Contents
Manufacturing Insight: Aluminum Die Cast Machines
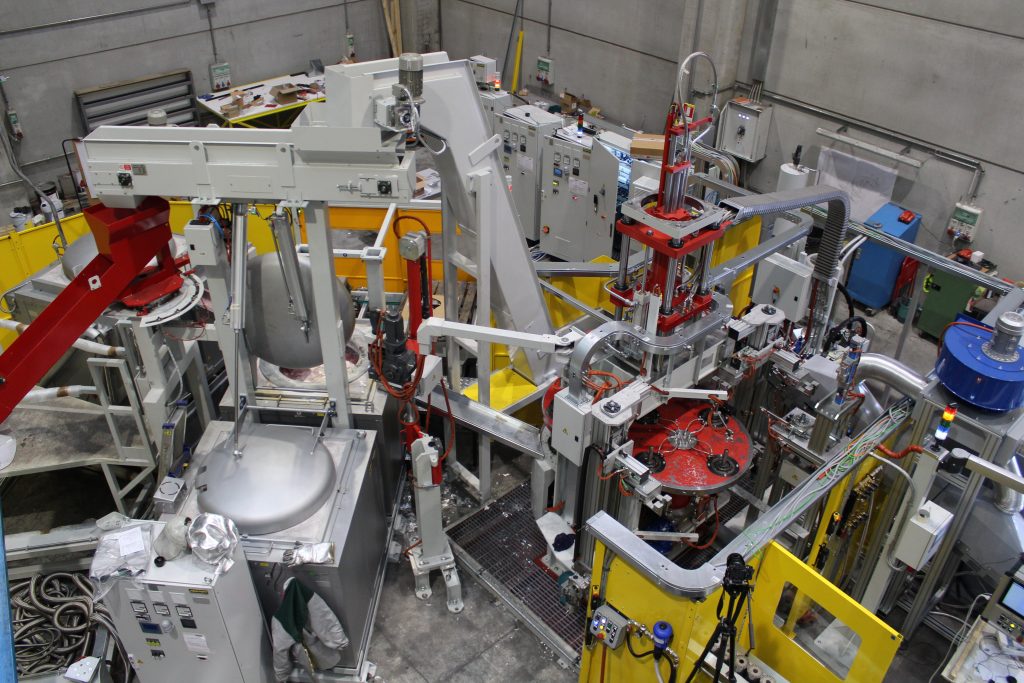
Aluminum die-cast machines demand cores, cavities and wear inserts that hold ±0.02 mm true-position day after day.
At Honyo Prototype we turn those demanding prints into reality: our 3-, 4- and 5-axis CNC centers mill, drill and thread P20, H13 and aluminum tooling grades at 24,000 rpm with in-machine probing that certifies every dimension before the electrode ever touches the mold. Whether you need a single prototype insert or a 500-piece production run of shot-sleeve liners, simply upload your STEP file—our online instant quote engine returns a CNC-machining proposal with lead time and DFM feedback in under five minutes, so your die-cast line can be back in action faster than ever.
Technical Capabilities

Important Clarification:
There is a critical misunderstanding in your query. Aluminum die casting machines do NOT perform 3/4/5-axis milling, turning, or tight-tolerance machining. These are fundamentally different manufacturing processes. Let me explain clearly:
🔧 Why Your Query is Misaligned
| Process | Die Casting Machines | CNC Machining (Milling/Turning) |
|———————-|———————————————————-|———————————————————|
| Function | Injects molten metal (e.g., aluminum, zinc) into steel molds under high pressure to form near-net-shape parts. | Cuts solid material (metals, plastics) using rotating tools to achieve precise geometries. |
| “Axes” Relevance | None. Die casting machines have clamping force, shot capacity, and mold movement (e.g., 2-axis mold opening/closing), not milling/turning axes. | Core feature: 3/4/5-axis CNC machines precisely control tool position along X/Y/Z (+ rotational axes) for complex geometries. |
| Materials | Only molten metals (e.g., Al alloys like A380, ADC12; NOT ABS/Nylon – plastics would burn/vaporize). Steel is used for molds, not as the cast material. | Solids only: Aluminum alloys, steel (e.g., 304SS), ABS, Nylon, etc. ABS/Nylon are machined, NOT die cast. |
| Tight Tolerance | Die casting achieves ±0.1–0.3 mm tolerances as-cast (post-machining may be needed for tighter specs). | Directly achieves tight tolerances (e.g., ±0.005 mm for precision 5-axis milling). |
Key Takeaway:
– Die casting = casting process (produces raw shapes from molten metal).
