Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for alodine vs anodize
In today’s global manufacturing landscape, selecting the right aluminum finishing process—whether Alodine or anodize—can pose a significant challenge for B2B buyers, particularly those operating in diverse markets such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. Understanding the nuances between these two processes is essential for sourcing materials that meet specific performance requirements, especially when it comes to corrosion resistance, electrical conductivity, and overall cost-effectiveness.
This comprehensive guide delves into the critical differences between Alodine (chemical conversion coating) and anodizing (electrolytic process), providing insights into their respective applications across various industries, including aerospace, automotive, and electronics. Buyers will find detailed information on the types of coatings available, their unique advantages, and the considerations for selecting the right supplier. Moreover, the guide addresses key factors such as cost implications, technical expertise required, and the impact of each process on product specifications.
By equipping international B2B buyers with the knowledge needed to make informed decisions, this guide serves as a valuable resource for optimizing sourcing strategies and ensuring compliance with regional standards. As markets continue to evolve, understanding the intricacies of Alodine versus anodize will empower businesses to enhance their operational efficiency and competitive edge.
Understanding alodine vs anodize Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Alodine Type I | Hexavalent chromium-based coating, thicker, maximum corrosion protection | Aerospace, military, automotive | Pros: Superior corrosion resistance; Cons: Environmental concerns due to hexavalent chromium. |
| Alodine Type II | Non-hexavalent chromium coating, versatile, thinner than Type I | Electronics, automotive, marine | Pros: Environmentally friendly; Cons: Less corrosion protection than Type I. |
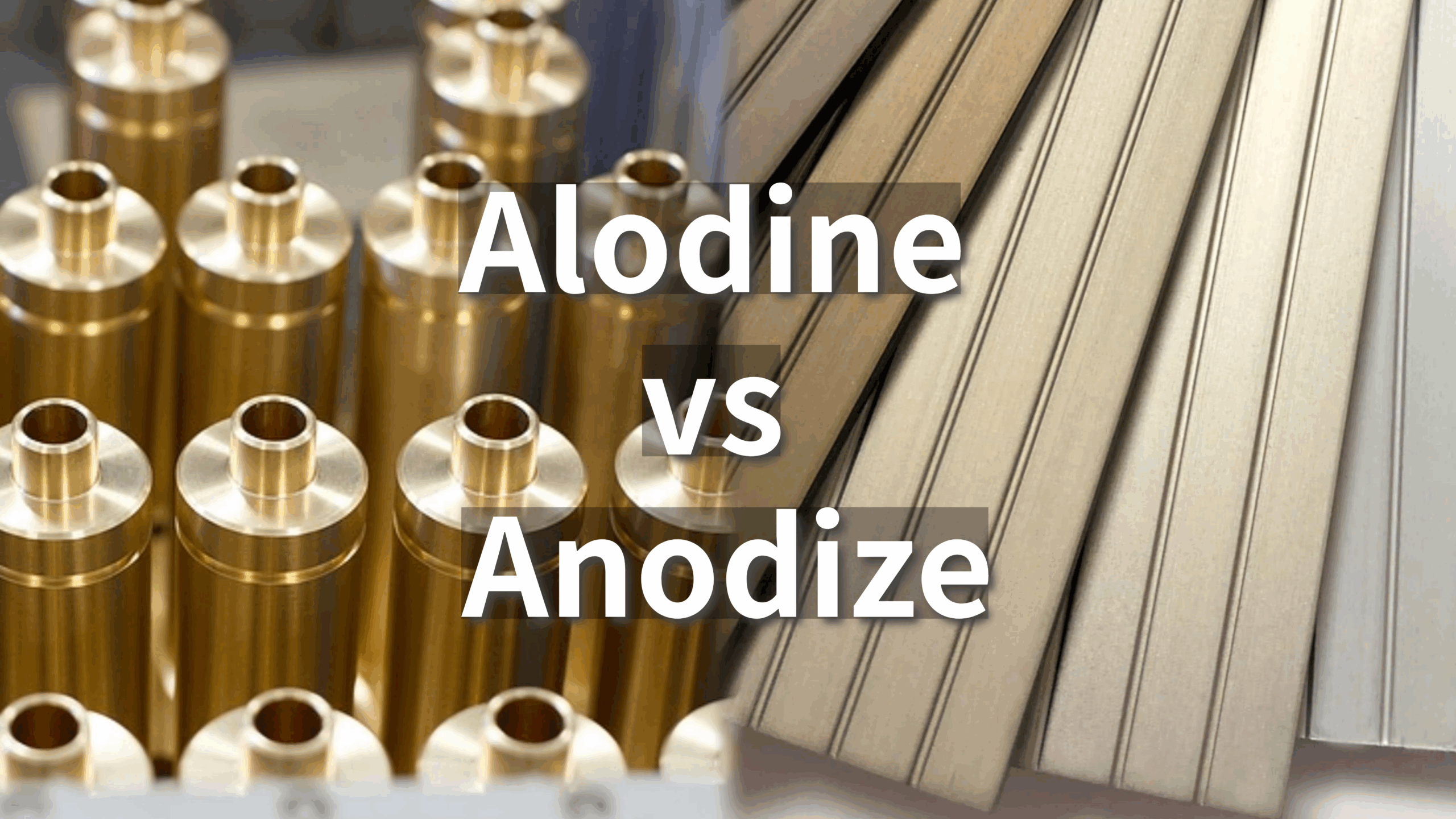
| Alodine Class 1A | Thick coating providing maximum protection, ideal for harsh environments | Aerospace, defense, marine | Pros: Excellent durability; Cons: May add weight to parts. |
| Alodine Class 3 | Thin coating, lightweight, designed for applications with low electrical resistance | Electronic components, heat sinks | Pros: Maintains conductivity; Cons: Limited corrosion protection compared to thicker coatings. |
| Anodizing Type II | Electrolytic process, enhances surface properties, allows for dyeing | Consumer products, aerospace, automotive | Pros: Improved corrosion resistance and aesthetics; Cons: Higher cost and technical expertise required. |
What Are the Characteristics of Alodine Type I and When Should It Be Used?
