Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for aluminum conversion coating
Navigating the complexities of sourcing aluminum conversion coatings can pose significant challenges for international B2B buyers, particularly in regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. The need for high-quality coatings that ensure corrosion resistance and enhance paint adhesion is critical in various industries, including automotive, aerospace, and electronics. This guide aims to demystify the aluminum conversion coating market by exploring the different types available, including chromate and non-chromate options, and their specific applications across diverse sectors.
Buyers will gain insights into the essential criteria for vetting suppliers, understanding compliance with international standards, and evaluating cost factors associated with these coatings. With a focus on actionable strategies, this guide empowers decision-makers to make informed purchasing choices that align with their operational needs and sustainability goals. By providing a comprehensive overview of the market landscape, we equip B2B buyers with the knowledge necessary to navigate their sourcing processes efficiently, ensuring they select the best aluminum conversion coatings for their applications, whether in Saudi Arabia, Nigeria, or beyond.
Understanding aluminum conversion coating Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Type I – Hexavalent Chromium | Offers excellent corrosion protection; soft coating; color varies from light to dark yellow. | Aerospace, automotive, and industrial applications. | Pros: Strong corrosion resistance, excellent paint adhesion. Cons: Environmental concerns due to hexavalent chromium. |
| Type II – Trivalent Chromium | Environmentally friendly; similar performance to Type I; typically lighter in color. | Automotive, aerospace, and electronics. | Pros: Meets environmental regulations, excellent adhesion. Cons: Slightly lower corrosion resistance compared to Type I. |
| Non-Chrome Conversion Coating | Utilizes no hexavalent chromium; focuses on bonding strength and surface preparation. | Automotive bonding applications, composites. | Pros: Environmentally safe, excellent bonding strength. Cons: May not provide as robust corrosion protection as chromate options. |
| Alodine / Chem Film | Transforms the metal surface into a protective layer; maintains electrical conductivity. | Aerospace, defense, and electronics sectors. | Pros: Durable, does not alter dimensions, enhances adhesion. Cons: Requires careful application to ensure effectiveness. |
| Iridite / Bonderite | Similar to Alodine, but with unique chemical formulations; provides a variety of colors. | General manufacturing, automotive, and aerospace. | Pros: Aesthetic appeal, effective corrosion resistance. Cons: May vary in performance based on specific alloy used. |
What Are the Key Characteristics of Hexavalent Chromium Coating?
Type I hexavalent chromium coatings are renowned for their exceptional corrosion resistance and are predominantly used in high-demand sectors like aerospace and automotive. This coating is soft and can vary in color, indicating the level of immersion in the chromate bath. Buyers should consider the environmental regulations surrounding hexavalent chromium, as this type may pose compliance challenges in certain markets.
How Does Trivalent Chromium Coating Compare?
Type II trivalent chromium coatings offer a similar performance level to hexavalent options but without the associated environmental risks. They are often employed in automotive and aerospace applications where compliance with regulations such as RoHS and REACH is necessary. Buyers should evaluate the specific corrosion protection needs of their applications, as Type II may not provide the same level of resistance as Type I.
What Benefits Do Non-Chrome Conversion Coatings Provide?
Non-chrome conversion coatings are gaining traction due to their environmentally friendly nature. These coatings focus on enhancing bonding strength, making them ideal for applications that require robust adhesive properties, particularly in automotive bonding. Buyers should assess the trade-off between corrosion protection and bonding strength when considering this option.
Why Choose Alodine or Chem Film Coatings?
Alodine, or chem film, is a unique conversion coating that transforms the aluminum surface into a protective layer while preserving electrical conductivity. It is widely utilized in aerospace and defense applications where both corrosion resistance and conductivity are critical. Buyers must ensure precise application to maintain the coating’s integrity and performance, especially in precision components.
What Makes Iridite or Bonderite a Viable Option?
Iridite and Bonderite coatings are variations of chromate conversion coatings that can provide aesthetic benefits alongside corrosion protection. These coatings are applicable across various manufacturing sectors, including automotive and aerospace. Buyers should be aware of the performance variability based on the specific alloy used, as this may affect the coating’s overall effectiveness.
Key Industrial Applications of aluminum conversion coating
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of Aluminum Conversion Coating | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Aerospace | Protective coating for aircraft components like hulls and struts | Enhances corrosion resistance and structural integrity of components | Compliance with aerospace standards (MIL-DTL-5541) |
| Automotive | Pre-treatment for painting aluminum automotive parts | Improves paint adhesion and durability, extending component life | Compatibility with various aluminum alloys and coatings |
| Electronics | Coating for heat sinks and electronic housings | Maintains electrical conductivity while protecting against corrosion | Requirements for precision coating without dimensional change |
| Construction | Coating for aluminum frameworks and facades | Increases longevity of structures exposed to environmental elements | Consideration of local climate and environmental factors |
| Defense | Coating for military vehicles and equipment | Provides essential corrosion protection and durability in harsh conditions | Adherence to military specifications and environmental standards |
How is Aluminum Conversion Coating Used in Aerospace Applications?
In the aerospace sector, aluminum conversion coatings are applied to critical components such as aircraft hulls, struts, and landing gear. These coatings enhance corrosion resistance and maintain the structural integrity of components subjected to extreme conditions. For international buyers, especially in regions like the Middle East and Europe, sourcing coatings that meet stringent aerospace standards, such as MIL-DTL-5541, is crucial. This ensures compliance with safety regulations and extends the service life of vital aircraft parts.
What Role Does Aluminum Conversion Coating Play in Automotive Manufacturing?
