Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for 52100 steel properties
In the complex landscape of industrial materials, sourcing high-quality 52100 steel properties poses a significant challenge for international B2B buyers. This chromium-alloy steel, renowned for its exceptional hardness, wear resistance, and reliability in demanding applications, is crucial for industries ranging from automotive to aerospace. However, navigating the myriad of global suppliers, understanding the nuances of chemical compositions, and evaluating the specific applications can be daunting.
This comprehensive guide delves into the essential aspects of 52100 steel, covering its various types, mechanical and thermal properties, and real-world applications. Additionally, it offers insights into the supplier vetting process, cost considerations, and market trends, empowering buyers to make informed purchasing decisions. With a focus on the unique needs of businesses in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe—including countries like Vietnam and Brazil—this resource is designed to equip decision-makers with actionable intelligence.
By addressing key challenges and providing a structured approach to sourcing 52100 steel, this guide aims to streamline the procurement process, ensuring that buyers can confidently select the right materials to meet their operational demands. Whether you’re seeking to enhance product performance or ensure compliance with international standards, this guide serves as your trusted companion in the global market for 52100 steel.
Understanding 52100 steel properties Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| 52100 Bearing Steel | High carbon content, excellent wear resistance, and hardness | Precision ball bearings, roller bearings | Pros: High durability, long lifespan; Cons: Can be more expensive than lower-grade steels. |
| 52100 Tool Steel | Optimized for cutting and shaping, high hardness and toughness | Cutting tools, dies, punches | Pros: Superior cutting performance; Cons: Requires careful heat treatment to maintain properties. |
| 52100 Spring Steel | Exceptional elasticity and fatigue resistance | Springs, automotive components | Pros: Excellent flexibility and strength; Cons: Limited corrosion resistance compared to other alloys. |
| 52100 High-Carbon Steel | High carbon content, good hardness and wear resistance | Industrial machinery, automotive parts | Pros: Cost-effective for high-strength applications; Cons: More prone to brittleness if not properly treated. |
| 52100 Stainless Steel | Alloyed with chromium for enhanced corrosion resistance | Marine applications, medical devices | Pros: Corrosion-resistant, good for harsh environments; Cons: Higher cost and complexity in manufacturing. |
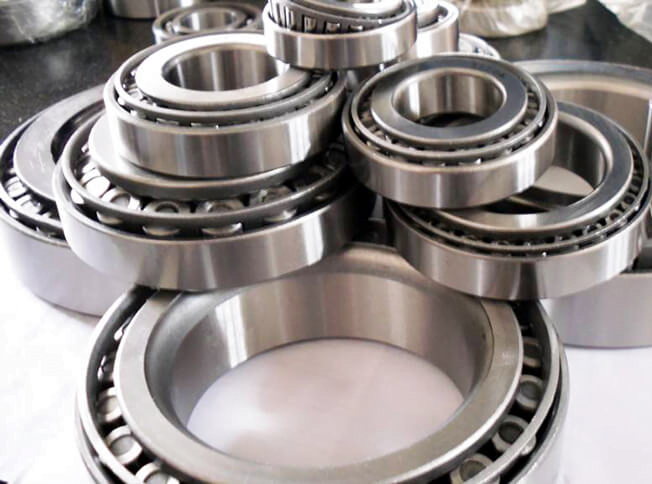
What Are the Characteristics and Applications of 52100 Bearing Steel?
52100 Bearing Steel is renowned for its high carbon content and chromium alloying, which provide exceptional hardness and wear resistance. It is primarily used in the manufacture of precision bearings, where rolling fatigue strength is critical. When purchasing, buyers should consider the specific hardness requirements and the operational environment, as this steel performs well under continuous operation at elevated temperatures.
How Does 52100 Tool Steel Stand Out in the Market?
52100 Tool Steel is specifically formulated for cutting and shaping applications, characterized by its high hardness and toughness. This type of steel is ideal for producing cutting tools, dies, and punches. B2B buyers should prioritize the heat treatment processes used, as they significantly influence the tool’s performance and longevity. While this steel offers superior cutting capabilities, it requires precise processing to avoid compromising its qualities.
What Makes 52100 Spring Steel Suitable for Various Industries?
52100 Spring Steel is recognized for its excellent elasticity and fatigue resistance, making it a preferred choice for springs and automotive components. It can withstand cyclic loading without failure, which is vital in applications demanding high performance under stress. Buyers should evaluate the steel’s treatment and tempering processes to ensure optimal performance, especially in dynamic applications. Its flexibility and strength are significant advantages, though its corrosion resistance may require additional treatment in harsh environments.
Why Choose 52100 High-Carbon Steel for Industrial Applications?
High-Carbon 52100 Steel is designed for high-strength applications, providing good hardness and wear resistance. It is commonly used in industrial machinery and automotive parts, where durability is crucial. Buyers should consider the cost-effectiveness of this material for high-strength applications, as it offers a balance between performance and price. However, the increased brittleness associated with high carbon content necessitates careful handling and processing.
What Are the Benefits of Using 52100 Stainless Steel?
52100 Stainless Steel incorporates chromium to enhance corrosion resistance, making it suitable for marine applications and medical devices. This variant combines the durability of 52100 steel with improved resistance to environmental factors. B2B buyers should assess the specific corrosion resistance needed for their applications, as well as the overall manufacturing complexity and costs associated with stainless variants. While offering excellent protection against rust, the higher price point may be a consideration for budget-sensitive projects.
