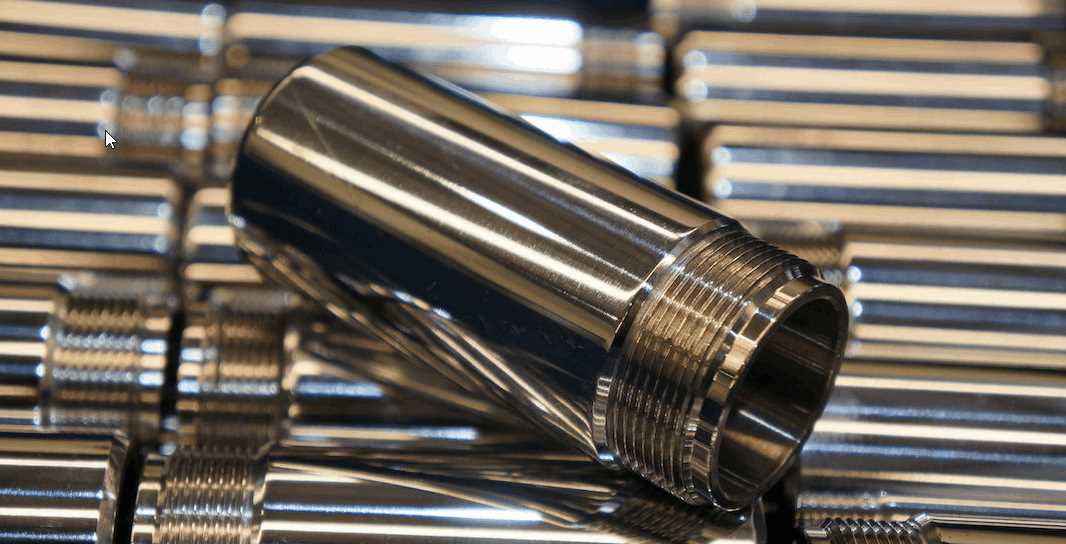
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for aluminum plating options
In the complex landscape of global manufacturing, sourcing the right aluminum plating options can be a daunting task for B2B buyers. With the increasing demand for lightweight, durable materials across diverse industries—from aerospace to telecommunications—understanding the nuances of aluminum plating becomes essential. This guide aims to demystify the various types of aluminum plating options available, including electroless nickel, tin, and precious metals like silver and gold.
Furthermore, we will delve into crucial aspects such as application suitability, the intricacies of supplier vetting, and cost considerations, ensuring you have a holistic view of the market landscape. Given the unique challenges faced by international buyers from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe—including regulatory hurdles, logistical complexities, and quality assurance—this comprehensive resource is designed to empower you with the knowledge needed to make informed purchasing decisions.
By addressing common pain points and providing actionable insights, this guide will help you navigate the global market for aluminum plating, ensuring that you select the best options tailored to your specific requirements. Whether you’re looking to enhance corrosion resistance, improve wear performance, or achieve aesthetic appeal, you will find the information necessary to drive your business forward in an increasingly competitive environment.
Understanding aluminum plating options Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Electroless Nickel Plating | Autocatalytic process, excellent adhesion, corrosion resistance | Aerospace, defense, telecommunications | Pros: Strong bond, high durability. Cons: Higher cost than other methods. |
| Zincate Process | Provides a thin zinc layer to prevent oxidation | Automotive, electronics, aerospace | Pros: Improves adhesion, prevents reoxidation. Cons: Additional step in the process. |
| Tin Plating | Cost-effective, provides a solderable surface | Food packaging, electrical components | Pros: Low cost, good corrosion resistance. Cons: Lower hardness compared to other coatings. |
| Silver Plating | High conductivity, aesthetic appeal | Electronics, jewelry, aerospace | Pros: Excellent conductivity, antimicrobial properties. Cons: Higher material cost, tarnishing issues. |
| Gold Plating | Superior corrosion resistance, excellent conductivity | High-end electronics, aerospace | Pros: Long-lasting, excellent conductivity. Cons: Very high cost, limited to specific applications. |
What are the characteristics of Electroless Nickel Plating?
Electroless nickel plating is distinguished by its autocatalytic process, which allows for uniform coating on complex geometries without the need for electrical current. This method provides excellent adhesion, corrosion resistance, and hardness, making it ideal for demanding applications in aerospace, defense, and telecommunications. B2B buyers should consider the higher cost associated with this process, which can be justified by its superior performance and longevity in critical applications.
How does the Zincate Process enhance aluminum plating?
The zincate process involves applying a thin layer of zinc to aluminum to prevent oxidation and improve the adhesion of subsequent coatings. This method is particularly beneficial in automotive and electronic applications, where reliable performance is crucial. While the zincate process adds an extra step to the plating procedure, the enhanced adhesion it provides makes it a valuable consideration for manufacturers looking for quality and durability in their finished products.
Why choose Tin Plating for aluminum components?
Tin plating is a cost-effective solution for aluminum components, offering good corrosion resistance and a solderable surface, making it popular in food packaging and electrical applications. While it is less hard than other plating options, its affordability can be a significant advantage for businesses looking to minimize costs without sacrificing essential properties. Buyers should weigh the benefits of lower costs against the need for durability based on their specific application requirements.
What benefits does Silver Plating offer to B2B buyers?
Silver plating is known for its high electrical conductivity and aesthetic appeal, making it a preferred choice in electronics and jewelry. Its antimicrobial properties also enhance its desirability in medical applications. However, buyers must consider the higher material cost and potential tarnishing issues, which may necessitate additional maintenance. This option is best suited for applications where performance and appearance are paramount.
When is Gold Plating the right choice for aluminum?
