Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for aluminium tin alloy
In the dynamic landscape of global manufacturing, sourcing aluminum tin alloy presents a unique challenge for international B2B buyers. This lightweight yet robust material is increasingly sought after for its superior wear resistance and corrosion properties, particularly in high-performance applications across diverse industries such as automotive, aerospace, and industrial equipment. However, navigating the complexities of supply chains, varying quality standards, and fluctuating market prices can be daunting.
This comprehensive guide delves into the multifaceted world of aluminum tin alloy, offering insights into its various types, applications, and the nuances of supplier vetting. From understanding the technical specifications that dictate performance to evaluating cost factors that influence procurement decisions, this resource is designed to empower B2B buyers from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe—including key markets like Saudi Arabia and Vietnam.
By providing actionable strategies and in-depth analyses, this guide equips decision-makers with the knowledge needed to make informed purchasing choices. Whether you are seeking reliable suppliers or exploring innovative applications for aluminum tin alloy, our goal is to enhance your purchasing process and ensure you secure the best materials for your operational needs.
Understanding aluminium tin alloy Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| AL1646 Aluminum Tin Alloy | High purity, customizable shapes, effective grain refining | Automotive, Aerospace, Industrial Equipment | Pros: Enhances strength and machinability; Cons: Higher initial cost compared to standard alloys. |
| AlSn50 Master Alloy | Pre-alloyed mixture, economical, energy-efficient production | Marine, Automotive, Aerospace | Pros: Low friction properties; Cons: Limited availability in some regions. |
| AlSn20 Alloy | Lower tin content, good for lightweight applications | General Manufacturing, Electronics | Pros: Cost-effective; Cons: Less wear resistance than higher tin variants. |
| AlSn10 Alloy | Balanced properties for diverse applications | Electrical Components, Industrial Machinery | Pros: Good machinability; Cons: May require additional treatments for enhanced durability. |
| AlSn5 Alloy | Very low tin content, ideal for specialized applications | Specialty Applications, High-Temperature Environments | Pros: Lightweight; Cons: Limited structural strength. |
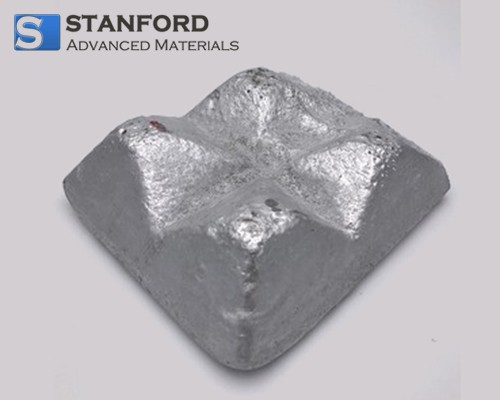
What are the Characteristics of AL1646 Aluminum Tin Alloy?
The AL1646 Aluminum Tin Alloy is known for its high purity and customizable characteristics, making it a preferred choice for applications requiring superior strength and machinability. Its effectiveness as a grain refiner allows for improved mechanical properties, which is crucial in industries such as aerospace and automotive. When considering B2B purchases, companies should evaluate the alloy’s compatibility with their production processes and the potential for energy savings during manufacturing.
How Does AlSn50 Master Alloy Stand Out?
AlSn50 Master Alloy contains a pre-alloyed mixture that provides significant economic benefits and energy efficiency during production. Its low friction properties make it ideal for components that experience wear, such as bearings and bushings, particularly in marine and automotive applications. Buyers should consider the alloy’s performance in specific environmental conditions to ensure it meets their durability requirements.
Why Choose AlSn20 Alloy for General Manufacturing?
AlSn20 Alloy features a lower tin content, making it suitable for lightweight applications where cost-effectiveness is essential. This alloy is commonly used in general manufacturing and electronics, where its properties can be optimized for various designs. When purchasing, businesses should weigh the benefits of lower costs against the potential need for enhanced wear resistance in high-stress applications.
What Benefits Does AlSn10 Alloy Provide?
AlSn10 Alloy offers a balanced set of properties that cater to diverse applications, including electrical components and industrial machinery. Its good machinability allows for easier manufacturing processes, which can be a significant advantage for buyers looking to reduce production times. However, it may require additional treatments for improved durability, and businesses should assess their specific needs before making a decision.
In What Situations is AlSn5 Alloy Ideal?
AlSn5 Alloy is characterized by its very low tin content, making it particularly suitable for specialized applications that demand lightweight materials. While it offers significant advantages in high-temperature environments, it may not provide the structural strength required for more demanding applications. Buyers should ensure that the alloy aligns with their performance requirements to avoid potential limitations in use.
Key Industrial Applications of aluminium tin alloy
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of aluminium tin alloy | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Automotive | Engine components such as pistons and cylinder heads | Enhanced wear resistance and reduced friction | Supplier reliability and alloy composition consistency |
| Aerospace | Lightweight structural components | Improved strength-to-weight ratio, crucial for fuel efficiency | Certifications and compliance with aerospace standards |
| Industrial Equipment | Bearings and bushings in machinery | Increased durability and reduced maintenance costs | Availability of customized shapes and sizes |
| Marine Applications | Corrosion-resistant components for marine environments | Longevity in harsh conditions, reducing replacement costs | Environmental resistance and compliance with marine regulations |
| Energy Storage & Batteries | Battery casings and components | Better thermal management and weight reduction | Quality assurance and compatibility with existing systems |
How is Aluminium Tin Alloy Used in the Automotive Industry?