Key Industrial Applications of 52100 steel properties
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of 52100 steel properties | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Automotive | Manufacturing of high-performance engine components | Enhanced durability and wear resistance, leading to longer service life | Availability of specific grades and compliance with industry standards |
| Aerospace | Production of precision bearings and landing gear | High strength-to-weight ratio and reliability in extreme conditions | Certification and traceability of materials; global sourcing options |
| Industrial Machinery | Fabrication of cutting tools and dies | Improved machining efficiency and reduced downtime | Sourcing from reputable suppliers with consistent quality control |
| Oil & Gas | Components for drilling equipment and pumps | Resistance to wear and corrosion, ensuring operational efficiency | Understanding local regulations and availability of specific sizes |
| Heavy Equipment | Manufacturing of gears and shafts | Enhanced performance under heavy loads, reducing maintenance costs | Consideration of lead times and logistics for international shipping |
How is 52100 Steel Used in the Automotive Sector?
In the automotive industry, 52100 steel is primarily utilized for manufacturing high-performance engine components such as crankshafts, camshafts, and gears. Its exceptional hardness and wear resistance address challenges like component fatigue and failure under high-stress conditions. International buyers must ensure that the steel meets specific automotive industry standards, such as ISO/TS 16949, to guarantee quality and performance. Additionally, sourcing from suppliers who can provide consistent material properties is crucial for maintaining production efficiency.
What Role Does 52100 Steel Play in Aerospace Applications?
Aerospace applications heavily rely on 52100 steel for the production of precision bearings and landing gear components. The steel’s high strength and fatigue resistance are vital for ensuring reliability during flight operations. Buyers from regions such as Europe and the Middle East must prioritize suppliers who can provide certified materials that comply with aerospace standards, such as AS9100. This compliance ensures that the components can withstand extreme temperatures and pressures, which are commonplace in aviation environments.
How is 52100 Steel Beneficial for Industrial Machinery?
In the industrial machinery sector, 52100 steel is essential for fabricating cutting tools and dies. Its superior machinability and hardness contribute to enhanced machining efficiency, resulting in reduced downtime and operational costs. For international B2B buyers, it is important to source 52100 steel from manufacturers who adhere to strict quality control measures, ensuring that the tools produced meet the necessary performance criteria. Additionally, understanding the specific machining processes required for this steel can further optimize production outcomes.
Why is 52100 Steel Important in the Oil & Gas Industry?
The oil and gas industry utilizes 52100 steel for critical components in drilling equipment and pumps. The steel’s resistance to wear and corrosion is vital for maintaining operational efficiency in harsh environments. Buyers must consider the availability of specific sizes and grades that comply with industry standards, such as API specifications. Moreover, understanding local regulations regarding material sourcing and environmental impact can facilitate smoother procurement processes in various regions, including Africa and South America.
How Does 52100 Steel Enhance Heavy Equipment Manufacturing?
In the heavy equipment sector, 52100 steel is predominantly used in the manufacturing of gears and shafts. Its high load-bearing capacity and durability significantly enhance performance, especially under heavy operational loads. For international buyers, evaluating suppliers based on their ability to provide timely deliveries and quality certifications is essential to meet project deadlines. Additionally, considering logistics and potential tariffs can impact sourcing decisions, especially when dealing with cross-border transactions.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘52100 steel properties’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Navigating the Confusion of Global Standards for 52100 Steel
The Problem:
B2B buyers often face significant challenges in understanding the various international standards and equivalents for 52100 steel. With multiple naming conventions—such as GCr15 in China, 100Cr6 in Europe, and SUJ2 in Japan—buyers can struggle to ensure they are sourcing the correct grade for their applications. This confusion can lead to costly mistakes, including delays in production, increased costs, and ultimately, dissatisfaction with the materials received.
The Solution:
To effectively navigate the complexities of global standards, buyers should create a comprehensive comparison chart of the different designations for 52100 steel across various regions. This chart should include key properties, such as chemical composition and mechanical characteristics, alongside the relevant standards (e.g., ASTM, DIN, JIS). Moreover, establishing strong relationships with reputable suppliers who have a deep understanding of international standards can enhance clarity. Requesting detailed material certifications from suppliers ensures the steel meets the specified standards and provides peace of mind in procurement. Additionally, leveraging resources like industry associations or steel databases can provide insights and updates on material standards, ensuring buyers stay informed.
Scenario 2: Addressing Machinability Challenges with 52100 Steel
The Problem:
Machinability is a critical concern for manufacturers using 52100 steel, particularly when working with high precision components. Buyers often encounter difficulties in achieving the desired finish or tolerances due to the inherent hardness of the material, which can lead to tool wear and increased production times. This situation is especially prevalent in industries requiring tight tolerances, such as aerospace or automotive, where component failure can have severe consequences.
The Solution:
To mitigate machinability issues, buyers should engage in the heat treatment process strategically. By specifying the correct heat treatment parameters—such as annealing before machining—manufacturers can significantly improve the machinability of 52100 steel. Additionally, using appropriate cutting tools designed for high-carbon steels can enhance performance. Suppliers can offer insights into tool selection, including coatings that reduce friction and heat. Implementing a thorough testing phase with different machining parameters can also help identify the optimal setup for specific applications, reducing wear and improving production efficiency.
Scenario 3: Overcoming Miscommunication on Material Properties
The Problem:
Miscommunication regarding the properties of 52100 steel between buyers and suppliers often leads to misunderstandings about performance expectations. Buyers may have specific applications in mind, such as bearings or cutting tools, but if the supplier does not fully understand the required properties—like wear resistance or hardness—they may supply an unsuitable grade. This can result in product failures, costly rework, and a damaged reputation in the marketplace.
