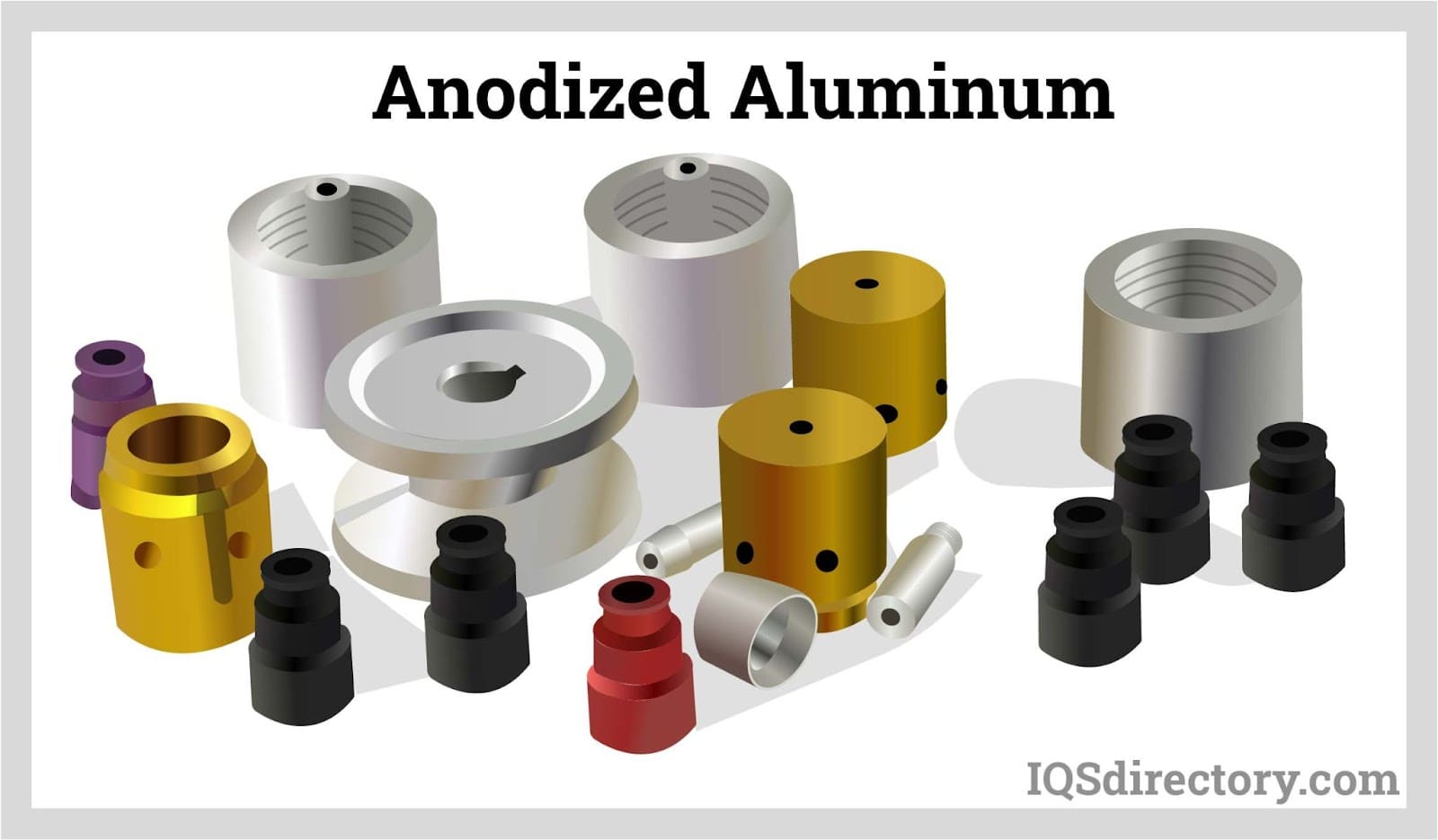
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for aluminum anodizing service
In an increasingly interconnected global marketplace, sourcing high-quality aluminum anodizing services can pose significant challenges for B2B buyers, especially those operating in diverse regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. These challenges include identifying reliable suppliers, understanding varying industry standards, and navigating the complexities of logistics and compliance. This comprehensive guide aims to demystify the aluminum anodizing service landscape, offering insights into the various types of anodizing processes, their applications across industries, and essential tips for vetting suppliers effectively.
Throughout this guide, we will explore the nuances of aluminum anodizing, including Type II and Type III anodizing, as well as specialized coatings and finishes that enhance durability and aesthetic appeal. We will also provide guidance on cost considerations, enabling buyers to make informed decisions that align with their budget and project requirements. By leveraging this resource, international B2B buyers will gain a deeper understanding of the aluminum anodizing market, empowering them to forge strategic partnerships with reputable suppliers, optimize their procurement processes, and ultimately enhance their product offerings. Whether you are based in Brazil, Nigeria, or anywhere in between, this guide is designed to equip you with the knowledge and tools necessary to navigate the complexities of sourcing aluminum anodizing services effectively.
Understanding aluminum anodizing service Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Type I Anodizing | Chromic acid process; offers good corrosion resistance; thicker oxide layer. | Aerospace, military, marine industries | Pros: Excellent corrosion resistance; durable. Cons: Limited color options; higher cost. |
| Type II Anodizing | Sulfuric acid process; available in various colors; enhances wear resistance. | Automotive, consumer electronics | Pros: Versatile color options; good wear resistance. Cons: Less durable than Type III. |
| Type III Anodizing | Hard anodizing process; significantly thicker oxide layer; very durable. | Industrial machinery, tooling, aerospace | Pros: Exceptional hardness; excellent wear and corrosion resistance. Cons: Higher processing costs; limited aesthetics. |
| Decorative Anodizing | Focuses on aesthetics; available in multiple colors; thinner oxide layer. | Consumer goods, architecture, signage | Pros: Wide range of colors; enhances appearance. Cons: Less protective; not suitable for harsh environments. |
| Chromate Conversion Coating | A chemical treatment that provides corrosion resistance without changing the base material’s properties. | Electronics, automotive, military | Pros: Lightweight; enhances adhesion for paints. Cons: Less durable than anodizing; requires careful handling. |
What are the Key Characteristics of Type I Anodizing?
