Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for alodine process
In today’s competitive landscape, sourcing effective solutions for aluminum corrosion protection, such as the Alodine process, presents a significant challenge for international B2B buyers. The Alodine process, also known as chromate conversion coating, is essential for enhancing the durability and reliability of aluminum components across various industries, including aerospace, electronics, and medical devices. This comprehensive guide explores the diverse applications of Alodine, the different types of coatings available, and the critical factors to consider when selecting a supplier.
As a B2B buyer, understanding the nuances of the Alodine process can empower you to make informed purchasing decisions that align with your operational needs and regulatory requirements. This guide will delve into the specific applications of Alodine in industries prevalent in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, highlighting how to effectively vet suppliers to ensure compliance with international standards. Additionally, it will cover cost considerations and the implications of environmental regulations on sourcing decisions.
By equipping you with actionable insights and expert knowledge, this guide aims to simplify the procurement process, ensuring that you choose the right Alodine solutions that not only enhance performance but also deliver value to your organization. Navigate the global market with confidence and secure the longevity and integrity of your aluminum products through effective Alodine applications.
Understanding alodine process Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Alodine 1200 | Offers a clear finish, suitable for electrical conductivity. | Aerospace, electronics, telecommunications | Pros: Excellent adhesion and conductivity. Cons: Limited to specific applications. |
| Alodine 6000 | Provides a thicker coating for enhanced corrosion resistance. | Automotive, military, industrial equipment | Pros: Superior corrosion protection. Cons: May affect surface dimensions. |
| Alodine 1500 | Trivalent chromium-based, more environmentally friendly. | Medical devices, consumer electronics | Pros: Reduced environmental impact. Cons: May have lower performance in extreme conditions. |
| Alodine 2000 | Designed for high-temperature applications with enhanced durability. | Aerospace, high-performance automotive | Pros: Exceptional thermal stability. Cons: Higher cost compared to standard options. |
| Alodine 2500 | Provides a non-conductive finish, ideal for insulating applications. | Electronics, electrical components | Pros: Prevents electrical conductivity issues. Cons: Not suitable for all metal types. |
What are the Characteristics of Alodine 1200 and Its Applications?
Alodine 1200 is characterized by its clear finish, which is essential for applications requiring electrical conductivity. This type of chromate conversion coating is prevalent in industries such as aerospace and telecommunications, where both corrosion resistance and electrical performance are critical. When purchasing, buyers should consider the specific conductivity requirements of their components, ensuring that Alodine 1200 aligns with their operational needs.
How Does Alodine 6000 Enhance Corrosion Resistance?
Alodine 6000 is recognized for its thicker coating that significantly enhances corrosion resistance, making it ideal for demanding environments like automotive and military applications. Buyers should evaluate the intended use of their aluminum parts, especially in harsh conditions, to determine if the added thickness and protection justify any potential dimensional changes during the coating process.
Why Choose Alodine 1500 for Environmentally Friendly Solutions?
Alodine 1500 utilizes trivalent chromium, providing an environmentally friendly alternative to traditional chromate coatings. This option is increasingly favored in industries such as medical devices and consumer electronics, where sustainability is a priority. Buyers should weigh the environmental benefits against the coating’s performance in specific applications, especially under extreme conditions.
What Makes Alodine 2000 Suitable for High-Temperature Applications?
Alodine 2000 is specifically designed to withstand high temperatures, making it suitable for aerospace and high-performance automotive applications. Its exceptional thermal stability is a key feature for parts that experience significant heat during operation. Buyers should assess the thermal requirements of their projects to ensure that Alodine 2000 meets their performance expectations.
When to Use Alodine 2500 for Electrical Insulation?
Alodine 2500 offers a non-conductive finish, making it ideal for insulating applications in electronics and electrical components. This variation is crucial for preventing electrical conductivity issues that could lead to component failure. Buyers should consider the electrical properties of their components and whether a non-conductive finish aligns with their design specifications.
Key Industrial Applications of alodine process
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of alodine process | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Aerospace | Corrosion protection for aircraft components | Enhances durability and compliance with stringent standards | Certification compliance (e.g., MIL-DTL-5541), reliability of suppliers |
| Electronics | Surface treatment for circuit boards | Ensures electrical conductivity and corrosion resistance | Quality assurance, testing for adhesion and conductivity |
| Medical Devices | Coating for surgical instruments and devices | Increases lifespan and ensures biocompatibility | Regulatory compliance, traceability of materials |
| Automotive | Protection of aluminum chassis and components | Reduces maintenance costs and improves safety | Compatibility with paint systems, environmental regulations |
| Telecommunications | Coating for hardware exposed to harsh environments | Improves performance and longevity of electronic components | Supplier reliability, testing for environmental resistance |
How is the Alodine Process Applied in Aerospace?
In the aerospace industry, the Alodine process is primarily used for corrosion protection on aircraft components, such as aluminum chassis and brackets. This treatment not only enhances the durability of parts but also ensures compliance with strict military and aerospace standards, such as MIL-DTL-5541. Buyers in this sector must focus on sourcing suppliers that offer certified processes, as reliability and traceability are critical for meeting regulatory requirements.
What Role Does Alodine Play in Electronics Manufacturing?
The electronics sector utilizes the Alodine process for surface treatment on circuit boards and electronic components. This coating provides essential corrosion resistance while maintaining electrical conductivity, which is vital for performance. International buyers should prioritize suppliers who can provide thorough quality assurance processes, including testing for adhesion and conductivity, to ensure the longevity and reliability of their products.