The Solution:
To overcome this challenge, B2B buyers should establish clear communication protocols with their suppliers. This includes providing detailed specifications that outline the expected performance characteristics, such as hardness (Rockwell C), tensile strength, and resistance to wear. Conducting joint reviews of application requirements can ensure alignment on expectations. Additionally, buyers should leverage supplier expertise by requesting samples or small trial orders before committing to larger quantities. This allows for real-world testing and validation of material properties in specific applications, minimizing the risk of miscommunication and ensuring the right product is sourced for the intended use.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for 52100 steel properties
When selecting materials for applications requiring specific properties, 52100 steel stands out due to its unique characteristics. This guide analyzes the key properties, advantages, disadvantages, and considerations for international B2B buyers regarding 52100 steel and its equivalents.
What Are the Key Properties of 52100 Steel?
52100 steel is known for its high carbon content (0.98-1.10%) and chromium (1.30-1.60%), which contribute to its exceptional hardness and wear resistance. With a Rockwell hardness rating of 60-67, it is particularly suited for applications that endure high stress and wear. Its thermal properties include a melting point of 1424°C (2595°F) and a thermal conductivity of 46.6 W/m·K, making it effective in high-temperature environments. Additionally, its fracture toughness ranges from 15.4 to 18.7 MPa·m½, which is crucial for applications involving impact loads.
What Are the Pros and Cons of Using 52100 Steel?
Pros:
– Durability: The high hardness and wear resistance make 52100 steel ideal for applications such as bearings, automotive components, and tooling.
– Cost-Effectiveness: Compared to other high-performance alloys, 52100 steel is relatively affordable, offering a good balance of performance and cost.
– Versatility: It can be heat-treated to enhance hardness and strength, making it adaptable for various applications.
Cons:
– Machinability: While it has a machinability rating of 40%, the high hardness can complicate manufacturing processes, requiring specialized tools and techniques.
– Corrosion Resistance: Although it offers some resistance, it is not as corrosion-resistant as stainless steels, necessitating protective coatings or treatments in corrosive environments.
How Does 52100 Steel Impact Application Performance?
The performance of 52100 steel is significantly influenced by its application. In anti-friction bearings, for instance, its high wear resistance and fatigue strength are critical for longevity and reliability. However, in environments with high humidity or exposure to corrosive substances, additional protective measures may be necessary to prevent degradation. Understanding the specific media compatibility—whether it be lubricants, environmental conditions, or mechanical loads—is essential for ensuring optimal performance.
What Should International B2B Buyers Consider?
For buyers in regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, compliance with international standards is paramount. 52100 steel is recognized under various standards, including ASTM A295 in the USA, DIN 17230 in Germany, and JIS G4805 in Japan. Buyers should ensure that suppliers can provide documentation confirming compliance with these standards. Additionally, understanding local market preferences, such as cost sensitivity or availability of alternative materials, can influence purchasing decisions.
Summary Table of 52100 Steel Properties
| Material | Typical Use Case for 52100 Steel Properties | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 52100 Steel | Anti-friction bearings, automotive components | Exceptional hardness and wear resistance | Moderate machinability; requires specialized tools | Medium |
| 100Cr6 | Tooling and industrial applications | High fatigue strength | Limited corrosion resistance | Medium |
| SUJ2 | Precision ball bearings | Cost-effective for high-performance applications | Requires heat treatment for optimal performance | Medium |
| 535A99/EN31 | High-stress mechanical components | Good availability in global markets | Less common than other grades | Medium |
This strategic material selection guide provides a comprehensive overview of 52100 steel properties, emphasizing its advantages, limitations, and considerations for international B2B buyers. By understanding these factors, businesses can make informed decisions that enhance their product performance and reliability.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for 52100 steel properties
What Are the Main Stages in the Manufacturing Process of 52100 Steel?
The manufacturing process of 52100 steel involves several critical stages that ensure the final product meets the stringent demands of industrial applications, particularly in bearings and other high-stress components. Understanding these stages helps B2B buyers assess quality and performance.
Material Preparation: How Are Raw Materials Processed?
The process begins with the careful selection and preparation of raw materials, which typically include high-quality iron, carbon, and chromium. These materials are precisely measured and combined in an electric arc or induction furnace, where they are melted together. This initial step is crucial for achieving the desired chemical composition, which significantly impacts the steel’s properties.
Once molten, the steel undergoes refining processes such as argon oxygen decarburization or vacuum degassing. These techniques eliminate impurities that could compromise the steel’s integrity. The refined molten steel is then cast into various shapes, including sheets, billets, and ingots, preparing it for the next stages of processing.
How Is 52100 Steel Formed and Processed?
After casting, the steel requires additional shaping and processing to enhance its performance characteristics. The first step in this stage is heating the cast forms to a specific temperature, followed by hot working techniques such as rolling or forging. These processes not only shape the steel but also align the grain structure, which is vital for mechanical strength.
Following hot working, the steel typically undergoes an annealing process. This step helps to relieve internal stresses and refine the microstructure, contributing to improved machinability and overall performance. The annealed steel is then subjected to heat treatment, which can include hardening and tempering, further enhancing its hardness and wear resistance.
What Finishing Techniques Are Commonly Used in 52100 Steel Manufacturing?
The finishing stage is where the steel is prepared for its final applications. Common techniques include grinding, polishing, and machining, which ensure that the steel meets precise dimensional and surface quality specifications. These finishing processes are critical, especially for components that require tight tolerances, such as bearings.