Gold plating provides exceptional corrosion resistance and conductivity, making it ideal for high-end electronics and aerospace applications. Its durability and long-lasting properties justify the higher costs associated with gold plating, especially in critical components where failure is not an option. B2B buyers should assess whether the benefits of longevity and performance outweigh the investment, especially for applications requiring the highest quality standards.
Key Industrial Applications of aluminum plating options
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of aluminum plating options | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Aerospace | Plating of aircraft components | Enhances corrosion resistance and reduces weight | Compliance with aerospace standards and certifications |
| Telecommunications | Plating of connectors and circuit boards | Improves conductivity and durability | Compatibility with various aluminum alloys |
| Defense | Coating of military equipment | Provides protection from environmental factors | Adherence to military specifications and standards |
| Automotive | Plating of engine and transmission parts | Increases wear resistance and thermal conductivity | Understanding of specific alloy requirements |
| Medical Equipment | Plating of surgical instruments and implants | Ensures biocompatibility and corrosion resistance | Compliance with health and safety regulations |
How is Aluminum Plating Used in Aerospace Applications?
In the aerospace sector, aluminum plating is critical for enhancing the performance of aircraft components. Plating options such as electroless nickel or silver provide superior corrosion resistance, which is essential in harsh atmospheric conditions. Buyers must ensure that their suppliers comply with stringent aerospace standards, as any failure in quality can lead to catastrophic outcomes. Additionally, the lightweight nature of aluminum plating contributes to overall fuel efficiency, a significant consideration for aerospace manufacturers.
What Role Does Aluminum Plating Play in Telecommunications?
The telecommunications industry relies heavily on aluminum plating for connectors and circuit boards. The plating process enhances the conductivity and durability of these components, ensuring reliable performance in demanding environments. For international buyers, especially in regions like Africa and South America, sourcing from suppliers that can provide specific alloy compatibility and quality certifications is crucial. These factors can impact the longevity and efficiency of telecommunications infrastructure.
How is Aluminum Plating Beneficial for Defense Applications?
In defense, aluminum plating is utilized to coat military equipment, including vehicles and communication devices. The added layer of protection against environmental factors, such as corrosion and wear, is vital for maintaining operational readiness. Buyers in this sector must prioritize suppliers that adhere to military specifications, ensuring that the plating processes used can withstand extreme conditions. This focus on quality can significantly extend the lifespan of critical defense assets.
Why is Aluminum Plating Important in the Automotive Industry?
The automotive industry employs aluminum plating for engine and transmission parts to enhance wear resistance and thermal conductivity. This application is crucial for improving the performance and longevity of vehicles. Buyers should consider the specific alloy requirements and the expertise of the plating provider to ensure that the coatings applied meet the rigorous demands of automotive standards. Understanding the balance between cost and quality is essential for making informed sourcing decisions.
How Does Aluminum Plating Ensure Safety in Medical Equipment?
In the medical equipment sector, aluminum plating is used for surgical instruments and implants to ensure biocompatibility and corrosion resistance. This application is critical for maintaining the integrity of medical devices that come into contact with the human body. Buyers must ensure that their suppliers comply with health and safety regulations, as any compromise in quality can lead to serious health risks. The ability to provide traceability and adherence to international medical standards is vital for sourcing decisions in this sector.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘aluminum plating options’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Difficulty in Achieving Adequate Adhesion of Coatings
The Problem: B2B buyers often encounter issues with the adhesion of coatings on aluminum parts. This challenge arises primarily due to aluminum’s propensity to oxidize quickly, creating a barrier that prevents effective bonding of the plating material. When manufacturers attempt to plate aluminum without proper surface preparation, they frequently face complications such as blistering or peeling, which can lead to product failure in critical applications, especially in industries like aerospace and automotive.
The Solution: To ensure strong adhesion, buyers should prioritize sourcing aluminum plating services that implement a rigorous pretreatment process. This includes a zincate process, where a thin layer of zinc is deposited on the aluminum surface to inhibit oxidation. It is essential to communicate specific requirements to suppliers about the aluminum grades and alloys being used. Buyers can also request detailed information about the pretreatment protocols employed by the supplier, ensuring that the process is tailored to the specific alloy composition. Additionally, conducting surface tests post-treatment can help verify adhesion strength before proceeding to the plating stage.
Scenario 2: Variability in Quality of Plated Finishes
The Problem: Many B2B buyers experience inconsistency in the quality of plated finishes on aluminum components. This issue can stem from a variety of factors, including the use of inadequate or non-specific pretreatment processes, inconsistent plating baths, or poorly controlled plating parameters. In industries where aesthetic appeal and functional performance are paramount, such variability can result in increased rework costs and delayed project timelines.
The Solution: Buyers should seek out suppliers that offer customized plating solutions based on their specific needs. When issuing requests for quotations, it is beneficial to include detailed specifications regarding the desired finish quality, including appearance, corrosion resistance, and thickness. Establishing a close working relationship with the plating provider can also facilitate better quality control measures. Regular audits and sample evaluations can help maintain standards, allowing buyers to catch any deviations in quality early in the production process. Investing in reliable suppliers with a proven track record will significantly reduce the risk of quality variability.
Scenario 3: Limited Understanding of Aluminum Alloy Compatibility
The Problem: A common pain point for B2B buyers is the complexity surrounding the compatibility of different aluminum alloys with various plating processes. Many manufacturers may not be fully aware of how the alloy’s composition impacts the plating outcome, leading to ineffective coatings and performance issues. This lack of understanding can result in increased costs and time spent on troubleshooting.