In the automotive sector, aluminium tin alloys are primarily utilized in engine components like pistons and cylinder heads. These alloys offer enhanced wear resistance, significantly reducing friction between moving parts, which leads to improved fuel efficiency and engine longevity. International buyers should consider sourcing from suppliers with a track record of producing high-quality alloys that meet stringent automotive standards, ensuring reliability and performance in their applications.
What Role Does Aluminium Tin Alloy Play in Aerospace Applications?
Aluminium tin alloy is crucial in the aerospace industry for manufacturing lightweight structural components. These alloys provide a superior strength-to-weight ratio, which is essential for improving fuel efficiency in aircraft. International buyers, particularly from regions with strict aerospace regulations, must prioritize sourcing from certified suppliers who adhere to industry standards, ensuring that components can withstand the demanding conditions of flight.
How is Aluminium Tin Alloy Beneficial for Industrial Equipment?
In industrial equipment, aluminium tin alloys are commonly used for bearings and bushings, which are critical in machinery operations. The alloy’s increased durability minimizes wear and tear, leading to lower maintenance costs and extended equipment life. B2B buyers should focus on suppliers that can provide customized shapes and sizes to meet specific machinery requirements, as well as those that offer reliable delivery schedules to avoid production downtime.
Why is Aluminium Tin Alloy Important for Marine Applications?
Marine applications benefit significantly from aluminium tin alloys due to their corrosion-resistant properties, making them ideal for components exposed to harsh saltwater environments. This longevity reduces replacement costs and maintenance efforts, crucial for businesses operating in marine industries. Buyers should ensure that their suppliers can provide alloys that comply with marine regulations and offer proven performance in corrosive conditions.
How Does Aluminium Tin Alloy Enhance Energy Storage Solutions?
In the energy sector, particularly in battery technology, aluminium tin alloys are used for casings and components that require excellent thermal management and weight reduction. These properties enhance the overall efficiency and performance of energy storage systems. International buyers should look for suppliers that can guarantee quality assurance and compatibility with existing battery technologies, ensuring seamless integration into their products.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘aluminium tin alloy’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Navigating Quality Assurance Challenges in Aluminium Tin Alloys
The Problem: B2B buyers often face difficulties in ensuring the quality and consistency of aluminium tin alloys. In industries such as aerospace and automotive, where precision is paramount, the risk of substandard materials can lead to costly production delays and compromised safety standards. Buyers may encounter variations in alloy composition, leading to discrepancies in mechanical properties, such as wear resistance and strength. This inconsistency can be particularly concerning when sourcing from multiple suppliers or across different regions.
The Solution: To mitigate quality assurance challenges, buyers should establish robust supplier evaluation criteria that prioritize manufacturers with a proven track record in producing high-purity aluminium tin alloys. It’s essential to request Certificates of Analysis (CoA) for each batch, detailing the alloy’s composition and mechanical properties. Additionally, engaging in regular quality audits can help maintain transparency and accountability. Buyers should also consider forming long-term partnerships with reliable suppliers who can provide tailored solutions and consistent product quality. Implementing a rigorous incoming materials inspection process can further ensure that only the highest quality materials are used in production.
Scenario 2: Understanding Application-Specific Requirements for Aluminium Tin Alloys
The Problem: Many B2B buyers struggle to understand the specific requirements for different applications of aluminium tin alloys. With diverse end-use applications ranging from automotive bearings to aerospace components, each requires unique material properties. This lack of clarity can lead to incorrect alloy specifications, resulting in performance failures or increased production costs due to rework or material wastage.
The Solution: To address this issue, buyers should invest in comprehensive training and resources to better understand the properties and applications of aluminium tin alloys. Collaborating with technical experts or material engineers can provide valuable insights into selecting the right alloy for specific applications. Buyers should also conduct thorough market research to understand industry standards and customer expectations. Creating detailed application profiles can guide the selection process, ensuring that the chosen alloy meets the mechanical and physical property requirements for its intended use. Engaging suppliers in the specification process can also yield customized solutions that align with the specific demands of each application.
Scenario 3: Managing Supply Chain Complexities in Sourcing Aluminium Tin Alloys
The Problem: Sourcing aluminium tin alloys can be complicated due to fluctuating market prices, geopolitical factors, and varying lead times across different regions. B2B buyers, particularly in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, may find themselves facing unexpected delays or cost increases, which can disrupt production schedules and strain budgets. These supply chain complexities can create significant operational challenges for businesses that rely on timely and cost-effective procurement.
The Solution: To effectively manage supply chain complexities, buyers should adopt a proactive approach to sourcing. This includes diversifying the supplier base to minimize dependency on any single source and exploring local suppliers who can offer shorter lead times and reduced shipping costs. Implementing a strategic sourcing framework that includes risk assessment and contingency planning can help anticipate and mitigate potential disruptions. Additionally, leveraging technology such as supply chain management software can provide real-time visibility into inventory levels, order statuses, and market trends, allowing buyers to make informed decisions. Establishing strong communication channels with suppliers can also facilitate quicker responses to market changes and enhance collaboration throughout the procurement process.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for aluminium tin alloy
What Are the Key Properties of Common Aluminium Tin Alloys?
Aluminium tin alloys are notable for their unique combination of properties that make them suitable for various industrial applications. Here, we will explore four common materials used in aluminium tin alloys, focusing on their properties, advantages, disadvantages, and considerations for international B2B buyers.
