Contents
Manufacturing Insight: 6-Axis Machining
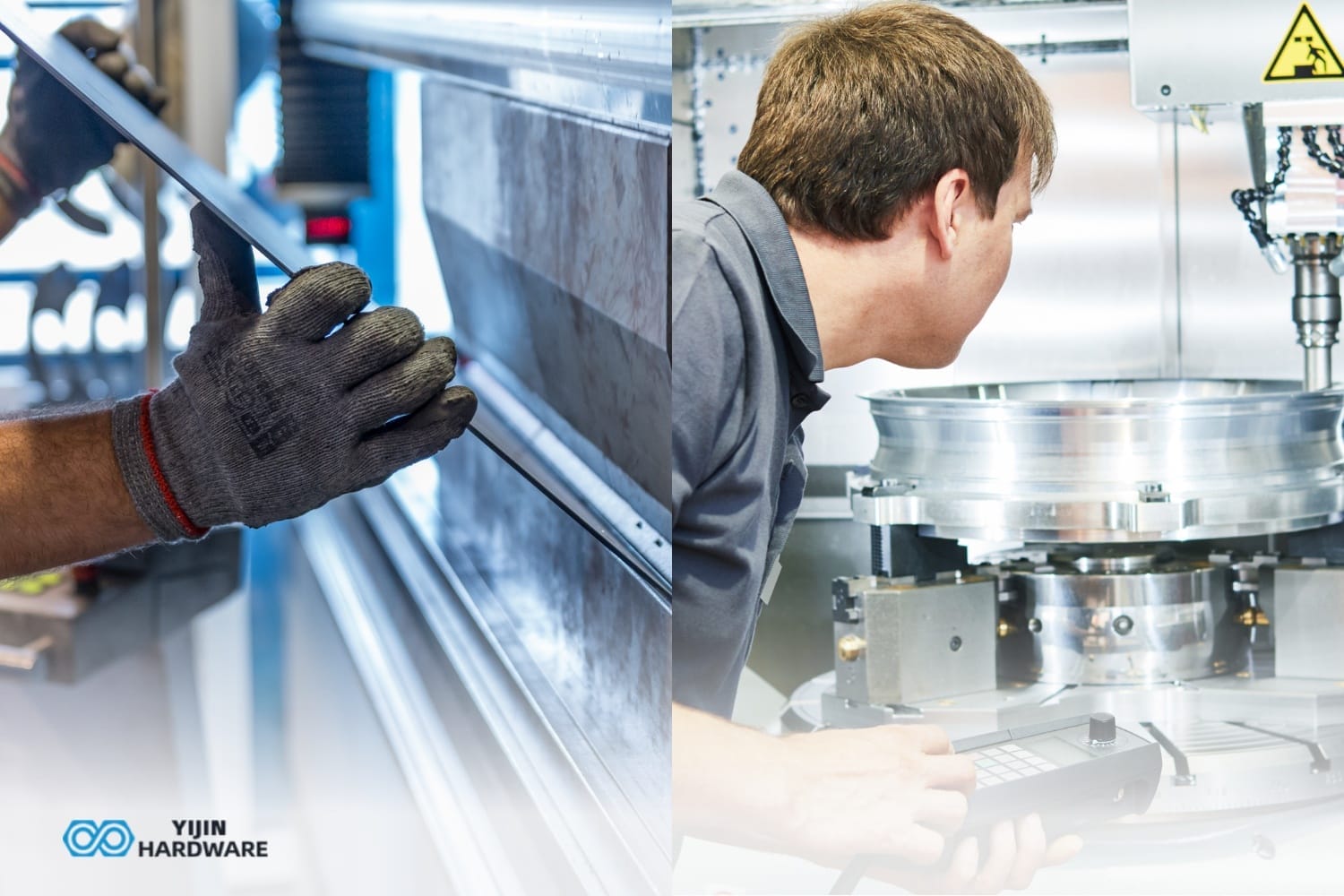

Precision Redefined: Honyo Prototype’s 6-Axis CNC Machining Capabilities
Honyo Prototype delivers advanced manufacturing solutions through our state-of-the-art 6-axis CNC machining services, engineered to tackle the most complex geometries with uncompromising precision. Unlike conventional 3-axis or 5-axis systems, our 6-axis technology integrates simultaneous rotational and linear movement, enabling the machining of intricate contours, undercuts, and organic forms in a single setup. This eliminates costly secondary operations, reduces cumulative tolerances, and ensures superior monolithic part integrity for aerospace components, medical devices, and high-performance industrial tooling.