Why is Alodine Important for Medical Devices?
In medical device manufacturing, the Alodine process is employed to coat surgical instruments and devices, enhancing their corrosion resistance and ensuring biocompatibility. This application is crucial for extending the lifespan of medical tools that must maintain strict hygiene standards. Buyers must consider suppliers that comply with medical regulations and can provide traceability for the materials used in their processes.
How Does Alodine Benefit the Automotive Industry?
For the automotive industry, the Alodine process is used to protect aluminum chassis and components from corrosion, which can significantly reduce maintenance costs and improve safety. This treatment is particularly important for vehicles operating in harsh environments. Buyers should look for suppliers who can demonstrate compatibility with various paint systems and adherence to environmental regulations to ensure a sustainable production process.
What Advantages Does Alodine Offer in Telecommunications?
In telecommunications, the Alodine process is applied to hardware exposed to challenging conditions, providing a protective layer that enhances both performance and longevity. This is particularly vital for components that face environmental stressors. When sourcing for this application, businesses should ensure that suppliers are reliable and capable of conducting rigorous testing for environmental resistance to meet industry standards.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘alodine process’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Ensuring Consistent Coating Quality Across Production Batches
The Problem: A manufacturer specializing in aerospace components faces challenges with inconsistent Alodine coating thickness across different production batches. This inconsistency leads to varied corrosion resistance and electrical conductivity, risking compliance with stringent military and aerospace specifications. As contracts with major aerospace clients hinge on reliability, any failure in meeting these standards not only jeopardizes current contracts but also damages future business prospects.
The Solution: To ensure consistent coating quality, manufacturers should implement a robust quality control system that includes automated coating verification methods. Investing in automated systems that measure coating thickness and adhesion can significantly reduce human error and enhance process reliability. Additionally, companies should establish a set of standardized operating procedures (SOPs) for the Alodine process, including precise specifications for immersion times and chemical concentrations. Regular training sessions for staff on these SOPs can further improve consistency. By integrating these practices, manufacturers can achieve uniform coating performance that meets or exceeds compliance requirements, thus safeguarding their business interests.
Scenario 2: Navigating Environmental Regulations in Alodine Coating Processes
The Problem: An electronics manufacturer operating in Europe is increasingly concerned about environmental regulations surrounding the use of hexavalent chromium in Alodine processes. With stricter laws being introduced, the company faces potential fines and operational disruptions if they fail to comply. Moreover, customers are becoming more environmentally conscious, demanding eco-friendly alternatives without compromising on performance.
The Solution: Transitioning to trivalent chromium alternatives for the Alodine process can help meet environmental regulations while maintaining the necessary corrosion protection and conductivity. Manufacturers should actively research and collaborate with suppliers who offer eco-friendly formulations that provide similar performance characteristics to traditional Alodine products. It’s essential to conduct comparative tests to ensure that these alternatives meet industry standards for performance and durability. By adopting these sustainable practices, companies can not only comply with regulations but also enhance their brand reputation and appeal to environmentally-conscious clients.
Scenario 3: Maximizing Adhesion for Subsequent Coatings on Alodine-Finished Parts
The Problem: A medical device manufacturer encounters difficulties with paint and adhesive adhesion on Alodine-coated aluminum parts. The lack of proper adhesion results in premature failure of components, leading to costly recalls and damaging the company’s reputation for quality and reliability in a highly regulated industry.
The Solution: To maximize adhesion for subsequent coatings, it is crucial to optimize the surface preparation before applying the Alodine process. Manufacturers should ensure that parts are thoroughly cleaned to remove any surface contaminants, using ultrasonic cleaning or chemical degreasers. Following the Alodine treatment, implementing a post-coating treatment such as a rinse with deionized water can enhance the coating’s properties, making the surface more conducive to adhesion. Additionally, utilizing a bonding primer designed for Alodine-finished surfaces can significantly improve adhesion and performance of paints and adhesives. By focusing on these preparatory steps, manufacturers can achieve reliable bonding, enhancing the durability of their products and maintaining compliance with regulatory standards in the medical device industry.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for alodine process
What Are the Common Materials Used in the Alodine Process?
The Alodine process, also known as chromate conversion coating, is critical for enhancing the corrosion resistance and surface integrity of various metals, particularly aluminum. Below, we analyze four common materials used in the Alodine process, focusing on their properties, advantages, disadvantages, and considerations for international B2B buyers.
Aluminum: The Preferred Material for Alodine Coating
Key Properties:
Aluminum is lightweight, has excellent corrosion resistance, and maintains good electrical conductivity. It typically performs well under a temperature range of -50°C to 150°C, depending on the alloy.
Pros & Cons:
Aluminum’s primary advantage is its low weight combined with high strength, making it ideal for aerospace and automotive applications. However, its lower melting point compared to other metals can complicate manufacturing processes that involve high temperatures.
Impact on Application:
Aluminum’s compatibility with various media, including water and oils, makes it suitable for diverse applications. The Alodine coating enhances its corrosion resistance, particularly in marine environments.
Considerations for International Buyers:
Buyers in regions like Africa and South America should be aware of local standards such as ASTM B449 for aluminum coatings. Compliance with these standards ensures that products meet performance expectations.
Zinc: A Cost-Effective Alternative
Key Properties:
Zinc offers excellent corrosion resistance and is often used as a sacrificial anode. It can withstand temperatures up to 200°C, making it suitable for various industrial applications.