1. AL1646 Aluminium Tin Master Alloy
Key Properties:
AL1646 is recognized for its excellent wear resistance and low friction characteristics, making it ideal for applications in automotive and aerospace industries. It typically contains around 50% tin, which enhances the alloy’s mechanical properties, including tensile strength and corrosion resistance.
Pros & Cons:
The primary advantage of AL1646 is its ability to improve the wear resistance of components, which is crucial in high-friction applications. However, its higher cost compared to standard aluminium alloys can be a barrier for some manufacturers. Additionally, its processing requires careful temperature control to avoid degradation of properties.
Impact on Application:
AL1646 is particularly suited for components like bearings and bushings, where low friction and high durability are essential. Its corrosion resistance also makes it suitable for marine applications.
Considerations for International Buyers:
Buyers from regions such as Africa and South America should ensure compliance with local standards, as AL1646 may need to meet specific certifications for automotive or aerospace applications. Understanding ASTM standards is crucial for ensuring product quality.
2. AlSn50 Alloy
Key Properties:
AlSn50 is a pre-alloyed mixture that excels in enhancing the physical and mechanical properties of other metals. It is characterized by its ability to act as a grain refiner, promoting a finer and more uniform grain structure in the final product.
Pros & Cons:
The main advantage of AlSn50 is its cost-effectiveness and energy efficiency in production, as it can replace pure metals in many applications. However, its performance can vary significantly depending on the processing conditions, which may complicate manufacturing.
Impact on Application:
This alloy is often used in automotive components and industrial machinery, where improved mechanical properties are required. Its ability to refine grain structure also enhances the overall strength of the final product.
Considerations for International Buyers:
For buyers in the Middle East and Europe, familiarity with the relevant DIN and JIS standards is essential to ensure compliance. The alloy’s versatility makes it a popular choice across various industries, but buyers should verify compatibility with specific applications.
3. AlSn10 Alloy
Key Properties:
AlSn10 is another variant that offers enhanced machinability and is particularly effective in applications requiring high wear resistance. Its composition typically includes 10% tin, which contributes to its low friction properties.
Pros & Cons:
The key advantage of AlSn10 is its excellent machinability, making it easy to work with during manufacturing. However, it may not provide the same level of corrosion resistance as other alloys, which could limit its use in harsh environments.
Impact on Application:
This alloy is ideal for sliding components in machinery and automotive applications, where low friction is critical. However, its limited corrosion resistance may necessitate additional protective coatings in certain environments.
Considerations for International Buyers:
Buyers should assess the environmental conditions of their applications, especially in coastal regions where corrosion resistance is paramount. Compliance with international standards like ASTM is also vital for ensuring product reliability.
4. AlSn20 Alloy
Key Properties:
AlSn20 is known for its high strength and excellent wear resistance, making it suitable for heavy-duty applications. Its higher tin content contributes to its superior performance in high-stress environments.
Pros & Cons:
The primary benefit of AlSn20 is its durability, which extends the lifespan of components in demanding applications. However, its higher cost can be a drawback for budget-sensitive projects.
Impact on Application:
AlSn20 is commonly used in applications such as construction and heavy machinery, where strength and wear resistance are critical. Its performance under stress makes it a preferred choice for structural components.
Considerations for International Buyers:
Buyers in Europe and the Middle East should consider local sourcing options to mitigate costs, as transportation can significantly impact pricing. Understanding the specific mechanical requirements of their applications will aid in selecting the right alloy.
Summary Table
| Material | Typical Use Case for aluminium tin alloy | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| AL1646 | Automotive and aerospace components | Excellent wear resistance | Higher cost compared to standard alloys | High |
| AlSn50 | Automotive and industrial machinery | Cost-effective and energy-efficient | Variable performance based on processing | Medium |
| AlSn10 | Sliding components in machinery | Excellent machinability | Limited corrosion resistance | Medium |
| AlSn20 | Construction and heavy machinery | High strength and durability | Higher cost for budget-sensitive projects | High |
This analysis provides a comprehensive overview of common aluminium tin alloys, highlighting their properties and considerations for international B2B buyers. Understanding these factors is crucial for selecting the right material for specific applications.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for aluminium tin alloy
What Are the Main Stages of Manufacturing Aluminium Tin Alloy?
The manufacturing of aluminium tin alloy involves several critical stages that ensure the final product meets the necessary specifications and quality standards. These stages include material preparation, forming, assembly, and finishing.
Material Preparation
The initial step in the manufacturing process is the preparation of the raw materials. High-purity aluminium (typically >99% Al) is sourced, along with tin, which is essential for enhancing the alloy’s properties. The materials are weighed and combined in specific ratios, often in a controlled environment to prevent contamination. This mixture is then loaded into a crucible for melting.
Forming Techniques
The melting process is typically conducted in a gas-fired lift-out crucible furnace, where the metal mixture is heated to approximately 710 °C, slightly above the melting point of aluminium. Once molten, the alloy is poured into molds to form ingots or other desired shapes. Techniques such as sand casting, die casting, and continuous casting may be employed, depending on the final application of the alloy.
Assembly and Secondary Processing
After forming, the ingots may undergo secondary processing, including extrusion or rolling, to achieve specific dimensions and mechanical properties. During this phase, the alloy can be further refined using techniques such as hot isostatic pressing or thermal spraying, enhancing its wear resistance and overall performance characteristics.
