Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for 6061 t6 vs 7075 t6
In the fast-evolving landscape of global manufacturing, sourcing the right aluminum alloy—specifically, 6061 T6 versus 7075 T6—poses a significant challenge for international B2B buyers. These two alloys, while both widely utilized, present distinct characteristics that can dramatically impact the performance of end products. This guide delves into the nuanced differences between 6061 T6 and 7075 T6 aluminum alloys, equipping decision-makers with the insights needed to make informed purchasing choices.
Throughout this comprehensive guide, we will explore critical aspects such as chemical composition, mechanical properties, machinability, corrosion resistance, and suitability for various applications. Additionally, we will provide actionable strategies for vetting suppliers, understanding cost implications, and identifying the best fit for your specific needs.
By addressing the unique requirements of industries across Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe—such as those in Nigeria and Saudi Arabia—this guide empowers B2B buyers to navigate the complexities of sourcing aluminum materials. With a clear understanding of the advantages and limitations of each alloy, businesses can optimize their procurement strategies, ensuring they select the ideal material to enhance product performance and durability.
Understanding 6061 t6 vs 7075 t6 Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| 6061 T6 | Good machinability, moderate strength, excellent corrosion resistance | Structural components, automotive parts, marine applications | Pros: Versatile, easy to machine and weld. Cons: Lower strength compared to 7075. |
| 7075 T6 | High strength, lower machinability, less corrosion resistant | Aerospace, military, high-stress applications | Pros: Exceptional strength, ideal for demanding applications. Cons: Difficult to weld and form. |
| 6061 T6 Anodized | Enhanced surface finish, improved corrosion resistance | Architectural applications, decorative items | Pros: Aesthetic appeal, excellent corrosion protection. Cons: Anodizing can add to costs. |
| 7075 T6 Annealed | Improved formability and weldability compared to standard 7075 | Custom components, specialized military applications | Pros: Better workability post-annealing. Cons: Requires careful handling during heat treatment. |
| 6061 T6 Extruded | Available in various shapes, good for custom profiles | Piping, structural beams, and custom fabrication | Pros: Versatile shapes, good mechanical properties. Cons: May have limitations in high-stress scenarios. |
What Are the Key Characteristics of 6061 T6 Aluminium Alloy?
6061 T6 is a versatile alloy known for its excellent machinability and moderate strength. It contains magnesium and silicon as its primary alloying elements, making it suitable for various applications, including structural components, automotive parts, and marine applications. B2B buyers should consider its ease of welding and forming, which allows for efficient fabrication processes. However, its strength is lower compared to 7075, making it less suitable for extremely high-stress applications.
How Does 7075 T6 Aluminium Alloy Compare in Strength?
7075 T6 is renowned for its exceptional strength, making it a preferred choice in aerospace and military applications. With zinc and copper as its primary alloying elements, it offers nearly double the tensile strength of 6061 T6. This alloy is ideal for high-stress applications but poses challenges in machinability and welding. Buyers should weigh the need for strength against the potential difficulties in forming and processing this alloy, which may impact project timelines and costs.
What Advantages Does Anodizing Offer for 6061 T6?
6061 T6 anodized provides a decorative and durable finish, enhancing its corrosion resistance. This process creates a transparent oxide layer, making it ideal for architectural applications and decorative items. B2B buyers may find this option appealing for products requiring both aesthetic and functional benefits. However, the anodizing process can increase production costs, which should be factored into budget considerations.
When Should 7075 T6 Be Annealed for Better Workability?
7075 T6 can be annealed to improve its formability and weldability, making it suitable for custom components in specialized applications. This process allows the alloy to be shaped and joined more easily, which can be advantageous for complex designs. However, buyers must ensure that they manage the heat treatment process carefully to maintain the desired mechanical properties, as improper handling can compromise performance.
What Are the Benefits of Using 6061 T6 in Extruded Forms?
6061 T6 extruded aluminium is available in a variety of shapes, making it highly versatile for applications like piping, structural beams, and custom fabrication. Its good mechanical properties and ease of fabrication are significant advantages for B2B buyers looking for tailored solutions. However, buyers should note that while it performs well in many scenarios, it may not be the best choice for applications subjected to high stress, necessitating careful selection based on project requirements.
Key Industrial Applications of 6061 t6 vs 7075 t6
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of 6061 t6 vs 7075 t6 | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Aerospace | Aircraft structures and components | High strength-to-weight ratio enhances performance and fuel efficiency | Certification standards (e.g., ASTM, ISO) for quality assurance |
| Automotive | Chassis and body components | Improved durability and reduced weight for better fuel economy | Compliance with regional automotive regulations |
| Marine | Boat fittings and structural components | Corrosion resistance ensures longevity in harsh environments | Availability of marine-grade materials and coatings |
| Construction | Structural frames and architectural elements | Versatility and ease of fabrication support diverse projects | Local sourcing of alloys to meet project timelines |
| Electronics | Enclosures and heat sinks | Enhanced thermal conductivity aids in efficient cooling | Compatibility with electronic components and designs |
How is 6061 T6 Used in Aerospace Applications?
In the aerospace sector, 6061 T6 aluminum is commonly utilized for aircraft structures and components due to its excellent machinability and corrosion resistance. This alloy provides a favorable strength-to-weight ratio, which is crucial for improving fuel efficiency in aircraft. International buyers must ensure that the materials meet stringent certification standards, such as ASTM and ISO, to guarantee safety and performance in aviation applications.
What Role Does 7075 T6 Play in Automotive Manufacturing?