B2B buyers should be aware that the type of finishing can influence the steel’s performance in applications. For example, polished surfaces may reduce friction in bearings, enhancing their operational lifespan. Buyers should inquire about the specific finishing techniques used by suppliers to ensure they align with their application requirements.
What International Standards Govern Quality Assurance for 52100 Steel?
Quality assurance (QA) is vital in the manufacturing of 52100 steel to ensure that it meets international and industry-specific standards. One of the most recognized standards is ISO 9001, which outlines the criteria for a quality management system. Compliance with this standard indicates that the manufacturer has established a framework for consistent quality and customer satisfaction.
Additionally, specific industries may require compliance with standards such as API (American Petroleum Institute) for oil and gas applications or CE marking for products sold in the European Economic Area. These certifications demonstrate that the steel meets safety, health, and environmental protection requirements.
What Are the Key Quality Control Checkpoints in the Manufacturing Process?
Quality control (QC) is embedded throughout the manufacturing process of 52100 steel, with several key checkpoints:
-
Incoming Quality Control (IQC): At this stage, raw materials are inspected to ensure they meet specified standards before processing begins. This may include chemical composition analysis and physical property assessments.
-
In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): During manufacturing, ongoing inspections are conducted to monitor the production process. Techniques like non-destructive testing (NDT) and metallurgical analysis are commonly employed to identify any defects early.
-
Final Quality Control (FQC): Once the manufacturing process is complete, the final product undergoes rigorous testing. This includes hardness testing, tensile strength evaluations, and microstructural examinations to ensure that the steel meets all required specifications.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control Practices?
For international B2B buyers, especially those from regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, it’s essential to verify the quality control practices of potential suppliers. Here are some actionable steps:
-
Conduct Supplier Audits: Regular audits of suppliers can provide insight into their manufacturing processes and quality control measures. This can be done through on-site visits or third-party audits.
-
Request Quality Reports: Suppliers should be able to provide comprehensive quality reports that detail the results of testing and inspections at various stages of production. This documentation should include certifications that confirm compliance with relevant standards.
-
Engage Third-Party Inspectors: Utilizing independent inspectors can add an additional layer of assurance. These professionals can conduct thorough assessments of the manufacturing processes and the final products, ensuring that they meet the specified quality standards.
What Are the Nuances of Quality Control Certifications for International Buyers?
International buyers should also be aware of the nuances associated with quality control certifications. Different countries may have varying requirements for compliance, and certain certifications may not be universally recognized. For instance, while ISO 9001 is widely accepted, local standards in countries like Brazil or Vietnam may also play a significant role in quality assurance.
Buyers should ensure that suppliers are not only compliant with international standards but also with local regulations that may impact product quality and safety. This dual compliance is crucial for mitigating risks associated with international trade and ensuring that products perform as expected in their intended applications.
Conclusion: Importance of Comprehensive QC in 52100 Steel Supply Chains
In summary, the manufacturing processes and quality assurance measures for 52100 steel are intricate and multifaceted. By understanding these stages, B2B buyers can make informed decisions when sourcing this critical material. Emphasizing quality control throughout the supply chain ensures that the steel’s properties meet the high standards required for demanding applications, ultimately leading to improved product performance and reliability.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘52100 steel properties’
In the competitive landscape of steel procurement, understanding the specific properties and applications of 52100 steel is crucial for making informed purchasing decisions. This guide outlines practical steps for B2B buyers looking to source 52100 steel effectively, ensuring that they meet their technical requirements while maintaining cost efficiency and supplier reliability.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Establishing clear technical specifications is the foundation of a successful procurement process. For 52100 steel, consider factors such as carbon content, hardness, and the specific applications you intend to use it for, such as bearings or automotive components. Document these specifications to communicate effectively with potential suppliers.
Step 2: Research Global Equivalents and Standards
Understanding the global naming conventions and standards for 52100 steel is essential, especially if you are dealing with international suppliers. Familiarize yourself with equivalents like 100Cr6 (Germany), SUJ2 (Japan), and EN31 (UK). This knowledge will help you ensure that the steel you are sourcing meets the required specifications for your market and application.
Step 3: Evaluate Potential Suppliers
Before making any commitments, conduct thorough evaluations of potential suppliers. Request company profiles, product catalogs, and case studies that demonstrate their capabilities in providing 52100 steel. Additionally, seek references from other buyers in your industry to gauge supplier reliability and service quality.
Step 4: Verify Supplier Certifications and Compliance
Ensuring that your supplier adheres to relevant industry standards is critical for quality assurance. Check for certifications such as ISO 9001 or compliance with ASTM A295 for bearing steel. These certifications indicate that the supplier follows stringent quality control processes, which can significantly reduce the risk of defects in your steel procurement.
Step 5: Request Material Test Reports
Ask for material test reports (MTRs) that verify the chemical composition and mechanical properties of the 52100 steel being offered. These reports should include details on hardness, tensile strength, and other critical properties. Reviewing MTRs is crucial for confirming that the steel will meet your operational requirements.
Step 6: Negotiate Pricing and Terms
Once you have identified a suitable supplier, engage in negotiations regarding pricing and payment terms. Consider factors such as bulk purchase discounts, delivery times, and payment options. Establish clear terms that protect your interests while ensuring a mutually beneficial relationship with the supplier.
Step 7: Plan for Logistics and Delivery
Effective logistics planning is essential for timely delivery of your 52100 steel. Discuss shipping options, lead times, and potential import duties with your supplier. Having a clear logistics plan helps prevent delays and ensures that your materials arrive when needed to keep your projects on schedule.