Finishing Processes
Finishing processes may involve machining, surface treatments, or coatings to improve the alloy’s durability and resistance to environmental factors. Common finishing methods include anodizing, plating, or applying protective coatings, which are crucial for applications in aerospace, automotive, and marine environments.
How Is Quality Assurance Implemented in the Manufacturing of Aluminium Tin Alloy?
Quality assurance (QA) is integral to the manufacturing process of aluminium tin alloy, ensuring that the final products meet both customer and regulatory standards. Several international standards and industry-specific certifications guide these QA practices.
What International Standards Should B2B Buyers Be Aware Of?
B2B buyers should familiarize themselves with international standards such as ISO 9001, which outlines quality management systems, and ISO 14001, focusing on environmental management. Industry-specific certifications, such as CE marking for European markets or API standards for oil and gas applications, are also critical as they signify compliance with safety and performance regulations.
What Are the Key QC Checkpoints in the Manufacturing Process?
Quality control (QC) involves several checkpoints throughout the manufacturing process:
-
Incoming Quality Control (IQC): This stage ensures that raw materials meet specified standards before production begins. Supplier certificates, material test reports, and visual inspections are typical methods used here.
-
In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): During manufacturing, various checks are conducted to monitor parameters such as temperature, pressure, and composition. This includes sampling and testing of molten metal and monitoring the casting process to identify defects early.
-
Final Quality Control (FQC): Once the product is completed, it undergoes final inspections and testing to confirm that it meets all specifications. This may include dimensional checks, mechanical property testing (e.g., tensile strength, hardness), and surface integrity evaluations.
What Testing Methods Are Commonly Used for Aluminium Tin Alloy?
Several testing methods are employed to ensure that aluminium tin alloys meet the necessary quality standards. Common techniques include:
-
Tensile Testing: This assesses the mechanical properties of the alloy, including yield strength, ultimate tensile strength, and elongation.
-
Brinell Hardness Testing: Used to measure the hardness of the alloy, this test is essential for determining wear resistance and durability.
-
Microstructural Analysis: Techniques such as optical microscopy and scanning electron microscopy (SEM) are used to evaluate the alloy’s microstructure, revealing information about grain size, phase distribution, and potential defects.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control?
B2B buyers have several options for verifying the quality control processes of their suppliers:
Conducting Audits
Regular audits can provide insights into a supplier’s quality management systems and manufacturing practices. These audits can be performed by the buyer’s quality assurance team or through third-party inspection services.
Requesting Documentation and Reports
Buyers should request detailed documentation, including quality control reports, certificates of analysis (COA), and compliance certifications. This documentation should outline the testing methods used and the results obtained, providing transparency into the supplier’s quality processes.
Utilizing Third-Party Inspection Services
Engaging third-party inspection services can add an additional layer of assurance. These organizations can perform independent testing and verification, ensuring that the products meet the agreed-upon specifications and standards.
What Are the Nuances of QC and Certification for International B2B Buyers?
For international B2B buyers, especially those in regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, understanding the nuances of QC and certification is crucial. Different regions may have varying requirements and standards, which can affect procurement strategies.
Regional Compliance Requirements
Buyers should be aware of local regulations and compliance requirements specific to their industry and region. For instance, products sold in the European Union must comply with CE marking, while those used in the oil and gas sector may require API certification.
Cultural and Communication Considerations
Effective communication with suppliers is essential for ensuring quality. Buyers should establish clear expectations regarding quality standards, testing methods, and documentation. Cultural differences may also impact negotiations and relationships, making it vital to approach discussions with sensitivity and openness.
Conclusion
Understanding the manufacturing processes and quality assurance practices for aluminium tin alloy is vital for B2B buyers seeking reliable suppliers. By familiarizing themselves with the manufacturing stages, quality standards, testing methods, and verification techniques, buyers can make informed decisions that enhance their procurement strategies and ensure product quality. This comprehensive approach not only mitigates risks but also fosters stronger partnerships in the global marketplace.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘aluminium tin alloy’
In the competitive landscape of B2B procurement, sourcing high-quality aluminium tin alloy is crucial for various applications, including automotive, aerospace, and industrial manufacturing. This guide serves as a practical checklist to streamline the sourcing process, ensuring you make informed decisions that meet your business needs.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Establishing clear technical specifications is the foundation of a successful sourcing strategy. Determine the alloy composition you need, such as the percentage of tin and any other alloying elements required for your application. This clarity will help you communicate effectively with suppliers and ensure that the products you receive meet your performance expectations.
Step 2: Research Potential Suppliers
Conduct thorough research to identify potential suppliers who specialize in aluminium tin alloys. Utilize online directories, industry forums, and trade shows to compile a list of manufacturers. Focus on suppliers with a proven track record in your industry, as this can significantly impact the quality and reliability of the materials you procure.
Step 3: Evaluate Supplier Certifications
Before finalizing your supplier, verify their certifications and compliance with international quality standards, such as ISO 9001 or ASTM specifications. Certifications indicate that a supplier adheres to established quality management practices, which is vital for maintaining product integrity. Additionally, check for any specific industry certifications relevant to your sector.
Step 4: Request Material Samples
Request samples of the aluminium tin alloy to assess their quality and suitability for your applications. Testing samples will allow you to evaluate properties such as tensile strength, corrosion resistance, and machinability. This step is essential for ensuring that the material meets your technical specifications and performance criteria.