Type I anodizing utilizes a chromic acid process to create a thick oxide layer that enhances corrosion resistance. This method is especially suitable for applications in aerospace, military, and marine industries, where durability is crucial. When considering Type I anodizing, B2B buyers should evaluate the trade-offs between its high protective qualities and the limited color options available, which may restrict design flexibility.
How Does Type II Anodizing Stand Out?
Type II anodizing employs a sulfuric acid process, resulting in a thinner oxide layer compared to Type I. It offers a variety of colors, making it popular in automotive and consumer electronics applications. Buyers should note that while Type II provides good wear resistance, it may not withstand harsh environments as effectively as Type III anodizing, making it essential to assess the specific requirements of their projects.
What Makes Type III Anodizing Ideal for Industrial Use?
Type III anodizing, often referred to as hard anodizing, significantly increases the thickness of the oxide layer, providing exceptional durability and wear resistance. This makes it a preferred choice for industrial machinery and aerospace applications. While the processing costs are higher, B2B buyers benefit from its long-term performance, especially in demanding environments where components face significant wear.
Why Choose Decorative Anodizing for Aesthetic Applications?
Decorative anodizing focuses primarily on enhancing the visual appeal of aluminum products, available in a broad spectrum of colors. This type is ideal for consumer goods, architecture, and signage. However, buyers should consider that while it enhances appearance, decorative anodizing offers less protection than other methods, making it unsuitable for applications in harsh conditions.
How Does Chromate Conversion Coating Compare to Anodizing?
Chromate conversion coating is a chemical treatment providing corrosion resistance while preserving the base material’s properties. Common in electronics and automotive applications, it is lightweight and improves paint adhesion. However, it is less durable than anodizing and requires careful handling. B2B buyers must weigh the benefits of enhanced adhesion against the need for more robust protection in their specific applications.
Key Industrial Applications of aluminum anodizing service
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of Aluminum Anodizing Service | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Aerospace | Lightweight aircraft components | Enhances corrosion resistance and durability | Compliance with aerospace standards and certifications |
| Automotive | Engine parts and exterior trims | Improves wear resistance and aesthetic appeal | Need for high-volume production and rapid turnaround |
| Electronics | Heat sinks and enclosures | Provides thermal management and electrical insulation | Customization options for specific electronic applications |
| Medical Devices | Surgical instruments and implants | Ensures biocompatibility and corrosion resistance | Strict adherence to regulatory standards and quality control |
| Construction & Architecture | Facades and structural components | Offers weather resistance and aesthetic variety | Availability of diverse color options and finishes |
How is Aluminum Anodizing Service Used in Aerospace?
In the aerospace sector, aluminum anodizing is critical for enhancing the performance of lightweight components. Anodizing provides a protective layer that significantly improves corrosion resistance, essential for parts exposed to harsh environmental conditions. Buyers in this industry must prioritize suppliers that adhere to stringent aerospace standards, ensuring that anodized components meet necessary certifications for safety and performance. International buyers should consider the supplier’s ability to handle complex geometries and provide rapid prototyping services to accommodate the fast-paced nature of aerospace projects.
What Role Does Aluminum Anodizing Play in Automotive Applications?
Automotive manufacturers leverage aluminum anodizing for various applications, including engine parts and exterior trims. The anodizing process enhances the durability of components, making them resistant to wear and corrosion, which is vital for vehicles operating in diverse climates. Additionally, anodized finishes can improve the aesthetic appeal of vehicles, offering a range of colors and finishes. B2B buyers in this sector should focus on suppliers capable of high-volume production and quick turnaround times to meet the demands of automotive assembly lines.
Why is Aluminum Anodizing Important for Electronics?
In the electronics industry, aluminum anodizing is often utilized for heat sinks and enclosures, where thermal management is critical. The anodized layer provides excellent electrical insulation while enhancing heat dissipation, which is vital for the longevity and performance of electronic devices. Buyers should seek suppliers that can customize anodizing processes to meet specific electronic applications, ensuring compatibility with different materials and designs. Additionally, understanding the supplier’s capabilities in terms of color finishes and surface treatments can help in achieving a product that meets both functional and aesthetic requirements.
How Does Aluminum Anodizing Benefit Medical Devices?
For medical devices, aluminum anodizing serves a dual purpose: it enhances the durability of surgical instruments and ensures biocompatibility. The anodized surface is resistant to corrosion, which is crucial in sterile environments. Buyers in the medical field must prioritize suppliers that maintain rigorous quality control measures and comply with regulatory standards, such as ISO certifications. This is particularly important for international buyers in regions with strict medical device regulations, as non-compliance can lead to significant market access issues.
What Advantages Does Aluminum Anodizing Offer in Construction and Architecture?
In construction and architecture, aluminum anodizing is used for facades and structural components, providing both aesthetic appeal and functional benefits. Anodized aluminum is weather-resistant, ensuring longevity and reduced maintenance costs for architectural applications. Buyers should consider sourcing from suppliers that offer a wide range of color options and finishes to meet design specifications. Additionally, understanding the supplier’s capabilities in terms of large-scale production and logistics is essential for meeting project timelines and budgets in the construction industry.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘aluminum anodizing service’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Navigating Quality Assurance Challenges in Anodizing
The Problem:
B2B buyers often grapple with quality assurance issues when sourcing aluminum anodizing services. Inconsistent finish quality can lead to significant setbacks, including project delays and increased costs. Buyers may receive anodized components that do not meet the required specifications, such as insufficient corrosion resistance or color inconsistencies. These challenges are particularly acute for industries like aerospace and automotive, where strict adherence to quality standards is non-negotiable. The pressure to ensure that suppliers deliver high-quality anodized products can create anxiety and frustration among procurement professionals.