The Solution: To address this knowledge gap, buyers should educate themselves about the specific aluminum alloys they are working with and how these alloys interact with various plating techniques. Engaging with suppliers who provide comprehensive technical support can be invaluable. Buyers should ask suppliers for detailed information about the compatibility of their specific alloys with different plating methods, such as electroless nickel or zinc immersion plating. Additionally, leveraging industry resources, attending webinars, or participating in forums can enhance understanding and facilitate better decision-making. Documenting alloy specifications and desired outcomes will also aid in selecting the most suitable plating option for their applications.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for aluminum plating options
What Are the Key Properties of Electroless Nickel for Aluminum Plating?
Electroless nickel plating is a widely used option for aluminum components, offering excellent hardness and corrosion resistance. This process involves depositing nickel onto the aluminum surface through an autocatalytic reaction, eliminating the need for electrical current. The key properties include a temperature rating of up to 300°C and exceptional wear resistance, making it suitable for demanding applications in industries such as aerospace and defense.
Pros & Cons: The primary advantage of electroless nickel is its uniform coating, which adheres well to complex geometries. However, the process can be more expensive than traditional electroplating methods, and the need for precise control during application can complicate manufacturing.
Impact on Application: Electroless nickel is compatible with various media, providing a robust barrier against corrosive environments, which is crucial for components exposed to harsh conditions.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers from regions like Africa and the Middle East should consider compliance with international standards such as ASTM B733 for electroless nickel coatings. Additionally, understanding local regulations regarding nickel usage is essential.
How Does Tin Plating Benefit Aluminum Components?
Tin plating is another common choice for aluminum, particularly in applications requiring solderability and corrosion resistance. Tin has a melting point of 232°C, making it suitable for applications where heat exposure is limited.
Pros & Cons: The advantages of tin plating include its cost-effectiveness and ease of application, especially for high-volume production. However, it is less durable than other coatings, which may limit its use in high-wear applications.
Impact on Application: Tin plating is particularly beneficial for electrical components, as it enhances conductivity and provides a surface that can be easily soldered.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should be aware of standards such as ASTM B545, which governs tin plating processes. This is particularly relevant for companies in South America, where regulatory compliance is increasingly scrutinized.
What Are the Advantages of Silver Plating on Aluminum?
Silver plating is often chosen for aluminum components requiring high conductivity and corrosion resistance. Silver has a high thermal and electrical conductivity, making it ideal for electrical connectors and components.
Pros & Cons: The primary advantage of silver plating is its excellent electrical properties, which enhance the performance of electronic components. However, silver is more expensive than other plating options, which can increase overall production costs. Additionally, silver can tarnish over time, which may affect its appearance and performance.
Impact on Application: Silver plating is especially suitable for applications in telecommunications and electronics, where conductivity is critical.
Considerations for International Buyers: Compliance with standards such as ASTM B700 for silver plating is crucial for international buyers, particularly in Europe, where regulatory frameworks are stringent.
What Are the Key Features of Gold Plating for Aluminum?
Gold plating is utilized for aluminum components in high-end applications where corrosion resistance and conductivity are paramount. Gold offers excellent resistance to oxidation and tarnishing, with a melting point of 1,064°C.
Pros & Cons: The key advantage of gold plating is its superior corrosion resistance and conductivity, making it ideal for critical electronic applications. However, the high cost of gold limits its use to applications where performance justifies the expense.
Impact on Application: Gold plating is often used in aerospace and high-frequency electronic applications, where reliability is non-negotiable.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should ensure compliance with standards like ASTM B488 for gold plating. This is particularly important for buyers in regions such as the Middle East, where high-value components are frequently used.
Summary Table of Aluminum Plating Options
| Material | Typical Use Case for aluminum plating options | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Electroless Nickel | Aerospace, defense components | Excellent hardness and uniformity | Higher cost and complexity | High |
| Tin | Electrical components, solderable surfaces | Cost-effective and easy application | Less durable than other coatings | Low |
| Silver | Telecommunications, electronic connectors | High conductivity | High cost and potential tarnishing | High |
| Gold | Aerospace, high-frequency electronics | Superior corrosion resistance | Very high cost | High |
This strategic material selection guide provides B2B buyers with essential insights into aluminum plating options, enabling informed decisions that align with their specific application needs and compliance requirements.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for aluminum plating options
What Are the Main Stages of Manufacturing Aluminum Plating?
Manufacturing processes for aluminum plating involve several critical stages, each designed to ensure high-quality finishes that meet specific industry standards. The primary stages include material preparation, forming, assembly, and finishing. Understanding these stages is essential for B2B buyers looking to source aluminum plating solutions effectively.
How Is Material Prepared for Aluminum Plating?
Material preparation is the foundational step that directly influences the quality of the final plated product. This process typically involves several sub-steps:
-
Cleaning: The aluminum surface must be meticulously cleaned to remove oils, grease, and contaminants. Common methods include ultrasonic cleaning and solvent degreasing.
-
Deoxidation: Due to aluminum’s tendency to form a rapid oxide layer, it is crucial to remove this layer through chemical treatments. The zincate process, where a thin layer of zinc is deposited onto the aluminum surface, is often employed to prevent reoxidation before plating.
-
Surface Activation: Depending on the type of subsequent plating (e.g., nickel, gold, silver), the surface may require activation treatments to enhance adhesion. Electroless nickel plating is a common choice for ensuring a strong bond.
What Techniques Are Used in the Forming Stage?
In the forming stage, aluminum components are shaped according to design specifications. Techniques can vary based on the application but typically include:
-
Extrusion: This process involves forcing aluminum through a die to create specific shapes. It’s commonly used for producing long sections of uniform cross-section, such as bars and tubes.
-
Casting: Used for complex shapes, casting involves pouring molten aluminum into molds. It is essential in industries where detailed geometries are required, like aerospace and automotive.