7075 T6 aluminum is favored in the automotive industry for manufacturing chassis and body components. Its superior tensile strength allows for lightweight designs that enhance vehicle performance while maintaining safety standards. Buyers must consider compliance with regional automotive regulations and certifications to ensure that the materials used will withstand the rigorous demands of automotive applications, especially in markets like Africa and South America where road conditions can vary significantly.
Why is 6061 T6 Preferred in Marine Applications?
In marine applications, 6061 T6 is widely used for boat fittings and structural components due to its excellent corrosion resistance. This characteristic is vital for materials exposed to harsh marine environments, thus ensuring longevity and reliability. Buyers in the marine sector should prioritize sourcing from suppliers that provide marine-grade materials and protective coatings to enhance durability, particularly in regions like the Middle East where seawater exposure is prevalent.
How Does 7075 T6 Benefit Construction Projects?
7075 T6 aluminum is utilized in construction for structural frames and architectural elements, where its high strength is essential. This alloy supports diverse project requirements while maintaining structural integrity. Buyers should focus on local sourcing of these alloys to meet project timelines and consider the specific mechanical properties required for different structural applications, ensuring they align with local building codes and standards.
What Advantages Does 6061 T6 Offer in Electronics?
In the electronics sector, 6061 T6 aluminum is employed for enclosures and heat sinks due to its excellent thermal conductivity. This property aids in efficient cooling of electronic components, enhancing performance and longevity. For international buyers, it is crucial to ensure compatibility with various electronic designs and components, as well as to source materials that meet international standards for safety and quality in electronic applications.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘6061 t6 vs 7075 t6’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Choosing the Right Alloy for High-Stress Applications
The Problem: Many B2B buyers in industries such as aerospace and defense grapple with selecting the appropriate aluminum alloy for components subjected to high stress. They may be torn between 6061 T6 and 7075 T6, unsure if the higher strength of 7075 justifies its cost and limited formability. This indecision can lead to costly mistakes, such as choosing an alloy that cannot withstand operational demands, resulting in component failures and project delays.
The Solution: To navigate this challenge, buyers should conduct a thorough assessment of their application’s specific requirements, including load conditions, environmental factors, and expected lifespan. For components that will face extreme loads or require high strength, opting for 7075 T6 is advisable due to its superior tensile and shear strength. However, for applications where machining and weldability are critical, 6061 T6 might be the more practical choice. Buyers should also consider consulting with material specialists or engineers to evaluate the long-term performance and cost implications of each alloy, ensuring they make an informed decision that balances performance and budget.
Scenario 2: Overcoming Corrosion Resistance Concerns
The Problem: Buyers in marine or outdoor industries often face the challenge of selecting aluminum alloys that can withstand harsh environmental conditions. While both 6061 T6 and 7075 T6 have good corrosion resistance, the copper content in 6061 makes it more susceptible to corrosion, which can lead to unexpected maintenance costs and reduced product lifespan.
The Solution: To address corrosion concerns, buyers should consider applying protective coatings to 6061 T6 components, enhancing their durability without sacrificing machinability or formability. Additionally, specifying anodized finishes can provide an extra layer of protection, improving corrosion resistance while maintaining aesthetic appeal. For applications where corrosion is a critical concern, opting for 7075 T6 may be beneficial, but it’s essential to ensure that the specific environment is suitable for its use. Engaging with suppliers who offer corrosion-resistant treatments or custom specifications can further mitigate risks associated with environmental exposure.
Scenario 3: Navigating Machinability Challenges
The Problem: In manufacturing settings, buyers often encounter difficulties when machining aluminum alloys. While 6061 T6 is known for its excellent machinability, 7075 T6 can pose challenges due to its hardness and potential for tool wear. This discrepancy can result in increased production costs and longer lead times, as machinists may need to adjust their techniques or invest in specialized tools to handle 7075 T6 effectively.
The Solution: To streamline the machining process, buyers should clearly communicate their production needs and challenges with their suppliers. When working with 7075 T6, it may be beneficial to source advanced cutting tools designed for high-strength materials, which can mitigate issues of tool wear and improve machining efficiency. Additionally, incorporating pre-machining treatments, such as annealing, can enhance the alloy’s machinability without compromising its strength. For projects primarily focused on high-volume production, leveraging the benefits of 6061 T6, such as its easier machining properties, may be more cost-effective. Engaging with experienced machinists who understand the nuances of both alloys can also lead to optimized processes and reduced waste, further improving overall project efficiency.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for 6061 t6 vs 7075 t6
What Are the Key Properties of 6061 T6 and 7075 T6 Aluminum Alloys?
When comparing 6061 T6 and 7075 T6 aluminum alloys, it is essential to understand their distinct properties that affect performance in various applications.
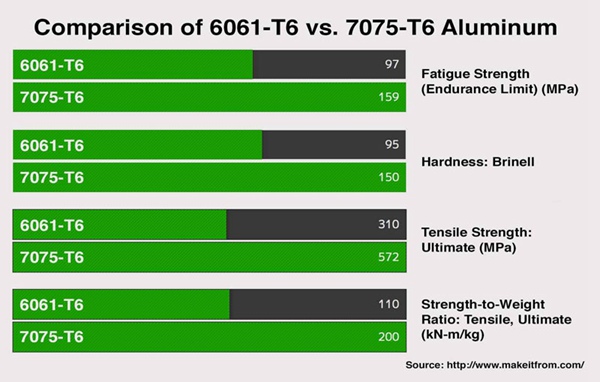
6061 T6 Aluminum Alloy is characterized by its excellent corrosion resistance, good weldability, and moderate strength. It typically has a yield strength of 276 MPa and a tensile strength of 310 MPa, making it suitable for structural applications where weight is a concern. Its thermal conductivity is relatively high, which is beneficial in applications requiring heat dissipation.