The Solution:
To mitigate quality assurance challenges, buyers should establish a clear set of specifications before engaging with anodizing service providers. This includes defining the required anodizing type (e.g., Type II or Type III), thickness, color, and performance characteristics such as wear resistance and corrosion protection. Conducting thorough research on potential suppliers is crucial; look for certifications like ISO 9001 that indicate adherence to quality management standards. Request samples of previous work and conduct a site visit to assess the facility’s capabilities. Additionally, consider implementing a quality control plan that includes regular inspections and testing of finished products to ensure compliance with industry standards. By fostering transparent communication with suppliers and setting clear expectations, buyers can enhance the quality of the anodizing services they receive.
Scenario 2: Managing Turnaround Time for Anodizing Services
The Problem:
In fast-paced industries, time is of the essence, and delays in anodizing services can derail production schedules. B2B buyers frequently encounter issues with long lead times for anodized components, which can lead to missed deadlines and strained client relationships. This is especially critical for projects with tight timelines or those that require just-in-time delivery. Buyers may find themselves in a situation where they need to expedite orders, but suppliers are unable to accommodate such requests due to their production schedules.
The Solution:
To manage turnaround times effectively, B2B buyers should develop a proactive sourcing strategy. Begin by identifying anodizing companies that specialize in rapid turnaround times and have proven capabilities in handling urgent requests. Engage in open discussions with potential suppliers about their production capacity and lead times. Setting up a contractual agreement that includes penalties for delays can incentivize suppliers to prioritize your orders. Additionally, consider implementing a buffer stock strategy where you maintain a small inventory of anodized parts for critical projects. This way, you can reduce the dependency on quick turnaround times for every order. Building strong relationships with a select few anodizing partners can also lead to preferential treatment during peak periods, ensuring that your projects stay on schedule.
Scenario 3: Understanding Cost Implications of Anodizing Services
The Problem:
Cost management is a common concern for B2B buyers when it comes to aluminum anodizing services. Many companies struggle with hidden costs that can arise from unexpected price increases, especially in bulk orders. Factors such as the complexity of the anodizing process, special color requirements, or post-processing needs can significantly impact overall costs. Buyers may feel uncertain about how to budget effectively for anodizing services, leading to financial strain and project overruns.
The Solution:
To better understand and manage cost implications, B2B buyers should engage in thorough upfront planning and transparent communication with anodizing suppliers. Request detailed quotes that break down all costs associated with the anodizing process, including any potential additional fees for special finishes or expedited services. Establishing a clear understanding of pricing structures and minimum order quantities can help in budgeting more effectively. Additionally, consider exploring bulk purchasing agreements or long-term contracts that can lock in prices and provide cost savings. It is also beneficial to compare quotes from multiple suppliers to gauge the market rate and identify competitive pricing. By prioritizing cost transparency and engaging in strategic sourcing, buyers can mitigate the risk of unexpected expenses and ensure that their projects remain financially viable.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for aluminum anodizing service
What Are the Key Materials for Aluminum Anodizing Services?
When considering aluminum anodizing services, selecting the right aluminum alloy is crucial for achieving optimal performance and durability in the final product. Below are analyses of four common aluminum alloys used in anodizing processes, focusing on their properties, advantages, disadvantages, and specific considerations for international B2B buyers.
Which Aluminum Alloys Are Commonly Used in Anodizing?
1. 6061 Aluminum Alloy
Key Properties:
6061 aluminum is known for its excellent mechanical properties, including good corrosion resistance, medium to high strength, and good weldability. It has a temperature rating of up to 150°C (302°F) and is suitable for various applications.
Pros & Cons:
The alloy’s strength and weldability make it ideal for structural applications. However, its cost is moderate compared to other alloys, which may be a consideration for budget-sensitive projects. Additionally, while 6061 anodizes well, it may not achieve the same surface hardness as harder alloys.
Impact on Application:
6061 is compatible with various media, including water and chemicals, making it suitable for automotive and marine applications.
International Considerations:
Buyers in regions like Africa and South America should ensure compliance with ASTM standards, particularly ASTM B580 for anodizing processes. The alloy’s popularity means it is widely available, but regional supply chain issues may affect pricing.
2. 7075 Aluminum Alloy
Key Properties:
7075 aluminum is known for its high strength-to-weight ratio and excellent fatigue resistance. It can withstand temperatures up to 120°C (248°F) and is commonly used in aerospace applications.
Pros & Cons:
The primary advantage of 7075 is its superior strength, making it ideal for high-stress applications. However, it is more expensive than 6061 and has lower corrosion resistance, which may necessitate additional protective coatings.
Impact on Application:
Due to its high strength, 7075 is often used in aerospace and military applications where performance is critical. Its compatibility with harsh environments is limited unless additional treatments are applied.
International Considerations:
B2B buyers should be aware of specific aerospace standards (e.g., MIL-A-8625) when sourcing 7075. Compliance with international regulations is essential, especially for military contracts.
3. 5052 Aluminum Alloy
Key Properties:
5052 aluminum is known for its excellent corrosion resistance and good weldability. It maintains its strength up to 65°C (149°F), making it suitable for marine and automotive applications.
Pros & Cons:
The alloy’s high corrosion resistance is a significant advantage for marine environments. However, it is less strong than 6061 and 7075, which may limit its use in structural applications.
Impact on Application:
5052 is ideal for products exposed to saltwater and corrosive environments. Its compatibility with various coatings enhances its durability.
International Considerations:
Buyers should consider compliance with ASTM B241 for anodizing and ensure that suppliers can meet local environmental regulations, particularly in the Middle East, where corrosion resistance is critical.
4. 2024 Aluminum Alloy
Key Properties:
2024 aluminum is characterized by its high strength and fatigue resistance, making it suitable for aerospace applications. It has a temperature rating of up to 120°C (248°F) and is less corrosion-resistant than other alloys.
Pros & Cons:
Its high strength is a significant advantage, particularly in aerospace applications. However, its lower corrosion resistance means it often requires additional protective measures, which can increase costs.
Impact on Application:
2024 is commonly used in aircraft structures where weight and strength are critical. Its compatibility with anodizing can enhance surface properties, but additional coatings may be necessary.
