Applications?
In the aerospace industry, anodized aluminum is widely used for aircraft components such as fuselage skins, wing structures, and landing gear. The anodizing process enhances the aluminum’s natural corrosion resistance while maintaining a lightweight profile, which is crucial for fuel efficiency. Buyers in this sector must ensure that anodized parts meet stringent aerospace standards (like MIL-A-8625) and possess the necessary certifications for safety and reliability. Furthermore, suppliers should be able to demonstrate expertise in handling complex geometries and provide traceability for materials used.
What Role Does Alodine Play in Automotive Electrical Components?
Alodine coatings are commonly applied to aluminum parts in the automotive industry, particularly for components requiring electrical conductivity, such as connectors and heat sinks. The chem-film process protects these parts from corrosion while allowing them to maintain their electrical properties. For international buyers, particularly in regions like Brazil and Nigeria, sourcing Alodine-treated components can lead to cost savings and faster production cycles. It is essential to partner with suppliers who understand local regulations and can provide consistent quality assurance to meet automotive standards.
Why is Anodizing Important for Military and Defense Equipment?
In military applications, anodized coatings are critical for enhancing the durability of tactical equipment, such as weapon systems and vehicles. The anodizing process not only provides corrosion resistance but also improves the surface hardness, which is vital in combat scenarios. Buyers in this sector must prioritize suppliers with a proven track record in military applications, ensuring compliance with defense standards. Additionally, the ability to withstand extreme environmental conditions is a key requirement, making it essential to evaluate the technical capabilities of potential partners.
How Does Alodine Protect Marine Components?
Marine applications often require robust protection against corrosion, particularly in saltwater environments. Alodine finishes are ideal for aluminum components such as boat hulls, fittings, and hardware, as they provide a barrier against corrosion without altering the dimensions of the parts. For businesses in the marine sector, sourcing Alodine-treated components can ensure longevity and reliability in harsh conditions. Buyers should consider suppliers who offer products that meet marine industry standards and can provide evidence of performance in real-world applications.
What Benefits Does Anodized Aluminum Provide in Electronics?
Anodized aluminum is extensively used in the electronics industry, particularly for heat sinks that manage thermal performance in devices. The anodizing process improves the thermal conductivity and surface finish, which is essential for efficient heat dissipation. International buyers, especially in Europe, should seek suppliers who can guarantee compatibility with existing electronic systems and provide detailed specifications on thermal performance. Additionally, understanding the anodized layer’s thickness and quality is critical for ensuring optimal performance in high-tech applications.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘anodized vs alodine’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Cost Efficiency in Coating Selection
The Problem: Many B2B buyers in industries such as aerospace, automotive, and electronics are often caught in a dilemma when it comes to selecting between anodized and Alodine finishes. They face a significant challenge in balancing budget constraints with the need for effective corrosion resistance and other performance properties. Anodizing is generally more expensive due to the complex electrolytic process and the required technical expertise. Buyers may feel pressured to choose the cheaper option, Alodine, but worry it might compromise quality and longevity.
The Solution: To navigate this challenge, buyers should conduct a comprehensive cost-benefit analysis before making a decision. First, assess the specific application requirements: Does the component need to retain electrical conductivity or undergo further painting? If so, Alodine may be more suitable despite its lower initial cost. On the other hand, if durability and enhanced corrosion resistance are paramount, investing in anodizing could lead to lower long-term costs by reducing maintenance and replacement expenses. Collaborating with a knowledgeable supplier who can provide detailed insights on the total cost of ownership for both options is vital. This approach allows buyers to make informed decisions that align with their budgetary constraints while ensuring product performance.
Scenario 2: Technical Expertise and Process Understanding
The Problem: B2B buyers often struggle with understanding the technical nuances of anodizing and Alodine processes. This lack of knowledge can lead to miscommunication with suppliers, resulting in incorrect specifications that could compromise the integrity of the finished product. For instance, a buyer may unknowingly request anodizing for a part that requires high electrical conductivity, not realizing that the anodizing process would compromise that feature.
The Solution: Buyers should invest time in educating themselves about the differences between anodizing and Alodine finishes. This includes understanding the specific requirements of their applications and how each process affects the material properties of aluminum. Engaging with reputable suppliers who offer educational resources, webinars, or workshops can greatly enhance understanding. Additionally, creating a checklist of performance requirements before reaching out to suppliers will facilitate more productive discussions. This proactive approach not only clarifies expectations but also ensures that the chosen finishing process aligns perfectly with the technical specifications needed for the application.
