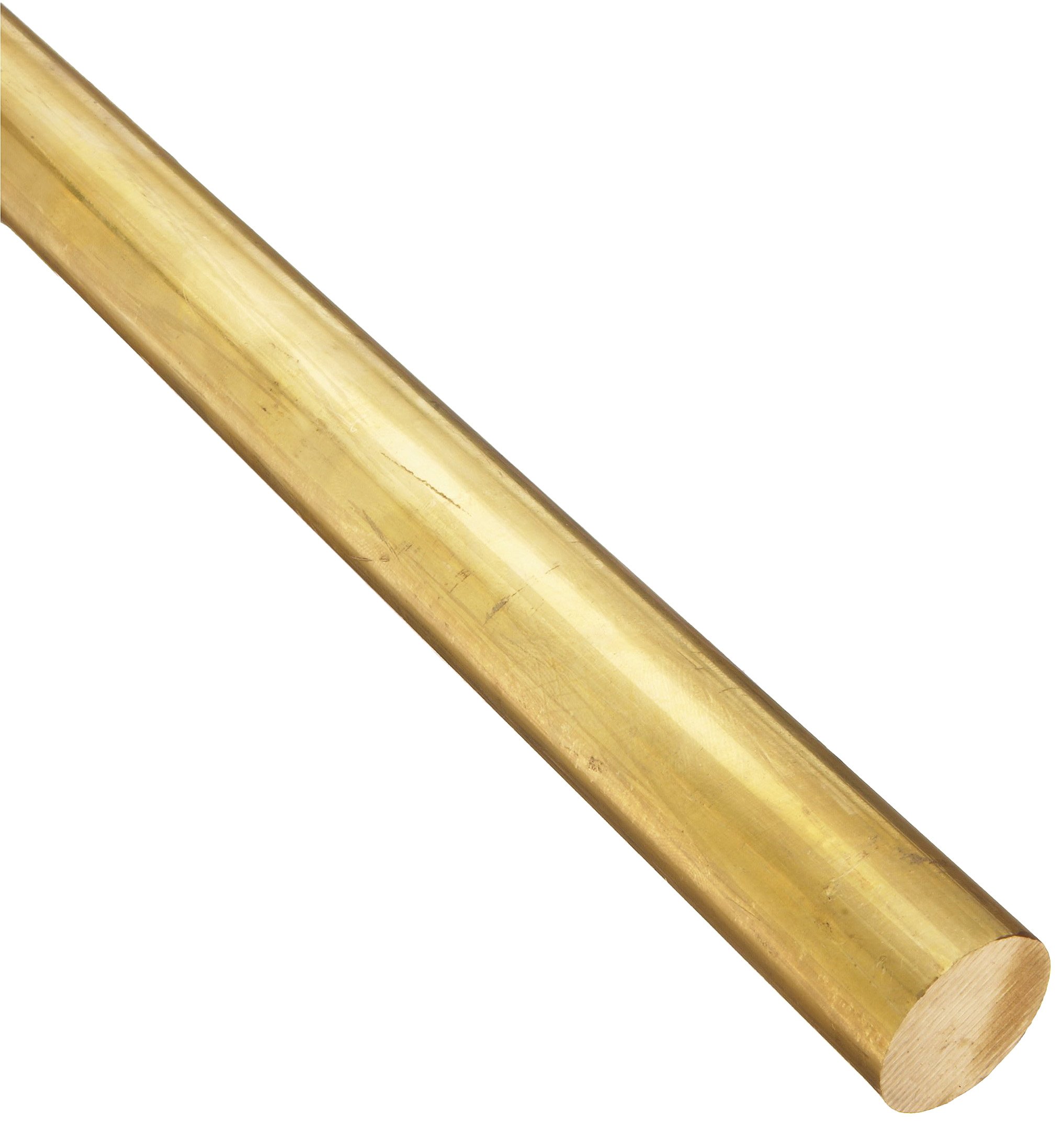
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for 385 brass
The global market for 385 brass, also known as architectural bronze, presents a unique set of challenges for international B2B buyers. One of the primary hurdles faced by organizations sourcing this versatile material is identifying reliable suppliers who can meet specific quality standards while offering competitive pricing. This guide is designed to empower procurement professionals by providing an in-depth analysis of 385 brass, including its composition, mechanical properties, and various applications across industries such as architecture, consumer products, construction hardware, and industrial sectors.
Within these pages, you will discover critical insights into the different forms of 385 brass available in the market, from rods and sheets to specialized extrusions. Additionally, we delve into effective supplier vetting strategies, ensuring that you can confidently select partners who align with your operational needs and quality expectations. Cost considerations and market trends will also be explored, equipping you with the knowledge necessary to make informed purchasing decisions.
This comprehensive guide is tailored for international buyers from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, including key markets like Brazil and Germany. By addressing the complexities of sourcing 385 brass, this resource aims to streamline your procurement process, ultimately enhancing your business’s operational efficiency and product quality.
Understanding 385 brass Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| C38500 (Architectural Bronze) | High copper content (55-59%), excellent machinability, good corrosion resistance in non-marine environments | Architecture, decorative hardware, construction | Pros: Versatile, excellent for hot working. Cons: Not suitable for cold forming or welding. |
| CDA 932 (High-Leaded Tin Bronze) | Contains higher lead content, lower tensile strength (35 KSI) | Bearings, bushings, gears, light-duty applications | Pros: Very machinable, effective for soldering. Cons: Limited to lighter applications, lower strength. |
| CDA 954 (High-Strength Bronze) | Contains minimum 83% copper, higher tensile strength (85 KSI) | High-load applications, outdoor structures, aircraft components | Pros: Exceptional corrosion resistance, high strength. Cons: More expensive, limited availability. |
| Free-Cutting Brass (C36000) | Lower copper content, high lead content, excellent for high-speed machining | Precision components, fasteners, fittings | Pros: Excellent machinability, suited for high-speed production. Cons: Lower corrosion resistance compared to C38500. |
| C385 (British Free Machining Brass) | Similar to C38500, specifically designed for machining | Ornamental hardware, architectural applications | Pros: High machinability, good surface finish. Cons: Not suitable for welding or high-stress applications. |
What Are the Key Characteristics of C38500 (Architectural Bronze)?