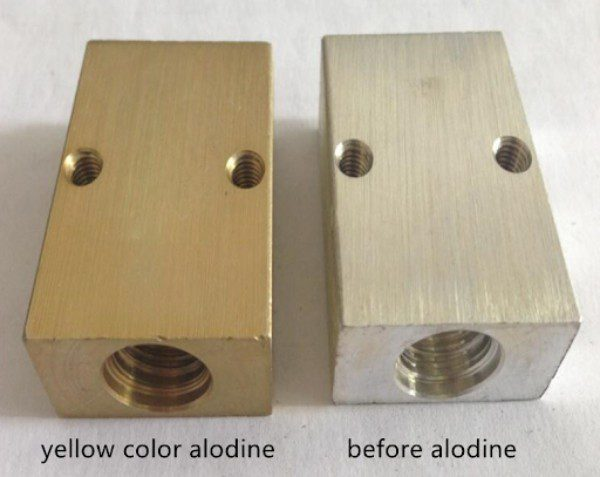
Alodine Type I is a chemical conversion coating that utilizes hexavalent chromium to create a thick, protective layer on aluminum surfaces. This type is particularly suited for industries where maximum corrosion resistance is critical, such as aerospace and military applications. Buyers should consider the environmental implications of using hexavalent chromium, as regulatory restrictions may apply in certain regions.
How Does Alodine Type II Differ from Other Variants?
Alodine Type II is a non-hexavalent chromium coating that offers versatility and environmental compliance. It is thinner than Type I, making it suitable for applications where weight is a concern, such as in electronics and automotive components. While it is more environmentally friendly, buyers should note that it may not provide the same level of corrosion protection as Type I.
What Makes Alodine Class 1A Ideal for Harsh Environments?
Alodine Class 1A coatings are known for their thickness and durability, making them ideal for harsh environments, particularly in aerospace and defense applications. This type offers superior corrosion protection but may add weight to the components. Buyers must balance the need for protection with potential weight constraints in their designs.
Why Choose Alodine Class 3 for Electrical Applications?
Alodine Class 3 coatings are designed to be thin and lightweight, making them perfect for electronic components and heat sinks where maintaining electrical conductivity is essential. While they offer less corrosion resistance than thicker coatings, their ability to retain conductivity makes them a preferred choice for applications requiring electrical grounding. Buyers should weigh the trade-off between protection and conductivity based on their specific needs.
What Are the Advantages of Anodizing Type II?
Anodizing Type II involves an electrolytic process that enhances the surface properties of aluminum, providing improved corrosion resistance and the option for dyeing. This process is widely used in consumer products and aerospace applications. However, it tends to be more expensive and requires a higher level of technical expertise for application. Buyers should consider the long-term benefits of anodizing, including aesthetics and durability, against the initial costs.
Key Industrial Applications of alodine vs anodize
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of alodine vs anodize | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Aerospace | Chem-film for aircraft components | Lightweight corrosion protection | Compliance with aerospace standards, lead times |
| Automotive | Anodized wheels and chassis parts | Enhanced durability and aesthetics | Cost-effectiveness, local regulations |
| Military & Defense | Chem-film on tactical equipment | Non-reactive surfaces for electronics | ISO certification, environmental impact considerations |
| Electronics | Anodized heat sinks and housings | Improved thermal management | Supplier reliability, technical support |
| Maritime | Chem-film for marine hardware | Resistance to saltwater corrosion | Material sourcing, compatibility with marine standards |
How is Alodine Used in Aerospace Applications?
In the aerospace sector, Alodine is frequently applied to aircraft components such as heat sinks, landing gear, and hulls. This chem-film process enhances corrosion resistance while maintaining the lightweight characteristics essential for aviation. The ability of Alodine to provide a non-reactive surface is crucial for parts that require electrical grounding. For international buyers, particularly in regions like Africa and the Middle East, ensuring compliance with stringent aerospace standards and certifications is vital when sourcing Alodine-treated components.
Why is Anodizing Preferred in Automotive Parts?
Anodizing is commonly utilized for automotive wheels and chassis parts, providing a durable finish that enhances both aesthetics and performance. The anodizing process improves corrosion resistance and allows for dyeing, which is particularly appealing for manufacturers looking to create visually striking products. For B2B buyers in South America and Europe, cost-effectiveness and adherence to local automotive regulations are critical factors when selecting anodized components. Additionally, the supplier’s technical expertise in anodizing can significantly impact the quality and longevity of the parts.
What Role Does Chem-film Play in Military Applications?
In military and defense industries, chem-film coatings are often applied to tactical equipment and vehicles. These coatings protect aluminum parts from corrosion without altering their dimensions, making them ideal for sensitive military applications. The non-reactive nature of Alodine is particularly beneficial for electronic components, ensuring reliable performance in challenging environments. Buyers from regions such as Saudi Arabia and Vietnam must consider suppliers that meet ISO certifications and can provide environmentally friendly options, given the increasing focus on sustainability in defense procurement.
How is Anodizing Utilized in Electronics?
Anodizing is essential in the electronics industry for components like heat sinks and housings. This process enhances thermal management by improving heat dissipation, which is critical for maintaining the performance of electronic devices. Moreover, anodized surfaces offer better adhesion for paints and adhesives, contributing to the overall durability of the products. For B2B buyers in Europe, supplier reliability and technical support are paramount, as the electronics sector often demands precise specifications and quick turnaround times.
Why is Chem-film Important for Maritime Hardware?
