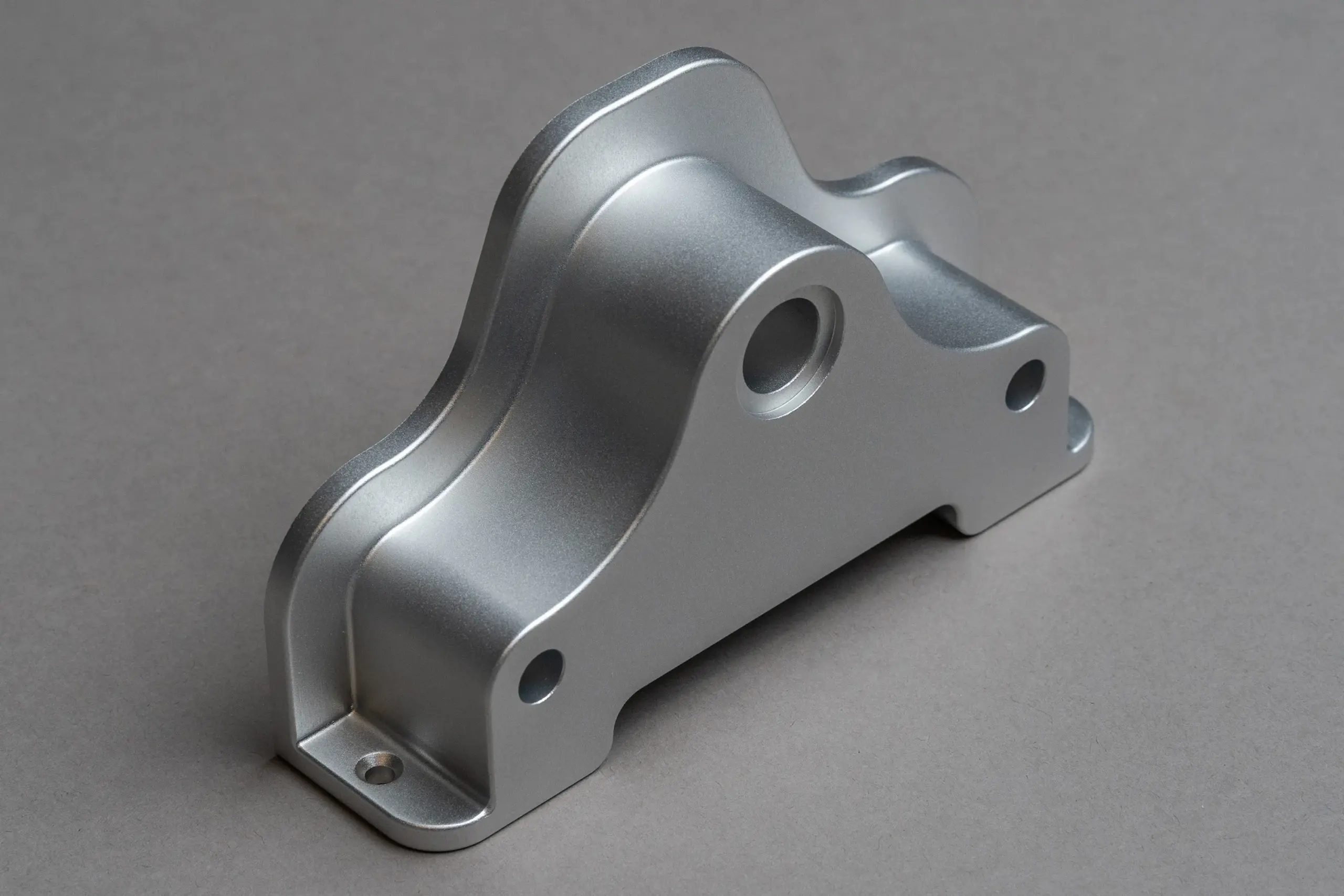
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for anodized aluminum service
In an increasingly interconnected global marketplace, sourcing reliable anodized aluminum services poses a significant challenge for B2B buyers. With the material’s unique properties—such as enhanced corrosion resistance, improved durability, and aesthetic versatility—understanding the intricacies of anodizing processes becomes crucial for making informed purchasing decisions. This guide serves as a comprehensive resource, detailing various types of anodizing services, their applications across diverse industries, and best practices for supplier vetting.
International buyers, particularly those from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, will find valuable insights tailored to their specific needs. By exploring factors such as cost considerations, quality standards, and turnaround times, this guide empowers businesses to navigate their sourcing journey with confidence. Additionally, we delve into the latest trends in anodized aluminum applications, including automotive, aerospace, and consumer goods, ensuring that readers remain at the forefront of industry developments.
Armed with this knowledge, B2B buyers can enhance their procurement strategies, mitigate risks, and ultimately secure high-quality anodized aluminum products that meet their operational requirements. Join us as we explore the dynamic landscape of anodized aluminum services, equipping you with the tools needed for success in the global market.
Understanding anodized aluminum service Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Type II Anodizing | Sulfuric acid process; enhances corrosion resistance and surface hardness. | Aerospace, automotive, and consumer goods. | Pros: Cost-effective, good wear resistance. Cons: Less durable than Type III. |
| Type III Anodizing | Hard coat anodizing; thicker, more durable layer for extreme conditions. | Military, industrial machinery, and electronics. | Pros: Excellent wear and corrosion resistance. Cons: Higher cost, limited color options. |
| Chromate Conversion | Creates a protective layer that enhances corrosion resistance while maintaining conductivity. | Aerospace, automotive, and electronics. | Pros: Effective for corrosion protection, retains electrical conductivity. Cons: Not as durable as anodized finishes. |
| Decorative Anodizing | Thin anodized layer that allows for dyeing; enhances aesthetic appeal. | Consumer products, architectural components. | Pros: Wide color range, improves product aesthetics. Cons: Less protection against wear and tear. |
| Laser Engraving | Precision engraving on anodized surfaces for branding or identification. | Manufacturing, automotive, and electronics. | Pros: Customizable, enhances branding. Cons: May require additional processing time. |
What are the Characteristics and Suitability of Type II Anodizing?