Step 5: Assess Production Capabilities
Understanding a supplier’s production capabilities is crucial for meeting your supply chain needs. Inquire about their manufacturing processes, lead times, and minimum order quantities. A supplier with advanced production capabilities can offer customization options, ensuring that you receive materials tailored to your specifications.
Step 6: Review Pricing and Payment Terms
Evaluate the pricing structure and payment terms proposed by potential suppliers. While cost is a significant factor, it’s essential to consider the overall value, including quality, reliability, and service. Negotiate payment terms that align with your cash flow and procurement strategy, ensuring that you can maintain a healthy financial balance.
Step 7: Establish a Communication Plan
Develop a clear communication plan with your chosen supplier. Regular updates on order status, quality checks, and any potential issues will help foster a strong partnership. Establishing open lines of communication is crucial for addressing concerns swiftly and ensuring a smooth supply chain experience.
By following this checklist, you can streamline the procurement of aluminium tin alloy, ensuring that you source high-quality materials that meet your business requirements.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for aluminium tin alloy Sourcing
What are the Key Cost Components for Aluminium Tin Alloy Sourcing?
When sourcing aluminium tin alloys, understanding the cost structure is crucial for international B2B buyers. The primary cost components include materials, labor, manufacturing overhead, tooling, quality control (QC), logistics, and supplier margin.
-
Materials: The cost of raw materials, specifically aluminium and tin, significantly influences the overall price. Market fluctuations for these metals can cause variability in pricing, making it essential for buyers to keep abreast of commodity market trends.
-
Labor: Labor costs vary by region and can impact the final product price. For instance, countries with higher labor costs, such as those in Western Europe, may have higher pricing structures compared to regions in South America or Africa where labor may be more affordable.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes expenses associated with production facilities, equipment maintenance, utilities, and administrative costs. Efficient operations can help mitigate these costs, but they are nonetheless a critical component of the pricing structure.
-
Tooling: The initial investment in tooling can be significant, especially for customized or specialized aluminium tin alloys. This upfront cost should be factored into the overall pricing, particularly if the buyer is looking for specific shapes or compositions.
-
Quality Control (QC): Ensuring that the alloys meet specific quality standards adds to the cost. This is particularly relevant for industries such as aerospace or automotive, where stringent regulations apply. The investment in QC can ultimately lead to reduced costs associated with defects or failures.
-
Logistics: Transportation and shipping costs can vary widely based on distance, mode of transport, and the chosen Incoterms. Buyers should account for these factors in their budgeting and pricing discussions.
-
Margin: Suppliers will typically include a profit margin on top of their costs, which can vary based on market demand, competition, and the perceived value of their product.
How Do Price Influencers Affect Aluminium Tin Alloy Costs?
Several factors can influence the pricing of aluminium tin alloys, which B2B buyers must consider:
-
Volume/MOQ: Purchasing in larger quantities can often lead to discounts. Buyers should negotiate minimum order quantities (MOQs) to achieve better pricing.
-
Specifications and Customization: Customized alloys with specific characteristics or properties may incur additional costs. Buyers need to clearly define their requirements to avoid unexpected expenses.
-
Material Quality and Certifications: Higher quality materials and certifications (e.g., ISO standards) typically come at a premium. Buyers should assess the necessity of these certifications based on their application needs.
-
Supplier Factors: The reputation and reliability of the supplier can impact pricing. Established suppliers with a track record of quality may charge more, but they can also provide assurance regarding product performance.
-
Incoterms: The choice of Incoterms (International Commercial Terms) can significantly impact logistics costs. Buyers should carefully consider terms such as FOB (Free On Board) or CIF (Cost, Insurance, and Freight) to understand their total cost responsibilities.
What Are the Best Negotiation Tips for International B2B Buyers?
To maximize cost efficiency when sourcing aluminium tin alloys, buyers should consider the following strategies:
-
Understand Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Beyond the initial purchase price, consider long-term costs such as maintenance, potential downtime, and disposal. A lower upfront cost may lead to higher TCO.
-
Leverage Relationships: Building strong relationships with suppliers can lead to better pricing and terms. Engage in regular communication and express interest in long-term partnerships.
-
Negotiate Based on Market Trends: Stay informed about market conditions for aluminium and tin. This knowledge can empower buyers to negotiate more effectively based on supply and demand dynamics.
-
Evaluate Multiple Suppliers: Obtaining quotes from several suppliers can provide leverage in negotiations. It also allows buyers to compare not only prices but also quality and service levels.
-
Be Cautious with Indicative Prices: Always consider that prices may fluctuate based on market conditions, and indicative prices should be viewed as a starting point rather than a final quote.
By understanding these cost components, price influencers, and negotiation strategies, B2B buyers can make informed decisions when sourcing aluminium tin alloys, ensuring they achieve the best possible value for their investments.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing aluminium tin alloy With Other Solutions
Understanding Alternative Solutions to Aluminium Tin Alloy
In the realm of metal alloys, selecting the right material for specific applications can significantly impact performance, cost, and overall success. Aluminium tin alloy (Al-Sn) is a popular choice due to its unique properties, but it is essential to consider alternative solutions that might better suit particular needs. This analysis compares aluminium tin alloy with other viable alternatives, focusing on their performance, cost, ease of implementation, maintenance, and best use cases.
| Comparison Aspect | Aluminium Tin Alloy | Bronze Alloy | Aluminum-Magnesium Alloy |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | Excellent wear resistance and low friction properties | High corrosion resistance and good strength | Lightweight with good strength-to-weight ratio |
| Cost | Moderate | Higher due to copper content | Generally lower than Al-Sn and bronze |
| Ease of Implementation | Requires specific melting and alloying processes | Relatively straightforward casting | Easy to fabricate, widely available |
| Maintenance | Low maintenance; good durability | Moderate; can require protective coatings | Low; resistant to corrosion |
| Best Use Case | Bearings, automotive components | Marine applications, sculptures | Aircraft components, automotive parts |
In-Depth Analysis of Alternative Solutions
Bronze Alloy
Bronze, primarily composed of copper and tin, offers excellent corrosion resistance and strength. It is particularly effective in marine environments where exposure to saltwater is a concern. However, the higher cost associated with copper can be a deterrent for some applications. Additionally, while bronze has good machinability, it can require more maintenance than aluminium tin alloy due to its susceptibility to oxidation and wear in certain conditions.