Pros & Cons:
Zinc is less expensive than aluminum and provides good protection against corrosion. However, it is heavier and may not be suitable for applications requiring lightweight materials.
Impact on Application:
Zinc’s compatibility with alkaline and acidic environments enhances its usability in chemical processing industries. However, its weight may limit its application in sectors like aerospace.
Considerations for International Buyers:
International buyers should consider compliance with standards such as ASTM A123 for hot-dip galvanized coatings. This ensures quality and performance in their specific applications.
Steel: Versatile but Needs Protection
Key Properties:
Steel is known for its high strength and durability, with a temperature rating of up to 600°C. However, it is prone to corrosion without proper treatment.
Pros & Cons:
Steel’s robustness makes it suitable for structural applications. However, its susceptibility to rust can be a significant drawback, necessitating additional protective coatings like Alodine.
Impact on Application:
Steel’s compatibility with various media, including oils and fuels, makes it versatile. The Alodine process enhances its corrosion resistance, making it suitable for automotive and industrial applications.
Considerations for International Buyers:
Buyers should be aware of standards such as ASTM A153 for zinc coatings on iron and steel, which can impact their procurement decisions.
Titanium: High Performance for Specialized Applications
Key Properties:
Titanium is known for its exceptional strength-to-weight ratio and corrosion resistance, particularly in harsh environments. It can withstand temperatures exceeding 400°C.
Pros & Cons:
Titanium’s durability and lightweight nature make it ideal for aerospace and medical applications. However, it is significantly more expensive and can be challenging to machine.
Impact on Application:
Titanium’s compatibility with aggressive media, including seawater and acids, makes it suitable for specialized applications. The Alodine process enhances its surface properties, further extending its lifespan.
Considerations for International Buyers:
International buyers should consider compliance with standards such as ASTM F136 for titanium alloys used in medical applications. Understanding these standards is crucial for ensuring product reliability.
Summary Table of Material Selection for Alodine Process
| Material | Typical Use Case for Alodine process | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Aluminum | Aerospace, automotive components | Lightweight, excellent corrosion resistance | Lower melting point complicates high-temp processes | Med |
| Zinc | Chemical processing equipment | Cost-effective, good corrosion protection | Heavier, less suitable for aerospace | Low |
| Steel | Structural applications | High strength and durability | Prone to rust without protection | Med |
| Titanium | Aerospace, medical devices | Exceptional strength-to-weight ratio | High cost, challenging to machine | High |
This analysis provides a comprehensive overview for B2B buyers considering the Alodine process, ensuring informed decisions based on material properties, advantages, and compliance requirements.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for alodine process
What Are the Main Stages of the Alodine Manufacturing Process?
The Alodine process, also known as chromate conversion coating, involves several key stages that ensure the effective application of the coating and the maintenance of quality standards. For B2B buyers, understanding these stages is crucial in selecting a reliable supplier who adheres to best practices in manufacturing.
1. Material Preparation: How Are Aluminum Parts Prepared for Alodine Coating?
The initial stage involves thorough cleaning and surface preparation of the aluminum parts. This may include:
- Degreasing: Removing any oils, grease, or contaminants using solvents or alkaline cleaners.
- Rinsing: Ensuring that all cleaning agents are completely washed off to prevent interference with the coating.
- Surface Activation: Sometimes, a mild etch or abrasive treatment is applied to enhance surface adhesion for the Alodine coating.
Proper material preparation is essential, as it directly affects the adhesion and effectiveness of the Alodine finish.
2. Forming: What Techniques Are Used in the Manufacturing of Aluminum Parts?
Forming techniques vary based on the final application of the aluminum parts. Common methods include:
- Extrusion: Ideal for creating complex profiles and shapes.
- CNC Machining: Provides precision and tight tolerances for critical components.
- Stamping and Bending: Useful for creating flat parts or components that require specific geometries.
Each method must ensure that the integrity of the metal is maintained, as any defects could compromise the effectiveness of the Alodine coating.
3. Assembly: How Are Components Integrated Before Coating?
Before applying the Alodine coating, components may be assembled into sub-assemblies. This stage includes:
- Fit and Tolerance Checks: Ensuring that parts fit together correctly without undue stress.
- Pre-assembly Cleaning: Repeating cleaning procedures to remove any contaminants introduced during assembly.
Assembly quality directly influences the performance of the final product, making it a critical step in the manufacturing process.
4. Finishing: What Are the Steps in the Alodine Coating Application?
The application of the Alodine coating is a delicate process that involves:
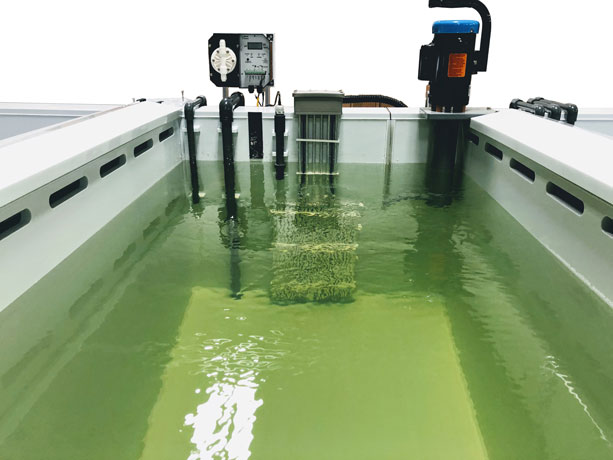
- Chromate Conversion Coating: The aluminum parts are immersed in a solution that facilitates a chemical reaction, forming a protective layer on the surface. This can be done via immersion or spraying techniques.