Our engineering team leverages ISO-certified processes and cutting-edge multi-axis controls to achieve micron-level accuracy across diverse materials—from titanium alloys and Inconel to engineering plastics and composites. Every project undergoes rigorous in-process inspection and final validation, ensuring adherence to AS9100 and ISO 13485 standards where required. The result is accelerated time-to-market, minimized waste, and parts that perform reliably in extreme operational environments.
Accelerate your prototyping and low-volume production with Honyo Prototype’s seamless workflow. Begin with our Online Instant Quote platform—input your CAD file and specifications to receive a detailed, engineer-validated cost and lead time estimate within hours, not days. This transparency empowers data-driven decisions without sacrificing the technical expertise that defines our manufacturing excellence.
Technical Capabilities

6-axis machining extends the capabilities of multi-axis CNC systems by incorporating additional rotational and translational axes, enabling highly complex geometries, improved tool access, and reduced need for part repositioning. While 3-axis, 4-axis, and 5-axis milling are more commonly used in production environments, true 6-axis machining is typically found in advanced robotic or hybrid systems. The following table outlines the technical specifications and capabilities relevant to 3-axis, 4-axis, and 5-axis milling processes—commonly referenced in high-precision manufacturing—as well as turning operations, with emphasis on tight tolerances and compatible materials such as Aluminum, Steel, ABS, and Nylon.
| Feature | 3-Axis Milling | 4-Axis Milling | 5-Axis Milling | CNC Turning | Notes on 6-Axis Capability |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Axes of Motion | X, Y, Z | X, Y, Z, A (rotary around X) | X, Y, Z, A, B (or C) | X, Z (rotary workpiece) | Adds two rotational axes (e.g., A+B or B+C), enabling full tool orientation and workpiece manipulation |
| Typical Positioning Accuracy | ±0.005 mm | ±0.005 mm | ±0.003 mm | ±0.005 mm | 6-axis systems can achieve ±0.002 mm with active compensation |
| Repeatability | ±0.002 mm | ±0.002 mm | ±0.001 mm | ±0.002 mm | Enhanced via real-time feedback in robotic 6-axis platforms |
| Tight Tolerance Capability | ±0.010 mm | ±0.010 mm | ±0.005 mm | ±0.010 mm (diameter) | 6-axis enables tolerances down to ±0.003 mm on complex surfaces |
| Surface Finish (Typical) | 0.8–3.2 µm Ra | 0.8–1.6 µm Ra | 0.4–1.6 µm Ra | 0.8–1.6 µm Ra | Improved tool angle control reduces step-over marks |
| Common Materials | Aluminum, Steel, ABS, Nylon | Aluminum, Steel, ABS, Nylon | Aluminum, Steel, ABS, Nylon | Aluminum, Steel, ABS, Nylon | Compatible with same materials; better for difficult-to-machine alloys due to optimized tool engagement |
| Material-Specific Notes | Aluminum: high MRR, minimal tool wear. Steel: requires rigid setup. ABS/Nylon: low melting point, requires sharp tools and low feed. | Same as 3-axis; A-axis enables wrap-around features on ABS/Nylon | Ideal for complex steel molds and aluminum aerospace parts. Nylon benefits from reduced setups | Efficient for cylindrical Aluminum, Steel, and plastic shafts | 6-axis allows simultaneous machining on non-prismatic parts in plastics and metals with minimal fixturing |
| Setup Complexity | Low | Medium | High | Low to Medium | 6-axis reduces setups but increases programming complexity |
| Typical Applications | Flat surfaces, prismatic parts | Indexing features, drilled holes around cylinder | Impellers, molds, aerospace components | Shafts, bushings, fasteners | Robotic deburring, hybrid additive-subtractive, sculptural components |
| Tool Path Flexibility | Limited to orthogonal cuts | Rotary indexing for side features | Full contouring with continuous tool engagement | Linear and radial cuts | Full 3D tool and workpiece orientation enables undercuts without fixtures |
Additional Notes:
5-axis milling is the practical upper limit for most high-precision CNC machining centers used in prototyping and low-volume production at Honyo Prototype.