C38500, commonly referred to as Architectural Bronze, is characterized by its high copper content (55-59%) and excellent machinability, making it ideal for a variety of applications. It is primarily used in architecture and decorative hardware due to its aesthetic appeal and good corrosion resistance in non-marine environments. Buyers should consider its suitability for hot working processes like forging and bending, while noting its limitations in cold forming and welding, which may affect certain applications.
How Does CDA 932 (High-Leaded Tin Bronze) Compare?
CDA 932 is known for its higher lead content and lower tensile strength compared to C38500. This alloy is particularly useful in lighter-duty applications, such as bearings and bushings, where high machinability is crucial. While it is excellent for soldering, the limitations in strength make it less suitable for high-stress applications. B2B buyers should weigh the cost-effectiveness of CDA 932 against its application limitations to ensure it meets their operational needs.
Why Choose CDA 954 (High-Strength Bronze)?
CDA 954 boasts a higher copper content (minimum 83%) and superior tensile strength (85 KSI), making it ideal for high-load and high-impact applications. This alloy is particularly effective in corrosive environments due to its ability to form a protective oxide layer. B2B buyers in sectors like aerospace or heavy machinery should consider CDA 954 for its durability and resistance to wear, although its higher cost and limited availability may be a deciding factor.
What Are the Advantages of Free-Cutting Brass (C36000)?
Free-Cutting Brass, or C36000, is designed for high-speed machining and features lower copper content. Its excellent machinability makes it suitable for precision components and fittings where speed and efficiency are critical. However, buyers should be aware of its lower corrosion resistance compared to C38500, which may limit its applications in harsh environments. The trade-off between cost and performance should be carefully evaluated.
How Does C385 (British Free Machining Brass) Fit In?
C385, known as British Free Machining Brass, shares similar properties with C38500 but is specifically optimized for machining. It offers high machinability and a good surface finish, making it suitable for ornamental hardware and architectural applications. However, like other brass types, it is not suitable for welding or applications requiring high-stress resistance. B2B buyers should consider the specific machining requirements of their projects when selecting this alloy.
Key Industrial Applications of 385 brass
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of 385 brass | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Architecture | Railings and decorative trim | Enhances aesthetic appeal and durability in building designs | Ensure compliance with local building codes and standards |
| Consumer Products | Decorative items like lamps and picture frames | Provides a premium finish and corrosion resistance | Look for suppliers that offer customization options |
| Construction Hardware | Hinges, locks, and drawer pulls | Offers reliable functionality and longevity in everyday use | Assess the lead content for safety regulations in specific regions |
| Industrial Equipment | Valve components and machinery parts | High machinability leads to efficient production processes | Verify the supplier’s ability to meet production timelines |
| Ordnance | Gun sights and hardware components | Precision engineering ensures reliability in critical applications | Source from manufacturers with experience in high-stakes environments |
How is 385 Brass Used in Architecture and What Problems Does It Solve?
In the architecture sector, 385 brass is primarily utilized for railings and decorative trim due to its aesthetic qualities and durability. This material resists corrosion effectively, making it ideal for both indoor and outdoor applications. For international buyers, especially in regions with varying climates, sourcing 385 brass that meets local building codes is crucial to ensure long-lasting installations.
What Are the Applications of 385 Brass in Consumer Products?
385 brass is favored in consumer products such as decorative lamps and picture frames, providing a premium finish that appeals to high-end markets. Its excellent machinability allows manufacturers to create intricate designs while maintaining structural integrity. Buyers should consider suppliers that can offer customization options to meet specific design needs, ensuring that products stand out in competitive markets.
How Does 385 Brass Benefit Construction Hardware?
In construction hardware, 385 brass is commonly used for hinges, locks, and drawer pulls, where reliable functionality is paramount. The material’s resistance to wear and corrosion enhances the lifespan of these components, making them ideal for both residential and commercial applications. Buyers should focus on sourcing from manufacturers who understand the regulatory requirements for lead content, particularly in regions with stringent safety standards.
What Role Does 385 Brass Play in Industrial Equipment?
In the industrial sector, 385 brass is used for valve components and various machinery parts, where high machinability is essential for efficient production. This alloy allows for precise manufacturing, reducing downtime and increasing productivity. Businesses should ensure that their suppliers can meet specific production timelines and offer consistent quality to avoid disruptions in operations.
Why is 385 Brass Important for Ordnance Applications?
For ordnance applications, 385 brass is utilized in gun sights and hardware components, where precision and reliability are critical. The high tensile strength and machinability of this material ensure that components can withstand rigorous conditions. International buyers should prioritize sourcing from manufacturers experienced in high-stakes environments to guarantee the quality and performance of these essential components.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘385 brass’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Inconsistent Quality Across Suppliers
The Problem: B2B buyers often face challenges with inconsistent quality when sourcing 385 brass from multiple suppliers. This inconsistency can lead to unexpected delays in production, increased scrap rates, and ultimately, dissatisfaction from end customers. Buyers may find that the chemical composition or mechanical properties do not match the specifications needed for their applications, which can jeopardize project timelines and budgets. This issue is particularly pronounced in regions where supply chain reliability is a concern.