In maritime applications, chem-film coatings are applied to marine hardware to provide resistance against saltwater corrosion. This is crucial for components like fittings, fixtures, and other aluminum parts exposed to harsh marine environments. The lightweight nature of Alodine-treated components also contributes to fuel efficiency in vessels. For international buyers, especially in regions with significant maritime activities, compatibility with marine standards and sourcing considerations related to local environmental regulations are essential when procuring chem-film coated products.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘alodine vs anodize’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Understanding the Cost Implications of Alodine vs Anodize
The Problem: Many B2B buyers, especially in regions with limited technical expertise or resources, face challenges in understanding the cost implications of choosing between Alodine and anodizing processes. They often struggle with the pricing differences, which can lead to unexpected budget overruns. For instance, buyers might select anodizing due to its perceived superior quality without realizing that the costs associated with the electrolytic process, such as setup, maintenance, and skilled labor, can significantly inflate project expenses. This financial strain can ultimately affect their competitiveness in the market.
The Solution: To navigate these cost challenges, buyers should conduct a comprehensive cost-benefit analysis before making a decision. Begin by gathering detailed quotes from multiple suppliers for both Alodine and anodizing processes, ensuring to include all hidden costs such as setup fees, labor, and long-term maintenance. Additionally, consider the total lifecycle cost of the finished products. For example, if thermal or electrical conductivity is critical for your applications, Alodine may provide a more cost-effective solution while meeting your performance needs. Establishing clear specifications and requirements upfront can help ensure that you are comparing equivalent services, leading to more informed financial decisions.
Scenario 2: Navigating Technical Expertise Requirements
The Problem: B2B buyers often encounter difficulties due to the varying levels of technical expertise required for Alodine and anodizing processes. Anodizing, being an electrolytic process, typically requires specialized knowledge and equipment. Companies in regions with limited access to skilled technicians may find themselves unable to implement anodizing effectively, leading to poor quality finishes or compliance issues. This lack of expertise can result in costly rework or delays in production schedules.
The Solution: To mitigate this risk, buyers should invest in training for their workforce or partner with experienced suppliers who can provide technical support. Prioritize suppliers that offer comprehensive training programs and resources to help your team understand the nuances of both processes. Additionally, consider starting with Alodine, which has a lower barrier to entry in terms of technical expertise. By gradually building internal capabilities and understanding the specific requirements of each process, companies can confidently transition to more complex finishes like anodizing when they are ready.
Scenario 3: Determining the Right Application for Alodine or Anodize
The Problem: Another common pain point for B2B buyers is the challenge of selecting the appropriate finishing process based on the specific application of their aluminum components. For instance, a buyer in the aerospace sector might be uncertain whether to use Alodine or anodizing for components exposed to harsh environments. This uncertainty can lead to selecting a process that does not provide the necessary corrosion resistance or electrical insulation, jeopardizing product integrity and safety.
The Solution: To address this issue, buyers should perform a detailed assessment of their application requirements. This includes understanding environmental conditions, required mechanical properties, and regulatory compliance factors. Create a matrix that outlines the benefits of each process in relation to your specific needs. For example, if you require a surface finish that maintains electrical conductivity while providing corrosion resistance, Alodine may be the better choice. Engaging with industry experts or consulting engineering professionals can also provide valuable insights, ensuring you make an informed decision tailored to your application requirements. Furthermore, conducting trials with both finishes on test components can yield practical data to guide your choice confidently.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for alodine vs anodize
What Are the Key Properties of Alodine and Anodize in Material Selection?
When selecting between Alodine (chem film) and anodizing for aluminum finishing, understanding the key properties of each process is crucial for optimizing product performance.
Alodine (Chem Film):
Alodine coatings enhance aluminum’s natural corrosion resistance without significantly altering its dimensions. They are particularly effective in environments where electrical or thermal conductivity is required. The process involves immersing aluminum in a chemical solution, making it less complex and more cost-effective than anodizing. Alodine coatings can withstand temperatures up to 150°C and provide a barrier against saltwater corrosion, making them suitable for marine applications.
Anodizing:
Anodizing transforms the aluminum surface into a durable anodic oxide layer through an electrolytic process. This layer not only increases corrosion resistance but also enhances paint adhesion and electrical insulation properties. Anodized aluminum can typically endure higher temperatures (up to 200°C) compared to Alodine. However, the process is more complex, requiring specialized equipment and expertise, which can increase production costs.
What Are the Pros and Cons of Alodine vs Anodize?
Pros and Cons of Alodine:
– Pros:
– Cost-Effective: Alodine is generally less expensive than anodizing, making it an attractive option for budget-conscious projects.
– Ease of Application: The process is simpler and quicker, requiring less technical expertise.
– Preservation of Conductivity: Alodine allows aluminum to retain its electrical and thermal conductivity, which is essential for many applications.
- Cons:
- Lower Durability: While Alodine offers good corrosion resistance, it may not be as durable as anodized finishes in harsh environments.
- Limited Aesthetic Options: Alodine finishes typically do not offer the same range of colors and aesthetic options as anodizing.
Pros and Cons of Anodizing:
– Pros:
– Superior Durability: Anodizing provides a thicker, more protective layer that enhances resistance to wear and corrosion.
– Aesthetic Versatility: The anodizing process allows for dyeing, providing a variety of color options for aesthetic applications.
– Improved Adhesion: Anodized surfaces promote better adhesion for paints and adhesives, making it suitable for multi-layer applications.
- Cons:
- Higher Cost: The complexity of the anodizing process typically results in higher costs.
- Technical Expertise Required: Anodizing requires skilled personnel and specialized equipment, which can be a barrier for some manufacturers.
How Do Alodine and Anodize Impact Application Compatibility?
The choice between Alodine and anodizing significantly impacts application compatibility. Alodine is preferred in applications requiring electrical grounding, such as in military and aerospace sectors, where conductivity is crucial. Conversely, anodizing is ideal for applications where aesthetics and enhanced durability are paramount, such as in consumer electronics and automotive components.
What Specific Considerations Should International B2B Buyers Keep in Mind?
For international B2B buyers, particularly those in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, compliance with local and international standards is essential. Understanding the relevant standards, such as ASTM, DIN, and JIS, can help ensure that the selected finishing process meets industry requirements. Additionally, regional preferences may influence the choice of finishing process; for instance, buyers in maritime industries may lean towards Alodine due to its corrosion resistance in saltwater environments, while those in automotive sectors may prefer anodizing for its aesthetic qualities.