Scenario 3: Environmental and Compliance Considerations
The Problem: In today’s global market, regulatory compliance regarding environmental standards is increasingly critical. Buyers in regions such as Europe and parts of South America may encounter stringent regulations regarding chemical processes and waste disposal. The choice between anodizing and Alodine can become complicated if the buyer is unaware of the environmental impact or the regulatory compliance required for each process. For example, anodizing can produce hazardous waste that requires specialized disposal, while certain Alodine processes may involve hexavalent chromium, which is heavily regulated.
The Solution: To address this pain point, buyers should thoroughly research the environmental regulations applicable in their regions and industries. Consulting with environmental compliance specialists or legal advisors can provide insights into the regulations that govern the finishing processes. When selecting a supplier, prioritize those who can demonstrate adherence to environmental standards and offer eco-friendly alternatives. For instance, opting for Alodine processes that do not use hexavalent chromium can simplify compliance and reduce environmental impact. Additionally, ensure that suppliers provide clear documentation regarding their waste disposal practices and compliance certifications, which will help mitigate risks associated with regulatory violations.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for anodized vs alodine
What Are the Key Properties of Anodized and Alodine Finishes?
When considering anodized versus Alodine finishes for aluminum components, understanding the properties of each material is crucial for B2B buyers.
-
Anodized Aluminum: Anodizing enhances aluminum’s natural oxide layer through an electrolytic process, resulting in improved corrosion resistance, wear resistance, and aesthetic appeal. It is suitable for applications requiring high durability, such as aerospace and automotive components. Anodized aluminum can withstand temperatures up to 150°C (302°F) and offers excellent adhesion for paints and adhesives.
-
Alodine (Chem-Film): Alodine, or chemical film, is a non-electrolytic process that creates a thin, protective layer on aluminum surfaces. It is particularly effective in environments where electrical conductivity is required, as it does not significantly impede the metal’s conductivity. Alodine coatings are typically suitable for temperatures up to 85°C (185°F) and provide good corrosion resistance, especially in marine applications.
What Are the Pros and Cons of Anodized and Alodine Finishes?
Anodized Aluminum:
– Pros:
– Superior corrosion resistance and durability.
– Enhanced surface hardness and wear resistance.
– Aesthetic versatility with the ability to dye in various colors.
– Cons:
– Higher manufacturing complexity and cost.
– Requires skilled technicians for quality control.
– Limited thermal conductivity compared to Alodine.
Alodine (Chem-Film):
– Pros:
– Lower cost and simpler application process.
– Maintains electrical and thermal conductivity.
– Quick application, making it suitable for high-volume production.
– Cons:
– Generally less durable than anodized finishes.
– May not provide sufficient protection in highly corrosive environments.
– Surface may require additional treatments for paint adhesion.
How Do Anodized and Alodine Finishes Impact Specific Applications?
The choice between anodized and Alodine finishes significantly impacts application suitability. Anodized finishes are ideal for components exposed to harsh environments, such as aircraft parts or automotive components, where durability and corrosion resistance are paramount. In contrast, Alodine is often preferred for electrical components and military applications, where maintaining conductivity is essential.
What Should International B2B Buyers Consider When Selecting Between Anodized and Alodine?
For international B2B buyers, particularly from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, compliance with local standards is critical. Buyers should be aware of relevant certifications such as ASTM (American Society for Testing and Materials), DIN (Deutsches Institut für Normung), and JIS (Japanese Industrial Standards). Additionally, preferences for specific coatings may vary by industry and region, with some markets favoring the cost-effectiveness of Alodine for mass production, while others may prioritize the superior performance of anodized finishes for specialized applications.
Summary Table of Material Selection
| Material | Typical Use Case for anodized vs alodine | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Anodized Aluminum | Aerospace, automotive parts | Superior corrosion and wear resistance | Higher cost and complexity | High |
| Alodine (Chem-Film) | Electrical components, military equipment | Maintains electrical conductivity | Less durable in harsh environments | Low |
| Anodized Aluminum | Architectural applications, consumer goods | Aesthetic versatility with color options | Requires skilled application | High |
| Alodine (Chem-Film) | Marine applications, heat sinks | Quick application and lower cost | May need additional treatment for paint adhesion | Low |
This analysis provides a strategic framework for B2B buyers to make informed decisions regarding the selection of anodized versus Alodine finishes, ensuring that their specific application needs and regional considerations are met effectively.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for anodized vs alodine
What Are the Key Manufacturing Processes for Anodized vs. Alodine Finishes?