- Rinsing: After coating, parts are rinsed to remove excess solution and ensure a clean finish.
- Drying: Parts must be thoroughly dried to prevent water spots and ensure a uniform coating.
The Alodine finish not only provides corrosion resistance but also enhances adhesion for subsequent paint or coating applications.
What Quality Assurance Measures Are Relevant for the Alodine Process?
Quality assurance is paramount in the Alodine process, especially for international B2B buyers who require compliance with various standards.
International Standards: What Certifications Should Buyers Look For?
Manufacturers of Alodine-coated components should comply with international standards such as:
- ISO 9001: This standard outlines criteria for a quality management system, ensuring consistent product quality and customer satisfaction.
- MIL-DTL-5541: Specifically relevant for the aerospace and defense industries, this standard governs the application of chromate conversion coatings for aluminum.
Adherence to these standards ensures that the manufacturer employs rigorous quality control measures throughout the production process.
Key Quality Control Checkpoints: What Are the Main QC Stages?
Quality control in the Alodine process typically involves several checkpoints:
- Incoming Quality Control (IQC): Verification of raw materials and components before they enter the production line.
- In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): Monitoring production processes and parameters during manufacturing to ensure compliance with specifications.
- Final Quality Control (FQC): Testing finished products to validate their performance against predetermined criteria.
These checkpoints help in identifying defects early in the process, thus reducing waste and rework.
What Common Testing Methods Are Used in the Alodine Process?
To ensure the effectiveness of the Alodine coating, various testing methods are employed, including:
- Adhesion Testing: Assessing the bond strength of the Alodine layer to the aluminum surface.
- Salt Spray Testing: Evaluating corrosion resistance by exposing coated parts to saline conditions.
- Coating Thickness Measurement: Ensuring the applied layer meets specified thickness requirements.
These tests help manufacturers confirm that their products meet both functional and regulatory requirements.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control?
For international B2B buyers, verifying the quality control measures of suppliers is essential. Here are some strategies:
- Conducting Audits: Regular audits of the supplier’s facilities can provide insights into their manufacturing practices and adherence to quality standards.
- Requesting Quality Reports: Suppliers should provide documentation of quality tests and compliance with international standards, including any certifications.
- Engaging Third-Party Inspectors: Independent inspection agencies can offer unbiased evaluations of the supplier’s quality processes and product quality.
What Are the Nuances of Quality Control for International B2B Buyers?
B2B buyers from diverse regions, including Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, should be aware of specific nuances related to quality control:
- Cultural Differences: Understanding the cultural context of suppliers may influence communication and expectations regarding quality standards.
- Regulatory Compliance: Buyers should ensure that suppliers are aware of and comply with local regulations and standards, which may vary significantly between regions.
- Logistics and Supply Chain Management: Quality assurance extends beyond manufacturing; effective supply chain management is crucial to maintaining quality throughout the product lifecycle.
By understanding the Alodine manufacturing processes and the associated quality assurance measures, B2B buyers can make informed decisions, ensuring they source high-quality, reliable products that meet their industry-specific requirements.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘alodine process’
Introduction
This guide serves as a comprehensive checklist for B2B buyers looking to procure the Alodine process, a critical chemical conversion coating method for aluminum and other metals. The Alodine process not only enhances corrosion resistance but also improves adhesion for subsequent coatings. Following this checklist will ensure that you make informed decisions, select reliable suppliers, and secure quality treatments for your manufacturing needs.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Establishing clear technical specifications is essential for aligning supplier capabilities with your project requirements. This includes defining the desired thickness of the coating, adhesion levels, and compatibility with other surface treatments. Providing detailed specifications helps suppliers understand your needs and ensures compliance with industry standards, such as MIL-DTL-5541.
Step 2: Research Industry Standards and Regulations
Understanding the relevant industry standards is crucial when sourcing the Alodine process. Familiarize yourself with regulations specific to your sector—be it aerospace, automotive, or electronics. Ensure that the suppliers you consider comply with these standards, as non-compliance can lead to significant operational risks and increased costs.
Step 3: Evaluate Potential Suppliers
Before making a commitment, thoroughly vet potential suppliers. Request company profiles, case studies, and references from other buyers in your industry or region. Look for suppliers with experience in handling projects similar to yours, as this can indicate their reliability and capability.
- Check for Certifications: Ensure that suppliers hold necessary certifications, such as ISO 9001 or NADCAP, which affirm their quality management systems.
- Review Client Testimonials: Seek feedback from previous clients to gauge the supplier’s performance and service quality.
Step 4: Request Samples and Test Results
Obtaining samples of the Alodine process application is critical for assessing quality. Request test results for adhesion, corrosion resistance, and other relevant performance metrics. This step allows you to evaluate the effectiveness of the coating under your specific conditions.
- Conduct In-House Testing: If possible, perform your own tests to verify that the samples meet your technical specifications.
- Compare Against Competitors: Evaluate samples from multiple suppliers to determine the best quality and performance.
Step 5: Negotiate Pricing and Terms
Once you’ve identified a suitable supplier, engage in negotiations regarding pricing and terms of service. Ensure that the pricing reflects the quality of service and materials provided. Discuss payment terms, lead times, and any warranties or guarantees offered.
- Consider Long-Term Partnerships: Explore the potential for long-term contracts, which may provide cost benefits and improved service reliability.