The Solution: To mitigate this problem, B2B buyers should prioritize working with suppliers who provide comprehensive documentation and certifications for their materials. Requesting mill test reports that detail the chemical composition and mechanical properties of the 385 brass being supplied can help ensure compliance with your specific requirements. Additionally, consider establishing long-term relationships with a select few trusted suppliers who can consistently meet your quality standards. Implementing a quality assurance protocol, such as regular audits of suppliers and their processes, can also help maintain consistency. This proactive approach not only enhances product quality but also fosters a collaborative relationship with suppliers, ultimately leading to more reliable service.
Scenario 2: Difficulty in Machining and Forming
The Problem: Buyers in industries that rely heavily on machining and forming 385 brass often encounter difficulties due to its specific fabrication properties. While 385 brass is known for excellent machinability, it is not suitable for cold working, which can limit its application in certain manufacturing processes. This challenge can lead to production delays and increased costs if the material does not perform as expected during machining or forming operations.
The Solution: To effectively address this pain point, buyers should ensure that their production processes are optimized for the hot working capabilities of 385 brass. When planning machining operations, it is essential to utilize the recommended hot working temperature range of 1150 to 1350°F. Investing in appropriate tooling and machinery that can handle these temperatures will not only improve the machining efficiency but also extend tool life. Furthermore, consider collaborating with experienced machinists who understand the nuances of working with 385 brass and can provide insights on best practices. Providing training for your production team on the specific characteristics of 385 brass can also help reduce errors and improve overall output quality.
Scenario 3: Corrosion Issues in Specific Environments
The Problem: B2B buyers may be unaware that while 385 brass offers excellent corrosion resistance in most environments, it is particularly vulnerable in marine settings or environments with ammonia and ammonia compounds. If projects are undertaken in these conditions without proper material consideration, it can lead to premature failure of components, increased maintenance costs, and potential safety hazards.
The Solution: To prevent corrosion-related issues, buyers should conduct a thorough environmental assessment prior to selecting 385 brass for specific applications. If the application is expected to be in a marine environment or involve exposure to ammonia, consider alternative materials that offer superior corrosion resistance, such as specific stainless steel grades or other bronze alloys like 954 bronze. Additionally, implementing protective coatings or finishes can enhance the longevity of 385 brass components in harsh environments. Providing training for project managers and engineers on the environmental limitations of 385 brass can further ensure that informed decisions are made during the material selection process, ultimately leading to improved project outcomes.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for 385 brass
What Are the Key Properties of 385 Brass Relevant to B2B Buyers?
385 brass, also known as architectural bronze (C38500), is a leaded brass alloy primarily composed of 55-59% copper, 2.5-3.5% lead, and the remainder being zinc. This composition provides excellent machinability, rated at 90%, making it suitable for various manufacturing processes. Its tensile strength is around 60 KSI, and it exhibits good corrosion resistance in non-marine environments. However, it is not recommended for cold working or welding, which limits its application in certain industries.
What Are the Advantages and Disadvantages of Using 385 Brass?
Advantages:
– Machinability: The high machinability rating allows for efficient production of intricate components, reducing manufacturing time and costs.
– Corrosion Resistance: It offers good resistance to corrosion in various environments, making it suitable for architectural and decorative applications.
– Hot Workability: The material excels in hot working processes such as forging and bending, providing flexibility in manufacturing.
Disadvantages:
– Limited Cold Working: The poor capacity for cold working restricts its use in applications requiring significant deformation at room temperature.
– Welding Limitations: The alloy is not suitable for welding, which can complicate assembly processes in some applications.
– Cost Considerations: While generally cost-effective, the presence of lead may increase the price compared to other non-leaded brass alloys.
How Does 385 Brass Impact Specific Applications?
In architectural applications, 385 brass is often used for components like railings, trim, and decorative fittings due to its aesthetic appeal and corrosion resistance. It is also suitable for consumer products, construction hardware, and industrial applications, where its properties can be effectively utilized. However, buyers must consider the specific media compatibility, especially in environments where ammonia or marine conditions are present, as these can induce stress corrosion cracking.
What Should International B2B Buyers Consider When Selecting 385 Brass?
International buyers, particularly from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, should be aware of compliance with local standards such as ASTM, DIN, or JIS. Different regions may have specific regulations regarding the use of lead in materials, which can affect the suitability of 385 brass for certain applications. Additionally, understanding the local market preferences, including cost sensitivity and material availability, is crucial for making informed purchasing decisions.
Summary Table of Material Analysis
| Material | Typical Use Case for 385 brass | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 385 Brass | Architectural components (railings, trim) | Excellent machinability | Poor cold working and welding | Medium |
| 932 Bronze | Bearings and bushings | High lead content for machinability | Lower tensile strength compared to 385 | Medium |
| 954 Bronze | High-load applications (gears, valves) | Superior corrosion resistance | Higher cost due to copper content | High |
| C36000 Brass | Precision machining parts | Very high machinability | Less corrosion resistance than 385 | Medium |
This analysis provides a comprehensive understanding of 385 brass and its alternatives, enabling B2B buyers to make informed decisions tailored to their specific needs and regional compliance requirements.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for 385 brass
What Are the Key Stages in the Manufacturing Process of 385 Brass?
The manufacturing of 385 brass, also known as architectural bronze, involves several critical stages that ensure the material’s properties meet industry standards. Understanding these stages can help B2B buyers assess the quality and reliability of their suppliers.
Material Preparation
The initial stage involves the careful selection of raw materials, primarily copper, zinc, and lead. The typical composition of 385 brass is approximately 55–59% copper, 36.7–42.5% zinc, and 2.5–3.5% lead, with trace amounts of iron. Suppliers often employ strict sourcing protocols to guarantee that the materials are free from impurities. The preparation process may include melting the metals together in a controlled environment to create a uniform alloy.