International Considerations:
B2B buyers must ensure compliance with aerospace standards and consider the availability of 2024 in their region, as it may not be as widely stocked as other alloys.
Summary Table of Aluminum Alloys for Anodizing
| Material | Typical Use Case for aluminum anodizing service | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 6061 Aluminum | Automotive, marine components | Good corrosion resistance | Moderate strength compared to others | Medium |
| 7075 Aluminum | Aerospace, military applications | High strength | Lower corrosion resistance | High |
| 5052 Aluminum | Marine, automotive applications | Excellent corrosion resistance | Lower strength | Medium |
| 2024 Aluminum | Aircraft structures | High strength | Requires additional coatings | High |
This guide serves as a valuable resource for B2B buyers looking to make informed decisions about aluminum anodizing services, ensuring that they select the right materials for their specific applications.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for aluminum anodizing service
What Are the Main Stages in the Aluminum Anodizing Manufacturing Process?
The aluminum anodizing process involves several crucial stages that transform raw aluminum into a durable, corrosion-resistant, and aesthetically appealing product. Understanding these stages is vital for B2B buyers aiming to select the right suppliers.
1. Material Preparation
The initial phase involves cleaning the aluminum substrates to remove oils, dirt, and oxidation. This is typically achieved through chemical cleaning methods such as alkaline degreasing or acid etching. The objective is to ensure a clean surface that promotes optimal adhesion of the anodized layer.
2. Forming
In many cases, the aluminum needs to be shaped or formed before anodizing. This can involve processes such as extrusion, machining, or bending, depending on the specific requirements of the final product. Forming must be executed with precision to ensure that the components fit correctly and maintain structural integrity.
3. Anodizing
The anodizing process itself generally involves immersing the prepared aluminum parts in an electrolytic bath, where an electrical current is applied. This causes the aluminum to oxidize, forming a controlled layer of aluminum oxide on the surface. There are different anodizing techniques, including:
- Type II Anodizing: Commonly used for decorative finishes and corrosion resistance, it provides a thinner layer.
- Type III Anodizing (Hard Anodizing): This method yields a thicker, harder surface suitable for demanding applications like aerospace and military.
4. Dyeing (Optional)
Following anodizing, parts can be dyed to achieve various colors. This step enhances aesthetic appeal without compromising the protective qualities of the anodized layer. Dyes are absorbed into the porous anodized layer, creating a vibrant finish.
5. Sealing
The final stage involves sealing the anodized layer to close the pores and enhance corrosion resistance. Sealing methods can include hot water sealing, cold sealing, or chromate sealing, depending on the desired properties and compliance with regulations.
How Is Quality Assurance Integrated into Aluminum Anodizing?
Quality assurance (QA) is a critical aspect of the aluminum anodizing process, ensuring that the final products meet industry standards and customer specifications. Effective QA involves several checkpoints and practices.
Relevant International Standards for Quality Assurance
B2B buyers should be aware of various international standards that apply to aluminum anodizing services. For instance:
- ISO 9001: This standard emphasizes quality management systems and is crucial for ensuring consistent quality in processes and products.
- CE Marking: Particularly important in Europe, CE marking indicates compliance with health, safety, and environmental protection standards.
- API Standards: For industries such as oil and gas, adherence to API (American Petroleum Institute) standards ensures that the anodized components can withstand harsh environments.
What Are the Key Quality Control Checkpoints?
Quality control (QC) checkpoints are integrated at various stages of the anodizing process to ensure adherence to specifications:
- Incoming Quality Control (IQC): This step involves inspecting the raw aluminum materials for defects or inconsistencies before processing.
- In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): During anodizing, samples are taken to monitor parameters such as bath chemistry and electrical current to ensure optimal anodizing conditions.
- Final Quality Control (FQC): After anodizing, products undergo rigorous inspection to assess the thickness of the anodized layer, color consistency, and overall finish.
Common Testing Methods in Quality Assurance
Several testing methods are employed to verify the quality of anodized aluminum, including:
- Thickness Measurement: Utilizing tools like micrometers or calipers to ensure the anodized layer meets specified thickness.
- Adhesion Testing: This involves tape tests to check the adhesion of the anodized layer to the aluminum substrate.
- Corrosion Resistance Testing: Salt spray tests or cyclic corrosion tests help determine how well the anodized surface withstands environmental stress.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control Processes?
B2B buyers need to ensure that their anodizing suppliers maintain robust quality control processes. Here are actionable steps to verify supplier QC:
Conduct Supplier Audits
Regular audits can provide insights into a supplier’s adherence to quality standards. This includes reviewing their processes, documentation, and compliance with international standards like ISO 9001.
Request Quality Assurance Reports
Ask suppliers for quality assurance reports that detail their QC processes, inspection results, and compliance with relevant standards. This documentation should outline their testing methods and any certifications they hold.
Engage Third-Party Inspectors
Utilizing third-party inspection services can provide an unbiased assessment of the supplier’s quality control measures. This is especially important for international transactions, where local regulations and standards may differ.
What Are the Quality Control Nuances for International B2B Buyers?
International B2B buyers, particularly from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, face unique challenges in verifying quality control. Here are key considerations:
- Understanding Local Standards: Different regions may have varying standards and certifications. It’s essential for buyers to familiarize themselves with these regulations to ensure compliance.
- Language and Communication Barriers: Effective communication is crucial in ensuring that quality expectations are understood and met. Buyers should establish clear lines of communication and possibly utilize translation services if necessary.
- Logistical Considerations: International shipping can complicate quality control. Buyers should consider how shipping times and conditions might affect product quality and factor this into their supplier evaluation.
By understanding the manufacturing processes and quality assurance protocols of aluminum anodizing services, B2B buyers can make informed decisions when selecting suppliers, ensuring they receive high-quality products that meet their specific needs.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘aluminum anodizing service’
To assist B2B buyers in procuring aluminum anodizing services effectively, this guide presents a structured checklist designed to streamline the sourcing process. By following these actionable steps, you can ensure that your selection meets both technical specifications and business needs.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Before reaching out to suppliers, clearly outline your technical requirements. This includes the type of anodizing (e.g., Type II, Type III), desired finishes (e.g., color, gloss level), and volume of parts. Understanding your specifications is crucial because it helps suppliers provide accurate quotes and ensures that the final product meets your quality standards.