By following these steps, B2B buyers can navigate the complexities of sourcing 52100 steel, ensuring they obtain high-quality materials that meet their specific needs while fostering strong supplier relationships.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for 52100 steel properties Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components in Sourcing 52100 Steel?
When sourcing 52100 steel, understanding the cost structure is essential for B2B buyers. The primary cost components include:
-
Materials: The cost of raw materials is a significant factor, influenced by global steel prices, which can fluctuate based on demand and supply dynamics. For 52100 steel, the main materials are high-carbon chromium, iron, and other alloying elements. Price variations may arise from sourcing these materials from different regions or suppliers.
-
Labor: Labor costs cover the wages of skilled workers involved in steel production, including those handling complex processes like heat treatment and machining. The labor market conditions in the supplier’s country can significantly impact these costs.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes expenses related to utilities, facility maintenance, and equipment depreciation. Efficient manufacturing processes can help mitigate overhead costs, contributing to overall pricing.
-
Tooling: Specific tooling is required for producing various shapes and sizes of 52100 steel. The complexity of the tooling can influence costs, particularly for customized orders.
-
Quality Control (QC): Ensuring that the steel meets international standards requires investment in quality control processes. Certifications and testing protocols can add to the overall cost but are essential for maintaining product reliability.
-
Logistics: Transporting steel products involves costs related to shipping, handling, and customs clearance, which can vary based on the destination and Incoterms used. International shipping rates can be particularly volatile, impacting total costs.
-
Margin: Suppliers will add a profit margin to cover their risks and operational costs, which can vary widely based on competition and market conditions.
How Do Price Influencers Affect 52100 Steel Sourcing?
Several factors can influence the pricing of 52100 steel, making it crucial for buyers to consider them when negotiating:
-
Volume/MOQ: Bulk purchases often lead to lower per-unit costs. Suppliers may offer discounts for larger orders, making it advantageous to consolidate needs when possible.
-
Specifications/Customization: Custom orders or specific grades of 52100 steel may incur additional costs. Clearly defining requirements can help manage expectations and costs.
-
Materials Quality and Certifications: Higher quality materials and recognized certifications (e.g., ISO, ASTM) can increase prices. Buyers should weigh the cost against the benefits of superior quality.
-
Supplier Factors: The supplier’s reputation, reliability, and geographic location can impact pricing. Engaging with well-established suppliers may offer benefits in terms of quality and service but can also lead to higher costs.
-
Incoterms: The choice of Incoterms (e.g., FOB, CIF) can significantly affect total landed costs, impacting logistics and insurance expenses. Understanding these terms can help buyers better estimate final costs.
What Are the Best Buyer Tips for Cost-Efficient Sourcing of 52100 Steel?
-
Negotiate Effectively: Building a relationship with suppliers can lead to better pricing and terms. Understanding market dynamics and being prepared to negotiate based on volume and long-term commitments can yield favorable results.
-
Focus on Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Instead of just considering the purchase price, evaluate the TCO, which includes maintenance, durability, and potential downtime costs. A lower initial price may not always translate to cost savings in the long run.
-
Be Aware of Pricing Nuances in International Markets: For buyers in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, currency fluctuations and trade tariffs can affect costs. Staying informed about regional trade agreements can help mitigate these risks.
-
Request Multiple Quotes: Gathering quotes from multiple suppliers can provide insights into market pricing and help identify the best value for your specific requirements.
-
Monitor Market Trends: Keeping an eye on global steel market trends can inform timing for purchases. Prices may fluctuate seasonally or due to geopolitical events, making it beneficial to purchase during favorable conditions.
Disclaimer on Indicative Prices
Prices for 52100 steel are subject to fluctuations based on market conditions and supplier-specific factors. Always request updated quotes and consider all associated costs when evaluating offers.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing 52100 steel properties With Other Solutions
Understanding Alternatives to 52100 Steel Properties
When considering materials for manufacturing applications, it’s crucial to evaluate not just one option, but also viable alternatives. The choice of steel or alloy can significantly impact product performance, cost, and application suitability. In this section, we will compare the properties of 52100 steel with two notable alternatives: AISI D2 Tool Steel and 440C Stainless Steel. Each material has distinct characteristics that may better serve specific needs depending on the application.
Comparison Table
| Comparison Aspect | 52100 Steel Properties | AISI D2 Tool Steel | 440C Stainless Steel |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | High hardness (60-67 Rc), excellent wear resistance, suitable for high-stress applications | High wear resistance, good toughness, suitable for cutting tools | Good corrosion resistance, decent hardness (58-62 Rc) |
| Cost | Moderate, widely available | Higher than 52100, specialized | Higher due to corrosion resistance |
| Ease of Implementation | Standard machining practices | Requires specific tooling, more challenging to machine | Easier to machine than D2, but still requires care |
| Maintenance | Low, but may require regular lubrication | Moderate; tools may need frequent sharpening | Low, generally more resistant to rust and wear |
| Best Use Case | Bearings, automotive components | Cutting tools, dies, and molds | Marine applications, medical devices, and food processing |
Detailed Breakdown of Alternatives
AISI D2 Tool Steel
AISI D2 is a high-carbon, high-chromium tool steel known for its excellent wear resistance and toughness. This steel is commonly used in the manufacturing of cutting tools, dies, and molds, making it ideal for applications that require durability under high stress. However, it can be more expensive than 52100 steel and poses challenges in machining due to its hardness, which necessitates specialized tooling. While it performs well in high-temperature applications, the increased cost and complexity of working with D2 may not be justified for all projects.