7075 T6 Aluminum Alloy, on the other hand, is known for its exceptional strength, with a yield strength of 503 MPa and a tensile strength of 570 MPa. This alloy is often referred to as “aircraft-grade” due to its high strength-to-weight ratio, making it ideal for aerospace and military applications. However, it has lower corrosion resistance compared to 6061 due to its higher copper content.
What Are the Pros and Cons of Each Alloy?
6061 T6 Aluminum Alloy:
– Pros:
– Good machinability and formability, making it easier to fabricate into complex shapes.
– Excellent corrosion resistance, suitable for marine and outdoor applications.
– Versatile for a wide range of applications, from automotive to construction.
– Cons:
– Lower strength compared to 7075, which may not be suitable for high-stress applications.
– Slightly more expensive than other alloys in the same category.
7075 T6 Aluminum Alloy:
– Pros:
– High strength, ideal for applications requiring durability and load-bearing capabilities.
– Suitable for high-stress components in aerospace and defense.
– Cons:
– Poorer machinability and formability, making it challenging to work with.
– Lower corrosion resistance, necessitating protective coatings in harsh environments.
How Do These Alloys Impact Specific Applications?
The choice between 6061 T6 and 7075 T6 can significantly impact application performance. For instance, 6061 T6 is often used in the manufacturing of structural components, marine fittings, and automotive parts due to its balance of strength and corrosion resistance. It is particularly effective in environments exposed to moisture and saltwater.
Conversely, 7075 T6 is predominantly utilized in aerospace components, military applications, and high-performance sporting equipment. Its superior strength makes it suitable for parts that undergo significant stress and strain, such as aircraft wings and fuselage structures. However, its lower corrosion resistance means that additional protective measures, such as anodizing, are often required to extend its lifespan in corrosive environments.
What Should International B2B Buyers Consider?
International buyers, particularly from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, must consider compliance with local standards when selecting between these alloys. Common standards such as ASTM (American Society for Testing and Materials), DIN (German Institute for Standardization), and JIS (Japanese Industrial Standards) can dictate the material specifications required for various applications.
Additionally, buyers should evaluate the availability and cost implications of sourcing these materials. For example, while 6061 T6 may be more readily available and cost-effective for general applications, 7075 T6 could be more suitable for specialized projects where performance cannot be compromised, despite potentially higher costs.
Summary Table of Material Selection
| Material | Typical Use Case for 6061 T6 vs 7075 T6 | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 6061 T6 | Structural components, marine fittings, automotive parts | Excellent corrosion resistance and good machinability | Lower strength compared to 7075 | Medium |
| 7075 T6 | Aerospace components, military applications, high-performance sporting equipment | Exceptional strength and durability | Poor machinability and lower corrosion resistance | High |
This strategic material selection guide provides B2B buyers with a comprehensive overview of the key differences between 6061 T6 and 7075 T6 aluminum alloys, enabling informed decision-making for their specific applications.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for 6061 t6 vs 7075 t6
What are the Typical Manufacturing Processes for 6061 T6 and 7075 T6 Aluminum Alloys?
Manufacturing aluminum alloys like 6061 T6 and 7075 T6 involves several critical stages, each tailored to the specific properties of the alloy. Understanding these processes is essential for B2B buyers looking to source materials that meet their project requirements.
Material Preparation: How is Raw Material Processed?
The manufacturing journey begins with material preparation, where aluminum ingots are sourced and inspected. For both 6061 and 7075, the raw materials undergo chemical analysis to ensure they meet specified compositions. The ingots are then heated to a specific temperature to facilitate easier manipulation.
For 6061, the focus is on ensuring the right balance of silicon and magnesium, while for 7075, the emphasis is on copper and zinc content. This step is crucial as it influences subsequent processes such as forming and machining.
Forming: What Techniques are Used to Shape the Alloys?
Forming is the next stage and can involve various techniques such as extrusion, rolling, and forging.
-
Extrusion: Both alloys are commonly extruded to create shapes like tubes and bars. The choice of extrusion method depends on the intended application. For 6061, which is easier to form, this process can be done at lower temperatures, while 7075 may require higher temperatures due to its hardness.
-
Rolling: Rolling is often employed for producing sheets and plates. The alloys are passed through rollers to achieve desired thickness and surface finish. The process is particularly important for applications requiring a specific strength-to-weight ratio.
-
Forging: This technique is more prevalent with 7075 due to its strength requirements. The alloy is hammered or pressed into shape, which enhances its mechanical properties.
Assembly: How are Components Joined Together?
Assembly techniques vary based on the alloy and the end-use application.
-
Welding: 6061 T6 is more amenable to welding due to its alloying elements, making it a popular choice for structural applications. Techniques like MIG and TIG welding are commonly used. In contrast, 7075 T6 can be challenging to weld and is generally not recommended unless in the annealed state.
-
Mechanical Fastening: Both alloys can be joined using bolts, rivets, and screws. This method is often preferred for applications where disassembly is necessary.
Finishing: What are the Final Touches Applied to the Alloys?
Finishing processes enhance the surface properties of the alloys and can include anodizing, painting, or coating.