Forming Techniques
Once the alloy is prepared, the next step is forming the brass into the desired shapes. This process can include:
-
Hot Working: Due to its excellent hot workability, 385 brass is often subjected to processes like hot forging, hot bending, and hot forming. This allows the material to be shaped without compromising its integrity.
-
Machining: 385 brass is known for its high machinability rating of 90%. Techniques such as turning, milling, and drilling are used to create precise components that meet the specifications required by various industries.
-
Extrusion and Pressing: The material can also be extruded into shapes such as rods, tubes, and profiles, or pressed into sheets and plates. These methods are particularly useful for architectural applications.
Finishing Processes
The finishing stage is crucial for enhancing the aesthetic and functional properties of 385 brass. Common techniques include:
-
Polishing: This process improves the surface finish, making the brass more visually appealing and suitable for decorative applications.
-
Electroplating: For certain applications, electroplating is employed to add a protective layer or improve corrosion resistance, especially in environments where the material may be exposed to moisture.
-
Annealing: To relieve stresses from the forming processes, 385 brass may undergo annealing, which involves heating the material to a specific temperature and then allowing it to cool gradually.
How Is Quality Assurance Implemented in 385 Brass Manufacturing?
Quality assurance is a cornerstone of the manufacturing process for 385 brass, ensuring that the final products meet both international and industry-specific standards.
Which International Standards Are Relevant for 385 Brass?
Several international standards guide the manufacturing and quality assurance of 385 brass. Key among these is ISO 9001, which focuses on establishing a quality management system. Compliance with ISO 9001 indicates that the manufacturer has a systematic approach to ensuring quality throughout the production process.
In addition, certifications like CE and API (American Petroleum Institute) may be relevant depending on the end application of the brass products. For example, architectural applications may require CE marking to demonstrate compliance with European safety and environmental standards.
What Are the Key Quality Control Checkpoints?
Quality control (QC) checkpoints are integral to the manufacturing process, ensuring that each stage meets specified criteria. Common QC checkpoints include:
-
Incoming Quality Control (IQC): At this stage, raw materials are inspected upon arrival for compliance with specifications. This includes chemical composition analysis and physical inspection for defects.
-
In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): Throughout the manufacturing process, samples may be taken at various stages to monitor parameters such as temperature, pressure, and dimensional accuracy. This helps identify any issues early on.
-
Final Quality Control (FQC): After finishing, the final products undergo rigorous testing to ensure they meet the required mechanical and chemical properties. This may include tensile strength tests, hardness tests, and corrosion resistance evaluations.
What Testing Methods Are Commonly Used for 385 Brass?
Testing is vital to verify that 385 brass meets the necessary specifications. Common testing methods include:
-
Tensile Testing: This evaluates the material’s strength and ductility, ensuring it can withstand the required loads in its intended application.
-
Hardness Testing: Techniques such as Rockwell or Brinell hardness tests are used to assess the material’s resistance to deformation.
-
Chemical Composition Analysis: Spectroscopic methods (e.g., XRF) are employed to confirm that the alloy composition aligns with specifications.
-
Corrosion Testing: Salt spray tests may be conducted to evaluate the material’s resistance to corrosion, particularly in environments prone to moisture.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control?
For international B2B buyers, especially those from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, verifying a supplier’s quality control processes is essential. Here are some actionable steps:
-
Supplier Audits: Conducting on-site audits of the manufacturing facilities can provide insights into the supplier’s quality management systems and processes. This includes reviewing documentation and observing production practices.
-
Requesting Quality Reports: Buyers should request detailed quality control reports, including results from testing methods and compliance certifications. This documentation provides transparency into the supplier’s quality assurance practices.
-
Third-Party Inspections: Engaging third-party inspection agencies can help validate the quality of products before shipment. These agencies can conduct independent tests to ensure compliance with industry standards.
What Are the Specific QC Considerations for International Buyers?
International buyers must be aware of specific nuances when dealing with quality control in different regions. For instance:
-
Regulatory Compliance: Understanding the local regulations in the buyer’s country is essential, as these may differ significantly from those in the supplier’s region. Ensuring compliance with both sets of standards can prevent issues during importation.
-
Cultural Differences in Quality Standards: Different regions may prioritize various aspects of quality assurance. Buyers should engage in discussions with suppliers to align expectations and standards.
-
Traceability: Buyers should ensure that suppliers maintain a system for traceability throughout the manufacturing process, allowing for accountability in case of defects or non-compliance.
By understanding the manufacturing processes and quality assurance measures associated with 385 brass, B2B buyers can make informed decisions, ensuring they receive high-quality materials that meet their specific needs.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘385 brass’
Introduction
This practical sourcing guide is designed to assist B2B buyers in efficiently procuring 385 brass, also known as architectural bronze. By following this step-by-step checklist, you can ensure that your sourcing process is thorough, cost-effective, and aligned with your technical requirements.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Before initiating the sourcing process, clearly outline your technical requirements for 385 brass. This includes specifying the desired dimensions, forms (e.g., sheets, rods, tubes), and chemical composition (typically 55-59% copper, 2.5-3.5% lead, and the remainder zinc). Knowing your specifications helps streamline communication with suppliers and ensures that you receive materials that meet your needs.
Step 2: Research Potential Suppliers
Conduct extensive research to identify reputable suppliers of 385 brass. Utilize industry directories, trade shows, and online platforms to compile a list of potential vendors. Look for suppliers with a proven track record in the nonferrous metals sector, particularly those with experience in serving markets similar to yours.
