Contents
Manufacturing Insight: 8620 Steel Machinability
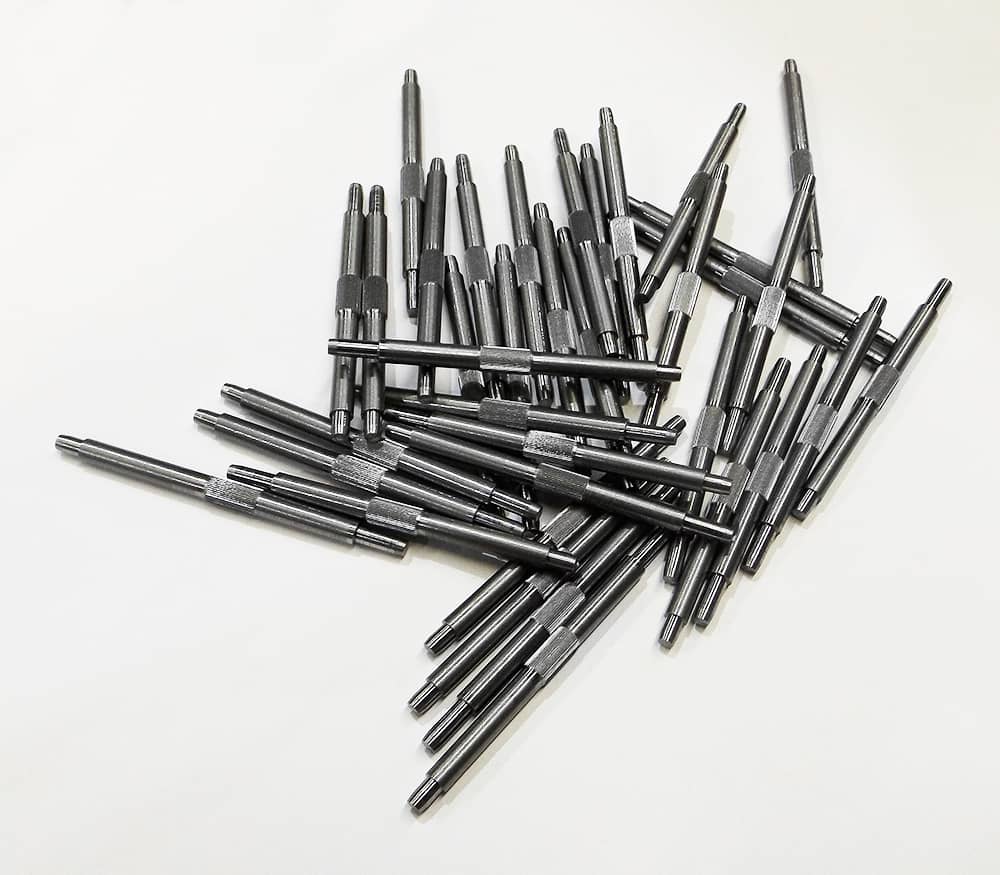

Mastering 8620 Alloy Steel Machinability for Precision Components
8620 alloy steel, valued for its excellent core toughness, hardenability, and fatigue strength, presents distinct challenges in high-precision CNC machining due to its nickel-chromium-molybdenum composition. Work hardening tendencies, thermal sensitivity during cutting, and the need for precise chip control require specialized process parameters to achieve tight tolerances and optimal surface finishes without compromising tool life or part integrity. At Honyo Prototype, our senior manufacturing engineering team leverages decades of metallurgical expertise to systematically overcome these hurdles. We deploy advanced CNC milling and turning centers with rigid tooling setups, optimized coolant strategies, and empirically validated feed/speed profiles specifically calibrated for 8620’s unique properties. This ensures consistent production of complex aerospace, automotive, and industrial components meeting AS9100 and ISO 9001 standards.
Honyo’s Precision CNC Machining Advantage
Our end-to-end manufacturing solution integrates material science insight with state-of-the-art 3-, 4-, and 5-axis machining capabilities, enabling efficient prototyping and low-volume production of 8620 steel parts with tolerances down to ±0.0002″. We prioritize first-pass yield through rigorous pre-machining analysis, including thermal deformation modeling and in-process metrology, minimizing scrap and accelerating time-to-part. For engineering teams evaluating 8620 for critical applications, Honyo eliminates quoting delays with our Online Instant Quote system. Upload your STEP or IGES file to receive a detailed manufacturability assessment and competitive pricing within hours—no RFQ forms or sales calls required. Accelerate your development cycle with machining expertise engineered for demanding alloys.