In the automotive industry, aluminum conversion coatings serve as a pre-treatment for aluminum parts before painting. This process significantly improves paint adhesion, leading to enhanced durability and aesthetic appeal of the finished product. For B2B buyers in regions like Africa and South America, understanding the compatibility of coatings with different aluminum alloys is essential. This knowledge helps ensure that the chosen coating meets the specific performance and environmental requirements of their automotive applications.
How Does Aluminum Conversion Coating Benefit Electronics Manufacturing?
Aluminum conversion coatings are vital in the electronics industry, particularly for heat sinks and electronic housings. These coatings protect against corrosion while preserving electrical conductivity, which is critical in electronic applications. International buyers must consider sourcing coatings that provide precision application without altering the dimensions of sensitive components. This ensures that their products maintain performance standards while benefiting from added durability.
Why is Aluminum Conversion Coating Important in Construction?
In construction, aluminum conversion coatings are applied to frameworks and facades to enhance their resistance to environmental factors. This protective layer increases the longevity of structures, especially in regions with harsh climates. Buyers from the Middle East and Africa should evaluate the coatings’ performance in local weather conditions to ensure optimal protection and reduced maintenance costs. Selecting the right coating can significantly impact the overall durability and aesthetics of construction projects.
How Does Aluminum Conversion Coating Enhance Defense Equipment?
In the defense sector, aluminum conversion coatings are applied to military vehicles and equipment to provide essential corrosion protection and durability in extreme conditions. For international buyers, compliance with military specifications and environmental standards is paramount. Sourcing coatings that meet these requirements ensures the longevity and reliability of defense materials, which is critical for operational effectiveness in challenging environments.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘aluminum conversion coating’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Inconsistent Coating Quality Across Different Aluminum Alloys
The Problem: B2B buyers often struggle with achieving consistent coating quality when applying aluminum conversion coatings to different alloys. Variations in alloy composition can lead to uneven coating thickness, poor adhesion, or inadequate corrosion resistance, which ultimately affects the durability and performance of the finished products. For instance, a buyer working in the aerospace sector may find that the same coating process yields drastically different results on a cast aluminum part compared to a wrought aluminum part, leading to compliance issues and potential failures in critical applications.
The Solution: To address this challenge, buyers should engage in thorough material assessment and testing before coating. Begin by identifying the specific aluminum alloys being used and understanding their unique characteristics. Conduct controlled tests to evaluate how each alloy reacts to the conversion coating process. This data can guide the selection of appropriate coating parameters—such as immersion time, temperature, and chemical composition. Additionally, consider collaborating with coating suppliers who can offer tailored solutions or even develop custom formulations to ensure consistent quality across different materials. Investing in training for your team on the nuances of various alloys can also significantly improve the application process and final product quality.
Scenario 2: Environmental Compliance and Toxicity Concerns
The Problem: Many B2B buyers face increasing pressure to comply with stringent environmental regulations, particularly regarding the use of hazardous materials like hexavalent chromium in traditional conversion coatings. This concern is particularly pronounced in regions with stringent regulations, such as Europe and North America. Buyers may find themselves torn between the need for effective corrosion protection and the obligation to adhere to environmental standards, risking non-compliance and potential legal repercussions.
The Solution: To mitigate these concerns, buyers should prioritize sourcing non-hexavalent chromium conversion coatings, which meet environmental regulations while still providing robust performance. Specifically, look for trivalent chromium-based options that offer similar corrosion resistance and paint adhesion without the associated toxicity. When evaluating suppliers, request documentation demonstrating compliance with standards such as RoHS, REACH, and other relevant regulations. Additionally, consider conducting an environmental impact assessment of your coating processes to identify areas for improvement and ensure ongoing compliance. Establishing a relationship with suppliers who prioritize sustainability can also lead to innovative solutions that align with both performance and environmental goals.
Scenario 3: Difficulty in Achieving Optimal Adhesion for Paint and Adhesives
The Problem: Achieving optimal adhesion for paint and adhesives is a common challenge for buyers in industries that rely on aluminum components, such as automotive and aerospace. Inadequate adhesion can lead to peeling, blistering, or failure of coatings, resulting in costly rework and diminished product reliability. Buyers often find themselves frustrated when the expected performance of their coatings does not align with real-world results, affecting customer satisfaction and brand reputation.
The Solution: To improve adhesion, buyers should implement a multi-faceted approach that starts with proper surface preparation. This includes cleaning the aluminum surface to remove any contaminants, such as oils or oxides, that could interfere with adhesion. Following surface preparation, applying a conversion coating specifically designed to enhance adhesion properties is crucial. It is beneficial to work with suppliers who can provide detailed specifications on how their coatings perform in adhesion tests. Additionally, consider conducting adhesion tests on samples before full-scale application to identify any potential issues early in the process. Using primers that are compatible with the selected conversion coating can further enhance adhesion and ensure a reliable bond. Regular training and updates on best practices for applying coatings will keep your team informed and help maintain high standards of quality and performance.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for aluminum conversion coating
What Are the Common Materials Used in Aluminum Conversion Coating?
When selecting materials for aluminum conversion coating, it is crucial to understand the properties, advantages, and limitations of various options available in the market. Below are analyses of four common materials used in aluminum conversion coatings, tailored for international B2B buyers.
1. Hexavalent Chromium Coatings (Type I)
Key Properties: Hexavalent chromium coatings are known for their excellent corrosion resistance and strong adhesion properties. They typically provide a soft, ductile surface that enhances paint adhesion without adding measurable thickness to the coated part.
Pros & Cons: While these coatings offer superior corrosion protection and are widely recognized in various industries, they are increasingly scrutinized due to environmental concerns associated with hexavalent chromium’s toxicity. This can lead to higher compliance costs and regulatory hurdles. Additionally, their application can be more complex, requiring specialized handling and disposal processes.