True 6-axis machining typically involves a robotic arm (6 degrees of freedom) combined with a spindle or hybrid system, used for specialized applications such as large-scale sculpting, repair, or multi-face machining without fixturing.
For tight tolerance work in Aluminum and Steel, thermal stability and machine rigidity are critical; 5-axis machines with direct drive rotary tables are preferred.
In polymers like ABS and Nylon, minimizing vibration and optimizing spindle speed is essential to maintain dimensional accuracy and surface quality.
Honyo Prototype leverages 5-axis CNC and precision turning for tight tolerance components, with capabilities traceable to ISO 2768-mK and customer-specific GD&T requirements.
From CAD to Part: The Process
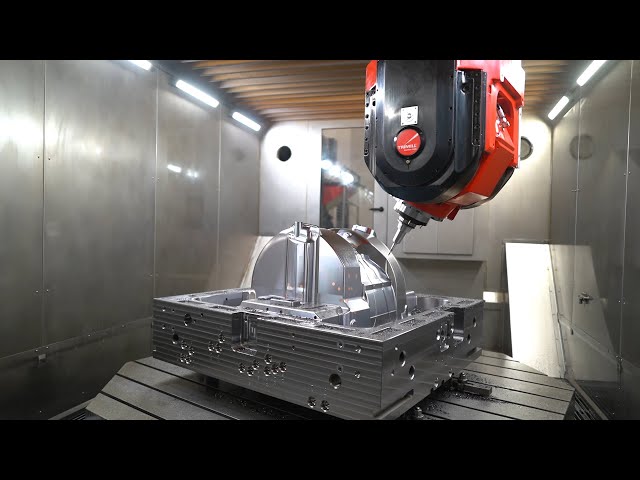

Honyo Prototype employs a rigorously defined workflow for 6-axis machining projects to ensure precision, efficiency, and adherence to client specifications. This integrated process spans from initial design submission through final delivery, leveraging advanced technology and engineering expertise at each stage.
CAD File Upload and Validation
Clients initiate the process by uploading native or neutral CAD formats (STEP, IGES, Parasolid) via our secure customer portal. Our system performs an immediate automated validation check for file integrity, unit consistency, and geometric completeness. Any detected anomalies—such as missing datums, non-manifold edges, or unit mismatches—trigger an instant notification to the client for correction. This step ensures the foundational geometry is error-free before proceeding, eliminating downstream delays caused by flawed input data.
AI-Powered Quoting and Feasibility Assessment
Validated CAD files enter our proprietary AI quoting engine, which analyzes geometric complexity, material requirements, tolerance density, and feature accessibility. The AI cross-references historical machining data from over 50,000 completed 6-axis projects to generate a preliminary cost estimate and lead time within hours. Crucially, this phase includes an automated manufacturability screen that flags potential issues such as undercut geometries requiring specialized tooling or features beyond standard 6-axis kinematic capabilities. A Senior Manufacturing Engineer validates all AI outputs, adding technical notes for complex geometries before the quote is released.