-
Anodizing: 6061 aluminum is well-suited for anodizing, creating a protective oxide layer that improves corrosion resistance and surface hardness. Although 7075 can also be anodized, care must be taken to avoid discoloration due to its zinc content.
-
Coating: Both alloys can receive additional protective coatings to enhance their durability, especially in corrosive environments.
How is Quality Assurance Ensured in the Manufacturing of 6061 T6 and 7075 T6?
Quality assurance (QA) is critical in the manufacturing process to ensure the final products meet industry standards and customer expectations. B2B buyers must be well-versed in these practices to mitigate risks associated with sourcing materials.
What International Standards Apply to Aluminum Manufacturing?
Manufacturers of 6061 T6 and 7075 T6 typically adhere to international quality standards such as ISO 9001. This standard emphasizes a systematic approach to quality management and continuous improvement. Other industry-specific certifications may include CE marking for European markets and API (American Petroleum Institute) standards for oil and gas applications.
What are the Key Quality Control Checkpoints During Production?
Quality control involves several checkpoints throughout the manufacturing process:
-
Incoming Quality Control (IQC): This initial step involves inspecting raw materials for compliance with specified chemical compositions and physical properties.
-
In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): During manufacturing, IPQC ensures that parameters such as temperature, pressure, and dimensions are maintained. This step is crucial for processes like extrusion and forging.
-
Final Quality Control (FQC): After the manufacturing is complete, FQC includes dimensional checks, surface inspections, and mechanical property testing to ensure that the final products meet the desired specifications.
What Common Testing Methods are Employed for 6061 T6 and 7075 T6?
Manufacturers utilize various testing methods to verify the quality of aluminum alloys:
-
Tensile Testing: This assesses the strength and ductility of the alloys, ensuring they meet specified yield and tensile strength requirements.
-
Hardness Testing: Methods like Rockwell or Brinell testing evaluate the hardness of the alloy, which is particularly important for applications involving wear and tear.
-
Corrosion Testing: Salt spray tests and other methods assess the corrosion resistance of the alloys, particularly for those intended for harsh environments.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control Practices?
B2B buyers should take proactive steps to verify the quality control practices of their suppliers:
-
Supplier Audits: Conducting regular audits helps ensure compliance with quality standards and identifies areas for improvement.
-
Quality Reports: Requesting detailed quality reports from suppliers can provide insights into their testing methods and results.
-
Third-Party Inspections: Engaging third-party inspection services offers an unbiased assessment of the supplier’s quality control processes and final products.
What are the Quality Control Considerations for International Buyers?
For international B2B buyers, particularly those from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, understanding the nuances of quality control is vital:
-
Certification Recognition: Ensure that the certifications held by suppliers are recognized in your region. For instance, CE marking is essential for European markets.
-
Cultural and Regulatory Differences: Be aware of any regional differences in quality standards and regulations that may affect product specifications.
-
Logistics and Supply Chain Considerations: Quality assurance extends to the logistics involved in transporting materials. Ensure that suppliers have robust processes for managing transportation to minimize damage or loss.
By comprehensively understanding the manufacturing processes and quality assurance protocols associated with 6061 T6 and 7075 T6 aluminum alloys, B2B buyers can make informed sourcing decisions that align with their specific project requirements.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘6061 t6 vs 7075 t6’
In the competitive landscape of B2B procurement, selecting the right aluminum alloy—specifically between 6061 T6 and 7075 T6—requires careful consideration of your project needs. This guide provides a practical checklist to help international buyers make informed decisions.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Establish clear technical requirements for your application. Determine the necessary properties such as tensile strength, corrosion resistance, and machinability based on the end use of the material. For instance, if strength is paramount, 7075 T6 may be more suitable, whereas 6061 T6 is better for projects requiring extensive machining.
Step 2: Identify Application Requirements
Understand the specific application for which you need the alloy. Different industries may have unique demands; for example, 7075 is commonly used in aerospace applications due to its superior strength, while 6061 is favored in automotive and marine sectors for its versatility. List these applications to guide your selection process.
Step 3: Evaluate Potential Suppliers
Conduct thorough research on potential suppliers. Request company profiles, certifications, and references from previous clients in similar industries or regions. Ensure they have experience with both alloys and can provide insights into their performance characteristics based on your specific needs.
- Check for ISO Certifications: Look for suppliers that adhere to international quality standards, ensuring consistent product quality.
- Review Customer Feedback: Seek testimonials or case studies that highlight the supplier’s reliability and service quality.
Step 4: Compare Pricing and Availability
Obtain quotes for both 6061 T6 and 7075 T6 alloys from multiple suppliers. Pricing can vary significantly based on alloy grade, supplier location, and order volume. Ensure you understand the total cost, including shipping and any potential tariffs, especially if sourcing from international suppliers.
Step 5: Assess Machinability and Fabrication Support
Evaluate the machinability of the alloys based on your manufacturing capabilities. 6061 T6 is generally easier to machine and weld compared to 7075 T6, which may require specialized equipment. Confirm that your supplier can provide additional fabrication services if needed.
- Ask About Support Services: Inquire if the supplier offers machining or finishing services that can streamline your production process.
Step 6: Verify Corrosion Resistance and Treatment Options
Understand the corrosion resistance of each alloy and any necessary treatments. While both alloys have good corrosion resistance, 6061 may require additional coatings for enhanced protection in harsh environments. Discuss treatment options like anodizing with your supplier to ensure long-term durability.
