Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for 3d printed desktop cnc mill
The growing interest in 3D printed desktop CNC mills is reshaping how businesses approach precision manufacturing. For international B2B buyers, particularly those in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, the challenge lies in sourcing reliable and efficient machinery that meets diverse production needs. This guide serves as a comprehensive resource, addressing the various types of 3D printed desktop CNC mills available, their applications across different industries, and the crucial considerations for supplier vetting.
Navigating the intricacies of the global market can be daunting, especially when it comes to understanding cost structures, functionality, and the technological advancements that differentiate products. By providing detailed insights into the features and benefits of these machines, the guide empowers buyers to make informed purchasing decisions that align with their operational goals. From evaluating the design and build quality to assessing after-sales support and warranty options, this resource equips stakeholders with the knowledge necessary to optimize their investments.
As you explore the sections that follow, you will gain a nuanced understanding of how to effectively integrate 3D printed desktop CNC mills into your production processes, ensuring that you remain competitive in an increasingly digital and automated landscape. Whether your focus is on prototyping, small-scale production, or educational applications, this guide is tailored to help you navigate the complexities of sourcing and implementing cutting-edge technology.
Understanding 3d printed desktop cnc mill Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| G300 CNC Mill | Budget-friendly, modular design, 600x450mm working area | Prototyping, small-scale manufacturing | Pros: Cost-effective, customizable. Cons: Limited precision for high-end applications. |
| Tiny 3D Printed CNC MK II | Compact size, 225x325mm working area, DIY assembly | Hobbyist projects, educational purposes | Pros: Affordable, easy to assemble. Cons: Not suitable for heavy-duty tasks. |
| LDO Milo V1.5 CNC Kit | Robust construction, designed for 3D printing integration | Small business applications, crafting | Pros: Durable, versatile. Cons: Higher cost than basic models. |
| Inventables X-Carve Pro | High precision, larger working area, advanced features | Professional manufacturing, design prototyping | Pros: Excellent precision, large capacity. Cons: Significant investment required. |
| Shapeoko 4 CNC Router | Hybrid table design, extensive material compatibility | Manufacturing, woodworking, metalworking | Pros: Versatile, strong community support. Cons: Complexity may deter beginners. |
What are the Characteristics of the G300 CNC Mill for B2B Buyers?
The G300 CNC Mill is an excellent choice for businesses looking for a cost-effective solution for small-scale manufacturing and prototyping. Its modular design allows for easy upgrades and customizations, making it ideal for companies that require flexibility. With a working area of 600x450mm, it can handle a variety of materials including wood, plastic, and potentially aluminum. Buyers should consider their specific needs for precision and durability, as this model may not meet the high standards required for more demanding applications.
How Does the Tiny 3D Printed CNC MK II Cater to Hobbyists and Educators?
The Tiny 3D Printed CNC MK II is designed primarily for hobbyists and educational institutions. Its compact size and affordable price point make it accessible for individuals or organizations with limited budgets. The machine has a working area of 225x325mm, which is suitable for small projects and learning environments. However, it is important for buyers to recognize that this model is not designed for heavy-duty tasks, so it may not be the best fit for businesses seeking to produce high-volume or industrial-grade outputs.
What Makes the LDO Milo V1.5 CNC Kit a Strong Option for Small Businesses?
The LDO Milo V1.5 CNC Kit stands out for its robust construction and integration with 3D printing technologies. This kit is particularly well-suited for small businesses that require a reliable machine for crafting and small-scale production. Its durability and versatility allow it to work with various materials, making it a valuable asset in diverse manufacturing processes. However, the higher initial investment compared to basic models may be a consideration for budget-conscious buyers.
Why Choose the Inventables X-Carve Pro for Professional Manufacturing?
The Inventables X-Carve Pro is designed for businesses that prioritize precision and larger working areas. This machine is well-suited for professional manufacturing and design prototyping, where accuracy is paramount. Its advanced features cater to a range of materials, providing flexibility in production. However, potential buyers should be prepared for a significant investment, as this model represents one of the higher price points in the market.
What Advantages Does the Shapeoko 4 CNC Router Offer to Manufacturers?
The Shapeoko 4 CNC Router combines a hybrid table design with extensive material compatibility, making it an attractive option for manufacturers in woodworking and metalworking. Its strong community support and versatility enhance its appeal to both new and experienced users. However, the complexity of the machine may deter beginners, and businesses should assess their team’s capabilities before investing. Overall, it is a solid choice for companies looking to expand their production capabilities.
Key Industrial Applications of 3d printed desktop cnc mill
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of 3D Printed Desktop CNC Mill | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Aerospace | Prototyping of Lightweight Components | Reduces material waste and accelerates R&D cycles | Sourcing high-quality materials that meet safety standards, and ensuring precision in production. |
| Automotive | Custom Tooling and Jigs | Enhances production efficiency and reduces lead times | Availability of compatible materials and components for specific vehicle models and manufacturing processes. |
| Electronics | Production of Enclosures and Custom Parts | Facilitates rapid prototyping and product iterations | Ensure compliance with electrical standards and sourcing of specialized electronic-grade materials. |
| Education and Research | Educational Kits and Research Prototypes | Provides hands-on learning and innovation opportunities | Consideration for educational partnerships and access to research grants for material sourcing. |
| Art and Design | Creation of Unique Sculptures and Functional Art | Supports creative expression and bespoke design solutions | Focus on sourcing diverse materials that can accommodate artistic needs and aesthetic quality. |
How is the 3D Printed Desktop CNC Mill Used in Aerospace Applications?
In the aerospace industry, 3D printed desktop CNC mills are primarily utilized for prototyping lightweight components, such as brackets or housings. These mills allow engineers to rapidly create and test designs, significantly reducing the time and material costs associated with traditional manufacturing methods. International buyers in this sector must focus on sourcing high-quality materials that comply with stringent safety standards, ensuring the durability and performance of the components.
What Role Does the 3D Printed CNC Mill Play in Automotive Custom Tooling?
The automotive sector benefits from 3D printed desktop CNC mills through the creation of custom tooling and jigs. This application enhances production efficiency by enabling manufacturers to quickly adapt tools for specific vehicle models or production lines. Buyers should consider the compatibility of materials with their existing manufacturing processes and the availability of specialized components that meet automotive standards, particularly in regions with varying industrial capabilities.
How Can Electronics Companies Leverage 3D Printed CNC Mills?