Impact on Application: Hexavalent chromium coatings are particularly effective in environments where parts are exposed to harsh conditions, such as automotive and aerospace applications. However, buyers must consider the regulatory landscape, especially in regions with stringent environmental laws.
Specific Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers from regions like Europe and the Middle East must ensure compliance with regulations such as REACH and RoHS, which restrict the use of hazardous substances. This may necessitate additional certifications or alternative materials.
2. Trivalent Chromium Coatings (Type II)
Key Properties: Trivalent chromium coatings offer similar performance characteristics to hexavalent coatings, including good corrosion resistance and excellent adhesion. They are more environmentally friendly and comply with various international regulations.
Pros & Cons: The primary advantage of trivalent coatings is their reduced environmental impact, making them a safer choice for manufacturers. However, they may not provide the same level of corrosion resistance as hexavalent coatings in extreme conditions, potentially limiting their use in certain applications.
Impact on Application: These coatings are suitable for a wide range of applications, including automotive and electronics, where both corrosion resistance and environmental compliance are critical. They can also be used as a primer for paint, enhancing overall durability.
Specific Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers in Africa and South America may find trivalent coatings advantageous due to their compliance with international standards, which can facilitate easier market entry and acceptance.
3. Non-Chromate Conversion Coatings
Key Properties: Non-chromate conversion coatings are designed to replace traditional chromate processes while providing good corrosion resistance and adhesion properties. They often utilize organic compounds to achieve similar performance metrics.
Pros & Cons: These coatings are environmentally friendly and can be easier to handle and dispose of compared to chromate options. However, they may not offer the same level of corrosion protection in highly demanding environments, which could limit their suitability for specific applications.
Impact on Application: Non-chromate coatings are increasingly used in industries that prioritize sustainability, such as consumer electronics and automotive sectors. They serve as effective primers for paint and adhesives.
Specific Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should verify that non-chromate coatings meet local and international standards, such as ASTM B921, to ensure compatibility with their specific applications.
4. Alodine/Chem Film Coatings
Key Properties: Alodine or chem film coatings are a type of chromate conversion coating that provides excellent corrosion resistance while maintaining electrical conductivity. They are often applied in a thin layer that does not significantly alter the dimensions of the part.
Pros & Cons: The key advantage of Alodine coatings is their versatility in applications requiring both corrosion resistance and electrical continuity. However, they may require precise application processes to ensure optimal performance, which can increase manufacturing complexity.
Impact on Application: These coatings are ideal for aerospace and defense applications where both performance and compliance with military specifications are critical. They also serve as effective primers for further coating processes.
Specific Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers from regions with stringent aerospace standards, such as Europe and the Middle East, should ensure that Alodine coatings comply with relevant military specifications (e.g., MIL-DTL-5541).
Summary Table of Material Selection for Aluminum Conversion Coating
| Material | Typical Use Case for aluminum conversion coating | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hexavalent Chromium Coatings | Aerospace, automotive components | Excellent corrosion resistance | Toxicity and environmental compliance issues | High |
| Trivalent Chromium Coatings | Automotive, electronics | Environmentally friendly | May offer lower corrosion resistance | Medium |
| Non-Chromate Conversion Coatings | Consumer electronics, automotive | Sustainable alternative | Limited corrosion protection in harsh environments | Medium |
| Alodine/Chem Film Coatings | Aerospace, defense applications | Combines corrosion resistance with conductivity | Requires precise application | High |
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for aluminum conversion coating
What Are the Key Stages in the Manufacturing Process of Aluminum Conversion Coating?
The manufacturing process of aluminum conversion coating involves several critical stages that ensure the final product meets performance and quality standards. These stages include material preparation, forming, assembly, and finishing.
How is Material Prepared for Aluminum Conversion Coating?
Material preparation is the foundational step in the manufacturing process. It typically involves cleaning the aluminum surface to remove any contaminants such as oils, grease, and oxidation. This is often achieved through chemical cleaning agents or abrasive methods, ensuring that the surface is free from particles that could interfere with the coating process.
Once the surface is cleaned, it may undergo etching to enhance adhesion. Etching modifies the surface roughness, increasing the area for the coating to bond effectively. After etching, rinsing is crucial to remove any residual chemicals, followed by drying to prevent moisture interference during the coating application.
What Techniques Are Used in the Forming and Assembly of Aluminum Components?
Forming and assembly are significant stages where aluminum components are shaped and joined. Common techniques include extrusion, stamping, and machining, which create parts with precise dimensions and tolerances. In industries such as aerospace and automotive, where precision is paramount, these processes must adhere to strict specifications to ensure compatibility with subsequent coating applications.
During assembly, components may be joined using various methods, including welding, riveting, or adhesive bonding. Each method has implications for the integrity of the final product, particularly in terms of how well the conversion coating can adhere to the joined surfaces.
What Finishing Processes Are Involved in Aluminum Conversion Coating?
Finishing is the final stage of the manufacturing process and involves the application of the conversion coating itself. There are various methods for applying aluminum conversion coatings, including dipping, spraying, and brushing. The choice of method can depend on the part’s size, complexity, and the desired characteristics of the final coating.
The coating application process typically involves immersing the prepared aluminum parts into a solution containing chromate or non-chromate compounds. The chemical reaction forms a thin, protective layer on the surface that enhances corrosion resistance and improves paint adhesion. Quality control during this stage is essential, as variables such as immersion time, temperature, and chemical concentration can significantly affect the coating’s properties.
How Is Quality Assurance Implemented in Aluminum Conversion Coating Manufacturing?
Quality assurance (QA) is integral to the manufacturing process, ensuring that products meet international standards and customer requirements. Various international and industry-specific standards guide the QA process, with ISO 9001 being a cornerstone for quality management systems globally. In addition, standards like MIL-DTL-5541 for military applications and ASTM B921 for industrial uses provide specific guidelines for aluminum conversion coatings.