440C Stainless Steel
440C stainless steel is a high-carbon martensitic stainless steel that offers a good balance between hardness and corrosion resistance. It typically achieves a hardness range of 58-62 Rc, making it suitable for applications where both wear resistance and corrosion protection are critical, such as in marine environments or medical instruments. While it is easier to machine compared to D2, it tends to be more expensive than 52100 due to its stainless properties. The maintenance of 440C is relatively low, as its corrosion resistance reduces the need for regular lubrication.
Conclusion: How to Choose the Right Solution
When selecting the right material for your application, consider factors such as performance requirements, cost constraints, ease of implementation, maintenance needs, and the specific use case. While 52100 steel offers excellent wear resistance and is cost-effective for applications like bearings and automotive components, alternatives like AISI D2 and 440C stainless steel may be more appropriate for specialized tasks requiring high toughness or corrosion resistance. A thorough understanding of these properties and how they align with your project’s demands will empower B2B buyers to make informed decisions that optimize performance and cost-efficiency in their manufacturing processes.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for 52100 steel properties
What Are the Key Technical Properties of 52100 Steel?
When considering 52100 steel for industrial applications, understanding its key technical properties is crucial. Here are some of the most critical specifications:
-
Chemical Composition:
– 52100 steel typically contains 0.98-1.10% carbon and 1.30-1.60% chromium. This high carbon and chromium content contribute to its superior hardness and wear resistance. For B2B buyers, knowing the precise chemical makeup is essential for ensuring that the steel meets the performance requirements of specific applications, especially in sectors like automotive and aerospace. -
Hardness:
– The Rockwell hardness of 52100 steel ranges from 60 to 67 HRC, depending on the heat treatment applied. This high hardness level makes it ideal for use in bearings and other applications where wear resistance is paramount. For buyers, hardness specifications are critical as they directly correlate to the material’s longevity and performance under stress. -
Machinability:
– With a machinability rating of approximately 40% (relative to AISI 1212), 52100 steel requires specific machining techniques and tools. Understanding this property helps B2B buyers gauge the cost-effectiveness of processing the material and plan for potential challenges in manufacturing. -
Fracture Toughness:
– The fracture toughness of 52100 steel falls within the range of 15.4-18.7 MPa·m½. This property indicates how well the material can withstand crack propagation. For industries dealing with high-stress components, this is a vital consideration to prevent catastrophic failures. -
Density and Thermal Properties:
– The density of 52100 steel is about 7.81 g/cm³, and it has a melting point of 1424°C (2595°F). These properties are important for applications requiring high-temperature stability and structural integrity. Buyers should consider these attributes when assessing compatibility with other materials and operational conditions.
What Are Common Trade Terms Relevant to 52100 Steel?
Navigating the procurement landscape for 52100 steel also involves understanding essential trade terminology. Here are some key terms to be familiar with:
-
OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer):
– This term refers to companies that produce parts or equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer. In the context of 52100 steel, understanding OEM relationships can help buyers identify the right suppliers for their specific needs. -
MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity):
– MOQ represents the smallest quantity of an item that a supplier is willing to sell. This term is significant for B2B buyers as it can affect inventory management and purchasing costs. Knowing the MOQ for 52100 steel can help buyers negotiate better terms and manage supply chain efficiency. -
RFQ (Request for Quotation):
– An RFQ is a document sent to suppliers to request pricing for specific products or services. For buyers of 52100 steel, issuing an RFQ can lead to competitive pricing and better supplier relationships, ensuring that they get the best value for their investment. -
Incoterms (International Commercial Terms):
– Incoterms define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in international transactions. They cover aspects such as shipping, insurance, and tariffs. For B2B buyers sourcing 52100 steel from different countries, understanding Incoterms is crucial to avoid misunderstandings and ensure smooth logistics. -
Heat Treatment:
– This is a controlled process used to alter the physical and sometimes chemical properties of a material. In the context of 52100 steel, heat treatment is essential for achieving the desired hardness and toughness. Buyers should be aware of the heat treatment specifications that affect the performance of the steel in their applications. -
Specification Standards:
– Specifications like ASTM A295 and DIN 17230 outline the requirements for 52100 steel. Familiarity with these standards is important for buyers to ensure compliance with industry regulations and quality assurance in their products.
Understanding these technical properties and trade terms can significantly enhance decision-making for B2B buyers in various industries, ensuring they select the right materials and suppliers for their manufacturing needs.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the 52100 steel properties Sector
What Are the Key Market Trends Influencing 52100 Steel Properties?
The global market for 52100 steel is shaped by several key drivers, including the increasing demand for high-performance materials in automotive and aerospace applications. As industries seek to enhance the durability and efficiency of components, 52100 steel’s exceptional wear resistance and fatigue strength have made it a preferred choice for anti-friction bearings and other critical applications. Additionally, the rise of advanced manufacturing technologies, such as additive manufacturing and precision machining, is facilitating more efficient sourcing and production processes, allowing international buyers to tailor their requirements more closely to their operational needs.
Emerging trends in the B2B landscape are leaning toward digitalization in procurement processes, with many companies adopting e-procurement platforms to streamline their supply chains. Buyers in regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe are increasingly utilizing data analytics for better forecasting and inventory management, which can significantly reduce costs and lead times. Furthermore, the ongoing shift toward localized sourcing is helping companies mitigate risks associated with international logistics, a trend that is particularly relevant in the current geopolitical climate.
How Can Sustainability and Ethical Sourcing Impact B2B Relationships in the 52100 Steel Sector?