Electronics manufacturers utilize 3D printed desktop CNC mills for producing enclosures and custom parts that fit intricate electronic designs. This application allows for rapid prototyping, enabling companies to iterate on designs quickly and reduce time to market. Buyers in this sector need to ensure that the sourced materials comply with electrical safety standards and are suitable for the required production specifications, especially in regions with varying regulatory environments.
In What Ways are Educational Institutions Using 3D Printed CNC Mills?
Educational institutions leverage 3D printed desktop CNC mills to create educational kits and research prototypes. This application provides students and researchers with hands-on experience in design and manufacturing processes, fostering innovation and technical skills. Buyers from educational sectors should consider partnerships with suppliers that offer educational discounts or grants for material sourcing, which can help reduce overall costs while enriching the learning experience.
How are Artists and Designers Benefiting from 3D Printed CNC Mills?
In the art and design industry, 3D printed desktop CNC mills are used to create unique sculptures and functional art pieces. These mills allow artists to experiment with complex shapes and materials, facilitating bespoke design solutions that push creative boundaries. Buyers in this field should focus on sourcing diverse materials that meet artistic needs while ensuring aesthetic quality, particularly in international markets where material availability may vary.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘3d printed desktop cnc mill’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Difficulty in Sourcing Quality Materials for 3D Printing
The Problem: One significant challenge faced by B2B buyers is sourcing high-quality materials necessary for constructing a 3D printed desktop CNC mill. Many manufacturers may struggle to find reliable suppliers for specific components like aluminum profiles, stepper motors, or specialized 3D printing filament. This can lead to delays in production, increased costs, and ultimately impact project timelines. Buyers might also be concerned about the quality and compatibility of sourced materials, which can affect the performance and durability of the CNC mill.
The Solution: To address this sourcing challenge, businesses should establish relationships with reputable suppliers who specialize in CNC components and 3D printing materials. Conducting thorough research to identify suppliers with a strong track record and positive customer reviews is essential. Additionally, buyers can leverage online platforms such as Alibaba or industry-specific forums to connect with manufacturers and distributors. It is advisable to request samples of materials before committing to larger orders, ensuring compatibility and quality. Furthermore, engaging with local distributors can provide logistical advantages, reducing shipping times and costs. By prioritizing quality sourcing and building strategic partnerships, buyers can enhance their production capabilities and ensure their 3D printed CNC mill meets operational needs.
Scenario 2: Overcoming Technical Challenges in Assembly and Operation
The Problem: Many B2B buyers encounter technical difficulties during the assembly and operation of 3D printed desktop CNC mills. Issues such as misalignment, software configuration, and wiring can lead to frustration and project delays. Additionally, without a deep technical understanding, operators may struggle to optimize the machine’s settings, resulting in subpar performance or even damage to components.
The Solution: To mitigate these technical challenges, companies should invest in comprehensive training and support resources. This includes detailed assembly guides, instructional videos, and access to online forums where users can share experiences and solutions. Buyers should also consider sourcing CNC kits that come with pre-configured components to minimize assembly complexity. Collaborating with manufacturers who offer customer support and troubleshooting services can further enhance operational efficiency. Additionally, implementing a robust maintenance schedule can help prevent issues before they arise, ensuring the CNC mill operates smoothly. By fostering a culture of continuous learning and support, businesses can empower their teams to maximize the performance of their 3D printed CNC mills.
Scenario 3: Ensuring Accuracy and Precision in Machining
The Problem: Achieving precise machining results is a critical pain point for many B2B buyers using 3D printed desktop CNC mills. Variability in 3D printed components, such as dimensional inaccuracies or material weaknesses, can lead to discrepancies in the final product. This is particularly concerning for industries where precision is paramount, such as aerospace or medical device manufacturing.
The Solution: To ensure accuracy and precision, businesses should implement rigorous quality control measures throughout the design and manufacturing process. This includes conducting regular calibration checks on the CNC mill and using high-quality, precisely manufactured components. Employing advanced design software, like Fusion 360, allows for detailed modeling and simulation, helping identify potential issues before production begins. Additionally, investing in a reliable slicing software with advanced settings for optimizing print quality can significantly enhance the precision of 3D printed parts. By prioritizing quality assurance and utilizing advanced technology, companies can improve the reliability of their CNC mills and produce consistent, high-quality outcomes.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for 3d printed desktop cnc mill
What Are the Key Materials for 3D Printed Desktop CNC Mills?
When selecting materials for a 3D printed desktop CNC mill, it is crucial to consider their mechanical properties, cost, and suitability for specific applications. Below, we analyze four common materials used in this context, focusing on their advantages and disadvantages, as well as their implications for international B2B buyers.
How Does PLA Perform in 3D Printed CNC Mills?
Polylactic Acid (PLA) is one of the most commonly used materials in 3D printing due to its ease of use and availability. PLA has a relatively low melting point, typically around 180-220°C, making it suitable for applications that do not require high thermal resistance.
Pros: PLA is biodegradable, cost-effective, and offers good dimensional stability. It is ideal for creating prototypes and non-functional parts where high strength is not a primary concern.
Cons: However, PLA is not very durable under high temperatures and can deform when exposed to heat. It also has limited resistance to moisture and chemicals, which may affect its performance in humid environments.
Impact on Application: PLA is best suited for applications involving light materials like wood and plastics, but it may not be compatible with metals or high-temperature processes.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers in regions like Europe and the Middle East should ensure compliance with environmental regulations regarding biodegradable materials. Standards such as DIN EN ISO 13432 for compostability may be relevant.
What Are the Benefits of ABS for CNC Mill Applications?
Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS) is another popular choice, known for its toughness and impact resistance. It has a higher melting point than PLA, around 210-250°C, making it suitable for more demanding applications.
Pros: ABS is durable, resistant to heat, and can be easily post-processed (e.g., sanding, painting). It is ideal for functional parts that require strength and resilience.
Cons: The primary drawback of ABS is its tendency to warp during printing, which can complicate the manufacturing process. Additionally, it emits fumes during printing, necessitating adequate ventilation.
Impact on Application: ABS is suitable for a variety of applications, including parts that require higher durability and heat resistance, such as housings and brackets.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should be aware of safety and environmental regulations regarding emissions. Compliance with standards like ASTM D6400 for biodegradability may also be important.
How Does PETG Compare in Terms of Performance?