Summary Table of Material Selection for Alodine vs Anodize
| Material | Typical Use Case for Alodine vs Anodize | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Alodine | Aerospace components, electrical housings | Cost-effective, preserves conductivity | Lower durability compared to anodizing | Low |
| Anodize | Automotive parts, consumer electronics | Superior durability, aesthetic versatility | Higher cost, requires technical expertise | High |
| Alodine | Marine applications, tactical equipment | Quick application, less complex | Limited aesthetic options | Low |
| Anodize | Architectural finishes, decorative items | Enhanced paint adhesion, color options | More complex process, longer lead times | High |
This guide provides a comprehensive overview of the strategic material selection between Alodine and anodize, enabling B2B buyers to make informed decisions tailored to their specific applications and regional requirements.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for alodine vs anodize
What Are the Main Stages in the Manufacturing Process for Alodine and Anodize?
The manufacturing processes for Alodine (chem film) and anodizing share some similarities but diverge significantly in their execution. Both processes begin with material preparation, which involves cleaning the aluminum surfaces to remove any contaminants, oils, or existing coatings. This step is crucial for ensuring optimal adhesion of the finishing layers.
How Does the Forming Process Differ Between Alodine and Anodize?
Forming involves shaping aluminum components to their desired specifications. This stage can include machining, stamping, or extrusion. While both processes can utilize similar forming techniques, the choice of finishing method can influence the design specifications due to the differing properties imparted by each coating.
What Are the Key Techniques in the Finishing Stage for Alodine vs. Anodize?
-
Finishing for Alodine: The Alodine process utilizes a chemical conversion coating that does not require electrical current. The aluminum parts are typically immersed in a tank containing a chromate solution at room temperature. This creates a thin, protective layer that enhances corrosion resistance while maintaining electrical conductivity. Alodine can also be applied using methods such as spraying or brushing, which allows for more flexibility in application.
-
Finishing for Anodize: Anodizing, in contrast, is an electrolytic process that involves immersing aluminum in an electrolyte solution while an electrical current is applied. This transforms the surface into a thicker anodic oxide layer, significantly enhancing corrosion resistance and improving other properties such as adhesion for paints and adhesives. The anodizing process requires specialized equipment and technical expertise, making it generally more expensive than Alodine.
What Are the Key Quality Control Standards Relevant to Alodine and Anodize?
Quality control (QC) is critical in ensuring that both Alodine and anodized finishes meet international and industry-specific standards. Many manufacturers adhere to ISO 9001, which outlines a framework for quality management systems. Compliance with ISO standards is crucial for international buyers, as it ensures consistency and reliability in manufacturing processes.
Which Industry-Specific Standards Should B2B Buyers Consider?
Beyond ISO 9001, different industries may require adherence to specific standards:
– Aerospace: AS9100 for quality management systems.
– Automotive: IATF 16949, which focuses on defect prevention and reduction of variation.
– Defense: MIL-DTL-5541 for chemical conversion coatings.
Understanding these standards can help B2B buyers assess the credibility of suppliers and ensure that the products meet necessary specifications.
What Are Common Quality Control Checkpoints in the Manufacturing Process?
Quality control typically involves several checkpoints throughout the manufacturing process:
-
Incoming Quality Control (IQC): This initial stage involves inspecting raw materials before they enter the manufacturing process. For Alodine and anodize, this includes verifying the quality of the aluminum and any chemicals used in the finishing processes.
-
In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): During the manufacturing stages, continuous monitoring is performed to ensure that the processes are being executed correctly. This includes checking the conditions of the chemical baths and electrical systems for anodizing.
-
Final Quality Control (FQC): Once the finishing processes are complete, final inspections are conducted. This can include visual inspections, thickness measurements of the coating, and adhesion tests to ensure that the finishes meet the required specifications.
What Testing Methods Are Commonly Used for Alodine and Anodize?
Testing methods for quality assurance can vary but often include:
-
Thickness Measurement: Utilizing tools like micrometers or eddy current devices to ensure the coating thickness meets specifications.
-
Adhesion Tests: Conducting tape tests to evaluate how well the coating adheres to the aluminum substrate.
-
Corrosion Resistance Testing: Performing salt spray tests or other environmental exposure tests to determine the effectiveness of the protective coatings.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control?
To ensure that suppliers maintain high-quality standards, B2B buyers should consider the following verification methods:
-
Audits: Conducting on-site audits to review manufacturing processes and quality control measures in place. This provides insight into the supplier’s operational capabilities and adherence to standards.
-
Quality Reports: Requesting detailed QC reports, including test results and certifications, can provide assurance of compliance with international standards.
-
Third-Party Inspections: Engaging third-party inspection services can provide an unbiased evaluation of the supplier’s quality management systems and product integrity. This is particularly valuable for international buyers who may not have direct access to suppliers.
What Are the Quality Control Nuances for International Buyers?
For international B2B buyers, particularly those from regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, understanding local regulations and quality standards is essential. Different countries may have specific requirements for imports, including certifications and documentation that verify compliance with safety and quality standards.
Additionally, cultural differences may influence communication and expectations regarding quality. Establishing clear lines of communication with suppliers and understanding regional practices can facilitate smoother transactions and enhance trust between parties.
By gaining a comprehensive understanding of the manufacturing processes and quality assurance practices related to Alodine and anodize, B2B buyers can make informed decisions that align with their operational needs and compliance requirements. This knowledge not only helps mitigate risks but also fosters long-term partnerships with reliable suppliers.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘alodine vs anodize’
This practical sourcing guide is designed to assist B2B buyers in making informed decisions when procuring aluminum finishing services, specifically comparing Alodine (chem film) and anodizing processes. By following this checklist, buyers can ensure they select the right option that meets their technical requirements, budget constraints, and operational needs.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Clearly outline the technical requirements of your project, including desired properties like corrosion resistance, electrical conductivity, and surface finish. Understanding these specifications will guide your decision between Alodine and anodizing, as each process offers unique benefits suited to different applications.