What Are the Key QC Checkpoints in the Manufacturing Process?
Quality control (QC) checkpoints are strategically placed throughout the manufacturing process to ensure compliance with established standards. Common QC checkpoints include:
- Incoming Quality Control (IQC): This involves inspecting raw materials and components upon receipt to ensure they meet specifications before being processed.
- In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): Continuous monitoring during the manufacturing stages, including material preparation, coating application, and curing, helps identify any deviations from standards in real time.
- Final Quality Control (FQC): The finished products undergo thorough testing and inspection to confirm that they meet all performance criteria before shipment.
What Testing Methods Are Commonly Used in Quality Assurance?
Various testing methods are employed to validate the quality and performance of aluminum conversion coatings. Common tests include:
- Adhesion Tests: These evaluate how well the coating adheres to the aluminum surface and are crucial for applications that require paint or adhesive bonding.
- Corrosion Resistance Tests: These tests, such as salt spray testing per ASTM B117, assess the coating’s ability to protect against corrosion in aggressive environments.
- Thickness Measurement: Utilizing tools like micrometers or eddy current gauges ensures that the coating thickness meets specified standards without compromising dimensional integrity.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control Practices?
B2B buyers should take proactive steps to verify the quality control practices of their suppliers. This can include:
- Audits: Conducting on-site audits to evaluate manufacturing processes, quality systems, and compliance with international standards.
- Reviewing Quality Reports: Requesting detailed quality control reports that outline testing results, non-conformities, and corrective actions taken by the supplier.
- Third-Party Inspections: Engaging independent inspection agencies to assess the supplier’s processes and products, ensuring unbiased verification of quality standards.
What Are the Quality Control Nuances for International B2B Buyers?
International buyers, particularly from diverse regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, may encounter unique challenges in verifying quality control. Different regions may have varying regulatory requirements and standards, impacting the quality assurance processes.
It is crucial for buyers to understand the local regulations and industry-specific standards that apply to their markets. Additionally, language barriers and cultural differences can complicate communication about quality expectations. Establishing clear channels of communication and setting explicit quality requirements in contracts can mitigate these challenges.
Conclusion: Why Is Understanding the Manufacturing Process and Quality Assurance Essential for B2B Buyers?
For international B2B buyers, a comprehensive understanding of the manufacturing processes and quality assurance measures associated with aluminum conversion coatings is vital. This knowledge allows buyers to make informed decisions, ensuring that the products they source meet their specific performance needs while adhering to the highest quality standards. By conducting thorough due diligence and maintaining open communication with suppliers, buyers can mitigate risks and foster long-term, successful partnerships in their supply chains.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘aluminum conversion coating’
Introduction
This sourcing guide provides a structured checklist for B2B buyers seeking aluminum conversion coating solutions. As aluminum parts are critical in various industries, including aerospace, automotive, and electronics, understanding the procurement process is essential for ensuring quality, compliance, and performance. This checklist will help you navigate the complexities of sourcing aluminum conversion coatings effectively.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Establishing clear technical specifications is the first step in your procurement process. Consider the type of aluminum alloys you will be treating and the specific performance requirements, such as corrosion resistance and paint adhesion.
– Key considerations: Identify whether you need hexavalent or trivalent coatings based on environmental regulations relevant to your region.
Step 2: Identify Industry Standards and Compliance Requirements
Ensure that the coatings meet relevant industry standards such as MIL-DTL-5541 or ASTM B921. Compliance with these standards guarantees that the coatings will perform as expected under specific conditions.
– Important factors: Verify if the supplier’s coatings are compliant with local environmental regulations like RoHS and REACH, especially if you are sourcing from regions with stringent laws.
Step 3: Evaluate Potential Suppliers
Before making a commitment, thoroughly vet potential suppliers. Request detailed company profiles, case studies, and references from other buyers in similar industries or geographic areas.
– What to look for: Assess their production capabilities, quality control processes, and previous project experiences to ensure they can meet your specific needs.
Step 4: Request Samples for Testing
Once you have a shortlist of suppliers, request samples of their aluminum conversion coatings. Testing these samples will provide valuable insights into their performance, including adhesion, corrosion resistance, and overall durability.
– Testing criteria: Conduct neutral salt spray tests (ASTM B117) and adhesion tests to evaluate how well the coatings perform under real-world conditions.
Step 5: Inquire About Production Capacity and Lead Times
Understanding a supplier’s production capacity and lead times is crucial for your planning and inventory management. Ensure they can meet your demands without compromising quality.
– Questions to ask: What are the typical lead times for orders? Can they accommodate rush orders if necessary?
Step 6: Verify Supplier Certifications
Ensure that the suppliers you are considering hold necessary certifications relevant to aluminum conversion coating processes. This may include ISO certifications or specific industry-related certifications.
– Why it matters: Certifications indicate a supplier’s commitment to quality and reliability, reducing the risk of issues down the line.
Step 7: Review Pricing and Payment Terms
Finally, compare pricing structures and payment terms from different suppliers. While cost is an important factor, consider the total value, including quality, service, and compliance.
– Considerations: Look for flexible payment options and potential discounts for bulk orders, but remember that the lowest price may not always equate to the best quality.
By following this checklist, you can ensure a comprehensive and informed approach to sourcing aluminum conversion coatings that meet your business needs and industry standards.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for aluminum conversion coating Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components in Aluminum Conversion Coating?
When sourcing aluminum conversion coating, understanding the cost structure is essential for buyers. The primary cost components include materials, labor, manufacturing overhead, tooling, quality control (QC), logistics, and supplier margin.