Polyethylene Terephthalate Glycol (PETG) is gaining popularity for its balance between ease of printing and mechanical properties. It has a melting point similar to ABS but offers better chemical resistance.
Pros: PETG is known for its flexibility, impact resistance, and clarity. It is less prone to warping than ABS and is suitable for parts that require transparency or chemical resistance.
Cons: While PETG is easier to print than ABS, it can still be challenging to achieve high-quality finishes. It may also be more expensive than PLA and ABS.
Impact on Application: PETG is ideal for applications requiring chemical resistance, such as containers or parts exposed to various substances.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should consider the availability of PETG in their region, as it may not be as widely stocked as PLA or ABS. Compliance with relevant safety and quality standards is also crucial.
What Role Does Nylon Play in CNC Mill Manufacturing?
Nylon is a versatile material known for its strength and flexibility. It has a high melting point, typically around 220-260°C, making it suitable for high-performance applications.
Pros: Nylon is incredibly strong, wear-resistant, and has excellent chemical resistance. It is ideal for functional parts that undergo significant stress.
Cons: The main challenges with nylon include its tendency to absorb moisture, which can affect its mechanical properties, and the difficulty in printing due to warping.
Impact on Application: Nylon is suitable for applications requiring high durability and flexibility, such as gears and functional mechanical parts.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should ensure that nylon complies with relevant standards for mechanical properties, such as ISO 527 for tensile properties. Additionally, they should consider the availability and cost of nylon in their respective markets.
Summary Table of Material Selection
| Material | Typical Use Case for 3D Printed Desktop CNC Mill | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PLA | Prototyping, non-functional parts | Biodegradable, cost-effective | Low heat resistance, moisture sensitivity | Low |
| ABS | Functional parts, housings | Durable, easy to post-process | Warping issues, fumes during printing | Medium |
| PETG | Chemical-resistant parts, containers | Flexible, impact-resistant | More expensive, printing challenges | Medium |
| Nylon | High-stress functional parts | Strong, wear-resistant | Moisture absorption, printing difficulty | High |
This strategic material selection guide provides a comprehensive overview for international B2B buyers looking to optimize their 3D printed desktop CNC mill applications. By understanding the properties, advantages, and limitations of these materials, buyers can make informed decisions that align with their specific needs and compliance requirements.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for 3d printed desktop cnc mill
What Are the Key Stages in the Manufacturing Process of a 3D Printed Desktop CNC Mill?
The manufacturing process of a 3D printed desktop CNC mill involves several stages: material preparation, forming, assembly, and finishing. Each stage plays a crucial role in ensuring the final product meets the desired specifications and quality standards.
How Is Material Prepared for 3D Printing CNC Components?
The first step in the manufacturing process is material preparation. For desktop CNC mills, commonly used materials include various thermoplastics such as PLA, ABS, and nylon. These materials are chosen for their strength, durability, and ease of printing. The preparation stage includes selecting high-quality filament and ensuring it is free from impurities. Proper storage of materials to prevent moisture absorption is also critical, as moisture can significantly affect print quality.
What Forming Techniques Are Used in 3D Printing CNC Parts?
Forming primarily involves the additive manufacturing process, where the 3D printer builds parts layer by layer. Techniques such as Fused Deposition Modeling (FDM) and Stereolithography (SLA) are popular in producing CNC components. FDM is often preferred for its speed and cost-effectiveness, while SLA can achieve higher precision and surface finish. The choice of technique will depend on the specific requirements of the CNC mill, such as dimensional accuracy and mechanical properties.
How Are Components Assembled in a 3D Printed Desktop CNC Mill?
After the individual components are printed, the assembly process begins. This includes integrating mechanical parts like motors, belts, and lead screws with the 3D printed elements. An effective assembly process requires attention to detail to ensure that all components fit correctly and are secured properly to avoid misalignment during operation. Companies may employ jigs or fixtures to maintain consistent assembly quality and speed.
What Finishing Techniques Are Commonly Applied to 3D Printed Parts?
Finishing is essential for enhancing the aesthetics and functionality of the CNC mill. Techniques may include sanding, painting, or applying protective coatings to the printed parts. These finishing touches can improve surface smoothness and protect against wear and tear during use. Additionally, post-processing can involve testing and calibrating the assembled machine to ensure it operates within the desired specifications.
How Is Quality Assurance Implemented in the Manufacturing of 3D Printed CNC Mills?
Quality assurance (QA) is critical throughout the manufacturing process to ensure that the final product meets industry standards and customer expectations. Implementing a robust QA framework involves adhering to international standards like ISO 9001, which emphasizes a systematic approach to managing quality.
What Are the Key International Quality Standards for CNC Mills?
For manufacturers targeting international markets, compliance with various quality standards is essential. ISO 9001 sets the foundation for quality management systems, while CE marking signifies compliance with EU safety, health, and environmental protection standards. In regions like Africa and South America, local regulations may also apply, and manufacturers should be aware of these to facilitate smoother market entry.
What Are the Checkpoints for Quality Control During Manufacturing?
Quality control (QC) involves several checkpoints throughout the manufacturing process. Incoming Quality Control (IQC) assesses the quality of raw materials before production begins. In-Process Quality Control (IPQC) monitors the manufacturing process to identify any deviations from specifications, while Final Quality Control (FQC) evaluates the finished product against established standards. Each of these checkpoints plays a vital role in ensuring that defects are caught early and corrective actions are implemented.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control Measures?
B2B buyers should implement thorough verification processes to ensure suppliers adhere to quality control standards. This can include requesting detailed QC reports, conducting audits, and engaging third-party inspection services. Audits allow buyers to assess the manufacturing environment, processes, and adherence to quality standards firsthand. Additionally, suppliers should be willing to share documentation of their quality assurance processes, including certifications and testing results.
What Testing Methods Are Commonly Used to Validate CNC Mill Quality?
Common testing methods include dimensional accuracy checks, functional testing, and material property evaluations. Dimensional accuracy checks involve using calipers and gauges to ensure that the components meet specified tolerances. Functional testing assesses the CNC mill’s operational capabilities, ensuring it can perform milling tasks accurately and efficiently. Material property evaluations may involve tensile testing and hardness tests to confirm that the materials used can withstand operational stresses.
How Do Quality Control Nuances Affect International B2B Buyers?