Type II anodizing is a widely used technique that employs a sulfuric acid solution to create a protective oxide layer on aluminum. This process enhances the material’s corrosion resistance and surface hardness, making it suitable for various applications, including aerospace and automotive industries. When considering Type II, B2B buyers should evaluate factors like cost-effectiveness and performance requirements, as it offers a balance between durability and affordability.
How Does Type III Anodizing Differ from Type II?
Type III anodizing, also known as hard coat anodizing, involves a thicker layer of oxide that provides superior durability and wear resistance. This type is ideal for applications that face extreme conditions, such as military and industrial machinery. Buyers should consider the higher cost associated with Type III anodizing against its long-term benefits, especially in high-wear environments where longevity is critical.
What Advantages Does Chromate Conversion Offer?
Chromate conversion is a unique anodizing alternative that produces a protective layer on aluminum while preserving its conductivity. This service is particularly beneficial in aerospace and automotive applications where corrosion resistance is paramount. B2B buyers should weigh the advantages of effective corrosion protection against the lower durability compared to anodized finishes, especially for components exposed to harsh conditions.
How Can Decorative Anodizing Enhance Product Appeal?
Decorative anodizing focuses on creating a visually appealing finish by allowing for dye absorption. This type is suitable for consumer products and architectural components, providing a wide range of color options. Buyers should consider the aesthetic benefits of decorative anodizing, keeping in mind that it may not offer the same level of protection against wear and tear as thicker anodized coatings.
What Role Does Laser Engraving Play in Anodized Aluminum Services?
Laser engraving on anodized surfaces allows for precise customization, making it an ideal choice for branding and identification purposes. This service is valuable across various sectors, including manufacturing and electronics. B2B buyers should factor in the potential added processing time for laser engraving when planning their projects, as it can enhance product differentiation but may extend lead times.
Key Industrial Applications of anodized aluminum service
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of anodized aluminum service | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Aerospace | Aircraft components and frames | Enhanced corrosion resistance and weight reduction | Compliance with aerospace standards (e.g., AS9100) and lead times for critical components. |
| Automotive | Chassis and body parts | Improved durability and aesthetic appeal | Need for precision engineering and adherence to safety regulations. |
| Electronics | Heat sinks and enclosures | Increased thermal management and electrical insulation | Specifications for thermal conductivity and electrostatic discharge (ESD) protection. |
| Medical Devices | Surgical instruments and implants | Biocompatibility and resistance to wear and corrosion | ISO certifications for medical applications (e.g., ISO 13485) and customization options. |
| Construction | Architectural elements and fixtures | Aesthetic versatility and long-lasting performance | Consideration for local climate conditions and design specifications. |
How is Anodized Aluminum Used in Aerospace Applications?
In the aerospace sector, anodized aluminum is crucial for manufacturing components such as aircraft frames and interior parts. The anodizing process enhances the aluminum’s natural corrosion resistance, making it ideal for high-altitude environments where exposure to moisture and temperature fluctuations can lead to rapid degradation. Buyers in this sector must ensure that suppliers comply with stringent aerospace standards like AS9100, as well as provide timely delivery for mission-critical components.
What Role Does Anodized Aluminum Play in Automotive Manufacturing?
The automotive industry utilizes anodized aluminum for chassis and body parts due to its lightweight nature and enhanced durability. Anodizing improves the aesthetic qualities of the aluminum while providing a robust surface that withstands harsh environmental conditions. For international buyers, understanding local safety regulations and ensuring precise engineering are key factors when sourcing anodized aluminum parts.
How Does Anodized Aluminum Benefit Electronics?
In the electronics sector, anodized aluminum is often used for heat sinks and enclosures, where its thermal management capabilities and electrical insulation properties are paramount. The anodizing process enhances the surface’s ability to dissipate heat, which is critical for maintaining the performance of electronic devices. Buyers should consider specifications related to thermal conductivity and electrostatic discharge (ESD) protection when sourcing anodized aluminum for electronic applications.
Why is Anodized Aluminum Important for Medical Devices?
Anodized aluminum plays a vital role in the medical device industry, particularly for surgical instruments and implants. The anodizing process not only improves wear resistance but also ensures biocompatibility, which is essential for devices that come into contact with human tissue. Buyers must seek suppliers with ISO certifications, such as ISO 13485, to guarantee that the anodized aluminum meets the rigorous standards required for medical applications.
How is Anodized Aluminum Used in Construction?
In construction, anodized aluminum is used for architectural elements and fixtures, providing both aesthetic appeal and long-lasting performance. The anodizing process allows for a variety of color finishes while ensuring resistance to weathering and corrosion. International buyers should consider local climate conditions and specific design requirements when sourcing anodized aluminum for construction projects, as these factors can significantly impact the longevity and appearance of the finished product.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘anodized aluminum service’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Difficulty in Achieving Consistent Quality in Anodized Parts
The Problem: B2B buyers often face challenges in ensuring that anodized aluminum parts meet their specific quality standards. Variability in the anodizing process can lead to differences in color, texture, and thickness, which may affect the part’s performance and aesthetics. This inconsistency can cause delays in production, increased costs due to rework or replacements, and ultimately dissatisfaction from end customers. For manufacturers in sectors like aerospace or automotive, where precision is critical, these quality fluctuations can pose significant risks.