Aluminum-Magnesium Alloy
Aluminum-magnesium alloys are known for their lightweight characteristics and good mechanical properties. They are easier to fabricate and widely available, making them a popular choice in various industries, including aerospace and automotive. The cost is generally lower than that of aluminium tin alloy and bronze, which makes it an attractive option for cost-sensitive applications. However, their corrosion resistance is not as strong as that of bronze or Al-Sn, which could limit their use in harsh environments.
How to Choose the Right Solution for Your Needs
When selecting an alloy for specific applications, B2B buyers should evaluate the unique requirements of their projects. Consider factors such as environmental exposure, required mechanical properties, budget constraints, and ease of manufacturing. Aluminium tin alloy is ideal for applications requiring low friction and wear resistance, while bronze excels in corrosion-prone environments. On the other hand, aluminum-magnesium alloys offer a lightweight solution with cost-effectiveness. By carefully weighing these aspects, buyers can make informed decisions that align with their operational goals and project specifications.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for aluminium tin alloy
What Are the Key Technical Properties of Aluminium Tin Alloys?
Aluminium tin alloys are recognized for their unique properties that enhance the performance of various industrial applications. Understanding these specifications is crucial for B2B buyers looking to optimize their production processes.
1. Material Grade
The material grade of aluminium tin alloys, such as AlSn50, indicates the specific composition and properties of the alloy. This grade signifies a mixture containing 50% tin and 50% aluminium, tailored for applications requiring enhanced wear resistance and low friction. Selecting the appropriate material grade is vital for ensuring the longevity and performance of components in industries such as automotive and aerospace.
2. Tensile Strength
Tensile strength refers to the maximum amount of tensile (stretching) stress that a material can withstand before failing. For aluminium tin alloys, this property is crucial, particularly in high-strength applications like structural components in buildings and vehicles. A higher tensile strength translates to a more durable product, reducing maintenance and replacement costs for manufacturers.
3. Hardness
The hardness of an aluminium tin alloy determines its resistance to deformation and wear. Measured using scales such as Brinell or Rockwell, hardness is essential for applications involving sliding components, such as bearings. A harder alloy can enhance the efficiency and lifespan of machinery, making it a preferred choice for industrial equipment.
4. Corrosion Resistance
Corrosion resistance is the ability of an alloy to withstand deterioration due to environmental factors, such as moisture and chemicals. Aluminium tin alloys exhibit excellent corrosion resistance, making them suitable for marine and chemical processing applications. This property is particularly important for B2B buyers who need reliable materials that can perform in harsh environments.
5. Machinability
Machinability refers to how easily a material can be machined to achieve desired shapes and finishes. Aluminium tin alloys are known for their good machinability, allowing for efficient processing and lower production costs. This characteristic is beneficial for manufacturers requiring precise components with tight tolerances.
What Are Common Trade Terms Related to Aluminium Tin Alloys?
Understanding industry-specific jargon is essential for effective communication and negotiation in the B2B marketplace.
1. OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
OEM refers to companies that produce parts or equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer. In the context of aluminium tin alloys, OEMs often require specific grades and specifications to meet their production needs. Buyers should consider the OEM requirements when sourcing materials to ensure compatibility and performance.
2. MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ is the smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell. This term is critical for B2B buyers as it impacts inventory management and cost efficiency. Understanding MOQ helps businesses plan their purchasing strategies and negotiate better terms with suppliers.
3. RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a document sent to suppliers requesting a quote for specific products or services. For aluminium tin alloys, providing detailed specifications in an RFQ can facilitate accurate pricing and timely responses from suppliers, streamlining the procurement process.
4. Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
Incoterms are standardized trade terms that define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in international transactions. Familiarity with Incoterms is essential for B2B buyers engaged in cross-border trade of aluminium tin alloys, as they dictate aspects such as shipping costs, risk, and delivery responsibilities.
5. Lead Time
Lead time is the period between the initiation of an order and its completion. This term is particularly important in manufacturing, where delays can impact production schedules. Buyers should inquire about lead times when ordering aluminium tin alloys to ensure they meet project deadlines.
By grasping these technical properties and trade terms, B2B buyers can make informed decisions, optimize their procurement strategies, and enhance their operational efficiency in working with aluminium tin alloys.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the aluminium tin alloy Sector
What Are the Key Trends and Market Dynamics Influencing the Aluminium Tin Alloy Sector?
The aluminium tin alloy market is currently experiencing notable growth, driven by increasing demand across various industries, including automotive, aerospace, and industrial machinery. One of the primary global drivers is the urgent need for lightweight, high-strength materials that can enhance fuel efficiency and reduce emissions in transportation sectors. The shift towards electric vehicles and advanced manufacturing techniques, such as additive manufacturing, further boosts the demand for specialized alloys that offer improved wear resistance and corrosion protection.