Engineering-Driven DFM Analysis
Upon quote acceptance, our Design for Manufacturability (DFM) team conducts a deep technical review. This is not a checklist exercise but a collaborative engineering dialogue. Key parameters evaluated include:
| DFM Parameter | Analysis Method | Critical Thresholds for 6-axis |
|---|---|---|
| Feature Accessibility | Kinematic simulation in Vericut | Minimum tool approach angle ≥ 15° |
| Wall Thickness | FEA-based deflection modeling | < 0.5mm requires adaptive step-downs |
| Tolerance Stack-up | GD&T simulation with Monte Carlo methods | ±0.005mm on critical datums |
| Material Removal Rate | Chip load/force calculation | < 85% machine capacity for hard metals |
The DFM report provides actionable redesign recommendations—such as consolidating features to minimize setups or adjusting radii for tool engagement—along with revised cost/time impacts. Client approval of the DFM package is mandatory before programming begins.
Precision 6-axis Machining Execution
Production leverages DMG MORI CMX 6-axis vertical machining centers with integrated Renishaw probing systems. The process eliminates manual repositioning through:
Simultaneous multi-face machining using RTCP (Rotational Tool Center Point) compensation
In-process probing for automatic work offset correction and first-article verification
Real-time vibration monitoring to maintain surface finish on thin-walled features
All programs undergo virtual machine simulation in NCSIMUL prior to shop floor deployment. For mission-critical components, we implement closed-loop tolerance control where in-machine probing data automatically adjusts subsequent toolpaths.
Certified Delivery and Traceability
Completed parts undergo comprehensive metrology using Zeiss CONTURA CMMs with 2D/3D comparison to original CAD. Each shipment includes:
First Article Inspection report per AS9102 standards
Material certification with mill test reports
Machining process documentation including toolpath verification logs
Digital twin dataset showing as-machined vs. nominal geometry
Parts are packaged in custom foam inserts with humidity control for sensitive alloys, with delivery tracking providing real-time GPS updates. Standard lead time from DFM sign-off to delivery is 7–12 business days for single prototypes, with expedited 72-hour options available for qualified geometries.
This end-to-end process ensures 6-axis projects achieve geometric complexity unattainable with lower-axis systems while maintaining Honyo Prototype’s 99.2% on-time delivery rate and sub-0.008mm Cpk capability for critical dimensions. All stages are ISO 9001:2015 audited with full digital traceability from CAD to shipping manifest.
Start Your Project
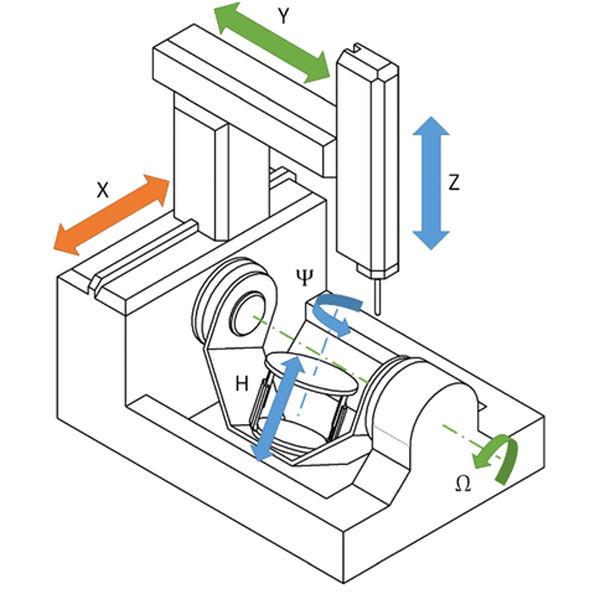
Achieve precision and complexity with our advanced 6-axis machining capabilities, ideal for high-performance prototypes and production components. Manufactured in-house at our Shenzhen factory, we deliver superior accuracy and efficiency for demanding applications.
Contact Susan Leo at [email protected] to discuss your project requirements and learn how our 6-axis machining services can support your engineering goals.
🚀 Rapid Prototyping Estimator
Estimate rough cost index based on volume.