Step 7: Finalize Your Purchase Agreement
Once you have selected a supplier and determined the appropriate alloy, finalize the purchase agreement. Ensure that all terms regarding pricing, delivery timelines, and quality assurances are clearly outlined. This step is crucial to prevent any misunderstandings during the procurement process.
By following this checklist, B2B buyers can make informed decisions when sourcing between 6061 T6 and 7075 T6 aluminum alloys, ultimately enhancing the quality and performance of their products.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for 6061 t6 vs 7075 t6 Sourcing
When sourcing aluminum alloys like 6061 T6 and 7075 T6, understanding the comprehensive cost structure and pricing dynamics is essential for B2B buyers, especially those operating in international markets such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe.
What Are the Key Cost Components in Sourcing 6061 T6 vs 7075 T6?
-
Materials: The primary cost driver in aluminum sourcing is the raw materials. 7075 T6 typically costs more than 6061 T6 due to its higher alloy content, particularly zinc and copper. Prices can fluctuate based on global aluminum market trends, which directly affect the cost per kilogram.
-
Labor: Labor costs vary significantly by region and the complexity of the machining or fabrication required. Since 6061 T6 is easier to machine and weld, it often incurs lower labor costs compared to 7075 T6, which may require specialized skills and additional handling due to its toughness.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes costs related to production facilities, equipment maintenance, and utilities. Given that 7075 T6 requires more advanced techniques for processing, its manufacturing overhead can be higher than that of 6061 T6.
-
Tooling: The tooling costs associated with each alloy can differ. 7075 T6 may necessitate more robust tooling to withstand its hardness, leading to higher initial investment costs for manufacturers, which can be reflected in the price.
-
Quality Control (QC): Ensuring that the materials meet the required specifications incurs costs that vary by alloy. 7075 T6 often requires stricter quality assurance protocols due to its applications in critical structural components.
-
Logistics: Transporting aluminum from suppliers to buyers can significantly impact costs, especially for international shipments. The weight difference, primarily due to density variations (6061 T6 is lighter), can influence shipping expenses.
-
Margin: Suppliers typically add a margin to cover risks and profit. This margin can vary based on demand, the supplier’s market position, and the strategic importance of the alloy in their product line.
How Do Price Influencers Affect the Cost of 6061 T6 and 7075 T6?
-
Volume/MOQ: Bulk orders often lead to price reductions. Suppliers are more inclined to offer discounts on larger volumes, which is crucial for B2B buyers looking to optimize costs.
-
Specifications and Customization: Custom orders that require unique specifications or additional treatments (e.g., anodizing or coating) can increase costs. Buyers should clearly communicate their needs to avoid unexpected expenses.
-
Material Quality and Certifications: Alloys with higher quality certifications (e.g., ISO standards) or specific performance attributes will cost more. It’s vital for buyers to assess their requirements against available certifications to ensure they receive appropriate materials.
-
Supplier Factors: The reputation, reliability, and location of suppliers can significantly impact pricing. Established suppliers may charge a premium for their products due to perceived quality and lower risk.
-
Incoterms: Understanding Incoterms is crucial for international buyers, as they define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in shipping. These terms can affect overall costs, including insurance, shipping, and duties.
What Are the Best Practices for Negotiating Prices on 6061 T6 vs 7075 T6?
-
Leverage Total Cost of Ownership: When negotiating, consider not just the upfront costs but also the Total Cost of Ownership (TCO), which includes maintenance, operational costs, and potential downtime. Presenting a TCO analysis can strengthen your bargaining position.
-
Build Long-term Relationships: Establishing long-term partnerships with suppliers can lead to better pricing and terms. Suppliers are often more willing to negotiate with repeat customers.
-
Stay Informed: Market conditions can shift rapidly, affecting pricing. Buyers should stay informed about global aluminum prices and trends to negotiate effectively.
-
Consider Regional Factors: For buyers in regions like Africa or South America, understanding local market dynamics, import tariffs, and logistics can provide leverage in negotiations.
-
Request Multiple Quotes: Always obtain quotes from several suppliers to ensure competitive pricing. This practice not only aids in cost comparison but also provides insights into market rates.
Disclaimer
The prices discussed are indicative and may vary based on market conditions, supplier negotiations, and specific buyer requirements. Always consult with suppliers for the most accurate and current pricing.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing 6061 t6 vs 7075 t6 With Other Solutions
Introduction: Exploring Alternatives to 6061 T6 and 7075 T6 Aluminium Alloys
When choosing materials for industrial applications, understanding the alternatives to popular options like 6061 T6 and 7075 T6 aluminium alloys is crucial for making informed decisions. Each alloy has distinct properties that make it suitable for specific applications, but there may be other materials that could meet or exceed the performance requirements while offering different advantages. This section explores viable alternatives, comparing their performance, cost, ease of implementation, maintenance, and ideal use cases.
Comparison Table
| Comparison Aspect | 6061 T6 Vs 7075 T6 | Carbon Steel | Titanium Alloys |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | Moderate strength, good corrosion resistance | High strength, less corrosion resistant | Excellent strength-to-weight ratio, corrosion resistant |
| Cost | Moderate (higher than carbon steel) | Low cost | High cost |
| Ease of Implementation | Good machinability and weldability | Easy to machine and weld | Difficult to machine, requires specialized tools |
| Maintenance | Low maintenance with anodizing | Moderate maintenance due to rust | Low maintenance, highly durable |
| Best Use Case | Structural applications, automotive | Construction, general fabrication | Aerospace, medical implants |
Detailed Breakdown of Alternatives
Carbon Steel
Carbon steel is a widely used material known for its strength and versatility. It is significantly cheaper than both 6061 T6 and 7075 T6 aluminium alloys, making it an attractive option for budget-sensitive projects. However, carbon steel is more susceptible to rust and corrosion, requiring regular maintenance and protective coatings. It is well-suited for construction and general fabrication, where high strength is necessary but weight is less of a concern.