Sustainability and ethical sourcing are becoming paramount in the procurement of 52100 steel properties. The environmental impact of steel production, including high carbon emissions and resource depletion, is prompting buyers to seek suppliers committed to sustainable practices. This shift is not only driven by regulatory pressures but also by a growing consumer expectation for companies to prioritize environmental stewardship.
To align with these values, buyers should consider suppliers who have adopted ‘green’ certifications, such as ISO 14001 for environmental management, or those who use recycled materials in their production processes. Implementing transparent supply chain practices, including audits and certifications, can enhance trust and foster long-term partnerships. Ethical sourcing also encompasses fair labor practices and community engagement, which can further strengthen a company’s brand reputation in an increasingly conscientious market.
How Has the 52100 Steel Market Evolved Over Time?
The evolution of the 52100 steel market can be traced back to its initial development for high-performance bearing applications in the early 20th century. Initially recognized for its superior hardness and wear resistance, 52100 steel quickly became the standard for anti-friction bearings in various industries, including automotive and aerospace. Over the decades, advancements in metallurgical processes have enhanced its properties, allowing for improved heat treatment techniques and more efficient manufacturing methods.
Today, 52100 steel is not only utilized in bearing production but has expanded its applications to include a wide range of high-stress components, reflecting the ongoing innovation in material science. The global market has also experienced shifts due to changing demand dynamics, driven by industrial growth in emerging economies, which has further diversified the applications of this versatile steel grade. As industries continue to evolve, the importance of 52100 steel properties will likely remain significant, underscoring its relevance in the future landscape of material procurement.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of 52100 steel properties
-
How do I ensure the quality of 52100 steel before purchase?
To ensure the quality of 52100 steel, request certification documents from suppliers, such as material test reports (MTRs) that verify chemical composition and mechanical properties. Consider conducting third-party inspections or audits to confirm compliance with international standards like ASTM A295. Additionally, ask about the supplier’s quality assurance processes and any industry certifications they hold. Establishing a robust quality control procedure is essential for preventing defects and ensuring the steel meets your specifications. -
What is the best application for 52100 steel in manufacturing?
52100 steel is best suited for applications that require high wear resistance and superior hardness, such as anti-friction bearings, automotive components, and precision tools. Its excellent rolling fatigue strength makes it ideal for manufacturing ball and roller bearings, while its machinability allows for effective production of intricate parts. When selecting 52100 steel for your application, consider the specific mechanical properties required, such as hardness and toughness, to ensure optimal performance. -
What factors should I consider when sourcing 52100 steel internationally?
When sourcing 52100 steel internationally, consider factors such as supplier reliability, compliance with local and international standards, and delivery timelines. Evaluate the supplier’s experience in exporting to your region, particularly in Africa, South America, or the Middle East. Additionally, assess their ability to customize orders based on your specifications, including dimensions and surface finishes. It’s also crucial to understand the logistics involved, including shipping costs and customs regulations. -
What minimum order quantities (MOQ) can I expect for 52100 steel?
Minimum order quantities for 52100 steel can vary widely among suppliers, typically ranging from 500 kg to several tons. It’s essential to communicate your specific needs with potential suppliers to understand their MOQ policies. Some suppliers may offer flexibility, especially for long-term contracts or repeat orders. If you’re a smaller buyer, consider consolidating orders with other manufacturers to meet MOQ requirements while ensuring you receive the necessary material for your projects. -
How can I customize my 52100 steel order to meet specific requirements?
Customization of your 52100 steel order can include variations in size, shape, heat treatment, and surface finish. When discussing your order with suppliers, clearly outline your specifications and any particular applications the steel will be used for. Many suppliers offer services such as cutting, forging, and machining to tailor the steel to your needs. Ensure that the supplier has the capability and experience to deliver customized solutions that maintain the integrity of the steel properties. -
What payment terms are commonly accepted for international steel purchases?
Payment terms for international steel purchases often include options like advance payment, letters of credit, or payment upon delivery. Terms may vary based on the supplier’s policies and the buyer’s creditworthiness. It’s advisable to negotiate favorable terms that align with your cash flow needs while ensuring the supplier feels secure in the transaction. Be sure to clarify any additional costs, such as shipping and customs fees, to avoid unexpected expenses. -
What quality assurance processes should I look for in a steel supplier?
When evaluating a steel supplier, inquire about their quality assurance processes, including ISO certification and adherence to industry standards like ASTM. Look for suppliers who conduct regular testing of their products, including chemical composition and mechanical property assessments. Additionally, ask about their traceability procedures, which ensure that the steel can be traced back to its source. A strong commitment to quality assurance reduces the risk of defects and ensures reliable performance in your applications. -
What are the logistics considerations for importing 52100 steel?
Logistics for importing 52100 steel involve several key considerations, including shipping methods, lead times, and customs regulations. Discuss with your supplier the best shipping options, such as sea freight or air freight, based on your budget and urgency. Familiarize yourself with the import regulations in your country, as tariffs and duties may apply. Partnering with a logistics provider experienced in handling steel imports can help streamline the process and ensure timely delivery of your materials.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.