-
Machining: After initial forming, machining processes such as milling, drilling, or turning may be necessary to achieve precise dimensions and surface finishes.
How Is Assembly Conducted in Aluminum Plating?
Once the components are formed, assembly becomes the next step. This stage may involve:
-
Joining Techniques: Common methods include welding, riveting, and adhesive bonding, depending on the application and desired strength of the final product.
-
Pre-Plating Inspection: Before plating, components undergo a thorough inspection to identify any defects or dimensional inaccuracies that could affect the plating process.
What Are the Key Finishing Processes in Aluminum Plating?
The finishing stage encompasses the actual plating process and any subsequent treatments to enhance the component’s properties:
-
Electroplating and Electroless Plating: These techniques deposit metal onto the aluminum surface. Electroplating requires an electric current, while electroless plating relies on a chemical reaction.
-
Post-Plating Treatments: After plating, components may undergo additional processes such as passivation or coating with protective layers to improve corrosion resistance and durability.
What Quality Control Measures Are Standard in Aluminum Plating?
Quality assurance is vital in the aluminum plating industry to ensure that products meet both customer expectations and regulatory requirements. B2B buyers should be aware of various quality control measures and international standards.
Which International Standards Apply to Aluminum Plating?
Adhering to international standards such as ISO 9001 ensures that manufacturers maintain a consistent quality management system. For specific industries, additional certifications may apply:
-
CE Marking: Important for products sold in Europe, indicating compliance with health, safety, and environmental protection standards.
-
API Standards: Relevant for manufacturers serving the oil and gas sector, focusing on quality and safety in equipment and materials.
What Are the Key Quality Control Checkpoints?
Quality control involves multiple checkpoints throughout the manufacturing process:
-
Incoming Quality Control (IQC): This initial inspection ensures that raw materials meet specified standards before production begins.
-
In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): Continuous monitoring during the manufacturing process helps identify issues early, ensuring adherence to specifications.
-
Final Quality Control (FQC): The final inspection assesses the finished products against quality standards before they are shipped to customers.
What Common Testing Methods Are Used?
To verify quality, various testing methods may be employed:
-
Adhesion Testing: Evaluates the bond strength between the aluminum substrate and the plating.
-
Thickness Measurement: Ensures that the plating meets specified thickness requirements, often using methods like X-ray fluorescence.
-
Corrosion Testing: Assesses the corrosion resistance of plated components under simulated environmental conditions.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control?
For B2B buyers, verifying a supplier’s quality control measures is crucial to ensure reliability and compliance with industry standards. Several strategies can be adopted:
What Are the Best Practices for Supplier Audits?
Conducting thorough audits of potential suppliers is essential. This may include:
-
On-Site Visits: Observing the manufacturing processes and quality control systems in action provides valuable insights into the supplier’s capabilities.
-
Reviewing Quality Documentation: Assessing quality manuals, process flow charts, and previous inspection reports can help gauge the supplier’s commitment to quality.
How Can Buyers Utilize Reports and Third-Party Inspections?
Requesting quality reports and certifications from suppliers is advisable. Additionally, engaging third-party inspection services can provide an unbiased assessment of the supplier’s quality control practices and product quality.
What Are the Quality Control Nuances for International Buyers?
B2B buyers from diverse regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe may encounter unique challenges related to quality control. Understanding these nuances can facilitate smoother transactions:
-
Regulatory Differences: Buyers should be aware of varying regulatory requirements across regions, which may impact product specifications and certification needs.
-
Cultural Considerations: Building strong relationships with suppliers can enhance communication regarding quality expectations and standards.
In conclusion, understanding the manufacturing processes and quality assurance measures for aluminum plating options is essential for B2B buyers. By focusing on the specific stages of production and implementing robust quality control practices, companies can ensure they receive high-quality, reliable products that meet their operational needs.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘aluminum plating options’
This guide aims to provide a clear and actionable checklist for B2B buyers seeking to procure aluminum plating options. With the growing demand for aluminum components across various industries, ensuring the right plating process can enhance durability, appearance, and functionality.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Understanding your specific requirements is crucial before engaging with suppliers. Consider factors such as the intended use of the aluminum components, environmental exposure, and desired finishes. Clearly outlining specifications like thickness, hardness, and corrosion resistance helps streamline the sourcing process.
Step 2: Research Available Plating Options
Aluminum can be plated using various techniques, including electroplating and electroless plating. Each method has its advantages and limitations, such as cost, adhesion strength, and application suitability. Familiarize yourself with options like electroless nickel, tin, and precious metal plating to determine which aligns best with your project needs.
Step 3: Evaluate Potential Suppliers
Before committing, it’s crucial to vet suppliers thoroughly. Request company profiles, case studies, and references from buyers in a similar industry or region. Consider suppliers’ experience with aluminum plating and their capacity to meet your specific requirements, as well as their reputation for quality and reliability.
Step 4: Verify Supplier Certifications
Ensure that potential suppliers hold relevant industry certifications and adhere to international quality standards. Certifications such as ISO 9001 or specific plating certifications indicate a commitment to quality control and best practices. This step is vital in mitigating risks associated with subpar plating processes.
Step 5: Assess Pretreatment Processes
The success of aluminum plating largely depends on the pretreatment process used. Inquire about the specific pretreatment methods, such as zincate application, employed by the supplier. Proper pretreatment is essential to remove oxides and ensure strong adhesion of the plating layer, preventing issues like blistering or pitting.
Step 6: Request Samples and Conduct Testing
Before placing a bulk order, request samples to evaluate the quality of the plating. Conduct tests for adhesion, corrosion resistance, and surface finish to confirm that the plating meets your specifications. This step minimizes the risk of defects and ensures that the final product performs as intended.