Step 3: Evaluate Potential Suppliers
Before committing, it’s crucial to vet suppliers thoroughly. Request company profiles, case studies, and references from buyers in a similar industry or region. Assess their manufacturing capabilities, quality control processes, and customer service responsiveness to ensure they align with your expectations.
- Check Certifications: Verify that the suppliers have relevant certifications, such as ISO or ASTM compliance, which can indicate adherence to industry standards.
Step 4: Request Quotes and Compare Pricing
Once you’ve narrowed down your supplier list, request detailed quotations that include pricing, lead times, and terms of sale. Compare these quotes not just on cost but also on the value offered, such as shipping options, payment terms, and after-sales support. This step helps you identify the best overall deal while ensuring that quality is not compromised.
Step 5: Assess Material Quality and Compliance
Before finalizing your order, ensure that the 385 brass offered meets your specified quality standards. Request material safety data sheets (MSDS), mill test reports, and certifications confirming the chemical composition and mechanical properties. This is critical, especially for applications in architecture and construction, where material integrity is paramount.
Step 6: Negotiate Terms and Place Your Order
Once you’ve selected a supplier, engage in negotiations to finalize terms. Discuss pricing, delivery schedules, and any potential discounts for bulk orders. Clear communication during this phase can lead to better pricing and favorable terms, enhancing your overall procurement efficiency.
Step 7: Plan for Logistics and Delivery
Finally, develop a logistics plan to manage the delivery of your 385 brass. Confirm shipping methods, delivery timelines, and any customs requirements, especially if you are importing from international suppliers. Efficient logistics management ensures that your materials arrive on time, allowing for uninterrupted production processes.
By following this checklist, B2B buyers can navigate the complexities of sourcing 385 brass effectively, ensuring high-quality materials that meet their specific needs.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for 385 brass Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components in Sourcing 385 Brass?
When sourcing 385 brass, understanding the detailed cost structure is crucial for B2B buyers. The primary cost components include:
-
Materials: The core component of cost, which typically encompasses copper, zinc, and lead. Prices fluctuate based on market conditions. Copper, comprising 55-59% of 385 brass, is particularly volatile, often influenced by global demand and mining output. Zinc and lead also contribute to the material cost but are generally less volatile.
-
Labor: This includes wages for workers involved in the manufacturing process. Labor costs can vary significantly based on geographical location, skill level, and local labor laws. In regions with higher labor costs, such as Europe, buyers might face increased pricing.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This encompasses utilities, facility maintenance, and administrative costs. Efficient manufacturing processes can lower overhead, but suppliers with higher operational costs may pass these onto buyers.
-
Tooling: The expense associated with the machinery and tools used in the production of 385 brass components. Custom tooling can be significant, especially for specialized parts, and is typically a one-time investment that can affect pricing depending on volume.
-
Quality Control (QC): Implementing stringent QC measures ensures that the final products meet specifications and standards. This is especially important in industries where material integrity is critical, such as construction and aerospace.
-
Logistics: Shipping and handling costs are pivotal, particularly for international transactions. Costs can vary based on the shipping method, distance, and weight of the materials being transported.
-
Margin: Suppliers will add a profit margin to their costs, which can vary based on competition, market demand, and the uniqueness of the product offering.
How Do Price Influencers Affect 385 Brass Sourcing?
Several factors influence the pricing of 385 brass, impacting the overall cost for buyers:
-
Volume/MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity): Suppliers often provide better pricing for larger orders due to economies of scale. Buyers should assess their needs and negotiate accordingly to benefit from volume discounts.
-
Specifications and Customization: Custom specifications can lead to higher costs due to additional tooling and processing requirements. Standardized products tend to have more competitive pricing.
-
Material Quality and Certifications: Higher quality materials or specific certifications (such as ISO standards) can increase costs. Buyers should weigh the importance of certifications against their budget constraints.
-
Supplier Factors: The reputation and reliability of suppliers can significantly influence pricing. Established suppliers may charge a premium for their products due to perceived quality and service.
-
Incoterms: Understanding shipping terms is vital. Different Incoterms (e.g., FOB, CIF) can shift costs and responsibilities between buyers and suppliers, impacting the total landed cost of the materials.
What Are Essential Buyer Tips for Cost-Efficiency in 385 Brass Sourcing?
International B2B buyers, particularly from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, should consider the following strategies for cost-effective sourcing of 385 brass:
-
Negotiate Effectively: Leverage your purchasing power by negotiating prices, especially if committing to large orders. Building long-term relationships with suppliers can also lead to better pricing over time.
-
Consider Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Evaluate not just the purchase price but also the long-term costs associated with maintenance, quality issues, and potential delays in the supply chain. TCO can provide a more accurate picture of the financial impact of sourcing decisions.
-
Be Aware of Pricing Nuances: Different regions may have varying pricing structures due to local market conditions, tariffs, and transportation costs. Understanding these nuances can help buyers make informed decisions and avoid unexpected expenses.
Are Indicative Prices Available for 385 Brass?
While specific pricing for 385 brass can vary widely based on the aforementioned factors, it is essential for buyers to request quotes from multiple suppliers to gauge the market rate. Always ask for detailed breakdowns of costs to ensure transparency and facilitate better negotiation outcomes.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing 385 brass With Other Solutions
Exploring Alternatives to 385 Brass: Key Comparisons for B2B Buyers
When selecting materials for architectural and industrial applications, it’s essential to consider alternatives to 385 brass (C38500). This alloy is popular for its machinability and aesthetic appeal, but there are other materials that can meet similar needs. This analysis compares 385 brass with two viable alternatives: 932 High-Leaded Tin Bronze and 954 Bronze. Each alternative brings unique advantages and disadvantages depending on the application and industry requirements.