International B2B buyers must navigate various quality control nuances when sourcing 3D printed desktop CNC mills. Cultural differences, regulatory requirements, and communication barriers can impact the quality assurance process. For example, buyers from Europe may expect more stringent quality documentation compared to suppliers in other regions. Thus, establishing clear expectations and maintaining open communication is crucial for successful transactions.
What Should Buyers Consider When Choosing a Supplier?
When selecting a supplier for a 3D printed desktop CNC mill, buyers should consider the supplier’s track record in quality management, their compliance with international standards, and their willingness to provide transparency in their processes. Additionally, assessing the supplier’s ability to adapt to local regulations in the buyer’s region can be a deciding factor in ensuring a smooth procurement process.
In conclusion, a comprehensive understanding of the manufacturing processes and quality assurance measures is essential for B2B buyers in the 3D printed desktop CNC mill market. By focusing on these elements, buyers can make informed decisions that enhance their operational capabilities and ensure they receive high-quality products that meet their specific needs.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘3d printed desktop cnc mill’
In the rapidly evolving landscape of manufacturing, 3D printed desktop CNC mills represent a significant advancement for businesses looking to enhance their production capabilities. This guide aims to provide B2B buyers with a structured checklist to facilitate the sourcing process for these machines, ensuring informed decision-making that aligns with operational needs.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Before exploring suppliers, it’s essential to outline the specific technical requirements of the CNC mill. Consider factors such as the materials you will be working with (e.g., wood, plastic, aluminum) and the desired working area dimensions. Clear specifications will help you narrow down options and ensure compatibility with your production goals.
Step 2: Identify Suitable Suppliers
Research potential suppliers that specialize in 3D printed CNC mills. Focus on those with a proven track record in your target regions—Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. Look for suppliers who offer detailed product information, including performance metrics and case studies, to assess their reliability and expertise.
Step 3: Evaluate Supplier Certifications
Certifications can serve as a benchmark for quality and safety standards. Verify if suppliers hold relevant industry certifications, such as ISO, CE, or UL, which can indicate adherence to international quality standards. This step helps mitigate risks associated with subpar products and ensures compliance with local regulations.
Step 4: Request Prototypes or Samples
Whenever possible, request prototypes or samples of the CNC mill to evaluate their functionality and build quality. Testing a unit firsthand allows you to assess its performance with your materials and ensures it meets your operational needs. Pay attention to aspects like ease of assembly, precision, and software compatibility.
Step 5: Analyze Cost and Total Ownership Value
When comparing different CNC mills, consider not just the purchase price but also the total cost of ownership. Evaluate factors such as maintenance requirements, energy consumption, and potential downtime. A machine that appears cheaper upfront may incur higher operational costs, making it less economical in the long run.
Step 6: Review Customer Support and Warranty Terms
Strong customer support is vital for smooth operations. Investigate the level of post-purchase support offered by suppliers, including training, troubleshooting assistance, and warranty terms. A comprehensive warranty can provide peace of mind and protect your investment against unforeseen issues.
Step 7: Consider Future Scalability
As your business grows, your production needs may change. Assess whether the CNC mill can be upgraded or modified to accommodate future requirements. Look for suppliers that provide options for additional features or accessories that can enhance the machine’s capabilities over time.
By following this checklist, B2B buyers can navigate the complexities of sourcing a 3D printed desktop CNC mill more effectively, ensuring that their investment aligns with both current and future operational demands.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for 3d printed desktop cnc mill Sourcing
What are the Key Cost Components in Sourcing 3D Printed Desktop CNC Mills?
When sourcing 3D printed desktop CNC mills, understanding the cost structure is crucial for B2B buyers aiming to make informed purchasing decisions. The primary cost components include:
-
Materials: The choice of materials significantly impacts the overall cost. Common materials used in 3D printed CNC mills include PLA, aluminum profiles, and various electronic components. The quality and availability of these materials can vary by region, influencing prices. For instance, sourcing high-quality aluminum may be more expensive in regions with limited access to metal suppliers.
-
Labor: Labor costs encompass design, assembly, and testing. In regions like Africa and South America, labor costs may be lower, but the availability of skilled labor for precise assembly and programming can affect overall expenses.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes expenses related to the production environment, such as utilities and rent. In Europe, for example, manufacturing overhead can be significantly higher due to stricter regulations and higher operational costs.
-
Tooling: Initial setup costs for tooling can be substantial, especially for custom designs. Buyers should consider whether the supplier has the necessary equipment and capabilities to meet specific design requirements.
-
Quality Control (QC): Ensuring the reliability of CNC mills requires robust QC measures. Costs for testing and certification can vary significantly based on the supplier’s quality assurance processes.
-
Logistics: Shipping costs are influenced by the distance between the supplier and the buyer, as well as the chosen Incoterms. International buyers should factor in customs duties and potential delays, especially when importing from regions with complex logistics systems.
-
Margin: Suppliers typically mark up their prices to cover costs and ensure profitability. Buyers should be aware of industry standards for margins in their specific regions to gauge fair pricing.
How Do Price Influencers Affect 3D Printed CNC Mill Costs?
Several factors influence the pricing of 3D printed desktop CNC mills, including:
-
Volume/MOQ: Larger orders often lead to lower per-unit costs due to economies of scale. Buyers should negotiate minimum order quantities (MOQs) that align with their production needs while maximizing cost efficiency.
-
Specifications and Customization: Custom designs or specific features can increase costs. Buyers should clearly communicate their requirements to avoid unexpected price increases during the sourcing process.
-
Materials: The choice between standard and premium materials can lead to significant cost variations. Buyers should assess their material needs carefully, balancing durability and cost-effectiveness.
-
Quality and Certifications: Suppliers with established quality certifications may charge higher prices due to the assurance of reliability. Buyers should weigh the importance of certifications against their project requirements.
-
Supplier Factors: The reputation and reliability of the supplier can impact pricing. Established suppliers may offer better warranties and support, justifying higher costs.
-
Incoterms: Understanding Incoterms is essential for managing logistics costs effectively. Terms like FOB (Free on Board) or CIF (Cost, Insurance, and Freight) can influence the final price, especially for international transactions.
What Tips Can Buyers Use to Negotiate Better Prices for CNC Mills?
To optimize sourcing costs, B2B buyers should consider the following strategies:
-
Negotiate Terms: Engage suppliers in discussions about pricing, payment terms, and delivery schedules. Building a relationship can lead to better terms and potential discounts.
-
Focus on Cost-Efficiency: Evaluate the Total Cost of Ownership (TCO), which includes initial purchase price, maintenance, and operational costs. A lower upfront cost may not always translate to overall savings.