Step 7: Establish Clear Communication Channels
Effective communication with your supplier is key to a successful partnership. Set expectations regarding timelines, quality standards, and reporting processes. Regular updates on production status and potential challenges will help maintain transparency and foster a productive working relationship.
By following this checklist, B2B buyers can navigate the complexities of sourcing aluminum plating options, ensuring they select the right processes and suppliers to meet their manufacturing needs.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for aluminum plating options Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components in Aluminum Plating Options?
Understanding the cost structure of aluminum plating options is crucial for international B2B buyers. The primary cost components include materials, labor, manufacturing overhead, tooling, quality control (QC), logistics, and supplier margins.
-
Materials: The type of plating material significantly impacts costs. Common options like nickel, tin, and precious metals such as silver and gold vary in price. For instance, while tin is relatively inexpensive, precious metals may substantially increase the overall cost.
-
Labor: Skilled labor is essential for the plating process, particularly for tasks requiring precision, such as pretreatment and application of coatings. Labor costs may vary based on the region and the complexity of the plating process.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This encompasses utilities, equipment maintenance, and facility costs. Advanced plating processes may require specialized equipment, thereby increasing overhead expenses.
-
Tooling: Initial investments in tooling can be significant, especially for custom projects. Specialized tools may be necessary for unique designs, impacting the overall cost.
-
Quality Control: Ensuring high-quality plating involves rigorous QC measures, which add to costs. This may include testing for adhesion, corrosion resistance, and overall finish quality.
-
Logistics: Shipping and handling costs are crucial, especially for international transactions. Factors such as distance, shipping method, and customs duties can significantly affect logistics expenses.
-
Margin: Suppliers typically add a margin to cover their costs and profit. Understanding the supplier’s pricing strategy is essential for negotiating favorable terms.
What Influences Pricing for Aluminum Plating Options?
Several factors influence the pricing of aluminum plating options, which international B2B buyers should consider:
-
Volume/MOQ: Pricing often improves with larger orders. Suppliers may offer discounts for bulk purchases, making it vital to consider minimum order quantities (MOQs) in pricing negotiations.
-
Specifications/Customization: Custom requirements may lead to increased costs. Buyers should be clear about specifications to avoid unexpected expenses.
-
Material Quality and Certifications: Higher quality materials and certifications (e.g., ISO, ASTM) can lead to increased costs. Buyers should evaluate the necessity of certifications based on their application needs.
-
Supplier Factors: The supplier’s reputation, location, and production capabilities can influence pricing. Established suppliers may charge more due to their experience and reliability.
-
Incoterms: Understanding Incoterms is crucial for international buyers. These terms define responsibilities for shipping, insurance, and tariffs, impacting total costs.
What Are the Best Practices for B2B Buyers in Sourcing Aluminum Plating?
International B2B buyers can employ several strategies to enhance cost-efficiency in sourcing aluminum plating:
-
Negotiate Terms: Leverage volume purchases and long-term contracts to negotiate better pricing and terms. Building a strong relationship with suppliers can also lead to favorable agreements.
-
Consider Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Beyond initial pricing, evaluate the TCO, which includes maintenance, durability, and performance over time. Cheaper options may incur higher costs in the long run.
-
Research Suppliers Thoroughly: Investigate potential suppliers’ capabilities, quality standards, and customer reviews. This diligence can lead to better decisions and lower risks.
-
Evaluate Shipping and Logistics: Consider logistics as a critical component of the cost structure. Opt for suppliers with efficient shipping practices to minimize delays and additional costs.
-
Stay Informed on Market Trends: Prices for raw materials fluctuate based on market conditions. Keeping abreast of these trends can help buyers make informed purchasing decisions and timing.
What Should International Buyers Be Aware of Regarding Pricing Nuances?
For B2B buyers from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, understanding pricing nuances is essential. Currency fluctuations, local market conditions, and regulatory requirements can impact overall costs. Additionally, the import/export duties and tariffs associated with aluminum products may vary significantly between countries, affecting the final pricing.
Disclaimer on Pricing
While this analysis aims to provide a comprehensive overview of the cost and pricing structure for aluminum plating options, actual prices may vary based on numerous factors, including supplier, location, and market conditions. Buyers are encouraged to conduct detailed quotations tailored to their specific needs and circumstances.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing aluminum plating options With Other Solutions
Exploring Alternatives for Aluminum Plating Solutions
When considering aluminum plating options, it’s essential to evaluate alternative methods that can achieve similar performance outcomes. This analysis focuses on comparing aluminum plating techniques with two viable alternatives: anodizing and powder coating. Each method has unique benefits and potential drawbacks, making it crucial for B2B buyers to understand their differences to make informed decisions.
Comparison Table
| Comparison Aspect | Aluminum Plating Options | Anodizing | Powder Coating |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | Excellent adhesion, corrosion resistance | High corrosion resistance, wear resistance | Good corrosion resistance, aesthetic appeal |
| Cost | Moderate to high, depending on process | Generally lower than plating | Cost-effective for large volumes |
| Ease of Implementation | Requires specialized equipment and expertise | Simpler process, less specialized equipment | Relatively easy, requires curing ovens |
| Maintenance | Requires periodic inspection and maintenance | Minimal maintenance once applied | Occasional cleaning, but durable |
| Best Use Case | High-stress applications, electronic components | Aerospace, automotive, consumer goods | General industrial applications, decorative items |
Detailed Breakdown of Alternatives
What Are the Benefits and Drawbacks of Anodizing as an Alternative?