-
Materials: The choice of conversion coating—whether chromate or non-chromate—affects the material costs significantly. Hexavalent chromium coatings tend to be more expensive due to regulatory compliance and environmental considerations. Non-chromate alternatives, while potentially more cost-effective, must still meet performance specifications.
-
Labor: Labor costs involve skilled technicians for the coating process, which can vary based on the complexity of the application and the location of the manufacturing facility. For instance, regions with higher labor costs may reflect this in the pricing.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes utilities, facility maintenance, and equipment depreciation. The overhead can vary widely based on the size and efficiency of the manufacturing operation.
-
Tooling: Custom tooling for specific applications can add significant upfront costs. Buyers should inquire about tooling costs if they require specialized coatings for unique aluminum alloys.
-
Quality Control (QC): Ensuring compliance with industry standards like MIL-DTL-5541 incurs additional costs. Rigorous QC processes are necessary to maintain product quality and prevent costly rework.
-
Logistics: Shipping costs can fluctuate based on the distance, shipping method, and Incoterms. For international buyers, understanding these costs is crucial for accurate budgeting.
-
Margin: Supplier margins vary, influenced by market demand, competition, and the supplier’s operational costs.
How Do Price Influencers Impact the Cost of Aluminum Conversion Coating?
Several factors can influence the pricing of aluminum conversion coatings, particularly for international buyers.
-
Volume and Minimum Order Quantity (MOQ): Higher volume orders often lead to lower per-unit costs. Suppliers are generally more willing to negotiate pricing for larger quantities.
-
Specifications and Customization: Customized coatings that meet specific performance requirements can lead to increased costs. Buyers should clearly communicate their needs to avoid unexpected charges.
-
Materials: The choice of raw materials significantly impacts costs. High-performance coatings, while more expensive, may offer better long-term value through enhanced durability.
-
Quality and Certifications: Coatings that comply with international standards or specific industry certifications often come at a premium. Buyers should weigh the costs against the benefits of enhanced performance and compliance.
-
Supplier Factors: Supplier reputation, reliability, and historical performance can influence pricing. Established suppliers may charge more due to their track record of quality and service.
-
Incoterms: Understanding the agreed-upon Incoterms is critical for international transactions. Terms like FOB (Free on Board) and CIF (Cost, Insurance, and Freight) can significantly affect overall costs.
What Are the Best Negotiation and Cost-Efficiency Tips for Buyers?
To maximize value when sourcing aluminum conversion coatings, buyers should consider the following strategies:
-
Negotiate Volume Discounts: Leverage larger orders to negotiate better pricing. Suppliers are often willing to provide discounts for bulk purchases.
-
Evaluate Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Consider not just the initial purchase price but the long-term costs associated with the coating’s performance, durability, and potential reapplication or maintenance.
-
Seek Multiple Quotes: Engage with multiple suppliers to compare pricing and services. This practice can help identify the best value and foster competitive pricing.
-
Understand Pricing Nuances for International Markets: Buyers in regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe should be aware of regional economic conditions, currency fluctuations, and trade tariffs that could affect pricing.
-
Request Detailed Quotes: Ensure quotes include a breakdown of all costs. This transparency can help identify areas for negotiation and clarify the total expenditure.
Conclusion
While this analysis provides a framework for understanding the cost and pricing dynamics of aluminum conversion coatings, it is essential to remember that actual prices may vary. Factors such as supplier capabilities, market conditions, and specific project requirements can significantly influence final costs. Buyers are encouraged to conduct thorough research and engage in discussions with suppliers to ensure they secure the best possible pricing and value for their needs.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing aluminum conversion coating With Other Solutions
Introduction: Exploring Alternatives to Aluminum Conversion Coating
When it comes to enhancing the performance of aluminum components, various solutions exist beyond aluminum conversion coatings. Each option offers unique benefits and limitations, making it essential for international B2B buyers to evaluate them based on specific operational needs. This analysis compares aluminum conversion coating with two viable alternatives: anodizing and powder coating, helping businesses make informed decisions.
Comparison Table
| Comparison Aspect | Aluminum Conversion Coating | Anodizing | Powder Coating |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | Excellent corrosion resistance and adhesion properties; maintains electrical conductivity. | Provides a thicker protective layer; enhances corrosion resistance and surface hardness. | Highly durable finish with excellent weather resistance; can be applied in various colors. |
| Cost | Generally lower initial costs; additional cost for surface preparation and application. | Higher upfront costs due to the anodizing process; cost-effective for large batches. | Moderate to high costs, depending on the complexity of application and materials used. |
| Ease of Implementation | Relatively straightforward application process; minimal dimensional changes. | Requires specialized equipment and facilities; more complex process. | Requires specialized equipment for electrostatic application; longer curing times. |
| Maintenance | Low maintenance due to durable finish; requires periodic inspection. | Generally low maintenance; surface may require cleaning to maintain appearance. | Low maintenance; chips or scratches may require repair or touch-up. |
| Best Use Case | Aerospace, automotive, electronics requiring corrosion resistance and paint adhesion. | Aerospace, automotive, and architectural applications where aesthetics and durability are priorities. | Industrial applications, outdoor furniture, and consumer goods where color and finish are critical. |
Detailed Breakdown of Alternatives
Anodizing:
Anodizing is an electrochemical process that thickens the natural oxide layer on aluminum, enhancing its durability and corrosion resistance. One of the main advantages of anodizing is the increased hardness it provides, making it ideal for applications requiring a robust surface. However, the process can be costlier and more complex than aluminum conversion coating, as it necessitates specialized equipment and facilities. Additionally, while anodized surfaces can be colored, they may not offer the same level of adhesion for paints and adhesives compared to conversion coatings.