The Solution: To overcome this issue, buyers should prioritize selecting suppliers with robust quality assurance processes. It’s essential to conduct thorough due diligence, including reviewing the supplier’s certifications (such as ISO 9001) and their track record with similar projects. Establishing clear specifications for the anodizing process—including desired thickness, color, and surface finish—can help set expectations. Additionally, implementing regular communication and feedback loops with the supplier can ensure that any discrepancies are promptly addressed. For high-volume orders, consider conducting pilot runs before full-scale production to validate the quality of the anodized finish.
Scenario 2: High Costs Due to Inefficient Anodizing Processes
The Problem: Many companies struggle with the high costs associated with anodizing services, often stemming from inefficient processes or a lack of understanding of the anodizing capabilities. Buyers may find themselves overpaying for services that do not align with their actual needs, leading to budget overruns. Additionally, if the anodizing process is not optimized for specific applications, it can result in waste—both in terms of materials and time.
The Solution: Buyers should engage in a detailed consultation with anodizing service providers to identify the most suitable anodizing processes for their specific applications. This includes understanding the differences between Type II and Type III anodizing, as well as the potential cost implications of each method. By specifying the exact requirements upfront, such as the intended use of the parts and expected environmental conditions, buyers can avoid unnecessary upgrades or treatments. Furthermore, collaborating with suppliers who offer comprehensive services—including design consultation and process optimization—can help streamline production and minimize costs.
Scenario 3: Challenges with Lead Times and Delivery Schedules
The Problem: In the fast-paced world of manufacturing, delays in the delivery of anodized aluminum parts can severely disrupt production schedules. Many B2B buyers encounter issues with suppliers who fail to meet agreed-upon lead times, resulting in project delays and financial penalties. This is particularly problematic for companies operating in competitive markets where timely delivery is critical to maintaining customer satisfaction and market position.
The Solution: To mitigate lead time challenges, buyers should establish clear expectations with anodizing service providers from the outset. This includes agreeing on realistic timelines, understanding the production capabilities of the supplier, and factoring in potential bottlenecks. Buyers can also explore working with suppliers that utilize advanced technologies, such as automated anodizing systems, which can significantly reduce processing times. Maintaining a safety stock of anodized parts or utilizing just-in-time delivery strategies can also provide a buffer against unexpected delays. Regular communication regarding project status and any potential issues can further ensure that both parties remain aligned throughout the production process.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for anodized aluminum service
What Are the Key Materials for Anodized Aluminum Services?
When selecting materials for anodized aluminum services, it is crucial to consider the specific properties and applications of various aluminum alloys. Below are analyses of four common materials used in anodized aluminum services, emphasizing their performance, advantages, disadvantages, and considerations for international B2B buyers.
1. 6061 Aluminum Alloy
Key Properties:
6061 aluminum is known for its good mechanical properties and excellent corrosion resistance. It has a temperature rating of up to 200°C and can withstand moderate pressure, making it suitable for a variety of applications.
Pros & Cons:
The alloy is highly versatile, offering good weldability and machinability. However, it may not be as strong as some other alloys, which could limit its use in high-stress applications. The cost is moderate, making it an economical choice for many projects.
Impact on Application:
6061 is compatible with various media, including water and certain chemicals, making it ideal for structural components and automotive parts.
Considerations for International Buyers:
Compliance with international standards such as ASTM and ISO is essential. Buyers from regions like Africa and South America should ensure that suppliers meet local regulations regarding material specifications.
2. 7075 Aluminum Alloy
Key Properties:
7075 aluminum is one of the strongest aluminum alloys available, with a temperature rating up to 120°C. It offers exceptional strength-to-weight ratios and excellent fatigue resistance.
Pros & Cons:
While 7075 is highly durable and suitable for aerospace and military applications, it is more expensive than other alloys. Its lower corrosion resistance compared to 6061 may necessitate additional protective coatings.
Impact on Application:
This alloy is ideal for high-stress applications, such as aircraft components and high-performance sporting goods, but may not be suitable for environments with high corrosion potential without additional treatment.
Considerations for International Buyers:
Buyers should be aware of the specific certifications required for aerospace applications, particularly in Europe and the Middle East, where compliance with stringent standards is critical.
3. 5052 Aluminum Alloy
Key Properties:
5052 aluminum is known for its excellent corrosion resistance, particularly in marine environments, and has a temperature rating of up to 150°C. It offers good workability and formability.
Pros & Cons:
This alloy is highly durable and cost-effective, making it suitable for a wide range of applications, including marine and automotive. However, its strength is lower than that of 6061 and 7075, which may limit its use in high-stress applications.
Impact on Application:
5052 is particularly effective in applications exposed to saltwater and other corrosive environments, making it a preferred choice in coastal regions.
Considerations for International Buyers:
Buyers should verify that the alloy meets local standards and consider the impact of environmental regulations on material selection, especially in regions with strict marine compliance.
4. 2024 Aluminum Alloy
Key Properties:
2024 aluminum is known for its high strength and fatigue resistance, with a temperature rating of up to 150°C. It is often used in aerospace applications due to its excellent mechanical properties.
Pros & Cons:
While 2024 offers superior strength, it has lower corrosion resistance and is more challenging to anodize, which may increase manufacturing complexity. The cost is relatively high, reflecting its specialized applications.
Impact on Application:
This alloy is ideal for aerospace and military applications where strength is paramount, but it may require additional protective measures in corrosive environments.
Considerations for International Buyers:
International buyers, particularly in the aerospace sector, should ensure that suppliers adhere to specific industry standards such as AS9100, which governs quality management systems in aviation.