When considering anodized versus alodine finishes for aluminum components, understanding the manufacturing processes involved is crucial for B2B buyers. Each process has distinct stages that impact the final product’s quality, durability, and performance.
What Are the Main Stages in the Manufacturing Process?
Both anodizing and alodine coating involve several key stages: material preparation, forming, assembly, and finishing.
-
Material Preparation:
– Surface Cleaning: Before any finishing process, aluminum parts must be thoroughly cleaned to remove any grease, dirt, or oxidation. This can involve chemical cleaning solutions or abrasive methods.
– Surface Inspection: Visual and instrumental inspections are performed to ensure the aluminum meets quality standards before proceeding. -
Forming:
– This stage involves shaping the aluminum into the desired specifications, which may include cutting, bending, or extruding. The forming process must be precise to ensure that the final dimensions align with engineering requirements. -
Assembly:
– In cases where multiple components are involved, they are assembled before finishing. This stage may include welding or mechanical fastening, which requires careful attention to avoid damaging the aluminum surface. -
Finishing:
– Anodizing: This electrolytic process involves immersing the aluminum in an electrolytic solution and applying an electrical current. This causes the aluminum to oxidize, creating a thick, protective anodic layer that enhances corrosion resistance and allows for dyeing.
– Alodine Coating: This chemical conversion process does not require electrical current. Instead, the aluminum is treated with a chemical solution that forms a protective layer, providing corrosion resistance while allowing for electrical conductivity.
How Is Quality Assurance Implemented in Manufacturing?
Quality assurance is vital in the manufacturing of anodized and alodine finishes. It ensures that the final products meet international standards and customer expectations.
What Are the Relevant International Standards for Quality Assurance?
B2B buyers should be aware of the various international standards applicable to anodizing and alodine processes. Common standards include:
- ISO 9001: This standard outlines requirements for a quality management system, ensuring consistency in product quality and customer satisfaction.
- CE Marking: Required for products sold in the European Economic Area, indicating compliance with health, safety, and environmental protection standards.
- API Spec Q1/Q2: Relevant for industries such as oil and gas, ensuring that products meet stringent quality criteria.
What Are the QC Checkpoints Throughout the Manufacturing Process?
Quality control (QC) checkpoints are essential at various stages of the manufacturing process to maintain quality standards.
-
Incoming Quality Control (IQC):
– Inspects raw materials and components upon arrival to ensure they meet specified standards. This includes verifying certificates of compliance and conducting material tests. -
In-Process Quality Control (IPQC):
– Conducted during manufacturing, this involves regular inspections and tests to monitor the quality of parts at each stage, particularly during the anodizing or alodine application. -
Final Quality Control (FQC):
– After finishing, the final products undergo comprehensive testing, including visual inspections, dimensional checks, and performance tests to ensure they meet quality standards.
What Common Testing Methods Are Used to Ensure Quality?
Testing methods play a crucial role in verifying the quality of anodized and alodine finishes. Common methods include:
- Thickness Measurement: Using micrometers or electronic thickness gauges to ensure the coating meets specified thickness requirements.
- Adhesion Testing: This includes tape tests or cross-cut tests to ensure that the anodized or alodine coating adheres well to the aluminum surface.
- Corrosion Testing: Salt spray tests or other accelerated corrosion tests help evaluate the durability of the finish under harsh conditions.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control Processes?
International B2B buyers, particularly from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, should implement several strategies to verify supplier quality control:
-
Supplier Audits: Conducting regular audits of suppliers can provide insights into their manufacturing processes, quality control measures, and compliance with international standards.
-
Quality Reports: Requesting detailed quality reports and certifications can help buyers assess the supplier’s adherence to standards like ISO 9001 or industry-specific certifications.
-
Third-Party Inspections: Engaging third-party inspection agencies can provide an unbiased evaluation of the supplier’s processes and products, ensuring that they meet required standards.
What Are the Quality Control and Certification Nuances for International B2B Buyers?
B2B buyers from diverse regions should be aware of the nuances in quality control and certification that may affect their purchasing decisions.
- Regional Standards: Different regions may have varying standards for quality control, which can affect product certification. Buyers should familiarize themselves with local regulations and certifications required for their specific markets.
- Cultural Differences: Understanding cultural differences in business practices can facilitate better communication with suppliers, ensuring that quality expectations are clearly outlined and understood.