Powder Coating:
Powder coating involves applying a dry powder to aluminum parts, which is then cured under heat to form a hard, protective layer. This method is celebrated for its aesthetic versatility, as it can produce a wide range of colors and textures. Powder coating offers excellent weather resistance and durability, making it suitable for outdoor applications. However, it typically requires more extensive equipment and longer curing times, which can affect the production schedule. Additionally, while powder coating provides a robust finish, it may not be as effective in enhancing adhesion for subsequent coatings as aluminum conversion coatings.
Conclusion: How to Choose the Right Solution for Your Needs
Selecting the appropriate surface treatment for aluminum components hinges on various factors, including performance requirements, budget constraints, and application specifics. Aluminum conversion coatings excel in providing corrosion resistance and adhesion for further coatings, making them ideal for industries such as aerospace and automotive. Conversely, anodizing and powder coating offer unique advantages in terms of durability and aesthetic appeal. By carefully assessing the trade-offs and aligning them with operational goals, B2B buyers can make informed decisions that enhance the longevity and performance of their aluminum products.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for aluminum conversion coating
What Are the Key Technical Properties of Aluminum Conversion Coating?
Understanding the technical specifications of aluminum conversion coatings is essential for B2B buyers, especially when selecting coatings for applications in diverse industries, such as aerospace, automotive, and electronics. Here are some critical specifications:
1. Material Grade
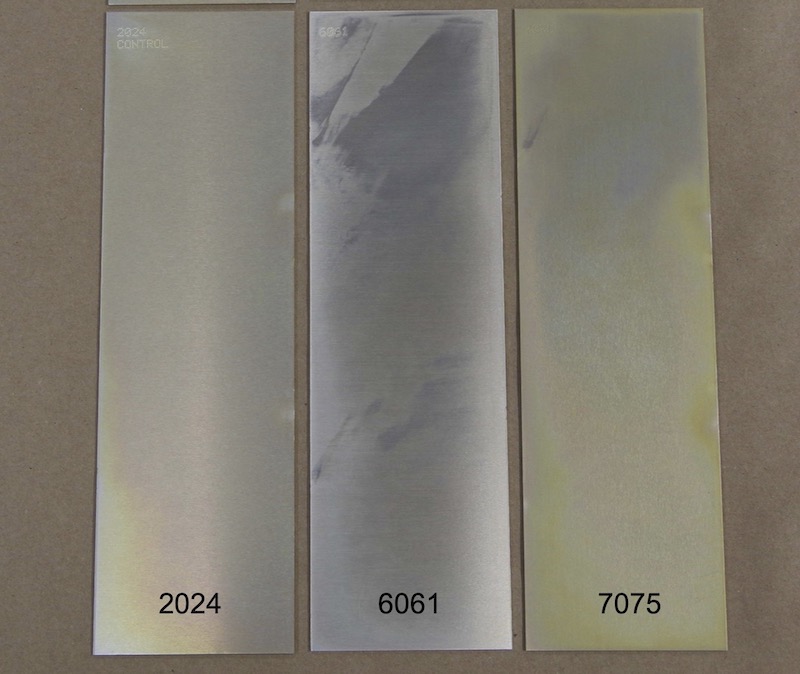
Material grade indicates the specific type of aluminum alloy being coated, which directly affects corrosion resistance and adhesion properties. Common grades used include 6061 and 7075. The right grade ensures compatibility with the intended application, particularly in environments that may expose the material to harsh conditions.
2. Coating Thickness
Coating thickness is a crucial specification as it determines the protective capabilities of the conversion coating. Typically, aluminum conversion coatings have a thickness of 0.1 to 0.5 microns. A thinner coating may offer less corrosion protection, while a thicker coating can affect dimensional tolerances. Understanding the required thickness helps ensure the coating meets performance and regulatory requirements.
3. Corrosion Resistance
Corrosion resistance is often quantified through standardized tests, such as ASTM B117, which evaluates the material’s performance in a salt spray environment. A high corrosion resistance rating is essential for applications in marine or industrial settings where exposure to moisture and salt is common. Buyers should prioritize coatings that demonstrate superior corrosion resistance to enhance product longevity.
4. Adhesion Strength
Adhesion strength measures the coating’s ability to bond with both the aluminum substrate and any subsequent layers, such as paint or adhesive. Specifications for adhesion strength can be found in standards like MIL-DTL-5541. Strong adhesion is critical in applications requiring painting or bonding, as it directly influences the durability and performance of the finished product.
5. Environmental Compliance
With increasing regulations on hazardous materials, compliance with standards such as RoHS (Restriction of Hazardous Substances) and REACH (Registration, Evaluation, Authorisation and Restriction of Chemicals) is vital. Non-chrome conversion coatings are often favored for their environmental safety, making them suitable for modern applications that prioritize sustainability.
What Are the Common Trade Terms Related to Aluminum Conversion Coating?
Navigating the B2B landscape involves understanding specific jargon and terminology that can influence purchasing decisions. Here are some commonly used terms:
1. OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
OEM refers to companies that produce parts or equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer. In the context of aluminum conversion coatings, understanding OEM specifications is crucial for ensuring that the coatings meet the standards required by the end product manufacturer.
2. MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ is the smallest amount of a product that a supplier is willing to sell. Knowing the MOQ is essential for buyers to manage inventory and cash flow effectively. It can also affect procurement strategies when sourcing aluminum conversion coatings, especially for large-scale projects.
3. RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a document issued by a buyer to solicit price quotes from suppliers. It typically includes detailed specifications for the products required, such as coating type and quantity. Issuing an RFQ helps buyers compare prices and services, ensuring they receive competitive offers.
4. Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
Incoterms are a set of international rules that define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in shipping and delivery. Understanding these terms is crucial for B2B transactions involving aluminum conversion coatings, as they outline aspects such as shipping costs, risk transfer, and delivery obligations.