Step 2: Research Potential Suppliers
Conduct thorough research to identify potential anodizing service providers. Look for companies with a proven track record in your industry, and consider their geographical location to reduce shipping costs and lead times. Utilize platforms like industry directories and trade shows to gather a list of qualified suppliers.
Step 3: Evaluate Supplier Certifications
Verify that the suppliers hold relevant industry certifications such as ISO 9001 or AS9100. These certifications indicate a commitment to quality management systems and industry best practices. Additionally, check if they comply with environmental regulations, which is particularly important for international sourcing.
Step 4: Request Samples and Case Studies
Before making a commitment, request samples of anodized parts similar to what you need. This allows you to assess the quality of their work firsthand. Also, ask for case studies or references from clients in similar industries to gauge their experience and reliability.
Step 5: Inquire About Turnaround Times and Capacity
Discuss the supplier’s production capacity and typical turnaround times. Understanding their ability to meet your deadlines is essential, especially if you are working on a tight schedule. Ensure that they can accommodate both your current needs and any future increases in demand.
Step 6: Understand Pricing Structures
Request detailed pricing information, including any minimum order quantities and bulk pricing options. It’s important to compare quotes not just based on price but also on the value offered, such as quality of service, speed of delivery, and any additional services like custom finishes or packaging.
Step 7: Establish Communication and Support Channels
Ensure that the supplier has responsive customer service and clear communication channels. This is vital for addressing any issues that may arise during production and for ongoing support. Establishing a good relationship with your supplier can lead to better service and potentially favorable terms in the future.
By following these steps, you can streamline the procurement process for aluminum anodizing services and establish a partnership with a supplier that aligns with your business goals.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for aluminum anodizing service Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components in Aluminum Anodizing Services?
When sourcing aluminum anodizing services, understanding the cost structure is essential for making informed purchasing decisions. The primary cost components include:
-
Materials: The type of aluminum used significantly impacts costs. Higher-grade alloys such as 6061 or 7075 may command higher prices due to their superior properties. Additionally, the cost of dyes and other chemicals used in the anodizing process contributes to overall material costs.
-
Labor: Skilled labor is crucial for the anodizing process, influencing pricing. Labor costs vary based on the complexity of the project and the expertise required. Companies often charge more for intricate designs or specialized finishes.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes costs related to facility maintenance, utilities, and equipment depreciation. Anodizing facilities with advanced technologies may have higher overhead, which could be reflected in service pricing.
-
Tooling: If custom tooling or fixtures are necessary, this will add to the initial costs. Tooling expenses can vary widely based on the complexity of the parts being anodized.
-
Quality Control (QC): Rigorous QC processes ensure that the anodized parts meet industry standards, particularly in sectors like aerospace and medical. The costs associated with testing and inspection contribute to the overall service price.
-
Logistics: Shipping and handling costs can vary based on the location of the supplier and the destination. International shipments may incur additional fees, including customs duties.
-
Margin: Suppliers will include a profit margin in their pricing. This margin can fluctuate based on competition, market demand, and the supplier’s reputation.
How Do Price Influencers Affect Aluminum Anodizing Costs?
Several factors can influence the pricing of aluminum anodizing services:
-
Volume/MOQ: Suppliers often provide tiered pricing based on order volume. Higher quantities usually lead to lower per-unit costs, making it advantageous for buyers to consolidate orders.
-
Specifications and Customization: Custom designs or specific finishes can lead to increased costs. It’s crucial to clearly define specifications to avoid unexpected charges.
-
Materials: The choice of aluminum alloy and additional treatments (like hardcoating) can significantly impact prices. Premium materials will increase costs but may offer better performance.
-
Quality and Certifications: Suppliers with quality certifications (e.g., ISO, AS9100) may charge higher fees due to their commitment to quality standards. Buyers should consider the long-term benefits of choosing certified suppliers.
-
Supplier Factors: The supplier’s location, reputation, and experience can influence pricing. Established suppliers may charge a premium for their services due to reliability and quality assurance.
-
Incoterms: Understanding shipping terms (Incoterms) is vital for international buyers. These terms dictate who bears the cost and risk during transportation, which can affect overall pricing.
What Are Some Buyer Tips for Cost-Efficiency in Sourcing Aluminum Anodizing Services?
-
Negotiate: Engage in discussions with suppliers to explore bulk discounts or flexible payment terms. Building a long-term relationship can lead to better pricing over time.
-
Consider Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Evaluate not only the upfront costs but also the long-term implications, including durability and maintenance. Higher-quality anodizing may reduce replacement costs.
-
Be Aware of Pricing Nuances: International buyers, particularly from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, should account for currency fluctuations, import duties, and shipping costs that can impact the final price.
-
Request Detailed Quotes: Ensure that quotes include a breakdown of all costs. This transparency allows for better comparisons between suppliers.
-
Evaluate Supplier Capabilities: Consider suppliers that can meet your specific needs without compromising quality. A well-aligned supplier can provide value beyond just pricing.
Disclaimer on Indicative Prices
Prices for aluminum anodizing services can vary widely based on the factors discussed. It is advisable for buyers to conduct thorough market research and obtain multiple quotes to ensure competitive pricing tailored to their specific needs.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing aluminum anodizing service With Other Solutions
Exploring Alternatives to Aluminum Anodizing Service
When evaluating surface treatment solutions for aluminum components, it is essential to consider various alternatives to aluminum anodizing. These alternatives can offer different performance characteristics, costs, and operational requirements. Understanding these options can help international B2B buyers make informed decisions based on their specific needs, industry standards, and budget constraints.