- Assess Total Cost of Ownership: Evaluate not just the initial costs but also the long-term value and durability of the Alodine process to your operations.
Step 6: Establish a Quality Assurance Plan
Develop a quality assurance plan that outlines inspection criteria and testing procedures for the Alodine process. This plan should include routine checks for coating thickness, adhesion, and environmental resistance. A robust QA plan ensures that the coatings applied meet the specified standards throughout the production cycle.
- Document Compliance: Keep meticulous records of testing results and inspections to ensure traceability and compliance during audits.
- Regularly Review Supplier Performance: Schedule periodic reviews to assess the supplier’s performance and make adjustments as needed.
Step 7: Monitor and Evaluate Post-Application Performance
After the Alodine process is applied, continuously monitor the performance of the coated components in their intended environment. Collect data on corrosion resistance, adhesion to subsequent coatings, and overall durability. This evaluation helps identify any issues early and informs future sourcing decisions.
- Feedback Loop: Establish a feedback mechanism with your supplier to discuss performance outcomes and any necessary improvements.
- Stay Updated on Innovations: Keep abreast of advancements in the Alodine process and alternative coatings that may enhance your product’s performance and compliance.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for alodine process Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components of the Alodine Process?
When evaluating the cost structure for the Alodine process, several components contribute significantly to the overall expense. These include:
-
Materials: The primary materials involved in the Alodine process include chromate compounds and various chemicals necessary for surface preparation. The cost of these materials can fluctuate based on global supply chains and regulatory changes affecting chemical usage.
-
Labor: Skilled labor is essential for applying the Alodine coating correctly. Labor costs will vary depending on the region, with higher costs often associated with countries that have stricter labor regulations or higher living expenses.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes costs associated with facility maintenance, utilities, and administrative expenses. These indirect costs can significantly impact pricing, especially for suppliers operating in regions with high operational costs.
-
Tooling: The initial setup for the Alodine process may require specialized equipment and tools, which can represent a significant upfront investment. However, these costs can be amortized over time with increased production volumes.
-
Quality Control (QC): Rigorous quality control measures are essential to ensure compliance with industry standards such as MIL-DTL-5541. The costs associated with testing, inspections, and certifications can vary widely based on the complexity and frequency of QC processes.
-
Logistics: Shipping and handling costs can also influence the overall pricing structure. Factors such as distance, mode of transport, and customs regulations play a vital role, especially for international transactions.
-
Margin: Suppliers typically add a margin to cover their risks and ensure profitability. This margin may vary based on market competition and supplier reputation.
How Do Price Influencers Affect Alodine Process Costs?
Several factors can influence the pricing of the Alodine process, including:
-
Volume and Minimum Order Quantity (MOQ): Higher order volumes often lead to lower unit prices due to economies of scale. Buyers should negotiate MOQs that align with their production needs to optimize costs.
-
Specifications and Customization: Customized solutions may incur additional costs. Buyers should clearly define their specifications to avoid unexpected charges during the production process.
-
Materials and Quality Certifications: The choice of materials, particularly regarding environmental regulations, can impact pricing. Suppliers offering certified eco-friendly alternatives may charge a premium, but this can lead to long-term cost savings.
-
Supplier Factors: The reputation and reliability of the supplier can affect pricing. Established suppliers may charge more due to their proven track record, while newer entrants might offer competitive pricing to gain market share.
-
Incoterms: Understanding the terms of shipping and delivery (Incoterms) is crucial for international buyers. These terms dictate who bears the risk and costs at each stage of transport, impacting the overall cost structure.
What Tips Can Buyers Use to Negotiate Better Prices for Alodine Process Sourcing?
International buyers, particularly from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, should consider the following strategies to enhance their cost-efficiency:
-
Negotiation: Leverage volume purchases to negotiate better prices. Building long-term relationships with suppliers can also lead to favorable terms and discounts.
-
Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Evaluate the TCO rather than just the initial purchase price. Consider factors such as durability, maintenance, and performance over time to make informed decisions.
-
Pricing Nuances: Be aware of regional pricing variations due to local market conditions, currency fluctuations, and economic stability. This knowledge can provide leverage during negotiations.
-
Explore Alternatives: Investigate alternative suppliers, particularly those offering trivalent chromium options that may be more environmentally compliant and cost-effective in the long run.
-
Documentation and Compliance: Ensure that all necessary certifications and compliance documentation are in order before finalizing contracts to avoid hidden costs associated with regulatory non-compliance.
By understanding the comprehensive cost structure and pricing dynamics of the Alodine process, buyers can make more informed sourcing decisions that align with their operational and budgetary needs.
Disclaimer
Prices mentioned in this analysis are indicative and may vary based on market conditions, supplier negotiations, and specific project requirements. Buyers should conduct thorough market research and supplier assessments to obtain accurate quotes tailored to their needs.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing alodine process With Other Solutions
Exploring Alternatives to the Alodine Process for Corrosion Protection
In the manufacturing and engineering sectors, selecting the right surface treatment is crucial for ensuring durability and performance, particularly for aluminum components. The Alodine process, or chromate conversion coating, is widely recognized for its excellent corrosion resistance and conductivity. However, there are several alternative methods available, each with its own set of benefits and limitations. This analysis aims to compare the Alodine process with anodizing and powder coating, two popular alternatives in the industry.