In conclusion, the choice between anodized and alodine finishes involves more than just understanding the processes; it requires a comprehensive approach to quality assurance. By being informed about manufacturing stages, quality standards, testing methods, and verification strategies, B2B buyers can make educated decisions that align with their product requirements and market expectations.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘anodized vs alodine’
Introduction
When sourcing aluminum finishing solutions, understanding the differences between anodized and Alodine (chem film) coatings is crucial for making informed purchasing decisions. This guide provides a structured checklist to help B2B buyers navigate the procurement process, ensuring they select the right coating method based on technical requirements and application needs.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Before initiating the sourcing process, clarify your project requirements. Determine the intended application of the aluminum parts and the specific performance characteristics needed, such as corrosion resistance, electrical conductivity, or surface finish.
- Key Considerations:
- Will the parts be exposed to harsh environments, such as saltwater?
- Do you require electrical insulation or conductivity?
Step 2: Understand Coating Processes
Familiarize yourself with the differences between anodizing and Alodine coatings. Anodizing uses an electrolytic process that enhances corrosion resistance and allows for coloring, while Alodine is a chemical conversion coating that retains electrical conductivity and is generally less expensive.
- Considerations:
- Assess whether your application benefits more from anodizing’s durability or Alodine’s conductivity.
- Review industry standards that may dictate which process is suitable for your needs.
Step 3: Evaluate Potential Suppliers
Thoroughly vet potential suppliers to ensure they have the capability and experience to meet your specifications. Request detailed company profiles, case studies, and references from other clients in your industry.
- Tips for Evaluation:
- Look for suppliers with certifications relevant to your industry, such as ISO 9001.
- Check for experience in your specific application field, whether aerospace, automotive, or military.
Step 4: Request Samples and Test Coatings
Once you have shortlisted suppliers, request samples of both anodized and Alodine-coated parts. Testing these samples in real-world conditions can provide insights into their performance and durability.
- Testing Considerations:
- Evaluate the coatings under conditions similar to those they will face in your application.
- Assess factors such as adhesion, corrosion resistance, and ease of painting or bonding.
Step 5: Inquire About Lead Times and Costs
Discuss the production timelines and pricing structures with your suppliers. Understanding lead times is essential for project planning, while cost considerations will impact your overall budget.
- Cost Factors:
- Compare the costs of anodizing versus Alodine and consider long-term value in terms of durability and maintenance.
- Look for volume discounts or long-term partnership opportunities.
Step 6: Verify Compliance with Industry Standards
Ensure that the coatings comply with relevant industry standards and regulations. This is particularly critical in sectors such as aerospace and defense, where compliance can affect safety and performance.
- Compliance Check:
- Request documentation proving adherence to standards like MIL-DTL-5541 for Alodine or MIL-A-8625 for anodized coatings.
- Ensure that suppliers follow best practices in environmental and safety regulations.
Step 7: Establish Clear Communication Channels
Finally, set up effective communication channels with your chosen supplier. Clear communication is vital for addressing any concerns that arise during production and ensuring that the final products meet your expectations.
- Communication Strategies:
- Regular check-ins during the production process can help mitigate issues.
- Establish a point of contact for quick resolutions to technical queries or changes in order specifications.
By following this checklist, B2B buyers can make well-informed decisions when sourcing anodized or Alodine-coated aluminum parts, ensuring their selections align with project requirements and industry standards.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for anodized vs alodine Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components When Sourcing Anodized vs Alodine Finishes?
When evaluating the costs associated with anodized and Alodine finishes, it’s essential to break down the various cost components involved. For both processes, the primary cost factors include materials, labor, manufacturing overhead, tooling, quality control (QC), logistics, and margin.
Materials: The raw materials for anodizing generally include aluminum and the electrolytic solution, which can vary in price based on purity and supplier. Alodine, on the other hand, uses chemical solutions for surface treatment, which are typically less expensive than anodizing materials. This difference often makes Alodine a more budget-friendly option.
Labor: Anodizing requires skilled labor for its complex electrolytic process, which can increase labor costs. In contrast, the Alodine application process is less technical, allowing for a broader pool of labor resources and potentially lower labor costs.
Manufacturing Overhead: The overhead for anodizing facilities can be higher due to the need for specialized equipment and maintenance. Alodine processes are generally less capital-intensive, contributing to lower overall manufacturing overhead.
Tooling: Both processes require specific tooling, but anodizing may necessitate more sophisticated setups, particularly if custom colors or finishes are desired. This can drive up initial tooling costs, especially for smaller runs.
Quality Control (QC): QC is critical in both processes, particularly for industries such as aerospace and defense. Anodized products often require more stringent testing protocols due to the critical nature of their applications, adding to the overall cost.
Logistics: The transportation costs for anodized versus Alodine products can differ based on weight and packaging requirements. Anodized parts may need special handling due to their surface finish, whereas Alodine-treated parts are often lighter and easier to transport.