- Corrosion Resistance: Determine the level of corrosion protection needed based on environmental exposure.
- Electrical Conductivity: If conductivity is critical, Alodine may be preferable since it does not inhibit electrical flow.
Step 2: Assess Your Budget Constraints
Establish your budget for the finishing process. Anodizing is generally more expensive due to its complex electrolytic process and higher technical requirements. In contrast, Alodine offers a cost-effective solution without compromising essential protective qualities.
- Cost Comparison: Gather quotes from multiple suppliers for both processes to identify the best option within your budget.
- Long-term Value: Consider the longevity and maintenance costs associated with each finish, as these factors can impact overall expenditure.
Step 3: Evaluate Potential Suppliers
Research and vet suppliers thoroughly to ensure they have the capability and expertise to meet your specifications. Request company profiles, case studies, and references from buyers in similar industries or regions.
- Supplier Experience: Look for suppliers with a proven track record in either Alodine or anodizing, especially within your specific industry.
- Certifications: Verify that suppliers hold relevant certifications, such as ISO standards, which indicate adherence to quality management practices.
Step 4: Request Samples and Test Results
Before finalizing your decision, ask potential suppliers for samples of their work or test results that demonstrate the effectiveness of their finishing processes. This will allow you to evaluate the quality and suitability of the coatings for your needs.
- Performance Testing: Consider requesting independent lab test results that verify corrosion resistance and other key performance metrics.
- Trial Runs: If possible, conduct trial runs with your components to assess compatibility and performance firsthand.
Step 5: Understand Lead Times and Capacity
Inquire about the lead times associated with each finishing process. Anodizing typically requires longer processing times due to its complexity, while Alodine can be applied more quickly. Understanding lead times will help you align your production schedules accordingly.
- Production Capacity: Ensure that the supplier can handle your order volume and deadlines without compromising quality.
- Scalability: Consider whether the supplier can accommodate future increases in demand or additional projects.
Step 6: Review Post-Finishing Support and Services
Evaluate the post-finishing support offered by suppliers, including warranties, maintenance recommendations, and rework options. This support can be critical in ensuring the longevity and performance of your finished products.
- Warranty Policies: Understand the terms of any warranties provided and what they cover in terms of defects or performance issues.
- Technical Assistance: Check if the supplier offers ongoing support for troubleshooting or technical inquiries related to the finishing process.
By following this checklist, B2B buyers can make informed decisions that enhance their procurement strategies for aluminum finishing, whether choosing Alodine or anodizing.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for alodine vs anodize Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components for Alodine and Anodizing Processes?
When evaluating the cost structure for Alodine (chem film) and anodizing, several components come into play. For both processes, the primary cost factors include materials, labor, manufacturing overhead, tooling, quality control (QC), logistics, and profit margins.
Materials: Alodine typically requires less expensive chemical solutions compared to anodizing, which necessitates specialized electrolytic baths and chemicals. This difference can lead to significant cost savings, particularly for large-scale operations.
Labor: Anodizing requires skilled labor due to the technical expertise involved in the electrolytic process. In contrast, Alodine application is less complex, often requiring fewer skilled personnel, which can reduce labor costs.
Manufacturing Overhead: The equipment needed for anodizing is generally more expensive and requires higher energy consumption, contributing to greater manufacturing overhead. Alodine processes, being simpler and less energy-intensive, can mitigate these costs.
Tooling and Quality Control: Both processes necessitate investment in tooling, but anodizing may require more sophisticated equipment for surface preparation and finishing. QC measures are critical for both methods to ensure compliance with industry standards, influencing overall costs.
Logistics: Shipping costs can vary based on the weight and volume of the treated parts. Alodine’s lighter coatings may result in lower shipping costs compared to anodized components, which can be bulkier depending on the application.
Margin: Suppliers often have higher margins on anodized products due to the added value of enhanced durability and aesthetic appeal. Understanding these margins can help buyers negotiate better pricing.
What Price Influencers Should International B2B Buyers Consider?
Several factors influence pricing, particularly for international buyers from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe.
Volume/MOQ: Pricing can significantly vary based on order volume. Bulk orders often lead to discounted rates. Understanding the minimum order quantity (MOQ) is crucial for buyers looking to optimize costs.
Specifications and Customization: Custom specifications can raise costs, especially for anodizing, which requires tailored processes. Buyers should clearly define their needs to avoid unexpected charges.
Materials and Quality Certifications: The quality of materials used in both processes affects pricing. Anodized products may require more stringent certifications, leading to higher costs. Buyers should consider the importance of certifications in their industry.
Supplier Factors: The reputation and reliability of suppliers can influence price. Established suppliers may charge more due to their proven track record, while less experienced vendors might offer lower prices but come with higher risks.
Incoterms: Understanding Incoterms is vital for international transactions, as they determine who is responsible for shipping costs, insurance, and tariffs. This knowledge can help buyers calculate total landed costs more accurately.
What Are the Key Buyer Tips for Cost-Efficiency in Alodine vs Anodize Sourcing?
To maximize cost-efficiency, buyers should consider the following tips:
- Negotiate Wisely: Always negotiate terms with suppliers. Leverage volume and long-term relationships to secure better pricing.
- Assess Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Evaluate not just the initial costs but also maintenance, longevity, and performance of coatings. Anodized parts may last longer, potentially offsetting higher upfront costs.
- Understand Pricing Nuances for International Markets: Different regions may have varying standards and expectations. Be mindful of local market conditions, currency fluctuations, and import duties.
- Explore Local Suppliers: Engaging local suppliers can reduce logistics costs and lead times. This is particularly important for regions with limited access to specific finishing technologies.
- Request Samples: Before committing to large orders, request samples to evaluate quality and suitability. This practice can prevent costly mistakes down the line.