Titanium Alloys
Titanium alloys offer an exceptional strength-to-weight ratio, making them an attractive alternative for applications where weight savings are critical, such as aerospace and medical implants. They are also highly resistant to corrosion, ensuring durability in challenging environments. However, titanium alloys come at a premium price and can be difficult to machine, requiring specialized tools and techniques. This makes them less suitable for applications where cost and ease of implementation are significant factors.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Solution for Your Needs
Selecting the right material for your project involves balancing performance, cost, and specific application requirements. While 6061 T6 and 7075 T6 aluminium alloys excel in many areas, alternatives like carbon steel and titanium alloys may provide better solutions depending on your goals. Carbon steel is ideal for cost-sensitive projects where weight is not a critical factor, while titanium alloys shine in high-performance applications that demand strength and corrosion resistance. Understanding these options allows B2B buyers to make informed decisions tailored to their unique operational needs, optimizing both performance and cost-effectiveness.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for 6061 t6 vs 7075 t6
What Are the Key Technical Properties of 6061 T6 and 7075 T6 Aluminium Alloys?
When comparing 6061 T6 and 7075 T6 aluminium alloys, understanding their critical specifications is crucial for informed purchasing decisions. Here are some key properties to consider:
- Material Grade:
- 6061 T6: A versatile aluminium alloy known for its excellent weldability and machinability, making it suitable for a wide range of applications, including structural components and automotive parts.
-
7075 T6: Known as “aircraft grade,” this alloy boasts high strength and is typically used in aerospace applications where high performance and reduced weight are critical.
-
Tensile Strength:
- 6061 T6: Approximately 276 MPa (40,000 psi).
-
7075 T6: Approximately 503 MPa (73,000 psi).
This difference highlights 7075 T6’s superior performance in high-stress environments, making it essential for industries requiring robust materials. -
Machinability:
- 6061 T6 is favored for machining due to its good workability. It allows for easier shaping and cutting processes, crucial for manufacturers needing precision components.
-
7075 T6 has fair machinability, making it less desirable for intricate machining tasks but still usable in less complex applications.
-
Corrosion Resistance:
-
Both alloys exhibit excellent resistance due to the formation of a protective oxide layer. However, 6061 T6 is slightly less resistant due to its copper content. Understanding this can help in selecting the appropriate alloy for environments prone to corrosion.
-
Density:
- 6061 T6 has a density of approximately 2.7 g/cm³, while 7075 T6 is denser at about 2.81 g/cm³. This difference can impact the overall weight and strength of components, particularly in aerospace and automotive industries where weight savings are paramount.
What Are Common Trade Terms Relevant to 6061 T6 and 7075 T6?
Familiarity with industry jargon can facilitate smoother transactions and better communication with suppliers. Here are some essential terms:
-
OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer): Refers to companies that produce parts or equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer. Understanding the OEM landscape is vital for sourcing components that meet specific project requirements.
-
MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity): The smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell. This term is crucial for B2B buyers to understand as it affects inventory management and cash flow.
-
RFQ (Request for Quotation): A document issued by a buyer to solicit price quotes from suppliers. An effective RFQ process can lead to better pricing and terms, ultimately affecting project budgets.
-
Incoterms (International Commercial Terms): A set of predefined commercial terms that delineate the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in international transactions. Familiarity with these terms can mitigate risks and clarify shipping responsibilities, crucial for international buyers in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe.
-
Lead Time: The time it takes from placing an order until it is delivered. Understanding lead times is essential for project planning and inventory management, especially in industries with tight production schedules.
By grasping these technical properties and trade terminologies, B2B buyers can make more informed decisions regarding the procurement of 6061 T6 and 7075 T6 aluminium alloys, ensuring that their choices align with their operational needs and project requirements.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the 6061 t6 vs 7075 t6 Sector
What Are the Current Market Dynamics and Key Trends for 6061 T6 vs 7075 T6 Aluminium Alloys?
The global aluminium alloy market, particularly for 6061 T6 and 7075 T6, is driven by increasing demand across various sectors, including aerospace, automotive, and construction. Emerging economies in Africa, South America, and the Middle East are witnessing rapid industrialization, leading to heightened demand for high-strength materials. The aerospace sector, notably in countries like Nigeria and Saudi Arabia, is increasingly leaning towards 7075 T6 due to its superior strength-to-weight ratio, making it ideal for aircraft components. Conversely, the versatility of 6061 T6 is being capitalized upon in the automotive and construction industries, where its excellent machinability and corrosion resistance are essential.
The rise of advanced manufacturing technologies, such as additive manufacturing and CNC machining, is also influencing sourcing trends. International buyers are increasingly seeking suppliers who can provide tailored solutions, including custom machining and finishing services. Additionally, digital platforms are streamlining procurement processes, enabling buyers to access a broader range of suppliers and compare offerings more efficiently. As companies focus on lean manufacturing, the demand for just-in-time (JIT) sourcing strategies is increasing, requiring suppliers to maintain flexibility and responsiveness.