Margin: Suppliers may set different profit margins based on the perceived value and demand for anodized versus Alodine finishes. Anodizing often commands a premium price due to its enhanced properties and applications.
What Influences the Pricing of Anodized and Alodine Finishes?
Several factors influence the pricing of anodized and Alodine finishes, particularly for international B2B buyers. Understanding these can lead to better negotiation outcomes.
Volume/MOQ: The minimum order quantity (MOQ) can significantly impact pricing. Larger orders typically lead to reduced unit costs for both anodized and Alodine finishes, as economies of scale come into play.
Specifications and Customization: Custom specifications can lead to increased costs, especially for anodizing, where the complexity of the finish may require specialized equipment and processes. Alodine, being less complex, may offer more flexibility in customization without significantly increasing costs.
Material Quality and Certifications: The quality of the aluminum and the certifications required (e.g., ISO, aerospace standards) can also influence pricing. Buyers must ensure that they are sourcing from suppliers who meet these requirements to avoid unexpected costs later.
Supplier Factors: Supplier reputation, reliability, and location can affect pricing. Established suppliers with a history of quality may charge a premium, while newer or less established suppliers may offer lower prices to gain market share.
Incoterms: Understanding Incoterms is crucial for international buyers. The chosen terms can affect shipping costs, insurance, and risk management, ultimately influencing the total price of the sourced products.
What Tips Can Buyers Utilize to Optimize Their Costs?
To maximize cost efficiency when sourcing anodized and Alodine finishes, buyers should consider the following strategies:
Negotiation: Engage in open discussions with suppliers to negotiate better pricing based on volume or long-term contracts. Highlighting the potential for repeat business can also strengthen your position.
Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Evaluate the total cost of ownership rather than just the upfront cost. Consider factors such as durability, maintenance, and performance in your specific application to determine the best value.
Pricing Nuances for International Buyers: Buyers from regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe should be aware of currency fluctuations, import duties, and local regulations that may affect pricing. Establishing relationships with local distributors can also help mitigate some of these costs.
Disclaimer
The prices and cost structures outlined are indicative and can vary based on market conditions, supplier negotiations, and specific project requirements. Always conduct thorough research and obtain multiple quotes to ensure competitive pricing.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing anodized vs alodine With Other Solutions
In the competitive landscape of metal finishing, choosing the right process can significantly impact product performance, cost-effectiveness, and overall project success. While anodizing and Alodine (chem film) are popular choices for enhancing aluminum’s corrosion resistance, it is essential to explore other viable alternatives. This analysis compares these two processes against two additional methods: powder coating and galvanizing, providing a comprehensive view for B2B buyers.
| Comparison Aspect | Anodized Vs Alodine | Powder Coating | Galvanizing |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | Excellent corrosion resistance, improved lubrication, and aesthetic appeal. | Good corrosion resistance, available in various colors, but less durable than anodized. | Superior corrosion resistance for structural steel, good for heavy-duty applications. |
| Cost | Generally higher due to technical requirements and equipment. | Moderate; cost-effective for large-scale applications. | Higher initial cost but cost-effective over time due to durability. |
| Ease of Implementation | Requires skilled technicians and specialized equipment. | Easier application process; can be done in-house. | Requires a dipping process; less control over thickness. |
| Maintenance | Low maintenance, but can be damaged by harsh chemicals. | Moderate; chips and scratches can compromise integrity. | Low maintenance; very durable, but can corrode if scratched. |
| Best Use Case | Aerospace, automotive, and decorative applications requiring high durability. | Consumer products, appliances, and furniture where aesthetics are important. | Infrastructure, construction, and automotive applications needing robust protection. |
What Are the Pros and Cons of Powder Coating?
Powder coating is a finishing process that applies a dry powder to metal parts, which is then cured under heat to form a protective layer. The primary advantage of powder coating is its versatility in color and finish, offering a wide range of aesthetic options. Additionally, it provides a good level of corrosion resistance and is less expensive than anodizing for large-scale applications. However, it may not offer the same level of durability or thermal/electrical conductivity as anodized or Alodine finishes, making it less suitable for high-performance applications.
How Does Galvanizing Compare to Anodized and Alodine?
Galvanizing involves coating steel or iron with a layer of zinc to protect against corrosion. This method is particularly effective for structural components exposed to harsh environments. The main advantage of galvanizing is its exceptional corrosion resistance and long lifespan, making it ideal for outdoor applications. However, it is primarily suited for ferrous materials and may not be applicable for aluminum. The process can also result in a thicker coating, which may not be suitable for all applications, particularly those requiring precise tolerances.