Disclaimer on Indicative Prices
It is essential to note that prices for Alodine and anodizing can vary widely based on specific project requirements, market conditions, and supplier capabilities. Buyers are encouraged to obtain detailed quotes tailored to their unique needs to ensure accurate budgeting and sourcing decisions.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing alodine vs anodize With Other Solutions
Exploring Alternatives for Aluminum Finishing: Alodine vs Anodize and Beyond
When selecting a surface treatment for aluminum components, understanding the various options available is essential for B2B buyers. Alodine and anodize are two popular methods known for enhancing corrosion resistance and other functional properties. However, there are alternative solutions that may better suit specific needs depending on performance requirements, cost constraints, and application contexts.
Comparison Table
| Comparison Aspect | Alodine Vs Anodize | Powder Coating | Electrophoretic Deposition (EPD) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | Good corrosion resistance; retains conductivity | Excellent durability; wide color range | High corrosion resistance; smooth finish |
| Cost | Lower cost; affordable for large volumes | Moderate to high cost | Moderate cost; varies by complexity |
| Ease of Implementation | Easier application; less technical expertise required | Requires skilled application; curing process needed | More complex setup; requires equipment |
| Maintenance | Minimal; easy to inspect | Moderate; can chip or scratch | Low; resistant to wear and chemicals |
| Best Use Case | Aerospace, electrical applications | Automotive, consumer goods | Marine, industrial equipment |
Detailed Breakdown of Alternatives
1. Powder Coating
Powder coating is a finishing process where a dry powder is applied electrostatically and then cured under heat. This method provides an exceptionally durable finish that is resistant to scratching, chipping, fading, and wearing. While the initial investment may be higher due to the need for specialized equipment and skilled labor, powder coating allows for a broad range of colors and textures, making it ideal for aesthetic-focused applications in the automotive and consumer goods industries. However, if the coating is damaged, it can be challenging to repair compared to other options.
2. Electrophoretic Deposition (EPD)
Electrophoretic deposition is a process where particles are deposited onto a substrate using an electric field. This technique can produce a uniform coating that is highly resistant to corrosion and wear, making it suitable for components exposed to harsh environments, such as marine or industrial applications. While EPD offers superior performance, it requires specialized equipment and a thorough understanding of the process, which could lead to higher upfront costs. Additionally, EPD can create a smoother finish than both Alodine and anodizing, which is beneficial for certain applications.
Conclusion: How to Choose the Right Aluminum Finishing Solution
Selecting the appropriate aluminum finishing method depends on various factors, including the specific requirements of the project, budget constraints, and the desired aesthetic qualities. For applications where electrical conductivity is crucial, Alodine may be the best choice due to its affordability and ease of application. Conversely, anodizing is preferable for components requiring enhanced durability and corrosion resistance, despite the higher costs and technical demands. Alternatives such as powder coating and electrophoretic deposition offer distinct advantages in terms of durability and finish quality but come with their own sets of challenges. By carefully evaluating these aspects, B2B buyers can make informed decisions that align with their operational goals and project specifications.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for alodine vs anodize
What Are the Key Technical Properties of Alodine and Anodize?
When considering aluminum finishing options, understanding the technical properties of Alodine (chem film) and anodizing is crucial for making informed purchasing decisions. Here are several key specifications that B2B buyers should be aware of:
-
Corrosion Resistance
Both Alodine and anodizing enhance aluminum’s natural corrosion resistance, but they achieve this through different mechanisms. Anodizing creates a thicker oxide layer that provides superior protection, especially in harsh environments. For industries like aerospace and automotive, where durability is paramount, selecting the right finish can significantly impact a component’s lifespan and reliability. -
Electrical Conductivity
Alodine coatings allow aluminum to retain its electrical conductivity, making them ideal for components that require grounding or electrical connections. In contrast, anodizing insulates the surface, which can be beneficial for certain applications but may not be suitable where conductivity is required. Buyers must assess their specific requirements to avoid operational failures. -
Cost Efficiency
Alodine processes tend to be less expensive and faster than anodizing due to their simpler application methods and lower technical requirements. For manufacturers looking to minimize costs without compromising quality, Alodine may be the preferred choice. Understanding the total cost of ownership, including application time and material handling, is vital for budget-conscious projects. -
Thickness and Weight
Anodizing typically adds a thicker layer to the aluminum surface compared to Alodine. This added thickness can improve wear resistance but may also increase the weight of the part, which is critical in aerospace and automotive applications. Buyers should evaluate the trade-offs between enhanced performance and weight considerations, especially in applications where weight savings are essential. -
Surface Preparation and Paint Adhesion
Both finishes provide a surface that promotes paint adhesion, but the methods of achieving this differ. Alodine is often used as a primer to prepare aluminum for painting, while anodized surfaces can also be painted but may require additional preparation. Understanding the nuances of surface treatment can influence the choice based on final application needs.
What Are Common Trade Terms Related to Alodine and Anodize?
Navigating the procurement process for Alodine and anodizing services involves familiarizing oneself with industry terminology. Here are several essential trade terms that B2B buyers should know:
-
OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
An OEM is a company that produces parts or equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer. When sourcing aluminum components, understanding the OEM’s specifications is crucial for ensuring compatibility and performance within your assembly. -
MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ refers to the smallest order quantity that a supplier is willing to accept. This term is particularly important for B2B buyers, as it can influence purchasing decisions and inventory management. Understanding MOQs helps businesses plan their procurement strategies and manage cash flow effectively. -
RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a formal process in which a buyer requests pricing and terms from suppliers for specific products or services. This document is crucial for comparing multiple vendors and ensuring that all proposals meet the required specifications and standards. -
Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
Incoterms are a set of internationally recognized rules that define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in shipping goods. Familiarity with these terms helps businesses understand shipping costs, risks, and obligations, which is essential for international trade, especially in regions like Africa and South America. -
Lead Time
Lead time refers to the amount of time it takes from placing an order to receiving the finished product. This term is crucial for project planning, as extended lead times can impact production schedules and delivery commitments.