– Milling/turning = subtractive machining process (removes material from solid blanks).
– ABS/Nylon cannot be die cast – they are thermoplastics processed via injection molding, not die casting.
📐 Correct Technical Specs for ALUMINUM DIE CASTING MACHINES
(Focus: Aluminum die casting – no milling/turning involved)
| Parameter | Typical Range for Aluminum Die Casting | Why It Matters |
|—————————-|———————————————————-|——————————————————–|
| Clamping Force | 100–5,000+ metric tons (e.g., 600T for automotive parts) | Prevents mold separation during injection; higher force = larger parts. |
| Shot Weight Capacity | 50g–15,000g (e.g., 2–10kg for typical parts) | Determines max part size/weight. Aluminum density ≈ 2.7 g/cm³. |
| Injection Pressure | 50–200 MPa (7,250–29,000 psi) | Ensures molten metal fills complex mold cavities. |
| Mold Temperature | 150–250°C (300–480°F) | Critical for part quality; affects surface finish, porosity. |
| Cycle Time | 15–90 seconds (depending on part complexity) | Impacts production efficiency. |
| Material Compatibility | Aluminum alloys only (e.g., A380, A356, ADC12). Steel is used for molds, not as cast material. ABS/Nylon are INCOMPATIBLE. | Die casting requires metals with low melting points; plastics would destroy the machine. |
| Tight Tolerance Capability | As-cast: ±0.1–0.3 mm. With post-machining: ±0.025 mm achievable. | Die casting alone cannot achieve sub-0.1mm tolerances; CNC machining is required for tighter specs. |
💡 Note: Die casting machines DO NOT have “axes” for milling/turning. They are hydraulic or electric presses with mold clamping systems and shot units – not CNC tools.
⚙️ If You Meant CNC MACHINING (Milling/Turning) for Aluminum, Steel, ABS, Nylon:
(This is likely what you intended – let’s clarify specs for CNC machines)
For 3/4/5-Axis Milling Machines:
| Parameter | Typical Specs (Precision Machine) |
|—————————-|———————————————————-|
| Positioning Accuracy | ±0.001–0.005 mm (ISO 230-2 standard) | Critical for tight-tolerance parts (e.g., aerospace components). |
| Repeatability | ±0.001 mm | Ensures consistency across batches. |
| Spindle Speed | 10,000–30,000 RPM (for aluminum); 5,000–15,000 RPM (for steel) | Higher speeds for soft materials (Al, ABS); lower for steel. |
| Table Size | 500x500mm to 1,500×1,500mm (customizable) | Determines max part size. |
| Tool Changer Capacity | 20–100+ tools (for complex multi-operation parts) | Reduces manual tool changes. |
| Coolant System | High-pressure (10–100 bar) for aluminum/steel; low-pressure for ABS/Nylon | Prevents thermal distortion; ABS/Nylon require flood coolant to avoid melting. |
| Material-Specific Notes| Aluminum: High-speed machining (e.g., 3,000+ mm/min feed rate). Steel: Carbide tools, slower speeds. ABS/Nylon: Sharp tools, low heat (prevents melting), dry cutting or minimal coolant. |
For Turning Machines (CNC Lathes):
| Parameter | Typical Specs (Precision Lathe) |
|—————————-|———————————————————-|
| Max Swing | 200–600mm | Determines max part diameter. |
| Spindle Speed | 50–6,000 RPM (variable) | Higher speeds for aluminum/ABS; lower for steel. |
| Tolerance Capability | ±0.005–0.01 mm (with live tooling for milling operations) | Achieves tight tolerances on cylindrical features. |
| Tool Stations | 8–12+ (for multi-axis turning/milling) | Enables complex geometries without re-fixturing. |
| Material-Specific Notes| Aluminum: High feed rates (e.g., 500 mm/min). Steel: Robust tooling (e.g., CBN inserts). ABS/Nylon: Low friction tools, no coolant if possible (to avoid warping). |
Tight Tolerance Requirements:
- General Machining: ±0.025 mm is standard for precision work.