Conclusion: How to Choose the Right Metal Finishing Solution?
Selecting the appropriate metal finishing solution involves assessing multiple factors, including performance needs, cost constraints, and application requirements. For high-performance applications, anodizing offers superior durability and aesthetic options, while Alodine provides a cost-effective alternative with good conductivity. Powder coating is ideal for projects prioritizing color and finish over extreme durability, whereas galvanizing excels in heavy-duty applications requiring robust protection. By carefully evaluating these aspects, B2B buyers can make informed decisions that align with their specific project goals and industry standards.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for anodized vs alodine
What Are the Critical Technical Properties of Anodized and Alodine Finishes?
Understanding the key technical properties of anodized and Alodine finishes is essential for B2B buyers, especially when selecting materials for specific applications. Here are some critical specifications to consider:
-
Corrosion Resistance
– Definition: This property indicates how well a material can withstand degradation due to environmental factors such as moisture, salt, and chemicals.
– B2B Importance: High corrosion resistance is vital for applications in harsh environments, such as aerospace and marine industries. Choosing the right finish can extend the lifespan of components, reducing maintenance costs and downtime. -
Electrical Conductivity
– Definition: This property refers to the ability of a material to conduct electric current.
– B2B Importance: Alodine finishes allow aluminum parts to retain their electrical conductivity, making them suitable for applications that require grounding. This is particularly relevant in electrical and electronic sectors where functionality depends on conductive properties. -
Thickness of Coating
– Definition: This refers to the measurement of the coating applied to the aluminum surface. Anodizing typically results in a thicker layer compared to Alodine.
– B2B Importance: The thickness affects durability and performance. Industries requiring robust protection against wear and corrosion may prefer anodized finishes, while those needing lighter coatings may opt for Alodine. -
Surface Hardness
– Definition: This property measures the resistance of a surface to deformation or scratching.
– B2B Importance: Anodized surfaces generally exhibit greater hardness, which is advantageous in high-wear applications like automotive and aerospace components. This can lead to enhanced performance and reduced wear and tear. -
Adhesion Properties
– Definition: This refers to how well a coating adheres to the substrate material.
– B2B Importance: Good adhesion is crucial for finishes that will be painted or bonded. Anodized surfaces provide superior adhesion for paints and adhesives, ensuring long-lasting performance in demanding applications. -
Weight Considerations
– Definition: This refers to the additional weight that coatings add to the original aluminum part.
– B2B Importance: For industries like aerospace where weight reduction is critical, Alodine’s lightweight nature may be preferable. Understanding weight implications can influence design and operational efficiency.
What Are the Common Trade Terms Used in Anodizing and Alodine Processes?
Familiarity with industry terminology helps facilitate smoother negotiations and communications among B2B buyers and suppliers. Here are some essential terms to know:
-
OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
– Definition: A company that produces parts or equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer.
– Importance: Understanding OEM relationships is crucial for sourcing high-quality components that meet specific industry standards. -
MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
– Definition: The smallest number of units that a supplier is willing to sell.
– Importance: Knowledge of MOQ helps buyers understand purchasing requirements and manage inventory effectively, especially in bulk transactions. -
RFQ (Request for Quotation)
– Definition: A document sent to suppliers to solicit pricing and terms for specific products or services.
– Importance: RFQs are essential for comparing costs and ensuring that buyers receive competitive pricing for anodized or Alodine finishes. -
Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
– Definition: A series of pre-defined commercial terms published by the International Chamber of Commerce, used in international trade contracts.
– Importance: Familiarity with Incoterms helps buyers understand shipping responsibilities, costs, and risks, which is crucial for international transactions. -
Lead Time
– Definition: The amount of time that elapses from the initiation of a process until its completion.
– Importance: Knowing lead times is vital for planning and ensuring that projects stay on schedule, particularly in industries with tight deadlines. -
Certification Standards
– Definition: Guidelines and benchmarks that products must meet to ensure quality and safety, such as ISO or military specifications.
– Importance: Understanding certification requirements is essential for compliance and quality assurance, particularly in regulated industries like aerospace and defense.
By grasping these technical properties and trade terms, B2B buyers can make informed decisions when selecting between anodized and Alodine finishes, ensuring that their procurement aligns with operational requirements and industry standards.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the anodized vs alodine Sector
What Are the Current Market Dynamics and Key Trends Influencing Anodized vs Alodine Sourcing?