| Comparison Aspect | 385 Brass | 932 High-Leaded Tin Bronze | 954 Bronze |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | Excellent machinability; good corrosion resistance in non-marine environments; not suitable for cold working. | Good machinability; lower tensile strength; often used in light-duty applications. | High tensile strength; excellent corrosion resistance; suitable for high-load applications. |
| Cost | Moderate cost; competitive pricing for architectural applications. | Generally lower cost due to abundant lead content. | Higher cost; premium pricing reflects superior properties. |
| Ease of Implementation | Easy to machine and fabricate; excellent for hot working processes. | Similar ease of machining; suitable for soldering and brazing. | More complex machining; may require specialized tools for optimal performance. |
| Maintenance | Low maintenance; resistant to wear in non-corrosive environments. | Requires regular inspection due to lower corrosion resistance. | Low maintenance; highly durable and resistant to harsh environments. |
| Best Use Case | Ideal for architectural features, decorative elements, and hardware. | Best for bearings, bushings, and light-duty components. | Optimal for high-load gears, valve components, and marine applications. |
In-Depth Look at Alternative Materials
932 High-Leaded Tin Bronze
This alloy is known for its excellent machinability and is often used in applications that require light-duty performance. Its lower tensile strength (around 35 KSI) compared to 385 brass makes it less suitable for high-stress environments. However, its affordability can be appealing for projects with tight budgets. It is commonly used in bearings, bushings, and various components where wear resistance is not the primary concern. While it offers good machinability, the presence of lead means that it may not be ideal for all environments, especially those requiring stringent safety standards.
954 Bronze
With a composition that ensures high tensile strength (up to 85 KSI) and excellent corrosion resistance, 954 bronze is a superior alternative for demanding applications. Its ability to withstand high loads and impacts makes it suitable for components such as gears and valve parts. However, the cost is typically higher, which can be a deterrent for projects with budget constraints. The machining process for 954 bronze can also be more complex, potentially requiring specialized tools and techniques. Nonetheless, its durability and performance in harsh environments can justify the investment for many industrial applications.
Choosing the Right Solution for Your Needs
When evaluating alternatives to 385 brass, B2B buyers must consider performance requirements, budget constraints, and the specific application. If cost is a primary concern and the application is light-duty, 932 High-Leaded Tin Bronze may be suitable. For high-performance needs, particularly in harsh environments, 954 bronze offers superior properties despite its higher price point. Ultimately, understanding the specific requirements of your project will guide you in selecting the most appropriate material for long-term success.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for 385 brass
What Are the Key Technical Properties of 385 Brass?
Understanding the technical properties of 385 brass, or C38500, is crucial for B2B buyers involved in industries such as architecture, construction, and manufacturing. Here are some essential specifications:
-
Chemical Composition: The alloy primarily consists of 55-59% copper, 36.7-42.5% zinc, and 2.5-3.5% lead, with minimal iron content. This specific composition contributes to its excellent corrosion resistance, particularly in non-marine environments, making it ideal for architectural applications.
-
Tensile Strength: With a tensile strength ranging from 54 KSI to 60 KSI, 385 brass exhibits robust mechanical properties. This strength is crucial for applications requiring durability, such as in construction hardware and industrial components.
-
Machinability Rating: Rated at 90%, 385 brass offers high machinability, akin to free-cutting brass. This property enables efficient manufacturing processes, reducing production time and costs for businesses that rely on precision components.
-
Hot Working Capability: 385 brass is excellent for hot working processes, including hot forging and bending, but is unsuitable for cold forming. This characteristic is significant for manufacturers that need to shape the material into complex designs without compromising integrity.
-
Thermal Conductivity: With a thermal conductivity of 854 BTU-in/hr-ft²-°F, 385 brass is effective in applications that involve heat transfer. This property is particularly valuable in industrial settings where heat dissipation is critical.
-
Corrosion Resistance: While it offers good resistance to corrosion, it is not suitable for marine environments or exposure to ammonia compounds. Buyers should consider these limitations based on their specific application needs.
What Are Common Trade Terms Related to 385 Brass?
Navigating the procurement process involves understanding specific trade terminology. Here are several key terms relevant to B2B buyers of 385 brass:
-
OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer): This term refers to companies that produce parts or equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer. Understanding the OEM landscape helps buyers identify reliable suppliers for their specific needs.
-
MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity): MOQ indicates the smallest quantity a supplier is willing to sell. Familiarity with MOQ is essential for budget management and ensuring that purchasing decisions align with production requirements.
-
RFQ (Request for Quotation): An RFQ is a formal process where a buyer requests pricing and terms from suppliers. Submitting an RFQ allows businesses to compare offers and negotiate better deals, ensuring they get the best value for their investment.
-
Incoterms: These are international commercial terms that define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in shipping and delivery. Knowledge of Incoterms is crucial for managing risk and ensuring clarity in international transactions.
-
Lead Time: This term refers to the time taken from placing an order to its delivery. Understanding lead times helps businesses plan their supply chain effectively, minimizing disruptions in production schedules.
-
Certification: In the context of materials like 385 brass, certification refers to documentation that verifies compliance with industry standards. Buyers should ensure their suppliers provide necessary certifications to maintain quality and regulatory compliance.
By grasping these technical properties and trade terminologies, B2B buyers can make informed decisions when sourcing 385 brass, ensuring they select the right materials for their applications while optimizing their procurement strategies.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the 385 brass Sector
What are the Current Market Dynamics and Key Trends in the 385 Brass Sector?
The global market for 385 brass, also known as architectural bronze, is experiencing a notable transformation driven by various factors. The increasing demand for architectural and decorative applications, particularly in emerging economies like Brazil and South Africa, is propelling market growth. This demand is fueled by urbanization and infrastructure development, leading to an uptick in construction activities. In Europe and the Middle East, there is a strong emphasis on high-quality materials that offer durability and aesthetic appeal, further solidifying the relevance of 385 brass in these markets.