-
Understand Regional Pricing Nuances: Be aware of the pricing trends in different regions. For instance, suppliers in Europe may have higher operational costs, impacting pricing compared to those in Asia or South America.
-
Leverage Local Market Knowledge: Utilize local contacts or sourcing agents who understand the regional market dynamics. They can provide insights into fair pricing and help identify reputable suppliers.
-
Stay Informed on Market Trends: Keeping abreast of technological advancements and material costs can provide leverage during negotiations. Being knowledgeable about the market can position buyers more favorably in discussions.
Disclaimer on Indicative Prices
Prices for 3D printed desktop CNC mills can vary widely based on the aforementioned factors. The prices discussed in this analysis are indicative and subject to change based on market conditions, supplier capabilities, and specific buyer requirements. Always conduct thorough due diligence and obtain multiple quotes before finalizing any sourcing agreements.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing 3d printed desktop cnc mill With Other Solutions
Exploring Alternatives to the 3D Printed Desktop CNC Mill
As businesses increasingly look for efficient manufacturing solutions, the 3D printed desktop CNC mill has emerged as a popular option. However, various alternatives are available, each offering unique advantages and disadvantages. This section will compare the 3D printed desktop CNC mill with two viable alternatives: traditional CNC milling machines and CNC routers.
Comparison Table
| Comparison Aspect | 3D Printed Desktop CNC Mill | Traditional CNC Milling Machine | CNC Router |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | Moderate precision; suitable for soft materials | High precision; versatile across materials | Good for softer materials; less precise than milling machines |
| Cost | Low initial investment (around $300-700) | High initial investment ($5,000 – $50,000) | Moderate investment ($1,500 – $10,000) |
| Ease of Implementation | DIY assembly; requires technical skills | Requires professional setup and training | Generally easier to set up and use |
| Maintenance | Low; mainly requires printer upkeep | Moderate; regular servicing needed | Low; minimal maintenance required |
| Best Use Case | Prototyping and hobby projects | Industrial manufacturing and precision parts | Woodworking and signage production |
Detailed Breakdown of Alternatives
Traditional CNC Milling Machine
Traditional CNC milling machines are well-established in the manufacturing industry, known for their high precision and ability to work with a wide range of materials, including metals and composites. These machines excel in mass production and high-tolerance applications, making them ideal for industries like aerospace and automotive. However, they come with a steep price tag and require significant space, as well as professional training for operation and maintenance. Businesses with high-volume needs and the budget to support such investments will find traditional CNC milling machines beneficial.
CNC Router
CNC routers are a popular choice for businesses focused on woodworking, signage, and light-duty machining. They are generally easier to operate and set up compared to traditional milling machines, making them accessible for small businesses and hobbyists alike. While CNC routers are cost-effective and versatile for softer materials like wood and plastics, they lack the precision required for more complex tasks, such as those found in metalworking. Companies that prioritize ease of use and lower costs while working with softer materials may find CNC routers to be a suitable alternative.
Making the Right Choice for Your Business Needs
When selecting the right solution for your business, consider your specific requirements, including the materials you’ll be working with, your budget, and the intended applications. The 3D printed desktop CNC mill offers an affordable entry point for prototyping and hobbyist projects, but may not meet the rigorous demands of industrial manufacturing. Traditional CNC milling machines provide unmatched precision but require a significant investment and expertise. Conversely, CNC routers strike a balance between cost and ease of use, making them ideal for woodworking and signage projects. Assessing these factors will help you determine the most appropriate solution for your operational goals and budget constraints.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for 3d printed desktop cnc mill
What Are the Key Technical Properties of a 3D Printed Desktop CNC Mill?
When considering a 3D printed desktop CNC mill, understanding the critical technical specifications is essential for making informed purchasing decisions. Here are some key properties to consider:
1. Material Grade
The material grade refers to the type of materials used in the construction of the CNC mill. Common materials include PLA, ABS, and aluminum for structural components. In a B2B context, selecting the right material is crucial for durability, performance, and application suitability. For example, while PLA is cost-effective and easy to print, it may not withstand high temperatures or heavy workloads, making it less suitable for industrial applications.
2. Tolerance
Tolerance measures the allowable deviation from a specified dimension. In CNC machining, tighter tolerances (e.g., ±0.01 mm) ensure precision in finished products, which is vital for industries like aerospace and automotive. Understanding the tolerance levels of a CNC mill can help buyers assess whether it meets the stringent quality standards required for their applications.
3. Working Area
The working area defines the maximum dimensions of the material that can be processed by the CNC mill. For instance, a mill with a working area of 600×450 mm allows for larger projects and more versatility. B2B buyers should consider their specific project requirements when selecting a machine with an appropriate working area to maximize operational efficiency.
4. Axis Configuration
The axis configuration indicates how many axes the machine can operate on, typically 3-axis or 5-axis systems. A 3-axis mill can perform basic operations, while a 5-axis mill provides more complex capabilities, allowing for intricate designs and reduced setups. Understanding the axis configuration helps buyers determine the machine’s suitability for their specific manufacturing needs.
5. Spindle Speed
Spindle speed, measured in RPM (revolutions per minute), indicates how fast the cutting tool rotates. Higher spindle speeds allow for faster material removal and better surface finishes. In a B2B context, knowing the spindle speed is crucial for optimizing machining operations and ensuring that the CNC mill can handle various materials effectively.
6. Power Rating
The power rating of the CNC mill’s motor directly impacts its cutting capacity and efficiency. A higher power rating enables the machine to handle tougher materials, which is essential for industries requiring robust machining solutions. Buyers should assess the power rating in relation to their expected workload to ensure optimal performance.
What Common Trade Terms Should Buyers Know in the CNC Industry?
Familiarity with industry terminology is critical for effective communication and negotiation in B2B transactions. Here are some key terms:
1. OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
OEM refers to a company that produces parts or equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer. In the context of CNC mills, understanding OEM relationships can help buyers identify reliable sources for replacement parts or additional components.
2. MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ is the smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell. This is particularly relevant for B2B buyers looking to negotiate bulk orders, as understanding MOQ can help them plan their purchasing strategies and manage inventory effectively.
3. RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a document issued by a buyer to invite suppliers to bid on specific products or services. In the CNC milling industry, submitting an RFQ can help buyers obtain competitive pricing and terms from multiple vendors, facilitating better decision-making.