The anodized and alodine sectors are experiencing significant shifts driven by global manufacturing demands and technological advancements. As industries across Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe seek to enhance product durability and performance, the demand for both anodized and alodine finishes is on the rise. Key drivers include the aerospace, automotive, and defense sectors, where corrosion resistance and electrical conductivity are paramount.
Emerging B2B technologies, such as automated surface treatment systems, are optimizing production processes, reducing lead times, and minimizing costs. This is particularly relevant for international buyers looking for efficiency in supply chains. Furthermore, the growing emphasis on lightweight materials in automotive design is pushing manufacturers toward anodizing for its superior weight-to-strength ratio, while alodine remains a cost-effective solution for parts requiring electrical grounding.
The competitive landscape is also evolving, with suppliers increasingly adopting lean manufacturing principles to enhance responsiveness to market demands. International buyers should stay attuned to these trends, as they can directly influence sourcing strategies and supplier selection, ensuring they are aligned with industry standards and technological advancements.
How Is Sustainability and Ethical Sourcing Impacting Anodized and Alodine Processes?
Sustainability is becoming a critical consideration in the anodized and alodine sectors. As global awareness of environmental issues rises, B2B buyers are increasingly prioritizing suppliers that demonstrate a commitment to ethical sourcing and sustainable practices. The anodizing process, while energy-intensive, can be made more environmentally friendly through advancements in technology and the use of less harmful chemicals.
On the other hand, alodine coatings can be produced with reduced environmental impact, especially when suppliers utilize hexavalent chromium-free formulas. Buyers should inquire about certifications such as ISO 14001, which indicates a company’s commitment to minimizing environmental impact.
In addition, sourcing from suppliers who adhere to ethical practices in their supply chains can enhance brand reputation and customer trust. This is particularly significant in markets like Africa and South America, where consumers are increasingly aware of sustainability issues. Engaging with suppliers who can provide transparent information about their sourcing and manufacturing processes will be vital for businesses looking to align with environmentally conscious trends.
What Is the Historical Context Behind Anodized and Alodine Finishes?
The evolution of anodizing and alodine finishes dates back to the early 20th century when anodizing was first developed as a method to enhance aluminum’s natural oxide layer. Over the decades, this electrolytic process has been refined, leading to widespread adoption in various industries, particularly aerospace and automotive.
Alodine, or chemical conversion coating, emerged as a simpler and more cost-effective alternative, providing essential corrosion resistance without the need for electrical currents. Its development offered manufacturers a versatile option for aluminum finishes, especially in applications requiring electrical conductivity.
Understanding this historical context is crucial for B2B buyers, as it highlights the technological advancements that have shaped the present landscape. The choice between anodized and alodine finishes is not just a matter of preference; it reflects the ongoing evolution of manufacturing processes and the growing emphasis on efficiency and sustainability in production practices.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of anodized vs alodine
-
How do I choose between anodized and alodine finishes for my aluminum parts?
Choosing between anodized and alodine finishes depends on your specific application requirements. Anodizing is an electrolytic process that enhances corrosion resistance and improves paint adhesion, making it suitable for applications needing durability and aesthetic appeal. In contrast, alodine (chem film) is a less expensive option that retains electrical conductivity, ideal for electrical components or situations where weight and dimensions cannot change. Evaluate factors such as environmental exposure, conductivity requirements, and budget constraints to make an informed decision. -
What are the key differences between anodized and alodine finishes?
The primary difference lies in the application process: anodizing uses electrical current in an electrolytic solution, while alodine is a chemical conversion process without electricity. Anodizing enhances corrosion resistance, lubricity, and color options, making it suitable for decorative purposes. Alodine provides corrosion protection while maintaining electrical and thermal conductivity, making it preferable for military, aerospace, and electrical applications. Understanding these differences helps align the finish with your project’s requirements. -
What are the minimum order quantities (MOQ) for anodized and alodine finishes?
Minimum order quantities can vary significantly based on the supplier and specific finishing process. Typically, anodizing might require higher MOQs due to the complexity and cost of the process, often ranging from 50 to several hundred units. Alodine finishes usually have lower MOQs since they are simpler and quicker to apply, potentially allowing orders as low as 10 units. Always discuss your project needs with suppliers to determine their specific requirements. -
What payment terms should I expect when sourcing anodized or alodine finishes?
Payment terms can vary widely among suppliers, but it’s common to encounter options such as net 30, net 60, or even payment in advance for first-time orders. For larger orders, consider negotiating terms that allow partial payments upon delivery or after inspection. Establishing clear payment terms in your contract helps ensure a smooth transaction and reduces the risk of misunderstandings. -
How can I ensure quality assurance (QA) for anodized and alodine finishes?