5. Certification Standards
Certification standards refer to industry regulations that ensure products meet specific safety and quality benchmarks. Common certifications for aluminum coatings include MIL-DTL-5541 and ASTM B921. Compliance with these standards is essential for buyers to ensure product reliability and performance in critical applications.
By familiarizing yourself with these technical properties and trade terms, you can make informed decisions that enhance the quality and performance of aluminum components in your projects.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the aluminum conversion coating Sector
What Are the Current Market Dynamics and Key Trends in the Aluminum Conversion Coating Sector?
The aluminum conversion coating market is experiencing significant growth driven by increased demand across various industries, particularly aerospace, automotive, and electronics. The global push for lightweight materials to enhance fuel efficiency and reduce emissions is propelling the adoption of aluminum components. As manufacturers look for effective corrosion protection and improved adhesion for paints and adhesives, conversion coatings have become essential. B2B buyers, especially in regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, are prioritizing suppliers that can offer advanced coating technologies, such as non-chrome options, which comply with stringent environmental regulations like RoHS and REACH.
Emerging trends include the integration of digital technologies in the sourcing process. Buyers are increasingly leveraging data analytics and AI to optimize their supply chains, enhancing transparency and efficiency. Additionally, the rise of e-commerce platforms is facilitating easier access to suppliers and manufacturers, streamlining procurement processes. The trend towards customization is also notable; businesses are seeking tailored solutions that meet specific industry standards and performance requirements. As the market evolves, international buyers are advised to stay informed about technological advancements and regulatory changes that may impact sourcing decisions.
How Is Sustainability Influencing Sourcing Trends in the Aluminum Conversion Coating Industry?
Sustainability has become a cornerstone of modern sourcing strategies in the aluminum conversion coating sector. With growing awareness of environmental impacts, B2B buyers are increasingly prioritizing suppliers who adhere to sustainable practices. The aluminum conversion coating process traditionally involved hazardous materials like hexavalent chromium, which have significant environmental implications. As a result, there is a noticeable shift toward non-chrome conversion coatings that offer similar performance without the associated risks.
Ethical sourcing is another critical consideration. Buyers are looking for suppliers who can demonstrate responsible sourcing of raw materials and adherence to social responsibility standards. Certifications such as ISO 14001 for environmental management and other green certifications provide buyers with assurance that their suppliers are committed to sustainable practices. Moreover, utilizing environmentally friendly coatings not only meets regulatory requirements but also enhances a company’s brand reputation in an increasingly eco-conscious market.
What Is the Historical Context Behind the Evolution of Aluminum Conversion Coating?
The practice of aluminum conversion coating dates back several decades, initially developed to enhance the corrosion resistance of aluminum and its alloys. The introduction of chromate conversion coatings revolutionized the industry, providing a reliable method for protecting aluminum components used in demanding applications, particularly in aerospace and automotive sectors. Over time, regulatory concerns regarding the toxicity of hexavalent chromium led to the development of non-chrome alternatives, which have gained traction in recent years due to their environmental benefits and compliance with modern legislation.
This evolution reflects a broader trend in the manufacturing sector toward safer and more sustainable practices, driving innovation in coating technologies. As the industry continues to adapt, B2B buyers must stay abreast of these historical shifts to make informed sourcing decisions that align with current market demands and future trends.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of aluminum conversion coating
-
How do I ensure the quality of aluminum conversion coatings from suppliers?
To ensure quality, it is crucial to vet suppliers thoroughly. Request certifications like ASTM B921 or MIL-DTL-5541, which demonstrate adherence to industry standards. Evaluate their manufacturing processes and quality control measures, such as regular testing and audits. It’s also beneficial to seek references from other clients and review their track record in fulfilling orders. Consider visiting their facilities if possible or request samples to assess the coating’s performance and consistency before placing larger orders. -
What are the key specifications I should look for in aluminum conversion coatings?
Key specifications include the type of coating (e.g., Type I Hexchrome or Type II Trivalent), thickness, adhesion strength, and corrosion resistance. It’s important to confirm compliance with international standards like RoHS, REACH, and WEEE for environmental regulations. Assess the coating’s suitability for your specific application, such as automotive, aerospace, or industrial, and ensure it meets relevant military or aerospace specifications if applicable. -
What is the best aluminum conversion coating for automotive applications?
For automotive applications, Type II Trivalent coatings are often preferred due to their excellent corrosion resistance and environmental compliance. They provide a strong foundation for paint adhesion and are less harmful than hexavalent chromium coatings. Additionally, these coatings enhance bonding strength in adhesive applications, making them ideal for critical automotive components. Always verify that the coating meets the specific requirements of your automotive standards and regulations. -
What are the minimum order quantities (MOQ) typically required by suppliers?
Minimum order quantities can vary significantly between suppliers and depend on factors such as coating type and application. Typically, MOQs may range from a few hundred to several thousand square feet of coated material. It is advisable to discuss your requirements upfront with suppliers to understand their MOQ and negotiate terms that suit your purchasing needs, especially if you are testing a new supplier or product. -
How can I customize aluminum conversion coatings for my specific needs?
Customization options may include adjusting coating thickness, specific chemical formulations, or adding properties like enhanced corrosion resistance or electrical conductivity. Engage with your supplier early in the process to discuss your requirements, and they can guide you through available options. Ensure that any customizations still comply with relevant industry standards and specifications to maintain product integrity. -
What payment terms should I expect when sourcing aluminum conversion coatings internationally?
Payment terms can vary based on the supplier and the nature of the transaction. Common terms include advance payment, letter of credit, or net 30/60 days after delivery. It’s important to clarify these terms during negotiations and consider the risks associated with international transactions, such as currency fluctuations and customs duties. Establishing a good relationship with your supplier can also facilitate more favorable payment arrangements. -
How do I manage logistics and shipping when importing aluminum conversion coatings?