Emerging technologies in sourcing, such as blockchain for traceability and Artificial Intelligence for predictive analytics, are reshaping how international buyers engage with suppliers. This trend is particularly relevant for B2B buyers in regions like Africa and South America, where supply chain transparency is increasingly prioritized. Additionally, the rise of Industry 4.0 is pushing manufacturers to adopt smart technologies that improve production efficiency and reduce waste, appealing to environmentally conscious buyers.
In regions like the Middle East and Europe, regulatory frameworks are evolving to favor materials that meet stringent environmental standards, further driving the demand for aluminium tin alloys. This regulatory landscape presents an opportunity for international buyers to partner with suppliers who are agile and compliant with these emerging standards, ensuring a competitive edge in their respective markets.
How Does Sustainability and Ethical Sourcing Impact the Aluminium Tin Alloy Industry?
Sustainability and ethical sourcing are becoming central tenets in the aluminium tin alloy sector. The environmental impact of aluminium production, particularly in terms of energy consumption and emissions, is prompting buyers to seek suppliers who prioritize sustainable practices. Companies that invest in energy-efficient production methods or utilize recycled materials are gaining favor among B2B buyers looking to enhance their corporate social responsibility (CSR) profiles.
The significance of ethical supply chains cannot be overstated. Buyers are increasingly aware of the social implications of their sourcing decisions, including labor practices and community impact. Certifications such as ISO 14001 for environmental management and Fair Trade for ethical sourcing are becoming essential criteria for supplier selection.
Moreover, the push for “green” materials is leading to innovations in aluminium tin alloy formulations that reduce environmental impact without compromising performance. Suppliers that can demonstrate their commitment to sustainability through certifications and transparent practices are likely to be more competitive in the global marketplace.
What Is the Historical Context of Aluminium Tin Alloys in B2B Applications?
The use of aluminium tin alloys dates back several decades, primarily emerging in the aerospace and automotive industries due to their lightweight and corrosion-resistant properties. Historically, these alloys were developed to meet the rigorous performance standards required in high-stress applications, such as engine components and structural elements in aircraft.
As industries evolved, so did the applications for aluminium tin alloys. The introduction of advanced manufacturing techniques and a deeper understanding of alloy compositions have led to their increased use in diverse sectors, including marine and industrial equipment. Today, the aluminium tin alloy is not only recognized for its mechanical strength but also for its role in enhancing the sustainability of products in various applications, reflecting the sector’s ongoing evolution in response to market demands.
In summary, navigating the aluminium tin alloy market requires an understanding of current trends, a commitment to sustainability, and an appreciation for the historical context that shapes modern applications. B2B buyers who focus on these aspects will be better positioned to make informed sourcing decisions that align with their strategic objectives.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of aluminium tin alloy
-
1. How do I select the right aluminium tin alloy for my application?
Choosing the appropriate aluminium tin alloy requires a thorough understanding of your specific application requirements. Consider factors such as mechanical properties, corrosion resistance, and thermal conductivity. For instance, if your application demands high wear resistance, opt for an alloy with a higher tin content. Additionally, consult with suppliers to evaluate customization options that may enhance performance for particular industries such as automotive or aerospace. -
2. What are the key benefits of using aluminium tin alloy in manufacturing?
Aluminium tin alloys offer numerous advantages, including improved wear resistance and enhanced machinability. These alloys are particularly effective in reducing friction, making them ideal for components like bearings and bushings. Furthermore, they exhibit excellent corrosion resistance, especially in marine and chemical environments, which increases the longevity and reliability of manufactured parts. -
3. What should I consider when vetting suppliers of aluminium tin alloy?
When vetting suppliers, evaluate their experience in the aluminium industry, quality certifications, and production capabilities. Request samples to assess material quality and compliance with industry standards. Additionally, consider their track record in international trade, particularly in your region, and ensure they have a reliable logistics framework to handle timely deliveries. -
4. Are there minimum order quantities (MOQ) for aluminium tin alloys?
Minimum order quantities can vary significantly among suppliers. Some may impose a MOQ based on production efficiency, while others may offer flexibility for smaller orders. It’s essential to discuss your needs upfront with potential suppliers to understand their policies and negotiate terms that align with your purchasing strategy, particularly for international shipments. -
5. What payment terms are typically offered by aluminium tin alloy suppliers?
Payment terms vary by supplier and often depend on the order size and buyer-supplier relationship. Common terms include upfront payment, partial payment upon order confirmation, and balance upon delivery. For international transactions, consider factors like currency fluctuations and payment methods (e.g., letters of credit, wire transfers) to mitigate risks and ensure a smooth transaction process. -
6. How can I ensure quality assurance for my aluminium tin alloy purchases?
To guarantee quality assurance, request certificates of analysis (COA) from suppliers that detail the alloy’s composition and mechanical properties. Establish clear quality standards and inspection protocols before placing orders. Some suppliers may offer third-party testing services, which can further validate the quality of the materials you receive, ensuring they meet your specifications. -
7. What logistics considerations should I keep in mind when sourcing aluminium tin alloy internationally?
When sourcing internationally, consider shipping methods, customs regulations, and potential tariffs that may affect your total cost. Discuss logistics options with your supplier to determine the most efficient and cost-effective shipping routes. Additionally, ensure that the supplier can provide appropriate packaging to protect the alloy during transit, minimizing damage risks. -
8. How does the customization of aluminium tin alloys work?
Customization of aluminium tin alloys typically involves altering the alloy’s composition or form to meet specific application requirements. Suppliers may offer tailored ratios of tin to aluminium or provide various shapes and sizes based on your needs. Engage in detailed discussions with potential suppliers about your application’s demands and any performance criteria to ensure the customized alloy meets your expectations.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.