Summary Table of Material Selection for Anodized Aluminum Services
| Material | Typical Use Case for anodized aluminum service | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 6061 Aluminum | Structural components, automotive parts | Good corrosion resistance | Moderate strength compared to others | Medium |
| 7075 Aluminum | Aerospace components, high-performance goods | Exceptional strength | Higher cost, lower corrosion resistance | High |
| 5052 Aluminum | Marine applications, automotive parts | Excellent corrosion resistance | Lower strength than some alloys | Low to Medium |
| 2024 Aluminum | Aerospace, military applications | High strength and fatigue resistance | Lower corrosion resistance, complex anodizing | High |
This guide provides a comprehensive overview of the strategic material selection process for anodized aluminum services, helping international B2B buyers make informed decisions based on their specific needs and regional compliance requirements.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for anodized aluminum service
What Are the Key Stages in the Manufacturing Process of Anodized Aluminum?
Manufacturing anodized aluminum involves several critical stages, each requiring precision and expertise to ensure a high-quality final product. The main stages include material preparation, forming, assembly, and finishing.
Material Preparation
The process begins with selecting high-grade aluminum alloys, which can include 6061, 6063, or 7075, depending on the application requirements. The aluminum is then cleaned to remove any surface contaminants. This often involves a combination of chemical cleaning and mechanical abrasion. Following this, the material undergoes etching, which enhances surface roughness and prepares the metal for anodization.
Forming
After preparation, the aluminum is shaped into the desired form using techniques such as extrusion, stamping, or machining. For instance, extrusion is widely used for creating complex profiles, while machining allows for precise tolerances and surface finishes. Each technique must be executed with care to maintain the integrity of the aluminum, as any defects at this stage can compromise the anodizing results.
Assembly
If the anodized aluminum is part of a larger assembly, components may be assembled at this stage. This can involve welding, riveting, or using adhesives. It’s crucial to ensure that the assembly process does not introduce contaminants that could affect the anodizing finish.
Finishing
The finishing stage involves the anodizing process itself, which is an electrolytic passivation method. This process increases the thickness of the natural oxide layer on the aluminum, improving its corrosion resistance and durability. The anodizing can be done in different types, such as Type II (sulfuric acid anodizing) for decorative purposes or Type III (hard coat) for enhanced wear resistance. After anodizing, components may undergo sealing, dyeing, or additional surface treatments to achieve specific aesthetic or functional properties.
How Is Quality Assurance Implemented in Anodized Aluminum Manufacturing?
Quality assurance (QA) is integral to the anodized aluminum manufacturing process, ensuring that products meet international standards and customer specifications. The QA process typically includes several checkpoints and adherence to various standards.
International Standards and Certifications
A key aspect of quality assurance in anodized aluminum services is compliance with international standards such as ISO 9001, which focuses on quality management systems. Additional certifications may include ISO 13485 for medical applications or AS9100 for aerospace components. These certifications signal to B2B buyers that the supplier adheres to rigorous quality standards.
Quality Checkpoints in the Manufacturing Process
Quality control (QC) is implemented at various stages, including:
-
Incoming Quality Control (IQC): This stage involves inspecting raw materials upon arrival to ensure they meet specified standards. This includes checking for alloy composition and surface quality.
-
In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): Throughout the manufacturing process, regular inspections are conducted to monitor compliance with specifications. This includes monitoring the anodizing bath conditions and ensuring that the anodizing thickness meets standards.
-
Final Quality Control (FQC): After finishing, products undergo a final inspection, which may include dimensional checks, visual inspections, and performance tests, such as corrosion resistance and adhesion tests.
What Testing Methods Are Commonly Used for Anodized Aluminum Quality Control?
Various testing methods are employed to validate the quality of anodized aluminum products. Common tests include:
-
Thickness Measurement: Utilizing tools like micrometers or calipers to ensure the anodized layer meets specified thickness requirements.
-
Adhesion Testing: This evaluates how well the anodized coating adheres to the aluminum substrate. Tests such as the cross-hatch tape test are often used.
-
Corrosion Resistance Testing: Salt spray tests (ASTM B117) or cyclic corrosion tests are performed to assess the durability of the anodized finish under adverse conditions.
-
Color Consistency Tests: For dyed anodized aluminum, color matching tests ensure uniformity across batches.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify the Quality Control Processes of Anodized Aluminum Suppliers?
For international B2B buyers, especially those from regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, verifying a supplier’s quality control processes is crucial. Here are several strategies to ensure a supplier meets your quality standards:
-
Supplier Audits: Conducting on-site audits allows buyers to assess the supplier’s manufacturing capabilities, quality systems, and adherence to industry standards firsthand. This includes reviewing documentation related to their certifications and quality control processes.
-
Requesting Quality Assurance Reports: Suppliers should provide detailed QA reports that outline their testing methodologies, results, and any corrective actions taken in case of non-conformance.
-
Engaging Third-Party Inspectors: Employing third-party inspection services can provide an unbiased assessment of the supplier’s processes and products. This is particularly useful for large orders or critical applications.
What Are the Quality Control Nuances for International B2B Buyers?
When dealing with international suppliers, quality control nuances can vary significantly. Buyers should consider the following:
-
Understanding Local Standards: Different countries may have varying standards and regulations regarding anodized aluminum. Understanding these can help buyers ensure compliance and quality.
-
Communication Barriers: Language differences can lead to misunderstandings regarding quality requirements. Establishing clear communication channels and documentation in both parties’ languages can mitigate this risk.
-
Cultural Considerations: Business practices and expectations can differ across cultures. Building a relationship based on trust and transparency can foster better collaboration and adherence to quality standards.
By understanding the manufacturing processes and quality assurance mechanisms in anodized aluminum services, B2B buyers can make informed decisions, ensuring they partner with suppliers who meet their quality expectations and industry standards.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘anodized aluminum service’
Introduction
This guide aims to provide B2B buyers with a comprehensive checklist for sourcing anodized aluminum services. Anodized aluminum offers enhanced durability, aesthetic appeal, and corrosion resistance, making it a popular choice across various industries. By following this step-by-step checklist, buyers can ensure they partner with reliable suppliers that meet their technical and operational needs.