Technological advancements in manufacturing processes are also influencing sourcing trends. Innovations such as advanced machining technologies and automated fabrication methods enhance the efficiency of 385 brass production, thereby reducing costs and lead times. Additionally, international B2B buyers are increasingly leveraging online platforms for sourcing materials, allowing for better price comparisons and access to a wider range of suppliers.
Furthermore, sustainability is emerging as a key focus area. Buyers are now prioritizing suppliers that demonstrate commitment to environmentally friendly practices, driving demand for recycled and ethically sourced materials. As such, B2B buyers must stay attuned to these trends, ensuring they partner with suppliers who not only meet their quality and cost requirements but also align with their sustainability goals.
How is Sustainability and Ethical Sourcing Impacting the 385 Brass Market?
Sustainability and ethical sourcing are becoming critical considerations for B2B buyers in the 385 brass sector. The environmental impact of metal production, including energy consumption and waste generation, has led companies to seek materials that reduce their carbon footprint. For 385 brass, sourcing from suppliers who utilize recycled materials can significantly mitigate these impacts.
The importance of ethical supply chains cannot be overstated. Buyers are increasingly looking for certifications that guarantee ethical sourcing practices, such as adherence to environmental regulations and fair labor practices. Certifications like ISO 14001 for environmental management and Fair Trade principles can enhance a supplier’s credibility, making them more attractive to international buyers.
Moreover, the industry is witnessing a shift towards ‘green’ materials and processes. Companies are investing in technologies that reduce emissions and waste during the manufacturing of 385 brass. As buyers become more aware of the sustainability landscape, they are likely to favor suppliers who can demonstrate a commitment to environmentally responsible practices. This trend not only supports global sustainability goals but also aligns with consumer preferences for ethically sourced products, thereby enhancing brand reputation in competitive markets.
What is the Historical Context of 385 Brass in B2B Transactions?
The evolution of 385 brass, or architectural bronze, is rooted in its unique composition and versatility, dating back to the early 20th century. Initially developed for architectural applications due to its aesthetic qualities and durability, 385 brass quickly gained traction in various industries, from construction to consumer goods.
Over the decades, its properties—such as excellent machinability and resistance to corrosion—have made it a preferred choice for manufacturers. As global markets evolved, so did the applications of 385 brass, extending its reach into decorative hardware and industrial components. Today, as sustainability and ethical sourcing take center stage, the historical significance of 385 brass is being re-evaluated through the lens of modern market demands, making it a vital material for B2B buyers focused on quality and responsibility.
In conclusion, understanding the market dynamics, sustainability imperatives, and historical context of 385 brass is essential for international B2B buyers looking to make informed sourcing decisions. Embracing these insights can lead to more strategic partnerships and enhanced market positioning.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of 385 brass
-
How do I determine the right specifications for 385 brass for my project?
To choose the appropriate specifications for 385 brass, consider the mechanical properties required for your application, such as tensile strength and corrosion resistance. Review the chemical composition, which typically includes 55-59% copper, 2.5-3.5% lead, and the remainder zinc. Assess the working conditions your product will face, such as exposure to moisture or high temperatures. Collaborating with suppliers who can provide detailed technical data sheets and samples can also help you make an informed decision tailored to your project’s unique needs. -
What industries commonly use 385 brass, and what are its key applications?
385 brass is widely utilized in various industries, particularly in architecture and construction, for items like railings, trim, and decorative fittings. Its excellent machinability makes it suitable for consumer products, including lamps and picture frames, as well as industrial applications like valve components and hardware. Understanding the specific applications in your industry can help you identify the most suitable forms and finishes of 385 brass for your projects. -
What are the typical lead times for ordering 385 brass internationally?
Lead times for international orders of 385 brass can vary based on supplier location, production capacity, and shipping logistics. Generally, you can expect lead times of 2-6 weeks for standard orders. However, custom orders or larger quantities may require additional time for fabrication and shipping. It’s advisable to discuss timelines upfront with your supplier to ensure that your project schedules align with their production capabilities. -
What should I look for when vetting suppliers of 385 brass?
When vetting suppliers for 385 brass, consider their industry reputation, experience in handling nonferrous metals, and adherence to international quality standards. Request references from previous clients and inquire about their production capabilities and certifications. It’s also essential to review their logistics and shipping arrangements, especially for international transactions, to ensure timely delivery and compliance with regulations in your region. -
Are there customization options available for 385 brass products?
Yes, many suppliers offer customization options for 385 brass, including variations in size, shape, and finish. Customization may involve specific machining processes, surface treatments, or alloy modifications to meet particular performance criteria. Discuss your requirements with potential suppliers to determine their capabilities and the feasibility of custom solutions for your projects. -
What are the minimum order quantities (MOQs) for 385 brass?
Minimum order quantities for 385 brass can vary significantly among suppliers, typically ranging from 100 kg to several tons. Factors influencing MOQs include the supplier’s production capacity and the nature of the order (standard vs. custom). It’s crucial to clarify MOQs during your initial discussions to ensure that your purchasing needs align with the supplier’s policies. -
What payment terms are commonly offered by suppliers of 385 brass?
Payment terms for 385 brass orders can vary widely depending on the supplier’s policies and your business relationship. Common options include upfront payment, partial payment upon order confirmation, and net payment terms (e.g., net 30 or net 60 days). Discuss payment options early in the negotiation process to find a mutually agreeable arrangement that accommodates your cash flow requirements. -
How can I ensure quality assurance (QA) for my 385 brass products?