Managing logistics involves selecting reliable freight forwarders familiar with international shipping regulations. Discuss shipping terms (Incoterms) with your supplier to clarify responsibilities for costs and risks during transit. Ensure all necessary documentation, including customs declarations and certificates of origin, is prepared. Plan for potential delays due to customs inspections, especially when importing to regions with strict regulations, such as the EU or Middle East. -
What are the common challenges in sourcing aluminum conversion coatings internationally?
Common challenges include navigating regulatory compliance, ensuring product quality, and managing lead times. Variations in standards across regions can complicate supplier selection, so thorough research is essential. Additionally, fluctuating shipping costs and potential delays due to customs can impact delivery schedules. To mitigate these challenges, build strong relationships with suppliers and logistics partners, and maintain open communication throughout the sourcing process.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.
Top 8 Aluminum Conversion Coating Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. Pioneer Metal – Aluminum Conversion Coatings
Domain: pioneermetal.com
Registered: 1997 (28 years)
Introduction: Aluminum Conversion Coatings are non-decorative coatings applied to aluminum parts to achieve a thin, electrically-conductive coating that provides corrosion resistance. They improve paint adhesion and bonding strength for aluminum parts. Types include Non-Chrome Conversion Coat (Type I and Type II).
Type I (Hexchrome):
– Color: Light yellow to dark yellow
– Performance: Good corrosion protect…
2. Best Technology Inc – Alodine Coating
Domain: besttechnologyinc.com
Registered: 2001 (24 years)
Introduction: Alodine, also known as chem film or chromate conversion coating, is a protective coating for aluminum and other metals that prevents corrosion. It is applied through a chemical reaction that transforms the metal surface into a protective layer, unlike plating which adds a new layer. Key benefits include enhanced corrosion protection, improved adhesion for organic coatings, and maintained electrica…
3. Protocase – Chemical Conversion Coating for Aluminum
Domain: protocase.com
Registered: 2001 (24 years)
Introduction: Chemical Conversion Coating for Aluminum, also known as chem film, chromate coating, or yellow chromate coating, is offered in-house by Protocase. This coating process applies chromate to aluminum substrates, providing corrosion resistance, durability, and stable electrical conductivity. It is suitable for protecting enclosures and metal parts, and serves as an effective pretreatment for powdercoa…
4. BONDERITE® – Chromate Conversion Coating
Domain: henkel-adhesives.com
Registered: 2000 (25 years)
Introduction: BONDERITE® – Chromate Conversion Coating for Aluminum. Improved corrosion protection properties for light metal surfaces. Used as a corrosion inhibitor, primer, decorative finish, or to retain electrical conductivity. Available in acid, liquid, and powder forms. Simplifies coating processes while ensuring high standards in corrosion protection and paint adhesion. Integral step in aluminum pre-trea…
5. AnoChem – TCP Conversion Coating
Domain: anoplate.com
Registered: 1996 (29 years)
Introduction: AnoChem TCP is a hex-chrome free, RoHS compliant chemical conversion coating for aluminum alloys. It replaces hexavalent chromate conversion coatings without sacrificing corrosion resistance, electrical contact resistance, or organic topcoat adhesion properties. It meets regulatory requirements of RoHS, WEEE, and ELV legislation. The coating exceeds the requirements of MIL-DTL-5541 and results in …
6. ENS Technology – MIL-DTL-5541F Chemical Conversion Coating
Domain: enstechnology.com
Registered: 2001 (24 years)
Introduction: MIL-DTL-5541F Chemical Conversion Coating for Aluminum and Aluminum Alloys. Approved for use by all departments and agencies of the U.S. Department of Defense (DoD). Used for corrosion resistance and as a primer for painting. Two types: Type 1 (contains hexavalent chromium, gold/brown color) and Type 2 (no hexavalent chromium, clear). Two classes: Class 1A (maximum corrosion protection, thicker co…
7. Valence Surface Tech – Chromate Conversion Coating
Domain: valencesurfacetech.com
Registered: 2014 (11 years)
Introduction: Chromate conversion coating is a chemical treatment applied primarily to zinc-plated or aluminum components to enhance corrosion resistance and improve adhesion for subsequent coatings. It forms a protective layer on the metal that provides excellent resistance to oxidation and corrosion, with finishes ranging from clear to various colors. Commonly used in industries such as automotive, aerospace,…
8. Finishing & Coating – Troubleshooting Guide
Domain: finishingandcoating.com
Registered: 2020 (5 years)
Introduction: This company, Finishing & Coating – Troubleshooting Guide, is a notable entity in the market. For specific product details, it is recommended to visit their website directly.
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for aluminum conversion coating
In conclusion, aluminum conversion coating presents a vital opportunity for businesses seeking enhanced corrosion resistance and improved adhesion for their aluminum products. By strategically sourcing quality coatings—whether chromate or non-chromate—companies can ensure compliance with international standards while also promoting sustainability in their operations. The choice between Type I and Type II coatings allows for tailored solutions that meet specific industry requirements, enhancing product longevity and performance across various applications, from aerospace to automotive.
For international B2B buyers in regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, recognizing the importance of these coatings in your supply chain can significantly impact product quality and operational efficiency. Engaging with reliable suppliers who prioritize innovation and compliance will not only safeguard your investments but also position your business advantageously in the competitive market landscape.
As the demand for high-performance coatings continues to grow, now is the time to evaluate your sourcing strategies. Consider partnerships with manufacturers that offer advanced conversion coating technologies and a commitment to environmental standards. Embrace this opportunity to lead in your industry and drive sustainable growth through informed sourcing decisions.