1. Define Your Technical Specifications
Before engaging with suppliers, clearly outline your project requirements, including dimensions, tolerances, and intended applications of the anodized aluminum components. This step is crucial as it helps to communicate your needs effectively and ensures that the supplier can meet your specific criteria. Consider factors such as:
– Type of anodizing required (e.g., Type II, Type III).
– Desired finish (e.g., color, gloss level).
2. Research Potential Suppliers
Conduct thorough research to identify potential suppliers that specialize in anodized aluminum services. Look for companies with a strong reputation in the industry, as well as positive reviews from past clients. Utilize online directories, industry trade shows, and networking events to compile a list of candidates. Key aspects to evaluate include:
– Experience in your industry.
– Diversity of anodizing techniques offered.
3. Evaluate Supplier Certifications
It is essential to verify that potential suppliers hold relevant industry certifications, such as ISO 9001 or AS9100. These certifications indicate adherence to quality management standards, which can significantly impact the reliability and quality of the anodizing process. Ensure to check for:
– Compliance with international standards.
– Certifications specific to your industry needs.
4. Request Samples and Case Studies
Before making a commitment, request samples of previous work and relevant case studies. This will provide insight into the supplier’s capabilities and the quality of their anodized finishes. Analyze the samples for:
– Consistency in finish and color.
– Durability through physical tests, if applicable.
5. Assess Production Capacity and Lead Times
Understanding a supplier’s production capacity and lead times is vital to ensure they can meet your project deadlines. Inquire about their operational capabilities and any bottlenecks that may affect timely delivery. Consider:
– Volume of orders they can handle.
– Flexibility in scaling production for future needs.
6. Discuss Pricing and Payment Terms
Engage in discussions about pricing structures and payment terms early in the sourcing process. Transparent pricing helps avoid unexpected costs later on. Look for suppliers that offer:
– Detailed quotes that break down costs.
– Flexible payment options, especially for large orders.
7. Establish Communication Protocols
Effective communication is key to a successful partnership. Establish clear communication protocols with your chosen supplier to ensure smooth interactions throughout the project. Important aspects to consider include:
– Designating points of contact for both parties.
– Setting expectations for updates and feedback loops.
By following this checklist, B2B buyers can navigate the sourcing process for anodized aluminum services with confidence, ensuring they select a supplier that aligns with their technical requirements and business goals.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for anodized aluminum service Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components in Sourcing Anodized Aluminum Services?
When sourcing anodized aluminum services, understanding the cost structure is essential for effective budgeting and negotiations. The primary cost components include materials, labor, manufacturing overhead, tooling, quality control (QC), logistics, and supplier margin.
-
Materials: The cost of aluminum alloys and anodizing chemicals significantly influences the total price. Premium materials, such as specific aluminum grades or environmentally friendly anodizing agents, can raise costs.
-
Labor: Skilled labor is required for both the anodizing process and quality assurance. Labor costs may vary based on geographic location and the complexity of the anodizing services provided.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes facility maintenance, utilities, and equipment depreciation. Efficient operational processes can help minimize overhead, impacting overall pricing.
-
Tooling: Initial investments in specialized equipment or molds can affect pricing, particularly for custom orders. Tooling costs may be amortized over larger production runs, making them less significant on a per-unit basis.
-
Quality Control: Ensuring that anodized parts meet industry standards often requires rigorous testing and inspection processes, which contribute to overall costs.
-
Logistics: Transportation and handling costs can vary widely, especially for international shipping. Factors such as distance, shipping method, and Incoterms chosen will impact logistics expenses.
-
Margin: Suppliers typically include a profit margin that reflects their operational costs, market conditions, and competitive positioning.
How Do Price Influencers Affect Anodized Aluminum Service Costs?
Several factors can influence the pricing of anodized aluminum services, particularly for B2B buyers from diverse regions:
-
Volume/MOQ: Higher order volumes or minimum order quantities (MOQs) often lead to lower per-unit costs. Suppliers may offer tiered pricing structures that incentivize larger orders.
-
Specifications and Customization: Custom specifications, such as unique anodizing colors or thicknesses, can increase costs. Complex designs may require additional labor and tooling, impacting overall pricing.
-
Material Quality and Certifications: Premium materials that meet specific quality standards or certifications (such as ISO or AS9100) can command higher prices. Buyers should consider the trade-off between cost and compliance with industry regulations.
-
Supplier Factors: The reputation, location, and expertise of the supplier can influence pricing. Established suppliers with a track record of quality may charge more due to their reliability.
-
Incoterms: The chosen Incoterms can significantly affect total costs. For example, DDP (Delivered Duty Paid) may include additional costs for customs clearance and duties, which should be factored into the overall price.
What Are Effective Buyer Tips for Negotiating Anodized Aluminum Service Costs?
Navigating the complexities of pricing in the anodized aluminum market requires strategic approaches:
-
Negotiation: Engaging in open discussions with suppliers about pricing can yield favorable terms. Highlighting your commitment to long-term partnerships may encourage suppliers to offer discounts or better pricing structures.
-
Cost-Efficiency: Consider the Total Cost of Ownership (TCO), which includes initial costs, maintenance, and potential rework. Investing in higher-quality anodizing may result in lower long-term costs due to improved durability and reduced maintenance needs.
-
Pricing Nuances for International Buyers: Buyers from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe should be aware of currency fluctuations, import duties, and regional supply chain dynamics that may affect pricing. Establishing local partnerships can mitigate some of these challenges.