By grasping these technical properties and trade terms, B2B buyers can navigate the complexities of selecting between Alodine and anodizing, ensuring that they make informed decisions that align with their operational requirements and budget constraints.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the alodine vs anodize Sector
What Are the Key Market Dynamics Influencing Alodine and Anodize Sourcing?
The global market for aluminum surface finishing is experiencing significant growth driven by increasing demand across various industries, particularly aerospace, automotive, and electronics. The Alodine (chem film) and anodize processes are pivotal in enhancing aluminum’s corrosion resistance and durability. Key trends include the rising preference for Alodine due to its cost-effectiveness and ease of application, particularly in regions where technical expertise may be limited. Additionally, the anodizing process is gaining traction as industries seek enhanced performance characteristics, such as improved electrical insulation and paint adhesion.
In emerging markets such as Africa and South America, the demand for affordable yet effective surface treatments has led to a surge in Alodine applications, especially in sectors like defense and automotive. Conversely, in developed regions like Europe and the Middle East, there is a growing inclination towards anodizing, attributed to its superior aesthetic and functional properties. These dynamics create a diverse landscape for international B2B buyers, necessitating careful consideration of the specific needs of their applications when sourcing these finishing processes.
How Is Sustainability Shaping Sourcing Practices in the Alodine vs. Anodize Market?
Sustainability is becoming a central theme in the sourcing of aluminum finishing processes. The environmental impact of both Alodine and anodizing processes is under scrutiny, especially regarding waste management and the use of hazardous materials. Anodizing, while effective, often involves the use of chemical agents that can be harmful if not managed properly. In contrast, Alodine processes can be less environmentally taxing, particularly when using hexavalent chromium-free solutions, which are gaining popularity.
B2B buyers are increasingly prioritizing ethical sourcing practices, demanding transparency in the supply chain. Suppliers that can demonstrate compliance with ‘green’ certifications, such as ISO 14001 or RoHS, stand out in the marketplace. Additionally, sourcing Alodine or anodizing services from suppliers who utilize eco-friendly materials and processes aligns with the growing emphasis on corporate social responsibility. For buyers from regions like the Middle East and Europe, where regulatory frameworks are stringent, ensuring that suppliers meet these sustainability standards is crucial for maintaining compliance and enhancing brand reputation.
What Is the Historical Context of Alodine and Anodize Processes?
The use of aluminum surface finishing processes dates back to the mid-20th century, driven by the material’s lightweight and corrosion-resistant properties. The anodizing process was developed as a way to enhance these characteristics through an electrolytic treatment that creates a thicker aluminum oxide layer. Alodine, or chem film, emerged as an alternative, offering a simpler and more cost-effective solution for industries requiring basic corrosion protection without altering the aluminum’s electrical properties.
Over the decades, advancements in technology and materials have refined both processes, leading to the development of more environmentally friendly formulations and methods. As industries evolve, the historical significance of these processes continues to shape their applications, influencing sourcing decisions for B2B buyers navigating the complexities of global markets.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of alodine vs anodize
-
How do I choose between Alodine and anodizing for my aluminum components?
Choosing between Alodine (chem film) and anodizing primarily depends on your specific application needs. If electrical or thermal conductivity is essential, Alodine is preferable, as it allows these properties to remain intact. Conversely, anodizing provides enhanced corrosion resistance and improved adhesion for paints, making it suitable for environments where aesthetic finishes are critical. Evaluate factors such as cost, technical expertise required, and the specific environmental conditions your components will face to make an informed decision. -
What is the best finishing option for aerospace applications: Alodine or anodizing?
For aerospace applications, both Alodine and anodizing offer unique benefits. Alodine is often favored for its ability to maintain electrical conductivity and provide a lightweight, corrosion-resistant coating. Anodizing, however, enhances durability and provides superior corrosion protection, making it ideal for components exposed to harsh environments. Ultimately, the best option will depend on the specific requirements of your aerospace components, including weight, conductivity, and environmental exposure. -
What are the typical lead times for Alodine and anodizing processes?
Lead times for Alodine and anodizing can vary significantly based on the supplier and the complexity of the order. Generally, Alodine processes are faster, often completed within a few days due to their simpler application. Anodizing may take longer, typically ranging from several days to a few weeks, depending on the desired finish and volume of parts. It’s advisable to discuss timelines with your supplier early in the procurement process to align expectations with project deadlines. -
What should I consider when vetting suppliers for Alodine or anodizing services?
When vetting suppliers, consider their experience in the specific coating process you require. Look for certifications such as ISO to ensure quality standards are met. Inquire about their technical expertise, equipment capabilities, and previous projects. Additionally, request samples or case studies to assess their work quality. Communication and customer support should also be evaluated to ensure a smooth partnership, especially for international transactions. -
What are the minimum order quantities (MOQ) for Alodine and anodizing services?
Minimum order quantities can vary by supplier and the specific coating process. Alodine services may have lower MOQs due to the simpler application, while anodizing might require higher quantities to justify setup costs. It’s crucial to discuss your project requirements with potential suppliers to determine their MOQs and negotiate terms that suit your needs. This is particularly important for B2B buyers in regions with fluctuating demand. -
What payment terms should I expect when sourcing Alodine or anodizing services internationally?
Payment terms for international sourcing can vary widely based on the supplier’s policies and your negotiation. Common terms include upfront deposits, payment upon delivery, or net payment terms (e.g., net 30, net 60). Be prepared to discuss and negotiate these terms, keeping in mind factors such as order size, supplier reputation, and your company’s cash flow needs. Additionally, consider using secure payment methods to mitigate risks associated with international transactions. -
How do quality assurance processes differ between Alodine and anodizing services?
Quality assurance processes for Alodine and anodizing typically involve rigorous testing and inspection to ensure the coatings meet industry standards. Anodizing often requires more extensive quality checks due to the complexity of the electrolytic process, including thickness measurements and adhesion tests. Alodine services may focus on visual inspections and corrosion resistance tests. Ensure that your chosen supplier has a robust QA program in place, including documentation and compliance with relevant standards. -
What logistical considerations should I keep in mind when sourcing these services internationally?