To ensure quality assurance, request certifications and compliance documents from suppliers, such as ISO 9001 or specific military standards (like MIL-DTL-5541 for alodine). Additionally, consider implementing a quality inspection process, either through third-party services or in-house checks, to verify the finish meets your specifications. Regular audits of your suppliers can also help maintain consistent quality over time. -
What logistics considerations should I keep in mind when sourcing aluminum finishes internationally?
When sourcing anodized or alodine finishes internationally, consider shipping costs, delivery times, and customs regulations. Ensure your supplier can provide accurate shipping timelines and that they comply with international shipping standards. Additionally, factor in potential tariffs and duties that may apply to your order, as these can significantly impact overall costs. Establishing a reliable logistics plan is crucial for timely and cost-effective delivery. -
Can I customize anodized or alodine finishes for my specific application?
Yes, both anodized and alodine finishes can be customized. Anodizing can be colored to match branding requirements or specific aesthetic needs, while alodine coatings can be tailored to different thicknesses and corrosion resistance levels. Discuss your customization needs with suppliers upfront to ensure they can meet your specifications and provide samples if necessary for evaluation. -
What industries commonly use anodized and alodine finishes?
Anodized and alodine finishes are widely used across various industries. Anodized aluminum is prevalent in aerospace, automotive, and consumer electronics for its durability and aesthetic appeal. Alodine finishes are commonly found in military, aerospace, and electrical applications due to their corrosion resistance and ability to maintain conductivity. Understanding the industry applications can help you select the right finishing process for your project needs.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.
Top 4 Anodized Vs Alodine Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. Gabrian – Alodine Finish
Domain: gabrian.com
Registered: 2000 (25 years)
Introduction: Alodine finish is a type of conversion coating for aluminum that creates a thin protective film to prevent corrosion and can serve as a primer for painting. It is often referred to as chromate conversion coating or chem film. The Alodine® product is a registered trademark of Henkel, Inc., with similar products available from other companies like Iridite 14-2®. The process is widely recognized unde…
2. CNC Parts X TJ – Alodine Corrosion Inhibitor
Domain: cncpartsxtj.com
Registered: 2019 (6 years)
Introduction: Alodine is a corrosion inhibitor used as a passivation process for aluminum and other metals. It is a water-soluble, organic compound that forms a protective barrier on the metal surface, enhancing durability and corrosion resistance. Alodine is applied through a chemical reaction involving chromic acid, resulting in a clear coating that hardens upon drying. It is suitable for various metals inclu…
3. Chem Research Co – Chem-Film vs. Anodize
Domain: chemresearchco.com
Registered: 1998 (27 years)
Introduction: Chem-Film (Alodine) vs. Anodize: Chem-Film is a chemical conversion coating that protects aluminum from corrosion and serves as a base for paint without altering dimensions. It is less expensive and easier to apply than anodizing, retaining thermal and electrical conductivity. Common uses include heat sinks, aircraft hulls, landing gear, tactical equipment, and automotive wheels. Types of Chem-Fil…
4. Sunrise Metal – Alodine Passivation Technique
Domain: sunrise-metal.com
Registered: 2015 (10 years)
Introduction: Alodine: A passivation technique suitable for internal parts of aluminum projects. Advantages include lower cost, improved protection against corrosion and scratches, good electrical and thermal conductivity, allows painting without primer, no cleanup needed, and minimal skill required. Disadvantages include easy removal of coating, potential micro-defects, environmental concerns, and skin irritat…
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for anodized vs alodine
In navigating the decision between anodizing and Alodine (chem film) for aluminum finishing, B2B buyers must consider critical factors such as cost, technical expertise, and specific application requirements. Anodizing offers superior corrosion resistance and enhanced properties like electrical insulation and paint adhesion, but it comes at a higher cost and requires specialized knowledge. Conversely, Alodine provides a more economical and simpler solution, particularly for applications needing thermal and electrical conductivity without altering the dimensions of the parts.
Strategic sourcing of these coatings can significantly impact product durability and performance, making it essential for international buyers—especially from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe—to align their choices with project needs and budgets. Establishing strong relationships with experienced suppliers will ensure access to the best solutions tailored to specific industry requirements.
As global markets continue to evolve, staying informed about advancements in aluminum finishing technologies will be crucial. Embrace this opportunity to optimize your sourcing strategies and make informed decisions that drive innovation and competitiveness in your industry. Reach out to your suppliers today to discuss how anodized or Alodine coatings can enhance your product offerings.