| Comparison Aspect | Alodine Process | Anodizing | Powder Coating |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | Excellent corrosion resistance, maintains electrical conductivity | High corrosion resistance, can be dyed for aesthetics | Good corrosion resistance, thick layer provides durability |
| Cost | Generally low to moderate | Moderate to high | Moderate to high |
| Ease of Implementation | Relatively simple, often requires specialized equipment | Requires precise control and can be more complex | Can be automated, requires curing time |
| Maintenance | Low, but requires regular inspection | Low, but surface can be scratched | Moderate, can chip and require touch-ups |
| Best Use Case | Aerospace, defense, and electronics | Aerospace, architectural applications | Automotive, consumer goods, and heavy machinery |
Anodizing: A Closer Look at Its Pros and Cons
Anodizing is an electrochemical process that converts the metal surface into a decorative, durable, and corrosion-resistant finish. One of the primary advantages of anodizing is its ability to create a thicker oxide layer on the aluminum surface, which enhances its corrosion resistance and can be dyed in various colors for aesthetic appeal. However, the process can be more complex and requires precise control, making it potentially more costly and time-consuming than the Alodine process. Additionally, while anodized surfaces are durable, they can be susceptible to scratching, which may require more frequent maintenance in high-wear applications.
Powder Coating: Understanding Its Strengths and Weaknesses
Powder coating involves applying a dry powder to the surface of a metal part, which is then cured under heat to create a tough, protective layer. This method provides excellent durability and can be formulated to offer a wide range of colors and finishes. The thick layer created by powder coating enhances corrosion resistance, making it suitable for outdoor applications. However, the process is more expensive than Alodine, and the curing time can slow production. Additionally, while powder-coated surfaces are robust, they can chip and may require touch-ups, particularly in high-impact environments.
Making the Right Choice for Your Business Needs
When selecting the appropriate surface treatment for aluminum components, B2B buyers should consider several factors, including performance requirements, budget constraints, and the specific environmental conditions the parts will face. The Alodine process is particularly advantageous for applications requiring electrical conductivity and minimal dimensional change, such as in the aerospace and electronics industries. In contrast, anodizing may be more suitable for applications that prioritize aesthetics and require enhanced surface durability. Powder coating stands out in scenarios where a thick protective finish is necessary, especially in consumer goods and automotive parts. Ultimately, understanding these alternatives will empower businesses to make informed decisions that align with their operational goals and product specifications.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for alodine process
What are the Key Technical Properties of the Alodine Process?
When considering the alodine process for aluminum and other metal components, it is essential to understand several critical specifications that directly impact performance, compliance, and overall project success. Here are some of the most important properties:
-
Coating Thickness
The thickness of the alodine coating is crucial for ensuring effective corrosion resistance and electrical conductivity. Typically, the coating thickness ranges from 0.0001 to 0.0003 inches. In B2B applications, adhering to specified thickness is vital to meet industry standards, such as MIL-DTL-5541, particularly in aerospace and defense sectors where precision is paramount. -
Adhesion Strength
Adhesion strength refers to the ability of the alodine coating to bond with the substrate material. It is typically assessed through various tests, such as tape tests or crosshatch adhesion tests. Strong adhesion is essential for ensuring that the coating remains intact during mechanical and thermal stresses, which is particularly important in high-performance environments like aerospace and automotive applications. -
Corrosion Resistance
The primary purpose of the alodine process is to enhance corrosion resistance. This is measured through accelerated corrosion tests such as salt spray tests. For international buyers, especially in regions with high humidity or saline environments, understanding the corrosion resistance properties of alodine-treated components can inform material selection and long-term performance expectations. -
Electrical Conductivity
Depending on the application, the alodine process can produce coatings with varying levels of electrical conductivity. This is particularly critical in electronic and aerospace applications where maintaining electrical pathways is essential. Buyers should specify their conductivity requirements to ensure that the coating meets their operational needs. -
Environmental Compliance
As regulations regarding hazardous substances evolve, the alodine process must comply with environmental standards, including RoHS and REACH. Understanding the environmental impact of the materials used in the alodine process can help buyers ensure compliance and avoid potential penalties in their respective markets. -
Compatibility with Subsequent Coatings
The alodine coating serves as a pretreatment for organic coatings, such as paints and powders. It is important for B2B buyers to assess the compatibility of the alodine finish with any additional coatings to ensure optimal performance and adhesion.
What are Common Trade Terms Used in the Alodine Process?
Familiarity with industry jargon is crucial for effective communication and negotiation in B2B transactions. Here are several common terms related to the alodine process:
-
OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
This term refers to companies that produce components that are used in another company’s end product. Understanding whether a supplier operates as an OEM can help buyers evaluate their expertise and capability to meet specific project requirements. -
MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ indicates the smallest number of units a supplier is willing to sell. This term is essential for buyers to understand, especially when budgeting for large-scale projects, as it directly affects inventory management and cost calculations. -
RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a document sent to suppliers to solicit pricing and terms for specific products or services. Buyers should prepare detailed RFQs to ensure they receive accurate and comparable quotes, which can aid in decision-making. -
Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
These are standardized terms that define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in international shipping and delivery. Familiarity with Incoterms helps buyers understand shipping costs, risk management, and delivery timelines. -
NADCAP (National Aerospace and Defense Contractors Accreditation Program)
NADCAP is a global cooperative accreditation program for aerospace engineering. Buyers in industries requiring high reliability should ensure that their suppliers have NADCAP accreditation to guarantee compliance with stringent industry standards. -
Chromate Conversion Coating
This term describes the chemical process that creates the alodine finish. Understanding this terminology allows buyers to communicate effectively about the specific processes and benefits they seek in metal finishing.