Furthermore, the push towards lightweight materials for energy efficiency is shaping market dynamics. Industries are increasingly prioritizing materials that not only meet performance specifications but also contribute to sustainability goals, positioning both 6061 T6 and 7075 T6 as critical components in future applications.
How Important Is Sustainability and Ethical Sourcing for 6061 T6 and 7075 T6 Aluminium?
Sustainability is becoming a central tenet in the sourcing of aluminium alloys, with significant implications for B2B buyers. The environmental impact of aluminium production is considerable, often involving high energy consumption and greenhouse gas emissions. Consequently, buyers are increasingly inclined to source materials from suppliers who adhere to sustainable practices, including the use of recycled aluminium. Both 6061 T6 and 7075 T6 alloys can be produced using recycled content, reducing the carbon footprint associated with their production.
Ethical supply chains are also gaining importance, particularly in regions like Africa and South America, where sourcing practices can significantly affect local communities. Buyers are encouraged to engage with suppliers who offer transparency regarding their sourcing processes, labor practices, and environmental impacts. Certifications such as ISO 14001 for environmental management and ASI (Aluminium Stewardship Initiative) certification for responsible sourcing are becoming essential criteria for procurement decisions.
The demand for ‘green’ certifications is not just a trend; it reflects a broader shift towards corporate responsibility. Companies are increasingly recognizing that sustainable practices can enhance brand reputation and attract environmentally conscious customers. As a result, integrating sustainability into the procurement process for 6061 T6 and 7075 T6 alloys is not merely a compliance measure, but a strategic advantage in a competitive marketplace.
How Has the History of 6061 T6 and 7075 T6 Aluminium Alloys Influenced Current Market Trends?
The evolution of 6061 T6 and 7075 T6 aluminium alloys dates back to the mid-20th century, with significant advancements in metallurgy and processing techniques. Initially developed for military and aerospace applications, these alloys have become foundational materials across various industries due to their distinct properties.
7075 T6, known for its exceptional strength, was primarily used in aircraft structures and military applications, earning its reputation as an “aircraft-grade” alloy. In contrast, 6061 T6 emerged as a versatile option for a wide range of applications, including automotive and construction, due to its excellent machinability and weldability.
As industries have evolved, so have the applications of these alloys. The historical significance of their development has paved the way for modern innovations, such as lightweight structures that enhance fuel efficiency and performance. Today, the legacy of these materials continues to drive demand, with ongoing research focused on improving their properties and expanding their applications in line with contemporary technological advancements. This historical context is vital for B2B buyers as it highlights the reliability and proven performance of these alloys in demanding applications.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of 6061 t6 vs 7075 t6
-
How do I choose between 6061 T6 and 7075 T6 for my project?
Choosing between 6061 T6 and 7075 T6 largely depends on the specific requirements of your project. If you need high strength and hardness, 7075 T6 is ideal, particularly for aerospace and defense applications. However, if your project involves machining, forming, or welding, 6061 T6 is more versatile due to its superior workability and corrosion resistance. Assess the mechanical properties and application requirements to determine which alloy aligns best with your needs. -
What are the key differences in strength between 6061 T6 and 7075 T6?
The primary distinction in strength between these two alloys lies in their tensile and shear strength. 7075 T6 boasts a tensile strength nearly double that of 6061 T6, making it suitable for high-stress applications. Additionally, the shear strength of 7075 T6 is approximately 1.5 times that of 6061 T6. For applications requiring maximum strength and durability, 7075 T6 is generally the preferred choice. -
Can 6061 T6 and 7075 T6 be welded?
While both alloys can be welded, they differ significantly in their weldability. 6061 T6 is known for its good weldability due to its alloying elements, making it suitable for welded structures. In contrast, 7075 T6 is less conducive to welding unless it is in an annealed state. If welding is a critical factor in your application, 6061 T6 would be the better option. -
What are the corrosion resistance properties of 6061 T6 compared to 7075 T6?
Both alloys exhibit excellent corrosion resistance due to the protective oxide layer formed when exposed to air or water. However, 6061 T6 has a slightly lower corrosion resistance compared to 7075 T6 due to its copper content. To enhance the corrosion resistance of 6061 T6, applying a protective coating is advisable. For applications in corrosive environments, consider the specific needs and potential coatings available. -
What is the minimum order quantity (MOQ) for 6061 T6 and 7075 T6?
Minimum order quantities can vary significantly depending on the supplier and the specific requirements of your order. Typically, MOQs for aluminum alloys like 6061 T6 and 7075 T6 can range from a few hundred kilograms to several tons. It is essential to discuss your project needs with suppliers to determine their MOQ and negotiate terms that suit your budget and project scope. -
How do I evaluate potential suppliers for 6061 T6 and 7075 T6?
When evaluating suppliers, consider their experience in the aluminum industry, their product quality certifications (such as ISO), and their ability to provide detailed specifications for the alloys. Additionally, inquire about their capacity for customization and lead times. Requesting samples can also help assess the quality of the material before making larger purchases. Building a relationship with reputable suppliers can facilitate smoother transactions. -
What payment terms should I expect when sourcing 6061 T6 and 7075 T6 internationally?
Payment terms can vary by supplier and region, but common practices include payment in advance, letters of credit, or net 30/60 days after delivery. It’s crucial to clarify these terms upfront to avoid misunderstandings. Additionally, consider the implications of currency fluctuations and international banking fees when negotiating payment terms, especially in cross-border transactions. -
What logistics considerations should I keep in mind when importing 6061 T6 and 7075 T6?