Anodizing is an electrochemical process that converts the aluminum surface into a durable, corrosion-resistant finish. It enhances the natural oxide layer, providing excellent resistance to wear and corrosion. One of the main advantages of anodizing is its cost-effectiveness compared to aluminum plating, particularly for large production runs. However, anodizing may not provide the same level of adhesion for additional coatings, which could limit its application in specific high-stress environments. Anodizing also requires less specialized equipment, making it easier to implement but may lack the aesthetic versatility of plating options.
How Does Powder Coating Compare to Aluminum Plating?
Powder coating involves applying a dry powder to the aluminum surface, which is then cured under heat to create a hard finish. This method offers good corrosion resistance and an appealing aesthetic, making it suitable for a range of industrial and decorative applications. The key advantage of powder coating is its cost-effectiveness, especially for large-scale projects. However, it may not provide the same level of performance in high-stress or high-temperature environments as aluminum plating. Additionally, while powder coating is relatively easy to apply, it requires specialized curing equipment, which may add to initial setup costs.
Conclusion: How Can B2B Buyers Choose the Right Solution?
Selecting the right aluminum finishing solution requires a careful assessment of specific project requirements, including performance, cost, and application environment. Buyers should consider the operational demands of their products and the long-term implications of maintenance and durability. If high performance in extreme conditions is critical, aluminum plating may be the best choice. Conversely, for projects with less stringent requirements or those prioritizing aesthetic appeal, anodizing or powder coating may offer a more cost-effective solution. Ultimately, understanding the nuances of each option will empower B2B buyers to make informed decisions that align with their operational goals and budgetary constraints.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for aluminum plating options
What Are the Key Technical Properties of Aluminum Plating Options?
When selecting aluminum plating options, understanding the technical properties that influence performance and compatibility is crucial for B2B buyers. Here are several key specifications to consider:
-
Material Grade
Aluminum alloys are categorized primarily into wrought and cast grades. Each grade has unique characteristics, such as strength and corrosion resistance, which affect the plating process. For example, 1000-series alloys are nearly pure aluminum, while 6000-series alloys contain copper and magnesium. B2B buyers must choose the appropriate grade to ensure optimal adhesion and performance of the plated finish, as different alloys require specific pretreatment processes. -
Thickness of Plating
The thickness of the plated layer impacts durability and performance. Thicker coatings may offer better corrosion resistance and wear protection but can increase weight and cost. Buyers should balance the desired thickness with application requirements, considering factors such as environmental exposure and mechanical stress. -
Tolerance
Tolerance refers to the permissible variation in dimensions and surface finishes of plated components. Tight tolerances are essential in industries like aerospace and defense, where precision is critical. Understanding tolerance requirements helps buyers communicate specifications clearly to suppliers, ensuring that the final product meets design standards. -
Corrosion Resistance
Different plating materials offer varying degrees of corrosion resistance. For example, electroless nickel plating provides excellent protection against oxidation, making it suitable for harsh environments. Buyers should assess the environmental conditions their products will face and select plating options that provide adequate protection, ultimately extending the life of the component. -
Adhesion Strength
The bond strength between the aluminum substrate and the plated layer is vital for the longevity of the coating. Processes like zincate pretreatment enhance adhesion by preventing oxidation during plating. Buyers should inquire about the adhesion properties of the chosen plating method to ensure that the coating will remain intact under operational conditions.
Which Trade Terms Should B2B Buyers Know When Considering Aluminum Plating?
Familiarity with industry terminology can streamline communication and negotiations in the aluminum plating market. Here are some essential trade terms:
-
OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
An OEM refers to a company that produces parts or equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer. Understanding OEM relationships is critical for B2B buyers when sourcing components, as it may affect pricing, quality, and warranty considerations. -
MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ is the smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell. Buyers need to be aware of MOQs to effectively manage inventory and production schedules. Negotiating MOQs can help buyers reduce costs, especially for high-volume orders. -
RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a formal document that solicits price quotes from suppliers for specific products or services. B2B buyers should prepare detailed RFQs that include technical specifications, quantities, and delivery requirements to receive accurate and competitive pricing. -
Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
Incoterms define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in international trade transactions. Familiarity with terms like FOB (Free On Board) or CIF (Cost, Insurance, and Freight) helps buyers understand shipping costs, risk responsibilities, and delivery obligations. -
Lead Time
Lead time refers to the time taken from placing an order to delivery. Understanding lead times is essential for planning production schedules and inventory management. Buyers should factor in lead times when selecting suppliers to ensure timely project completion. -
Surface Finish
Surface finish denotes the texture and quality of the surface of a plated component. It can affect aesthetic appeal, corrosion resistance, and functionality. Buyers should specify surface finish requirements to ensure that the final product meets their performance and aesthetic standards.
By grasping these technical properties and trade terms, B2B buyers can make informed decisions regarding aluminum plating options, ultimately leading to successful procurement and project outcomes.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the aluminum plating options Sector
What Are the Current Market Dynamics and Key Trends in the Aluminum Plating Options Sector?
The aluminum plating sector is experiencing robust growth driven by several global factors. The increasing demand for lightweight materials in industries such as aerospace, automotive, and telecommunications is a significant driver. Aluminum’s inherent properties, such as corrosion resistance and lightweight nature, make it an ideal choice for manufacturers looking to enhance performance while reducing overall weight and costs. Moreover, advancements in plating technologies, including electroless nickel and zincate processes, are enabling manufacturers to achieve superior adhesion and finish quality, which is crucial for high-performance applications.