By grasping these technical properties and trade terminologies, B2B buyers can make informed decisions regarding the alodine process, ensuring that they select the right materials and suppliers for their projects.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the alodine process Sector
What Are the Current Market Dynamics and Key Trends in the Alodine Process Sector?
The global market for the Alodine process, also known as chromate conversion coating, is witnessing significant growth driven by increasing demand for corrosion-resistant materials across various industries, including aerospace, automotive, electronics, and telecommunications. As international B2B buyers, particularly from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, look for reliable and efficient surface treatment solutions, the Alodine process stands out for its ability to enhance aluminum’s durability without altering its dimensions.
Emerging technologies such as automation in surface treatment processes and advancements in chemical formulations are reshaping sourcing trends. Automated systems not only increase efficiency but also ensure consistent quality and compliance with stringent industry standards like MIL-DTL-5541. Furthermore, the rise of e-commerce platforms is facilitating easier access to suppliers and manufacturers, enabling buyers in developing regions to source high-quality Alodine finishes with greater convenience.
Another key trend is the growing preference for trivalent chromium alternatives due to environmental regulations and health concerns associated with hexavalent chromium. This shift is essential for companies looking to maintain compliance while still achieving the desired performance characteristics. As these dynamics evolve, B2B buyers must stay informed and agile, ensuring that their sourcing strategies align with both current market demands and future innovations.
How Is Sustainability and Ethical Sourcing Influencing the Alodine Process?
The increasing focus on sustainability and ethical sourcing is significantly impacting the Alodine process sector. Environmental regulations are pushing manufacturers to adopt greener practices, leading to the development of trivalent chromium-based coatings as alternatives to traditional hexavalent chromium options. These alternatives not only comply with stringent environmental standards but also offer comparable corrosion resistance, making them attractive to international buyers seeking sustainable solutions.
Ethical supply chains are gaining importance as businesses recognize the value of corporate social responsibility. Buyers are more inclined to partner with suppliers who prioritize ethical sourcing, transparency, and environmental stewardship. Certifications such as ISO 14001 (Environmental Management) and OHSAS 18001 (Occupational Health and Safety) can serve as indicators of a supplier’s commitment to sustainability.
Moreover, as the global market increasingly values ‘green’ certifications and materials, companies that adopt sustainable practices in their Alodine process can enhance their brand reputation and customer loyalty. This trend not only reflects a commitment to environmental responsibility but also aligns with the evolving preferences of end-users who are more conscious about the sustainability of the products they purchase.
What Is the Brief History and Evolution of the Alodine Process?
The Alodine process dates back to the mid-20th century when it was developed as a means to enhance the corrosion resistance of aluminum and its alloys, particularly for aerospace applications. The technique uses a chemical conversion coating that transforms the surface of aluminum into a protective layer through a chemical reaction, rather than adding a new layer like traditional plating methods.
Over the years, the Alodine process has evolved significantly, driven by advancements in chemistry and manufacturing technologies. The introduction of more environmentally friendly formulations, such as trivalent chromium options, reflects a growing awareness of environmental impacts and regulatory pressures. As a result, the Alodine process has become a critical component in industries where performance, reliability, and compliance with safety standards are paramount.
In summary, the Alodine process has not only maintained its relevance in precision-driven sectors but has also adapted to meet contemporary demands for sustainability and ethical sourcing, making it a vital consideration for international B2B buyers.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of alodine process
-
How do I ensure the quality of Alodine coatings for my aluminum components?
To ensure high-quality Alodine coatings, start by selecting suppliers with relevant certifications such as NADCAP or ISO 9001. Request detailed documentation on their coating processes, including adherence to military and aerospace specifications like MIL-DTL-5541. It’s also beneficial to conduct regular quality audits and inspections, focusing on adhesion, corrosion resistance, and coating thickness. Consider suppliers that offer process validation testing to confirm compliance with your specifications. Establishing a clear communication channel with your supplier will help address any quality concerns promptly. -
What is the best Alodine process for corrosion resistance in aerospace applications?
The most effective Alodine process for aerospace applications is typically the MIL-DTL-5541 chromate conversion coating. This process enhances corrosion resistance while maintaining electrical conductivity, which is critical for aerospace components. Ensure that the supplier follows this standard and can provide evidence of compliance through testing results. Moreover, consider discussing specific environmental conditions your components will face, as some variants of Alodine may offer enhanced resistance to particular corrosive agents. -
What are the customization options available for Alodine coatings?
Customization options for Alodine coatings include variations in color, thickness, and application methods. Depending on your project requirements, you can specify the desired level of conductivity—either conductive or non-conductive. Additionally, you may want to discuss specific pretreatment processes that enhance adhesion for subsequent coatings. Always communicate your specific needs to the supplier and ask for samples to ensure the final product meets your expectations. -
What is the minimum order quantity (MOQ) for Alodine coatings?
Minimum order quantities for Alodine coatings can vary widely depending on the supplier and the specific coating process. Generally, suppliers may set MOQs ranging from a few hundred to several thousand parts. It’s advisable to discuss your project’s scope and requirements directly with potential suppliers to negotiate favorable terms. Some suppliers may offer flexibility for smaller projects or allow for sample orders before committing to larger quantities. -
What payment terms should I expect when sourcing Alodine processes internationally?