Comparison Table
| Comparison Aspect | Aluminum Anodizing Service | Powder Coating | Chromate Conversion Coating |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | Excellent corrosion resistance, enhanced wear and aesthetic appeal. | Good durability, varied colors, but less corrosion resistance than anodizing. | Moderate corrosion resistance, mainly used for protection and adhesion. |
| Cost | Moderate to high, depending on complexity and volume. | Generally lower, especially for bulk orders. | Cost-effective for large volumes, but may vary based on application. |
| Ease of Implementation | Requires specialized equipment and expertise. | Easier to apply; can be done with standard spray equipment. | Requires specific application techniques and environmental controls. |
| Maintenance | Low maintenance with long-lasting results. | Moderate maintenance; may require reapplication over time. | Minimal maintenance but can wear off under severe conditions. |
| Best Use Case | Aerospace, automotive, electronics, where durability is critical. | Automotive, home appliances, and decorative items. | Industrial applications where corrosion protection is necessary but aesthetics are less critical. |
Detailed Breakdown of Alternatives
What Are the Benefits and Drawbacks of Powder Coating?
Powder coating is a popular alternative that provides a durable finish through an electrostatic application of powdered paint, which is then cured under heat. One of its main advantages is the vast array of colors and finishes available, allowing for customization. Additionally, the process is generally more cost-effective than anodizing, especially for larger production runs. However, powder coating does not offer the same level of corrosion resistance as anodizing, making it less suitable for industries where environmental exposure is a concern, such as aerospace or military applications.
How Does Chromate Conversion Coating Compare to Aluminum Anodizing?
Chromate conversion coating involves the application of a chemical treatment that provides corrosion resistance to aluminum. This method is often used as a preparatory step before painting or other finishing processes. The primary advantage of chromate conversion is its cost-effectiveness and ease of application, especially in high-volume settings. However, it lacks the aesthetic appeal and durability of anodizing. It is best suited for industrial applications where the primary goal is to protect aluminum from corrosion rather than enhance its appearance.
Conclusion: How Should B2B Buyers Choose the Right Solution?
Choosing the right surface treatment for aluminum components depends on various factors, including performance requirements, budget, and application context. Aluminum anodizing service is ideal for applications demanding high durability and corrosion resistance, particularly in industries like aerospace and automotive. In contrast, powder coating may be more suitable for decorative applications where cost efficiency and color variety are prioritized. Chromate conversion coating can serve as an effective solution in industrial contexts where basic protection is needed without the aesthetic considerations. By carefully assessing these alternatives against their specific needs, B2B buyers can make informed decisions that align with their operational goals and industry standards.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for aluminum anodizing service
What Are the Essential Technical Properties of Aluminum Anodizing Services?
When considering aluminum anodizing services, understanding the critical technical properties is essential for making informed procurement decisions. Here are key specifications that should be on your radar:
1. Material Grade
Material grade refers to the specific type of aluminum alloy used in manufacturing. Common grades include 6061, 5052, and 7075. Each alloy has unique properties, such as strength, corrosion resistance, and machinability. B2B buyers should select the appropriate grade based on the application requirements to ensure optimal performance and durability.
2. Anodizing Thickness
Anodizing thickness is the depth of the anodized layer applied to the aluminum surface, typically measured in microns. The thickness can range from 5 to 25 microns for decorative anodizing and up to 100 microns for hard anodizing. The thickness directly influences the part’s corrosion resistance, wear resistance, and aesthetic qualities. Understanding the required thickness is crucial for compliance with industry standards and application longevity.
3. Tolerance Levels
Tolerance levels denote the permissible limit of variation in a physical dimension or measured value. In aluminum anodizing, tight tolerances are vital for parts that must fit precisely in assemblies. Specifying tolerance levels ensures that the anodized parts meet the required specifications, minimizing the risk of defects and rework.
4. Color Consistency
Color consistency refers to the uniformity of the anodized finish across a batch of parts. This is particularly important for aesthetic applications, where visual appeal is paramount. B2B buyers should inquire about color matching capabilities and quality control processes to ensure that their products maintain a consistent appearance, especially when dealing with large orders.
5. Corrosion Resistance
Corrosion resistance is the ability of anodized aluminum to withstand environmental factors that can lead to degradation. Anodizing enhances this property significantly, making it a crucial consideration for applications in harsh environments. Buyers should assess the specific corrosion resistance ratings relevant to their industry to ensure long-lasting performance.
6. Wear Resistance
Wear resistance is the ability of the anodized surface to resist abrasion and surface degradation. Hard anodizing, in particular, offers superior wear resistance, making it ideal for parts exposed to friction or mechanical wear. Understanding the wear resistance requirements of your application will guide you in selecting the right anodizing process.
What Are the Common Trade Terms Associated with Aluminum Anodizing Services?
Familiarizing yourself with industry jargon can streamline communication and negotiations in the aluminum anodizing market. Here are some key terms to know:
1. OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
An OEM refers to a company that manufactures products that are sold under another company’s brand. In the context of aluminum anodizing, an OEM may require anodized components for their products, necessitating a reliable anodizing partner.
2. MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ is the smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell. Understanding the MOQ is essential for budgeting and inventory management. B2B buyers should clarify MOQ requirements to ensure they align with their project needs.
3. RFQ (Request for Quote)
An RFQ is a document sent to suppliers requesting pricing and terms for specific products or services. B2B buyers utilize RFQs to compare quotes from multiple anodizing service providers, aiding in cost-effective decision-making.
4. Incoterms
Incoterms are international commercial terms that define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers regarding shipping, insurance, and tariffs. Familiarity with Incoterms is crucial for B2B transactions, as they clarify who bears the risk and cost during the transportation of anodized products.
5. Lead Time
Lead time is the period between placing an order and receiving the finished product. Understanding lead times helps B2B buyers plan their projects effectively and manage expectations regarding delivery schedules.
6. Certification Standards
Certification standards, such as ISO and AS9100, indicate that a supplier adheres to quality management practices. B2B buyers should seek anodizing service providers with relevant certifications to ensure compliance with industry regulations and consistent quality.