Emerging B2B tech trends, such as automation in plating processes and the adoption of Industry 4.0 principles, are revolutionizing how companies approach aluminum plating. Automation not only increases efficiency but also improves precision in plating applications, reducing waste and operational costs. Additionally, digital platforms are facilitating better sourcing strategies, allowing international buyers from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe to access a broader range of suppliers and technologies. This increased connectivity is vital for businesses aiming to stay competitive in a global market.
Furthermore, the rise of custom plating solutions tailored to specific alloy grades underscores the need for specialized knowledge in the supply chain. As manufacturers seek to optimize their processes, understanding the metallurgical properties of various aluminum alloys becomes essential. This trend is particularly relevant for buyers in sectors with stringent regulatory requirements, such as aerospace and defense, where the integrity and reliability of plated components are paramount.
How Are Sustainability and Ethical Sourcing Influencing B2B Decisions in Aluminum Plating?
Sustainability and ethical sourcing are increasingly becoming priorities for B2B buyers in the aluminum plating sector. The environmental impact of aluminum production and processing is significant, contributing to greenhouse gas emissions and resource depletion. As a result, companies are seeking suppliers who demonstrate a commitment to sustainable practices, such as using recycled aluminum and minimizing water and energy usage in plating processes.
The importance of ethical supply chains cannot be overstated. Buyers are increasingly scrutinizing their suppliers for compliance with environmental regulations and labor standards, seeking partners who prioritize transparency and social responsibility. Certifications such as ISO 14001 (Environmental Management) and ISO 9001 (Quality Management) are becoming critical in supplier selection, offering assurance that suppliers are adhering to best practices in sustainability and quality control.
Moreover, the adoption of “green” materials in aluminum plating processes is gaining traction. Alternatives like eco-friendly plating solutions and non-toxic chemicals are being developed to replace traditional methods that may pose environmental risks. This shift not only enhances a company’s sustainability profile but can also improve marketability, as consumers and businesses alike are increasingly favoring environmentally responsible products.
What Is the Historical Context of Aluminum Plating in the B2B Sector?
The evolution of aluminum plating can be traced back several decades, with significant advancements occurring in the mid-20th century as industries began to recognize the unique benefits of aluminum. Initially, plating processes were rudimentary, often leading to challenges with adhesion and finish quality due to aluminum’s tendency to oxidize rapidly.
Over time, the development of specialized pretreatment processes, such as zincate and electroless nickel plating, transformed the industry. These innovations allowed for better adhesion and more durable finishes, paving the way for aluminum to be used in critical applications across aerospace, automotive, and telecommunications sectors. As the demand for lightweight and corrosion-resistant materials continues to grow, the aluminum plating sector remains poised for further advancements, driven by both technological innovations and a strong commitment to sustainability.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of aluminum plating options
-
1. How do I solve adhesion issues when plating aluminum?
Adhesion problems in aluminum plating often stem from the rapid oxidation of the aluminum surface. To mitigate this, ensure that proper pretreatment processes are employed, such as a zincate process that deposits a thin layer of zinc to prevent oxidation before plating. Additionally, using electroless nickel plating can enhance adhesion by forming a strong bond with the aluminum surface. Always collaborate with suppliers who offer customized pretreatment solutions tailored to specific aluminum alloys to achieve optimal results. -
2. What is the best aluminum plating option for corrosion resistance?
For superior corrosion resistance, electroless nickel plating is often the best choice. This process provides a uniform coating that adheres well to the aluminum substrate, effectively sealing it from corrosive environments. Alternatively, tin and silver plating can also offer corrosion protection but may not provide the same durability as nickel. Evaluate the specific environmental conditions your products will face to select the most suitable plating option. -
3. How can I ensure the quality of aluminum plating from suppliers?
To ensure quality in aluminum plating, request certifications and quality assurance documentation from potential suppliers. Look for suppliers that adhere to international standards such as ISO 9001. Additionally, inquire about their plating processes, including pretreatment methods and the types of metals used. Conducting a factory audit or requesting samples for testing can also provide insights into their quality management practices. -
4. What are the minimum order quantities (MOQ) for aluminum plating services?
Minimum order quantities for aluminum plating can vary significantly between suppliers, typically ranging from a few hundred to several thousand units. It’s essential to discuss your specific needs with suppliers to understand their MOQ policies. Some suppliers may offer flexibility based on the type of plating required or the complexity of the project. Always clarify MOQ during initial discussions to avoid potential issues later in the procurement process. -
5. What payment terms should I negotiate with aluminum plating suppliers?
Payment terms can vary by supplier and region, but common practices include net 30 or net 60 days after delivery. For larger orders, consider negotiating payment schedules that might include a deposit upfront, with the balance due upon completion. Always ensure that the terms are clearly outlined in the contract to avoid misunderstandings. Additionally, consider using secure payment methods that provide protection for both parties. -
6. How do I evaluate the reliability of an international aluminum plating supplier?
Evaluating an international supplier’s reliability requires thorough research. Start by checking their reputation through reviews and testimonials from previous clients. Look for experience in your specific industry and their ability to handle international logistics. Additionally, ensure they have robust communication practices and are responsive to inquiries. Request references and consider visiting their facility if possible to assess their capabilities firsthand. -
7. What logistics considerations should I keep in mind when sourcing aluminum plating internationally?
When sourcing aluminum plating internationally, factor in shipping times, customs regulations, and potential tariffs that may affect costs and delivery schedules. Collaborate with suppliers who have experience in international shipping and can navigate logistics efficiently. Consider using freight forwarders or customs brokers to simplify the process. It’s also wise to discuss packaging standards to prevent damage during transit. -
8. Can I customize aluminum plating services to meet specific project requirements?
Yes, many aluminum plating suppliers offer customization options to meet unique project specifications. This may include variations in coating thickness, finish types, and specific alloy treatments. When discussing your project, provide detailed information about your requirements and desired outcomes. A reputable supplier will work with you to develop a tailored solution that meets your needs while ensuring compliance with industry standards.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.