Payment terms for international sourcing of Alodine processes typically involve upfront deposits and balance payments upon delivery. Common arrangements include 30% upfront and 70% upon shipment, but this can vary. Be sure to clarify payment methods accepted (e.g., wire transfers, letters of credit) and any additional fees related to currency exchange or international transactions. Establishing clear payment terms in the contract can help prevent misunderstandings. -
How do I vet suppliers for Alodine coatings effectively?
Vetting suppliers for Alodine coatings involves several steps. Begin by checking their industry certifications, such as ISO 9001 or NADCAP. Look for customer testimonials and case studies to assess their experience in your specific industry. Request references and conduct site visits if possible to observe their processes firsthand. Additionally, evaluate their responsiveness to inquiries and willingness to provide technical support, as these factors can indicate a reliable partnership. -
What logistics considerations should I be aware of when sourcing Alodine coatings?
When sourcing Alodine coatings internationally, consider logistics factors such as shipping methods, lead times, and customs regulations in both the supplier’s and your country. Ensure the supplier can provide timely shipping options and track shipments. Additionally, clarify who will be responsible for duties and taxes, as these can significantly affect your overall cost. Establishing a reliable logistics partner can help streamline the import process and reduce potential delays. -
How can I ensure compliance with environmental regulations when using Alodine coatings?
To ensure compliance with environmental regulations when using Alodine coatings, select suppliers who utilize trivalent chromium alternatives that meet current environmental standards. Familiarize yourself with local regulations regarding hazardous materials and ensure your supplier adheres to these requirements. Regular audits and environmental assessments can help maintain compliance, and consider requesting Material Safety Data Sheets (MSDS) for any chemicals involved in the Alodine process to understand their environmental impact.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.
Top 6 Alodine Process Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. Best Technology Inc – Alodine Coating Solutions
Domain: besttechnologyinc.com
Registered: 2001 (24 years)
Introduction: Alodine, also known as chem film or chromate conversion coating, is a protective coating for aluminum and other metals that prevents corrosion. It is a type of chemical conversion coating that transforms the existing metal surface into a protective layer through a chemical reaction, rather than adding a new layer like plating. Key benefits include enhanced corrosion protection, improved adhesion f…
2. Gabrian – Alodine Finish
Domain: gabrian.com
Registered: 2000 (25 years)
Introduction: Alodine finish is a type of conversion coating for aluminum that creates a thin protective film to prevent corrosion while allowing electrical conductivity. It is often used in the electronics industry. Alodine is a registered trademark of Henkel, Inc., and is sometimes referred to as chromate conversion coating or chem film. The process involves dipping aluminum parts in a chemical bath to form a…
3. Rapid Axis – Chromate Conversion Coating
Domain: rapidaxis.com
Registered: 2018 (7 years)
Introduction: Alodine, Chem Film, and Chromate Conversion Coating are terms used interchangeably for a surface treatment process for aluminum and its alloys. Chromate Conversion Coating (CCC) involves immersing parts in a chromic acid solution to form a protective layer that enhances corrosion resistance and improves adhesion for subsequent coatings. Chem Film is industry slang for CCC, while Alodine is a brand…
4. Elhco – Alodine Chromic Finish
Domain: elhco.com
Registered: 2001 (24 years)
Introduction: Alodine is a chromic finish for aluminium parts, specifically designed for the aeronautic industry according to the I+D-P-202 specification. The Alodine process is a chemical conversion process that creates a layer of oxide/hydroxide on aluminium, providing corrosion protection and serving as a base for organic finishes. There are two types of chemical conversion: Type I (Alodine 1200) with a yell…
5. Valence Surface Tech – Alodine Coating
Domain: valencesurfacetech.com
Registered: 2014 (11 years)
Introduction: Alodine coating, also known as chromate conversion coating, is a chemical treatment process primarily used on aluminum and its alloys, but can also be applied to other metals like steel, magnesium, and copper. It involves applying a chromic acid-based chemical compound that reacts with the metal surface to form a protective, corrosion-resistant film. This film prevents oxidation and enhances paint…
6. Wayken RM – Alodine Coatings
Domain: waykenrm.com
Registered: 2013 (12 years)
Introduction: Alodine is a chemical substance used for chromate conversion coatings on metals, particularly aluminum alloys. It forms a protective coating that enhances aesthetic appeal and serves as a base for painting and priming while preserving electrical conductivity. Alodine finishes are categorized into Type 1 and Type 2 according to the MIL-DTL-5541 standard. Type 1 contains hexavalent chromium, produci…
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for alodine process
The Alodine process stands as a critical component in the strategic sourcing framework for businesses focused on high-performance applications. By leveraging chromate conversion coatings, manufacturers can significantly enhance the corrosion resistance and surface integrity of aluminum components, particularly in industries such as aerospace, defense, and electronics. The ability to maintain tight tolerances without altering dimensions makes Alodine an ideal choice for precision-driven sectors, ensuring compliance with rigorous industry standards.
Strategic sourcing of Alodine services allows businesses to not only optimize their production processes but also to align with evolving environmental regulations, such as the shift toward trivalent chromium alternatives. This adaptability is crucial for international buyers, especially in emerging markets across Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. By engaging with reliable suppliers who understand regional compliance and quality standards, organizations can secure a competitive edge in their respective industries.
As we look to the future, the demand for effective and sustainable surface finishing solutions will only grow. International B2B buyers are encouraged to explore partnerships that prioritize innovation and quality in the Alodine process, ensuring their products meet the challenges of tomorrow.