When sourcing Alodine or anodizing services internationally, consider shipping times, customs regulations, and potential tariffs that may apply to your order. It’s important to work with suppliers who have experience in international logistics to ensure smooth transportation of your components. Additionally, clarify the terms of delivery (e.g., FOB, CIF) to understand who is responsible for shipping costs and risks at various points. Proper logistical planning will help avoid delays and additional costs in your procurement process.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.
Top 9 Alodine Vs Anodize Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. Best Technology Inc – Aluminum Finishing Solutions
Domain: besttechnologyinc.com
Registered: 2001 (24 years)
Introduction: Alodine (chem film) and anodizing are both processes used in aluminum finishing to improve corrosion resistance. The primary difference is that anodizing is an electrolytic process requiring electrical current, while Alodine is not. Anodizing is generally more expensive and requires greater technical expertise. Alodine is less expensive, requires less technical expertise, and allows aluminum to re…
2. Gabrian – Alodine Finish
Domain: gabrian.com
Registered: 2000 (25 years)
Introduction: Alodine finish is a type of conversion coating for aluminum that creates a thin protective film to prevent corrosion while allowing electrical conductivity. It is often used in the electronics industry and is interchangeable with terms like chromate conversion coating and chem film. The Alodine® product is a registered trademark of Henkel, Inc., and similar products include Iridite 14-2®. The proc…
3. Chem Research Co – Chem-Film & Anodize Solutions
Domain: chemresearchco.com
Registered: 1998 (27 years)
Introduction: Chem-Film (Alodine) and Anodize are two aluminum coating processes that enhance corrosion resistance. Chem-Film is a chemical conversion coating that protects aluminum without altering dimensions, is less expensive, and easier to apply, retaining thermal and electrical conductivity. It is suitable for various industries including aerospace and military, and is used for heat sinks, aircraft hulls, …
4. CNC Parts XTJ – Alodine Corrosion Inhibitor
Domain: cncpartsxtj.com
Registered: 2019 (6 years)
Introduction: Alodine is a corrosion inhibitor used as a passivation process for aluminum and other metals. It is a water-soluble, organic compound that forms a protective barrier against corrosion. Alodine is applied as a chromate conversion coating, enhancing durability without altering the metal’s characteristics. It is suitable for various metals including stainless steel, copper, aluminum, brass, and bronz…
5. Sunrise Metal – Alodine Passivation Solution
Domain: sunrise-metal.com
Registered: 2015 (10 years)
Introduction: Alodine: A passivation technique suitable for internal parts of aluminum projects. Advantages include lower cost, improved corrosion and scratch protection, good electrical and thermal conductivity, no need for primer, and minimal skill required. Disadvantages include easy removal, micro-defects, environmental concerns, and potential skin irritation. Anodizing: An electrolytic process that creates…
6. Practical Machinist – Anodizing & Alodizing Solutions
Domain: practicalmachinist.com
Registered: 2000 (25 years)
Introduction: 1) Anodizing: An electro-chemical process that increases the natural oxide layer (Al2O3) on aluminum parts by submerging them in an acid bath and applying electric current. 2) Alodizing: A proprietary term for a chemical treatment using Alodine solution, which provides a light anti-oxidizing coating and improves paint adhesion. 3) Cost for anodizing typically starts at $75 minimum, with prices ran…
7. Eng-Tips – Aerospace Surface Treatment Solutions
Domain: eng-tips.com
Registered: 1997 (28 years)
Introduction: 2024-T3 bare anodize and Alodine are two surface treatment options for aerospace parts. The part in question was originally intended to be made from 2024-T3 alclad but was made from 2024-T3 bare. The specifications allow for anodic coating per Mil-A-8625 or Alodined per Mil-C-5541, followed by one coat of primer. Previous batches were alodined, and the user seeks justification for using chromic an…
8. Tuofa – Alodine and Anodize Finishing Solutions
Domain: tuofa-cncmachining.com
Registered: 2022 (3 years)
Introduction: Alodine and anodize are two types of finishing processes for aluminum. Alodine, also known as chromate conversion or chemical film, is a chemical process that creates a protective layer on aluminum objects without using electric current. It involves cleaning the aluminum and immersing it in a chemical bath at room temperature, resulting in a thin film of chromium. Alodine is economical, retains el…
9. Jiga – Alodining Solutions
Domain: jiga.io
Registered: 2020 (5 years)
Introduction: Alodining (chromate conversion) is a chemical treatment for Aluminum and some metals to enhance corrosion resistance and improve paint adhesion. It is used in aerospace, automotive, electronics, and military applications. Alodine creates a thin, electrically conductive coating ideal for precision parts. Common types include Alodine 1200, 1000, and 600 series, with Alodine 871 being hex-free. Anodi…
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for alodine vs anodize
What Are the Key Takeaways for B2B Buyers in Choosing Between Alodine and Anodize?
In the competitive landscape of metal finishing, understanding the nuances between Alodine and anodizing is essential for making informed purchasing decisions. Alodine (chem film) offers cost-effectiveness, ease of application, and the ability to retain electrical and thermal conductivity, making it ideal for industries that require quick turnaround and specific electrical properties. Conversely, anodizing provides superior corrosion resistance and aesthetic options through dyeing, but demands higher investment and technical expertise.
How Can Strategic Sourcing Enhance Your Supply Chain?
For B2B buyers in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, strategic sourcing of these finishing processes can lead to significant cost savings and operational efficiencies. By evaluating suppliers based on their expertise in either Alodine or anodizing, companies can tailor their sourcing strategies to align with project requirements, ensuring optimal performance and compliance with international standards.
What’s Next for International Buyers?
As markets evolve, the demand for specialized aluminum finishing solutions will continue to grow. International buyers should stay abreast of technological advancements and supplier innovations in both Alodine and anodizing processes. Engage with experienced providers to assess how these coatings can meet your specific needs and enhance your product offerings. Consider initiating discussions with potential suppliers today to leverage the benefits of strategic sourcing in your operations.