-
Research and Comparison: Conduct thorough market research to compare prices and services from multiple suppliers. This enables informed decision-making and helps identify the best value propositions.
-
Requesting Quotes: Utilize Request for Quote (RFQ) processes to gather competitive pricing from various suppliers. Detailed specifications in RFQs can lead to more accurate and tailored pricing, reducing the risk of unexpected costs.
Disclaimer
The prices mentioned in this analysis are indicative and may vary based on numerous factors, including market conditions, supplier pricing strategies, and specific project requirements. Buyers are encouraged to conduct thorough due diligence and obtain multiple quotes to ensure competitive pricing.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing anodized aluminum service With Other Solutions
Understanding Alternatives to Anodized Aluminum Service
When considering surface treatment options for aluminum components, it’s essential to evaluate the alternatives to anodized aluminum service. Each solution offers unique benefits and potential drawbacks, impacting performance, cost, and suitability for specific applications. Below, we compare anodized aluminum service with two viable alternatives: Powder Coating and Chromate Conversion Coating.
| Comparison Aspect | Anodized Aluminum Service | Powder Coating | Chromate Conversion Coating |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | Excellent corrosion and wear resistance, enhances aesthetics | Good durability and corrosion resistance, offers a wide range of colors | Provides moderate corrosion resistance, primarily for aluminum |
| Cost | Moderate to high cost, depending on complexity | Generally lower cost, especially for large batches | Low to moderate cost, often used as a preparatory step |
| Ease of Implementation | Requires specialized equipment and expertise | Easier application, can be done in-house | Simple application, but requires careful handling |
| Maintenance | Low maintenance due to durability | Moderate maintenance; can chip or scratch | Low maintenance, but may require reapplication |
| Best Use Case | Aerospace, automotive, and high-end consumer products | Consumer products, outdoor furniture, and appliances | Industrial applications, military, and aerospace components |
What Are the Advantages and Disadvantages of Powder Coating?
Powder Coating is a popular alternative that involves applying a dry powder to a surface, which is then cured under heat. This process results in a thick, durable finish that is resistant to chipping, scratching, and fading.
Pros:
– Cost-effective, especially for larger production runs.
– Available in a wide variety of colors and finishes, making it suitable for decorative applications.
– Easier to apply than anodizing, often allowing for in-house processing.
Cons:
– While durable, it may not offer the same level of corrosion resistance as anodized aluminum.
– The coating can chip or scratch under heavy wear, requiring touch-ups or replacement.
– Less effective on complex geometries compared to anodizing, as the coating may not adhere as well in intricate areas.
What Makes Chromate Conversion Coating a Viable Option?
Chromate Conversion Coating is a chemical treatment that provides a protective layer on aluminum surfaces. This method enhances corrosion resistance while allowing for excellent adhesion of subsequent coatings.
Pros:
– Generally more cost-effective and quicker to apply than anodizing.
– Provides a good base for paint or other finishes, enhancing overall durability.
– Suitable for military and aerospace applications due to its protective qualities.
Cons:
– Offers moderate corrosion resistance compared to anodized finishes.
– The protective layer can wear off over time, necessitating reapplication.
– Environmental concerns regarding the use of chromate chemicals may limit its acceptance in some markets.
How Should B2B Buyers Choose the Right Solution?
When selecting the appropriate surface treatment for aluminum components, B2B buyers should consider their specific application requirements, budget constraints, and desired aesthetic outcomes. Anodized aluminum service is ideal for high-performance applications requiring superior durability and corrosion resistance, particularly in demanding industries like aerospace and automotive. In contrast, powder coating may be more suitable for products that prioritize cost-effectiveness and a wide range of color options, while chromate conversion coating serves well in industrial settings where moderate protection is sufficient. Ultimately, understanding the unique advantages and limitations of each option will enable buyers to make informed decisions aligned with their operational needs and market demands.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for anodized aluminum service
What Are the Key Technical Properties of Anodized Aluminum Service?
When considering anodized aluminum for your projects, understanding its critical technical properties is essential. Here are some of the most important specifications:
1. Material Grade
Material grade refers to the specific alloy composition of aluminum used in the anodizing process. Common grades include 6061 and 7075, each offering different mechanical properties and corrosion resistance. The choice of grade affects the performance and suitability of the finished product for various applications, such as aerospace, automotive, or architectural uses. Selecting the correct grade ensures that the anodized aluminum meets the required strength and durability standards.
2. Thickness of Anodic Coating
The thickness of the anodic coating, measured in microns, is a critical specification that influences wear resistance and corrosion protection. Standard anodized coatings range from 5 to 25 microns for decorative finishes (Type II) and can exceed 50 microns for hard coatings (Type III). Understanding the required thickness helps in determining the longevity and maintenance needs of the parts, which is vital for B2B buyers focused on performance and lifecycle costs.
3. Tolerance
Tolerance defines the permissible limits of variation in a physical dimension or measured value. In anodized aluminum service, tight tolerances are crucial for ensuring that parts fit correctly in assemblies. Precise tolerances prevent issues during installation and enhance the overall functionality of the component. This is particularly important in industries such as aerospace and automotive, where components must meet stringent specifications.
4. Corrosion Resistance
Corrosion resistance is a significant property enhanced through anodizing, which creates a protective oxide layer on the aluminum surface. This property is vital for applications exposed to harsh environments, such as marine or industrial settings. Buyers should evaluate the specific corrosion resistance requirements based on their operational conditions to ensure long-lasting performance.
5. Wear Resistance
Anodized aluminum exhibits improved wear resistance, making it suitable for high-friction applications. The anodic layer is harder than the underlying aluminum, providing protection against abrasion and extending the life of components. Understanding the wear resistance properties is crucial for industries like manufacturing and transportation, where component longevity is a key concern.