Technical Capabilities
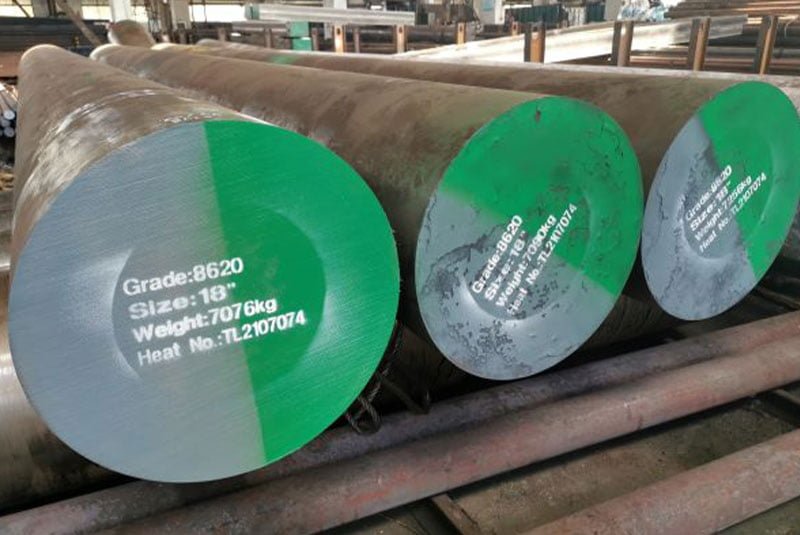

Technical Specifications and Machinability of 8620 Steel in Precision 3/4/5-Axis Milling and Turning Operations
8620 steel is a low-carbon, nickel-chromium-molybdenum alloy steel known for its excellent toughness, core strength, and case-hardening capabilities. It is commonly used in applications requiring high surface hardness with a tough interior, such as gears, pins, and shafts. When machining 8620 for tight-tolerance components using 3-, 4-, or 5-axis milling and turning processes, specific parameters must be optimized to maintain dimensional accuracy, surface finish, and tool life.
Below is a comparative table highlighting the machinability characteristics of 8620 steel relative to other common prototype and production materials such as aluminum, steel (general), ABS, and nylon—all in the context of high-precision CNC operations.
| Material | Hardness (HB) | Machinability Rating (%) | Recommended Cutting Speed (SFM) | Tooling Recommendations | Coolant Requirement | Typical Tolerance Capability (±) | Notes for 3/4/5-Axis Milling & Turning |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 8620 Steel | 150–200 | 60–65 | 180–250 (milling), 200–300 (turning) | Carbide end mills, CVD/PVD-coated inserts | Required (flood or high-pressure) | 0.0005″ (12.7 µm) with proper fixturing and process control | Moderate chip control challenges; sensitive to work hardening; requires rigid setups for tight tolerances; pre-heat treated condition preferred for stability |
| Aluminum (6061-T6) | 95–105 | 90–100 | 800–1500 (milling), 1000–2000 (turning) | Carbide or HSS with polished flutes, high rake angles | Recommended (to prevent built-up edge) | 0.0002″ (5 µm) | Excellent for high-speed milling; low cutting forces; ideal for complex 5-axis contours and thin walls |
| Steel (1018/1045) | 120–220 | 70–85 | 250–400 (milling), 300–500 (turning) | Carbide with TiAlN coating | Required | 0.0005″ (12.7 µm) | More consistent than 8620 in as-rolled condition; less alloy content improves machinability |
| ABS (Plastic) | 90–100 | 80–90 | 500–800 (milling), 600–1000 (turning) | Sharp carbide tools, large clearance angles | Optional (air blast recommended) | 0.001″ (25 µm) | Low melting point; prone to chatter; requires high spindle speeds and light passes; minimal tool wear |
| Nylon (PA6/PA66) | 80–90 | 75–85 | 400–700 (milling), 500–800 (turning) | Polished carbide, non-coated | Optional (air or mist) | 0.001″ (25 µm) | Exhibits creep; fixturing critical; avoid excessive heat; post-machining dimensional shift possible |
Key Considerations for 8620 Steel in Tight-Tolerance Machining:
Pre-Conditioning: 8620 is typically machined in the annealed or normalized condition (not case-hardened) to achieve tight tolerances. Final case hardening is performed post-machining.