To ensure quality assurance for your 385 brass products, request detailed material certifications and inspection reports from your supplier. Many suppliers adhere to international standards such as ISO 9001, which outlines quality management principles. Additionally, consider implementing a quality inspection process upon receipt of goods, including dimensional checks and material testing, to verify that the products meet your specifications and performance standards.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.
Top 10 385 Brass Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. Sequoia – 385 Architectural Bronze
Domain: sequoia-brass-copper.com
Registered: 1998 (27 years)
Introduction: 385 Architectural Bronze (C38500 Brass) is a versatile material with the following key properties:
– Composition: 55–59% copper, 2.5–3.5% lead, 0.35% iron, remainder zinc.
– Tensile Strength: 60 KSI
– Yield Strength: 20 KSI
– Coefficient of Thermal Expansion: 11.6
– Modulus of Elasticity in Tension: 14,000 KSI
– Hot Working Temperature Range: 1150 to 1350° F
– Annealing Temperature Range: 800 to …
2. Online Metals – Brass 385
Domain: onlinemetals.com
Registered: 1997 (28 years)
Introduction: {“name”: “Brass 385”, “trade_names”: [“UNS C38500”, “CDA 385”, “C385”, “ISO CuZn39Pb3”, “British Free Machining Brass”], “applications”: [“architectural applications”, “ornamental hardware”], “specifications”: {“ASTM”: “B455”}, “mechanical_properties”: {“density”: “0.306 lb/in3”, “ultimate_tensile_strength”: “54 ksi”, “yield_tensile_strength”: “18 ksi”, “shear_strength”: “33 ksi”, “shear_modulus”:…
3. McMaster – Brass Alloy 385 Selection
Domain: mcmaster.com
Registered: 1994 (31 years)
Introduction: This company, McMaster – Brass Alloy 385 Selection, is a notable entity in the market. For specific product details, it is recommended to visit their website directly.
4. Fast Metals – Architectural Bronze Angle 385
Domain: fastmetals.com
Registered: 2013 (12 years)
Introduction: Architectural Bronze Angle 385, 20% Off Purchases Over $200! Use Code FASTMETALS20
5. Kormax – Alloy 385 Brass Products
Domain: kormax.com
Registered: 1998 (27 years)
Introduction: Kormax 385 brass comes in a range of bars, tubes, and rounds including angle bars. It is ideal for architectural and tooling usage, with superior machining characteristics and long tooling life. The material is closely monitored throughout its extrusion to ensure high specifications. Alloy 385 is susceptible to dezincification under certain conditions and is classified as a category III alloy. Com…
6. AW Fraser – Alloy 385
Domain: awfraser.co.nz
Introduction: {“Alloy Name”: “Alloy 385”, “Manufacturer”: “AW Fraser Ltd”, “Standard”: “ASTM B455”, “Type”: “Free machining brass/architectural bronze”, “Key Features”: “Maximum productivity and tool life on high speed repetition work.”, “Full Alloy Description”: “A.W. Fraser Alloy 385 is a high speed turning and screwing brass conforming to the requirements of A. S. 1567 alloy 385. 385 has been developed for u…
7. Materials Plus – Brass Alloy 385
Domain: materialsplus.com
Registered: 2000 (25 years)
Introduction: Brass Alloy 385, also known as Architectural Bronze, is a leaded brass with a composition of approximately 58% copper, 40% zinc, and 2% lead. It has excellent machinability, making it suitable for intricate machining, engraving, and stamping operations. The addition of lead enhances its free-cutting properties. Brass C385 exhibits good corrosion resistance, making it suitable for architectural app…
8. Interlloy – 385 Brass
Domain: interlloy.com.au
Introduction: {‘product_name’: ‘385 Brass’, ‘description’: ‘Brass alloy 385 has been specifically developed for the mass production of brass components in high speed lathes, providing maximum output and long tool life.’, ‘typical_applications’: [‘nuts’, ‘bolts’, ‘screw threads’], ‘colour_code’: ‘Red (Bar End)’, ‘stocked_sizes’: {’rounds’: ‘4.76 mm to 101.6 mm diameter’, ‘squares’: ‘9.52 mm to 50.8 mm A/F’, ‘hex…
9. RCGroups – Brass Machining Insights
Domain: rcgroups.com
Registered: 2001 (24 years)
Introduction: The discussion revolves around the suitability of various types of brass for machining. Key points include: 1. Free-machining brass (Alloy 360) is recommended for its excellent machinability due to its lead content. 2. Other brass alloys mentioned include Alloy 353 (engraver’s brass), Alloy 385 (architectural brass), Alloy 260 (formable brass), Alloy 330 (machinable and formable brass), Alloy 464 …
10. MatWeb – Material Property Data
Domain: matweb.com
Registered: 1997 (28 years)
Introduction: This company, MatWeb – Material Property Data, is a notable entity in the market. For specific product details, it is recommended to visit their website directly.
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for 385 brass
In the evolving landscape of nonferrous metals, 385 brass, also known as architectural bronze, stands out for its exceptional machinability, corrosion resistance, and versatility across various applications. For international B2B buyers, especially those from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, understanding the unique properties of this alloy is vital for making informed procurement decisions. Its excellent hot workability and ease of fabrication make 385 brass a preferred choice for industries ranging from architecture to consumer goods.
Strategic sourcing of 385 brass not only ensures access to high-quality materials but also fosters long-term supplier relationships that can lead to cost savings and improved supply chain efficiency. As global demand for durable and aesthetically pleasing materials rises, now is the time for businesses to leverage the benefits of this alloy.
Looking ahead, companies should prioritize partnerships with reliable suppliers who can provide consistent quality and support sustainable practices. By doing so, buyers can position themselves competitively in their respective markets and meet the increasing demands of their customers. Engage with suppliers today to explore the possibilities that 385 brass can unlock for your business growth.