By grasping these essential technical properties and trade terms, B2B buyers can navigate the aluminum anodizing landscape more effectively, ensuring that they select the right partners and materials for their specific needs.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the aluminum anodizing service Sector
What Are the Current Market Dynamics and Key Trends in the Aluminum Anodizing Service Sector?
The global aluminum anodizing market is witnessing significant growth, driven by the rising demand for durable and corrosion-resistant aluminum products across various industries, including aerospace, automotive, electronics, and construction. This trend is particularly pronounced in emerging markets such as Africa and South America, where infrastructure development is accelerating. Additionally, European manufacturers are increasingly focusing on lightweight materials to enhance fuel efficiency and reduce emissions, further propelling the demand for anodized aluminum.
Technological advancements are reshaping the sourcing landscape. Automation in anodizing processes is improving efficiency and precision, leading to reduced production times and costs. Furthermore, the integration of digital platforms is facilitating easier communication between buyers and suppliers, allowing for swift quotations and streamlined order management. For international B2B buyers, particularly those in Brazil and Nigeria, leveraging these technologies can optimize sourcing strategies and enhance supply chain transparency.
Another notable trend is the customization of anodizing services. Many suppliers are now offering tailored solutions that cater to specific industry needs, including unique color finishes and varying thicknesses of anodized layers. This level of customization not only meets aesthetic requirements but also enhances the functional performance of aluminum products, making them more appealing to diverse markets.
How Is Sustainability and Ethical Sourcing Impacting the Aluminum Anodizing Service Sector?
As global awareness of environmental issues grows, sustainability has become a key concern for businesses in the aluminum anodizing sector. The anodizing process itself can have significant environmental impacts, particularly concerning water usage and chemical waste. Therefore, B2B buyers are increasingly seeking suppliers that demonstrate a commitment to sustainable practices. This includes utilizing eco-friendly anodizing solutions, such as non-toxic dyes and chemicals, and implementing water recycling systems in their operations.
Ethical sourcing is also gaining traction, with buyers prioritizing suppliers that adhere to fair labor practices and responsible sourcing of raw materials. Certifications such as ISO 14001 (Environmental Management) and AS9100 (Quality Management Systems for Aerospace) are becoming essential for suppliers aiming to attract conscientious buyers. By choosing suppliers with these certifications, businesses can ensure they are part of a responsible supply chain that prioritizes both environmental and social governance.
Moreover, the use of recycled aluminum in anodizing processes is a growing trend. This not only reduces the carbon footprint associated with aluminum production but also appeals to buyers looking to enhance their own sustainability credentials. By sourcing anodized products made from recycled materials, companies can contribute to a circular economy and reduce their overall environmental impact.
What Is the Brief Evolution and History of Aluminum Anodizing Services?
Aluminum anodizing has evolved significantly since its inception in the early 20th century. Initially developed for decorative purposes, the process gained popularity in the 1950s and 1960s as industries began to recognize the functional benefits of anodized aluminum, such as enhanced corrosion resistance and improved wear characteristics. Over the decades, advancements in technology and chemistry have led to more sophisticated anodizing techniques, including hard anodizing and color anodizing, which offer additional protective features and aesthetic options.
Today, aluminum anodizing is a well-established service with applications across a myriad of industries. As the demand for high-performance aluminum products continues to rise, the anodizing sector is poised for further innovation and growth, aligning with the needs of modern B2B buyers focused on quality, sustainability, and customization.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of aluminum anodizing service
-
How do I choose the right aluminum anodizing service provider?
Selecting the right aluminum anodizing service provider involves several key considerations. First, evaluate their experience and expertise in the specific anodizing processes you require, such as Type II or Type III anodizing. Check for certifications such as ISO 9001, which indicates adherence to quality management standards. Additionally, assess their capacity for handling both low and high-volume orders, as well as their customer service responsiveness. Request samples of their previous work to gauge quality and finish, and consider their logistical capabilities, especially if you are sourcing from different continents. -
What types of anodizing finishes are available for aluminum?
There are several anodizing finishes available for aluminum, each serving different aesthetic and functional purposes. The most common types include Type II sulfuric anodizing, which enhances corrosion resistance and allows for dyeing, and Type III hard anodizing, which offers superior wear resistance and is often used in industrial applications. Additionally, some providers may offer decorative anodizing options that enhance the visual appeal of aluminum parts without compromising durability. Be sure to discuss your specific needs with suppliers to find the best finish for your project. -
What are the minimum order quantities (MOQ) for aluminum anodizing services?
Minimum order quantities (MOQ) can vary significantly between anodizing service providers. Some may have no minimums, allowing you to order as few as one part, while others may set MOQs based on production efficiency, such as 100 or 500 pieces. It’s essential to clarify this with potential suppliers early in your discussions, especially if you are a smaller business or a startup. Understanding MOQs will help you manage your budget and production timelines effectively. -
How do I ensure quality control during the anodizing process?
To ensure quality control during the anodizing process, first, select a supplier that adheres to recognized quality standards, such as ISO certifications. Discuss their quality assurance processes, including testing for thickness, color consistency, and adhesion. Request samples or prototypes before committing to larger orders to verify the quality of the anodizing finish. Additionally, inquire about their capabilities for post-anodizing inspections and certifications, which can provide further assurance of product integrity. -
What payment terms should I expect when sourcing anodizing services internationally?
Payment terms can vary widely among international suppliers. Common practices include upfront payments, partial payments before and after production, or payment upon delivery. It’s advisable to negotiate terms that align with your cash flow and operational needs. Be mindful of currency exchange rates and transaction fees, especially when dealing with suppliers from different countries. Utilizing secure payment methods such as letters of credit or PayPal can also offer added protection in international transactions. -
How can I effectively communicate my anodizing specifications to suppliers?
Effective communication of your anodizing specifications starts with providing detailed documentation, including drawings, dimensions, and desired finishes. Clearly outline any color preferences, tolerances, and performance requirements. Use industry-standard terminology to avoid misunderstandings, and consider sharing reference samples if applicable. Establishing a direct line of communication with the supplier can facilitate discussions and adjustments, ensuring that both parties are aligned on expectations throughout the process. -
What logistics considerations should I keep in mind when sourcing aluminum anodizing services?