What Are Common Trade Terms in Anodized Aluminum Service?
Familiarity with industry jargon can streamline communication and facilitate smoother transactions. Here are several key terms relevant to anodized aluminum service:
1. OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
An OEM is a company that produces parts or equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer. In the context of anodized aluminum, buyers often source components from OEMs to ensure compatibility with existing systems. Understanding the role of OEMs helps buyers assess the quality and reliability of parts.
2. MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ refers to the smallest number of units a supplier is willing to sell in a single order. This term is essential for B2B buyers to understand, as it impacts inventory management and procurement strategies. Knowing the MOQ can help businesses plan their orders to avoid overstocking or stockouts.
3. RFQ (Request for Quote)
An RFQ is a document that solicits price proposals from suppliers for specific products or services. This process is crucial for B2B buyers looking to compare costs and secure competitive pricing for anodized aluminum services. A well-prepared RFQ can lead to better supplier relationships and more favorable terms.
4. Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
Incoterms are standardized trade terms that define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in international transactions. Familiarity with Incoterms helps B2B buyers understand shipping responsibilities, risk transfer, and costs associated with transporting anodized aluminum products, facilitating smoother international trade.
5. Lead Time
Lead time is the period between the initiation of an order and its completion. Understanding lead times is crucial for project planning, as it affects delivery schedules and inventory levels. Buyers should inquire about lead times to ensure that their production timelines align with their operational needs.
By grasping these technical properties and trade terms, B2B buyers can make informed decisions when sourcing anodized aluminum services, ultimately enhancing their operational efficiency and product quality.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the anodized aluminum service Sector
What Are the Current Market Trends in the Anodized Aluminum Service Sector?
The anodized aluminum service sector is experiencing significant growth, driven by increasing demand across various industries, including automotive, aerospace, and electronics. The global push for lightweight materials that enhance durability and corrosion resistance is a key market driver. Emerging technologies, such as advanced anodizing processes and automated finishing systems, are also reshaping the landscape, allowing for quicker turnaround times and improved quality control. For international B2B buyers, particularly from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, it is crucial to understand these dynamics. The rise of e-commerce platforms and digital marketplaces has made sourcing anodized aluminum services more accessible, enabling buyers to compare suppliers and request quotes efficiently.
Additionally, there is a growing trend towards customization, with companies increasingly seeking tailored anodizing solutions that meet specific project requirements. This shift towards personalized service necessitates strong communication and collaboration between buyers and suppliers. Furthermore, the market is seeing a notable increase in the adoption of sustainable practices, as companies prioritize eco-friendly solutions in their sourcing strategies. As a result, anodizing service providers that can demonstrate innovation and responsiveness to customer needs are well-positioned to thrive in this competitive environment.
How Can Sustainability and Ethical Sourcing Impact Your Anodized Aluminum Supply Chain?
Sustainability has become a focal point in the anodized aluminum service sector, influencing purchasing decisions for B2B buyers. The environmental impact of anodizing processes, including energy consumption and waste generation, is under scrutiny. As such, companies are increasingly seeking suppliers that adopt sustainable practices, such as using energy-efficient anodizing technologies and recycling water in their processes. Ethical sourcing is equally important; buyers are looking for suppliers that adhere to fair labor practices and maintain transparency in their supply chains.
Green certifications, such as ISO 14001 for environmental management systems, can enhance a supplier’s credibility and appeal to environmentally conscious buyers. Additionally, the use of eco-friendly materials, such as non-toxic dyes and chemicals in the anodizing process, is becoming a critical consideration. By prioritizing sustainability and ethical sourcing, companies can not only reduce their carbon footprint but also align with the values of their customers, enhancing brand reputation and fostering long-term loyalty.
What is the Historical Context of Anodized Aluminum Services?
The anodized aluminum service sector has evolved significantly since the anodizing process was first developed in the early 20th century. Originally used primarily in the aerospace industry for its lightweight and corrosion-resistant properties, anodizing has expanded into various sectors, including automotive, consumer electronics, and architectural applications. The introduction of different anodizing types, such as Type II and Type III, has allowed for greater customization and performance, catering to diverse industry needs.
With advancements in technology, the anodizing process has become more efficient and environmentally friendly. The shift towards automation and digital solutions has streamlined operations, resulting in faster delivery times and enhanced quality assurance. As the market continues to grow, understanding the historical context of anodized aluminum services provides valuable insights into current trends and future opportunities for B2B buyers navigating this dynamic landscape.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of anodized aluminum service
-
How do I choose the right anodized aluminum service provider?
When selecting an anodized aluminum service provider, consider factors such as their industry experience, certifications (like ISO 9001), and reputation in the market. Request samples of their work to assess quality and finish. It’s also crucial to inquire about their capabilities in handling your specific requirements, including customization options, turnaround times, and production volumes. Finally, examine their customer service responsiveness, as strong communication is essential for successful collaboration. -
What types of anodizing processes are available for aluminum?
There are several anodizing processes to choose from, including Type II and Type III anodizing. Type II provides a decorative finish and moderate corrosion resistance, while Type III, or hard coat anodizing, offers superior durability and wear resistance, making it ideal for industrial applications. Additionally, some providers offer specialty anodizing that includes dyeing for aesthetic enhancements. Understanding your specific needs will help you select the most appropriate process. -
What are the minimum order quantities (MOQ) for anodized aluminum services?
Minimum order quantities can vary significantly between suppliers and depend on the complexity of the anodizing process. Some providers may have a low MOQ for standard anodizing services, while custom finishes or specialized coatings might require larger orders. It’s advisable to discuss your project details with potential suppliers to understand their MOQ policies and explore options for small batch production if needed. -
What quality assurance measures should I expect from anodizing suppliers?