Top 8 Aluminium Tin Alloy Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. SAMaterials – Aluminum Tin Master Alloy
Domain: samaterials.com
Registered: 2013 (12 years)
Introduction: {“Product Name”: “Aluminum Tin Master Alloy”, “Catalog No.”: “AL1646”, “Shape”: “Ingot”, “Content”: “AlSn50 customized”, “Applications”: [{“Type”: “Hardeners”, “Description”: “Used for enhancing the physical and mechanical properties of metal alloys.”}, {“Type”: “Grain Refiners”, “Description”: “Used for controlling the dispersion of individual crystals in metals to produce a finer and more unifor…
2. Reddit – Aluminum vs. Tin: A Discussion on Sourcing and Applications
Domain: reddit.com
Registered: 2005 (20 years)
Introduction: The discussion revolves around the similarities and differences between aluminum and tin, with a focus on sourcing actual tin and its applications. Users mention that tin is more expensive than aluminum and is not commonly used due to its lower strength. Tin is noted as a main ingredient in pewter and is alloyed with copper to create bronze. Sources for tin include radiator shops and online retail…
3. Belmont Metals – Aluminum-Based Alloys
Domain: belmontmetals.com
Registered: 1997 (28 years)
Introduction: Aluminum-Based Alloys:
1. Scalmalloy:
– Overview: High-performance aluminum alloy for additive manufacturing.
– Nominal Composition: Al Bal, Mg 4%, Sc 0.7%, Mn 0.5%.
– Forms: Ingot Waffle.
– Features: Good weldability, high strength, low density.
2. 50/50 Magnesium Aluminum:
– Overview: Improves mechanical, fabrication, and welding characteristics of aluminum.
– Nominal …
4. ATTElements – Aluminium Tin Copper Alloy
Domain: attelements.com
Registered: 2022 (3 years)
Introduction: {“Product Code”: “AL-AlSnCu-NN-CU”, “Description”: “Aluminium Tin Copper Alloy, a high purity alloy used in automotive plain bearings and various deposition processes.”, “Applications”: “Used in automotive plain bearings, sputtering targets, Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD), Physical Vapor Deposition (PVD), water treatment, fuel cell, and solar applications.”, “Standard Powder Particle Sizes”: “- 3…
5. ResearchGate – Aluminium-Tin Alloy Preparation
Domain: researchgate.net
Registered: 2008 (17 years)
Introduction: This company, ResearchGate – Aluminium-Tin Alloy Preparation, is a notable entity in the market. For specific product details, it is recommended to visit their website directly.
6. Total Materia – Tin Applications
Domain: totalmateria.com
Registered: 2013 (12 years)
Introduction: Tin is a crucial industrial metal with applications in tinplate production, electroplating, solders, bearing materials, and various alloys. Key details include:
– Tinplate accounts for approximately 40% of world tin consumption, primarily used for food and beverage packaging.
– Electroplating utilizes tin in anodes and electrolytes, with applications in both acid and alkaline solutions.
– Solde…
7. Substech – Aluminum Bearing Materials
Domain: substech.com
Registered: 2007 (18 years)
Introduction: Aluminum based bearing materials provide a good combination of moderate fatigue strength and anti-friction properties. Key details include:
– Structure: Most have a bi-metal structure with a steel back and an aluminum-tin alloy layer.
– Cost: Less expensive than copper-based materials.
– Environmental: Contain no or low hazardous lead.
– Corrosion Resistance: Good corrosion resistance and low wear…
8. Britannica – Tin Processing
Domain: britannica.com
Registered: 1995 (30 years)
Introduction: Tin processing involves various applications and products, primarily categorized into traditional and new industrial uses. Key products include: 1. Tinplate: Accounts for about 30% of total tin consumption, made from steel with a tin coating, traditionally produced by hot-dipping but now mainly by continuous electroplating. Modern lines can produce up to 300,000 tons annually. 2. Tin and tin-alloy…
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for aluminium tin alloy
The strategic sourcing of aluminium tin alloys represents a vital opportunity for international buyers, particularly in regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. As industries increasingly seek materials that offer enhanced wear resistance, corrosion resistance, and improved mechanical properties, aluminium tin alloys emerge as an optimal choice. These alloys serve critical applications across sectors such as automotive, aerospace, and industrial equipment, making them indispensable for manufacturers aiming to elevate product performance.
By focusing on strategic sourcing, buyers can ensure access to high-quality aluminium tin alloys tailored to their specific requirements. This not only enhances production efficiency but also contributes to cost savings and energy efficiency throughout the supply chain. Engaging with reliable suppliers who offer customized solutions and robust support services can further streamline operations and drive competitive advantage.
Looking ahead, the demand for aluminium tin alloys is set to rise, driven by advancements in technology and a growing emphasis on sustainability in manufacturing processes. Now is the time for B2B buyers to capitalize on these trends by forging strong partnerships and investing in high-performance materials. Embrace the future of manufacturing by prioritizing strategic sourcing of aluminium tin alloys to stay ahead in a rapidly evolving market.