4. Incoterms
Incoterms (International Commercial Terms) are a set of predefined international rules governing the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in shipping goods. Familiarity with Incoterms is vital for B2B transactions, as they define who is responsible for costs, risks, and insurance during transit, which can significantly impact overall project budgets.
5. Lead Time
Lead time refers to the amount of time it takes from placing an order to receiving the product. Understanding lead times is essential for B2B buyers to effectively manage their production schedules and avoid delays that could impact project timelines.
By grasping these technical properties and trade terms, B2B buyers can make more informed decisions when investing in a 3D printed desktop CNC mill, ensuring that their choices align with their operational needs and market demands.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the 3d printed desktop cnc mill Sector
What Are the Current Market Dynamics and Key Trends in the 3D Printed Desktop CNC Mill Sector?
The 3D printed desktop CNC mill sector is experiencing significant growth, driven by the increasing demand for customized manufacturing solutions across various industries. Global drivers include the rise of small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs) looking for cost-effective production methods and the growing trend towards automation and precision engineering. In regions like Africa and South America, where traditional manufacturing capabilities may be limited, 3D printed CNC mills offer an accessible entry point into advanced manufacturing technologies. Meanwhile, markets in Europe, particularly Germany, are leveraging these innovations to enhance their competitive edge through rapid prototyping and reduced lead times.
Emerging B2B tech trends include the integration of IoT capabilities within CNC machines, facilitating real-time monitoring and predictive maintenance. This shift is particularly valuable for international buyers, as it enhances operational efficiency and minimizes downtime. Additionally, there is a noticeable trend towards modular designs, allowing for easy upgrades and customization based on specific production needs. As businesses increasingly prioritize sustainability, sourcing trends are leaning towards suppliers who provide eco-friendly materials and components, making it crucial for buyers to identify partners that align with these values.
How Is Sustainability Shaping the Sourcing of 3D Printed Desktop CNC Mills?
Sustainability is becoming a cornerstone of B2B purchasing decisions in the 3D printed desktop CNC mill sector. The environmental impact of manufacturing processes is under scrutiny, prompting businesses to seek solutions that minimize waste and energy consumption. The use of biodegradable materials, such as PLA for 3D printed components, is gaining traction, as it reduces the carbon footprint associated with production.
Moreover, the importance of ethical supply chains cannot be overstated. Buyers are increasingly looking for suppliers who prioritize transparency, fair labor practices, and responsible sourcing of materials. Certifications such as ISO 14001 for environmental management and other ‘green’ certifications can serve as indicators of a supplier’s commitment to sustainable practices. In a competitive market, aligning with suppliers who uphold these values not only enhances a company’s brand reputation but also meets the growing consumer demand for environmentally responsible products.
What Has Been the Evolution of the 3D Printed Desktop CNC Mill Sector?
The evolution of the 3D printed desktop CNC mill sector can be traced back to the early days of both 3D printing and CNC machining technologies. Initially, these technologies were largely confined to industrial applications; however, advancements in materials and technology have democratized access, allowing hobbyists and small businesses to utilize these tools effectively.
Over the past decade, the convergence of 3D printing and CNC milling has led to the development of hybrid machines that combine the strengths of both processes. This innovation has facilitated the creation of complex geometries and high-precision components at a fraction of the traditional costs, making it feasible for smaller enterprises to engage in sophisticated manufacturing. As the sector continues to evolve, the integration of smart technologies and sustainable practices will likely define its future trajectory, offering B2B buyers new opportunities for innovation and growth.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of 3d printed desktop cnc mill
-
How do I solve issues with sourcing reliable suppliers for 3D printed desktop CNC mills?
To address sourcing concerns, conduct thorough research on potential suppliers. Look for manufacturers with a strong reputation in the industry, positive customer reviews, and a robust online presence. Utilize platforms like Alibaba, ThomasNet, or industry-specific trade shows to find credible suppliers. Additionally, request samples of their products to evaluate quality and performance before making larger commitments. -
What is the best material for 3D printed desktop CNC mills?
The optimal material for 3D printed desktop CNC mills typically includes PLA, ABS, and PETG. PLA is favored for its ease of printing and rigidity, making it suitable for prototypes and low-stress applications. ABS offers better durability and heat resistance, ideal for components that experience significant wear. PETG strikes a balance between strength and flexibility, making it suitable for various applications. Assess your specific needs to choose the most appropriate material. -
How can I customize my 3D printed desktop CNC mill to fit my specific needs?
Customization can be achieved through various methods, including modifying design files or selecting specific components. Many suppliers provide CAD files or STL models that allow you to alter dimensions, add features, or improve functionality. Additionally, consider working directly with the manufacturer to discuss bespoke options, such as unique attachments or software configurations, ensuring the machine meets your operational requirements. -
What are the minimum order quantities (MOQ) for 3D printed desktop CNC mills?
Minimum order quantities can vary significantly between suppliers. Generally, smaller manufacturers may have lower MOQs, sometimes accepting orders of just one unit, while larger suppliers may require bulk orders to reduce production costs. It’s advisable to discuss your needs directly with potential suppliers to determine their flexibility regarding MOQs and negotiate terms that suit your business. -
What payment terms are typically offered for B2B purchases of CNC machines?
Payment terms can vary based on the supplier’s policies and your business relationship. Common practices include a deposit (typically 30-50%) upfront, with the balance due upon shipment or delivery. Some suppliers may offer credit terms for established clients. Always clarify payment options before finalizing orders and consider using secure payment methods to protect your investment. -
How can I ensure quality assurance (QA) when purchasing a 3D printed desktop CNC mill?
To ensure quality assurance, request detailed specifications and certifications from the supplier, such as ISO standards. It’s beneficial to ask for sample parts or prototypes to evaluate the quality firsthand. Additionally, consider implementing a third-party inspection service before shipment to verify that the products meet your requirements. Establishing clear communication with the supplier regarding quality expectations is also essential. -
What logistics considerations should I keep in mind when importing CNC machines?
When importing CNC machines, consider shipping costs, customs duties, and local regulations that may impact delivery. It’s crucial to work with a logistics partner experienced in handling machinery to ensure safe transport and compliance with international trade laws. Additionally, factor in lead times for shipping and customs clearance, as these can affect your project timelines. -
How do I handle after-sales support and maintenance for my CNC machine?