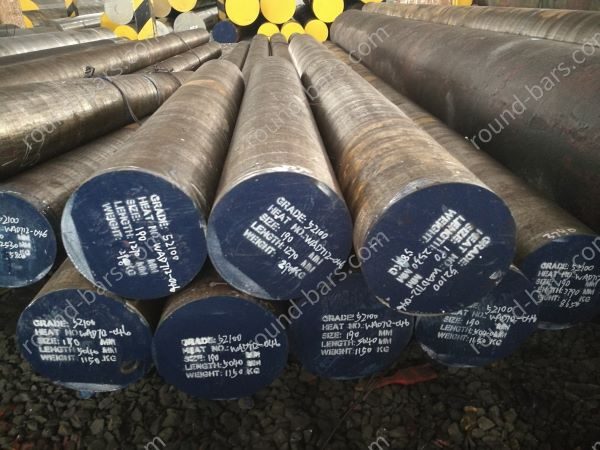
Top 7 52100 Steel Properties Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. AZOM – AISI 52100 Alloy Steel
Domain: azom.com
Registered: 1999 (26 years)
Introduction: AISI 52100 Alloy Steel (UNS G52986) is a high carbon, chromium-containing low alloy steel.
**Chemical Composition:**
– Iron (Fe): 96.5 – 97.32%
– Chromium (Cr): 1.30 – 1.60%
– Carbon (C): 0.980 – 1.10%
– Manganese (Mn): 0.250 – 0.450%
– Silicon (Si): 0.150 – 0.300%
– Sulfur (S): ≤ 0.0250%
– Phosphorous (P): ≤ 0.0250%
**Physical Properties:**
– Density: 7.81 g/cm³ (0.282 lb/in³…
2. ASTM Steel – ASTM 52100 Bearing Steel
Domain: astmsteel.com
Registered: 2015 (10 years)
Introduction: Product Name: ASTM 52100 Bearing Steel
Other Names: 100Cr6, SUJ2, EN31
Standard Specification: ASTM A295
Type: High carbon, chromium containing low alloy steel
Features: High wear resistance, rolling fatigue strength, through hardening
Hardness: 60-67 on Rockwell hardness scale (Rc) at room temperature
Operating Temperature: Up to 120°C
Supply Range:
– Round Bar: diameter 8mm – 800mm
– Plate: thi…
3. MatWeb – Material Property Database
Domain: matweb.com
Registered: 1997 (28 years)
Introduction: This company, MatWeb – Material Property Database, is a notable entity in the market. For specific product details, it is recommended to visit their website directly.
4. Knife Steel Nerds – 52100 Steel
Domain: knifesteelnerds.com
Registered: 2018 (7 years)
Introduction: 52100 steel is a high carbon steel with 1% carbon and 1.5% chromium, along with small amounts of manganese (Mn) and silicon (Si). It has been in use since at least 1905 and was originally developed for bearings. It is known by several other names including 100Cr6, 1.3505, GCr15, En31, and SUJ2. The steel is recognized for its high hardenability, which allows it to achieve full hardness with less s…
5. Castle Metals – E52100 Round Bar
Domain: castlemetals.com
Registered: 1996 (29 years)
Introduction: {“Item Number”: “11557”, “Alloy”: “E52100”, “Shape”: “Round”, “Temper”: “5 IN Round”, “Length Range”: “216.0000-288.0000 IN”, “Specifications”: [“AMS.2301”, “AMS.6440”, “ASTM.A295”, “ASTM.A29”, “ASTM.A322”, “ASTM.A892”, “UNS.G52986”], “Weight per Foot”: “68.218 LBS/FT”, “Grade”: “E52100”, “AISI”: “52100”, “UNS”: “G52986”, “Properties”: {“Hardness Max”: “248 Brinell”, “Relative Machinability”: “50%…
6. MakeItFrom – SAE-AISI 52100 Chromium Steel
Domain: makeitfrom.com
Registered: 2009 (16 years)
Introduction: {“Material Name”: “SAE-AISI 52100 (G52986) Chromium Steel”, “Type”: “Alloy Steel”, “UNS Number”: “G52986”, “Common Variations”: [“Annealed 52100 Chromium Steel”, “Cold Finished 52100 Chromium Steel”, “Hardened 52100 Chromium Steel”], “Mechanical Properties”: {“Brinell Hardness”: “180 to 210”, “Elastic Modulus”: “190 GPa (27 x 10^6 psi)”, “Elongation at Break”: “10 to 20 %”, “Fatigue Strength”: “25…
7. Alro – AISI 52100 Deep Hardening Alloy
Domain: alro.com
Registered: 1996 (29 years)
Introduction: {“Alloy”: “AISI 52100 Alloy”, “Type”: “Deep Hardening Alloy”, “Chemical Composition”: {“Carbon”: “0.98%-1.10%”, “Chromium”: “1.30%-1.60%”, “Manganese”: “0.25%-0.45%”, “Silicon”: “0.15%-0.30%”, “Sulfur”: “.025% or Less”, “Phosphorous”: “.025% or Less”}, “Properties”: “Moderately deep hardening alloy with high resistance to wear, medium toughness, and low resistance to softening at high temperatures…
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for 52100 steel properties
In conclusion, 52100 steel stands out as a premier choice for applications demanding high wear resistance and superior hardness. Its composition, featuring high carbon and chromium content, not only enhances its performance in challenging environments but also makes it a cost-effective solution for international buyers. Understanding its global equivalents and sourcing options allows companies to align their procurement strategies with regional availability and standards, ensuring they access the best materials for their manufacturing needs.
Strategic sourcing is crucial in the current global marketplace, particularly for B2B buyers in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. By leveraging partnerships with reliable suppliers of 52100 steel, businesses can enhance their operational efficiency and product quality while minimizing costs.
As we move forward, the demand for high-performance materials like 52100 steel is expected to rise, driven by advancements in technology and manufacturing processes. International buyers should proactively engage with suppliers to secure favorable terms and ensure a steady supply of this essential material. Embrace the opportunity to enhance your product offerings with 52100 steel and position your business for success in a competitive landscape.