Top 9 Aluminum Plating Options Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. Advanced Plating Technologies – Aluminum Plating Solutions
Domain: advancedplatingtech.com
Registered: 2013 (12 years)
Introduction: Advanced Plating Technologies offers plating on aluminum alloys, including cast and wrought types, with finishes such as electroless nickel, tin, silver, and gold plating. The company employs barrel, vibratory, and rack methods based on component geometry and application. Their aluminum plating process has been refined over sixty years for industries like power transmission, energy, defense, telec…
2. Sharrett’s Plating – Aluminum Electroplating Solutions
Domain: sharrettsplating.com
Registered: 2001 (24 years)
Introduction: Aluminum is a soft, lightweight, durable metal used in various applications including aircraft, vehicle parts, food containers, and more. The aluminum electroplating process enhances corrosion protection, wear resistance, and appearance. Electroplating involves immersing aluminum in an electrolytic solution and applying electric current to deposit another metal. Electroless plating is an alternati…
3. Armoloy – AL-COAT® Aluminum Plating
Domain: armoloy.com
Registered: 1997 (28 years)
Introduction: AL-COAT® Aluminum Plating is a specially engineered thin, medical-grade chromium coating for aluminum substrates. It addresses issues with aluminum alloys such as softness, galling, and corrosion. Compatible with sterilization methods like steam autoclave and gamma radiation, it is ideal for medical applications but also effective in aerospace and oil and gas industries. The coating features a mic…
4. US Chrome – Chrome Plating Solutions
Domain: uschrome.com
Registered: 1999 (26 years)
Introduction: Chrome Plating Aluminum – Electroplating Aluminum. Key Finishes: Hard Chrome, Flash Chrome, Thin Dense Chrome, Electroless Nickel, Electrolytic Nickel, Cerakote, Alternative Coatings. Industries Served: Aerospace, Agriculture, Alternative Energy, Defense, Medical, Oil & Gas. Locations: Connecticut, Florida, Illinois, New York, Ohio, Wisconsin. Features & Benefits: Freedom of Design, Increase in We…
5. Gabrian – Aluminum Finishes Guide
Domain: gabrian.com
Registered: 2000 (25 years)
Introduction: 9 Types of Aluminum Finishes: 1. Mill Finish – Basic finish with die marks, dull appearance, and oxidation; suitable for low-cost applications. 2. Anodizing – Improves corrosion and wear resistance; electrochemical process thickens aluminum oxide layer; limited color options. 3. Powder Coating – Bright, long-lasting colors; high UV resistance; environmentally friendly; requires baking to cure. 4. …
6. Protolabs – Finishing Options for CNC Machining and Sheet Metal Fabrication
Domain: protolabs.com
Registered: 2006 (19 years)
Introduction: Protolabs offers various finishing options for CNC machining and sheet metal fabrication, including plating, anodizing, sealing, powder coating, painting, and passivation. Key plating options include: 1. Bright Nickel Plating: Applied through electroplating, providing a shiny finish with thickness ranging from 0.00005 in. to 0.001 in. 2. Electroless Nickel Plating: Suitable for high-volume applica…
7. Keronite – Electro-plating Aluminium Alloys
Domain: blog.keronite.com
Registered: 1999 (26 years)
Introduction: 1. **Electro-plating Aluminium Alloys**: Enhances properties of aluminium through electrochemical conversion coating. Techniques include electroless and electrolytic. Improves wear resistance and tribological performance. Nickel plating can prevent galvanic corrosion but is application-dependent. Electroless nickel (EN) plating is popular for its high hardness, ductility, and abrasion resistance, …
8. AlumiPlate – Pure Aluminum Electroplating Services
Domain: alumiplate.com
Registered: 1996 (29 years)
Introduction: AlumiPlate offers pure aluminum electroplating services with 99.99% purity, designed to protect critical components from corrosion in extreme environments. The coating complies with MIL-DTL-83488 and NAS4006 standards and is suitable for industries such as aerospace, semiconductor fabrication, thermal management, optics, and medical devices. Key features include superior anti-corrosion properties,…
9. Wayken – Machined Aluminum & Anodizing Solutions
Domain: waykenrm.com
Registered: 2013 (12 years)
Introduction: 1. As Machined Finish: Original state of machined aluminum, no extra cost, suitable for applications without finish requirements, surface roughness Ra 0.2 – 3.2µm, visible machine tool marks. 2. Anodizing: Electrochemical process creating a durable, corrosion-resistant oxide layer, offers various coating thicknesses, enhances aesthetic appeal with vibrant colors, improves longevity and wear resist…
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for aluminum plating options
In navigating the complexities of aluminum plating, international B2B buyers must prioritize strategic sourcing to ensure optimal outcomes. Understanding the various plating techniques—such as electroless nickel and electroplating—along with their respective advantages, is crucial for enhancing product durability, appearance, and performance. Moreover, recognizing the significance of tailored pretreatment processes for different aluminum alloys can prevent common issues like poor adhesion and corrosion.
Investing in high-quality plating not only improves the longevity of aluminum components but also aligns with industry standards across sectors such as aerospace, telecommunications, and defense. As global markets continue to evolve, suppliers who can offer specialized solutions and robust support will stand out as valuable partners.
Looking ahead, B2B buyers in regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe should actively seek out suppliers that demonstrate expertise in aluminum plating options. By forging strategic partnerships and leveraging advanced technologies, companies can position themselves for success in a competitive landscape. Now is the time to explore innovative aluminum plating solutions that can drive efficiency and performance in your operations.