- High-Precision: ±0.005 mm achievable with:
- Temperature-controlled environments (±1°C).
- Vibration-damped foundations.
- Laser calibration and thermal compensation.
- ABS/Nylon Note: These plastics are highly sensitive to heat – machining requires specialized tooling (e.g., diamond-coated bits) and strict temperature control to avoid melting or warping.
✅ Summary & Next Steps
- Die casting machines ≠ CNC machines. They are entirely different technologies.
- ABS/Nylon cannot be die cast – they require injection molding or CNC machining.
- For aluminum die casting: Focus on clamping force, shot weight, and mold design.
- For CNC machining: Focus on axis accuracy, spindle speed, and material-specific parameters.
If you need:
– Detailed specs for aluminum die casting machines (e.g., for a project requiring high-volume metal parts),
– Or detailed specs for CNC milling/turning (for tight-tolerance parts in aluminum, steel, ABS, or nylon),
– Please clarify your exact need, and I’ll provide a technical deep-dive.
As a Senior Manufacturing Engineer at Honyo Prototype, I’d be happy to help you choose the right process for your application! 🛠️
From CAD to Part: The Process

Honyo Prototype – Aluminum Die-Cast Workflow (upload to dock-side)
- Upload CAD
Customer drops any mix of 3-D solids (STEP, Parasolid, Creo, NX, Catia, SolidWorks) + 2-D PDF drawing into the secure web portal. - Geometry is auto-repaired and healed for draft, wall-stock and under-cut detection.
-
Instant file-size / complexity score is generated so the AI engine knows which machine class (125 T – 1 250 T Buhler, LK, Toshiba) will be required.
-
AI Quote (≤ 30 min)
- Machine-learning model trained on 15 000+ historical shots predicts cycle time, shot weight, biscuit size, trim force and yield.
- Real-time raw-metal (A380, ADC12, AlSi10Mg, etc.) and energy pricing is pulled from exchanges; scrap credit is netted.
- Secondary ops (CNC, impregnation, powder coat, anodize) are auto-selected from the drawing call-outs.
-
Customer sees an itemised PDF + clickable 3-D cost driver heat-map; one click converts it into a binding PO.
-
DFM (2 – 4 calendar days)
a. Tooling design- Multi-slide vs. conventional ejector layout chosen by AI; mould-fill and solidification simulation run in Magma / FLOW-3D.
- Runner & gating optimised for ≤ 3 % porosity at critical stress zones.
- Draft ≥ 0.5°, fillets ≥ 0.5 mm, parting line balanced to minimise flash.
b. Part refinement - Customer gets interactive DFM report: suggested rib thickness, boss OD, window placement, ejector-pin locations, machining allowances.
c. Order locks - Steel grade (H13 or 8407), cavity count, shot-peen texture, heat-treat hardness (44–48 HRC) and tool life guarantee (≥ 100 k shots) are signed off.
-
Production
Tool build (lead-time 15 – 25 days)- High-speed Mikron CNC → vacuum heat treat → OPS-Ingersoll graphite high-speed mill for ribs → OD / ID grinding → spotter → texture or polish.
- T1 sample with full layout, X-ray, CT porosity scan and CPK report supplied to customer for approval.
Die-casting
– Closed-loop Buhler Carat or LK DC-J machines with real-time shot-profile monitoring: injection speed, metal temperature, vacuum level, die temperature.
– Automatic ladle + dosing furnace keeps melt ±5 °C; vacuum ≤ 50 mbar achieved with Vacural or Schaublin valve.
– Robotic extract + trim in same cell; 100 % leak-test (pressure decay 0.3 bar / 30 s) on hydraulic ports when specified.
Post-cast ops (same building)
– 3-axis to 5-axis Mazak & Brother CNC for datum and finish machine; 0.02 mm true-position routinely held.
– Impregnation (MIL-STD-276), wet paint or powder coat Class A, chem-film, hard anodize Type III, trivalent chrome-free seal.
– CMM report, PPAP level 3, material cert, RoHS & REACH statement supplied with every lot.
- Delivery
- Parts vacuum-sealed + VCI paper; custom dunnage for fragile ribs or cosmetic faces.
- DAP, DDP, FCA or FOB Shenzhen options; daily consolidated air to EU & US, 3-day express or sea freight for volume.