When sourcing aluminum anodizing services internationally, logistics considerations are crucial. Evaluate the supplier’s shipping capabilities, including shipping costs, lead times, and customs clearance procedures. Understand the import regulations in your country to avoid delays and additional fees. Additionally, consider the location of the supplier in relation to your operations to minimize transit times. Establishing a reliable logistics partner can also streamline the process and ensure timely delivery of your anodized products. -
What are the environmental impacts of aluminum anodizing, and how can I ensure compliance?
Aluminum anodizing can have environmental impacts, particularly concerning waste management and chemical use. To ensure compliance with environmental regulations, choose a supplier that practices sustainable anodizing processes and adheres to local environmental laws. Inquire about their waste disposal methods and whether they utilize eco-friendly anodizing solutions. Engaging with suppliers who are committed to sustainability can not only help you meet regulatory requirements but also enhance your brand’s reputation in the global market.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.
Top 8 Aluminum Anodizing Service Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. SendCutSend – Metal Anodizing Services
Domain: sendcutsend.com
Registered: 2015 (10 years)
Introduction: Metal Anodizing Services: Type II, Class II sulfuric anodizing process that enhances durability and appearance of parts. Adds a protective oxide layer for increased corrosion and wear resistance without significant thickness. Available in five colors: black, clear, blue, gold, and red. No minimum quantity required. Pricing starts at $0.50 per part in bulk. Free shipping in the U.S. and starting fr…
2. Alexandria Metal Finishers – Aluminum Anodizing Services
Domain: alexandriametalfinishers.com
Registered: 2000 (25 years)
Introduction: Aluminum Anodizing Services at Alexandria Metal Finishers include:
1. **Types of Anodizing:**
– Type II Sulfuric Acid Anodizing (Conventional Anodizing)
– Type III Sulfuric Acid Anodizing (Hardcoat Anodizing)
2. **Standards and Certifications:**
– MIL-A-8625/MIL-PRF-8625
– AMS-2469
– AMS-2471
– AMS-2472
3. **Capabilities:**
– Large-capacity anodizing for unique projects
…
3. Alumacoat – High Quality Anodizing Services
Domain: alumacoat.com
Registered: 2010 (15 years)
Introduction: High Quality Anodizing Services including Decorative Anodizing, Architectural Anodizing, Color Anodizing, and Automated Shot-Blasting.
1. **Decorative Anodizing**: Color and protect aluminum parts for aesthetic appeal; can match most architectural colors.
2. **Architectural Anodizing**: Protects large aluminum parts; Type II – Class I & II anodizing builds up aluminum oxide on the surface and i…
4. Aluminum Anodizing – Enhancing Durability and Aesthetics
Domain: aluminumanodizing.com
Registered: 2000 (25 years)
Introduction: Aluminum anodizing is a finishing process that enhances the durability, corrosion resistance, and aesthetic appeal of aluminum products. It involves creating a protective oxide layer on aluminum surfaces through electrolytic passivation. Key anodizing methods include: 1. Sulfuric Acid Anodizing (Type II): Common and versatile, provides moderate thickness (0.0005″–0.001″) with superior corrosion re…
5. Midwestern Anodizing – Key Metal Finishing Products
Domain: midwesternanodizing.com
Registered: 2003 (22 years)
Introduction: Midwestern Anodizing specializes in aluminum anodizing and metal finishing. Key product details include:
– Anodizing to Military Spec. 8625 Type 2 (Class 1 and 2)
– Chromate Conversion to MIL-DTL-5541F Type 2 (Class 1 and 3)
– Stainless Steel Passivation per QQP-35 (ASTM A-967: Citric 5)
– Masking
– Aluminum Etching
– High volumes or custom small piece runs
– Large inventory of standard rac…
6. Hubs – Aluminum Anodizing Services
Domain: hubs.com
Registered: 1998 (27 years)
Introduction: Aluminum anodizing services offered include anodizing type II and III. Anodizing strengthens aluminum parts and is available in several colors. Anodizing type II features surface preparation options such as as machined, bead blasted, and brushed, with colors including Clear, Black, Red, Blue, Orange, and Gold. Glossiness options range from glossy (above 20 GU) to matte (below 10 GU). Minimum thick…
7. ModMyMods – Custom Aluminum Anodizing Service
Domain: modmymods.com
Registered: 2013 (12 years)
Introduction: ModMyMods Custom Aluminum Anodizing Service
8. Anodize Inc – Metal Finishing Services
Domain: anodizeinc.com
Registered: 2007 (18 years)
Introduction: Anodize offers metal finishing services specializing in anodizing, mirror polishing, and laser etching. Key features include:
– Types of anodizing: Medical & Surgical Grade, Military Spec Type II & II B, Bright Dip.
– Anodizing for aluminum products with a wide array of colors, including extreme colors and clear.
– ISO 9001:2015 certified and NADCAP compliant.
– Anodizing process involves electrol…
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for aluminum anodizing service
In navigating the landscape of aluminum anodizing services, strategic sourcing emerges as a vital approach for international B2B buyers. By understanding the diverse capabilities of suppliers—ranging from custom finishes to advanced protective coatings—businesses can select partners that align with their specific needs. The value of high-quality anodized products is clear: enhanced durability, improved aesthetics, and superior corrosion resistance can significantly impact product performance and longevity.
For buyers in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, leveraging local and international suppliers can provide competitive advantages. Engaging with reputable anodizing companies not only ensures compliance with industry standards but also fosters innovation through collaboration on tailored solutions. As demand for anodized aluminum continues to rise across various sectors—such as aerospace, automotive, and electronics—investing in strategic sourcing becomes essential.
Looking ahead, B2B buyers should actively seek partnerships that prioritize quality, efficiency, and customer service. Embrace the opportunity to explore new suppliers and technologies in the aluminum anodizing space, and position your business for success in an increasingly competitive market. Reach out today to discover how strategic sourcing can elevate your anodizing projects and drive growth.