Logistics is a critical factor when importing aluminum alloys. Ensure you understand the shipping regulations and tariffs applicable to your region. Collaborate with suppliers who can provide information on shipping options, estimated delivery times, and handling procedures. Also, consider the costs associated with customs clearance and potential delays, which can affect your project timelines. Partnering with an experienced logistics provider can streamline the import process.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.
Top 8 6061 T6 Vs 7075 T6 Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. Thyssenkrupp – 7075 Aluminium
Domain: thyssenkrupp-materials.co.uk
Registered: 2017 (8 years)
Introduction: 7075 Aluminium:
– Series: 7XXX
– Main Alloying Elements: Copper, Zinc
– Chemical Composition: Aluminium (97.9%), Zinc (5.6%), Magnesium (2.5%), Chromium (0.23%), Copper (1.6%)
– Strength: High tensile strength (nearly double that of 6061 T6), higher shear strength (1.5 times that of 6061 T6), harder than 6061 T6
– Machinability: Fair machinability
– Formability and Welding: Not conducive unl…
2. Reddit – Aluminum Comparison
Domain: reddit.com
Registered: 2005 (20 years)
Introduction: 6061 aluminum:
– Generally used for billet lowers.
– Not as tough as 7075 aluminum.
– Yield strength of ~35,000 psi.
– Suitable for most casual users, with adequate strength for normal use.
7075 aluminum:
– Preferred for forged lowers.
– Has double the tensile strength of 6061, making it more durable at stress points like takedown pins.
– Considered the best cost-effective solutio…
3. Make It From – Aluminum Alloys 6061-T6 & 7075-T6
Domain: makeitfrom.com
Registered: 2009 (16 years)
Introduction: This company, Make It From – Aluminum Alloys 6061-T6 & 7075-T6, is a notable entity in the market. For specific product details, it is recommended to visit their website directly.
4. Kormax – Aluminium 6061 vs 7075 Comparison
Domain: kormax.com
Registered: 1998 (27 years)
Introduction: Aluminium 6061 vs 7075 Comparison:
– Composition:
– 6061: Higher silicon content, excellent corrosion resistance, good weldability.
– 7075: Higher zinc concentration, exceptional strength and hardness.
– Strength and Durability:
– 6061: Yield strength of 276 MPa, robust but not as strong as 7075.
– 7075: Significantly higher yield strength, nearly double that of 6061, suitable for hi…
5. Practical Machinist – Aluminum Alloys 7075-T6 vs 6061-T6
Domain: practicalmachinist.com
Registered: 2000 (25 years)
Introduction: 7075-T6 and 6061-T6 are two aluminum alloys discussed in terms of their machining characteristics. 7075-T6 is noted for better chip breaking compared to 6061-T6, which is described as gummy and difficult to manage during machining. Users report that 6061-T6 can lead to issues like bird nesting of chips, requiring adjustments in machining parameters such as speed, feed, and depth of cut. 6262-T9 is…
6. 6061 vs 7075 Aluminum – Key Differences
Domain: bikeforums.net
Registered: 2001 (24 years)
Introduction: 6061 aluminum is much softer than 7075 aluminum. 6061 is easier to machine with CNC due to its softness, but chainrings made from 6061 last significantly less than those made from 7075 due to the difference in hardness. The post emphasizes the importance of distinguishing between these two types of aluminum, especially when purchasing chainrings, as some sellers may misrepresent the material.
7. Metal Supermarkets – Aluminum Alloy Grades
Domain: metalsupermarkets.com
Registered: 1996 (29 years)
Introduction: 6061 and 7075 are two popular aluminum alloy grades used in structural applications.
– **Alloy Series & Chemical Composition:** 6061 is in the 6XXX series with higher silicon content, while 7075 is in the 7XXX series with higher zinc and copper content. Both contain significant amounts of magnesium.
– **Mechanical Properties:** 7075-T6 has nearly double the tensile strength and 1.5 times the s…
8. Online Metals – Aluminum 6061 vs 7075
Domain: onlinemetals.com
Registered: 1997 (28 years)
Introduction: Aluminum 6061 vs 7075: 6061 is versatile, used in structural components, vehicles, and consumer products; good for welding and machining. 7075 is high strength, used in aerospace and military applications; preferred for high strength and low weight. Mechanical Properties: 6061 (T651) – Tensile Strength: 45,000 psi, Yield Point: 40,000 psi, Brinell Hardness: 95, Elongation at Break: 12%, Shear Stre…
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for 6061 t6 vs 7075 t6
In summary, the choice between 6061 T6 and 7075 T6 aluminum alloys ultimately hinges on the specific requirements of your application. For projects demanding exceptional strength and durability, such as aerospace and military applications, 7075 T6 stands out due to its superior tensile and shear strength. Conversely, if your focus is on versatility, workability, and corrosion resistance, 6061 T6 is the more suitable option, making it ideal for a wide range of applications from automotive to structural components.
Strategic sourcing plays a critical role in optimizing your supply chain, ensuring that you select the right materials that align with your project specifications and budget constraints. As international B2B buyers from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe navigate the complexities of sourcing aluminum alloys, it is crucial to consider not only the mechanical properties but also the long-term implications of material selection on performance and cost-efficiency.
Looking ahead, staying informed about market trends and advancements in aluminum alloy technologies will empower you to make informed sourcing decisions. Engage with reliable suppliers and explore partnerships that can enhance your operational efficiency and product quality. Your proactive approach today can pave the way for successful projects tomorrow.