Tool Wear: Due to the alloying elements (Ni, Cr, Mo), 8620 causes faster tool wear than plain carbon steels. Use of PVD/TiAlN-coated carbide tools is recommended.
Thermal Management: Consistent coolant application is critical to control thermal expansion and maintain dimensional stability during multi-axis operations.
Fixturing: High rigidity is required to minimize deflection during deep pockets or long-reach milling—common in 5-axis setups.
Surface Finish: Achieves fine finishes (32–64 µin Ra) with proper parameters but may require light finishing passes to meet stringent requirements.
In comparison to aluminum, ABS, and nylon, 8620 steel demands more robust tooling, slower cycle times, and tighter process control. However, it offers superior mechanical properties for functional, load-bearing components where plastics or mild steels are insufficient.
From CAD to Part: The Process

Honyo Prototype applies specialized expertise when machining 8620 steel, a nickel-chromium-molybdenum low-alloy steel known for its case-hardening properties but challenging machinability due to work hardening tendencies and gummy chip formation. Our end-to-end process integrates material-specific protocols at each stage to ensure precision, efficiency, and part integrity.
CAD Upload and Material Specification
Upon receiving your CAD file, our system explicitly identifies 8620 steel requirements. Engineers verify critical factors including section thickness (to anticipate distortion during subsequent carburizing), geometric complexity affecting chip evacuation, and tolerance zones sensitive to thermal effects. We cross-reference your material certification against our internal 8620 database to confirm hardenability ranges and sulfur content, which directly impact machinability.
AI-Powered Quoting with Material Intelligence
Our AI quoting engine dynamically adjusts parameters for 8620 versus standard carbon steels. It factors in:
25-30% reduced cutting speeds compared to 1045 steel
Mandatory use of coated carbide tooling (TiAlN or AlCrN)
Required flood coolant pressure (min. 1,000 psi) to prevent BUE (built-up edge)
Extended cycle time allowances for interrupted cuts
The quote includes a material-specific risk assessment highlighting potential issues like poor surface finish on radii or distortion in thin-walled features.
DFM Analysis Focused on 8620 Challenges
Our DFM review targets 8620-specific vulnerabilities:
Recommending 0.015″ minimum fillet radii to reduce stress concentrations exacerbated by machining
Flagging deep cavities requiring specialized tool holders to prevent chatter-induced work hardening
Proposing pre-machining allowances (0.005-0.010″) for post-heat-treat grinding where carburized case depth exceeds 0.030″
Suggesting alternative geometries to avoid sharp corners where chips weld during milling
We provide documented justification for all recommendations using ISO 6892-1 tensile property correlations.
Production Execution with Optimized Parameters
Machining 8620 follows our controlled process:
| Parameter | 8620 Steel Specification | Standard Carbon Steel Comparison |
|---|---|---|
| Cutting Speed | 80-120 SFM | 180-220 SFM (for 1045) |
| Feed Rate | 0.004-0.008 IPT | 0.010-0.015 IPT |
| Coolant | High-pressure soluble oil | Standard emulsion |
| Tool Geometry | Positive rake (+12°) | Neutral rake (0°) |
| Depth of Cut | ≤1.5x tool diameter | ≤2x tool diameter |
All operations use rigid setups with minimized tool overhang. We implement in-process hardness testing (5 points per batch) to detect anomalous work hardening. Critical diameters undergo post-machine stress relief per AMS 2759/3 before final inspection.
Delivery and Documentation
Final delivery includes:
CMM reports with thermal growth compensation data for carburizing
Machinability certification showing achieved surface roughness (Ra ≤ 32 μin typical)
Tool wear logs specific to your 8620 heat number
Recommendations for post-machining heat treatment sequencing
We maintain full traceability from raw bar certification through final inspection, with all process parameters archived against your PO for future production runs. This integrated approach ensures 8620 components meet stringent aerospace and power transmission requirements while minimizing scrap rates typically associated with this alloy.
Start Your Project
For detailed insights into the machinability of 8620 steel and how it can be optimized for your prototyping or production needs, contact Susan Leo at [email protected]. With our advanced machining capabilities and metallurgical expertise, Honyo Prototype ensures precision and efficiency when working with 8620 alloy steel.
Our manufacturing facility is located in Shenzhen, enabling rapid turnaround and strict quality control for both prototype and low-volume production runs. Reach out today to discuss material selection, machining parameters, or custom fabrication requirements.
🚀 Rapid Prototyping Estimator
Estimate rough cost index based on volume.