- Digital twin file (actual scan vs. CAD colour map) uploaded to customer portal before shipment; full traceability barcode on every carton.
Typical end-to-end lead-time:
Prototype tool + 500 pcs T1 samples in 18 days; production tool + 2 k pcs in 22 days; repeat lots 7–10 days dock-to-dock.
Start Your Project
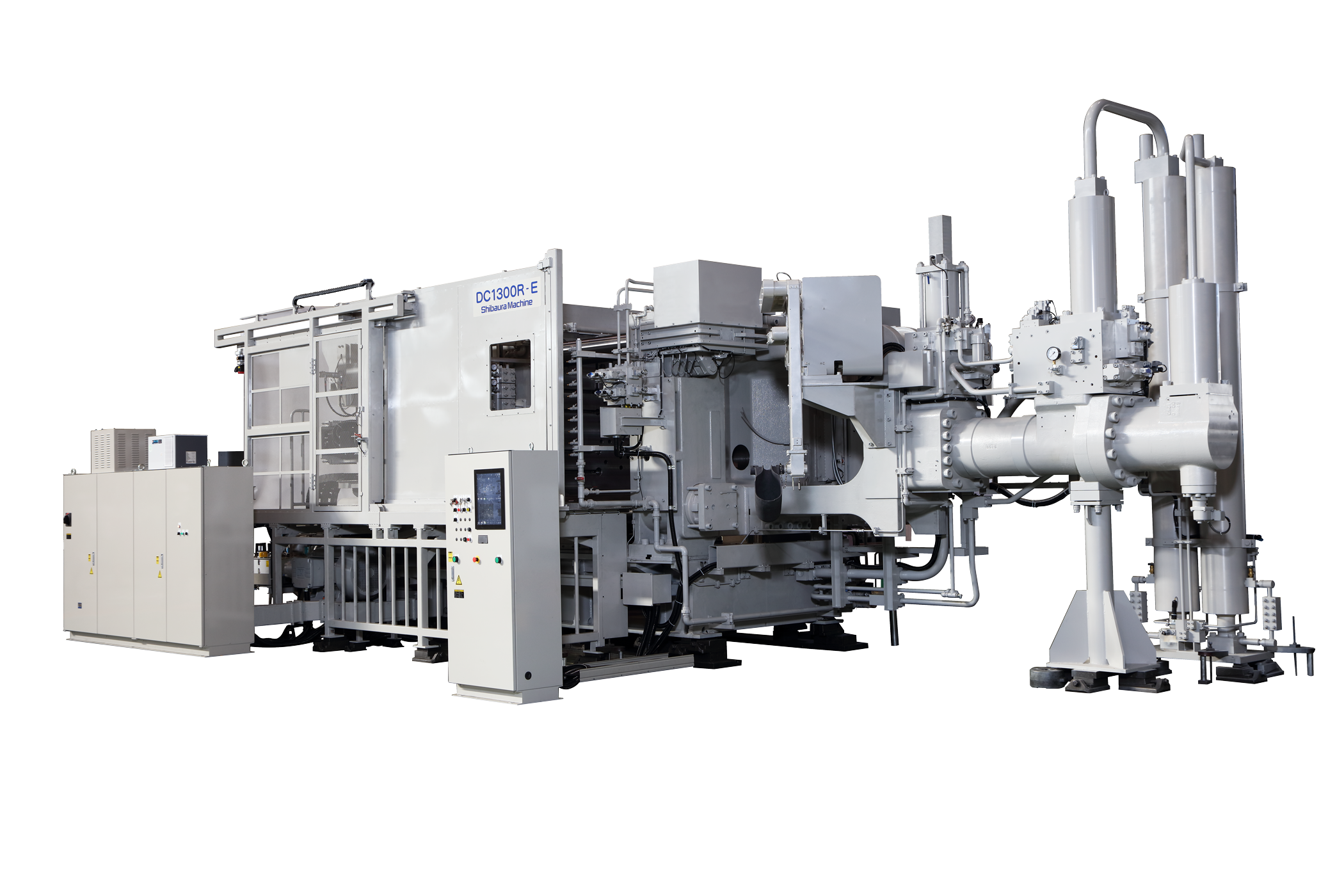
🚀 Rapid Prototyping Estimator