After-sales support is vital for the longevity of your CNC machine. Ensure that your supplier offers comprehensive support, including warranty terms, access to spare parts, and technical assistance. Establish a maintenance schedule to keep the machine running efficiently and address any issues proactively. Additionally, consider joining user forums or communities related to your CNC model for shared tips and troubleshooting advice.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.
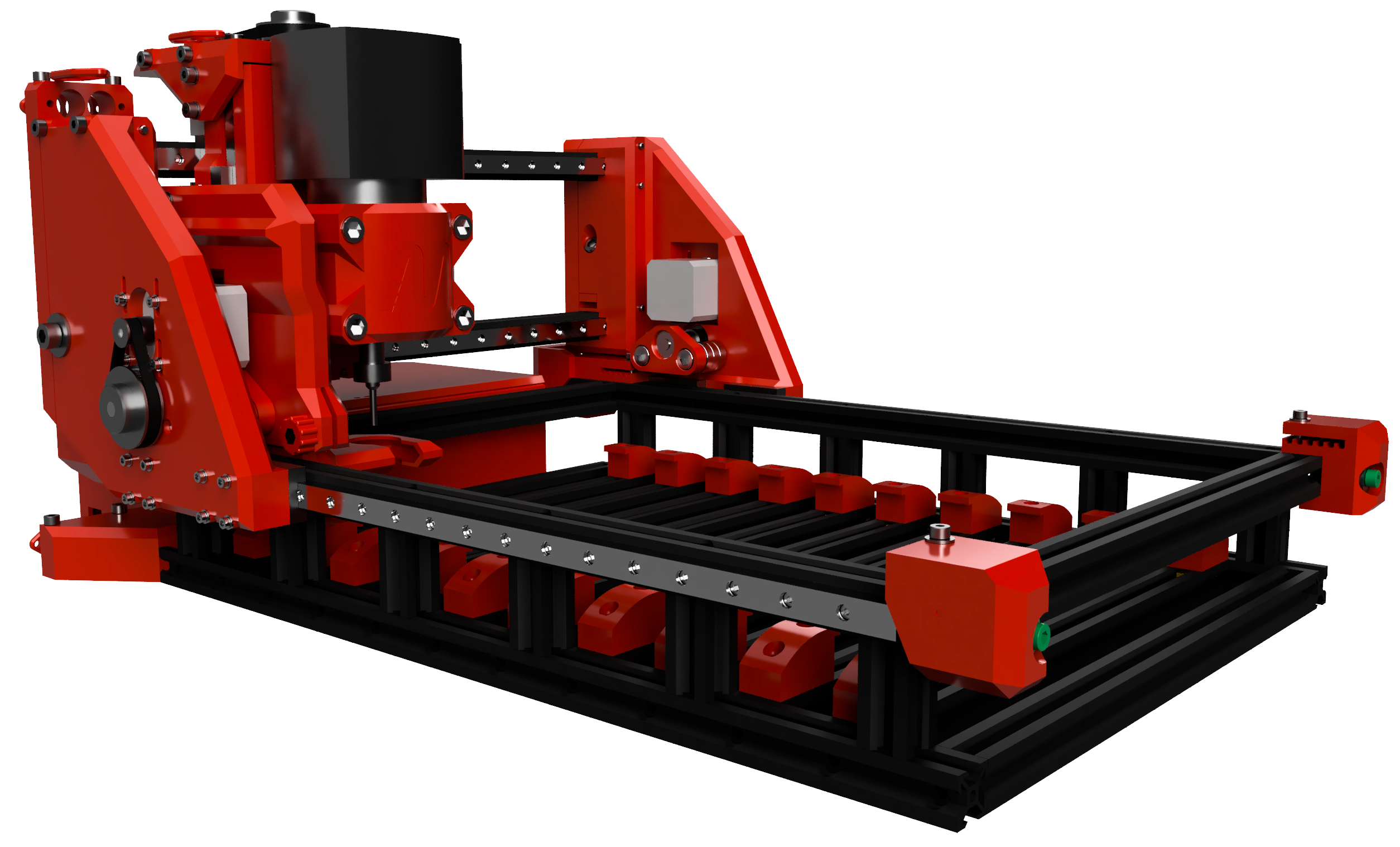
Top 10 3D Printed Desktop Cnc Mill Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. MPCNC – Versatile 3D Printed CNC for Aluminum Milling
Domain: reddit.com
Registered: 2005 (20 years)
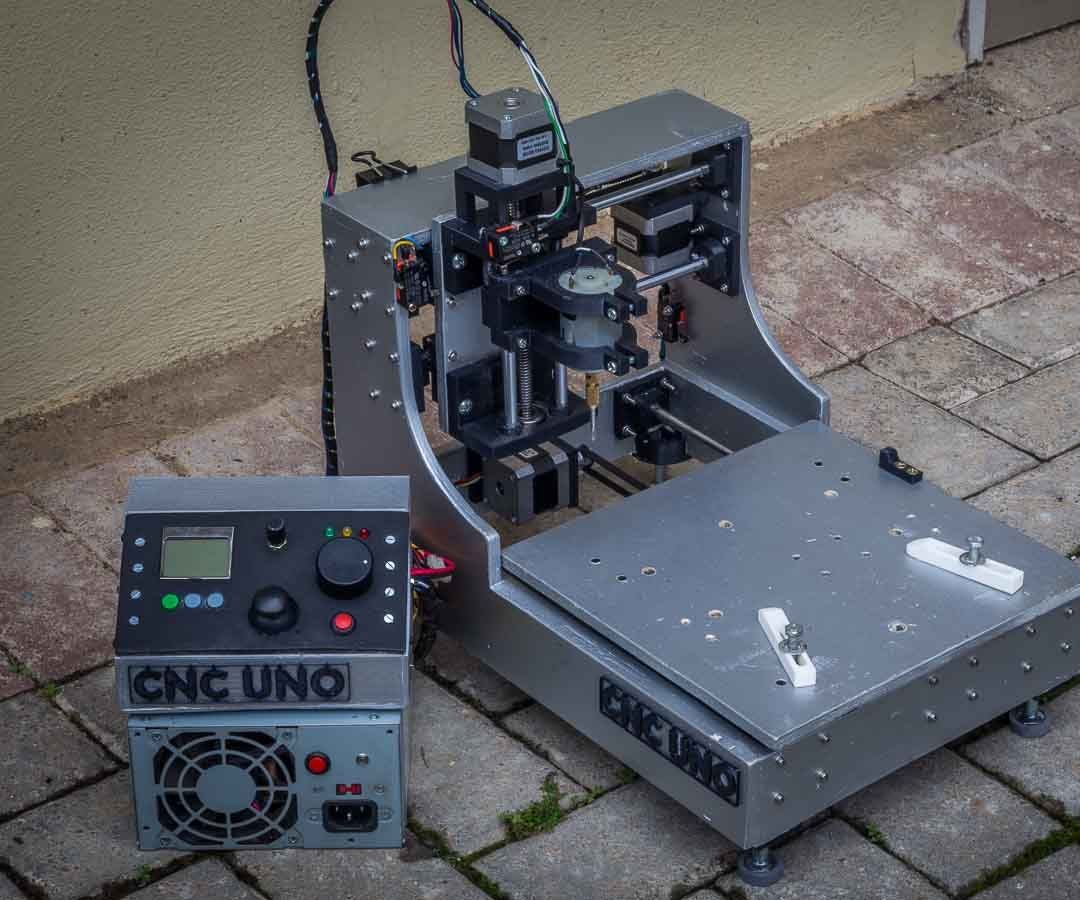
Introduction: The user is looking for a 3D printed CNC machine suitable for milling aluminum, specifically for creating small enclosures (6 x 3 x 2 inches). They are interested in a design that is popular, actively developed, upgradable, and well-documented, with a budget of under $500. The MPCNC (Mostly Printed CNC) is mentioned as a potential option that meets these criteria.