Reputable anodizing suppliers implement stringent quality assurance measures to ensure the consistency and reliability of their products. This includes routine inspections, adherence to industry standards, and certifications such as ISO 9001. You should also inquire about their testing processes for coatings, such as thickness testing, adhesion tests, and corrosion resistance evaluations. Understanding these measures can help you gauge the supplier’s commitment to quality. -
How do I handle international shipping and logistics for anodized aluminum parts?
When sourcing anodized aluminum parts internationally, it’s crucial to discuss shipping logistics upfront with your supplier. Ensure they are familiar with international shipping regulations and can provide appropriate packaging to prevent damage during transit. Inquire about shipping options, estimated delivery times, and any additional costs. Additionally, consider working with a logistics provider experienced in handling customs clearance to streamline the process. -
What payment terms should I negotiate with anodized aluminum suppliers?
Payment terms can vary based on the supplier’s policies and your business relationship. Common options include upfront payments, partial payments upon order confirmation, and balance upon delivery. For international transactions, consider discussing letters of credit or payment via escrow services for added security. It’s advisable to clarify these terms early in the negotiation process to ensure mutual understanding and avoid any potential disputes. -
Can I customize anodized aluminum finishes to match specific requirements?
Yes, many anodizing service providers offer customization options to meet specific project requirements. This includes the ability to select colors, textures, and thicknesses of the anodized layer. Some suppliers may also offer additional services such as laser engraving or surface treatments to enhance functionality. Discuss your specific needs with potential suppliers to ensure they can accommodate your desired customizations. -
What industries commonly utilize anodized aluminum services?
Anodized aluminum is widely used across various industries due to its enhanced durability and aesthetic qualities. Common sectors include aerospace, automotive, medical, electronics, and construction. Each industry has specific requirements regarding corrosion resistance, weight reduction, and appearance, making anodized aluminum an ideal choice. If you’re in a specialized field, inquire whether the supplier has experience working with similar applications to ensure they understand your unique needs.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.
Top 6 Anodized Aluminum Service Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. SendCutSend – Anodizing Services
Domain: sendcutsend.com
Registered: 2015 (10 years)
Introduction: Online sheet metal anodizing service that enhances durability and appearance of parts. Type II, Class II sulfuric anodizing process adds a protective oxide layer for increased corrosion and wear resistance without significant thickness. Available in five colors: black, clear, blue, gold, and red. No minimum quantity required. Pricing starts as low as $0.50 per part in bulk. Free shipping in the U….
2. Aluminum Anodizing – Specialized Anodizing Services
Domain: aluminumanodizing.com
Registered: 2000 (25 years)
Introduction: Aluminum anodizing services including black anodizing, bright dip anodizing, clear anodizing, color anodizing, and hard anodizing. Companies listed include Tompkins Metal Finishing, Anoplate Corporation, Val-Kro, and others, offering specialized anodizing solutions for various industries such as aerospace, defense, medical, automotive, and electronics. Services include premium surface finishing, e…
3. Hubs – Aluminum Anodizing Services
Domain: hubs.com
Registered: 1998 (27 years)
Introduction: Aluminum anodizing services include anodizing type II and III, which are ideal surface finishes for aluminum parts. Anodizing strengthens aluminum and is available in several colors. Key details include:
– **Anodizing Type II:**
– Surface Preparation: As machined, Bead blasted, Brushed
– Colors: Clear, Black, Red, Blue, Orange, Gold
– Glossiness: Glossy (Above 20 GU), Matte (Below 10 GU…
4. ModMyMods – Custom Aluminum Anodizing Service
Domain: modmymods.com
Registered: 2013 (12 years)
Introduction: ModMyMods Custom Aluminum Anodizing Service
5. Alumacoat – High Quality Anodizing Services
Domain: alumacoat.com
Registered: 2010 (15 years)
Introduction: High Quality Anodizing Services including Decorative Anodizing, Architectural Anodizing, Color Anodizing, and Automated Shot-Blasting.
1. **Decorative Anodizing**: Color and protect aluminum parts for aesthetic appeal; can match most architectural colors.
2. **Architectural Anodizing**: Protects large aluminum parts; Type II – Class I & II anodizing builds up aluminum oxide on the surface and i…
6. Anodize Solutions – Soft Anodize Coating
Domain: anodizesolutions.com
Registered: 2014 (11 years)
Introduction: { “services”: [ { “name”: “Soft Anodize”, “type”: “Mil 8625 Type II”, “description”: “A general-purpose coating that provides a good combination of durability and cosmetics. Can be dyed many vibrant colors.”, “coating_thickness”: { “clear”: “0.0002” , “black”: “0.001” }, “applications”: [ “medical equipment”, “dental equipment”, “outdoor products”, “bicycle components”, “climbing gear” ] }, { “nam…
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for anodized aluminum service
In navigating the competitive landscape of anodized aluminum services, strategic sourcing emerges as a critical component for international B2B buyers, particularly those in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. By partnering with reliable anodizing providers, businesses can access superior products that enhance durability, corrosion resistance, and aesthetic appeal. The variety of anodizing types—such as Type II and Type III hard coatings—offers tailored solutions to meet specific industry requirements across sectors like aerospace, automotive, and electronics.
Moreover, maintaining a focus on quality certifications such as ISO and AS9100 ensures that sourced products meet rigorous industry standards, fostering trust and long-term relationships. As companies continue to prioritize sustainability and innovation, the demand for anodized aluminum is set to rise, making it essential for buyers to stay informed about advancements and capabilities in the market.
Looking ahead, international buyers should actively engage with anodizing specialists to leverage their expertise and capabilities. By doing so, they can not only enhance their product offerings but also position themselves advantageously in a dynamic global marketplace. Start exploring your anodized aluminum sourcing options today to stay ahead of the curve and drive business growth.