2. LDO – Milo V1.5 CNC Kit
Domain: matterhackers.com
Registered: 2012 (13 years)
Introduction: {“Product Name”: “LDO Milo V1.5 CNC Kit with 3D Printed Parts”, “Manufacturer”: “LDO”, “Type”: “CNC Milling Machine”, “Assembly”: “Self-Assembly”, “Dimensions”: {“Machine”: {“Width”: “735mm”, “Depth”: “670mm”, “Height”: “670mm”}, “Motion”: {“Width”: “1155mm”, “Depth”: “670mm”, “Height”: “670mm”}}, “Working Volume”: {“X”: “340mm”, “Y”: “160mm”, “Z”: “120mm”}, “Traveling Speed”: {“X”: “2000mm/min”, …
3. All3DP – Best 3D Printed CNC Machines
Domain: all3dp.com
Registered: 2013 (12 years)
Introduction: The article discusses the best 3D printed CNC machines, highlighting their ability to enhance home workshops. It emphasizes the use of 3D printers to create CNC devices, providing a DIY approach for enthusiasts.
4. Instructables – G300 3D Printed CNC Machine
Domain: instructables.com
Registered: 2005 (20 years)
Introduction: G300 – 3D Printed CNC Machine; Designed for milling works; Overall budget target: €300; Intended materials: wood, plastic sheets (PP and PE), aluminum; Frame: 2040 aluminum profiles; Wheels: 625ZZ V-Slot; Belts: GT2 fiber-reinforced; Z-axis: Lead Screw; 3D printed parts: PLA; Controller: Arduino with GRBL; Motors: Nema23 with TB6600; Router: Katsu (Makita RT0700C clone); Working area: 600x450mm; V…
5. TINY – 3D PRINTED CNC MK II
Domain: ivanmiranda.com
Registered: 2011 (14 years)
Introduction: Product Name: TINY 3D PRINTED CNC MK II
Price: $25.00 USD
Included Items:
– Bill of Materials in an Excel file with amounts and lengths
– Folder with all STL files of the 3D printed parts
– Link to the source Fusion360 model for download and modification
– Readme file with extra information, print orientation and settings, extrusions, options
Working Area: Approximately 225×325 mm (235×325 mm wit…
6. Printables – Rock Solid Milling Machine V0.9
7. Carbide 3D – Free STL Files for CNC Accessories
Domain: carbide3d.com
Registered: 2013 (12 years)
Introduction: Carbide 3D offers a curated collection of free STL files for 3D printed CNC accessories and replacement parts compatible with their CNC routers and Desktop CNC Machines. The accessories include: Active Project Tray, Aluminium Gator Tooth Caddy, Bit Box Caddy, Bit Caddy, BitZero Caddy, Cam Clamp, Clamp Steps, Corner Square Spacer, Corner Squares, Crush It Essentials Caddy, Crush It Hard Stop, Edge …
8. Thingiverse – 3D Printed CNC Milling Machine
Domain: thingiverse.com
Registered: 2008 (17 years)
Introduction: 3D Printed Desktop CNC Milling Machine by crille
9. Scribd – 3D Printed Desktop CNC Mill
Domain: scribd.com
Registered: 2006 (19 years)
Introduction: 3D Printed Desktop CNC Mill: A project aimed at building a small, affordable desktop CNC milling machine for hobby and educational use. The document includes step-by-step instructions, an overview of the project, and a list of required materials and tools, such as 3D printed plastic parts, plywood, stepper motors, and an Arduino board. Key steps involve cutting wood frame pieces, assembling plasti…
10. Bantam Tools – Desktop CNC Milling Machine
Domain: hardwarecanucks.com
Registered: 2006 (19 years)
Introduction: Bantam Tools’ Desktop CNC Milling Machine: Built as a simple, self-contained system for precision CNC machining & 3-D aluminum prototyping. Optimized for aluminum, fully-automated, features ¼” tooling, and operates at 28K RPM.
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for 3d printed desktop cnc mill
As the global demand for precision manufacturing continues to rise, the strategic sourcing of 3D printed desktop CNC mills presents a transformative opportunity for international B2B buyers. By leveraging innovative designs and cost-effective materials, businesses can enhance their production capabilities while keeping operational costs manageable. Key takeaways include the importance of evaluating supplier reliability, understanding local market conditions, and investing in scalable solutions that accommodate future growth.
Investing in 3D printed CNC technology not only enables rapid prototyping and customization but also fosters a culture of innovation within organizations. This adaptability is particularly vital for businesses in emerging markets across Africa, South America, and the Middle East, where local demand for tailored manufacturing solutions is increasing.
Looking ahead, it is essential for B2B buyers to stay informed about advancements in technology and materials, ensuring they can make informed sourcing decisions. Embrace the potential of 3D printed desktop CNC mills to streamline your operations and drive competitive advantage. Engage with suppliers who understand your unique needs, and position your business for success in an evolving manufacturing landscape.